Experimental Study on Key Techniques for the Construction of High Asphalt Concrete Core Rockfill Dam under Unfavorable Geological Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study on Compaction Characteristics of Original Graded Dam Materials
2.1. Research Background
2.2. The Influence of the Compaction Mechanism on the Compaction Characteristic Index
2.3. Large-Scale Field Relative Density Test of Bamudun Reservoir
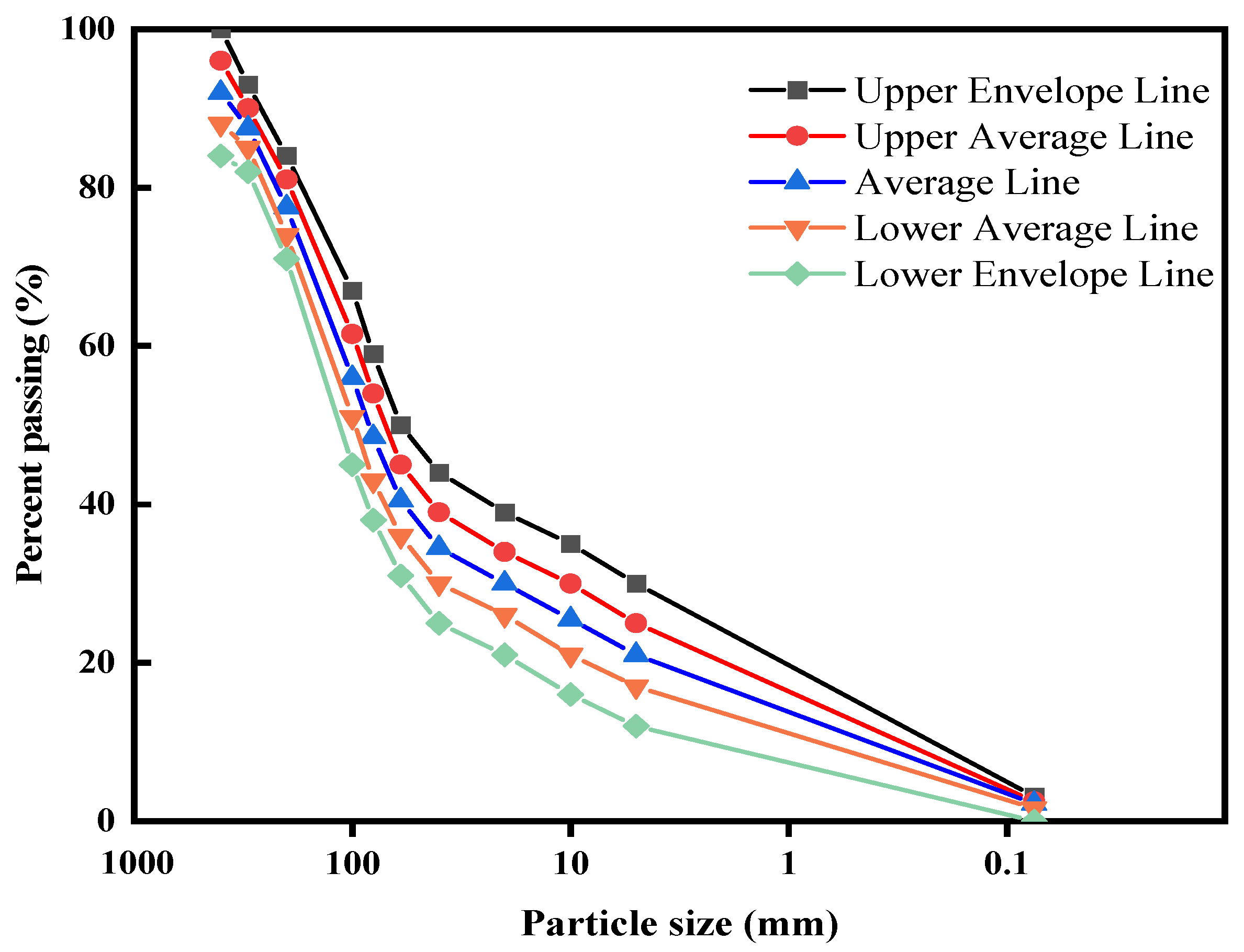
2.3.1. Experimental Soil Material and Gradation
2.3.2. Field Relative Density Test Process
2.3.3. Test Results
3. Optimization Design of the Connection between Asphalt Concrete Core Wall and Bedrock in Narrow Valley
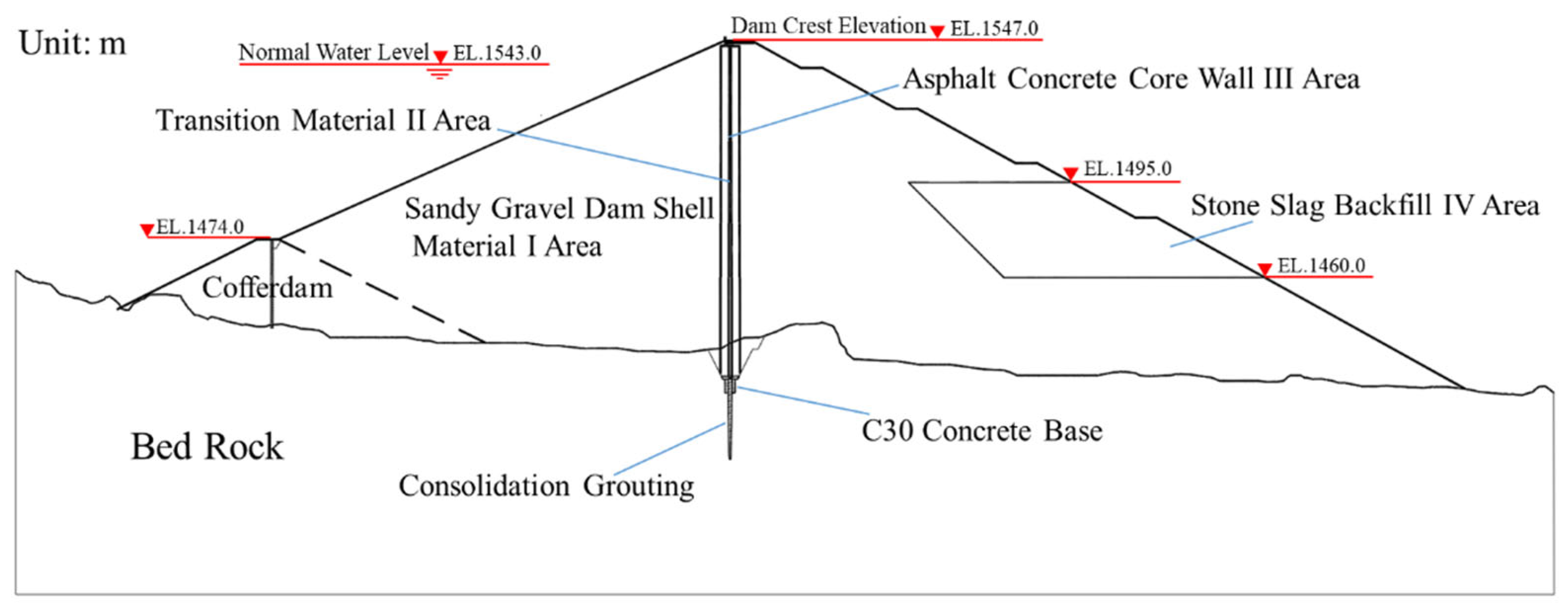
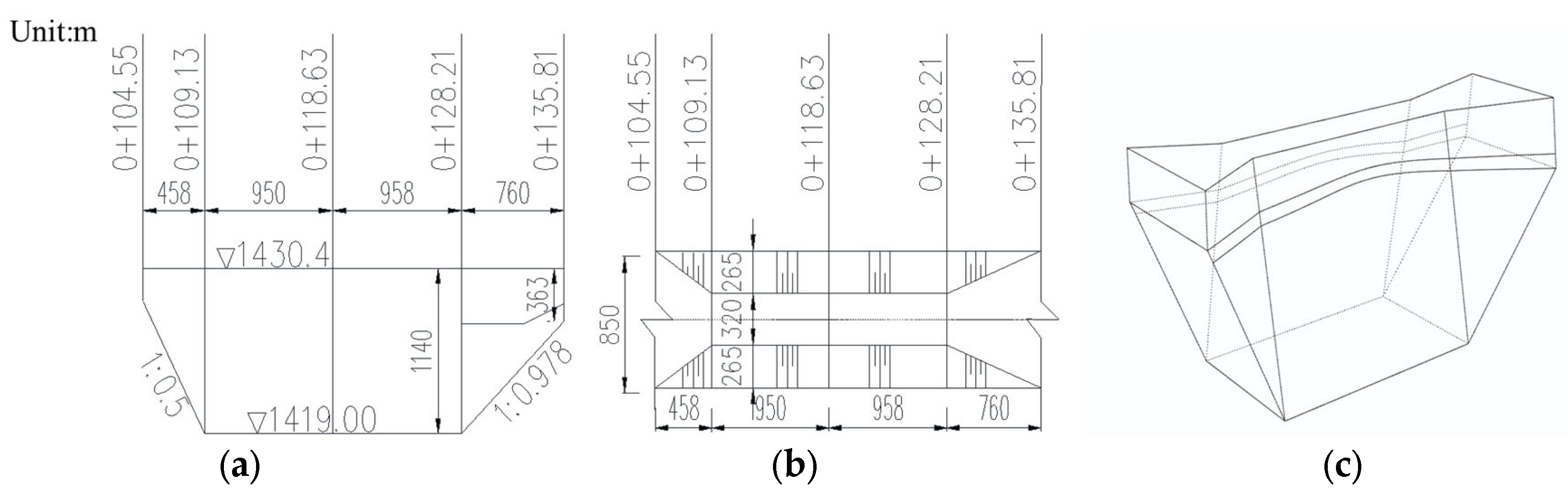
3.1. Dimensional Details of Dam
3.2. Form of Base Arrangement
3.3. Three-Dimensional Static Finite Element Analysis of Bamudun Dam
3.3.1. Finite Element Model
3.3.2. Intrinsic Model and Calculation Parameters
3.3.3. Result Analysis
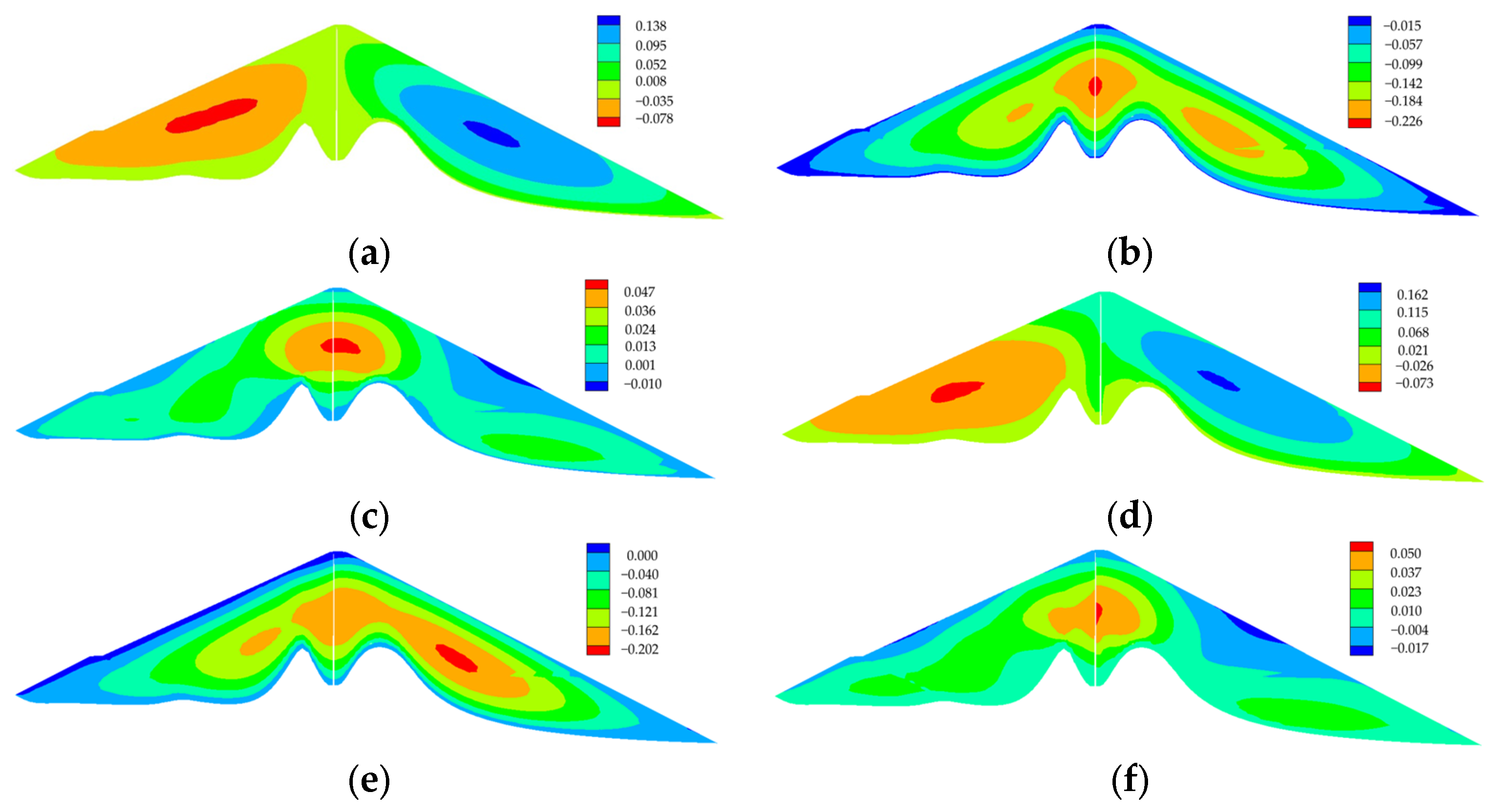
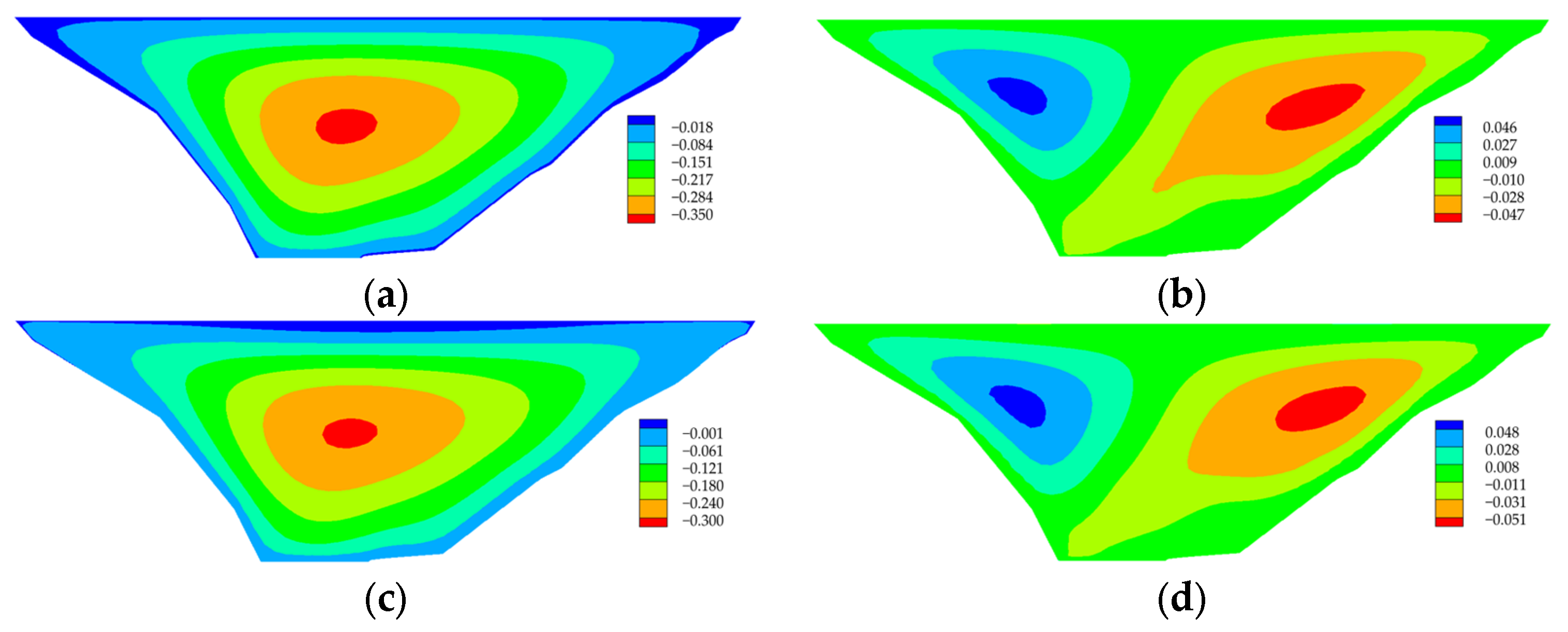
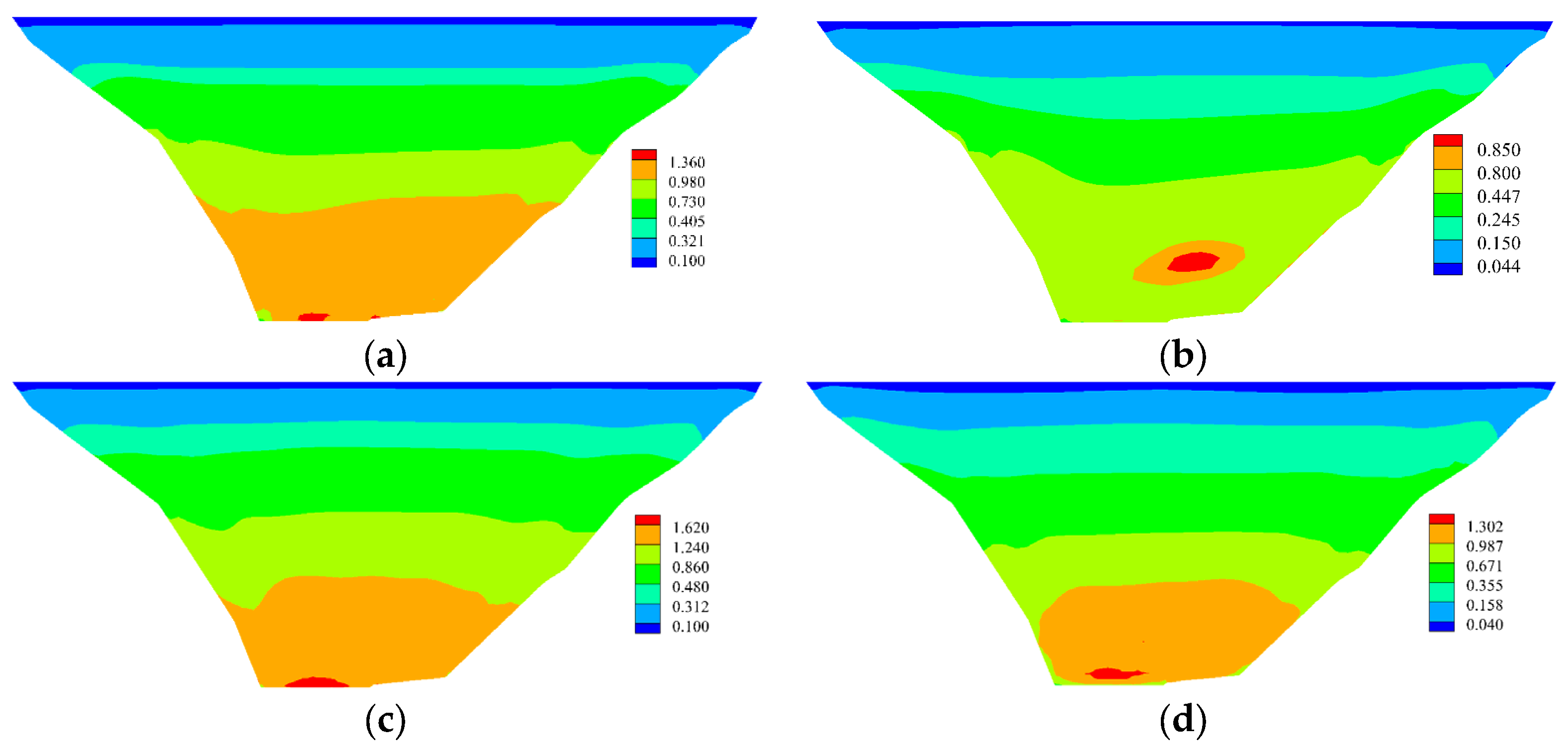
Deformation and Stress of the Dam
Deformation and Stress of Core Wall
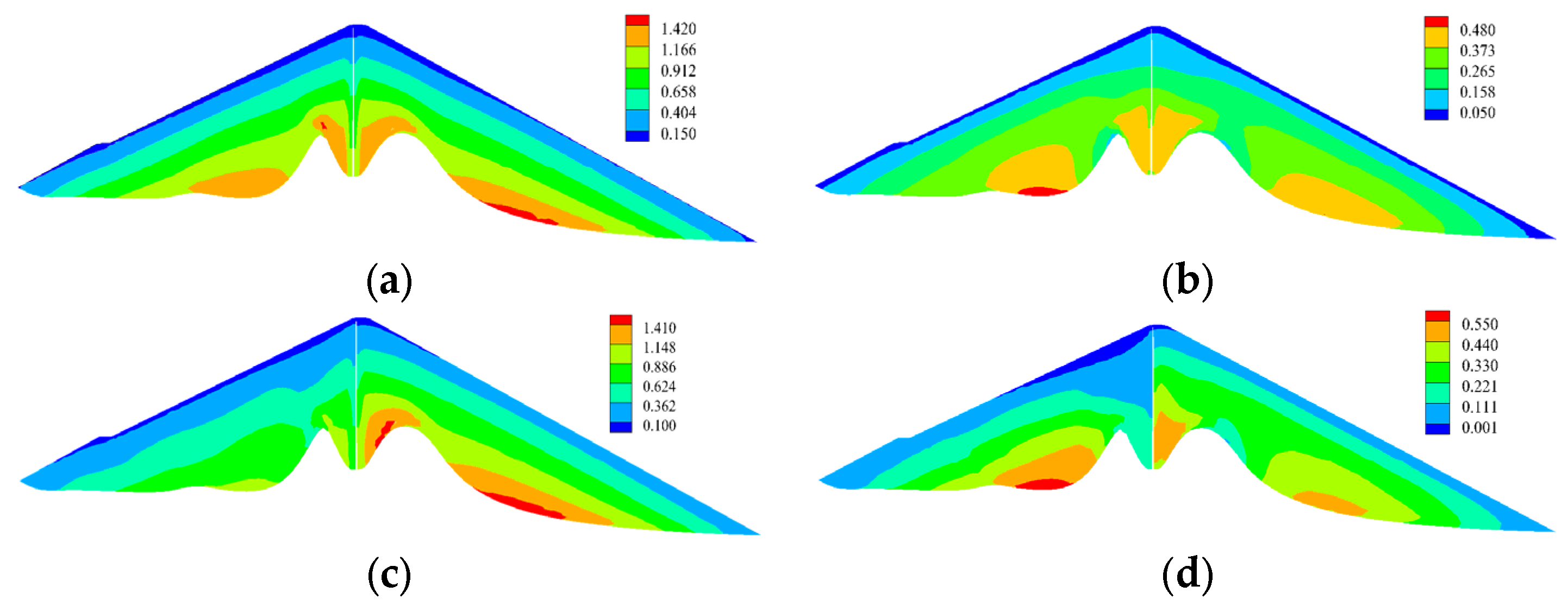
Base Stress
3.4. Base Mass Concrete Construction Temperature Control
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The maximum dry density measured by the shaking table method is 2.29 g/cm3, and the maximum dry density measured by the surface vibration method is 2.35 g/cm3. The results show that the surface vibration method can have a better compaction effect under the condition that the compaction work of the surface vibration method and the shaking table method is equal.
- (2)
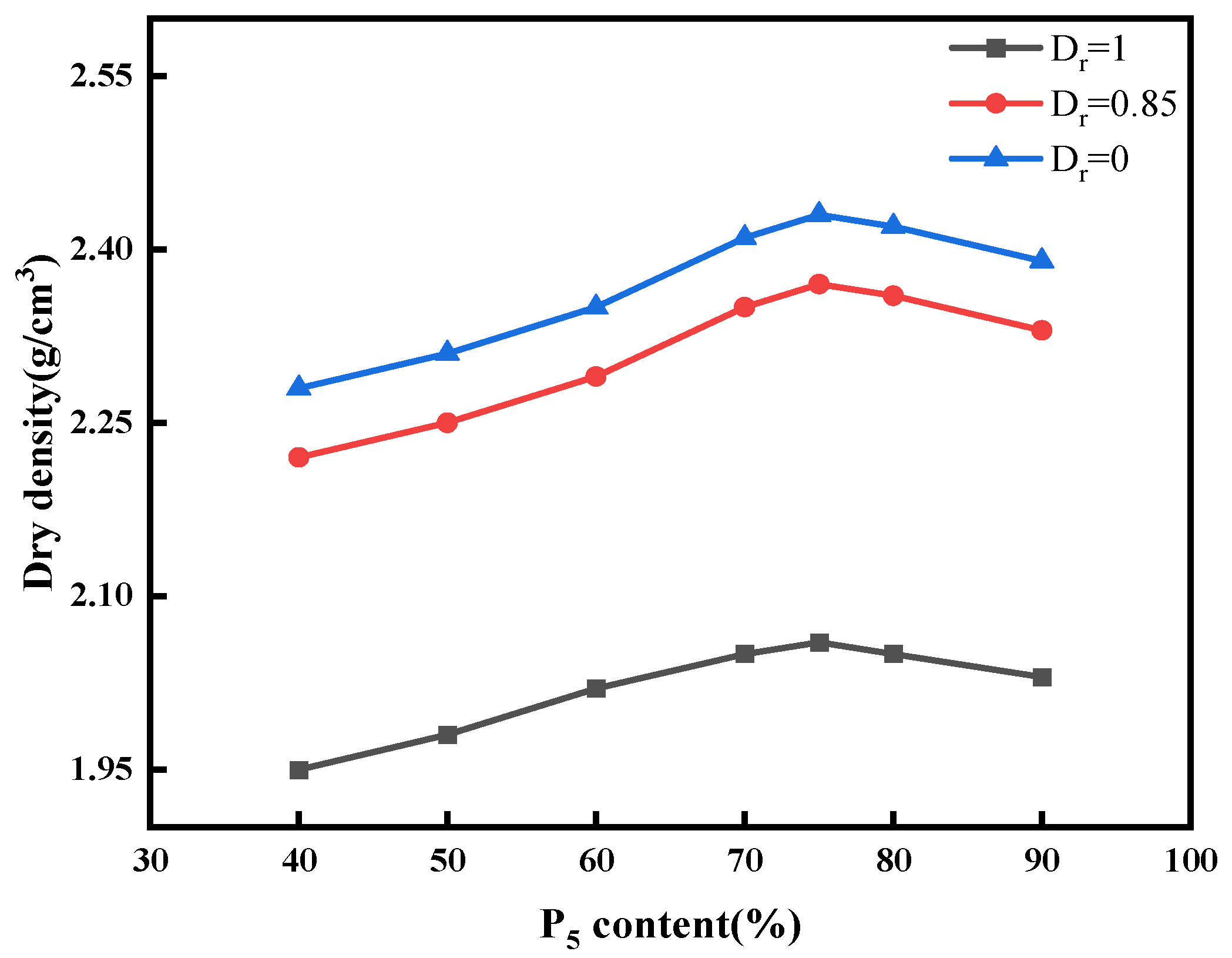
- The maximum dry density obtained by the original grading curve of the material field is 2.43 g/cm3, and the minimum dry density is 2.06 g/cm3. The corresponding optimal gravel content is 75%, and the compaction density is the highest. With the increase in gravel content, the maximum and minimum dry density values of gravel increase first and then decrease.
- (3)
- The results of a three-dimensional fine analysis show that the stress level of the dam core wall is low and there is no tensile stress. The hydraulic fracturing resistance of the dam core wall is guaranteed. The maximum compressive stress of the foundation during the completion period is 4.01 MPa. After the impoundment, the compressive stress on the downstream side of the foundation increases to 5.30 MPa, and the tensile stress is small.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noroozi, A.G.; Ajalloeian, R.; Bayat, M. Experimental study of the role of interface element in earth dams with asphalt concrete core-Case study: Mijran dam. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hu, Z.; Yu, L.; Pang, Y.; She, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Qi, C.J.M. Dynamic Characteristics of Asphalt Concrete as an Impervious Core in Embankment Dams under Varying Temperatures and Stress States. Materials 2023, 16, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Wang, W.; Hu, W.; Deng, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, C.; Höeg, K. Design and performance of the Quxue asphalt-core rockfill dam. Soils Found. 2020, 60, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhong, Q.; Hu, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, H. Model tests and numerical simulation of overtopping-induced breach process of the asphalt concrete core dam. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 157, 107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Höeg, K.; Zhang, Y. Design and performance of the Yele asphalt-core rockfill dam. Can. Geotech. J. 2010, 47, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wen, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, W. Reliability Analysis of Tensile Crack Resistance in High Asphalt Core Based on Mixed-Level Uniform Design and Response Surface Method. Int. J. Geomech. 2023, 23, 04022269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wen, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Si, Z.; Wu, L. Influence of difference in deformation modulus between asphalt concrete core and transition layer on core behavior and difference threshold determination. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 169, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, K.; Feng, S.; Zhao, R. A case study on asphalt core construction rate for the Zhaobishan embankment dam. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Deng, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Du, M. Seismic performance assessment of high asphalt concrete core rockfill dam considering shorter duration and longer duration. Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1204–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Ding, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, L. Research and Application of Key Technologies for the Construction of Cemented Material Dam with Soft Rock. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Ma, G.; Zhou, H.; Wang, D.; Lu, X.; Zhou, W. DEM investigation of the microscopic mechanism of scale effect of sandy gravel material. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, G. Research and application on large-scale coarse-grained soil filling characteristics and gradation optimization. Granul. Matter 2022, 24, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Chai, J.; Xu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y. A statistical review of the behaviour of concrete-face rockfill dams based on case histories. Géotechnique 2018, 68, 749–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Kong, X.; Zou, D.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z. Linear elastic and plastic-damage analyses of a concrete cut-off wall constructed in deep overburden. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 69, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, W.; Xiaodong, L.; Beixiao, S.; Ning, H.E. Experimental study on permeability characteristics of sandy gravel with high fines content. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 45, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yu-fei, Z.; Yi, W.; Nasier, Y.; Wen-bo, W.; Peng-fei, L.; Biao, L. Gradation of filling materials of sand-gravel dams based on multi-dimensional probability distribution. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 44, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Z. Design filling index and deformation control of high concrete faced rockfill dam in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 52, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tulamaiti, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G. Refined numerical simulation of a concrete cut-off wall in the thick overburden of dam foundation. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 4407–4420. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Ma, H.; Huang, R.; Peng, J.; Luo, S. Deep-seated toppling deformations at the dam site of the Miaowei Hydropower Station, Southwest China. Eng. Geol. 2022, 303, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamah, E.; El-Hasan, T.; Abu-Jamah, M. Dam Safety in Jordan: Factors Affecting Dam Safety, Responsibilities and Required Actions. Engineering 2023, 15, 514–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Won, M.-S. Behavior of rockfill dam under complex terrain condition. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkarak, R.; Jongpradist, P.; Pramthawee, P. A modified valley shape factor for the estimation of rockfill dam settlement. Comput. Geotech. 2019, 108, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wen, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, W. Influence of complex geological conditions on core arching of earth-rock dam. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1564–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Dang, F.; Ma, Z. Investigation for the key technologies of ultra-high asphalt concrete core rockfill dams. Soils Found. 2019, 59, 1740–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Song, G.; Wang, S. Effect of Interlayer Bonding Temperature on the Bending Properties of Asphalt Concrete Core Wall. Materials 2023, 16, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Hua, Z.; Mo, L.; Qi, C.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yu, H.; Ke, J. Evaluation on the performance of hydraulic bitumen binders under high and low temperatures for pumped storage power station projects. Materials 2022, 15, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, L.; Rampello, S.; Donatelli, R. Seismic performance of two classes of earth dams. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, C.; Wen, L.; Chen, A.; Wang, L.; Qiu, W.; Zhou, H. A study of the overtopping breach of a sand-gravel embankment dam using experimental models. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 124, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; Wu, G.-J.; Gan, B.-R.; Jiang, W.-H.; Zhou, J.W. Physical and compaction properties of granular materials with artificial grading behind the particle size distributions. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8093571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ye, Y.; He, M.; Duan, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Tan, Y. Mixing uniformity of irregular sand and gravel materials in a rotating drum with determination of contact model parameters. Powder Technol. 2019, 354, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Soil Test Method. Ministry of Building and Construction: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Tian, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Influencing factors of scale effects in large-scale direct shear tests of soil-rock mixtures based on particle breakage. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 31, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Dai, G. Estimation of the soil-water characteristic curve from the grain size distribution of coarse-grained soils. Eng. Geol. 2020, 267, 105502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, G. Effects of rock block content and confining pressure on dynamic characteristics of soil-rock mixtures. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.; Zhu, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. Effect of gradation on the compactability of coarse-grained soils. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, X.; Qiao, S.; Wang, G.; Yu, P. Field study of compaction quality control parameters and compaction mechanism of large particle size stone-filled embankment. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 3687–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodikara, J.; Islam, T.; Sounthararajah, A. Review of soil compaction: History and recent developments. Transp. Geotech. 2018, 17, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, K.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W. Laboratory investigation of the effect of initial dry density and grain size distribution on soil–water characteristic curves of wide-grading gravelly soil. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Yang, X.; Yao, Q.; Li, H. Assessment of Real-Time Compaction Quality Test Indexes for Rockfill Material Based on Roller Vibratory Acceleration Analysis. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 2879321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zou, D.; Kong, X.; Yu, X. An efficient nonlinear octree SBFEM and its application to complicated geotechnical structures. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 96, 226–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Chen, K.; Kong, X.; Liu, J. An enhanced octree polyhedral scaled boundary finite element method and its applications in structure analysis. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2017, 84, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

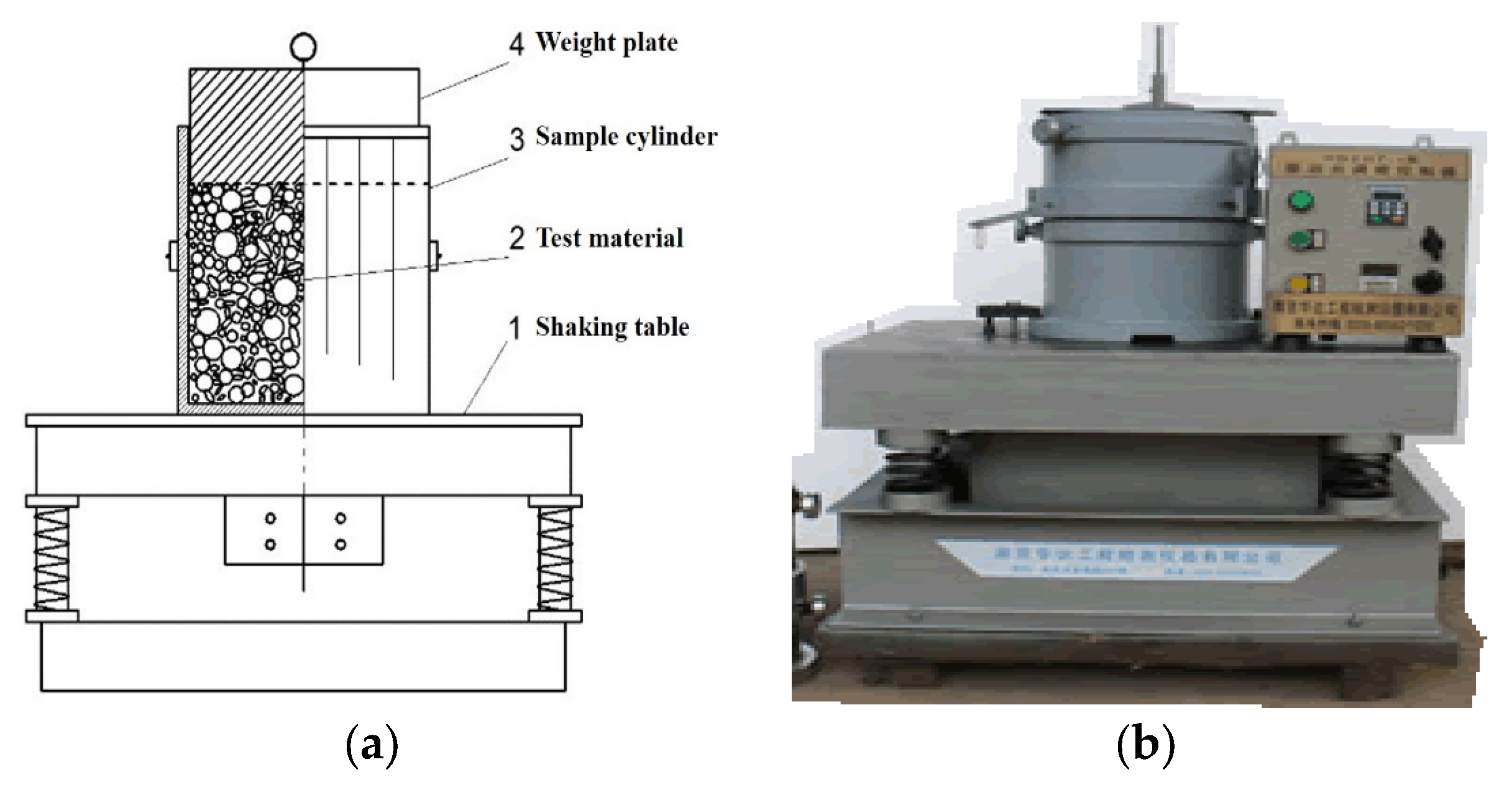
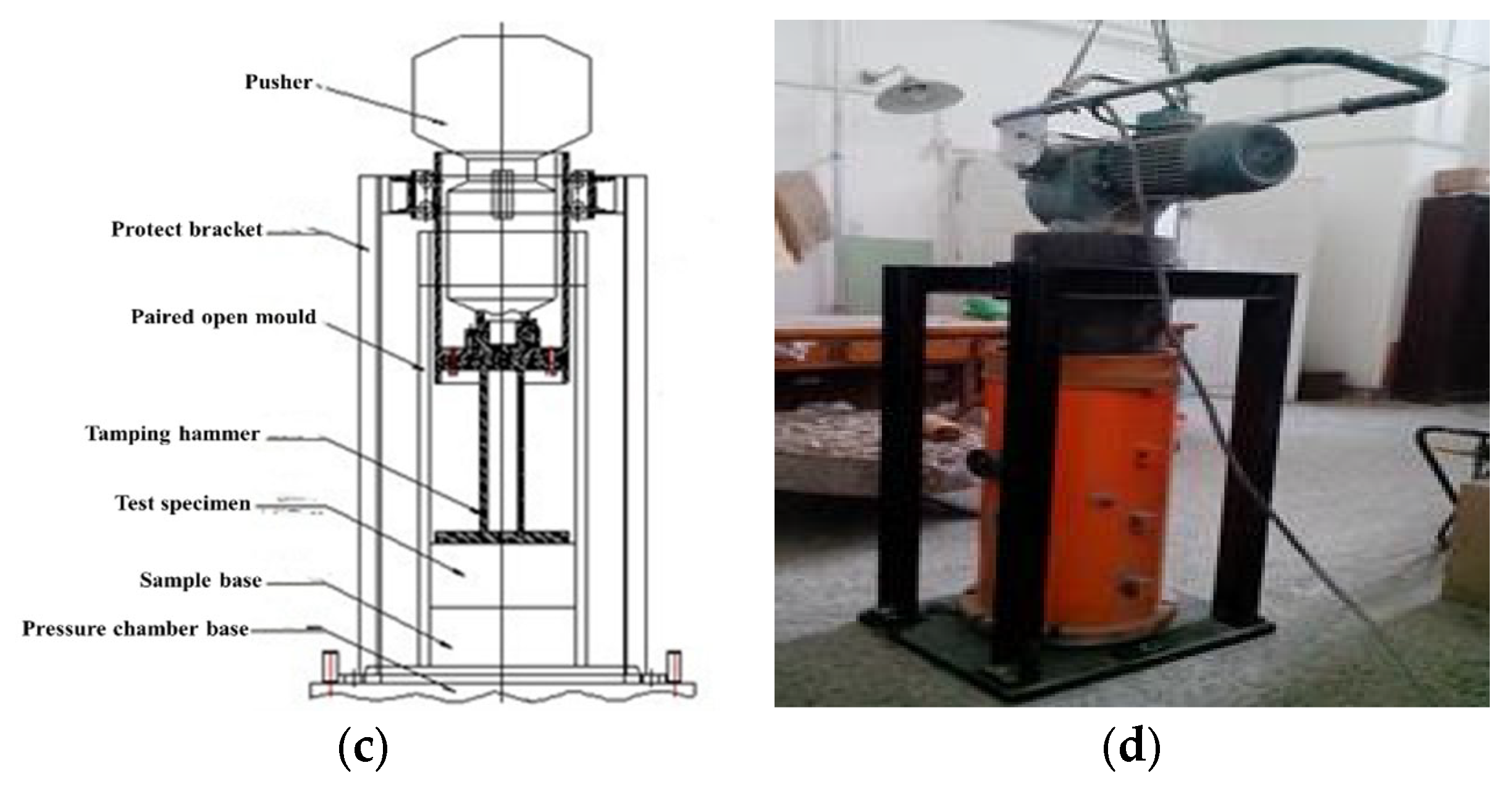



| Serial Number | Dam Name | Dam Height (m) | Dam Length (m) | Total Storge (BCM) | Installation (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Niya reservoir | 131 | 352 | 0.422 | 6 |
| 2 | Dashimen reservoir | 128 | 205 | 1.27 | 60 |
| 3 | Shimen hydropower station | 106 | 312.5 | 0.7975 | 95 |
| 4 | Wu Yi reservoir | 102.5 | 374 | 0.968 | 15 |
| 5 | Gilgrade reservoir | 101.5 | 345 | 0.61 | 20 |
| 6 | Kushitayi hydropower station | 91.1 | 439 | 1.59 | 100 |
| 7 | Nu’er reservoir | 80 | 740 | 0.68 | 62 |
| 8 | Xiabandi reservoir | 78 | 406 | 8.67 | 150 |
| 9 | Kezigar reservoir | 64 | 355 | 1.767 | 5 |
| Indoor Experiment | Minimum Dry Density (g/cm3) | Maximum Dry Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|
| Shaking table method | 0.36 | 11 |
| Surface vibration method | 0.42 | 13 |
| Material | ρ (g/cm3) | E (GPa) | υ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bed rock | 2.60 | 18.0 | 0.200 |
| Pedestal | 2.40 | 25.5 | 0.167 |
| Site | ρd (g/cm3) | K | n | Rf | φ | c (kPa) | Kb | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower part of the core wall | 2.42 | 410 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 26.7 | 325 | 2884 | 0.11 |
| Above the core wall | 2.42 | 380 | 0.10 | 0.58 | 26.1 | 390 | 2455 | 0.23 |
| Sand–gravel material | 2.25 | 1250 | 0.30 | 0.75 | 41.9 | 126 | 920 | 0.11 |
| Transition material | 2.20 | 970 | 0.20 | 0.77 | 39.5 | 105 | 520 | 0.08 |
| Item | Maximum Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completion of dam construction | Core wall deformation (cm) | along river | up current | 2.1 |
| downriver | 0.1 | |||
| hill-and-dale | 35.0 | |||
| dam axial direction | 4.7 | |||
| Core wall stress (MPa) | maximum compressive stress | 1.36 | ||
| maximum tensile stress | — | |||
| Full impoundment stage | Core wall deformation (cm) | along river | up current | 5.0 |
| downriver | 12.0 | |||
| hill-and-dale | 30.0 | |||
| dam axial direction | 5.1 | |||
| Core wall stress (MPa) | maximum compressive stress | 1.62 | ||
| maximum tensile stress | — | |||
| Item | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Completion of dam construction | maximum compressive stress (MPa) | 4.01 |
| maximum scale tension stress (MPa) | 0.20 | |
| Full impoundment stage | maximum compressive stress (MPa) | 5.30 |
| maximum scale tension stress (MPa) | 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; He, J.; Zhong, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Experimental Study on Key Techniques for the Construction of High Asphalt Concrete Core Rockfill Dam under Unfavorable Geological Conditions. Buildings 2024, 14, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071968
Li H, He J, Zhong S, Liu L, Yang W. Experimental Study on Key Techniques for the Construction of High Asphalt Concrete Core Rockfill Dam under Unfavorable Geological Conditions. Buildings. 2024; 14(7):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071968
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hao, Jianxin He, Shihua Zhong, Liang Liu, and Wu Yang. 2024. "Experimental Study on Key Techniques for the Construction of High Asphalt Concrete Core Rockfill Dam under Unfavorable Geological Conditions" Buildings 14, no. 7: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071968
APA StyleLi, H., He, J., Zhong, S., Liu, L., & Yang, W. (2024). Experimental Study on Key Techniques for the Construction of High Asphalt Concrete Core Rockfill Dam under Unfavorable Geological Conditions. Buildings, 14(7), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14071968






