Strength Prediction of Smart Cementitious Materials Using a Neural Network Optimized by Particle Swarm Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
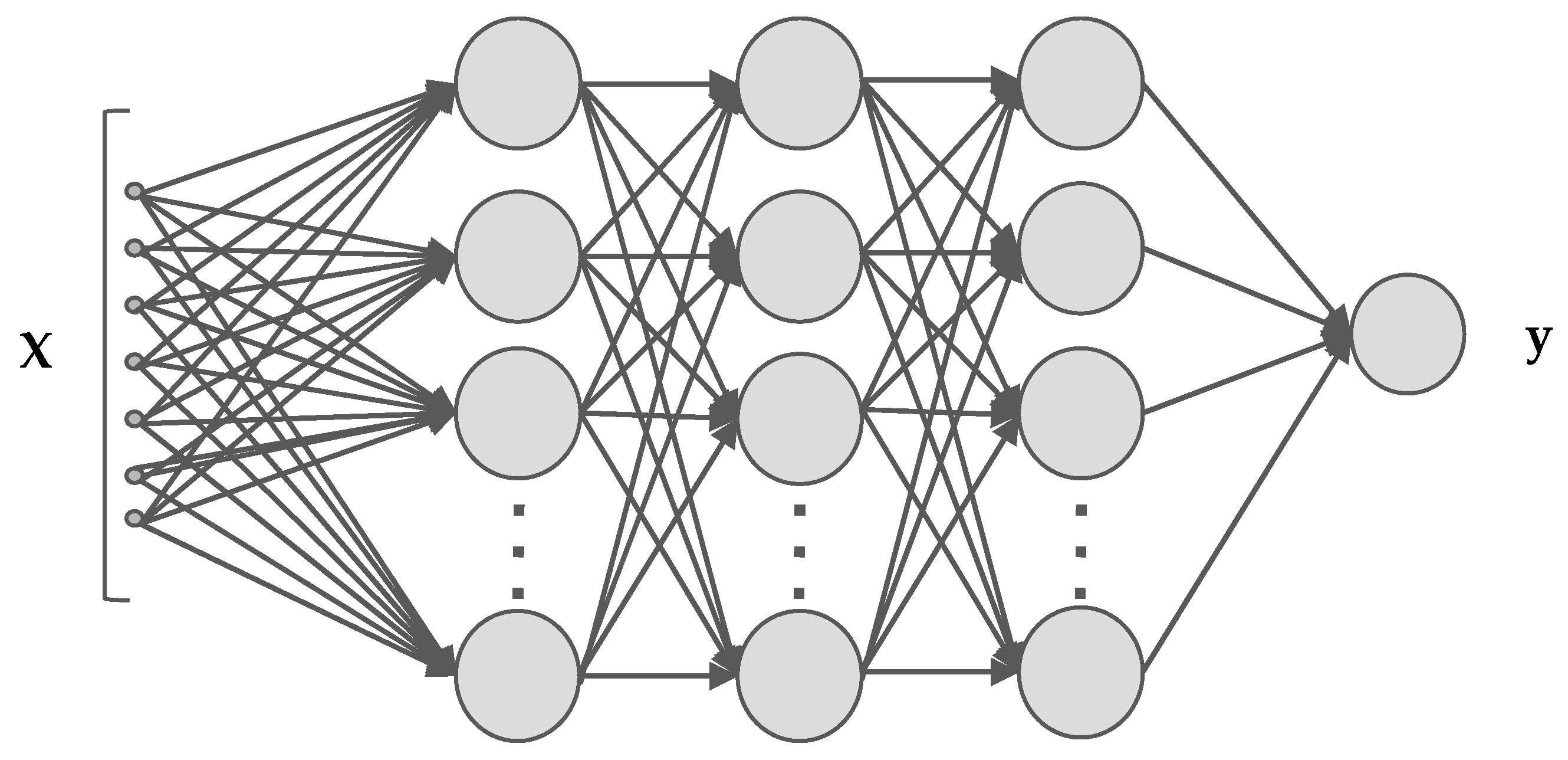
2.1. Back Propagation Neural Network
2.2. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Particle swarm optimization |
| 1. Initialization. For each of the N particles: a. Initialize the position and velocity ; b. Initialize the particle’s own best position ; c. Compute the fitness value of each particle and if , initialize the global best solution as ; 2. Repeat the following steps until the termination condition is met: a. Update the particle velocity using the following equation: ; b. Update the particle position using the following equation: ; c. Compute the fitness value of each particle ; d. If , update the personal best position: ; e. If , update the personal best position: ; 3. Output the optimal result. |
2.3. PSO–BPNN
| Algorithm 2 PSO-BPNN |
|
3. Application Examples and Discussions
3.1. 3D Printed Fiber Reinforced Concrete
3.1.1. Data Collection and Description
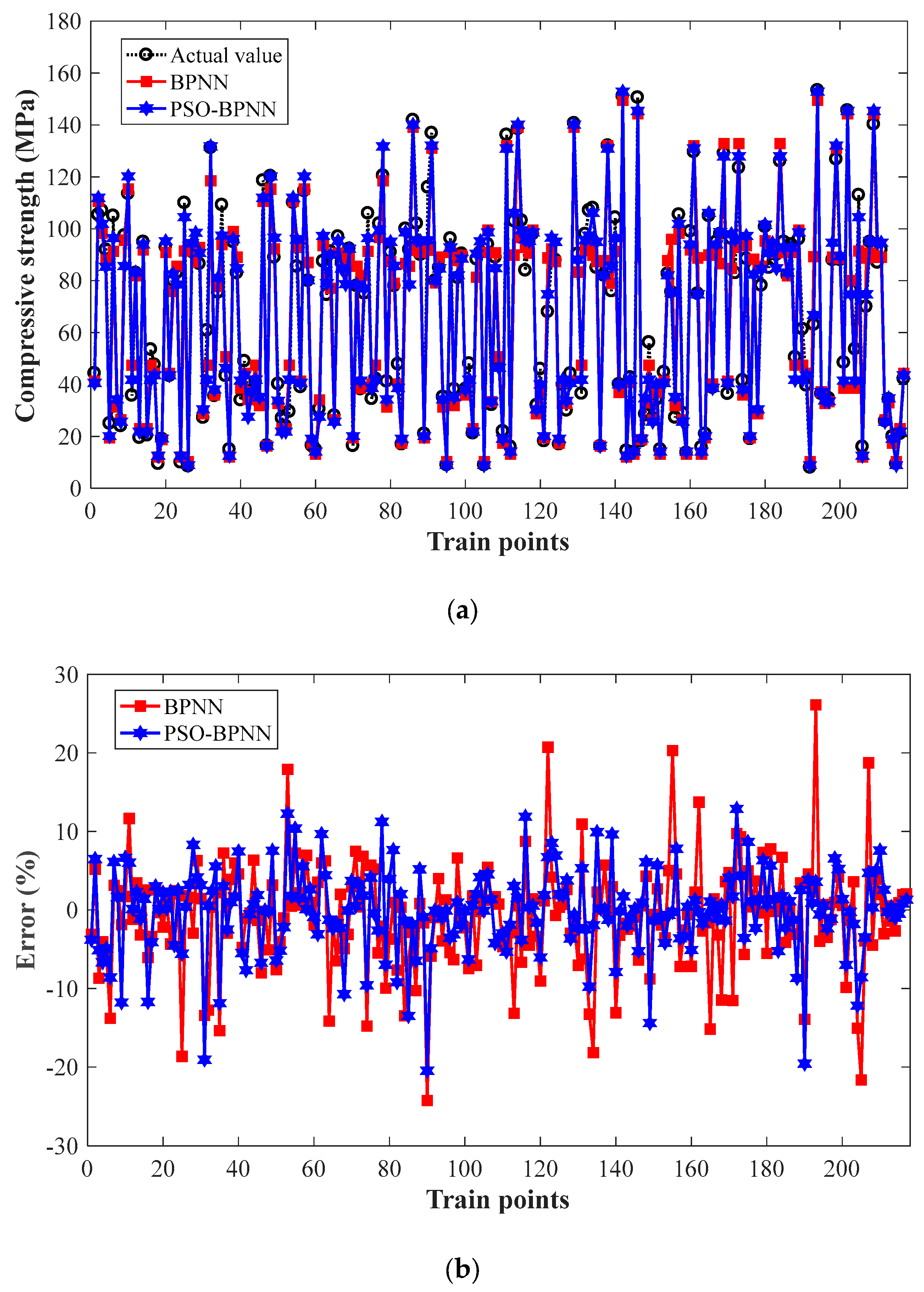
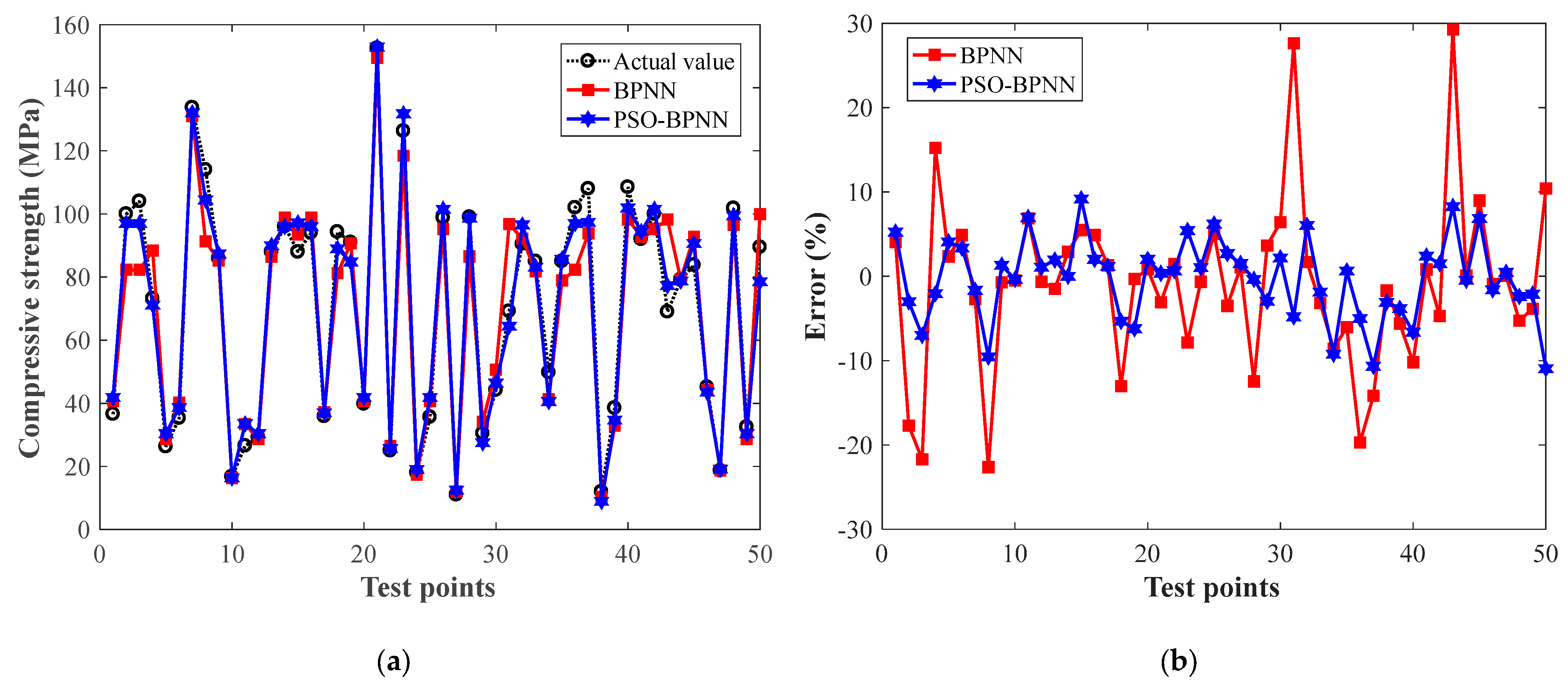
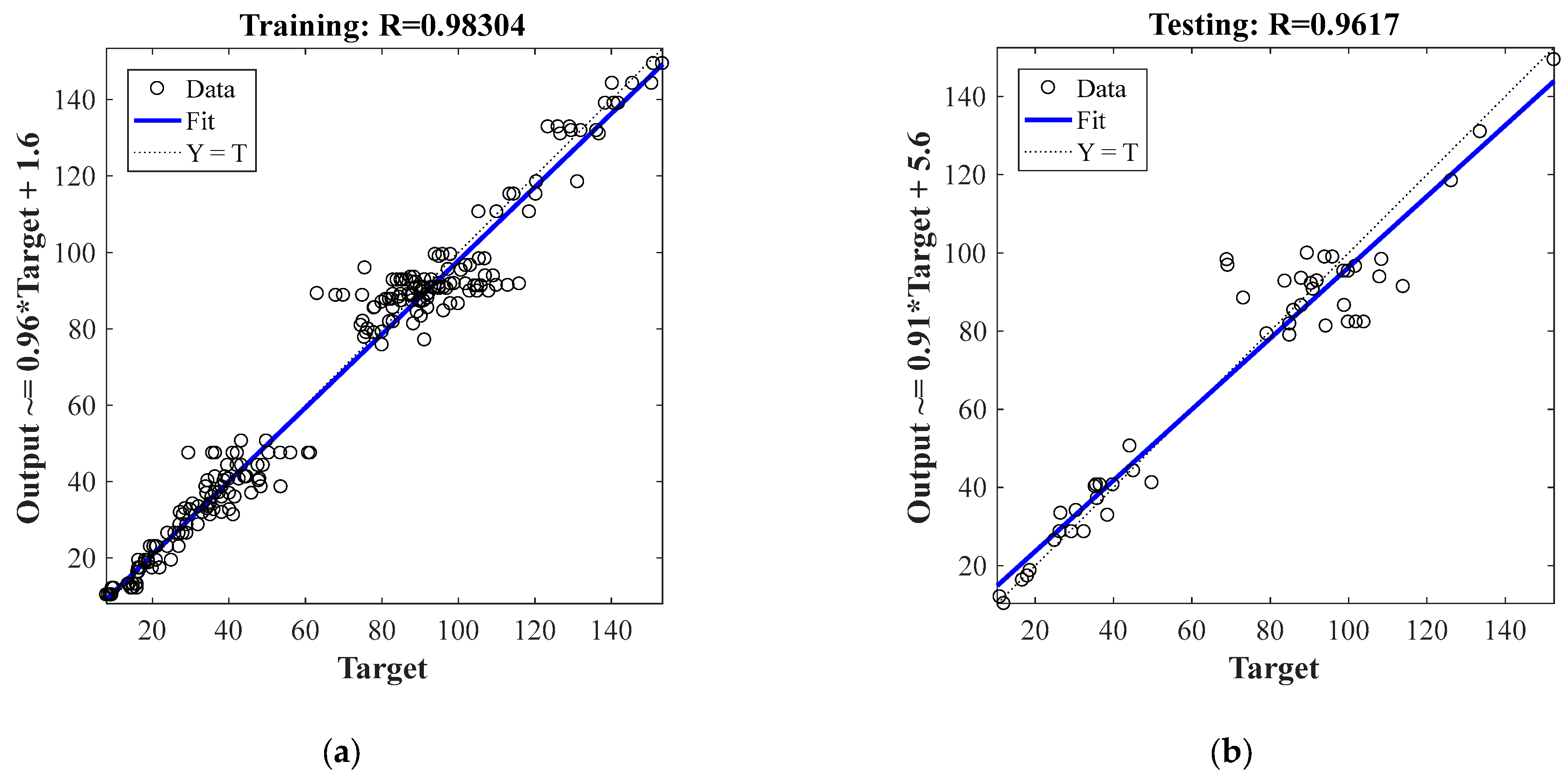
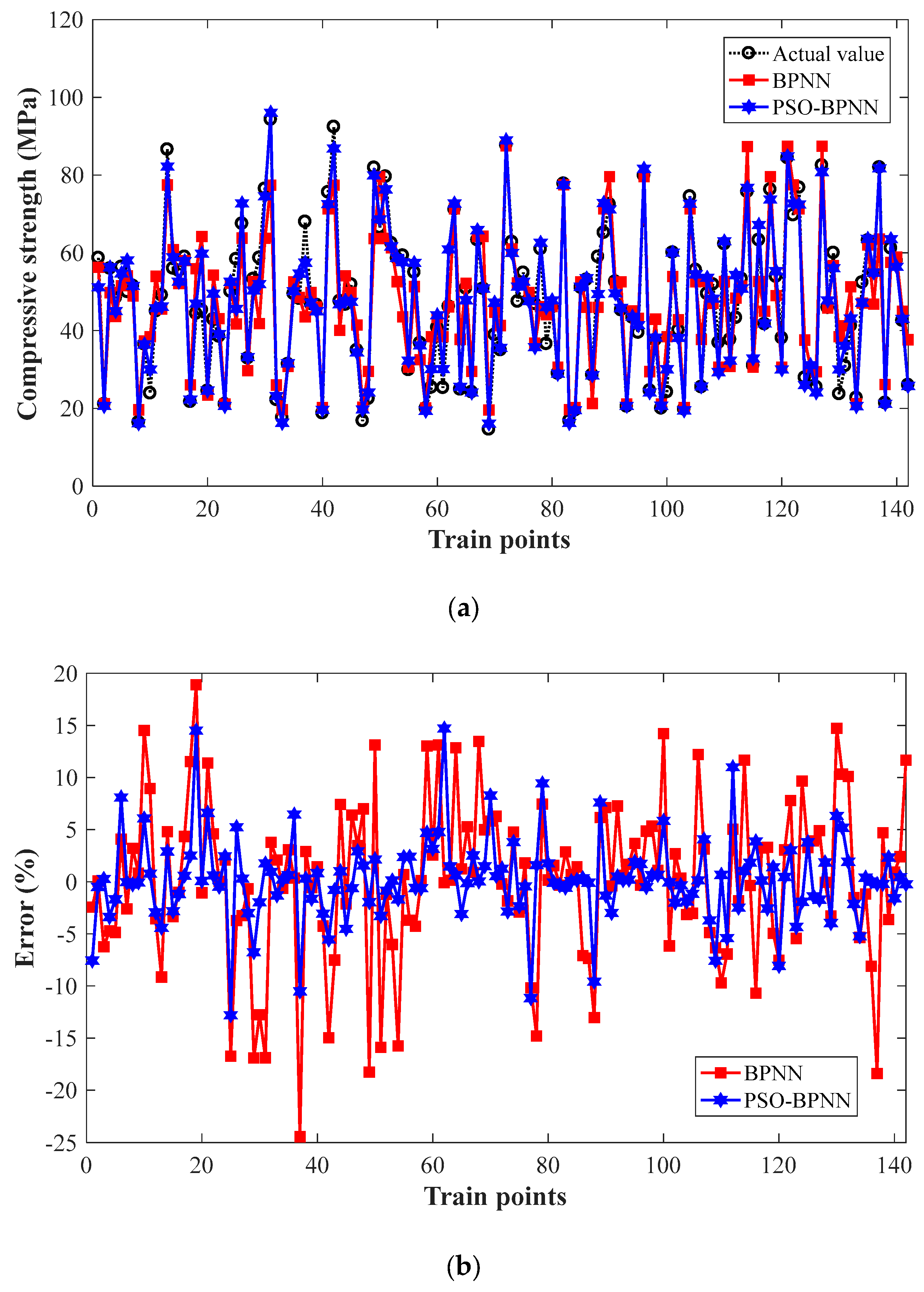
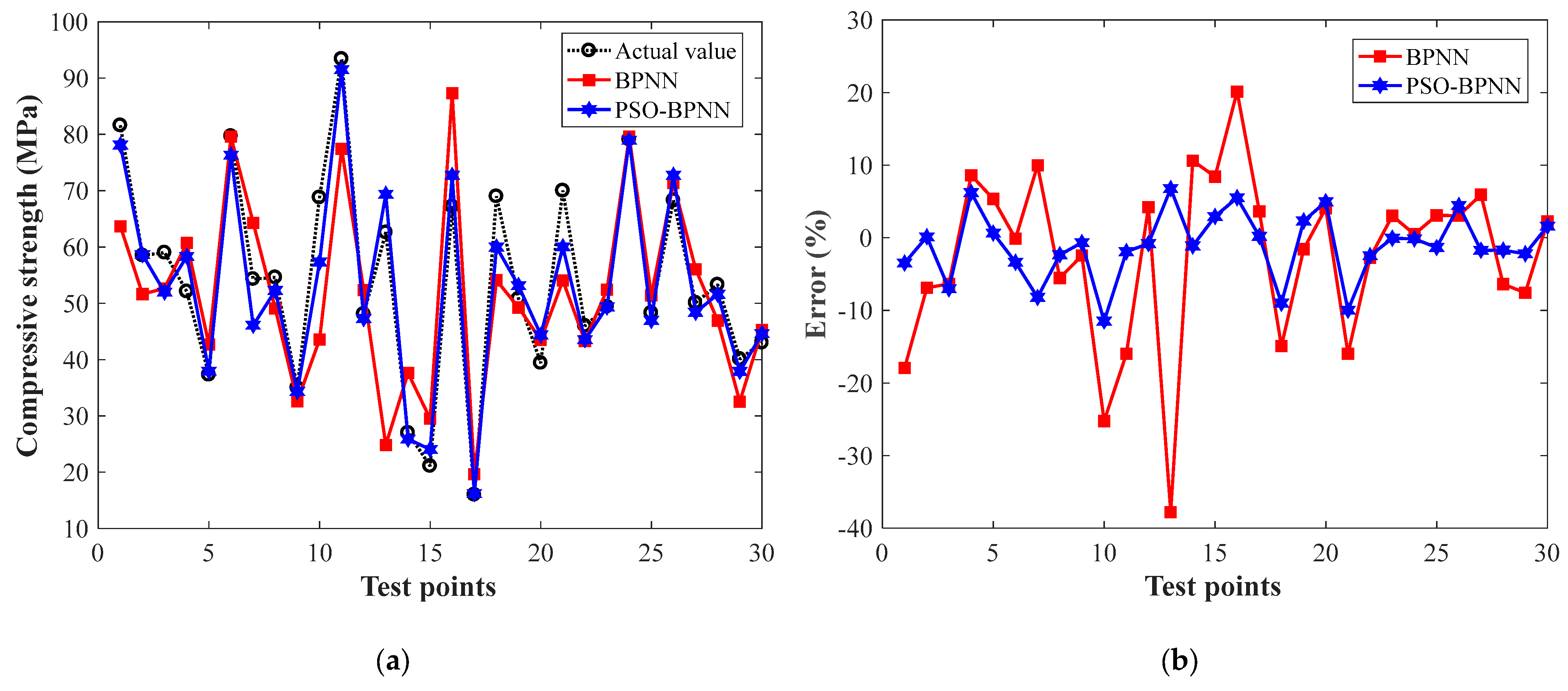
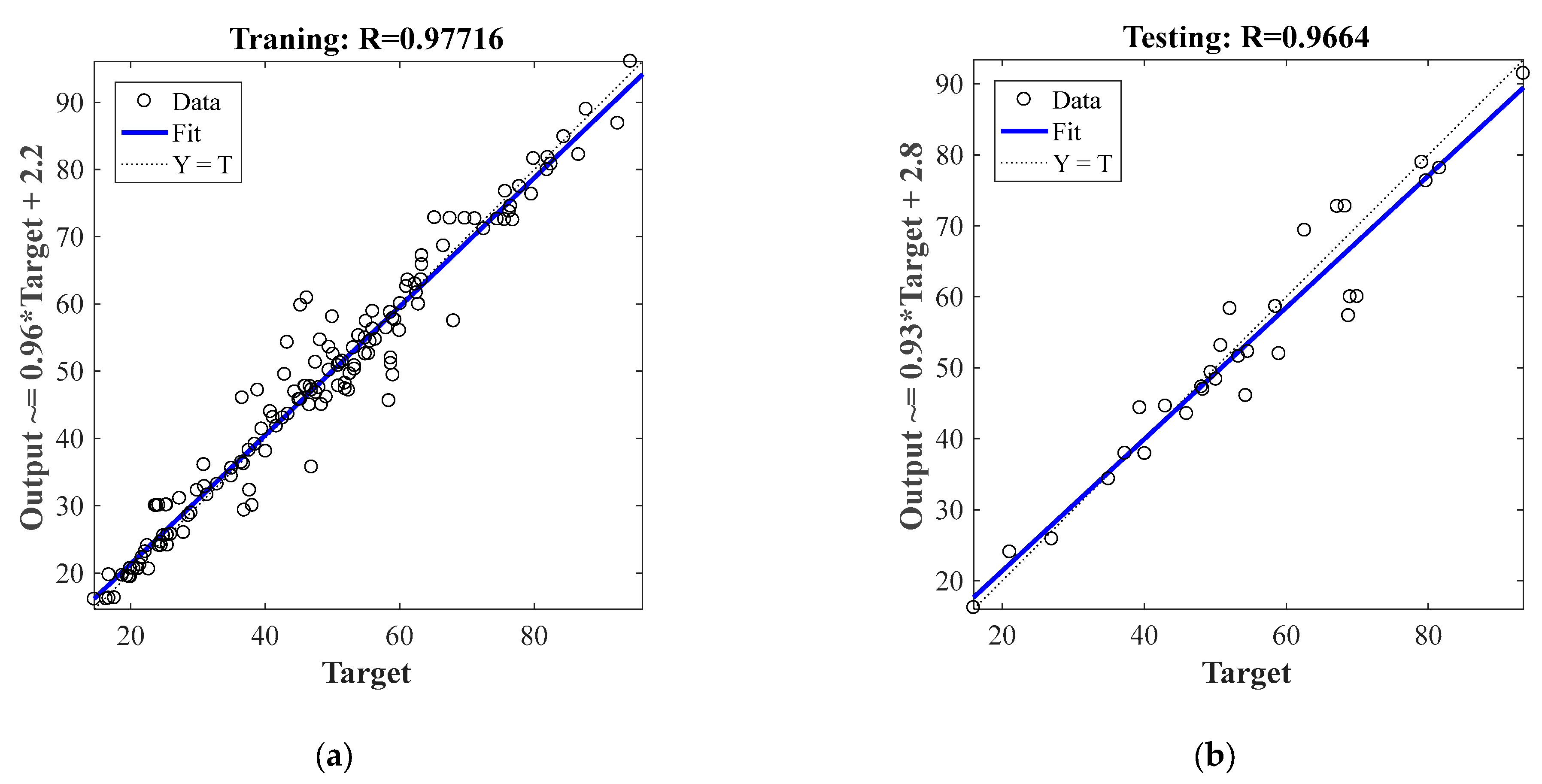
3.1.2. Results and Discussions
3.2. Graphene Nanoparticles Reinforced Cementitious Composites
3.2.1. Data Collection and Description
3.2.2. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larrard, F.D. Concrete Mixture Proportioning: A Scientific Approach; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Sun, S.; Ding, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Review of nanocarbon-engineered multifunctional cementitious composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 70, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, S. Efficient quasi-brittle fracture simulations of concrete at mesoscale using micro CT images and a localizing gradient damage model. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 400, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, L.; Huang, Y.-J.; Wriggers, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.-H. Investigation on fracture behaviour of UHPFRC using a mesoscale computational framework. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 421, 116796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, S.; Yu, X.; Han, B.; Ou, J. Multifunctional cementitious composites modified with nano titanium dioxide: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 111, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Li, Q.; Xu, S. A review of self-sensing ultra-high performance concrete: Towards next-generation smart structural materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 145, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qu, F.; Dong, W.; Mishra, G.; Shah, S.P. A comprehensive review on self-sensing graphene/cementitious composites: A pathway toward next-generation smart concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makul, N. Advanced smart concrete—A review of current progress, benefits and challenges. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 274, 122899. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Smart concretes and structures: A review. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1303–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-W.; Chung, D.D.L. Carbon fiber reinforced concrete for smart structures capable of non-destructive flaw detection. Smart Mater. Struct. 1993, 2, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Kamila, S. Introduction, classification and applications of smart materials: An overview. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 10, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Yu, J.; Das, A.K.; Leung, C.K. A review of self-sensing and self-healing ‘smart’cement based materials-bridging the gap between research and adoption. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Service Life Design for Infrastructures, Delft, The Netherlands, 27–30 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Aza, C.A. Self sensing carbon nanotube (CNT) and nanofiber (CNF) cementitious composites for real time damage assessment in smart structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ding, S.; Yu, X. Intrinsic self-sensing concrete and structures: A review. Measurement 2015, 59, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Tao, Z.; Wang, K. Piezoresistive properties of cement-based sensors: Review and perspective. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Aslani, F. A review on material design, performance, and practical application of electrically conductive cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, B.; Vlachakis, C.; Al-Tabbaa, A.; Haigh, S.K. Characterization and piezo-resistivity studies on graphite-enabled self-sensing cementitious composites with high stress and strain sensitivity. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, F.; Nasir Amin, M.; Khan, K.; Rehan Sadiq, M.; Faisal Javed, M.; Aslam, F.; Alyousef, R. A comparative study of random forest and genetic engineering programming for the prediction of compressive strength of high strength concrete (HSC). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-S.; Chiu, C.-K.; Farfoura, M.; Al-Taharwa, I. Optimizing the prediction accuracy of concrete compressive strength based on a comparison of data-mining techniques. J. Comput. Civil. Eng. 2011, 25, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, S.; Yang, J.; Amin, M.N.; Khan, K.; Javed, M.F.; Althoey, F. Formulation of estimation models for the compressive strength of concrete mixed with nanosilica and carbon nanotubes. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 13, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, C.; Shen, J. The study of effect of carbon nanotubes on the compressive strength of cement-based materials based on machine learning. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 358, 129435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Sy, T.; Wakim, J.; To, Q.-D.; Vu, M.-N.; Nguyen, T.-D.; Nguyen, T.-T. Predicting the compressive strength of concrete from its compositions and age using the extreme gradient boosting method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Ye, J.; Deng, B.; Li, L.; Yu, K. Interpretable machine learning for predicting the strength of 3D printed fiber-reinforced concrete (3DP–FRC). J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, P.Y.; Jaf, D.K.I.; Abdalla, A.A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Faraj, R.H.; Mahmood, W.; Mohammed, A.S. Prediction of the compressive strength of strain-hardening cement-based composites using soft computing models. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 6761–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piro, N.S.; Mohammed, A.S.; Hamad, S.M. Multiple analytical models to evaluate the impact of carbon nanotubes on the electrical resistivity and compressive strength of the cement paste. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shentu, J.; Xie, N.; Huang, Y.; Lei, G.; Hu, H.; Guo, P.; Gong, X. Predicting triaxial compressive strength of high-temperature treated rock using machine learning techniques. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 2072–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Sanjayan, J. Mechanical anisotropy of aligned fiber reinforced composite for extrusion-based 3D printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Xiao, J.; Zou, S.; Zhou, X. Anisotropic behavior in bending of 3D printed concrete reinforced with fibers. Compos. Struct. 2020, 254, 112808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Putten, J.; Rahul, A.V.; De Schutter, G.; Van Tittelboom, K. Development of 3D printable cementitious composites with the incorporation of polypropylene fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Leung, C.K.Y. Impact of 3D printing direction on mechanical performance of strain-hardening cementitious composite (SHCC). In Proceedings of the First RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication—Digital Concrete, Zurich, Switzerland, 10–12 September 2018; pp. 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Arunothayan, A.R.; Nematollahi, B.; Ranade, R.; Bong, S.H.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Khayat, K.H. Fiber orientation effects on ultra-high performance concrete formed by 3D printing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 143, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Cui, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, K.; Xiao, J. Fresh and anisotropic-mechanical properties of 3D printable ultra-high ductile concrete with crumb rubber. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 211, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.; Tran, P.; Sanjayan, J. Steel fibres reinforced 3D printed concrete: Influence of fibre sizes on mechanical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; McGee, W.; Ng, T.Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, V.C. 3D–printable engineered cementitious composites (3DP–ECC): Fresh and hardened properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 143, 106388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.; Lin, X.; Gravina, R.J.; Tran, P. Influence of PVA and PP fibres at different volume fractions on mechanical properties of 3D printed concrete. In Proceedings of the 16th East Asian-Pacific Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction, Brisbane, Australia, 3–6 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alyami, M.; Khan, M.; Fawad, M.; Nawaz, R.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Najeh, T.; Gamil, Y. Predictive modeling for compressive strength of 3D printed fiber-reinforced concrete using machine learning algorithms. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, J.; Yang, Y.; Gu, C. Study on dispersion, mechanical and microstructure properties of cement paste incorporating graphene sheets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 199, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, T.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; Fu, Y.; Shi, S. Study of mechanical properties and early-stage deformation properties of graphene-modified cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ling, L.; Ren, Z.; Memon, S.A.; Xing, F. Effect of graphene oxide/graphene hybrid on mechanical properties of cement mortar and mechanism investigation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Monasterio, M.; Cui, H.; Han, N. Experimental study of the effects of graphene oxide on microstructure and properties of cement paste composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 102, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, C.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Effect of graphene oxide nanosheets of microstructure and mechanical properties of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxa, Z.S. Exfoliated graphene nanoplatelet cement-based nanocomposites as piezoresistive sensors: Influence of nanoreinforcement lateral size on monitoring capability. Ciência Tecnol. Dos Mater. 2016, 28, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Q.; Gao, R.; Tong, T. Experimental investigation on mechanical and piezoresistive properties of cementitious materials containing graphene and graphene oxide nanoplatelets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C. Effect of graphene on mechanical properties of cement mortars. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ouyang, D. Effect of graphene oxide on mechanical properties of cement mortar and its strengthening mechanism. Materials 2019, 12, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Han, B.; Jiang, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Ou, J. Nano graphite platelets-enabled piezoresistive cementitious composites for structural health monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Q. Effect of GO nanosheets on shapes of cement hydration crystals and their formation process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Ge, Y.; Cai, C.S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Mechanical properties and microstructure of graphene oxide cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 194, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, M.; Jiang, S.; Tao, D. Research on electrical conductivity of graphene/cement composites. Adv. Cem. Res. 2020, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Pang, B. Mechanical property and toughening mechanism of water reducing agents modified graphene nanoplatelets reinforced cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kothiyal, N.C. Comparative Effects of pristine and ball-milled graphene oxide on physico-chemical characteristics of cement mortar nanocomposites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jiang, R.; Wu, Z. Investigation of the mechanical properties and microstructure of graphene nanoplatelet-cement composite. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Pang, B.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; She, W.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on preparation and multifunctionality of reduced graphene oxide cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 275, 122119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, I.; Arena, N.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Graphene nanoplatelet reinforced concrete for self-sensing structures—A lifecycle assessment perspective. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 240, 118202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazizadeh, S.; Duffour, P.; Skipper, N.T.; Bai, Y. Understanding the behaviour of graphene oxide in portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 111, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, C. Influence of graphene oxide additions on the microstructure and mechanical strength of cement. New Carbon Mater. 2015, 30, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, S. Reinforcing mechanism of graphene and graphene oxide sheets on cement-based materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shuang, D. Effect of Graphene nanoplatelets on the properties, pore structure and microstructure of cement composites. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.S.; Panesar, D.K. Nano reinforced cement paste composite with functionalized graphene and pristine graphene nanoplatelets. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 197, 108063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, P.T.; Tragazikis, I.K.; Trakakis, G.; Galiotis, C.; Dassios, K.G.; Matikas, T.E. Multifunctional cement mortars enhanced with graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2021, 21, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Pang, S.D. Enhancement of barrier properties of cement mortar with graphene nanoplatelet. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Ting, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Use of Graphene oxide nanosheets to regulate the microstructure of hardened cement paste to increase its strength and toughness. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 8508–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Pan, Z.; Korayem, A.H.; Qiu, L.; Li, D.; Collins, F.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Reinforcing effects of graphene oxide on portland cement paste. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, A4014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baomin, W.; Shuang, D. Effect and mechanism of graphene nanoplatelets on hydration reaction, mechanical properties and microstructure of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; She, W.; Du, F.; Xu, K. Experimental study on mechanical and functional properties of reduced graphene oxide/cement composites. Materials 2020, 13, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Tan, S.; Yu, Q. Investigation of the effects of graphene and graphene oxide nanoplatelets on the micro- and macro-properties of cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Nassar, R.-U.-D.; Anwar, W.; Rasheed, M.; Najeh, T.; Gamil, Y.; Farooq, F. Forecasting the strength of graphene nanoparticles—Reinforced cementitious composites using ensemble learning algorithms. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N | c1 | c2 | |||
| 10 | 2 | 2 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 50 |
| Variables | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Kurtosis | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC (kg/m3) | 534.00 | 194.92 | 1112.3 | 285.30 | 4.07 | 1.16 |
| W/B | 0.21 | 0.055 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 2.82 | 0.87 |
| S (kg/m3) | 804.04 | 414.72 | 1902 | 246 | 2.61 | 0.10 |
| FA (kg/m3) | 315.98 | 424.54 | 1141.4 | 0 | 1.96 | 0.81 |
| GS (kg/m3) | 170.00 | 170.84 | 450 | 0 | 1.18 | 0.077 |
| SF (kg/m3) | 182.46 | 128.41 | 377.80 | 0 | 1.71 | −0.27 |
| SP (kg/m3) | 6.98 | 4.95 | 20 | 0 | 2.47 | 0.43 |
| HPMC (kg/m3) | 0.83 | 1.26 | 3.8 | 0 | 3.39 | 1.30 |
| W (kg/m3) | 258.54 | 84.49 | 427.90 | 182 | 1.61 | 0.45 |
| Vf (%) | 0.01 | 0.0073 | 0.02 | 0 | 1.65 | 0.23 |
| CA (days) | 24.25 | 8.76 | 28 | 1 | 4.86 | −1.94 |
| LD (x, y, z) | 2.14 | 0.81 | 3 | 1 | 1.56 | −0.26 |
| Df (μm) | 45.64 | 52.54 | 200 | 15 | 7.62 | 2.52 |
| Lf (mm) | 7.20 | 3.57 | 18 | 0 | 3.98 | 0.95 |
| Ftype | 2.43 | 0.99 | 5 | 1 | 2.94 | 0.58 |
| CS (MPa) | 67.95 | 37.65 | 153.40 | 8 | 1.93 | 0.13 |
| Model | R2 | MAE | MSE | RMSE | MAPE |
| Training | |||||
| BPNN | 0.98 | 5.03 | 49.25 | 7.02 | 8.97% |
| PSO–BPNN | 0.99 | 4.86 | 28.95 | 5.38 | 7.25% |
| Testing | |||||
| BPNN | 0.96 | 6.76 | 98.24 | 9.91 | 9.94% |
| PSO–BPNN | 0.99 | 3.72 | 22.66 | 4.76 | 6.72% |
| Model | R | MAE | RMSE |
| SVR | 0.84 | 10.245 | 18.717 |
| DT | 0.987 | 4.644 | 6.589 |
| RF | 0.986 | 3.989 | 7.134 |
| SVR–Bagging | 0.897 | 10.771 | 19.007 |
| GB | 0.986 | 3.901 | 7.211 |
| SVR–Boosting | 0.961 | 9.491 | 12.833 |
| GEP | 0.985 | 5.691 | 6.405 |
| Variables | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Kurtosis | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 1.37 | 1.49 | 3 | 0 | −1.99 | 0.16 |
| GD (μm) | 3.38 | 6.87 | 50 | 0.07 | 35.55 | 5.60 |
| GT (nm) | 3.39 | 5.19 | 27.6 | 0.7 | 14.18 | 3.63 |
| GC (wt%) | 0.26 | 0.94 | 6.4 | 0.01 | 31.12 | 5.44 |
| w/c | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.72 | 0.2 | 1.43 | 1.24 |
| US (h) | 0.49 | 0.82 | 3 | 0 | 4.66 | 2.37 |
| CA (days) | 19.70 | 10.82 | 28 | 1 | −1.49 | −0.62 |
| CS (MPa) | 48.51 | 19.10 | 94.26 | 14.59 | −0.60 | 0.20 |
| Model | R2 | MAE | MSE | RMSE | MAPE |
| Training | |||||
| BPNN | 0.92 | 5.80 | 59.63 | 7.72 | 13.81% |
| PSO–BPNN | 0.98 | 2.71 | 16.54 | 4.07 | 6.24% |
| Testing | |||||
| BPNN | 0.77 | 8.68 | 141.91 | 11.91 | 16.51% |
| PSO–BPNN | 0.97 | 3.49 | 21.96 | 4.69 | 6.32% |
| Model | R | MAE | RMSE |
| DT | 0.87 | 4.60 | 5.44 |
| AR | 0.82 | 4.54 | 6.44 |
| BR | 0.80 | 5.42 | 6.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Kong, F.; Hai, L. Strength Prediction of Smart Cementitious Materials Using a Neural Network Optimized by Particle Swarm Algorithm. Buildings 2024, 14, 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072033
Zhang P, Kong F, Hai L. Strength Prediction of Smart Cementitious Materials Using a Neural Network Optimized by Particle Swarm Algorithm. Buildings. 2024; 14(7):2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072033
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pengfei, Fan Kong, and Lu Hai. 2024. "Strength Prediction of Smart Cementitious Materials Using a Neural Network Optimized by Particle Swarm Algorithm" Buildings 14, no. 7: 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072033
APA StyleZhang, P., Kong, F., & Hai, L. (2024). Strength Prediction of Smart Cementitious Materials Using a Neural Network Optimized by Particle Swarm Algorithm. Buildings, 14(7), 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072033






