Artificial Neural Network Model for Evaluating Load Capacity of RC Deep Beams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Simple beams h/le > 0.5
- Continuous beam end spans h/le > 0.4
- Continuous beam inner spans h/le > 0.3
- Cantilever beams h/le > 1
1.1. The Problem of Deep Beams
1.2. Behavior of Deep Beams
1.3. Scope and Motivation of the Research
1.4. Research Objectives
- -
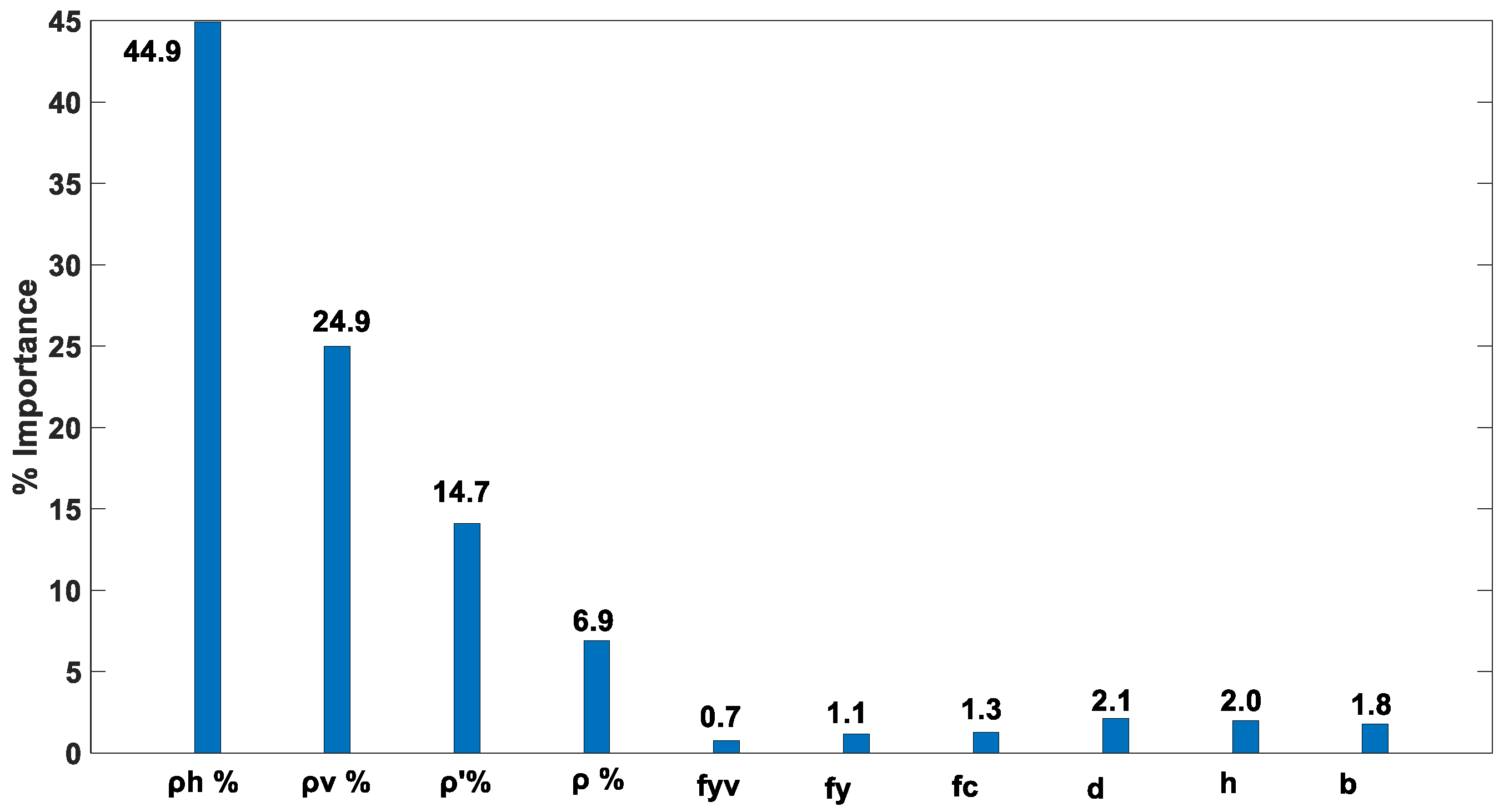
- A standard investigation using the trained neural network is conducted to determine the importance of each criterion that affects the shear capacity of the deep beams.
- -
- An equation from the practical results is derived to estimate the ultimate of the deep beams.
- -
- Study the influence of each input factor on the strength capacity of the deep beams is conducted.
2. Artificial Neural Networks
Data Collection and Preparation
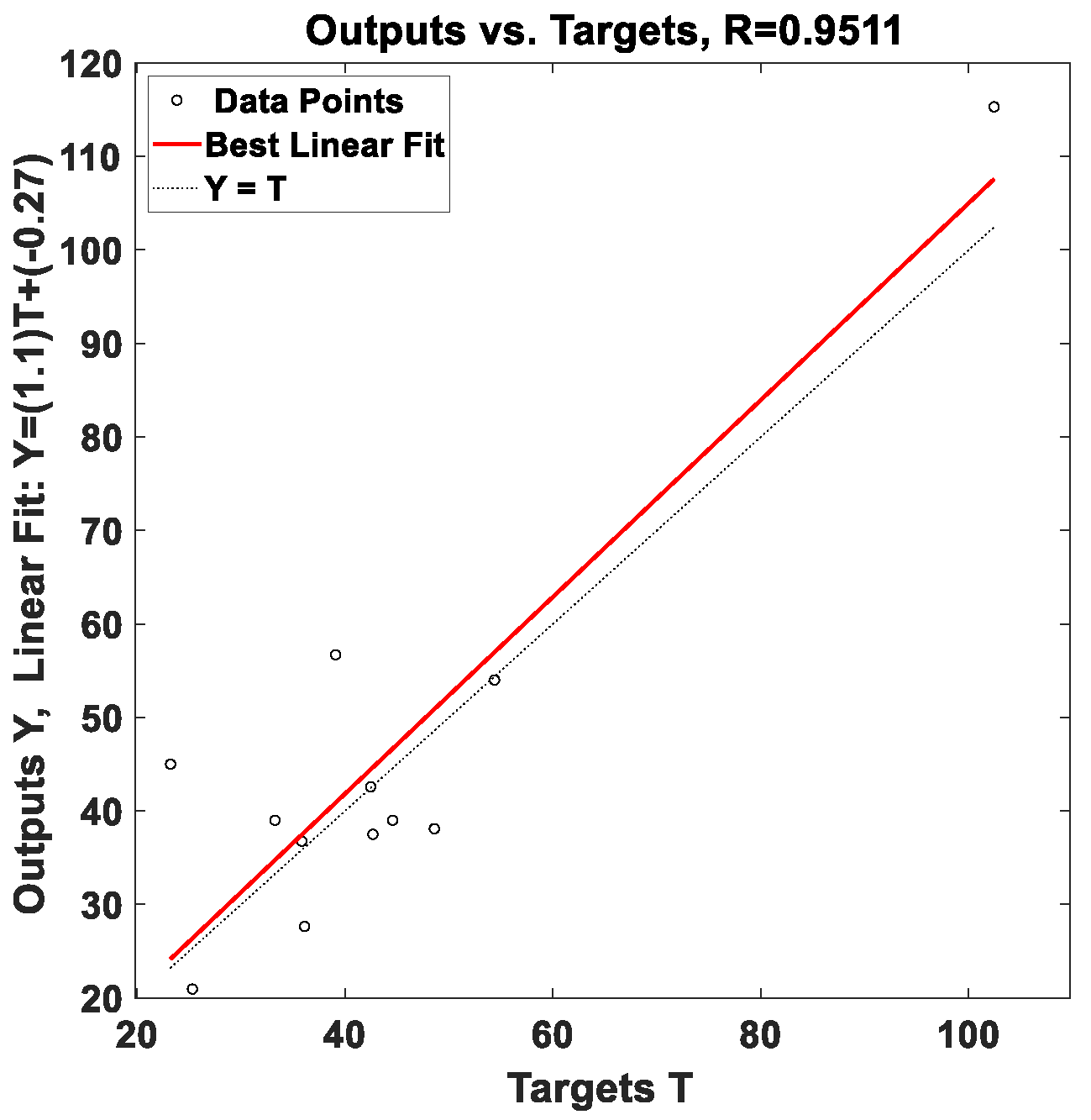
3. Results and Discussion
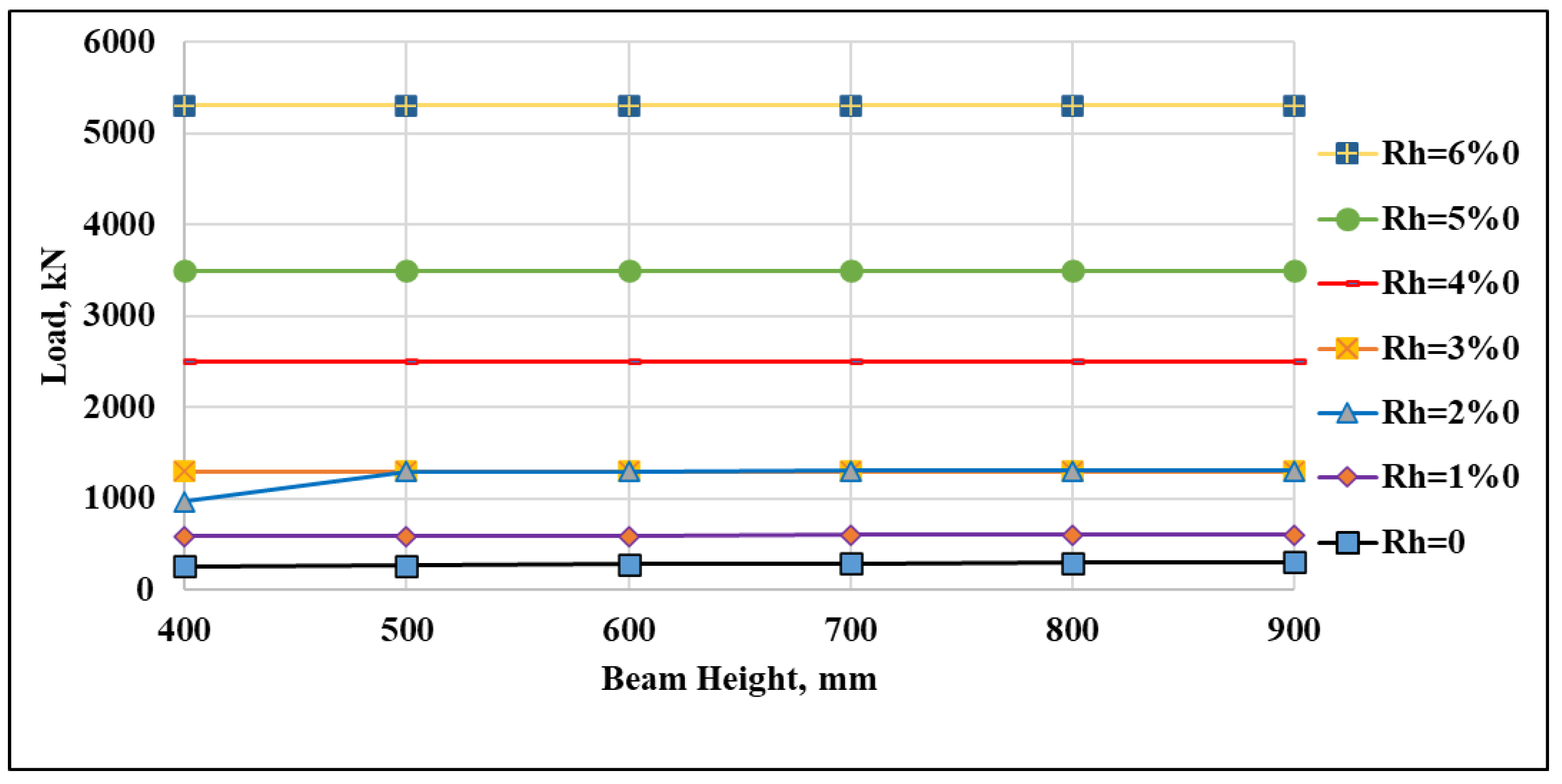
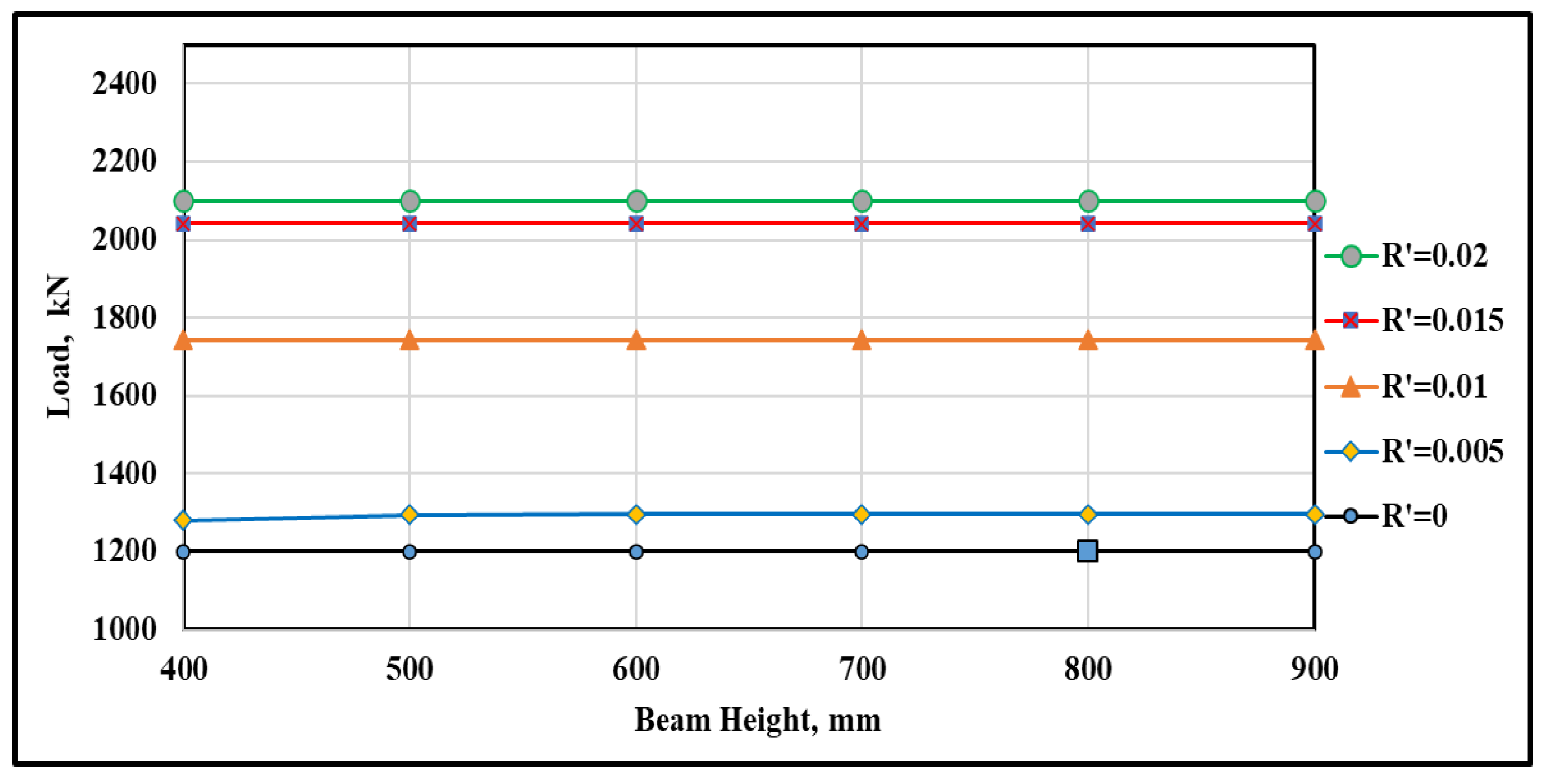
3.1. Influence of the Horizontal Reinforcement %
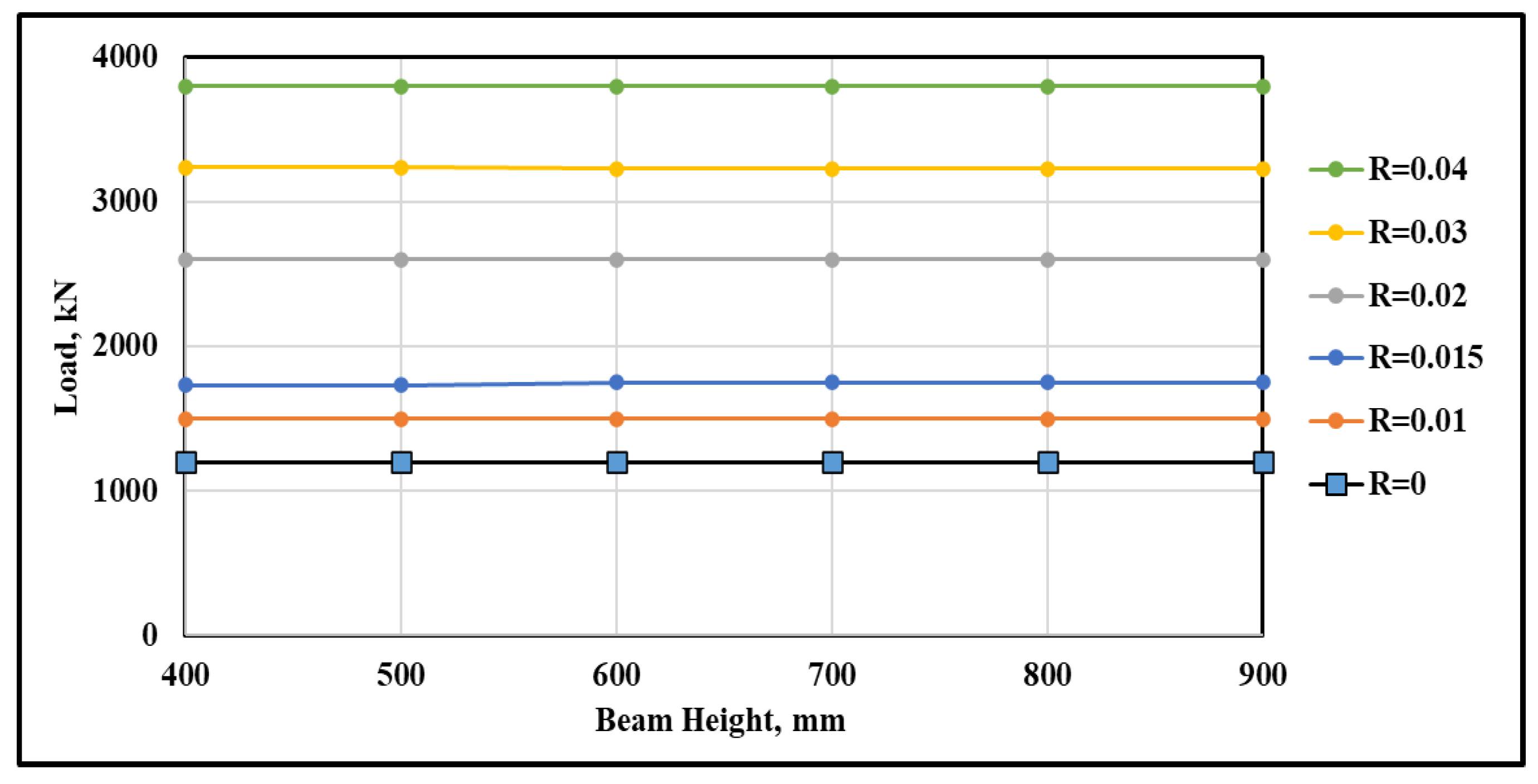
3.2. Influence of the Vertical Reinforcement %
3.3. Influence of the Compression Reinforcement %
3.4. Influence of the Tension Reinforcement %
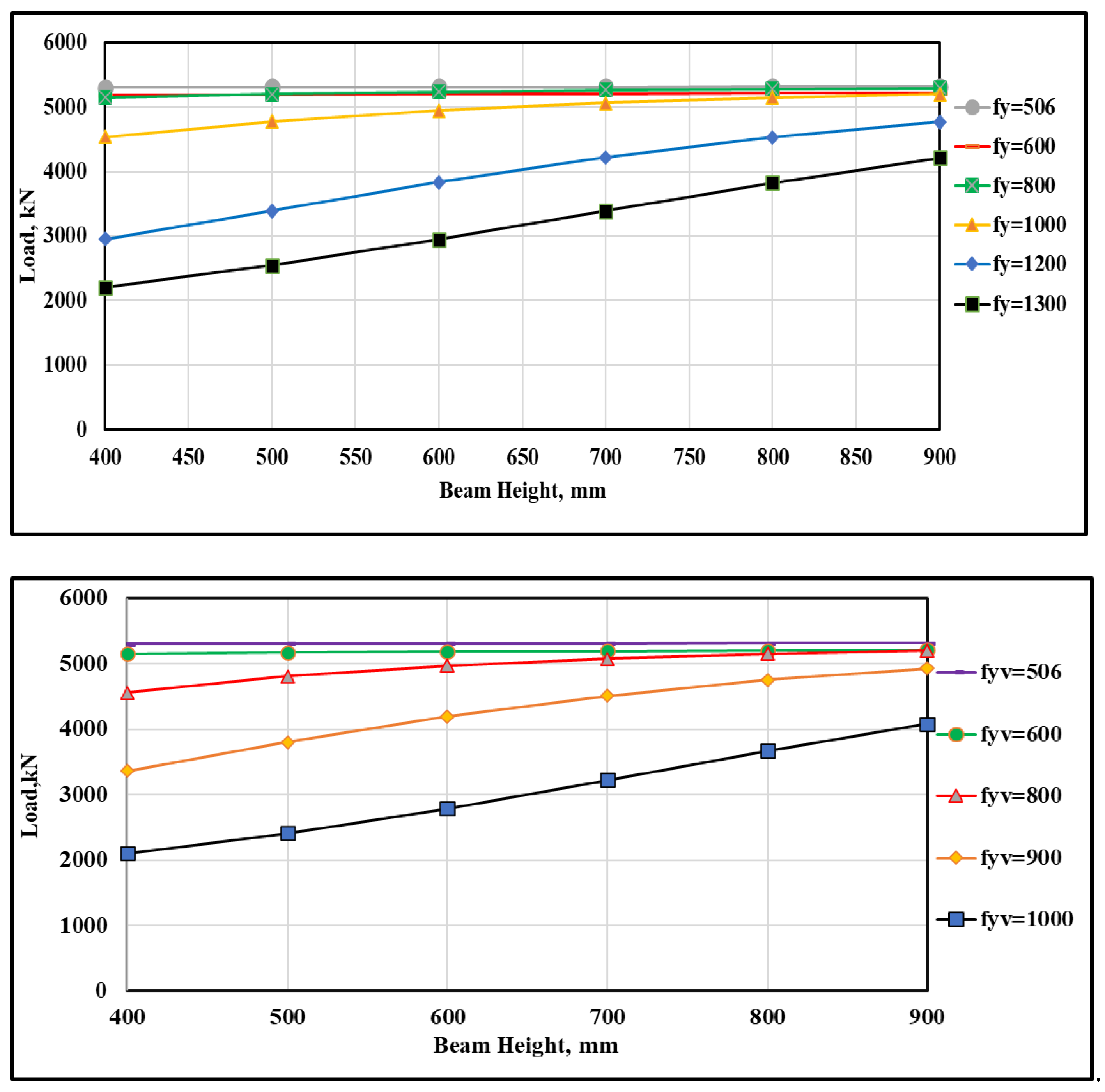
3.5. Effects of the Tensile Yields of Vertical and Horizontal Steel Bars
3.6. The Impact of the Compressive Strength of Concrete

4. ANN Model Advancements for Predicting the Load Capacity of Deep Beams
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Hidden Layer Nodes | Weight Transfer from Node i in the Input Layer to Node j in the Hidden Layer. | Hidden Threshold | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i = 1 | i = 2 | i = 3 | i = 4 | i = 5 | i = 6 | i = 7 | i = 8 | i = 9 | i = 10 | ||
| J = 11 | 9.0 | 221.2 | −150.9 | −32.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 | −1.8 | 2.3 | −12.7 | −8.7 | −2.2 |
| J = 12 | −262.5 | 352.3 | −149.0 | 25.8 | 16.5 | 12.8 | −5.8 | −13.2 | 5.4 | 16.8 | −3.0 |
| J = 13 | −491.9 | −254.0 | −52.0 | −72.18 | 0.0024 | 0.0019 | −0.0319 | 0.0003 | 0.0006 | 0.0027 | −72.1 |
| J = 14 | −443.5 | −29.7 | 148.4 | −0.63 | 0.0024 | −0.0001 | 0.0259 | −0.0030 | 0.0006 | −0.0032 | −0.63 |
| J = 15 | −458.1 | 69.6 | −36.4 | 2.0 | −10.0 | −15.1 | −16.7 | −36.8 | −26.1 | −84.2 | −0.4 |
| J = 16 | 322.7 | 195.4 | −113.6 | −82.5 | 20.4 | 12.9 | 24.5 | −3.5 | −11.8 | 1.4 | 1.7 |
| J = 17 | −104.6 | 202.4 | −66.0 | 15.6 | 6.1 | −1.4 | −1.4 | 49.0 | −53.3 | 15.4 | 3.0 |
| J = 18 | 324.2 | 118.9 | −46.7 | 107.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| Output layer nodes | weight between hidden layer node i to output layer node j | ||||||||||
| 671.6 | −311.3 | 47.8 | −61.7 | −6.0 | 2.3 | −12.2 | −0.6 | −1.3 | 6.5 | ||
References
- ACI-318-19; 318-19 Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.K. Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Starčev-Ćurčin, A.; Rašeta, A.; Malešev, M.; Kukaras, D.; Radonjanin, V.; Šešlija, M.; Žarković, D. Experimental Testing of Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams Designed by Strut-And-Tie Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, T. CEB-FIP: Model Code 1990 for Concrete Structures; Comite Euro-International du Beton, Lausanne: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- CSA Technical Committee on Reinforced Concrete Design, Design of Concrete Structures; Canadian Standards Association: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1994.
- Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings; British Standards Institution (BSI): London, UK, 2014.
- Liu, M.-Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. Probabilistic Shear Strength Prediction for Deep Beams Based on Bayesian-Optimized Data-Driven Approach. Buildings 2023, 13, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, K. Prediction and reliability analysis of shear strength of RC deep beams. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gburi, M.; Jonasson, J.E.; Yousif, S.T.; Nilsson, M. Simplified Methods for Crack Risk Analyses of Early Age Concrete Part 2: Restraint Factors for Typical Case Wall-on-Slab. Nord. Concr. Res. 2012, 46, 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Gburi, M. Restraint Effects in Early Age Concrete Structures; Lulea University of Technology: Luleå, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Gburi, M.; Yusuf, S.A. Investigate the effect of mineral additives on concrete strength using ANN. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 23, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaros, N.D. Artificial Neural Networks Applied in Civil Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafeh, A. Applications of Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.J.; Golbert, R.I. Experimental studies on high-strength concrete deep beams. ACI Struct. J. 1998, 95, 382–390. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, K.G.; Viest, I.M.; Elstner, R.C.; Hognestad, E. Shear strength of reinforced concrete beams part 1—Tests of simple beams. ACI J. 1954, 51, 317–332. [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky, D.M.; MacGregor, J.G.; Ong, S.Y. Tests of reinforced concrete deep beams. ACI J. 1986, 83, 614–623. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.S.; Deschenes, D.J.; Bayrak, O. Strut-And-Tie Model Design Examples for Bridges; Center for Transportation Research: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.-K.; Shin, S.-W. Shear Strength of Reinforced High-Strength Concrete Deep Beams. Struct. J. 2001, 98, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xie, W. Experimental Study and Calculation Methods of Shear Capacity for High-Strength Reinforced Concrete Full-Scale Deep Beams. Materials 2022, 15, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gburi, M.; Jonasson, J.E.; Nilsson, M. Using Artificial Neural Network to Predict the Restraint in Concrete Tunnel at Early Age. Struct. Eng. Int. 2015, 25, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrcher, D.B.; Tuchscherer, R.G.; Huizinga, M.; Bayrak, O. Depth effect in deep beams. ACI Struct. J. 2014, 111, 31–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.D.; Sankovich, C.L.; Bayrak, O.; Jirsa, J. Behavior and efficiency of bottle shaped struts. ACI Struct. J. 2006, 103, 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.P. Diagonal tension in reinforced concrete beams. ACI J. 1951, 48, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, T.K.; Seliem, H.M.; Dwairi, H.; Rizkalla, S.H.; Zia, P. Shear behavior of large concrete beams reinforced with high-strength steel. ACI Struct. J. 2008, 105, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, M.; Lertsrisakulrat, T.; Yanagawa, A.; Niwa, J. Shear behavior of RC deep beams with stirrups. Trans. Jpn. Concr. Inst. 2002, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, J.; Viest, I.M. Shear strength of reinforced concrete frame members without web reinforcement. ACI J. 1957, 53, 833–869. [Google Scholar]
- Tanimura, Y.; Sato, T. Evaluation of shear strength of deep beams with stirrups. Q. Rep. RTRI 2005, 46, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walraven, J.C.; Lehwalter, N. Size effects in short beams loaded in shear. ACI Struct. J. 1994, 91, 585–593. [Google Scholar]
- Watstein, D.; Mathey, R.G. Strains in beams having diagonal cracks. ACI J. 1958, 55, 717–729. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.-H.; Chung, H.-S.; Lee, E.-T.; Eun, H.-C. Shear characteristics of high-strength concrete deep beams without shear reinforcements. Eng. Struct. 2003, 25, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Tan, K.-H. Size effect in RC deep beams: Experimental investigation and STM verification. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, G.D. Interpreting Neural Network Connection Weights. Artif. Intell. 1991, 6, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.S.; Jin, T.C.; Zheng, L.A.; Zhang, G.Y.; Li, H.M.; Chen, A.J.; Xie, W. Experimental Study of Shear Performance of High-Strength Concrete Deep Beams with Longitudinal Reinforcement with Anchor Plate. Materials 2023, 16, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-khreisat, A.; Abdel-Jaber, M.; Ashteyat, A. Shear Strengthening and Repairing of Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams Damaged by Heat Using NSM–CFRP Ropes. Fibers 2023, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charif, A.; Mourad, S.M.; Khan, M.I. Flexural behavior of beams reinforced with steel bars exceeding the nominal yield strength. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 13, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh-Sobeh, A.; Kachouh, N.; El-Maaddawy, T. Numerical Analysis of Concrete Deep Beams Reinforced with Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Bars. Buildings 2023, 13, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayhood, E.K.; Mohammed, N.S.; Hilo, S.J.; Salih, S.S. Comprehensive Empirical Modeling of Shear Strength Prediction in Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
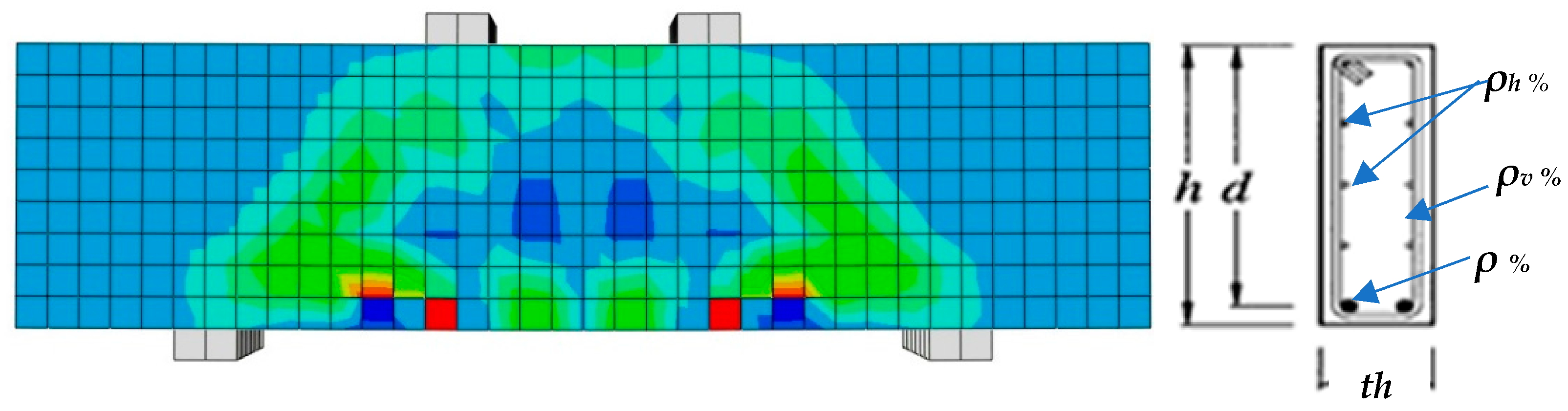



| Input | Description | Min | Max | Parametric Study | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρh% | Horizontal reinforcement % | 0 | 0.61 | 0.4 | - |
| ρv% | Vertical reinforcement % | 0 | 1.22 | 0.5 | - |
| ρ’% | Compression reinforcement % | 0 | 2.13 | 0 | - |
| ρ% | Tension reinforcement % | 0 | 4.25 | 0 | - |
| fyv | Tensile yield of vertical steel bars | 0 | 1051 | 503 | MPa |
| fy | Tensile yield of horizontal steel bars | 0 | 1330 | 503 | MPa |
| fC | Compressive strength of concrete | 13.8 | 104 | 30 | MPa |
| d | Effective Depth of beam | 355 | 2000 | 350 | mm |
| h | Height of the beam | 400 | 2050 | 400 | mm |
| th | Thickness of the beam | 125 | 915 | 200 | mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Gburi, M.; Alhayani, A.A.; Almssad, A. Artificial Neural Network Model for Evaluating Load Capacity of RC Deep Beams. Buildings 2025, 15, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081371
Al-Gburi M, Alhayani AA, Almssad A. Artificial Neural Network Model for Evaluating Load Capacity of RC Deep Beams. Buildings. 2025; 15(8):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081371
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Gburi, Majid, A. A. Alhayani, and Asaad Almssad. 2025. "Artificial Neural Network Model for Evaluating Load Capacity of RC Deep Beams" Buildings 15, no. 8: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081371
APA StyleAl-Gburi, M., Alhayani, A. A., & Almssad, A. (2025). Artificial Neural Network Model for Evaluating Load Capacity of RC Deep Beams. Buildings, 15(8), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081371







