Research on the Support-Free Replacement Method of Suspenders for Long-Span Self-Anchored Rail Special Suspension Bridges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis
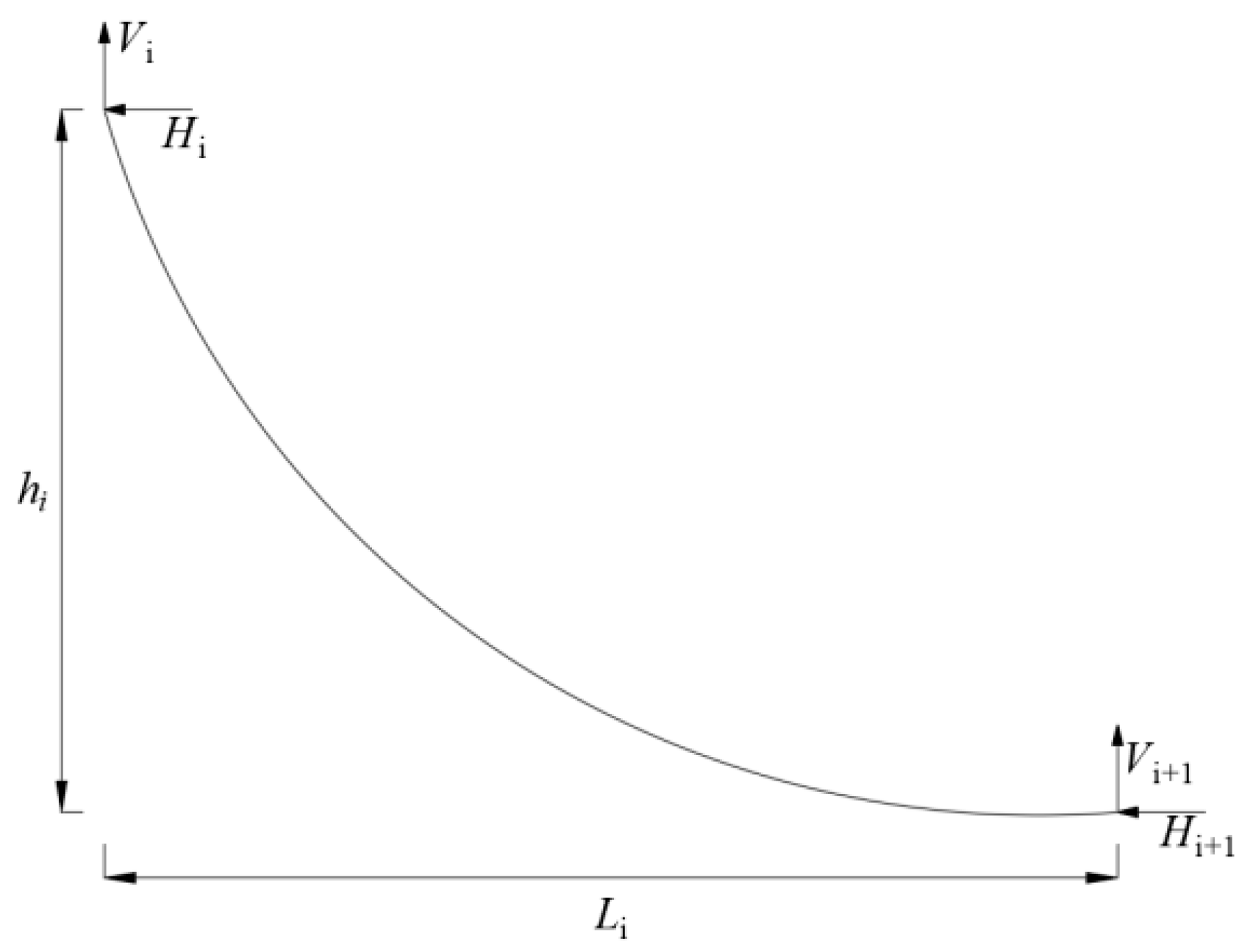
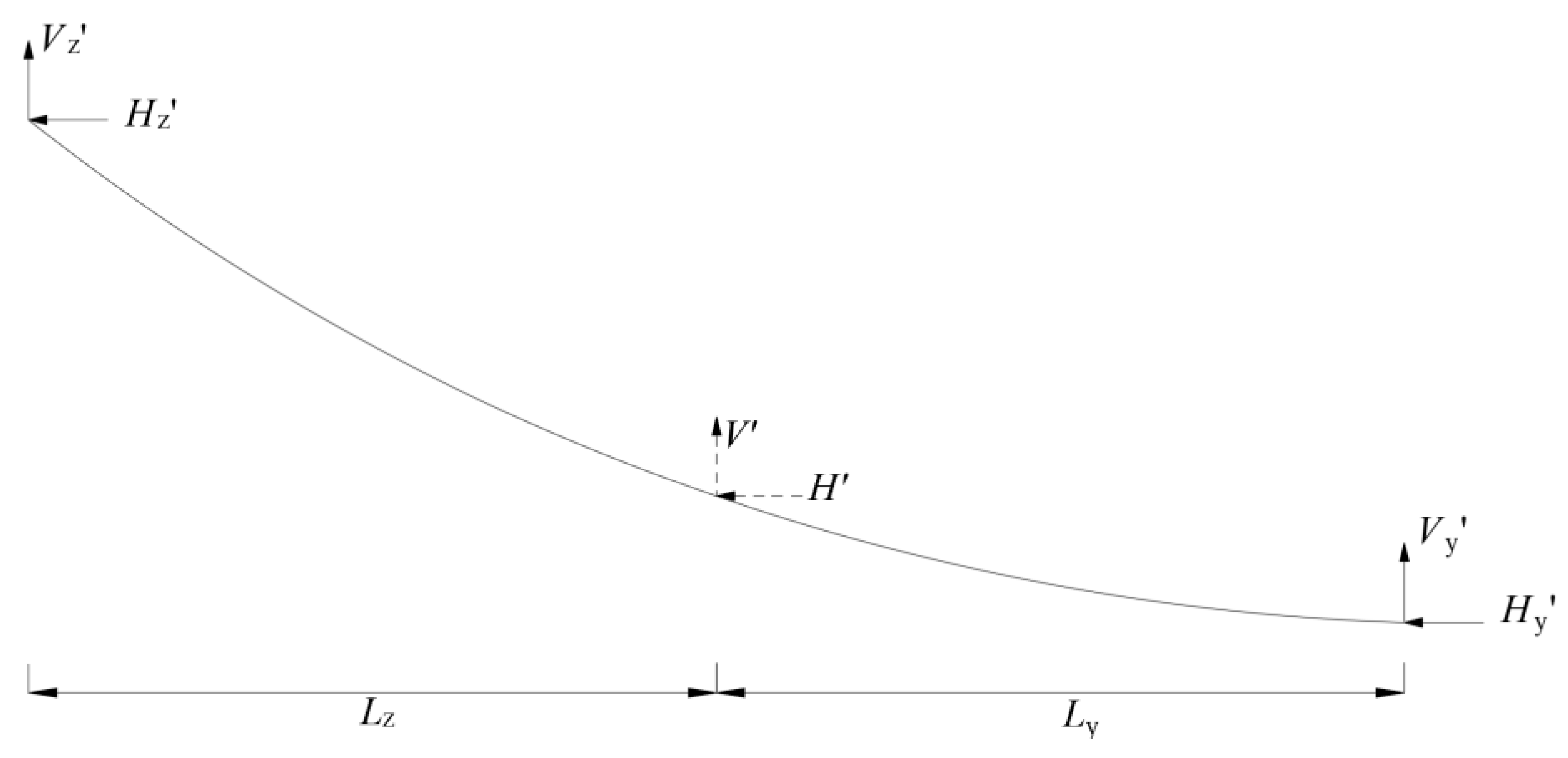
2.1. The Catenary Principle
2.2. Main Cable Deformation Safety Index
2.3. Cable Force Safety Index
2.4. Theoretical Analysis of Deformation of Stiffening Beam
2.4.1. Calculation Assumption
2.4.2. Safety Index of Displacement of the Stiffened Beam
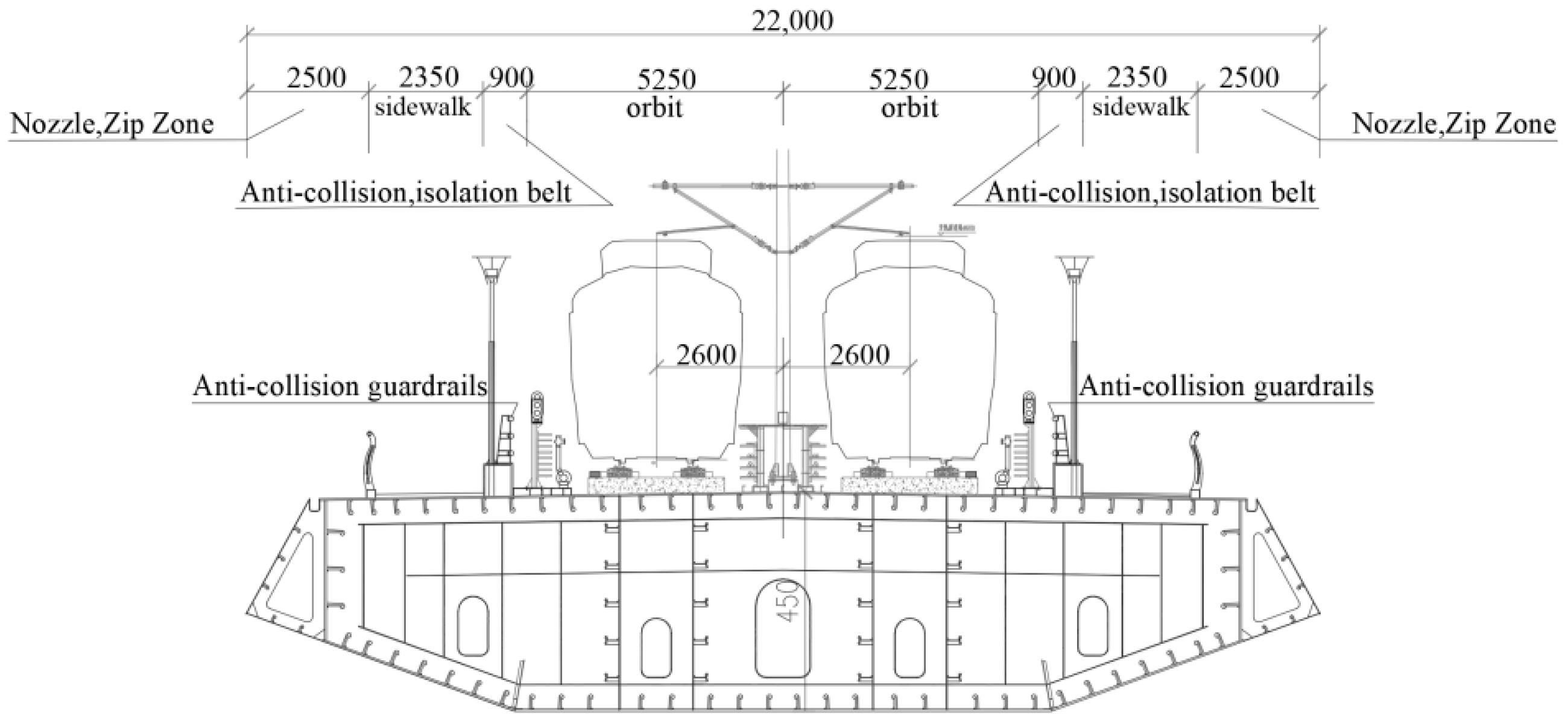
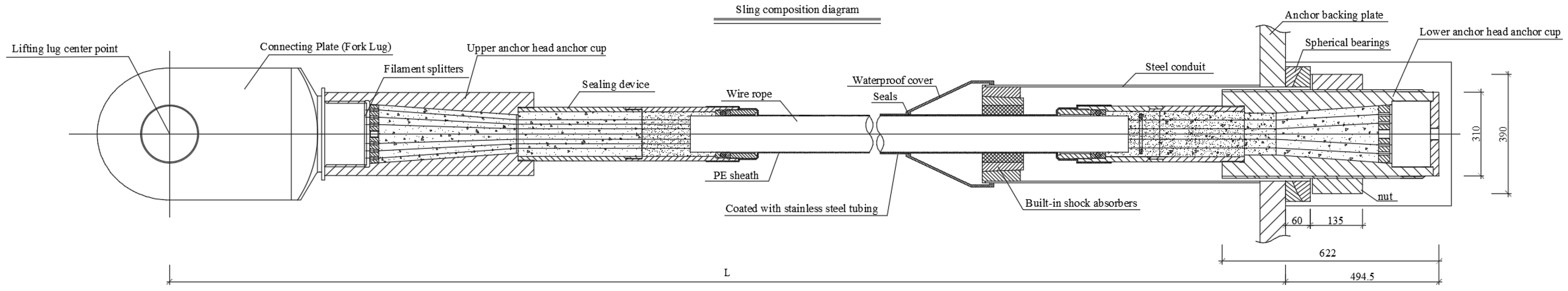
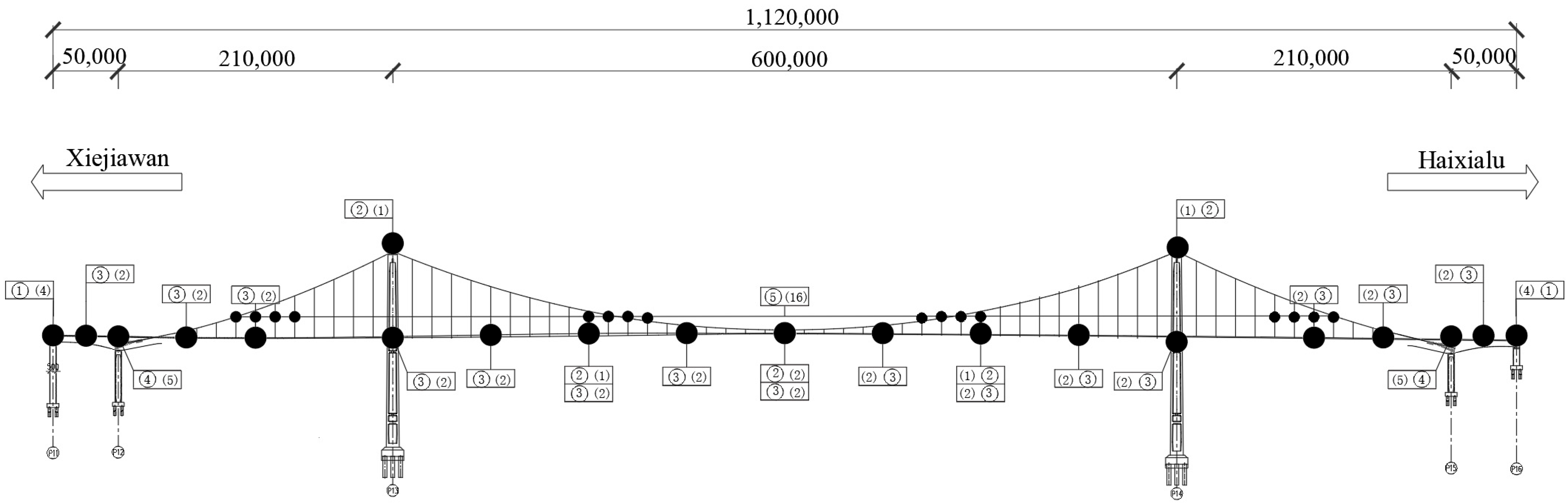
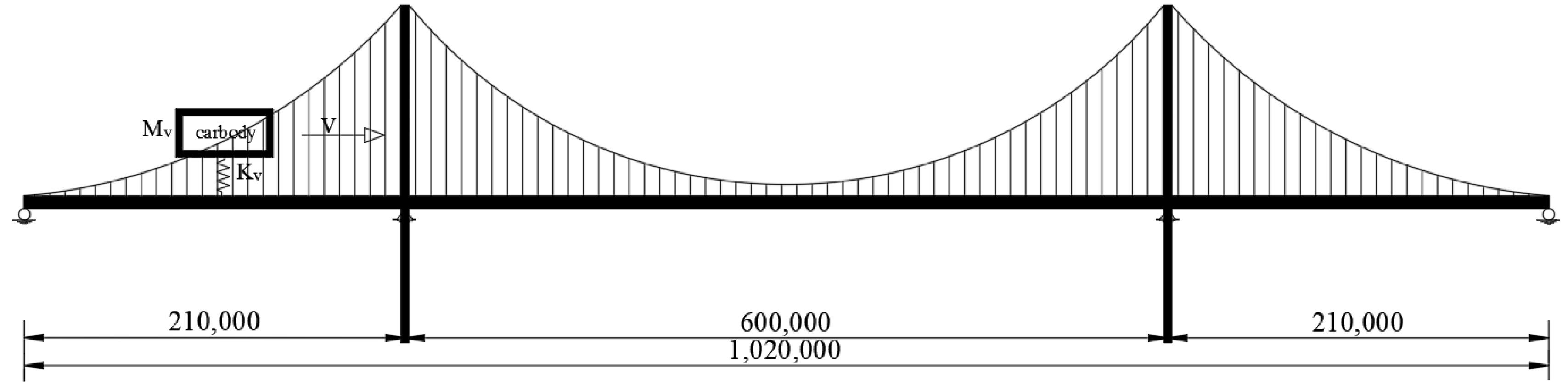
3. Project Background
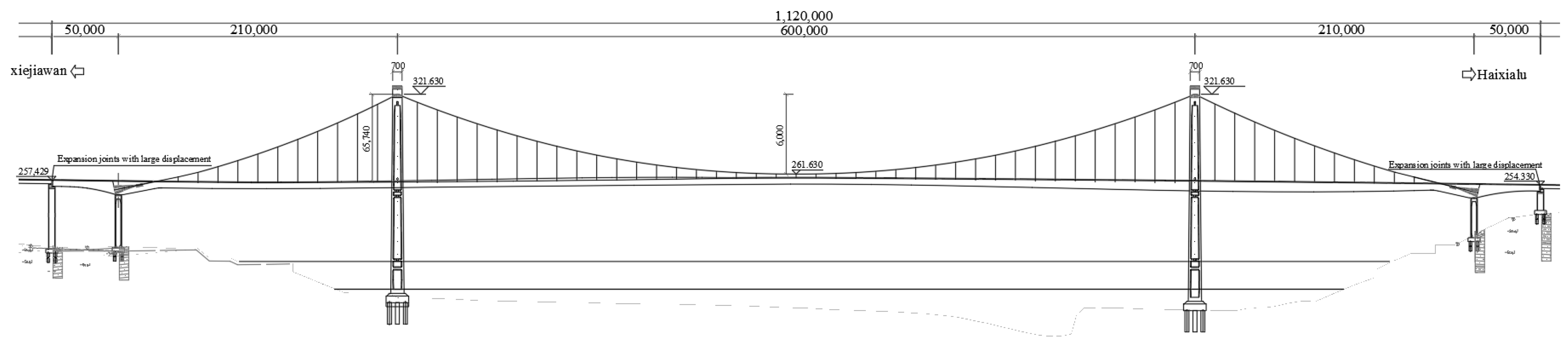
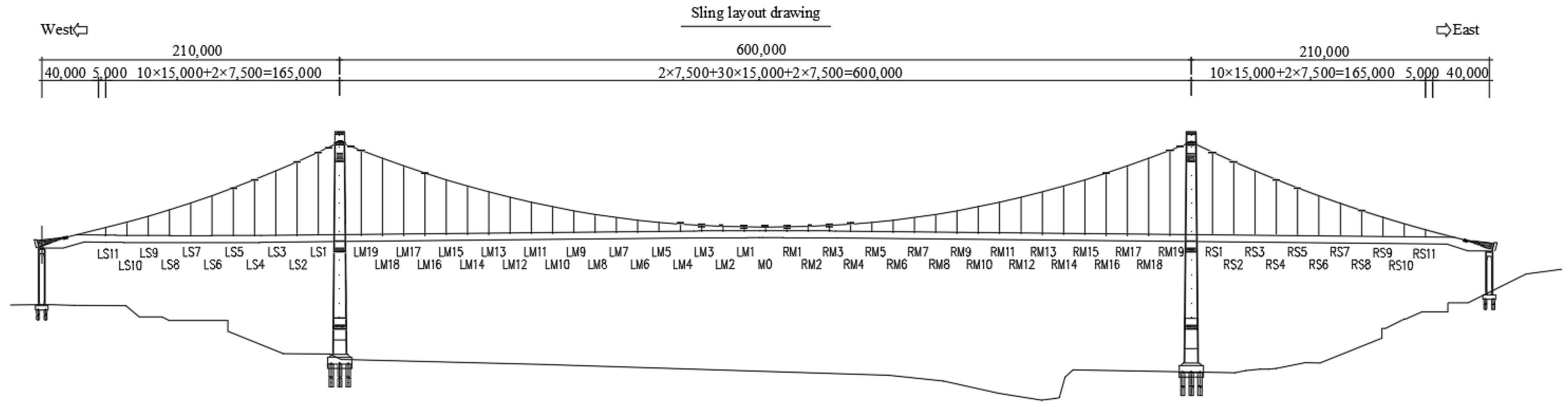
3.1. Project Overview
3.2. Structural Deformation and Cable Force Monitoring System
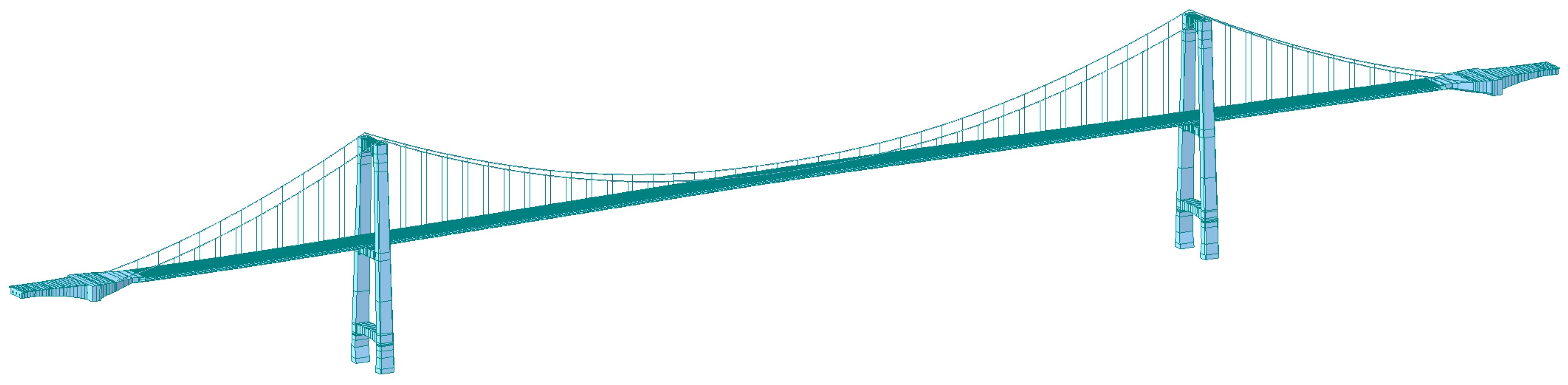
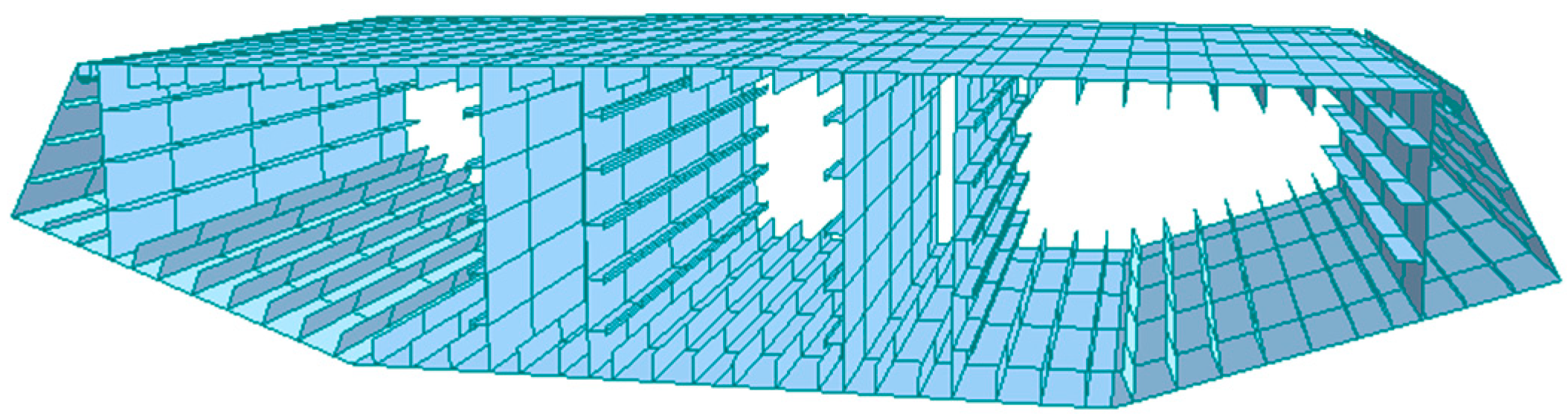
3.3. Finite Element Analysis
3.3.1. Finite Element Model
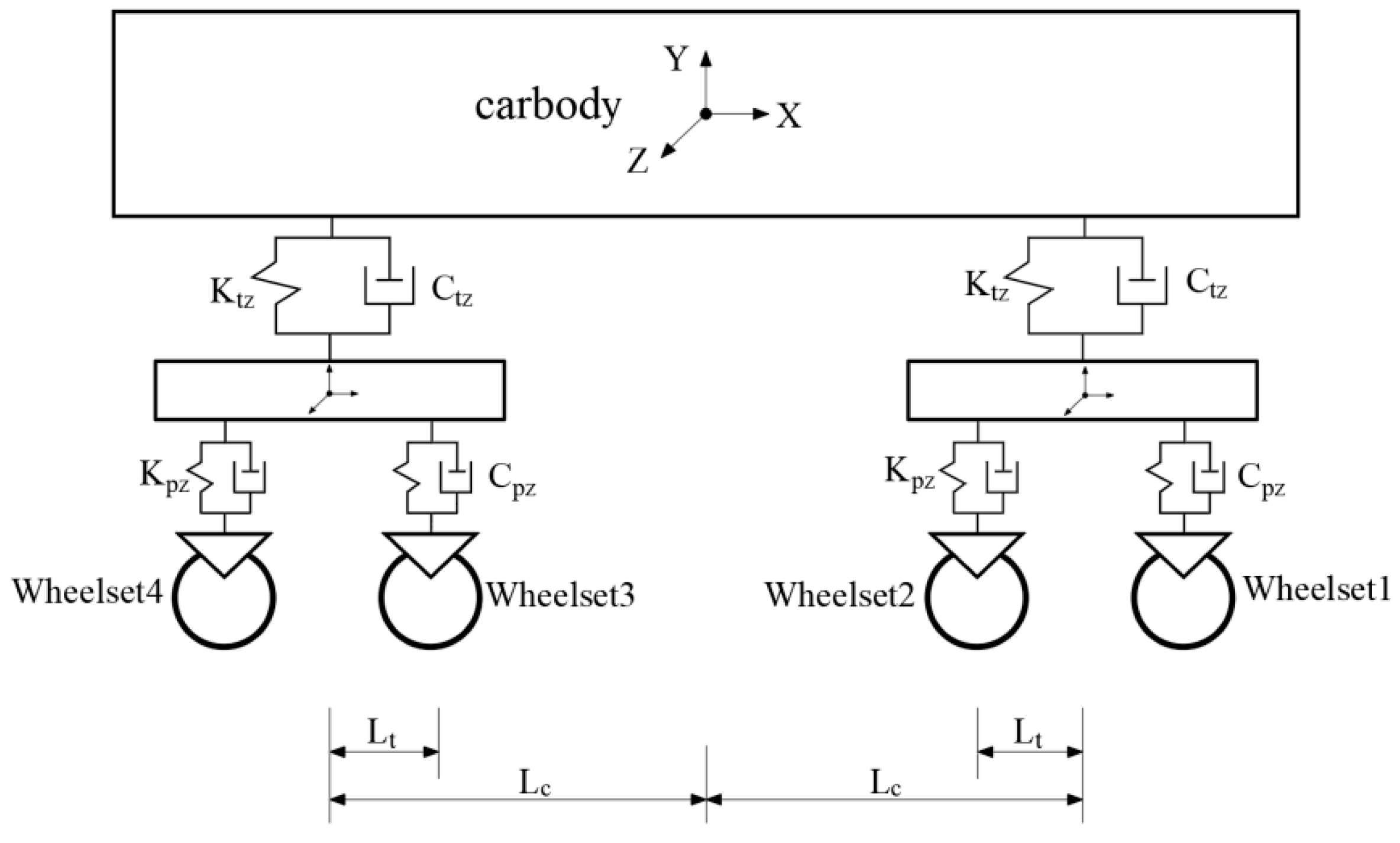
3.3.2. Train Model
3.3.3. Model Verification
4. Experiment and Discussion
4.1. Structural Response Analysis Under Static State
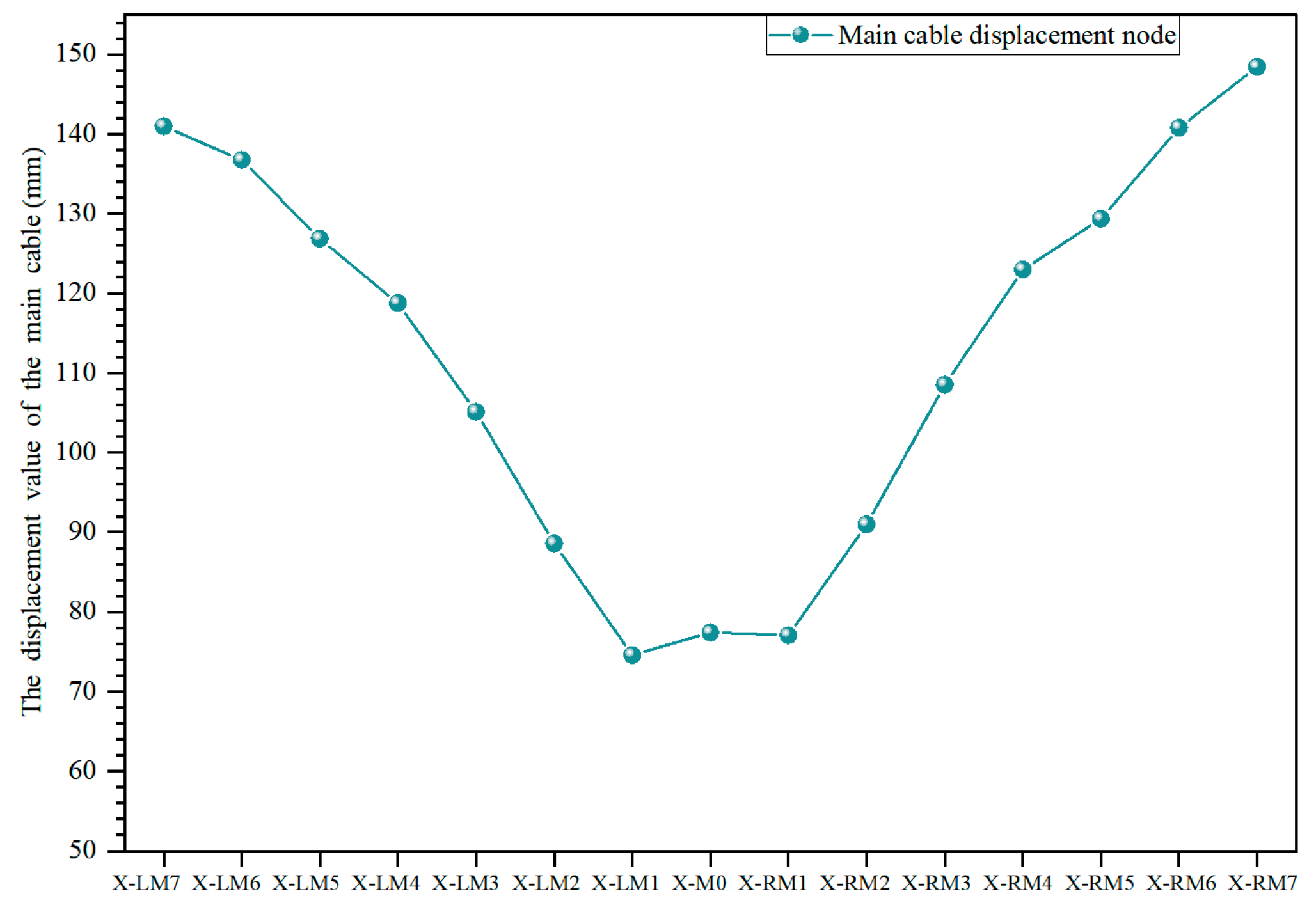
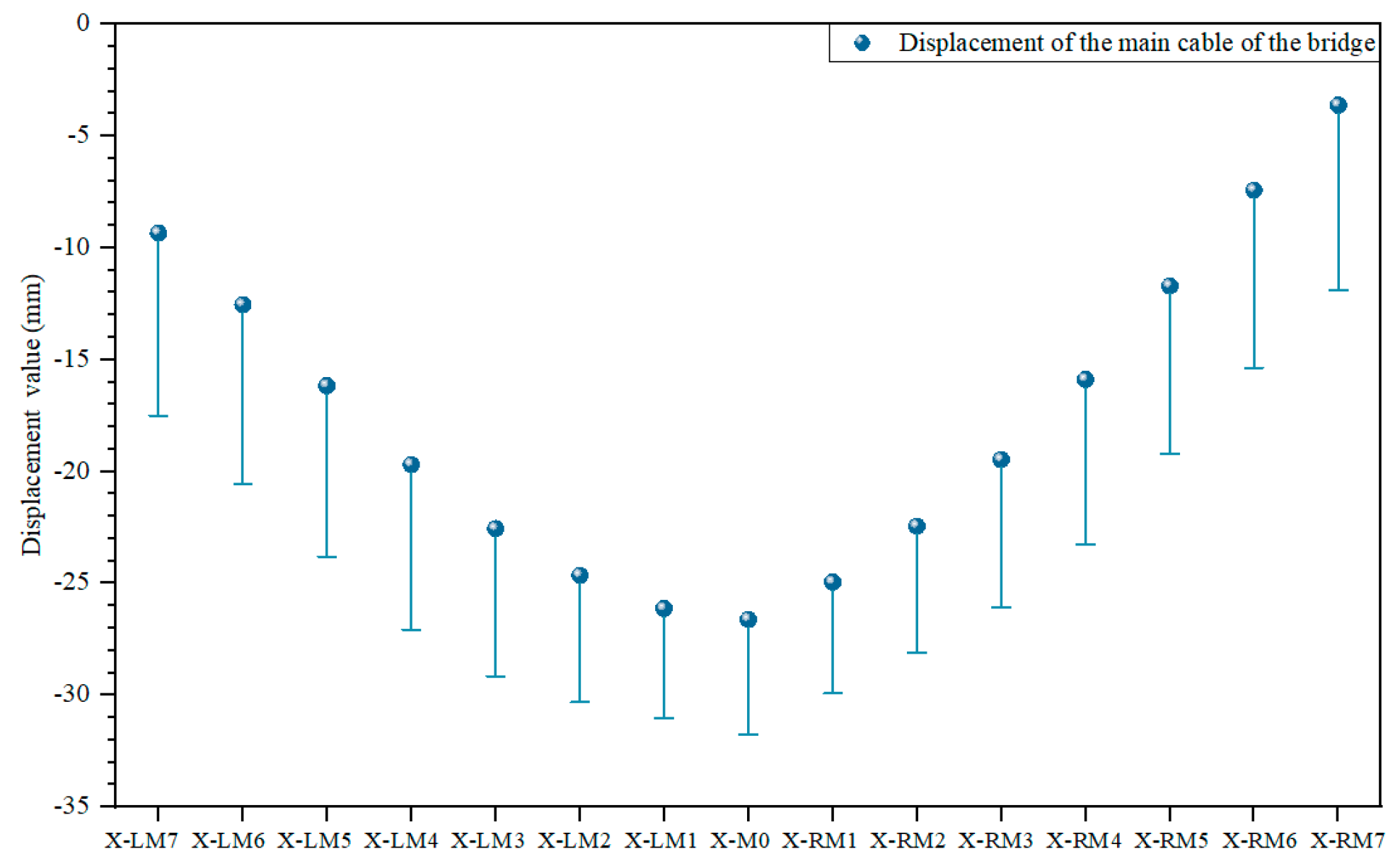
4.1.1. Main Cable Deformation Analysis
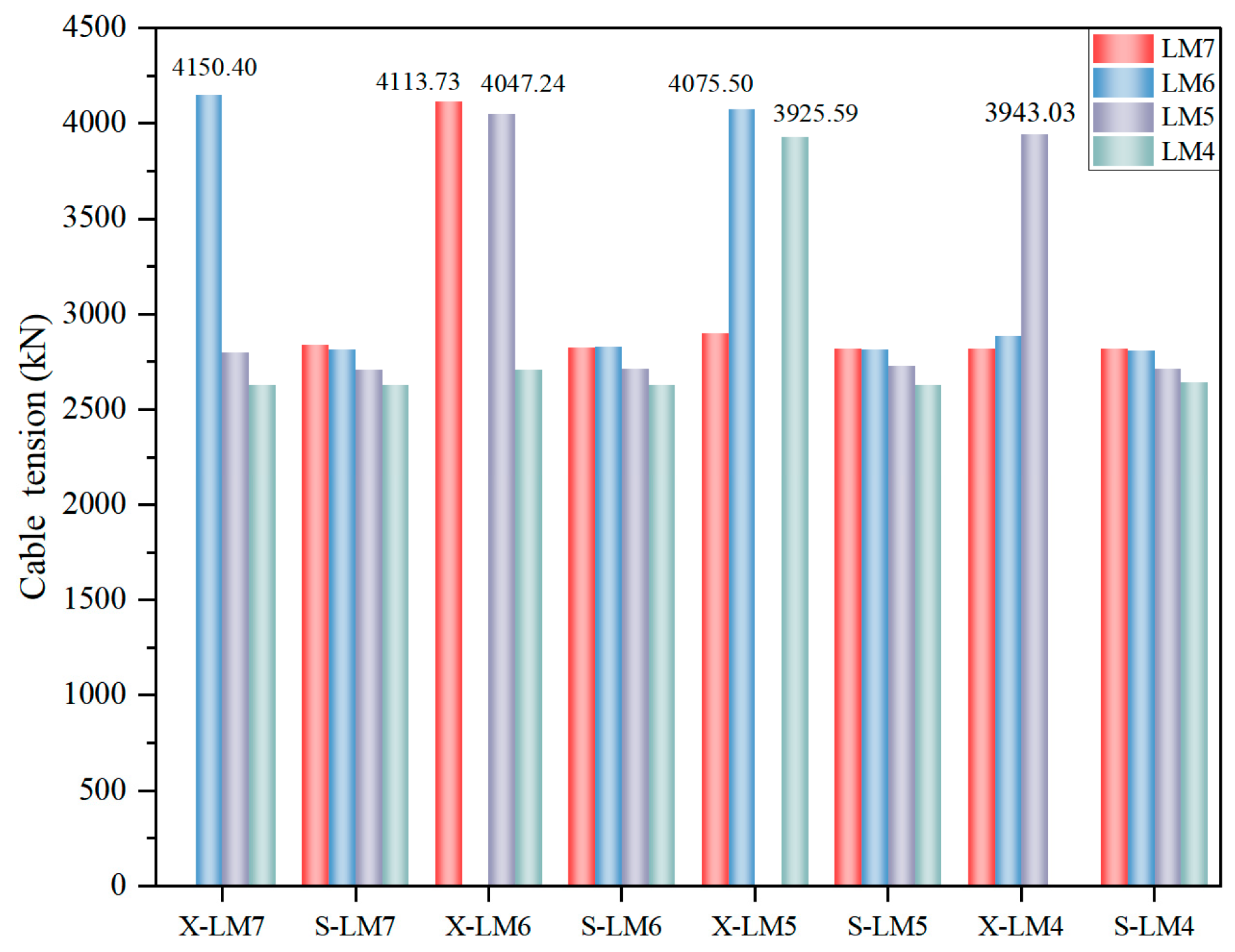
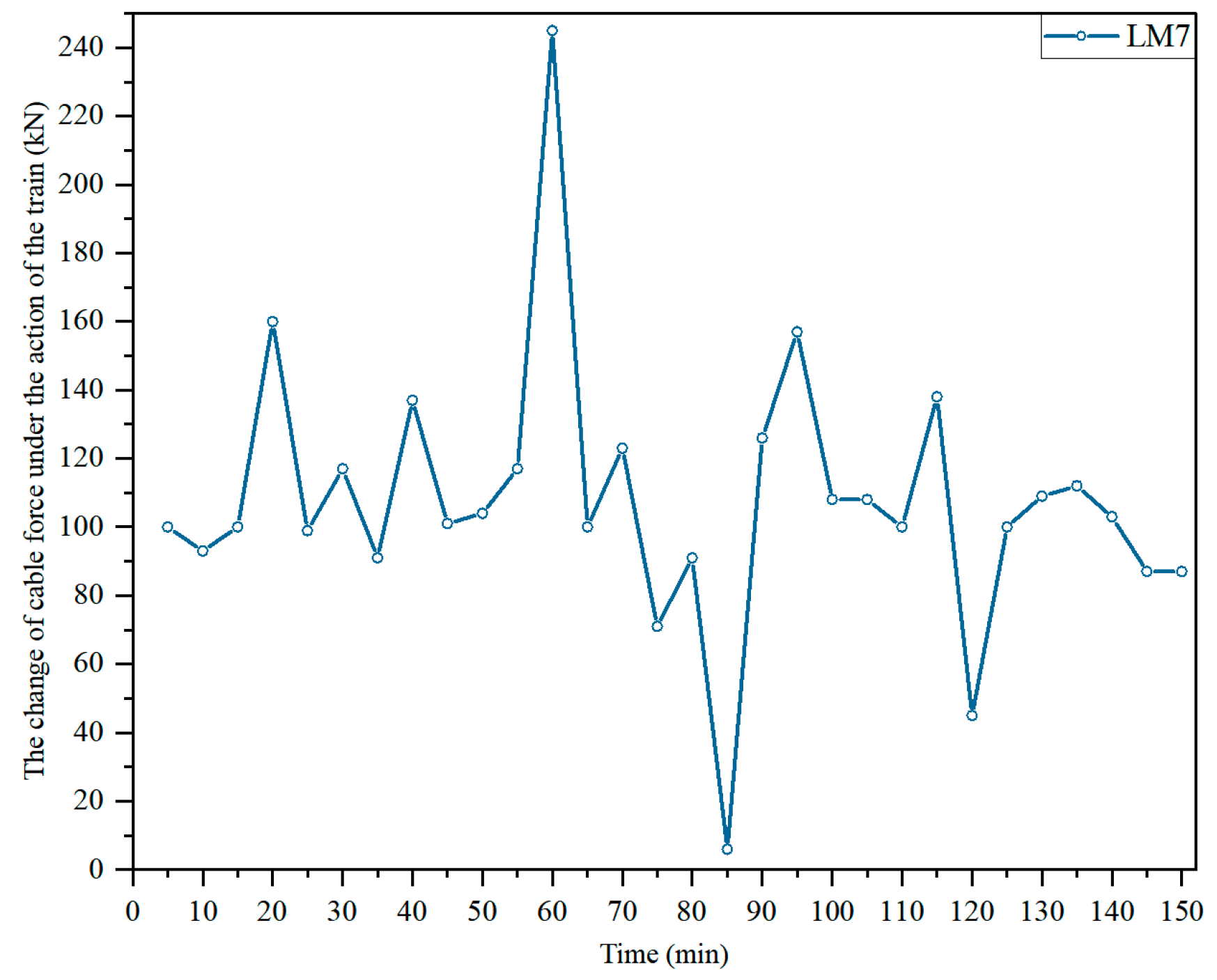
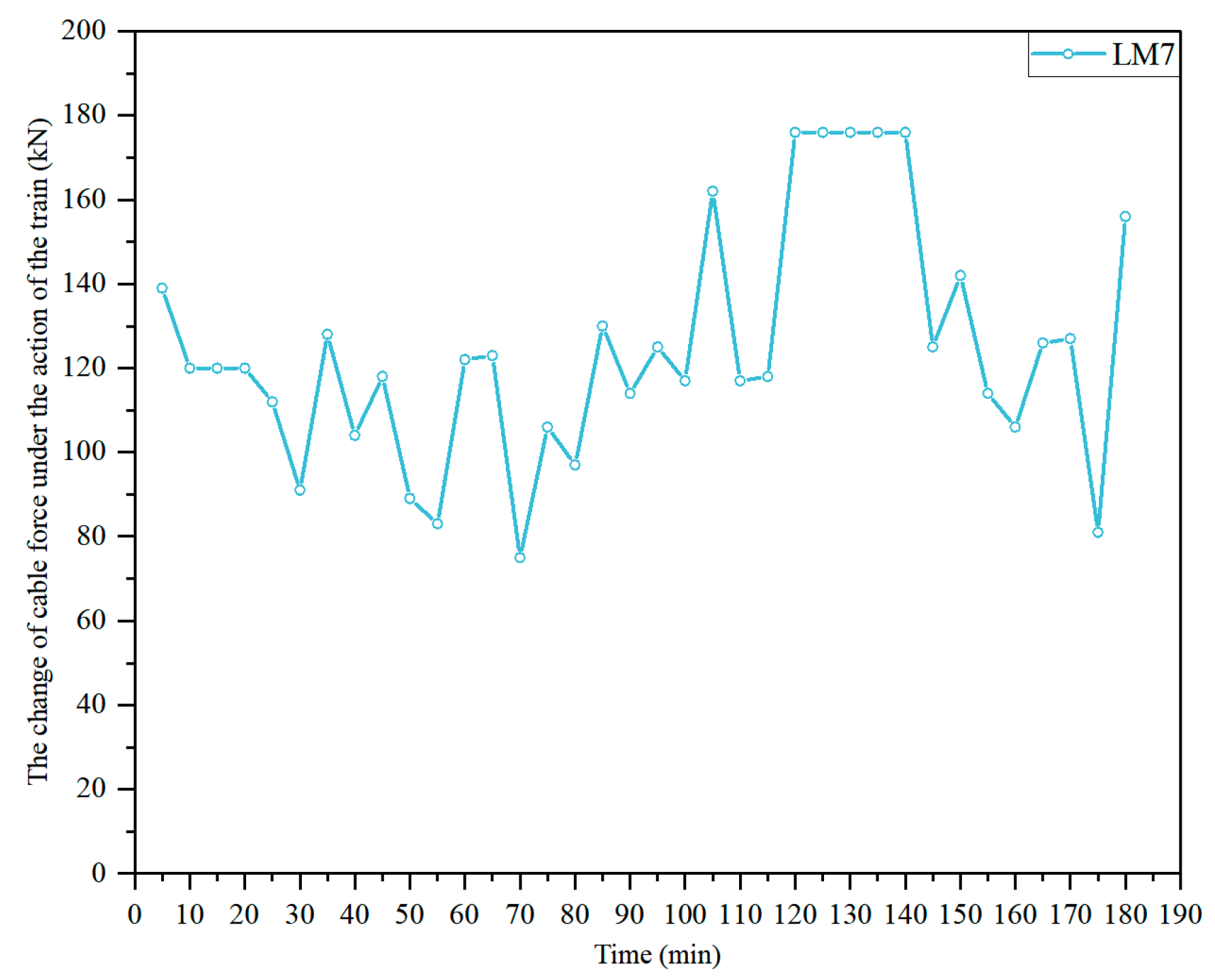
4.1.2. Incremental Analysis of Cable Force of the Adjacent Suspender
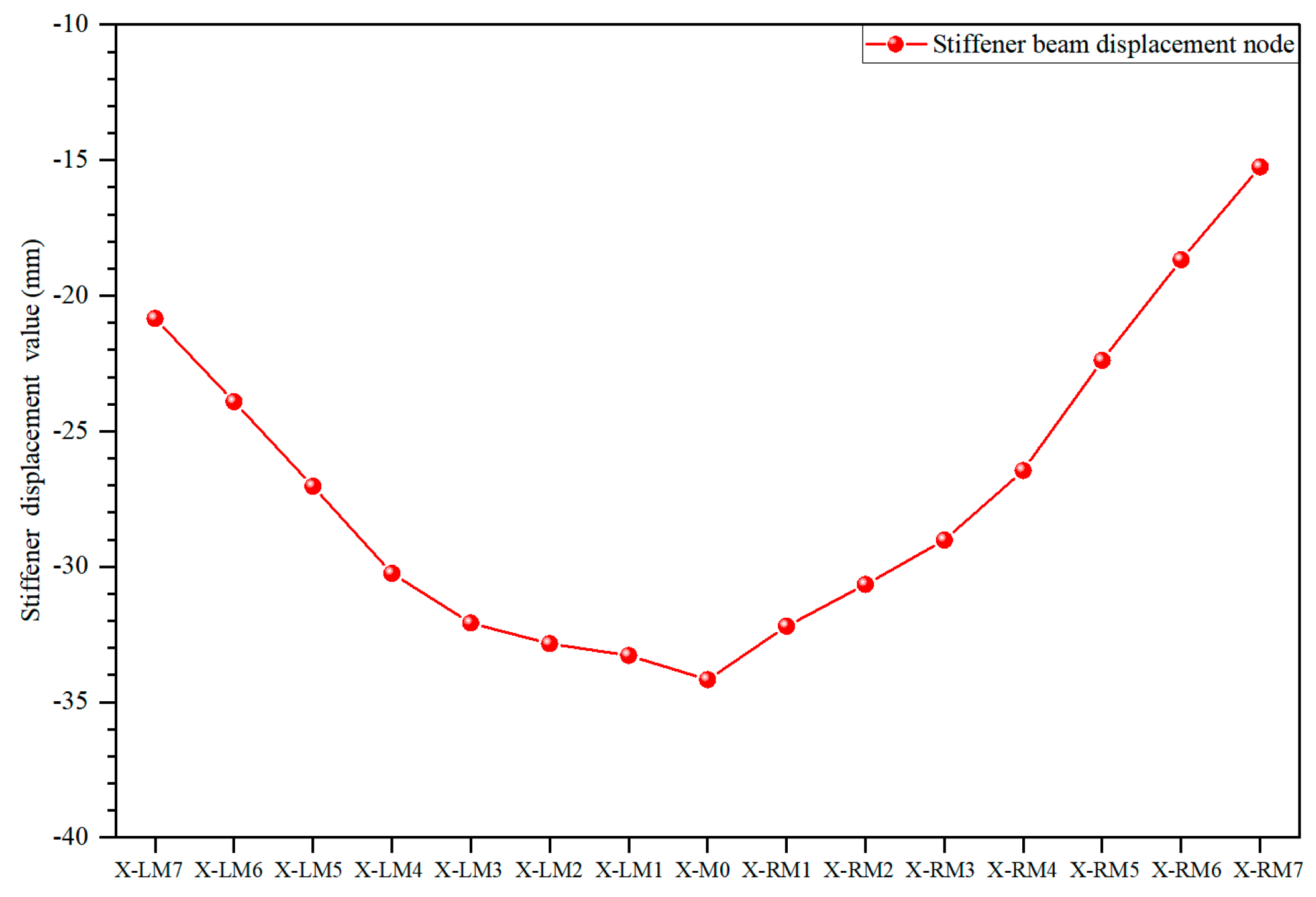
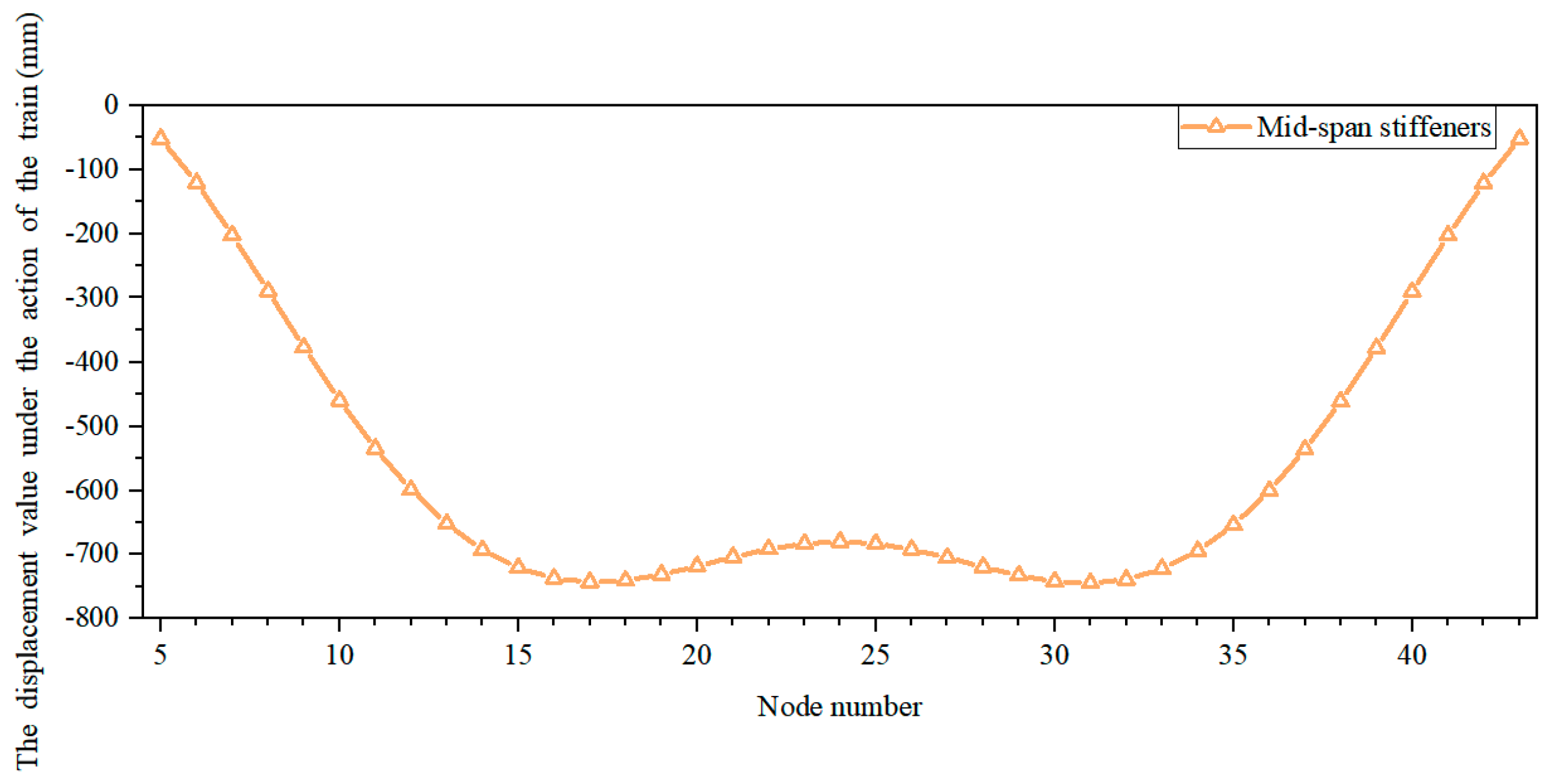
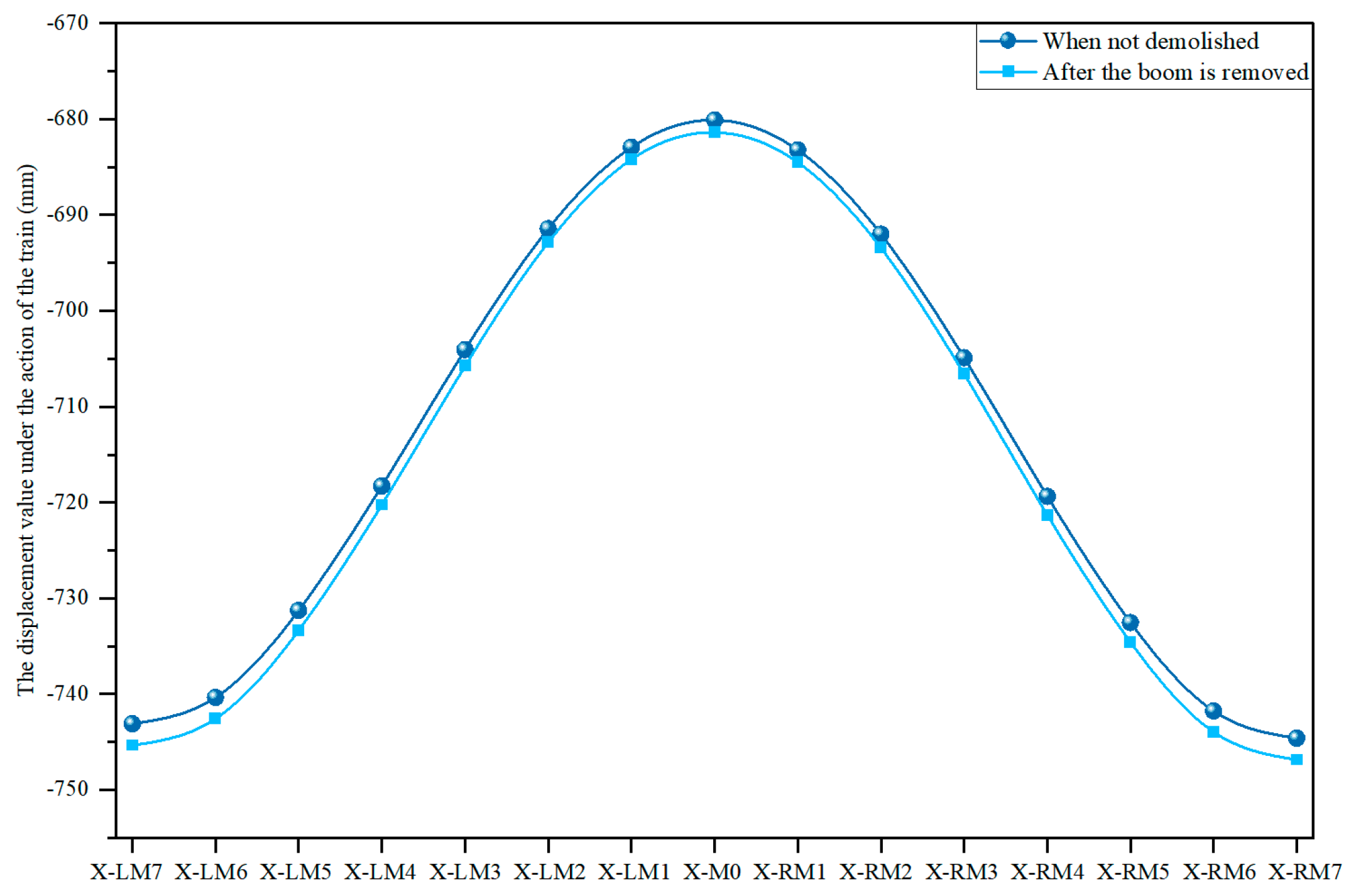
4.1.3. Deformation Analysis of Stiffened Beam
4.2. Structural Response Analysis of Train Under Full Load
4.2.1. Main Cable Deformation Analysis
4.2.2. Incremental Analysis of Cable Force of the Adjacent Suspender
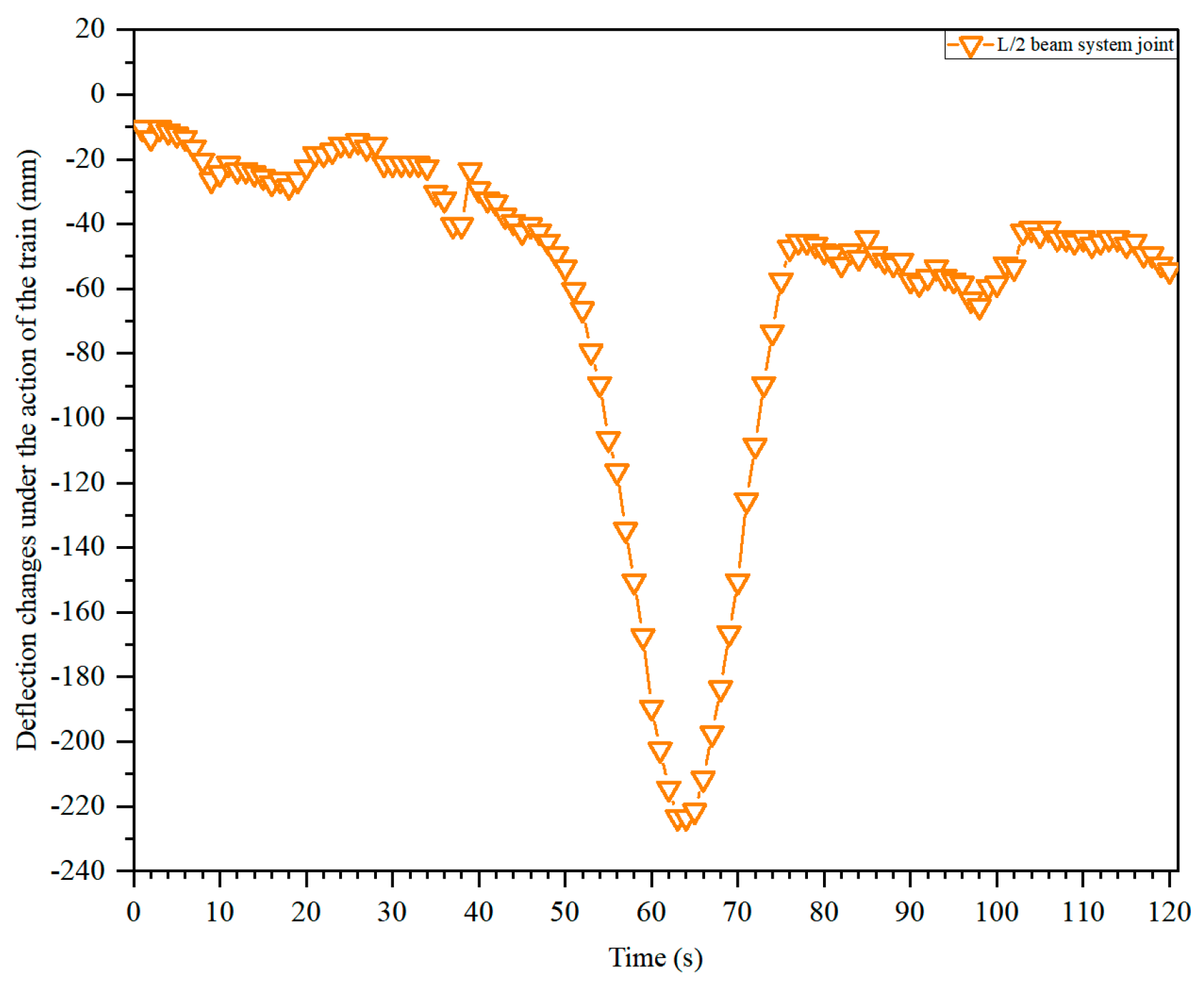
4.2.3. Analysis of Vertical Deformation of the Stiffened Beam
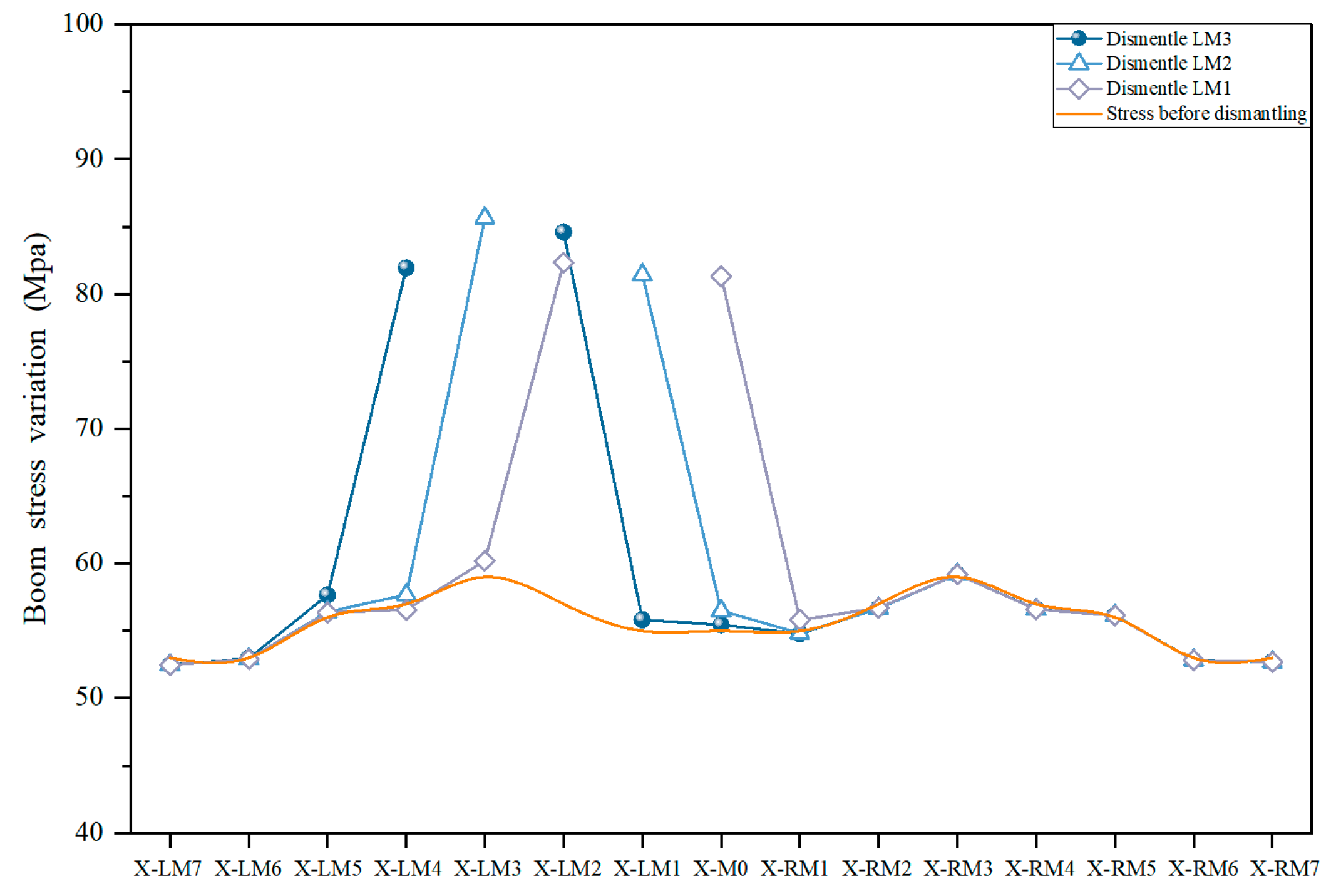
4.3. Safety Control Index Analysis
4.4. Real Bridge Monitoring
5. Conclusions and Prospect
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, D.; Mauch, C.; Summerville, S.; Fernandez, O. Suspender Replacement for a Signature Bridge. J. Bridge Eng. 2018, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Hu, Y. Analysis of mechanical properties of space network suspension rod tied arch bridge by suspension rod fracture. J. Shijiazhuang Tiedao Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 36, 28–33+68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Yang, T.; Xia, Y.; Qian, L.; Dong, L.; Jin, X. Replacement of the Fire-Damaged Long Suspenders of the Runyang Suspension Bridge. Struct. Eng. Int. 2022, 32, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, Z.; Tong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, R. Experimental Study on Fatigue Characteristics and Life Prediction of Rotating Restricted Short Suspender in Suspension Bridge. Buildings 2025, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Cao, M.; Li, Y. Bridge-Train-Passenger Coupling Vibration and Riding Comfort Analysis of Urban Track Line. J. Vib. Meas. Diagn. 2023, 43, 584–592+625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; Gong, K.; Qin, J. Influence of fastener failure on vertical vibration responses of the high-speed train-ballastless track-bridge coupled system. J. Rail Way Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y. The Application of a BiGRU Model with Transformer-Based Error Correction in Deformation Prediction for Bridge SHM. Buildings 2025, 15, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ning, S.; Shen, Y. Failure Investigation and Replacement Implementation of Short Suspenders in a Suspension Bridge. J. Bridge Eng. 2017, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, C.L. Construction and monitoring of suspension replacement project for Shantou Bay Bridge. Highw. Automot. Appl. 2015, 6, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Research on Replacement Methods and Bearing Capacity of Suspender Cables of In-Service Suspension Bridges. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojevic, D.; Kirkwood, K.F.; Matson, D.D. A Tale of Two Bridges: Extending the Lifetimes of the Lions Gate and Angus L. Macdonald Suspension Bridges. Struct. Eng. Int. 2019, 29, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adanur, S.; Okur, E.K.; Altunisik, A.C.; Gunaydin, M.; Rahwan, B.R. Investigation of the structural behaviors of Bosphorus suspension bridge with vertical hangers replaced by inclined hangers. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 65, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D. Investigation on the dynamic responses of a road-rail suspension bridge and the trains on bridge in case of suspender fracture. J. Vib. Shock. 2023, 42, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 39559.2-2020; Specifications for Operational Monitoring of Urban Rail Transit Facilities-Part 2. Bridge. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- JTG/T J21-2011; Specification for Inspection and Evaluation of Load-bearing Capacity of Highway Bridges. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JTG/T D65-05-2015; Design Code for Highway Suspension Bridges. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- JT/T 449-2021; Suspender of Highway Suspension Bridge. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 51234-2017; Code for Design of Urban Rail Transit Bridge. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S. Analysis on near influence of cable force in large-span self-anchored suspension bridges. China Civ. Eng. J. 2016, 49, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S. Displacement characteristics analysis on the main cable of large-span self-anchored suspension bridge. China Civ. Eng. J. 2015, 48, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; He, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Analysis on the Displacement Characteristics of the Main Cable in the Transformation Process of Cable-suspension System of Self-anchored Suspension Bridge. Highw. Eng. 2021, 46, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Practical calculation analysis of system transformation of self-anchored suspension bridge. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2021, 53, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, G. Suspension force loss analysis of self-anchored suspension bridge. J. China Foreign Highw. 2020, 40, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T/CECS G-M61-01-2019; Technical Specifications for Road Concrete Bridge Demolition. China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Zang, Y.; Dai, J.; Shao, C. Key Design Techniques for Egongyan Railway Transit Bridge. Bridge Constr. 2020, 50, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, R.-L.; Bai, L.-H.; Zhang, S.-H. Ultimate capacity of narrow type steel box section for railway self-anchored suspension bridge under bias compression. Adv. Steel Constr. 2019, 15, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Ding, P.; Qi, Y. Reasonable Stiffness Limits for Long-Span Track Suspension Bridge. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 37, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- JTG D60-2015; General Specifications for Design of Highway Bridges and Culverts. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Dynamic Response of Cable-Stayed Bridge and Trains on Bridge Under Cable Breaking Conditions. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2024, 59, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhi, L.; Lu, J.; Yu, X.; Beach, D. Broken cable-induced dynamic response of long-span concrete cable stayed bridge during construction. J. Vib. Shock. 2021, 40, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Monitoring Item | Serial Number | Device Type | Monitoring Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load monitoring | (1) | odometer | 0.1% F.S |
| Static and dynamic response monitoring of the whole structure | (2) | GNSS | 1/S |
| (3) | Intelligent digital static level | 0.01 mm | |
| Structure local response monitoring | (4), (5) | String type digital through the core anchor cable meter | ±1 kN |
| Main Component Characteristic Parameters | Materials | Unit Weight (kN/mm3) | Elastic Modulus (kN/mm2) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main cable | 1860 MPa high strength steel wire | 7.85 × 10−8 | 200 | 0.3 |
| Suspender | 1770 MPa high strength steel wire | 7.85 × 10−8 | 200 | 0.3 |
| Stiffening beam | C55 Concrete | 2.5 × 10−8 | 35.5 | 0.2 |
| Q420 | 7.85 × 10−8 | 206 | 0.31 |
| Boom LS6 | Boom RS6 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Days (D) | Measured Value (kN) | Theoretical Value (kN) | Matching Degree | Measured Value (kN) | Theoretical Value (kN) | Matching Degree |
| 1 | 145 | 150 | 97% | 156 | 164 | 95% |
| 2 | 142 | 150 | 95% | 158 | 164 | 96% |
| 3 | 146 | 150 | 97% | 156 | 164 | 95% |
| 4 | 145 | 150 | 97% | 157 | 164 | 96% |
| 5 | 142 | 150 | 95% | 158 | 164 | 96% |
| 6 | 143 | 150 | 95% | 159 | 164 | 97% |
| 7 | 144 | 150 | 96% | 156 | 164 | 95% |
| Boom LM6 | Boom RM6 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Days (D) | Measured Value (kN) | Theoretical Value (kN) | Matching Degree | Measured Value (kN) | Theoretical Value (kN) | Matching Degree |
| 1 | 328 | 340 | 96% | 324 | 335 | 97% |
| 2 | 325 | 340 | 96% | 320 | 335 | 96% |
| 3 | 323 | 340 | 95% | 318 | 335 | 95% |
| 4 | 333 | 340 | 98% | 325 | 335 | 97% |
| 5 | 327 | 340 | 96% | 323 | 335 | 96% |
| 6 | 326 | 340 | 96% | 333 | 335 | 99% |
| 7 | 324 | 340 | 95% | 330 | 335 | 99% |
| Item | Category | Item | Category | Item | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working condition 1 | Remove LM7 suspender | Working condition 6 | Remove LM2 suspender | Working condition 11 | Remove RM3 suspender |
| Working condition 2 | Remove LM6 suspender | Working condition 7 | Remove LM1 suspender | Working condition 12 | Remove RM4 suspender |
| Working condition 3 | Remove LM5 suspender | Working condition 8 | Remove M0 suspender | Working condition 13 | Remove RM5 suspender |
| Working condition 4 | Remove LM4 suspender | Working condition 9 | Remove RM1 suspender | Working condition 14 | Remove RM6 suspender |
| Working condition 5 | Remove LM3 suspender | Working condition 10 | Remove RM2 suspender | Working condition 15 | Remove RM7 suspender |
| Suspender Number | Working Condition | East (R) Side (mm) | West (L) Side (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-LM7 | Working condition 1 | 3.05 | / |
| X-LM6 | Working condition 2 | 2.18 | 4.72 |
| X-LM5 | Working condition 3 | 0.95 | 2.91 |
| X-LM4 | Working condition 4 | 0.53 | 2.03 |
| X-LM3 | Working condition 5 | −0.01 | 0.95 |
| X-LM2 | Working condition 6 | −0.10 | 0.71 |
| X-LM1 | Working condition 7 | −0.10 | 0.29 |
| X-M0 | Working condition 8 | −0.08 | −0.08 |
| X-RM1 | Working condition 9 | 0.28 | −0.11 |
| X-RM2 | Working condition 10 | 0.71 | −0.11 |
| X-RM3 | Working condition 11 | 0.96 | −0.01 |
| X-RM4 | Working condition 12 | 2.05 | 0.54 |
| X-RM5 | Working condition 13 | 2.91 | 0.98 |
| X-RM6 | Working condition 14 | 4.72 | 2.27 |
| X-RM7 | Working condition 15 | / | 3.07 |
| Suspender Number | Working Condition | East (R) Side (mm) | West (L) Side (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-LM7 | Working condition 1 | −8.17 | / |
| X-LM6 | Working condition 2 | −7.95 | −8.14 |
| X-LM5 | Working condition 3 | −7.48 | −7.68 |
| X-LM4 | Working condition 4 | −7.15 | −7.38 |
| X-LM3 | Working condition 5 | −6.37 | −6.53 |
| X-LM2 | Working condition 6 | −5.36 | −5.54 |
| X-LM1 | Working condition 7 | −4.65 | −4.70 |
| X-M0 | Working condition 8 | −4.90 | −4.91 |
| X-RM1 | Working condition 9 | −7.42 | −4.72 |
| X-RM2 | Working condition 10 | −5.55 | −5.38 |
| X-RM3 | Working condition 11 | −6.55 | −6.39 |
| X-RM4 | Working condition 12 | −7.40 | −7.17 |
| X-RM5 | Working condition 13 | −7.53 | −7.34 |
| X-RM6 | Working condition 14 | −8.06 | −7.87 |
| X-RM7 | Working condition 15 | / | −8.28 |
| Working Condition | Static Load | Structural Response Under Full Load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safety Factor (KS) | Average Difference of Main Cable Deformation (mm) | Deformation Limit of Stiffened Beam (mm) | Cable Force Limit (kN) | Main Cable Deformation Limit (mm) | Deformation Limit of Stiffened Beam (mm) | |
| Working condition 1 | 2.67 | −8.01 | −11.58 | 460.78 | −16.42 | −745.35 |
| Working condition 2 | 2.61 | −9.56 | −11.41 | 456.34 | −16.54 | −742.58 |
| Working condition 3 | 2.66 | −8.62 | −10.87 | 457.96 | −16.32 | −733.35 |
| Working condition 4 | 2.58 | −7.72 | −10.52 | 451.35 | −16.50 | −720.24 |
| Working condition 5 | 2.77 | −6.21 | −9.49 | 441.05 | −16.05 | −705.76 |
| Working condition 6 | 2.97 | −5.19 | −8.17 | 424.52 | −15.59 | −692.87 |
| Working condition 7 | 3.16 | −4.31 | −7.12 | 415.81 | −15.16 | −684.20 |
| Working condition 8 | 3.32 | −4.34 | −7.44 | 411.36 | −15.39 | −681.38 |
| Working condition 9 | 3.15 | −4.36 | −7.23 | 416.58 | −15.22 | −684.51 |
| Working condition 10 | 2.95 | −5.20 | −8.20 | 425.50 | −15.61 | −693.45 |
| Working condition 11 | 2.67 | −6.23 | −9.51 | 441.62 | −16.06 | −706.6 |
| Working condition 12 | 2.59 | −7.74 | −10.54 | 451.01 | −16.52 | −721.32 |
| Working condition 13 | 2.69 | −8.51 | −10.68 | 457.20 | −16.26 | −734.60 |
| Working condition 14 | 2.63 | −9.59 | −11.30 | 456.02 | −16.51 | −743.98 |
| Working condition 15 | 2.68 | −9.32 | −11.73 | 460.77 | −16.47 | −746.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Ding, P.; Luo, L.; Huang, X.; Li, X. Research on the Support-Free Replacement Method of Suspenders for Long-Span Self-Anchored Rail Special Suspension Bridges. Buildings 2025, 15, 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091406
Li X, Zhou M, Ding P, Luo L, Huang X, Li X. Research on the Support-Free Replacement Method of Suspenders for Long-Span Self-Anchored Rail Special Suspension Bridges. Buildings. 2025; 15(9):1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091406
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaogang, Minglin Zhou, Peng Ding, Ling Luo, Xiangsheng Huang, and Xiang Li. 2025. "Research on the Support-Free Replacement Method of Suspenders for Long-Span Self-Anchored Rail Special Suspension Bridges" Buildings 15, no. 9: 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091406
APA StyleLi, X., Zhou, M., Ding, P., Luo, L., Huang, X., & Li, X. (2025). Research on the Support-Free Replacement Method of Suspenders for Long-Span Self-Anchored Rail Special Suspension Bridges. Buildings, 15(9), 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15091406





