Thermal Evaluation of a Water-to-Air Heat Exchanger Combined with Different Roof Configurations for Passive Cooling
Abstract
1. Introduction
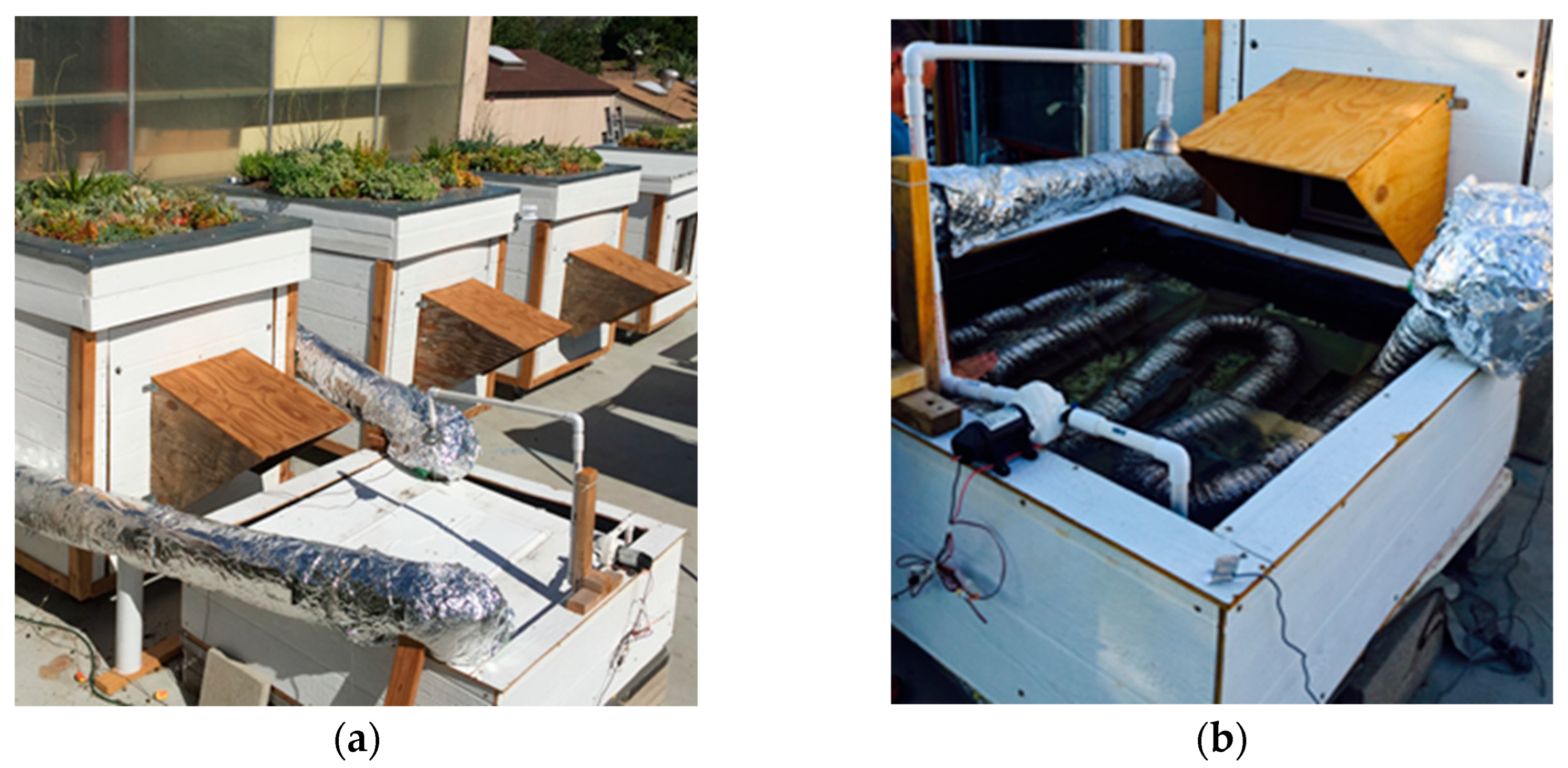
2. Configuration of the Test Systems
2.1. Configuration of the Green Roof
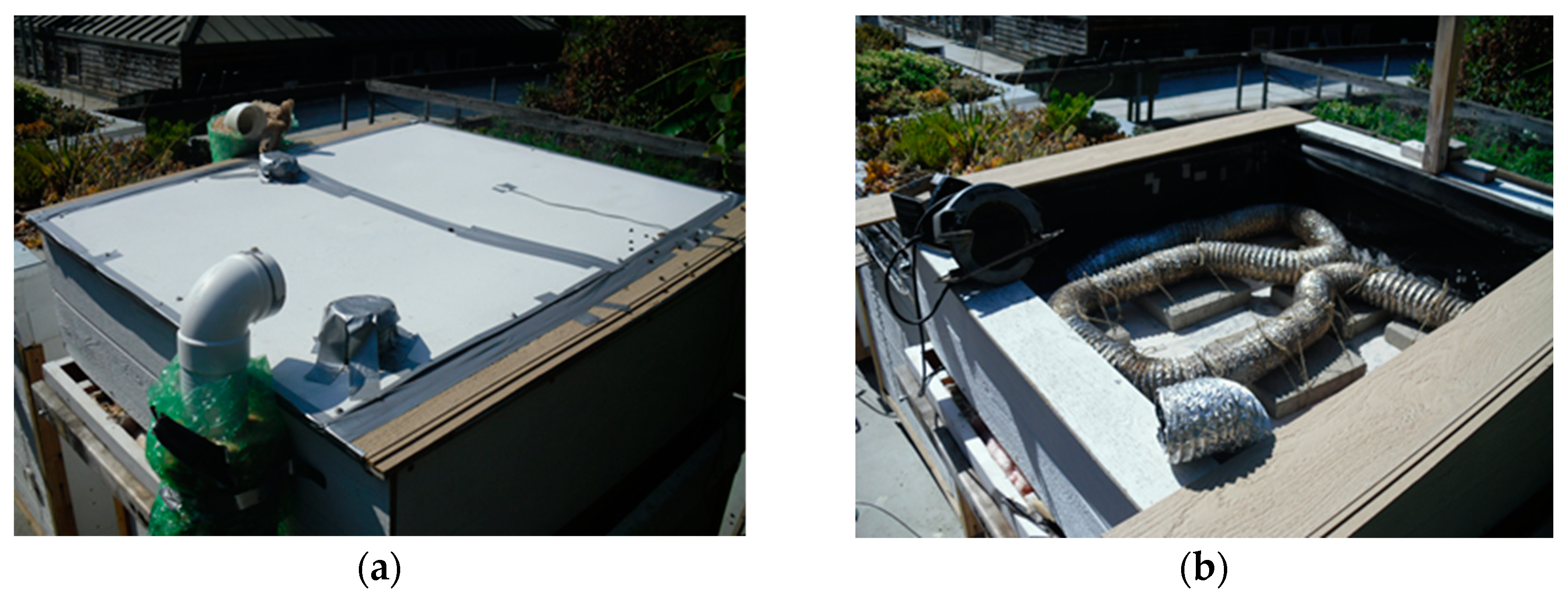
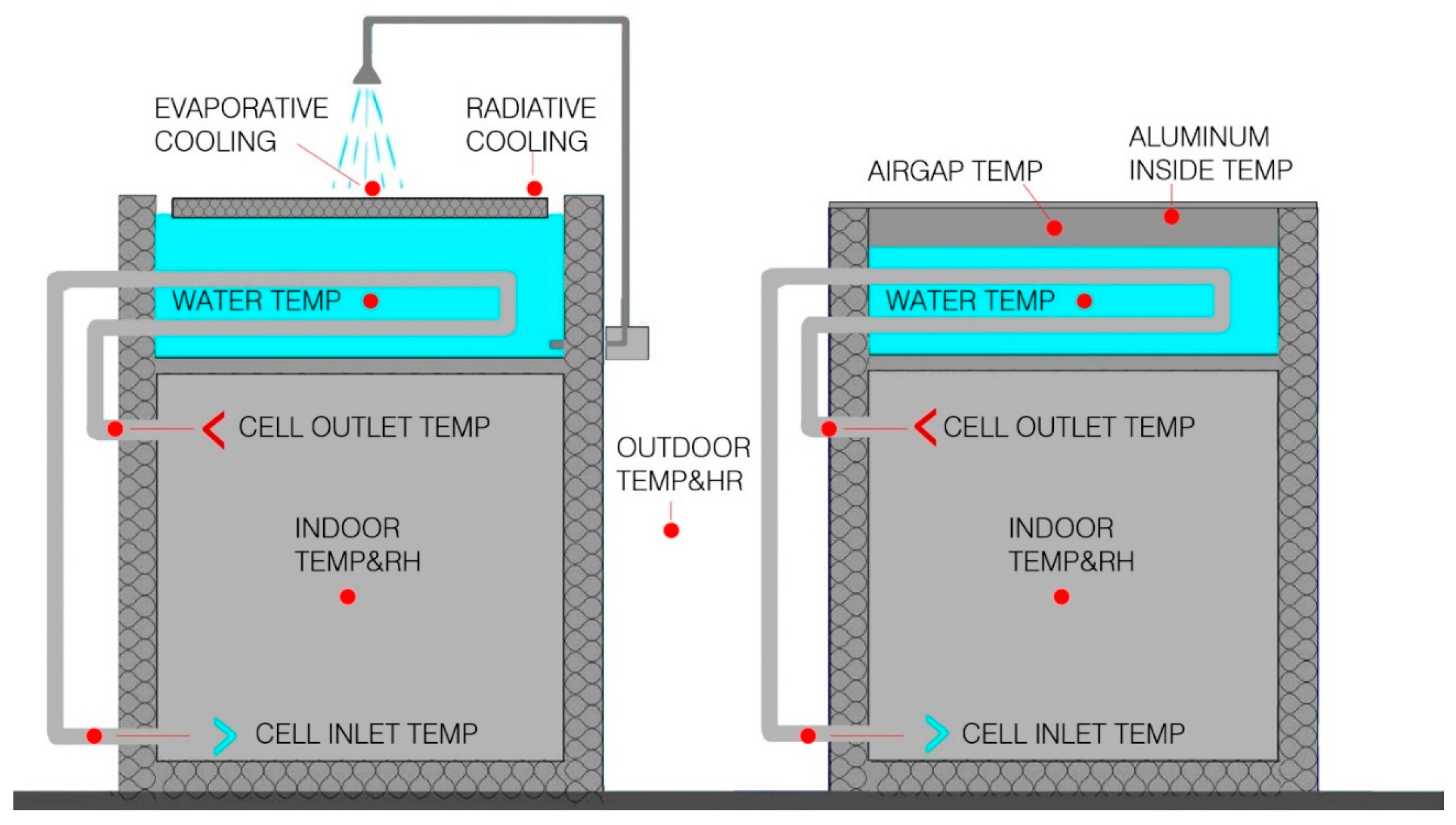
2.2. Configuration of the Roof Pond with Insulation and Nighttime Spraying
2.3. Configuration of the Roof Pond Sealed by an Aluminum Sheet
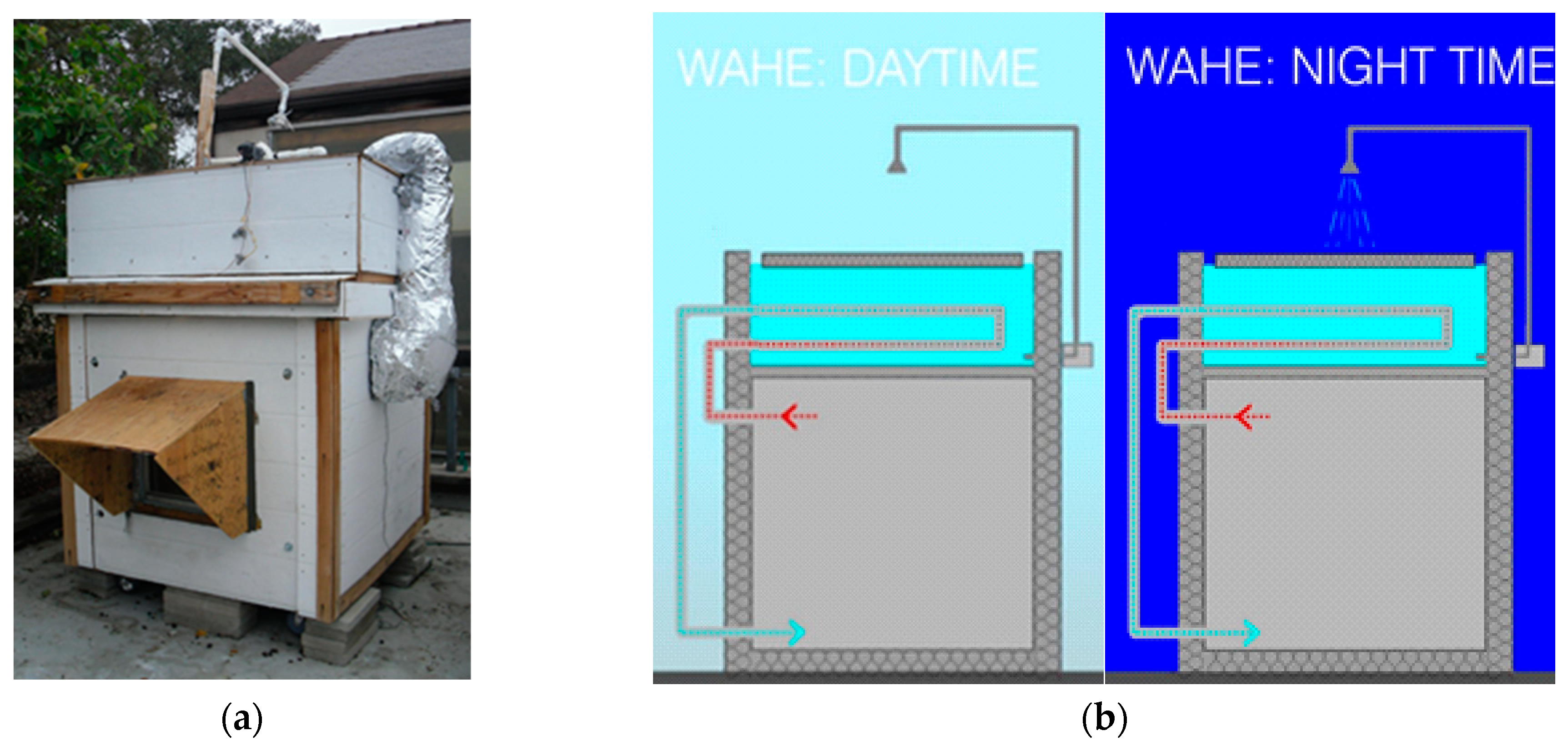
2.4. Configuration of the WAHE
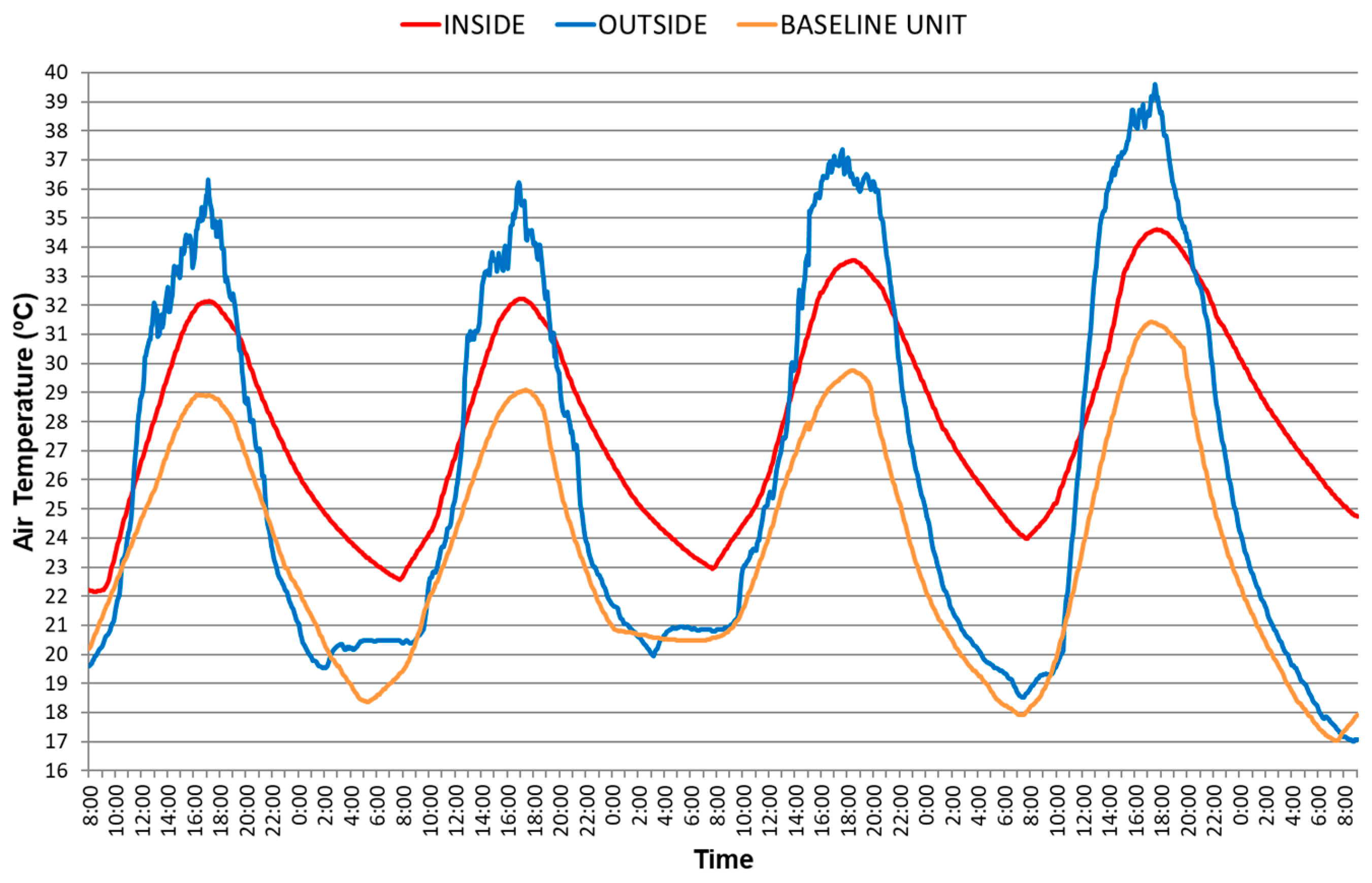
3. Analysis of Findings
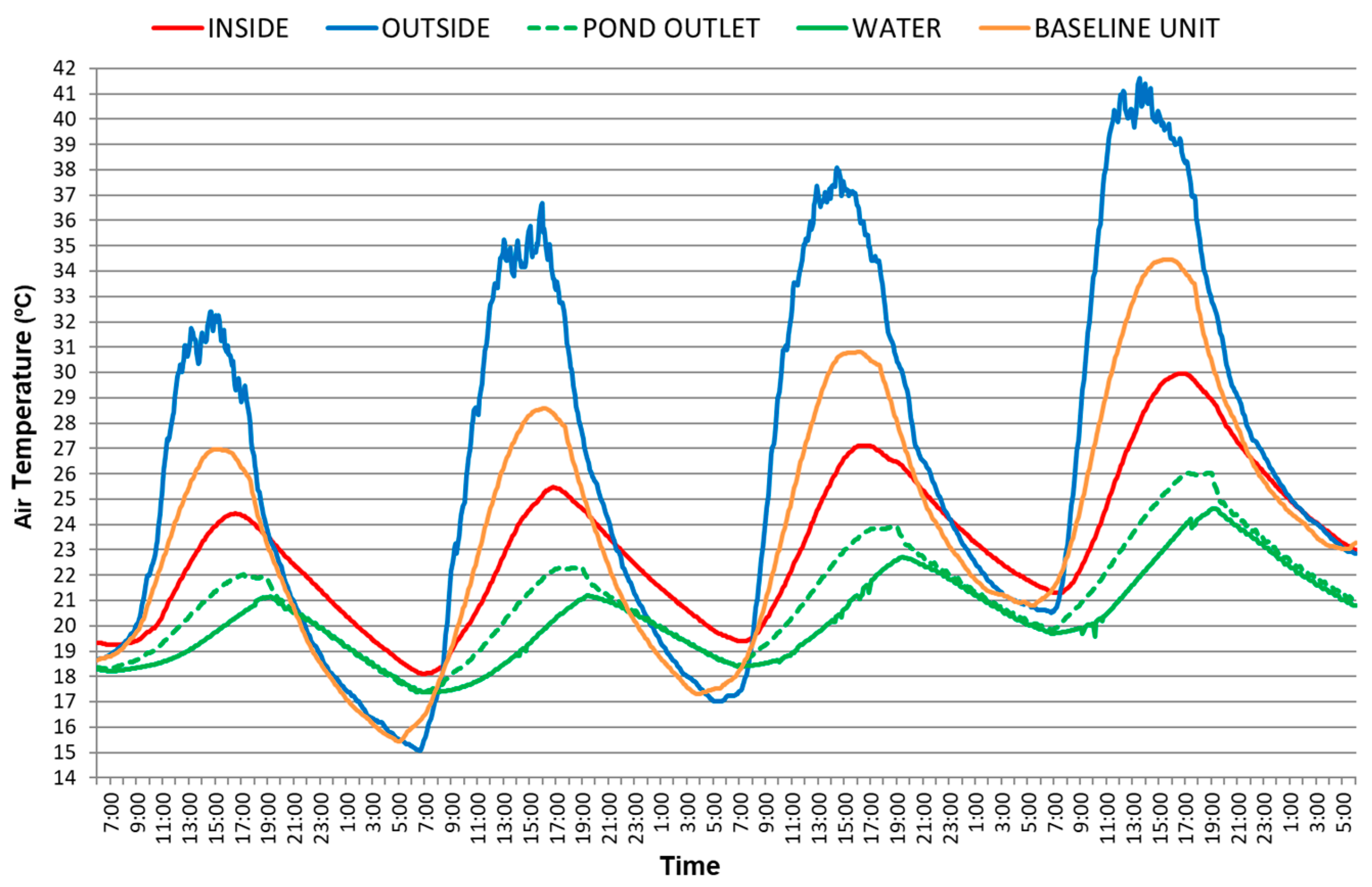
3.1. Green Roof
3.1.1. Green Roof When the WAHE Is Inactive
3.1.2. Green Roof When the WAHE Is Active
3.2. Roof Pond with Insulation and Nighttime Spraying
3.2.1. Roof Pond with Insulation and Nighttime Spraying When the WAHE Is Inactive
3.2.2. Roof Pond with Insulation and Nighttime Spraying When the WAHE Is Active
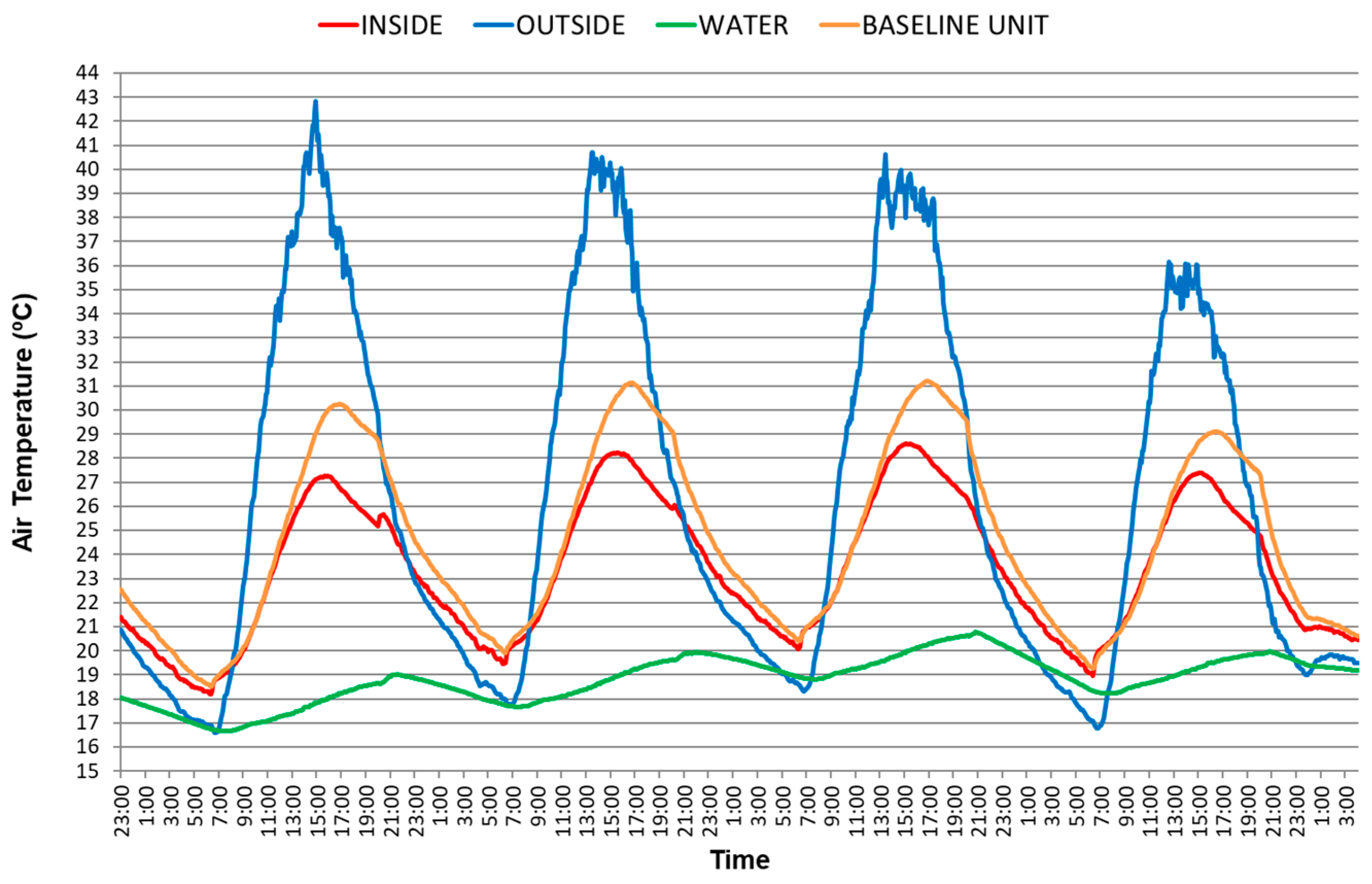
3.3. Roof Pond Sealed by an Aluminum Sheet
3.3.1. Roof Pond Sealed by an Aluminum Sheet When the WAHE Is Inactive
3.3.2. Roof Pond Sealed by an Aluminum Sheet When the WAHE Is Active
4. Comparison of Test Outcomes
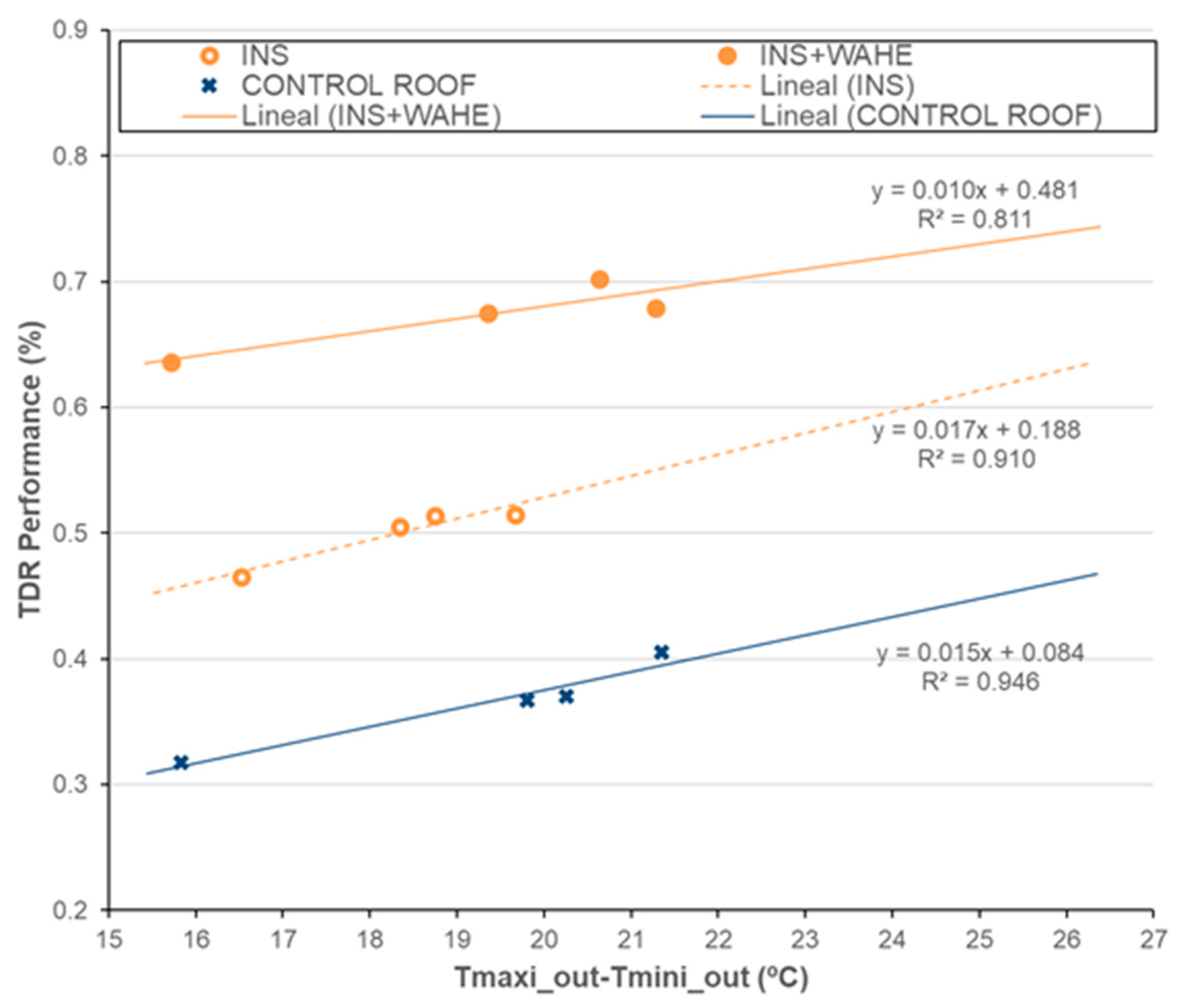
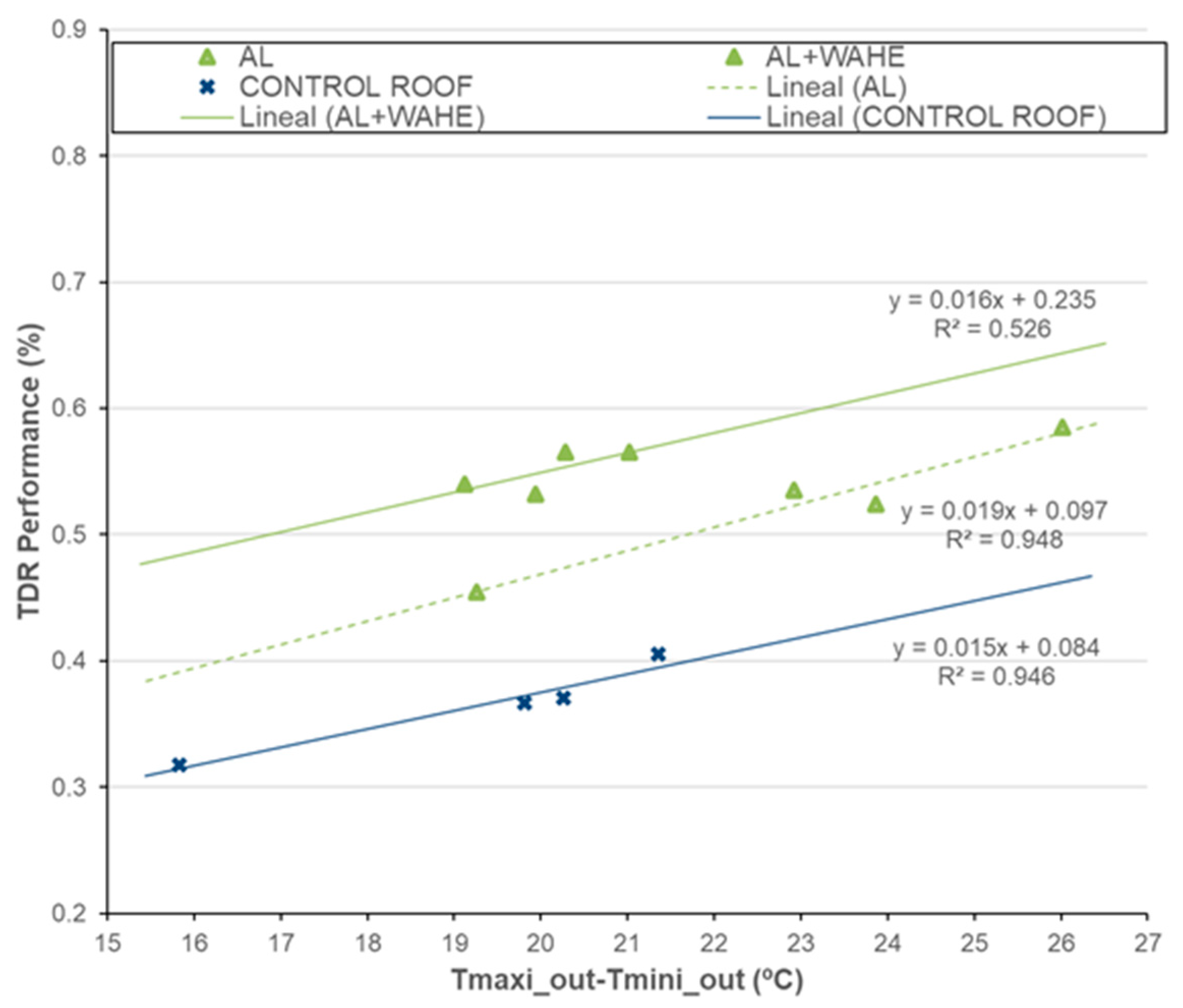
5. Temperature Difference Ratio (TDR) Estimation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- La Roche, P.; Berardi, U. Comfort and energy savings with active green roofs. Energy Build. 2014, 82, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valero, L.; Flores-Sasso, V.; Prieto-Vicioso, E.; Fernández-Flores, G. Assessment of Vernacular Housing in the Dominican Republic Using Simulations. Buildings 2024, 14, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, N.M.; Sharma, P.; Purohit, M.M. Studies on solar passive cooling techniques for arid areas. Energy Convers. Manag. 1999, 40, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Rahmatollahi, N.; Hou, H. The impact of roof systems on cooling and building energy efficiency. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.Y.; Rodler, A.; Musy, M.; Guernouti, S.; Teller, J. Influence of urban morphology on potential of green roofs in regulating local microclimate: A case study of Liège, Belgium. Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouldboukhitine, S.E.; Belarbi, R.; Jaffal, I.; Trabelsi, A. Assessment of green roof thermal behavior: A coupled heat and mass transfer model. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 2624–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.Y.; Teller, J. Assessing urban heat island mitigation potential of realistic roof greening across local climate zones: A highly-resolved weather research and forecasting model study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Qian, C.; Li, J. The Evapotranspiration Characteristics and Evaporative Cooling Effects of Different Vegetation Types on an Intensive Green Roof: Dynamic Performance Under Different Weather Conditions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Di Perna, C.; D’Orazio, M.; Olivieri, L.; Neila, J. Experimental measurements and numerical model for the summer performance assessment of extensive green roofs in a Mediterranean coastal climate. Energy Build. 2013, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.Y.; Minor, J. Performance Evaluation of an Extensive Green Roof, Green. In Proceedings of the Rooftops Sustainable Communities Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 5–6 May 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Saqib, A.; Khan, M.S.U.; Rana, I.A. Bridging nature and urbanity through green roof resilience framework (GRF): A thematic review. Nat. Based Solut. 2024, 6, 100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, C.C.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Life at the Top: Extensive Green Roof Plant Species and Their Traits for Urban Use. Plants 2025, 14, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, M.; Yüksel, A.; Aouinet, H.; Wang, D.; Arıcı, M.; Sammouda, H. Efficiency Assessment on Roof Geometry and Trombe Wall Shape for Improving Buildings’ Heating Performance. Buildings 2024, 14, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollschläger, N.; Schlink, U.; Trabitzsch, R.; Moeller, L. Weather dynamics affect the long-term thermal and hydrological performance of different green roof designs. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Wu, X.; Chiew, Y.M.; Li, Y. A green roof test bed for storm water management and reduction of urban heat island effect in Singapore. Br. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelena Aleksejeva, J.; Gerasimos Voulgaris, G.; Alexandros Gasparatos, A. Systematic review of the climatic and non-climatic benefits of green roofs in urban areas. Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Cook, L.M.; Middel, A.; Yang, S. Carbon dioxide reduction from green roofs: A comprehensive review of processes, factors, and quantitative methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 182, 113412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaria, J.; Susca, T. Analytic Hierarchy Processes (AHP) evaluation of green roof- and green wall- based UHI mitigation strategies via ENVI-met simulations. Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Taubenböck, H.; Zhu, X.X. Identification of the potential for roof greening using remote sensing and deep learning. Cities 2025, 159, 105782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Cooling the cities—A review of reflective and green roof mitigation technologies to fight heat island and improve comfort in urban environments. Sol. Energy 2014, 103, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, E.; Chau, H.W.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A. Review on the cooling potential of green roofs in different climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo Del Barrio, E. Analysis of the green roofs cooling potential in buildings. Energy Build. 1998, 27, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Oppenheimer, M. The effectiveness of cool and green roofs as urban heat island mitigation strategies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommese, F.; Diana, L. A holistic framework for the implementation of green roofs on existing buildings: A case study in the Mediterranean climate of Naples. Build. Environ. 2025, 274, 112811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S.; Vitaliano, S. Innovative green roof technologies in Mediterranean climate: Implications for sustainable design of the built environment. Build. Environ. 2025, 273, 112715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J. Passive Cooling; MIT Press: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, H.R.; Yellot, J. Natural air conditioning with roof pools and movable insulation. ASHRAE Transact. 1978, 75, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Givoni, B. Passive and Low Energy Cooling; Van Nostrand Reinhold: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kalz, D.E.; Wienold, J.; Fischer, M.; Cali, D. Novel heating and cooling concept employing rainwater cisterns and thermos-active building systems for a residential building. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrufa, S.N.; Adil, Y. Roof pond cooling of buildings in hot arid climates. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Yamagata, Y. Roof ponds as passive heating and cooling systems: A systematic review. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 336–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanaki, A.; Tsoutsos, T.; Kolokotsa, D. On the selection and design of the proper roof pond variant for passive cooling purposes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3523–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, F.; Bellia, L.; Minichiello, F. Earth-to-air heat exchangers for Italian climates. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretti, C.; Zarrella, A.; De Carli, M.; Zecchin, R. The design and environmental evaluation of earth-to-air heat exchangers (EAHE): A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, S.; Tirumalachetty, H.; Athikesavan, M.M. A comprehensive review on experimental, numerical and optimization analysis of EAHE and GSHP systems. Envrion. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 67559–67603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, A.; Maerefat, M.; Sobhani, S.M.J. Analytical investigation on the optimal tube length of Earth-to-Air Heat Exchanger (EAHE). Geothermics 2025, 127, 103250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidrissi, Y.; Wakil, M.; Najib, M.; Kaitouni, S.I.; Mghazli, M.O.; Bakhouya, M. EAHE-D: A dataset for modeling and performance evaluation of earth to air heat exchangers. Data Brief. 2024, 57, 111110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, S.; Heidt, F.D.; Scholer, D. Calculation tool for earth heat exchangers GAEA. In Proceedings of the Fifth International IBPSA (International Building Performance Simulation Association) Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–10 September 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Comprehensive review on climatic feasibility and economic benefits of Earth-to-Air Heat Exchanger (EAHE) systems. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 68, 103862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, M.N.H.; Yadav, S.; Panda, S.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Tiwari, G.N.; Hachem-Vermette, C. Assessment of annual performance of quonset GiPVT system combined with an earth-air heat exchanger (EAHE) for hot and dry climatic conditions. Renew. Energy 2024, 223, 119990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Yan, C.; Ji, J.; An, Z. Performance measurement and configuration optimization based on orthogonal simulation method of earth-to-air heat exchange system in cold-arid climate. Energy Build. 2024, 308, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Yang, B. Feasibility analysis of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger (EAHE) in a sports and culture center in Tianjin, China. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, H.; Tuna, O. Investigation of Photovoltaic Assisted Misting System. Int. J. Photoenergy 2015, 2015, 748219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Sun, Q.; Feng, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, A.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Meng, X. Experimental and numerical research on the thermal performance of a vertical earth-to-air heat exchanger system. Geothermics 2025, 125, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Panda, S.K.; Hachem-Vermette, C. Assessment of year-round performance of SPVT greenhouse system with EAHE employing periodic thermal model. Sol. Energy 2024, 282, 112941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, Z. The effect of operation modes on the thermal performance of a novel multi-tubular phase change material-filled earth-air heat exchanger. Renew. Energy 2024, 237 Pt D, 121887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, N.; Rosa, N.; Monteiro, H.; Costa, J.J. Advances in standalone and hybrid earth-air heat exchanger (EAHE) systems for buildings: A review. Energy Build. 2021, 253, 111532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.H.; Cheong, D.K.W.; Yan, H.; Soh, J.; Ong, C.L.; Sia, A. The effects of rooftop garden on energy consumption of a commercial building in Singapore. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Gheibi, M.; Wacławek, S.; Behzadian, K. A novel smart framework for optimal design of green roofs in buildings conforming with energy conservation and thermal comfort. Energy Build. 2023, 291, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Roche, P. Carbon-Neutral Architectural Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tavana, M.; Kammerud, R.; Akbari, H.; Borgers, T. A Simulation Model for the Performance Analysis of Roof Pond Systems for Heating and Cooling; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1980. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/698610bd (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Yannas, S.; Erell, E.; Molina, J.L. Roof Cooling Techniques: A Design Handbook; Earthscan: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- La Roche, P.; Givoni, B. Indirect Evaporative Cooling with an Outdoor Pond. In Proceedings of the Passive and Low Energy in Architecture Conference, Cambridge, UK, 11–13 July 2000; pp. 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, E.; Gonzalez, E.; Givoni, B. Effectiveness of indirect evaporative cooling and thermal mass in a hot arid climate. Build. Environ. 2010, 46, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Cheikh, H.; Bouchair, A. Passive cooling by evapo-reflective roof for hot dry climates. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givoni, B. Indoor temperature reduction by passive cooling systems. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1692–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, D.; La Roche, P. Investigation on the cooling performance of a green roof with a radiant cooling system. Energy Build. 2017, 149, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Material | Thickness mm | Conductivity W/mK | U-Value W/m2K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green roof | Soil | 130 | 0.610 | |
| Gravel | 20 | 2.000 | ||
| Waterproofing | 1 | 0.210 | 0.282 | |
| Metal plate | 2 | 44.00 | ||
| OSB | 11 | 0.130 | ||
| Fiberglass | 21 | 0.044 | ||
| XPS | 127 | 0.043 | ||
| Gypsum board | 11 | 0.180 | ||
| Insulated roof pond | Polystyrene | 30 | 0.033 | |
| Water | 300 | 0.591 | ||
| Waterproofing membrane | 1 | 0.210 | 0.272 | |
| Metal plate | 2 | 44.00 | ||
| Aluminum roof pond | Aluminum sheet | 1 | 0.610 | |
| Air gap | 100 | 0.233 | ||
| Water | 200 | 0.591 | 1311 | |
| Waterproofing membrane | 1 | 0.210 | ||
| Metal plate | 2 | 44.00 | ||
| Baseline unit roof | Metal plate | 1 | 44.00 | |
| Waterproofing membrane | 1 | 0.21 | ||
| OSB | 11 | 0.130 | ||
| Air gap | 38 | 0.233 | 0.306 | |
| XPS | 140 | 0.043 | ||
| Gypsum board | 11 | 0.180 | ||
| Wall section | Gypsum board | 10 | 0.180 | |
| Fiberglass | 89 | 0.044 | ||
| OSB | 11 | 0.130 | ||
| Vapor barrier | 1 | - | 0.308 | |
| XPS | 51 | 0.043 | ||
| Air gap | 13 | 0.079 | ||
| Laminated wood | 5 | 0.130 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almodóvar-Melendo, J.-M.; La Roche, P. Thermal Evaluation of a Water-to-Air Heat Exchanger Combined with Different Roof Configurations for Passive Cooling. Buildings 2025, 15, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071098
Almodóvar-Melendo J-M, La Roche P. Thermal Evaluation of a Water-to-Air Heat Exchanger Combined with Different Roof Configurations for Passive Cooling. Buildings. 2025; 15(7):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071098
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmodóvar-Melendo, José-Manuel, and Pablo La Roche. 2025. "Thermal Evaluation of a Water-to-Air Heat Exchanger Combined with Different Roof Configurations for Passive Cooling" Buildings 15, no. 7: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071098
APA StyleAlmodóvar-Melendo, J.-M., & La Roche, P. (2025). Thermal Evaluation of a Water-to-Air Heat Exchanger Combined with Different Roof Configurations for Passive Cooling. Buildings, 15(7), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071098







