Assessment of Elaboration and Performance of Rice Husk-Based Thermal Insulation Material for Building Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Description
2.3. Experimental Design
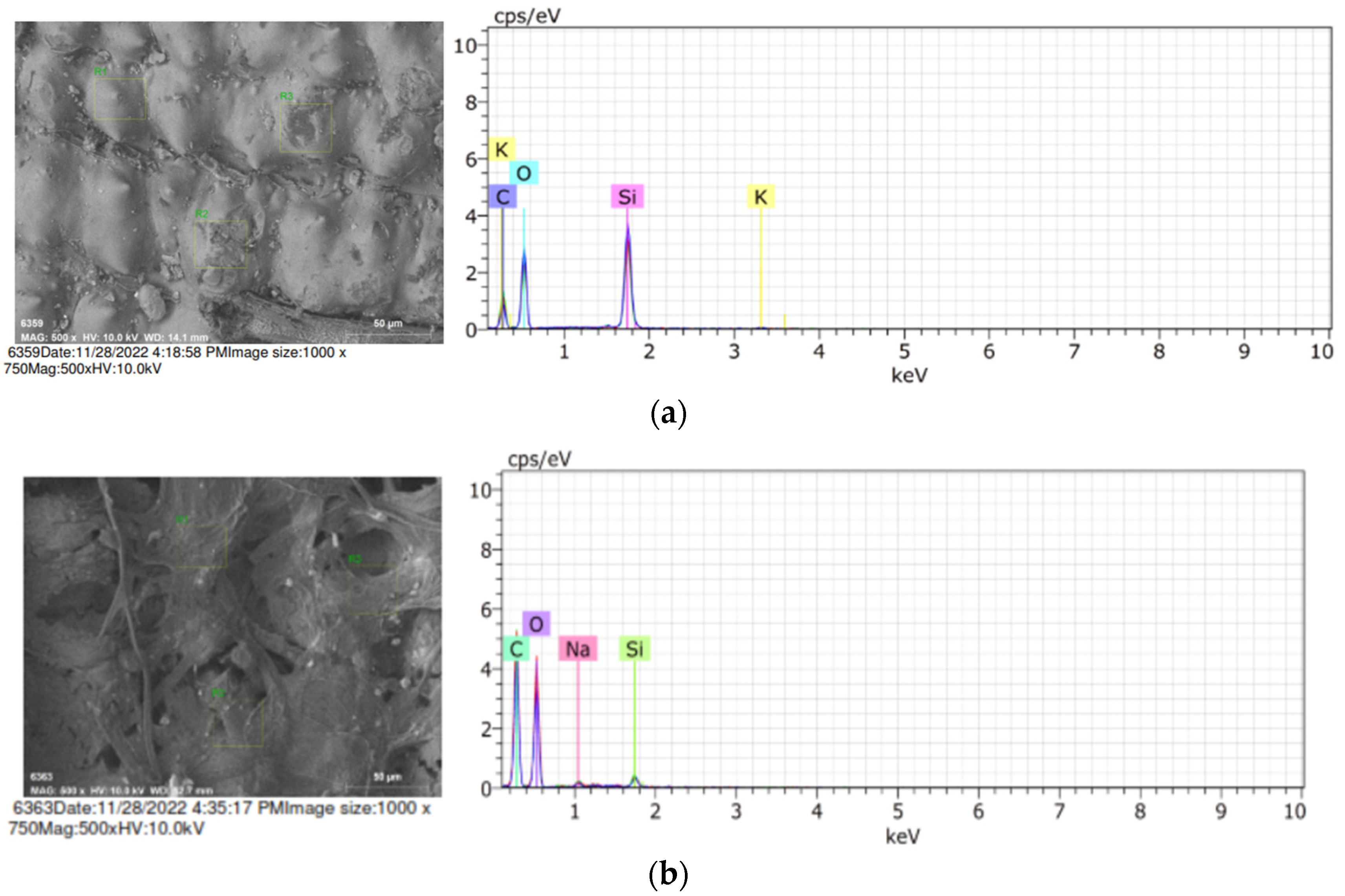
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Thermal Tests
2.5.1. Thermal Stability
2.5.2. Thermal Conductivity Density and Moisture
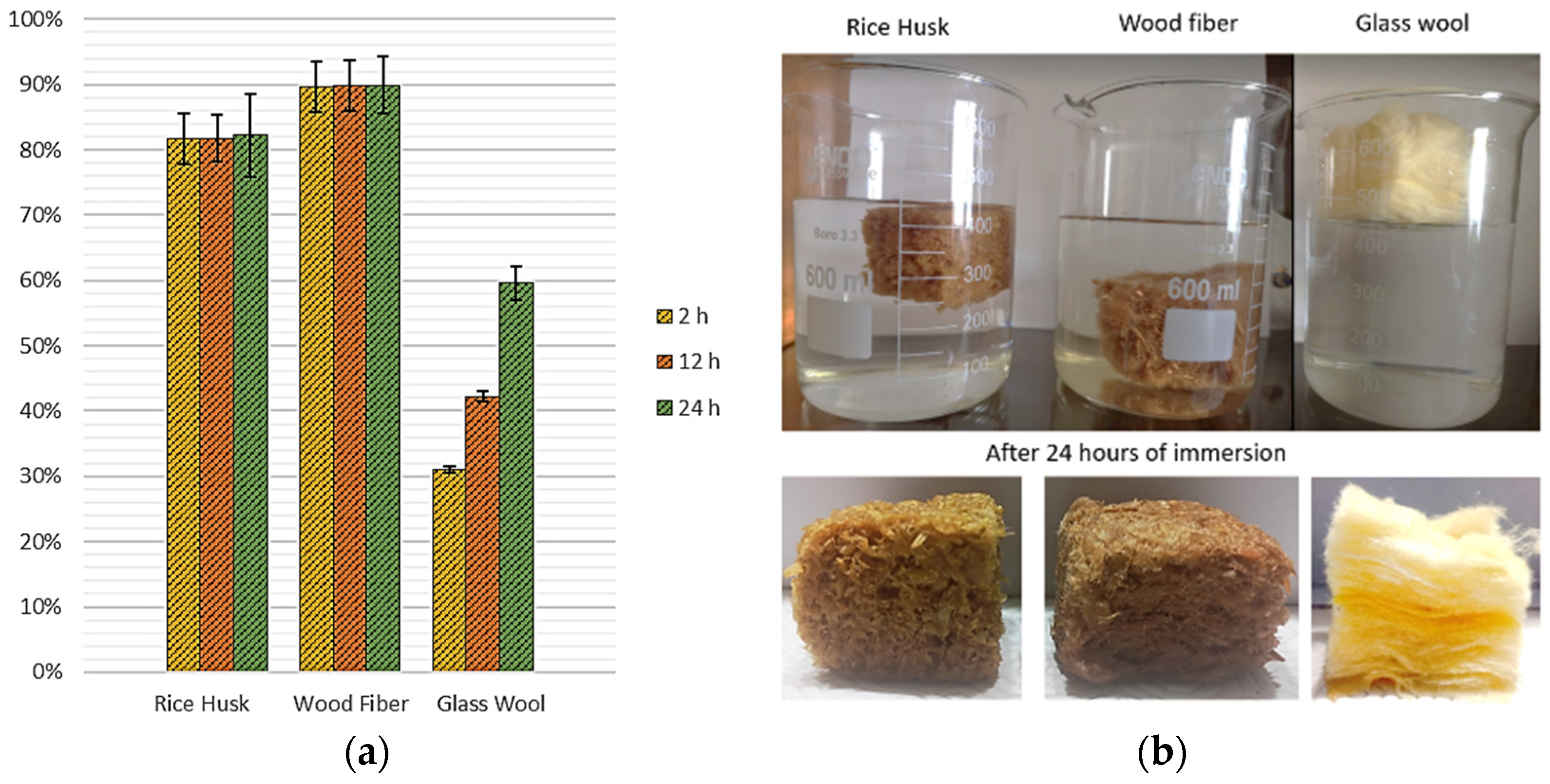
2.6. Water Absorption
2.7. Fire Behavior
2.7.1. Epiradiator Test
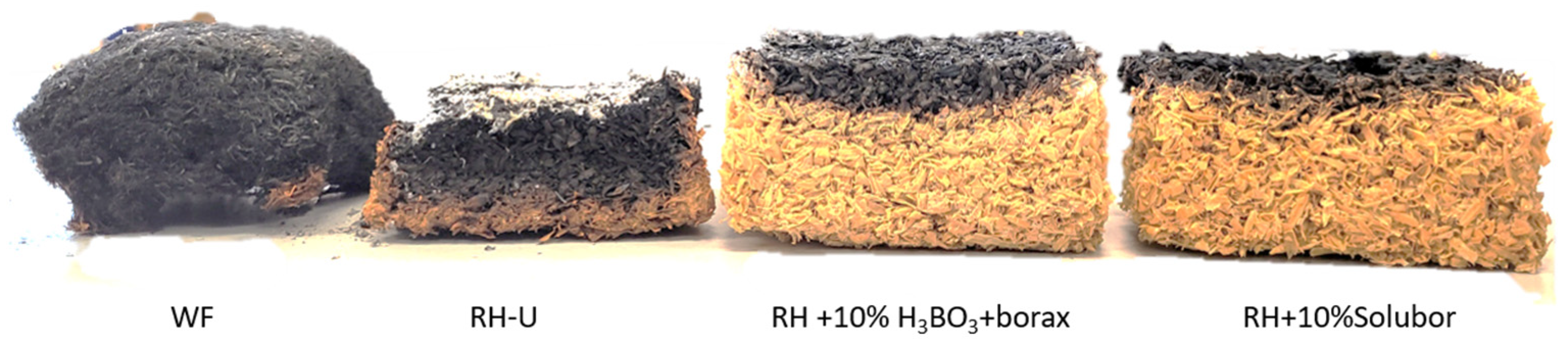
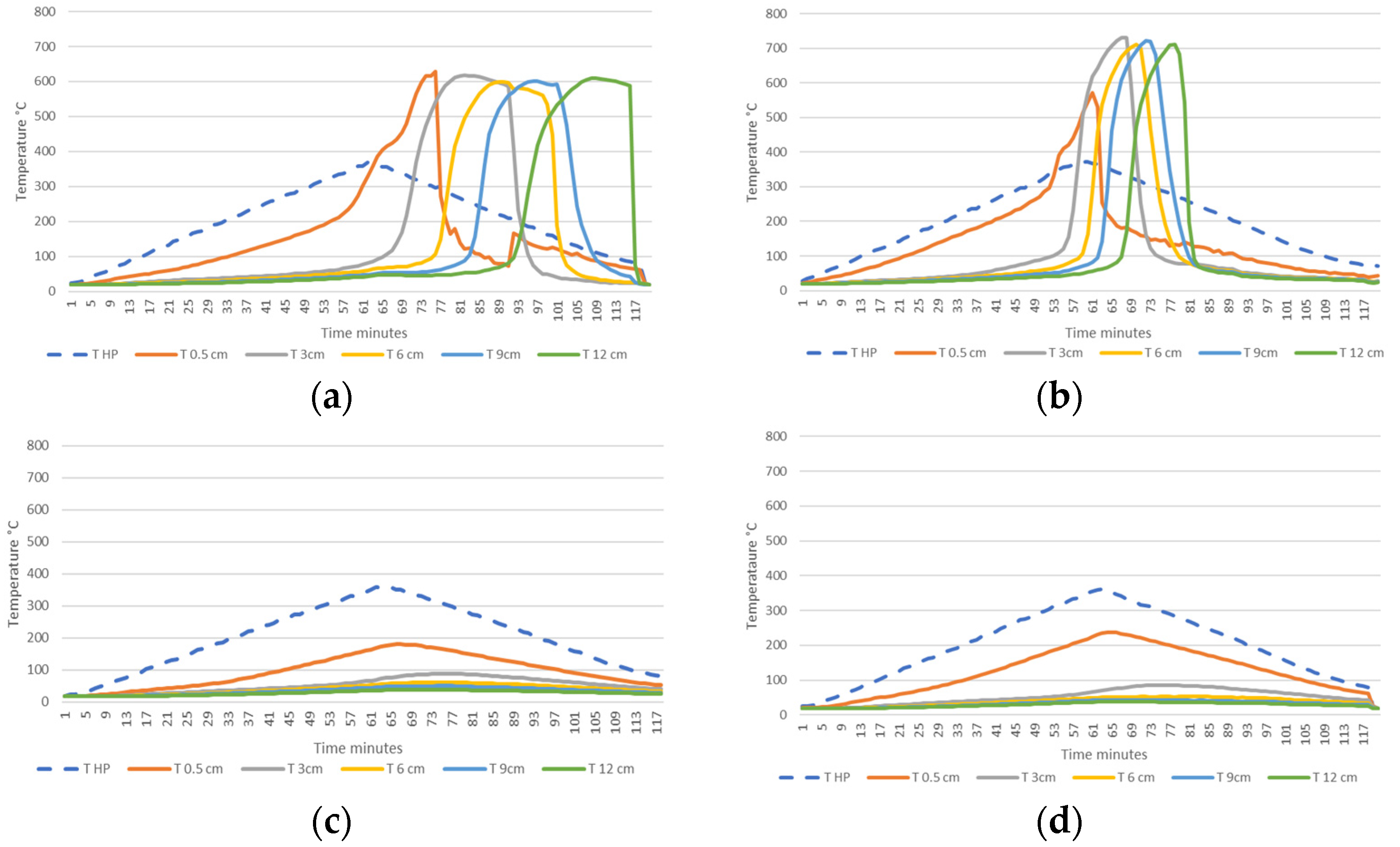
2.7.2. Smoldering Combustion Analysis Test
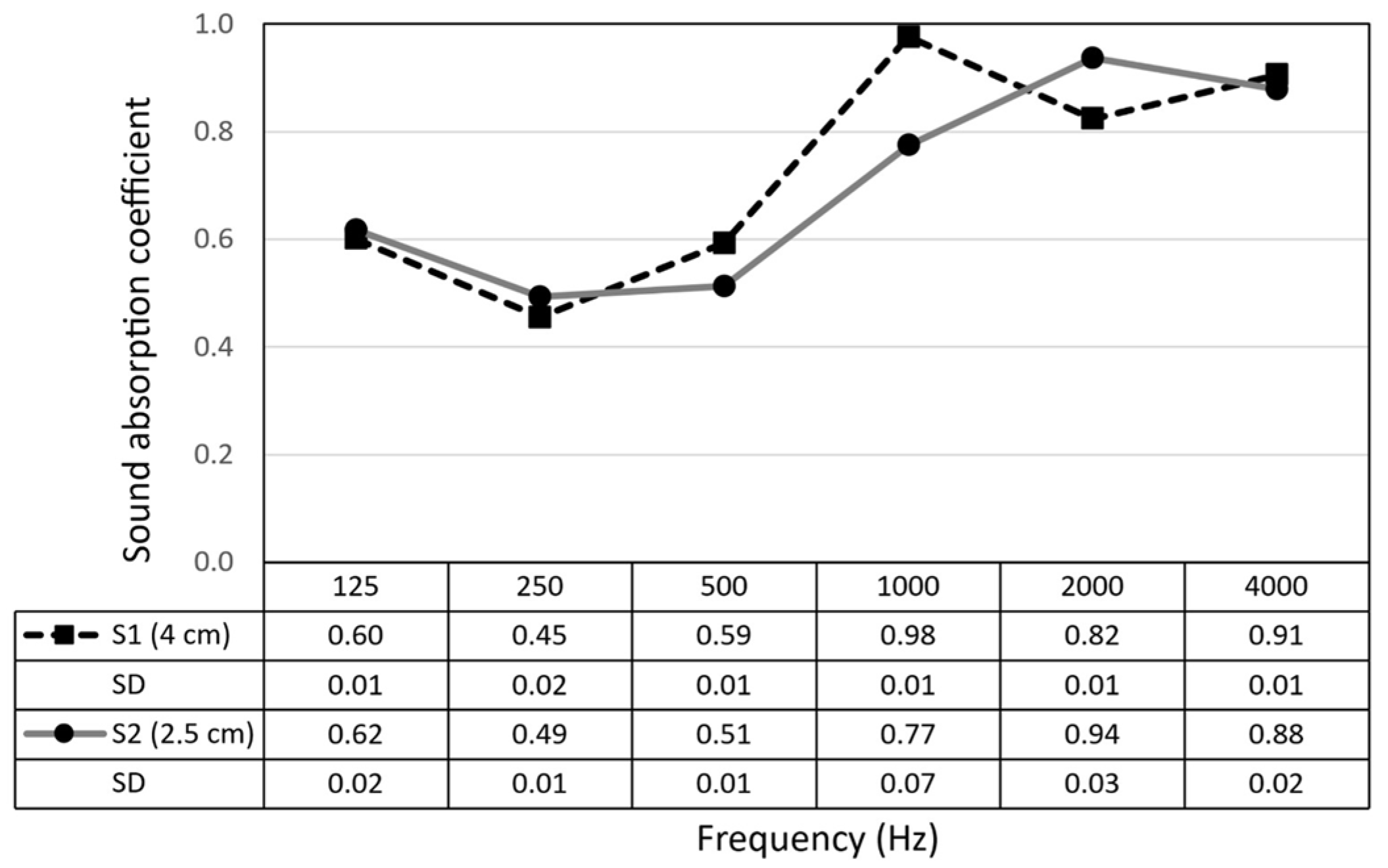
2.8. Acoustic Test
Sound Absorption Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
3.2. Thermal Test
3.2.1. Thermal Stability
3.2.2. Thermal Conductivity
3.2.3. Density and Moisture
3.3. Water Absorption
3.4. Fire Behavior
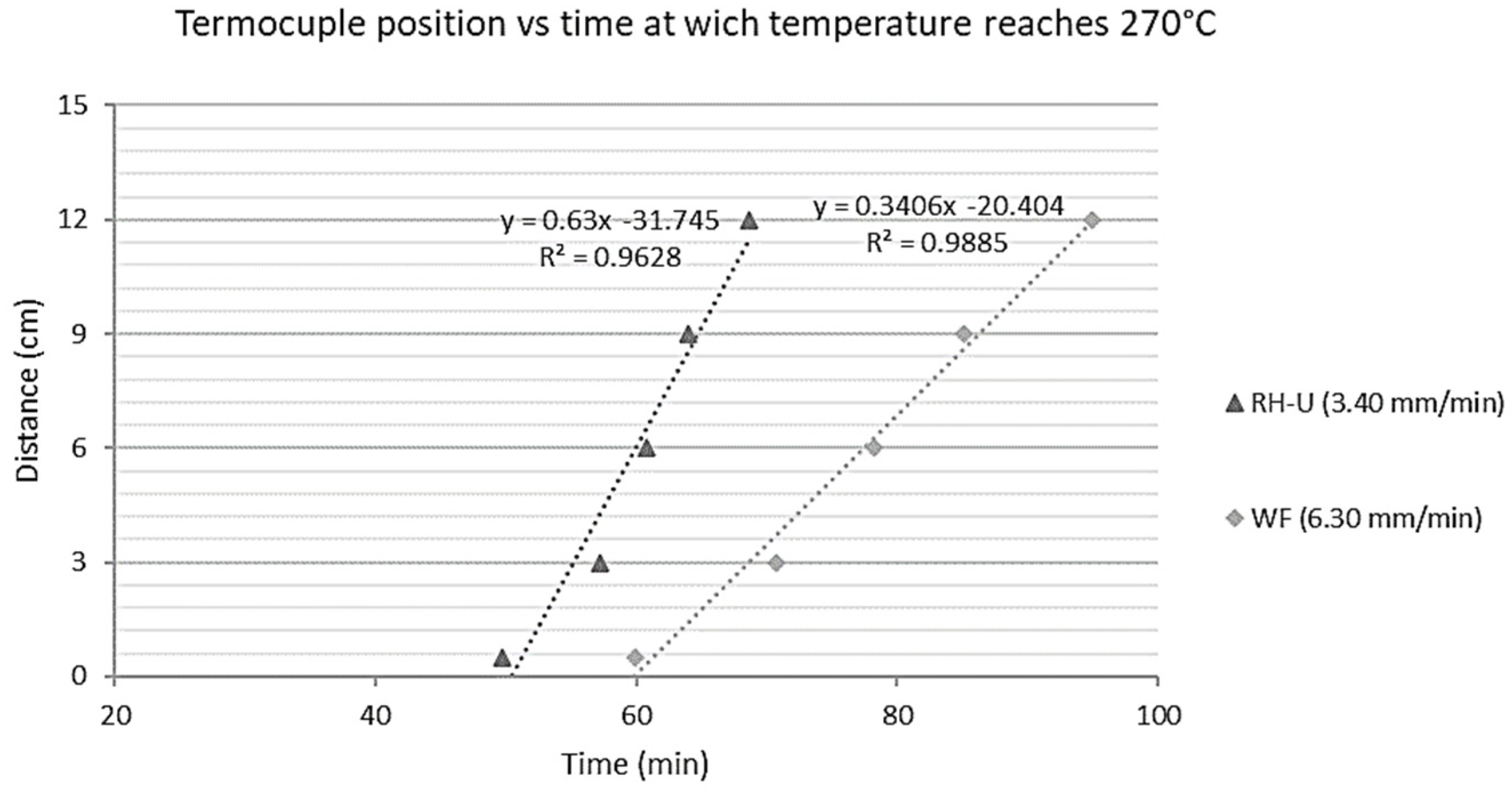
3.4.1. Epiradiator Test
3.4.2. Smoldering Combustion Analysis Test
3.5. Sound Absorption Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, W.; Hao, J.L.; Qiang, G. Three-level modular grid system for sustainable construction of industrialized residential buildings: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 395, 136379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Miralles, J.A.; Hermoso-Orzáez, M.J.; Martínez-García, C.; Rojas-Sola, J.I. Comparative study on the environmental impact of traditional clay bricks mixed with organic waste using life cycle analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; D’Alessandro, F.; Schiavoni, S. A review of unconventional sustainable building insulation materials, Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2015, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmen, N.; Ozkan, S.T.E. Unconventional Insulation Materials. In Insulation Materials in Context of Sustainability; InTech: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, M.A.B.; Noguchi, T. A conceptual framework for understanding the contribution of building materials in the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangmesh, B.; Patil, N.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Gowrishankar, T.P.; Selvakumar, K.K.; Jyothi, M.S.; Jyothilakshmi, R.; Kumar, S. Development of sustainable alternative materials for the construction of green buildings using agricultural residues: A review, Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korjenic, A.; Petránek, V.; Zach, J.; Hroudová, J. Development and performance evaluation of natural thermal-insulation materials composed of renewable resources. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 2518–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintura, E.; Nunes, L.; Esteves, B.; Faria, P. Agro-industrial wastes as building insulation materials: A review and challenges for Euro-Mediterranean countries. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, P.; Cillari, G.; Miino, M.C.; Collivignarelli, M.C. Valorization of agro-industry residues in the building and environmental sector: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.; Navarro, A.; Avellaneda, J.; Lacasta, A.M. Characterization of thermal insulation materials developed with crop wastes and natural binders. In Proceedings of the World Sustainable Buildings Conference “WSB 14 Barcelona Sustainable Buildings”, Barcelona, Spain, 28–30 October 2014; pp. 188.1–188.10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zou, S.; Zhang, G. Experimental research on a feasible rice husk/geopolymer foam building insulation material. Energy Build. 2020, 226, 110358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Belloni, E.; Lascaro, E.; Merli, F.; Ricciardi, P. Rice husk panels for building applications: Thermal, acoustic and environmental characterization and comparison with other innovative recycled waste materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, B.; Tadeu, A.; António, J.; Almeida, J.; de Brito, J. Mechanical, thermal and acoustic behaviour of polymer-based composite materials produced with rice husk and expanded cork by-products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.; Faria, P.; Silva, V.; Brás, A. Rice husk-earth based composites: A novel bio-based panel for buildings refurbishment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraj, R.; Lacoste, C.; Lacroix, P.; Bergeret, A. Sustainable thermal insulation biocomposites from rice husk, wheat husk, wood fibers and textile waste fibers: Elaboration and performances evaluation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 135, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Calvo, N.; González-Serrud, S.; James-Rivas, A. Thermal insulation material produced from recycled materials for building applications: Cellulose and rice husk-based material. Front. Built Environ. 2023, 9, 1271317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.; Cea, M.; Iriarte, A.; Valdés, G.; Navia, R.; Cárdenas-R, J.P. Thermal insulation materials based on agricultural residual wheat straw and corn husk biomass, for application in sustainable buildings. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 20, e00102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, R.; Cea, M.; Rosas-Díazand, F.; Cárdenas, R.J.P. Physical, chemical and mechanical (1). IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2018, 16, 2441–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Quispe, I.; Navia, R.; Kahhat, R. Life Cycle Assessment of rice husk as an energy source. A Peruvian case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aza-Medina, L.C.; Palumbo, M.; Lacasta, A.M.; González-Lezcano, R.A. Characterization of the thermal behavior, mechanical resistance, and reaction to fire of totora (Schoenoplectus californicus (C.A. Mey.) Sojak) panels and their potential use as a sustainable construction material. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 105984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.O.; Espinoza, R.E.; Horn, M.J.; Gómez, M.M. Thermal performance evaluation of isolation and two activesolar heating systems for an experimental module: A ruralPeruvian case at 3700 masl. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1173, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, E.; Jessica, J.M.; Manfred, H.; Gómez Mónica, M. Bioclimatic concepts and their applicability to andean rural area:San Francisco de Raymina Community(SFR) Case-Ayacucho. TECNIA 2015, 25, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarbrough, D.W.; Wilkes, K.E.; Olivier, P.A.; Graves, R.S.; Vohra, A. Title: Apparent Thermal Conductivity Data and Related Information for Rice Hulls and Crushed Pecan Shells Authors. Therm. Conduct. 2005, 27, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, M.; Formosa, J.; Lacasta, A.M. Thermal degradation and fire behaviour of thermal insulation materials based on food crop by-products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 79, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titiloye, J.O.; Bakar, M.S.A.; Odetoye, T.E. Thermochemical characterisation of agricultural wastes from West Africa. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 47, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Barford, J.P.; Hellgradt, K.; Mckay, G. A comparison of chemical treatment methods for the preparation of rice husk cellulosic fibers. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2016, 2, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, C.M.; George, C.R. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, M.; Rojas, C.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P. Characterization of a Thermal Insulating Material Based on a Wheat Straw and Recycled Paper Cellulose to Be Applied in Buildings by Blowing Method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.; Vera, M.; Parra, K.; Rojas, C.; Cárdenas, J.P. Potential of the Residual Fibers of Pisum Sativum (PS), for use in a Development of a Thermal Insulator Material. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 503, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quidel, G.R.; Acuña, M.J.S.; Herrera, C.J.R.; Neira, K.R.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P. Assessment of Modular Construction System Made with Low Environmental Impact Construction Materials for Achieving Sustainable Housing Projects. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier, R.H.C.; Karin, R.N.; Pablo, C.-R.J. Valorization of Wheat Crop Waste in Araucanía, Chile: Development of Prototype of Thermal Insulation Material for Blowing Technique and Geographical Analysis. Buildings 2023, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D5334-00; Standard Test Method for Determination of Thermal Conductivity of Soil and Soft Rock by Thermal Needle Probe Procedure. ASTM Int.: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Guna, V.; Ilangovan, M.; Hu, C.; Venkatesh, K.; Reddy, N. Valorization of sugarcane bagasse by developing completely biodegradable composites for industrial applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 131, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría del CTN AESPI-TECNIFUEGO. Norma Española UNE 23-725-90 Ensayos de Reacción al Fuego de los Materiales de Construcción; 1990. Available online: https://www.une.org/encuentra-tu-norma/busca-tu-norma/norma?c=N0002467 (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Rosa, A.C.; Teixeira, I.; Lacasta, A.M.; Haurie, L.; Soares, C.A.P.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Haddad, A. Experimental Design for the Propagation of Smoldering Fires in Corn Powder and Cornflour. Eng 2022, 4, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.; Lacasta, A.M.; Navarro, A.; Giraldo, M.P.; Lesar, B. Improvement of fire reaction and mould growth resistance of a new bio-based thermal insulation material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Van Keulen, W.; Tijs, E.; Van De Ven, M.; Molenaar, A. Sound absorption measurement of road surface with in situ technology. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 88, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijs, E. Study and Development of an In Situ Acoustic Absorption Measurement Method. PhD Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.K.S.; Mathur, L.; Roy, P.K. Rice husk/rice husk ash as an alternative source of silica in ceramics: A review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 6, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-R, J.P.; Cea, M.; Santín, K.; Valdés, G.; Hunter, R.; Navia, R. Characterization and application of a natural polymer obtained from Hydrangea macrophylla as a thermal insulation biomaterial. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 132, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakatovich, A.; Davydenko, N.; Gaspar, F. Thermal insulating plates produced on the basis of vegetable agricultural waste. Energy Build. 2018, 180, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Acoustic characterization of natural fibers for sound absorption applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; Schiavoni, S.; Horoshenkov, K.V. A review of sustainable materials for acoustic applications. Build. Acoust. 2012, 19, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
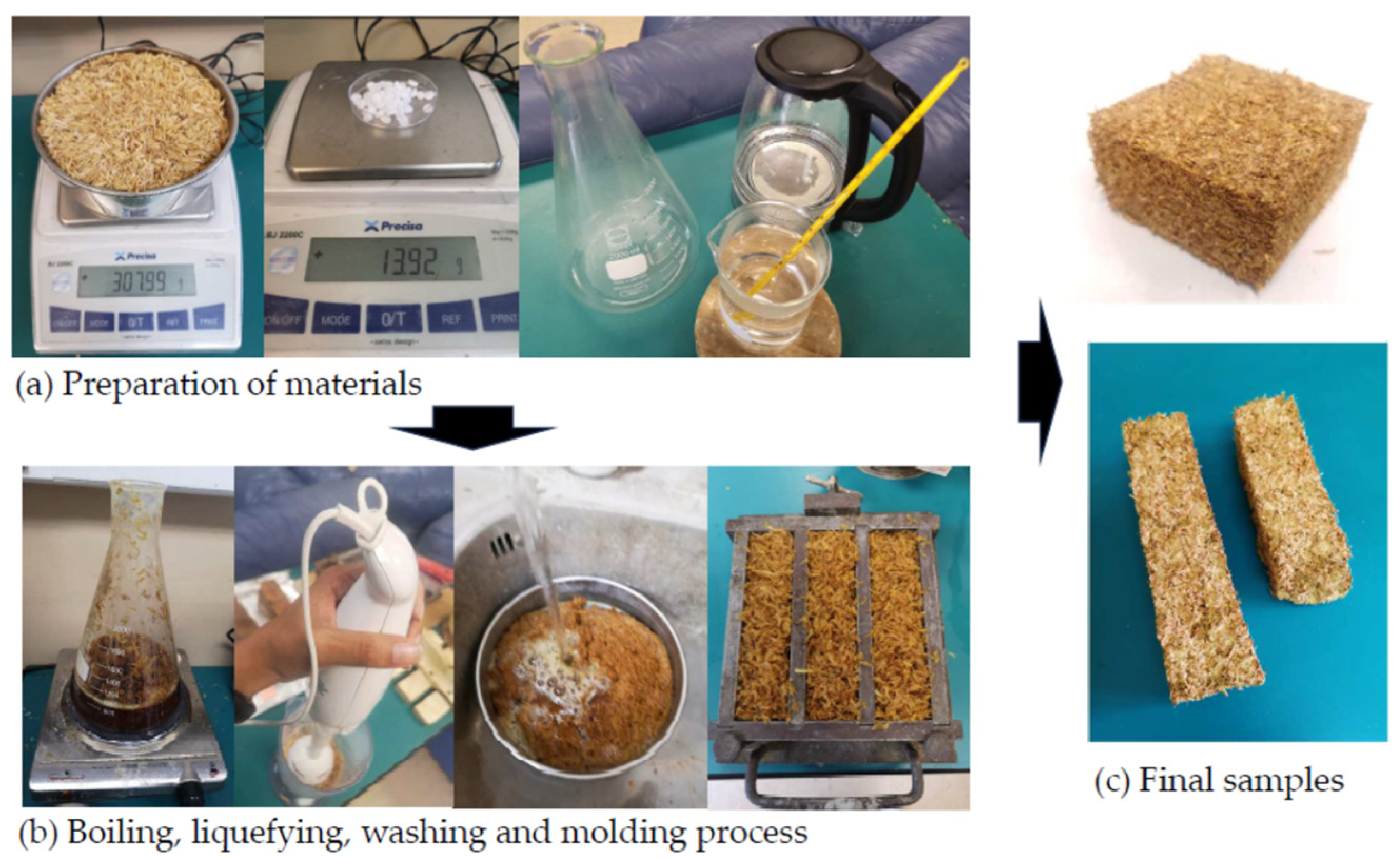
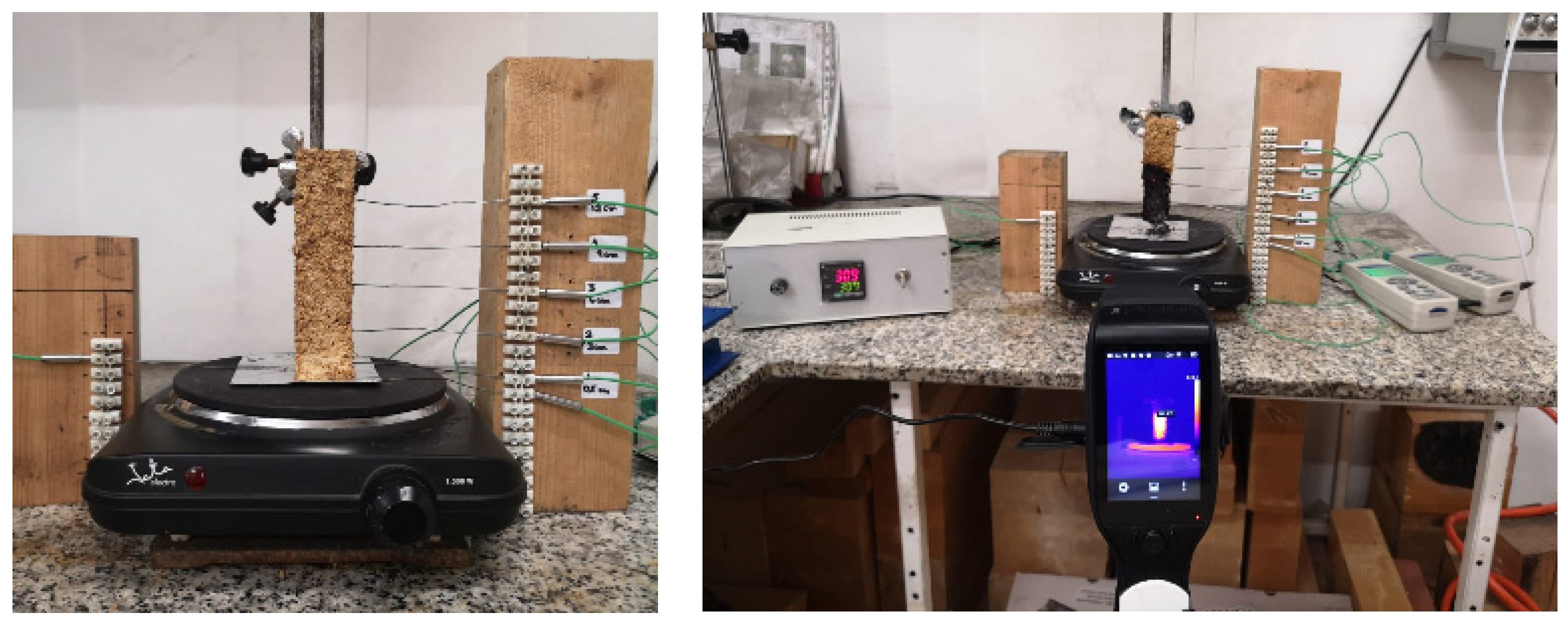









| Cellulose (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Lignin (%) | Silica (%) | Ash (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24.3 | 24.3 | 14.3 | 9–14 | 15.3 | [24] |
| 37.34 | 10.07 | 41.08 | - | 11.51 | [25] |
| 31.13 | 18.59 | 28.25 | 15–17 | 16.50 | [26] |
| Factor | Proof 1 | Proof 2 | Proof 3 | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boiling time | 30 | 45 | 60 | min |
| NaOH concentration | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | % |
| Blending time | 5 | 10 | 20 | s |
| Proof | Thermal Conductivity W/mK | Density kg/m3 | Consistency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.038 | 70.31 | 3 |
| 2 | 0.042 | 97.66 | 2 |
| 3 | 0.067 | 130.63 | 1 |
| Control Factor | Level | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||
| A | 45 | 60 | 75 | min |
| B | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | % |
| C | 10 | 15 | 20 | sec |
| Trial Number | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Factor | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling time | 60 | min |
| Additive concentration | 1 | % |
| Blending time | 15 | sec |
| Thermal Conductivity | AVG | SD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | |||
| Sample 1 | 0.033 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.035 | 0.033 | 0.0014 |
| Sample 2 | 0.038 | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.045 | 0.042 | 0.0029 |
| Sample 3 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.0005 |
| Sample 4 | 0.036 | 0.038 | 0.035 | 0.038 | 0.037 | 0.0015 |
| Thermal conductivity W/mK | 0.037 | 0.0016 | ||||
| Biomass | Processed Type | Thermal Conductivity W/mK | Density kg/m3 | Moisture % | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH Optimal Prototype 1 | Pulp method | 0.037 ± 0.001 | 97.32 ± 6.42 | 8.78 ± 0.17 | |
| Rice Husk | Without | 0.049 | 149 | - | [23] |
| Wheat straw | Pulp method | 0.046 | 104.84 | 7.54 | [17] |
| Corn husk | Pulp method | 0.047 | 118.79 | 7.65 | [17] |
| Rice husk ecovio | Bio-polymer composite | 0.08 | 378 | - | [15] |
| Rice husk | Binder liquid gas | 0.068 | 230 | - | [41] |
| Rice husk | Gluting and pressing | 0.070 | 170 | [12] |
| Treatments | First Ignition Time (s) | N° of Ignitions | Average Combustion Extent (s) | Initial Mass (g) | Final Mass | Loss | Percentage % | Smoldering |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WF | 3 | 30 | 9 | 17.87 | 3.64 | 14.23 | 79.63 | Yes |
| RH-U | 7 | 29 | 4 | 36.22 | 5.96 | 30.26 | 83.55 | Yes |
| RH + 10% H3BO3 + borax | 36 | 12 | 4 | 39.59 | 29.1 | 10.49 | 26.50 | Yes |
| RH + 10% Solubor | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33.59 | 25.76 | 7.83 | 23.31 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez Neira, K.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P.; Rojas-Herrera, C.J.; Haurie, L.; Lacasta, A.M.; Torres Ramo, J.; Sánchez-Ostiz, A. Assessment of Elaboration and Performance of Rice Husk-Based Thermal Insulation Material for Building Applications. Buildings 2024, 14, 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061720
Rodríguez Neira K, Cárdenas-Ramírez JP, Rojas-Herrera CJ, Haurie L, Lacasta AM, Torres Ramo J, Sánchez-Ostiz A. Assessment of Elaboration and Performance of Rice Husk-Based Thermal Insulation Material for Building Applications. Buildings. 2024; 14(6):1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061720
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez Neira, Karin, Juan Pablo Cárdenas-Ramírez, Carlos Javier Rojas-Herrera, Laia Haurie, Ana María Lacasta, Joaquín Torres Ramo, and Ana Sánchez-Ostiz. 2024. "Assessment of Elaboration and Performance of Rice Husk-Based Thermal Insulation Material for Building Applications" Buildings 14, no. 6: 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061720
APA StyleRodríguez Neira, K., Cárdenas-Ramírez, J. P., Rojas-Herrera, C. J., Haurie, L., Lacasta, A. M., Torres Ramo, J., & Sánchez-Ostiz, A. (2024). Assessment of Elaboration and Performance of Rice Husk-Based Thermal Insulation Material for Building Applications. Buildings, 14(6), 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061720










