Abstract
Considering the current role of technology, this research aims to investigate the impact of the metaverse on social development and psychological well-being in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The focus remains on Generation Z, as an important portion of the country’s metaverse users. Supported by the technology determinism theory, this research used a structured questionnaire to gather data from 363 respondents. The analysis indicates that metaverse technology significantly impacts social development and psychological well-being. The effect of metaverse technology on social development remained positive, with the p-value at p > 0.000. In addition, metaverse technology also has a significant positive effect on psychological well-being (p > 0.000), with the findings showing strong statistical support for this relationship. These results confirm that metaverse technology plays a significant role in improving both social and psychological facets. Thus, it is concluded that the metaverse creates immersive virtual environments that help unique forms of social interaction and connectivity, confounding geographical barriers. This can improve social skills and communication and promote a strong sense of community. The metaverse offers a directed and engaging space to practice social interactions and gain confidence, indicating its positive, constructive role in society.
1. Introduction
The immediate advancement of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) in recent years has made smartphones, tablets, and their applications critical to daily life, especially among the current generation (Kathuria 2023). The ability to stay constantly connected has significantly increased the time users spend online, making web and mobile applications an integral part of their daily lives (Popaitoon 2022).
This widespread use of digital applications has greatly changed how users interact with their peers, access information, and build social relationships (Benvenuti et al. 2023). It has also profoundly influenced their health and well-being, including their cognitive development and attention span while accomplishing tasks. Consequently, the generational transformations within communities are mainly driven by shifts occurring on a global scale.
Notably, the relationship between society and technology characterizes a continuous interaction between social needs and desires and the abilities of technological systems. Society drives technological innovation, and in turn, technology shapes the world’s normative and social fabric, values, and norms. Iqbal and Campbell (2023), stated that the future advanced metaverse aims to provide users with a more immersive digital experience. Typically, there are two types of metaverses: one that users can build from scratch and another that offers a pre-existing environment for immediate exploration.
Users can interact within the metaverse just as they would in the physical world, allowing them to create and invest across different platforms. This presents a compelling opportunity for the users. Having grown up with the internet and the rise of smartphones, members of Generation Z are deemed digital natives (Lamba et al. 2021). According to a recent study, youngsters spend more time online or connected to smart devices than earlier generations, averaging about three hours daily (Tankovic et al. 2022). Many organizations also use new technologies to improve efficiency and speed, improving user engagement and experiences. The advancement in IT has enabled digitalization in services, enabling social growth and development. Thus, with its ability to deliver improved realism and presence, the metaverse provides a promising new platform for significantly improving the social needs of young people as public events and social interactions have declined significantly. Research has shown that social interactions contribute significantly to psychological well-being through the exchange of social support (Oh et al. 2023).
Consequently, metaverse technology is becoming increasingly popular in the UAE. Recent statistics show that around 25% of residents have engaged with metaverse technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). The UAE government is actively promoting the metaverse, with Dubai’s Metaverse Strategy aiming to create 40,000 virtual jobs and attract over USD 4 billion in investments by 2030. The industry is experiencing rapid growth, with investments expected to surpass USD 1.5 billion by 2025. Additionally, virtual real estate transactions are rising, placing the UAE among the leading countries in investing in digital assets. Notably, around 40% of Generation Z in the UAE regularly use metaverse platforms for activities like socializing, gaming, and education, highlighting significant engagement among young people.
Metaverse technology is a collective virtual shared space created by converging virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual reality. It comprises a range of digital environments and interactions facilitated by advanced technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and blockchain. In the metaverse, users can interact with a computer-generated world and other users in real time, using avatars and digital interfaces. This technology enables immersive experiences where individuals can socialize, work, play, and create within a seamless, interconnected virtual realm beyond traditional digital platforms (Jiaxin and Gongjing 2022).
Online supportive interactions similarly improve users’ social presence and psychological well-being (e.g., Oh et al. 2014). Unlike text-based communication platforms, the metaverse’s 3D virtual environment provides an increased sense of social belonging. According to Dionisio et al. (2013), 3D environments provide users with precise visual cues about their surroundings, improving their communication by moving across different settings and manipulating the space. Avatar-mediated communication in the metaverse generates rich communication cues, i.e., appearance, gestures, and behavior. This sense of co-existence and cue-rich communication creates a sense of belonging, making users feel that others are physically present in the same environment (Dong and Lee 2022). This social illusion encourages positive interactions by motivating individuals to preserve a good impression and aim for social approval from others (Naikoo et al. 2018).
Generally, generations are named based on the prevalent industry or technology during their formative years (Ajmain 2020). For instance, during the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, societal changes were affected by digital technology and the internet. The current generation’s attitude, perspectives, and culture are deeply interwoven with these digital advancements, shaping their behavior significantly (Răduț 2021).
Therefore, social and psychological changes and technology have become central topics for Generation Z. For example, Jeljeli and Farhi (2024), consider metaverse technology accompanied by immersive experiences as prominent aspects of technology, particularly for Generation Z. In this context, one of the critical elements that could drive the success of the metaverse is its constant activity and real-time existence. Considering technology’s utmost importance and impact, this research aims to address the preceding questions about its impacts on Gen Z.
In this regard, technology determinism supports the idea of Gen Z adopting and using metaverse technology. Technology determinism is the idea that technological advancements shape and determine how societies evolve and individuals behave. The development and use of technology directly influence social structures, cultural norms, and human interactions, essentially driving changes in how people live and think. This concept emphasizes that technology primarily shapes human experiences and societal transformations (Hallström and Kaijser 2022).
Thus, the primary aim of this research is to investigate the influence of metaverse technology on Generation Z’s social development and psychological well-being in the UAE. The study further addresses two primary research questions: (i) how metaverse technology impacts Gen Z’s social development in the UAE and (ii) how metaverse technology impacts Gen Z’s psychological well-being.
Research Gaps
Notably, “social development” and “psychological well-being” refer to different aspects of how individuals interact with others and sustain their mental health. In this research, “social development” involves how Generation Z in the UAE builds relationships, communicates, and engages with their community through metaverse technology. This includes enhanced social skills, i.e., increased confidence in social interactions and the improved ability to form and maintain relationships. “Psychological well-being” encompasses individuals’ overall mental health and emotional state. This research highlights how metaverse technology affects feelings of happiness, stress levels, and the ability to cope with mental health challenges. Particularly, the study examines how the use of metaverse technology can lead to improvements in individuals with social disorders by providing a virtual space for interaction that may feel safer and more controlled than face-to-face interactions. Further, it investigates how these virtual interactions can reduce feelings of isolation and anxiety, thus contributing to better mental health outcomes.
Notably, this research addresses a significant empirical gap in the existing literature. Specifically, there needs to be more research on the impact of metaverse technology on Generation Z in the UAE, especially concerning their social development and psychological well-being. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of various technologies (Farhi 2024; Farhi et al. 2023), including the metaverse, leading to a transformative digital shift. However, the specific consequences of this shift on the UAE’s younger population have yet to be thoroughly examined. This study aims to fill this gap by examining how the increased use of metaverse technology during and after the pandemic has influenced Generation Z’s social interactions and mental health in this region. Also, the research will analyze the reciprocal relationship between metaverse technology use, social development, and psychological well-being, thoroughly analyzing how these factors interplay and impact one another (Youssef et al. 2024).
This research has significant implications for comprehending the transformative effect of metaverse technology on Generation Z’s social development and psychological well-being in the UAE. Grounded in the technology determinism theory, this study aims to explain how Generation Z’s pervasive adoption of metaverse technology reshapes their social exchanges and psychological experiences. By examining the reciprocal relationship between metaverse technology use, social development, and psychological well-being, this research not only contributes to the academic literature on technology’s impact on human development but also provides practical insights for policymakers, educators, and mental health professionals in composing interventions and support systems designed to the requirements of this digital-native generation.
2. Review of Literature
2.1. Technology Determinism Theory
The technology determinism theory, which asserts that technological advancements shape human behavior and societal structures, underpins this research by providing a framework to apprehend how metaverse technology affects Generation Z’s social development and psychological well-being in the UAE. It aims to determine whether technology or other factors overpower human experiences, presenting questions about how technological factors shape human thought and behavior (Țicău and Hadad 2021).
Technological determinism can be delineated back to classical economics and the early days of sociology, especially with scholars like Marx and Weber and the Frankfurt School. However, there are differing understandings of which theories fall under this category. These scholars analyzed the transformations brought about by contemporary society due to the trend in scientific and technical rationalization, with technology acting as a central component of societal identity (Hallström and Kaijser 2022). This perspective usually involves the reification of technology, specifically in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, where technology is noticed as having metaphysical powers and acting as an independent force pushing social change. The theory is deemed relevant to current research as technology has increased communication opportunities between people from different cultures and languages, exchanging ideas and discussion in the digital landscape (Feng 2022).
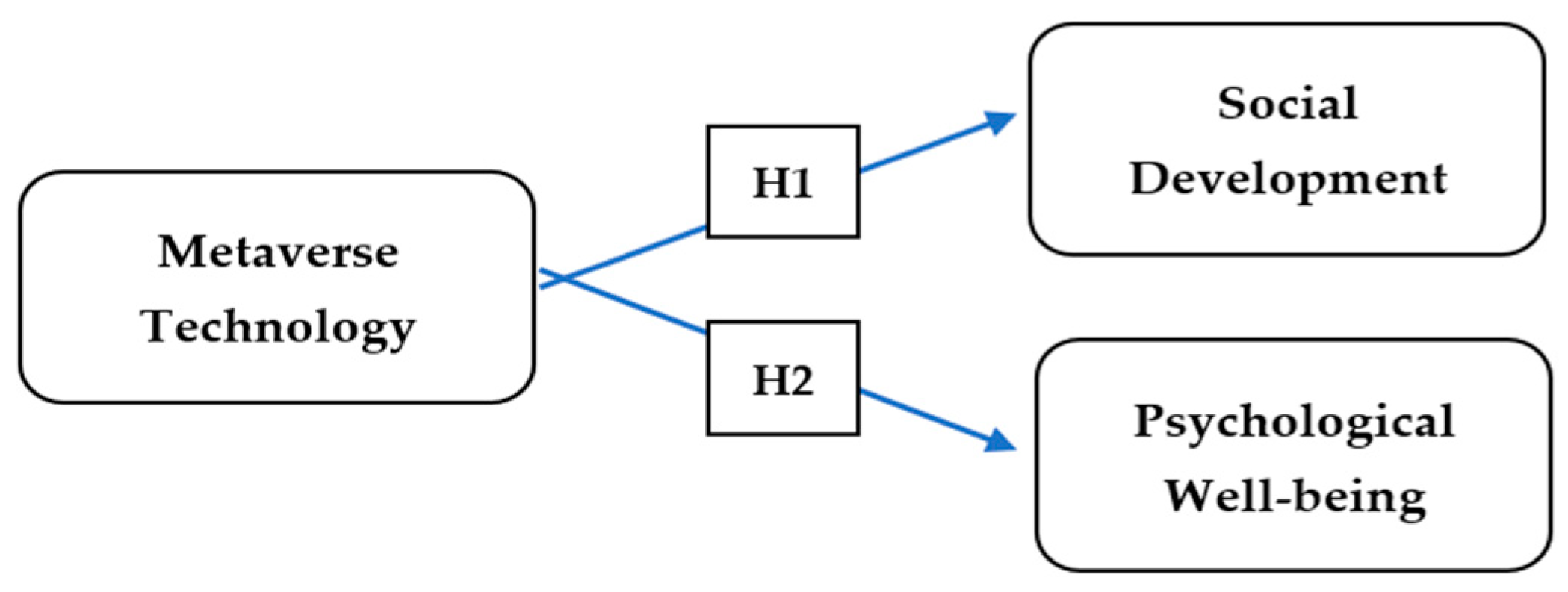
Although communication and society are different aspects, technology determinism provides a pathway to determine how the current era of digitalization is transforming Generation Z by improving communication and facilitating interaction between users regardless of geographical boundaries and limitations. Also, it is assumed that technology has facilitated communication by eradicating language barriers and promoting language acquisition and learning among users. According to Gil-Garcia et al. (2014), technology can change how society, including Generation Z, interacts and adopts new social behaviors. Technology and society are embedded, indicating individuals, as a part of social systems, are destined to interact with technology and become a part of the social development process. Thus, considering the relevance of technology determinism theory with the current study, Figure 1 illustrates the conceptual framework of current research. At the same time, Table 1 provides the operationalization of constructs in the current research.
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework of current research.

Table 1.
Definitions of key terms in the current study.
2.2. An Overview of Metaverse Technology in the UAE
The United Arab Emirates is a hub of social and economic activities, implying overall growth and development as an integral aspect of the region (Farhi et al. 2023). The current technological revolution in the UAE is a part of UAE 2023’s sustainable development agenda, necessitating technology integration in every aspect of life. Consequently, today, the Dubai Metaverse Strategy seeks to drive innovation, increase the metaverse’s social and economic impact through research and development partnerships, and facilitate advanced ecosystems. It seeks to develop talent and future skills by providing education in the metaverse for developers, content creators, and digital platform users. This strategy aims to position the UAE among the top 10 global metaverse powers and establish it as a leading hub for the metaverse community. Building on the UAE’s success in attracting over 1000 companies in blockchain and metaverse fields, the strategy also strives to support the creation of over 40,000 virtual jobs by 2030 (UAE 2023), further supporting the UAE’s economy and aligning with the UAE government’s vision to increase the number of technology companies fivefold.
The strategy’s main pillars comprise extended reality, which combines the physical and virtual worlds, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), mixed reality, and digital twins, virtual representations of objects or systems. The strategy uses real-time data through machine learning, IoT, AI simulation, and blockchain to improve human decision-making processes. The metaverse strategy’s technological bases include data, network, cloud, and edge computing (Farhi 2024). It highlights the investment, validation, storage, processing, and management of real-world data. The strategy also enables the deployment of 5G networks to facilitate edge computing, allowing data to be accumulated, stored, and processed locally through smart devices and local networks instead of relying solely on the cloud.
According to Teng et al. (2022), the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is becoming a significant power in advancing metaverse technology. The metaverse, a virtual world presenting users with a fully immersive experience, is transforming many sectors in the UAE (Youssef et al. 2024). The Dubai Future Foundation (DFF) is a significant contributor to this development, a government entity committed to encouraging innovation and technological advancement in Dubai. The DFF has formed a technical metaverse team focused on creating an immersive and interactive virtual environment. Their projects include developing a virtual marketplace where users can purchase and sell goods and services using digital currencies (The Government of UAE 2023). Numerous companies and government entities in the UAE are also investing in developing metaverse technology.
2.3. Metaverse Technology and Social Development
Technology and social development are interwoven concepts, accompanied by social communication and interaction skills. Any disturbances in the communication process can impact the fulfillment of social roles and potentially lead to social isolation. Effective, uninterrupted communication enables individuals to form interpersonal relationships and meet their needs for social cooperation (Jiaxin and Gongjing 2022). The idea that humans are intrinsically social beings, first proposed by ancient philosophers like Antisthenes and Aristotle, has impacted modern sociological and psychological perspectives. As a result, despite “metaverse” being a current buzzword, it effectively represents an expansion of communication technologies. Unlike these earlier technological concepts, the metaverse presents a new domain for human interaction, promoting virtual communication to a more immersive level (Ud Din and Almogren 2023).
This new form of interaction will be an immersive virtual communication space, making virtual interactions a significant facet of social communication and development. People have pursued more suitable, personal, and direct social relations since the beginning of the internet, from handwritten letters to WeChat and video chats. The pursuit of more affluent, more immersive online social experiences has been ongoing. After transitioning through PC social networks, mobile social networks, and algorithm-driven interest platforms, social networking is entering its fourth era—metaverse social interaction (Hutson 2022).
Metaverse social networking provides users with a virtual world that reflects real life, enabling them to transfer their real-world activities into virtual space. They can sing, watch movies, play games, shop, and travel in this space, achieving “present” social interaction in a virtual environment. This metaverse-supported social interaction revolutionizes methods and social engagement, creating a world where virtual and real experiences blend seamlessly (Gonzalez-Moreno et al. 2023). H1: The use of metaverse technology positively impacts the social development of Generation Z in the United Arab Emirates. Specifically, increased engagement with metaverse platforms improves social skills, facilitates relationship-building, and encourages more effective communication among young individuals in this demographic.
2.4. Metaverse Technology and Psychological Well-Being
Usmani et al. (2022) showed metaverse technology’s success in treating social anxiety disorder and improving social interactions and communication skills. For example, Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET) uses virtual reality simulations to expose patients to fear-inducing situations in a supervised and safe environment. This approach has proven effective in treating different psychological conditions, i.e., phobias, PTSD, anxiety, and depression. Benrimoh et al. (2022) found that VRET significantly decreases symptoms of phobia and PTSD, thereby improving patients’ quality of life. Also, virtual reality can enhance social skills training. Hennig-Thurau and Ognibeni (2022) witnessed that virtual reality could decrease social anxiety and improve social skills in those with social anxiety disorder.
Similarly, Oyanagi et al. (2022) suggested that virtual reality might improve empathy and prosocial behavior in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. The metaverse provides new socialization opportunities, can impact social interactions, and poses challenges like cyberbullying and social isolation (Hennig-Thurau and Ognibeni 2022). Furthermore, ample time in virtual worlds could change social interactions, positively affecting mental well-being.
They presented a framework for understanding social interactions in the metaverse and suggested a future research roadmap. Oh et al. (2023) found that social presence, supporting interaction, and social self-efficacy correlate with decreased loneliness in the metaverse, making it a confirming platform for those with face-to-face communication difficulties or those in secluded areas. H2: The use of metaverse technology positively affects the psychological well-being of Generation Z in the United Arab Emirates. Specifically, increased engagement with metaverse platforms decreases anxiety, improves mood, and improves overall mental health among young individuals in this demographic.
3. Methodology
This research study is based on a quantitative, cross-sectional design, including a quantitative, closed-ended questionnaire for data-gathering purposes. Notably, cross-sectional studies are widely preferred as they involve short data-gathering times, ensuring the generalizability of research findings (Bayley 2013). The gathered data are further evaluated and coded for analysis using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS Ver 26) and partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM).
3.1. Study Population and Sampling
The population used in the current research includes individuals categorized as Generation Z, aged 15 to 27 years old. Recent data indicate that approximately 1.4 million individuals in the UAE are currently in this generation (Ameen and Anand 2020). Thus, based on the total population, the sample size is further determined using the Qualtrics (2023) sample size calculator, indicating a sample size of 385 respondents with a 95% confidence interval and 5% margin of error as the ideal for the current research study.
This study selected a sample size of 385 participants based on a power analysis to ensure adequate statistical power for detecting meaningful effects in the relationships between metaverse technology, social development, and psychological well-being. This sample size aligns with the study objectives by providing a strong representation of Generation Z in the UAE, allowing for the reliable analysis of the impact of metaverse technology on these results. This sample size was chosen to balance statistical significance and practical feasibility, ensuring that results are precise and generalizable within the study context.
Further, simple random sampling was employed to select participants from Generation Z in the UAE in this research. This method ensured that every individual within the target demographic had an equal probability of being included in the study, providing a representative sample of Generation Z and allowing for generalizable insights into the impact of metaverse technology on this age group.
The surveys were distributed among the respondents using the online survey services provided by You.Gov UAE as a digital poll to collect data for research practices (YouGov 2022). The survey questionnaire remained available online from 16 February 2024 to 28 April 2024. Once the data were gathered within the given period, the acquired data were carefully calculated, indicating 363 responses. This showed a response rate of 94.2%, which is higher than the threshold of 60% (Deutskens et al. 2004), affirming the generalizability of the results.
However, while interpreting this study’s findings, it is essential to consider the influence of demographic factors, i.e., gender, age, locality, and education. Our sample shows a higher proportion of males (64.5%) than females (35.5%), which may affect the findings, especially regarding how different genders engage with and perceive metaverse technology. Gender-specific preferences and usage patterns could affect the results, making it crucial to recognize these potential biases when discussing the impacts of metaverse technology.
The age distribution also indicates that most respondents are between 19 and 22 (54.5%). This age group is highly active and likely more engaged with emerging technologies, which might influence their experiences and perceptions of the metaverse. Thus, the results may particularly reflect this younger segment of Generation Z, and further research could explore the experiences of slightly older or younger individuals to provide a more comprehensive view.
With 97.0% of respondents living in urban areas, the study’s outcomes may be skewed toward the experiences of urban residents, who likely have greater access to and engagement with metaverse technologies than those in rural areas. This urban bias should be considered when generalizing the findings to the broader population of Generation Z in the UAE.
The educational background among respondents varies, with a significant portion having higher secondary education or below (38.6%). This diversity in education levels may influence the familiarity with and usage of metaverse platforms, impacting the study’s findings on social development and psychological well-being. Lastly, the geographic distribution shows a predominance of respondents from Dubai (50.1%) and Sharjah (31.1%). While this provides insight into these major urban centers, future research should consider including more respondents from other emirates to ensure the findings represent the entire UAE.
These demographic factors are considerable when interpreting the study’s results, as they provide context for the observed impacts of metaverse technology on social development and psychological well-being among Generation Z in the UAE.
3.2. Survey Instrument
The current research’s survey instrument is a quantitative questionnaire designed on a five-point Likert scale. Notably, the items are adopted from studies investigating social development and psychological well-being. After minor formatting, the items are employed in the current research to ensure consistency with the topic and problem. The first part of the questionnaire is based on the demographics of respondents, such as age, gender, locality, education, and name of emirate (residence).
The second part involves statement five concerning metaverse technology. The third section is based on eight items about social development, measured on two dimensions: social interaction and communication skills and community engagement and participation. Finally, the fourth section involves eight statements regarding psychological well-being measured by focusing on its two dimensions, i.e., emotional well-being and sense of life purpose and satisfaction. Table 2 represents the details of survey items and their sources. Further, before conducting the full-scale survey, pilot testing was conducted to determine the reliability of the study tool. Questionnaires were distributed among a sample of 40 individuals. The results indicated that the Cronbach Alpha values surpassed the threshold of 0.7 (metaverse technology 0.835, social development 0.865, and psychological well-being 0.901), suggesting that the research tool is reliable.

Table 2.
Items and sources or survey instrument.
4. Analysis and Results
This research is grounded in three primary hypotheses comprising a structural model; the analysis used a two-step approach employing partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM), especially “inner model and outer model analysis.” The first step, inner model analysis, includes testing the reliability and validity of the measurement instrument. The second step scrutinizes the relationships suggested by the study’s hypotheses. Thus, this research also involves relevant analyses to provide insights about the gathered data and final results.
4.1. Inner Model Analysis
Initially, the inner model is tested to ensure its reliability and validity. In this regard, convergent validity is assessed to determine the internal consistency among the measurement items for each construct (Cheung and Wang 2017). In addition, discriminant validity is tested to confirm no correlation between the study constructs (Carlson and Herdman 2010).
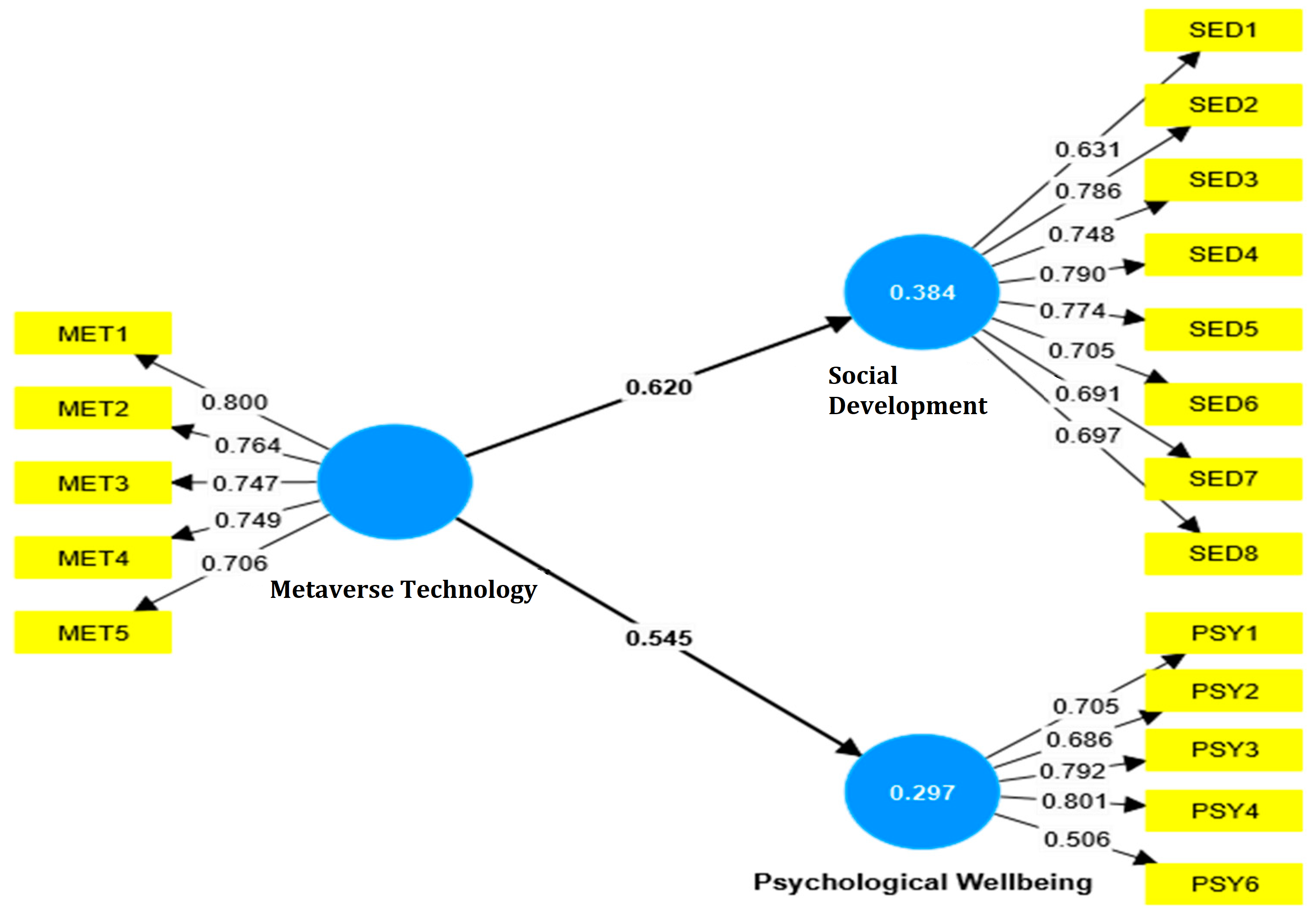
Figure 1 presents the results of the convergent validity analysis, showing that all factor loadings of the measurement items over-reach the suggested threshold value of 0.5 (Chin and Yao 2014). Furthermore, the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values are above the minimum threshold of 0.5, implying strong internal consistency among the items (metaverse technology 0.568, social development 0.553, and psychological well-being 0.598).
However, some loading values from psychological well-being are below 0.5, necessitating testing the goodness of fit after removing the relevant items (Magno et al. 2022). In addition, the construct reliability first indicated that all the Cronbach Alpha values surpass the threshold value of 0.7 (metaverse technology 0.810, social development 0.875, and psychological well-being 0.747). Further, the construct reliability values remain satisfactory, surpassing the threshold value of 0.7 (metaverse technology 0.868, social development 0.901, and psychological well-being 0.829). Table 3 summarizes the results of the convergent validity analysis.

Table 3.
Convergent validity analysis.
The goodness of fit suggests that the study model accurately represents the observed data. The Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR) value is 0.016, much lower than the criterion of 0.850 (Sarstedt et al. 2020). This low SRMR value suggests minimal discrepancies between the observed and predicted correlations, proposing an excellent fit. The Normed Fit Index (NFI) value remains at 0.918.
As NFI values range between 0 and 1, with values more relative to 1 showing a better fit, an NFI of 0.918 indicates that the model fits the data well compared to a null model. In addition, the Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI) value is 1.037, surpassing the criterion of 0.90 (Schuberth et al. 2022). This implies that the model’s fit is not only good but excellent. Notably, a TLI value above 1 is mainly substantial, showing that the model performs well even when modified for the number of parameters. Finally, the chi-square value is 1.839, which is below the criterion of 3.0. Lower chi-square values indicate a better fit, and a value of 1.839 indicates a good match between the observed data and the model’s predictions. Table 4 summarizes the goodness of fit results, while Figure 2 illustrates the measurement model finalized after testing the goodness of fit.

Table 4.
Goodness of fit.
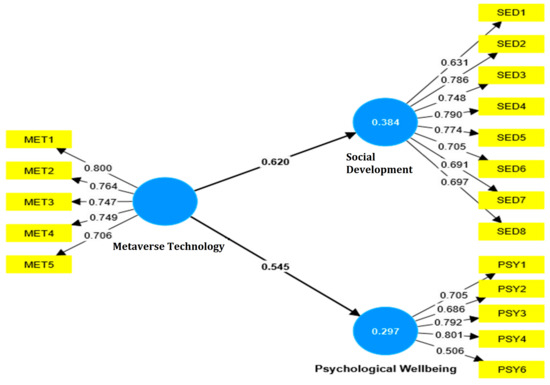
Figure 2.
Final measurement model.
After assessing the goodness of fit, discriminant validity is tested, as suggested by Rönkkö and Cho (2022). First, results from the Fornell–Larcker scale indicate that all the calculated correlation values are distinct and that the calculated square roots of AVE values are higher. Further, testing the Heterotrait–Monotrait Ratio shows that all the HTMT values are less than the threshold value of 0.85, indicating that discriminant validity is established in the current study. Table 5a,b summarize the discriminant validity results in the current study. Table 5 provides reuslts of descriminant validity.

Table 5.
Fornell–Larcker criterion; b Heterotrait–Monotrait Ratio Scale.
4.2. Outer Model Analysis
Coefficients of determination (R2) are further tested to examine the predictive power of the independent construct (metaverse technology). Notably, the coefficients of determination (R2) show the variance ratio in the dependent variables that the independent variables in the model can describe (Sarstedt et al. 2020). Hence, for psychological well-being, the R-square value is 0.297, and the R-square adjusted value is 0.295, implying that the predictors in the model explain around 29.7% of the variance in psychological well-being. The adjusted R-square, which accounts for the number of predictors compared to the sample size, is slightly lower at 29.5%. This small discrepancy suggests that the model’s explanatory power is constant and not raised by the number of predictors. Furthermore, for social development, the R-square value is 0.384, and the R-square adjusted value is 0.382. This implies that the predictor in the model justifies about 38.4% of the variance in social development. The adjusted R-square is 38.2%, slightly lower than the unadjusted R-square, indicating that the model’s explanatory power is strong and not affected by the predictor construct. Table 6 represents the results of Coefficient of determination (R2).

Table 6.
Coefficient of determination (R2).
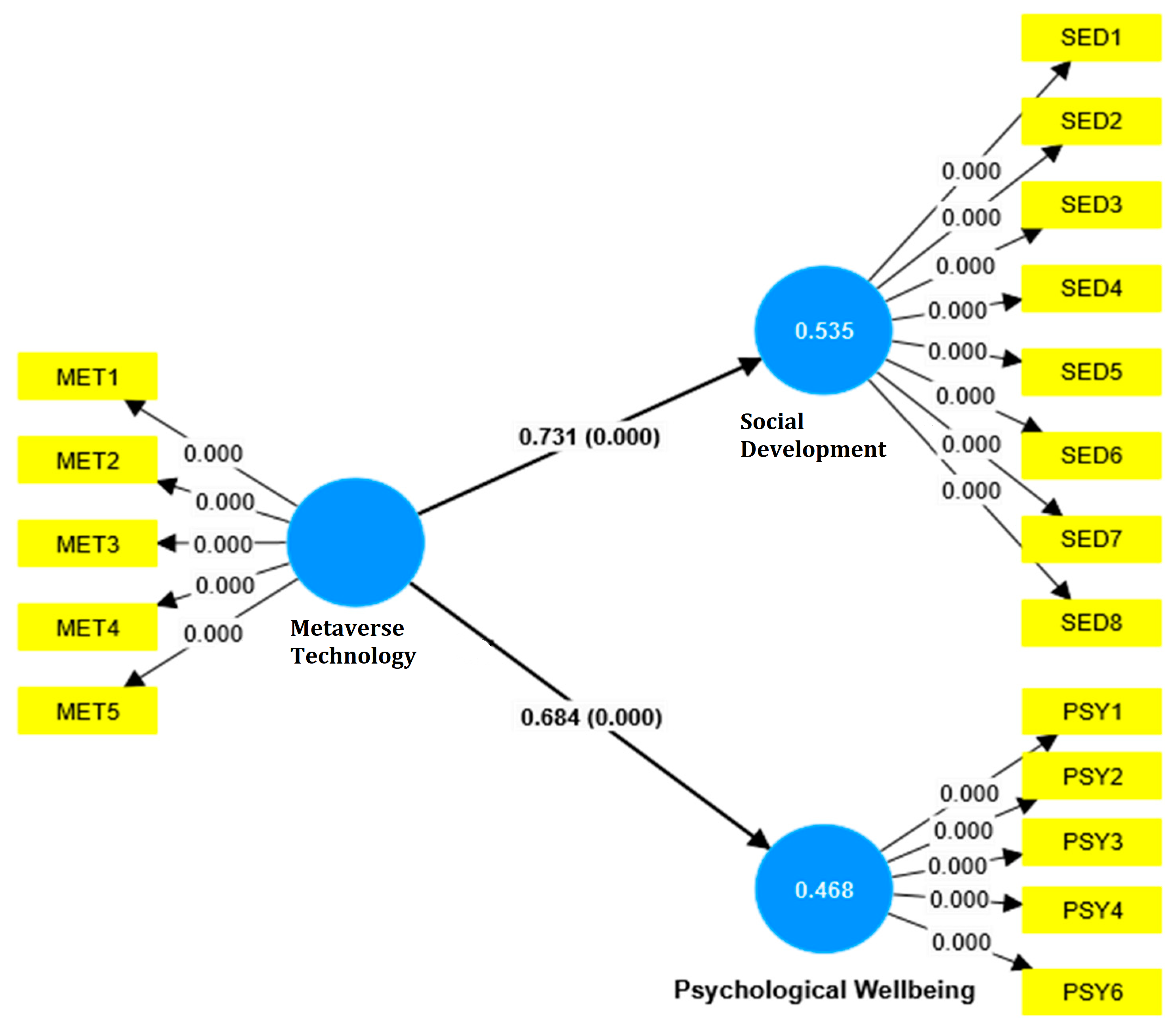
Finally, path analysis is conducted (Streiner 2005) to investigate the effect of metaverse technology on social development and psychological well-being. The results revealed that the first hypothesis regarding the impact of metaverse technology on social development is supported by the path coefficient value of 0.731, which indicates a strong positive relationship. The mean value is 0.739 with a standard deviation (STDEV) of 0.04, implying that this relationship is consistent across the sample. The T statistic is 18.411, significantly higher than the threshold of 1.96, and the p value is 0.000, suggesting that the relationship is statistically significant.
Testing the second hypothesis proposes the positive effect of metaverse technology on psychological well-being, supported by the path coefficient value of 0.684, demonstrating a strong positive relationship. The mean value is 0.691, with a standard deviation of 0.049, indicating consistency across the sample. The T statistic is 13.882, above the threshold of 1.96, and the p value is 0.000, ensuring that the proposed relationship is statistically significant. Hence, the second hypothesis proposes that “The use of metaverse technology positively impacts the social development of Generation Z in the United Arab Emirates”. Specifically, increased engagement with metaverse platforms improves social skills, facilitates relationship-building, and encourages more effective communication among young individuals in this demographic, which is accepted. Table 7 and Figure 3 represent the results of path analysis.

Table 7.
Path analysis (regression weights).
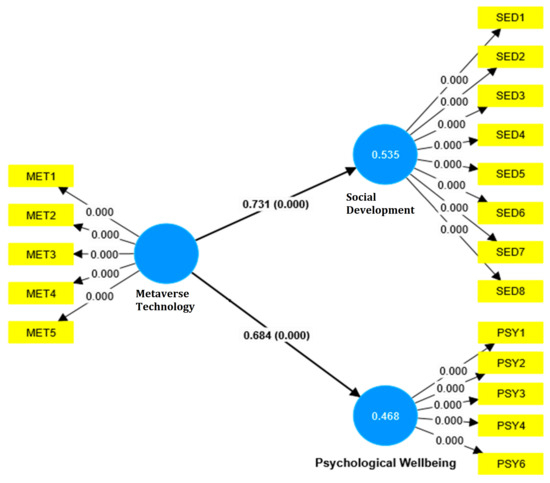
Figure 3.
Final Structural Model.
5. Discussion of Results
This research examined the impact of metaverse technology on the social development and psychological well-being of Generation Z in the UAE, driven by technology determinism theory. The preliminary purpose was to understand how metaverse technology impacts these aspects and how social development affects psychological well-being. The investigation assessed three hypotheses using a closed-ended questionnaire and partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The results demonstrated that metaverse technology significantly and positively impacts social development and psychological well-being. Also, the model explained 29.7% of the variance in psychological well-being and 38.4% in social development. These results affirm the theory and emphasize the crucial role of metaverse technology in shaping the experiences of Generation Z.
Regarding the gathered data, the respondents indicated strong agreement regarding the use and benefits of metaverse technology in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Table 8 and Table 9 represent the descriptives of the gathered data. According to most respondents, they can engage in diverse virtual environments using a single avatar within the metaverse, which helps them access different online activities with just a single login. Respondents further argued that the metaverse appears to allow each user to immerse themselves in their own unique experience within the virtual environment. They also agreed that their interactions and engagement within the metaverse continue even when they are not actively using it, as activity accumulates over time.

Table 8.
Descriptives of gathered data.

Table 9.
Descriptives of gathered data.
Consequently, users feel more engaged and immersed in the online world when using the metaverse. These findings show consistency with the proposition by Vieira and Medeiros (2023), indicating immersion as an integral and significant aspect of metaverse technology. As noted, immersion is essential for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) success in the metaverse technology, as it mainly affects user engagement. Users become profoundly absorbed when immersed, leading their attention from the physical world to the digital domain. High-quality graphics, sound, haptic feedback, and other sensory stimulants improve the VR experience and immersion. A high degree of immersion, merged with an engaging virtual environment, can elicit strong emotions and a deep sense of involvement, enabling users to suspend uncertainty and disbelief easily (Buragohain et al. 2023).
Further regarding H1 of the study,
H1.
Metaverse technology has a positive impact on the social development of Generation Z in the United Arab Emirates.
This hypothesis addresses the impact of metaverse technology on social development among Generation Z in the UAE, most of the respondents agreed that communication is more effective and feasible with it, and it is destined to improve communication and interaction in society. Respondents further agreed that metaverse technology is improving their communication skills as participating in social activities within the metaverse has enabled them to understand different perspectives better.
According to the study respondents, interacting with others in virtual environments within the metaverse has enhanced their communication abilities. Consequently, they feel that contending with others in virtual environments has made them more confident in starting discussions with new people. Further, regarding social development, respondents agreed that their capability to collaborate with others has been enhanced due to their experiences in the metaverse. Thus, respondents indicated that their interaction with metaverse technology has positively enhanced their social skills. Thus, using wearable devices, brain–computer interfaces, extended reality (XR), and other cutting-edge technologies, communication in the metaverse provides a multisensory experience. This will help fully immersive interactions that incorporate text, 3D visuals, and sound, further enabling the users in real-life experiences (Song 2022).
Here, Lee et al. (2022) examined the potential advantages of metaverse technology for individuals with autism spectrum disorder regarding the advantages of employing metaverse technology to improve social communication skills. It was found that by engaging in virtual social scenarios, individuals can practice and develop social skills in a secure and structured setting. The intervention involved sessions conducted through the metaverse platforms Roblox and Zoom, where people participate in activities prepared to enhance their social responsiveness and interaction capabilities. In addition, the results indicated that this approach could significantly help people with ASD by providing an engaging and available platform for social skills development. The program’s effectiveness is estimated through psychological and behavioral assessments, revealing progress in social interaction and emotional regulation.
Finally, the impact of metaverse technology on psychological well-being is proposed in H2,
H2.
Metaverse technology has a positive impact on the psychological well-being of Generation Z in the United Arab Emirates.
The respondents indicated strong agreement. They agreed with the fact that using metaverse technology helps them manage their stress and anxiety, as engaging with it enhances their overall mood. The study respondents also agreed that they feel happy and less lonely when they connect with others using the metaverse and feel more like they are part of social and communication systems. It was also found that the metaverse helps study respondents feel more connected to people, leading to an improved sense of belonging among them. Finally, the study respondents agreed they use metaverse technology to participate in social discussions and share their constructive opinions.
These findings indicate the importance of metaverse technology in improving Generation Z’s confidence and communication abilities in the UAE, implying its usefulness and productivity usage. Considering these results, Arslan (2018) stated that social communication and technology interaction increase self-esteem and encourage social wellness. This helps establish limitations that promote effective communication, trust, and conflict management. Social development is important for building emotional stability and enhancing personal relationships through compassion and active efforts to ensure well-being. As has been noted (Trabelsi 2022), well-being encompasses more than the scarcity of disease; it is a multifaceted blend of physical, mental, emotional, and social health. It is closely linked to happiness and life satisfaction, defined by positive emotions, life control, ambition, and positive relationships. The “well-being” index, which involves around 44 indicators across society, economy, and environment, highlights that social, human, natural, and economic capital should be harnessed to promote well-being.
Accordingly, our interactions with family, friends, colleagues, and the community significantly impact our health and well-being. Healthy social connections and stable, supportive relationships promote healthier options and enhance mental and physical health (Temizkan et al. 2023). On the other hand, Samreen and Majeed (2019) link social development with life satisfaction and happiness. As noted, although social growth and development have improved the quality of life in different ways, some societies still struggle to attain happiness. Research has identified many factors contributing to low levels of happiness, including social issues and mental health problems. Zhou and Lin (2016) argue that an insufficiency of social development is an influential factor behind this unhappiness. Conventionally, social development has been equated with economic progress, but in recent years, researchers and policymakers have also highlighted social development’s significance.
5.1. Study Implications
The theoretical implications of this research provide practical insights into the role of metaverse technology in shaping the social development and psychological well-being of Generation Z. First, the results highlight the importance of technology determinism theory, which indicates that technological advancements impact societal structures and individual experiences. By showing the significant impact of metaverse technology on social development and psychological well-being, this research is consistent with the primary principles of this theory. It underlines that the pervasive integration of metaverse technology in the lives of Generation Z individuals in the UAE not only shapes their social interactions but also affects their mental health and overall well-being. In addition, this research contributes to the constant debate surrounding the digital transformation of society, especially among younger generations.
It emphasizes the need for scholars and policymakers to recognize the distinctive challenges and prospects metaverse technology presents in social development and psychological well-being. The results indicate that while metaverse technology presents new routes for connectivity and expression, it also introduces intricacies that require careful consideration. Comprehending how metaverse technology impacts Generation Z’s social fabric and mental health is important for designing and implementing informed strategies to sustain their development in an increasingly digital world. Finally, this research’s theoretical implications stimulate further investigation into the evolving relationship between technology and society in the digital age, providing a pathway for informed interventions and policy decisions to support the well-being of future generations.
The findings of this study also offer practical insights for various stakeholders, including educators, policymakers, and mental health professionals, on how to leverage metaverse technology effectively while managing potential risks. For educators, the strong positive relationship between metaverse technology and social development suggests that incorporating virtual environments into learning can improve students’ communication skills, collaboration, and social interaction. Educators should consider integrating metaverse platforms into curricula to provide immersive learning experiences that encourage active participation and skill-building. However, they should also ensure that these platforms are used in moderation to prevent potential issues like excessive screen time or social isolation.
Policymakers can use these results to support the development of regulations and guidelines that promote the responsible use of metaverse technology. Since technology positively impacts social skills and psychological well-being, policymakers should advocate for initiatives incorporating metaverse tools in public services and community programs. They should also work to address any accessibility issues to ensure that all segments of the population can benefit from these technologies. Ensuring robust data privacy and security measures will be crucial to mitigate potential risks associated with virtual interactions.
Mental health professionals can leverage the metaverse’s ability to improve psychological well-being by using virtual environments as therapeutic tools. This study’s results suggest that metaverse technology can help manage stress, enhance mood, and foster a sense of belonging. Mental health programs could incorporate metaverse-based activities to create supportive virtual spaces where individuals can engage in stress-relief exercises and social interactions. Professionals need to monitor users’ engagement with these platforms to prevent dependency or overuse, which could potentially lead to adverse outcomes.
While metaverse technology presents significant opportunities for enhancing social and psychological outcomes, all stakeholders must implement it thoughtfully, ensuring its benefits are maximized while mitigating associated risks.
5.2. Conclusions
The study’s findings underline the significant role of metaverse technology in promoting social and psychological development among Generation Z in the UAE, offering new insights into the digital landscape of this specific context. The results highlight how metaverse technology, deeply integrated into Emirati society, is reshaping social interactions and contributing to the well-being of young individuals by providing immersive, geographically unbound virtual environments. These environments facilitate improved social skills, better communication, and a stronger sense of community, especially among those struggling with social interactions in traditional settings.
However, the conclusions drawn from this study, while significant, are context-specific and may not fully grasp the broader implications of metaverse technology in different cultural or social environments. Future research could build on these results by applying similar methodologies in diverse regions and populations, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the metaverse’s impact. Such studies would validate the current results and extend them to other contexts, thereby enriching the global discourse on the role of emerging technologies in social and psychological development. The potential of metaverse technology to improve social connections and support mental well-being could be further explored through continued research, leading to more refined applications and strategies that benefit a more comprehensive array of individuals across diverse settings.
5.3. Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
Although this research fills an essential empirical gap, it has some basic limitations. First, this research is focused only on Generation Z in the UAE, which narrows its scope. Future research can replicate this study and focus on diverse sample characteristics for a broader generalizability of results. Second, this research is based on a single methodological approach, while this limitation can be overcome by adopting other methods, i.e., mix-method and triangulation techniques.
In discussing the current study’s findings, it is important to note that the cross-sectional nature of our research limits our ability to make causal inferences about the impact of metaverse technology on social development and psychological well-being. This snapshot approach only provides a view of the data at a single time and does not account for changes that might occur over a more extended period. To address this limitation, future research should consider longitudinal studies that track participants over time to understand better how prolonged use of metaverse technology affects social skills and mental health. Additionally, exploring alternative research designs, i.e., experimental studies with control groups or mixed-methods approaches, could offer more detailed insights and validate our findings further. These approaches clarify the long-term effects and mechanisms through which metaverse technology influences users.
Finally, this limitation involves the geographical generalizability of results. As this research was conducted in the UAE, the generalizability of results can be considered as a major limitation. Future researchers can replicate the current research design and conduct research in different regions to delimit this scope. Finally, while this study provides valuable insights into the impact of metaverse technology on Generation Z’s social development and psychological well-being in the UAE, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. The research is focused on a specific demographic within a specific region, which allows for a detailed understanding of that context but may limit the generalizability of the findings. Given these considerations, future research could extend this study to include a more diverse range of participants from different regions and backgrounds. This expansion would validate the findings across various contexts and provide a more comprehensive understanding of how global metaverse technology influences social development and psychological well-being. By addressing these broader perspectives, future studies can build on the foundation laid by this research and contribute to a more nuanced and extensive body of knowledge.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.Y. and S.A.; methodology, M.M.; software, N.B.Y.; validation, E.Y., M.M. and N.B.Y.; formal analysis, E.Y.; investigation, M.M.; resources, S.A.; data curation, S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, E.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.M.; visualization, S.A.; supervision, S.A.; project administration, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This article is funded by Ajman university Internal Grant Number (DRG Ref no. AP/P505208/3). The findings represented in this research are solely the responsibility of the author.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research is approved by Research Ethics Committee Ajman University, United Arab Emirates (2023-IRG-HBS-9).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the respondents to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
No data regarding this study are attributed or available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ajmain, Talhah. 2020. Impacts and Effective Communication on Generation Z in Industrial Revolution 4.0 Era. JETAL: Journal of English Teaching & Applied Linguistic 1: 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, Muteerah. 2023. The Role of Metaverse in Developing Soft Skills Among ESL Learners. International Journal of Social Science and Human Research 6: 7944–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, Nisreen, and Amitabh Anand. 2020. Generation Z in the United Arab Emirates: A Smart-Tech-Driven iGeneration. In The New Generation Z in Asia: Dynamics, Differences, Digitalisation. Edited by Elodie Gentina and Emma Parry. The Changing Context of Managing People. Bradford: Emerald Publishing Limited, pp. 181–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, Gökmen. 2018. Social Exclusion, Social Support and Psychological Wellbeing at School: A Study of Mediation and Moderation Effect. Child Indicators Research 11: 897–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, Robert. 2013. The Quantitative Paradigm. In The Handbook of Language Variation and Change. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., pp. 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benrimoh, David, Forum D. Chheda, and Howard C. Margolese. 2022. The Best Predictor of the Future—The Metaverse, Mental Health, and Lessons Learned From Current Technologies. JMIR Mental Health 9: e40410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuti, Martina, Michelle Wright, John Naslund, and Anne C. Miers. 2023. How Technology Use Is Changing Adolescents’ Behaviors and Their Social, Physical, and Cognitive Development. Current Psychology 42: 16466–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, Sudip, Sandip Bhattacharya, Vidisha Vallabh, Roy Rillera Marzo, Ruchi Juyal, and Ozden Gokdemir. 2023. Digital Well-Being Through the Use of Technology–A Perspective. International Journal of Maternal and Child Health and AIDS 12: e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Chaeeun, and Ayoung Suh. 2024. Developing Scales for Assessing Metaverse Characteristics and Testing Their Utility. Computers in Human Behavior Reports 13: 100366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragohain, Dipima, Sushank Chaudhary, Grisana Punpeng, Abhishek Sharma, Nutthee Am-in, and Lunchakorn Wuttisittikulkij. 2023. Analyzing the Impact and Prospects of Metaverse in Learning Environments Through Systematic and Case Study Research. IEEE Access 11: 141261–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, Kevin D., and Andrew O. Herdman. 2010. Understanding the Impact of Convergent Validity on Research Results. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1094428110392383 (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Cheung, Gordon W., and Chang Wang. 2017. Current Approaches for Assessing Convergent and Discriminant Validity with SEM: Issues and Solutions. Academy of Management Proceedings 2017: 12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Ching-Lan, and Grace Yao. 2014. Convergent Validity. In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research. Edited by Alex C. Michalos. Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 1275–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopik, William J. 2016. The Benefits of Social Technology Use Among Older Adults Are Mediated by Reduced Loneliness. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking 19: 551–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutskens, Elisabeth, Ko De Ruyter, and Martin Wetzels. 2004. Response Rate and Response Quality of Internet-Based Surveys: An Experimental Study|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/B:MARK.0000021968.86465.00 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Dionisio, John David N., William G. Burns Iii, and Richard Gilbert. 2013. 3D Virtual Worlds and the Metaverse: Current Status and Future Possibilities. ACM Computing Surveys 45: 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Haiwei, and Jeannie S. A. Lee. 2022. The Metaverse from a Multimedia Communications Perspective. IEEE MultiMedia 29: 123–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, Faycal. 2024. Examining the Factors Fostering Metaverse Experience Browser Acceptance under Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT). Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development 8: 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, Faycal, Riadh Jeljeli, Khaled Zamoum, Yamine Boudhane, and Faten Ben Lagha. 2023. Metaverse Technology in Communication Practices: A Case Study of IT Products Retailers in the UAE. Emerging Science Journal 7: 928–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Qianyu. 2022. Analysis of Technological Determinism and Social Constructionism. Amsterdam: Atlantis Press, pp. 1391–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Garcia, J. Ramon, Leonardo F. Vivanco, and Luis F. Luna-Reyes. 2014. Revisiting the Problem of Technological and Social Determinism: Reflections for Digital Government Scholars. In Electronic Government and Electronic Participation. Amsterdam: IOS Press, pp. 254–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Moreno, Maria, Paula Andrade-Pino, Carlos Monfort-Vinuesa, Antonio Piñas-Mesa, and Esther Rincon. 2023. Improving Humanization through Metaverse-Related Technologies: A Systematic Review. Electronics 12: 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumińska, Natalia, and Edel Smiley. 2015. Effective Communication as an Option for a Better Social Functioning for People with Autism from an International Perspective 2. Available online: https://www.ijrhss.org/pdf/v2-i1/2.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Hallström, Jonas, and Arne Kaijser. 2022. Socially Constructed and Society Shaping: Investigating Characteristics of Technological Systems for Technology Education. In Teaching and Learning about Technological Systems: Philosophical, Curriculum and Classroom Perspectives. Edited by Jonas Hallström and P. John Williams. Contemporary Issues in Technology Education. Singapore: Springer Nature, pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Dai-In, Yoy Bergs, and Natasha Moorhouse. 2022. Virtual Reality Consumer Experience Escapes: Preparing for the Metaverse. Virtual Reality 26: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig-Thurau, Thorsten, and Björn Ognibeni. 2022. Metaverse Marketing. NIM Marketing Intelligence Review 14: 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, James. 2022. Social Virtual Reality: Neurodivergence and Inclusivity in the Metaverse. Societies 12: 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Muhammad Zahid, and Abraham G. Campbell. 2023. Metaverse as Tech for Good: Current Progress and Emerging Opportunities. Virtual Worlds 2: 326–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeljeli, Riadh, and Faycal Farhi. 2024. PR Leadership and Immersive Environment in Metaverse Technology Adoption: The Mediation of Horizon Workrooms and Embodied Social Presence. In Information and Communication Technology in Technical and Vocational Education and Training for Sustainable and Equal Opportunity: Education, Sustainability and Women Empowerment. Edited by Reem Khamis Hamdan, Allam Hamdan, Bahaaeddin Alareeni and Rim El Khoury. Singapore: Springer Nature, pp. 377–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaxin, Li, and Gao Gongjing. 2022. Socializing in the Metaverse: The Innovation and Challenge of Interpersonal Communication. Amsterdam: Atlantis Press, pp. 2128–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, Vinish. 2023. Gen Z’s Engagement with the Metaverse: Mediated Role of Symbolic Gratification and Desired Enhancement of Reality and Moderated Role of Gender. Metamorphosis 22: 133–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirbas, Omer, and Fatih Dogan. 2023. Modeling Development and Validation of Metaverse Attitude Scale. International Journal of Technology in Education 6: 155–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, Sumeet Singh, Reena Malik, Sumeet Singh Lamba, and Reena Malik. 2021. Into the Metaverse: Marketing to Gen Z Consumers. Chapter. Into-the-Metaverse. Available online: https://www.igi-global.com/chapter/into-the-metaverse/309306 (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Lee, JooHyun, Tae Seon Lee, and SeungWoo Lee. 2022. JMIR Research Protocols-Correction: Development and Application of a Metaverse-Based Social Skills Training Program for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder to Improve Social Interaction: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial 11. Available online: https://www.researchprotocols.org/2022/11/e43864 (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Lin, Hong, Zirun Gan, Wensheng Gan, Zhenlian Qi, Yuehua Wang, and Philip S. Yu. 2023. Interaction in Metaverse: A Survey. Paper presented at 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, December 15–18; pp. 2473–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magno, Francesca, Fabio Cassia, and Christian M. Ringle. 2022. A Brief Review of Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Use in Quality Management Studies. The TQM Journal 36: 1242–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, Aasif Ali, Shashank Shekhar Thakur, Tariq Ahmad Guroo, and Aadil Altaf Lone. 2018. Development of Society under the Modern Technology—A Review. Scholedge International Journal of Business Policy & Governance 5: 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Hyun Jung, Elif Ozkaya, and Robert LaRose. 2014. How does online social networking enhance life satisfaction? The relationships among online supportive interaction, affect, perceived social support, sense of community, and life satisfaction. Computers in Human Behavior 30: 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Hyun Jung, Junghwan Kim, Jeongheon J. C. Chang, Nohil Park, and Sangrock Lee. 2023. Social Benefits of Living in the Metaverse: The Relationships among Social Presence, Supportive Interaction, Social Self-Efficacy, and Feelings of Loneliness. Computers in Human Behavior 139: 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyanagi, Akimi, Takuji Narumi, Jean-Luc Lugrin, Kazuma Aoyama, Kenichiro Ito, Tomohiro Amemiya, and Michitaka Hirose. 2022. The Possibility of Inducing the Proteus Effect for Social VR Users. In HCI International 2022–Late Breaking Papers: Interacting with eXtended Reality and Artificial Intelligence: 24th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, HCII 2022, Virtual Event, June 26–July 1. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 143–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquin, Vincent, Manuela Ferrari, Harmehr Sekhon, and Soham Rej. 2023. Time to Think ‘Meta’: A Critical Viewpoint on the Risks and Benefits of Virtual Worlds for Mental Health. JMIR Serious Games 11: e43388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popaitoon, Patchara. 2022. Fostering Work Meaningfulness for Sustainable Human Resources: A Study of Generation Z. Sustainability 14: 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualtrics. 2023. Sample Size Calculator. Qualtrics. Available online: https://www.qualtrics.com/blog/calculating-sample-size/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Răduț, Florin. 2021. Generation ‘Z’ and Social Networks. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3918595 (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Rönkkö, Mikko, and Eunseong Cho. 2022. An updated guideline for assessing discriminant validity. Organizational Research Methods 25: 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samreen, Isma, and Muhammad Tariq Majeed. 2019. Does Social Development Increase the Happiness Level? Evidence from Global Panel Data. Turkish Economic Review 6: 320–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sarstedt, Marko, Christian M. Ringle, and Joseph F. Hair. 2020. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. In Handbook of Market Research. Edited by Christian Homburg, Martin Klarmann and Arnd E. Vomberg. Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuberth, Florian, Manuel E. Rademaker, and Jörg Henseler. 2022. Assessing the Overall Fit of Composite Models Estimated by Partial Least Squares Path Modeling. European Journal of Marketing 57: 1678–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Ziying. 2022. Interpersonal Communication Research in Metaverse. Amsterdam: Atlantis Press, pp. 2377–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, Emmanouil G., Silvina Santana, Manolis Tsiknakis, Kostas Marias, Vangelis Sakkalis, António Teixeira, Joris H. Janssen, Henri de Jong, and Chariklia Tziraki. 2016. Technology-Based Innovations to Foster Personalized Healthy Lifestyles and Well-Being: A Targeted Review. Journal of Medical Internet Research 18: e4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streiner, David L. 2005. Finding Our Way: An Introduction to Path Analysis. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 50: 115–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankovic, Ana Cuic, Jelena Kapeš, and Dragan Benazić. 2022. Communication Skills in Generation Z as Future Tourism Employees. Communication Research and Practice 8: 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temizkan, Ege, Barkın Köse, and Sedef Şahin. 2023. Social Determinants of Life Satisfaction in Emerging Adults. Children and Youth Services Review 151: 107050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Zhuoqi, Yan Cai, Yu Gao, Xiying Zhang, and Xinlong Li. 2022. Factors Affecting Learners’ Adoption of an Educational Metaverse Platform: An Empirical Study Based on an Extended UTAUT Model. Mobile Information Systems 2022: 5479215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Government of UAE. 2023. Dubai Metaverse Strategy|The Official Portal of the UAE Government. Available online: https://u.ae/en/about-the-uae/strategies-initiatives-and-awards/strategies-plans-and-visions/government-services-and-digital-transformation/dubai-metaverse-strategy (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Trabelsi, Mohamed Ali. 2022. What Is the Impact of Social Well-Being Factors on Happiness? European Journal of Management Studies 28: 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twenge, Jean M. 2019. More Time on Technology, Less Happiness? Associations Between Digital-Media Use and Psychological Well-Being. Current Directions in Psychological Science 28: 372–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Țicău, Iulia Ruxandra, and Shahrazad Hadad. 2021. Technological Determinism vs. Social Shaping of Technology. The Influence of Activity Trackers on User’s Attitudes. Management Dynamics in the Knowledge Economy 9: 147–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UAE Minister of State for Artifical Intelligence, Digital Economy and Remote Work Applications Office. 2023. Responsible Metaverse Self-Governance Framework. Available online: https://ai.gov.ae/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Responsible-Metaverse-Self-governance-Framework-2023-EN.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Ud Din, Ikram, and Ahmad Almogren. 2023. Exploring the Psychological Effects of Metaverse on Mental Health and Well-Being. Information Technology & Tourism 25: 367–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, Sadia Suhail, Medha Sharath, and Meghana Mehendale. 2022. Future of Mental Health in the Metaverse. General Psychiatry 35: e100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E., and F. Medeiros. 2023. Feasibility of immersive environments in the metaverse for remote practical education in computer networks. In ICERI2023 Proceedings. Seville: IATED, pp. 7301–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YouGov. 2022. UAE National Omnibus. Available online: https://business.yougov.com/product/realtime/uae-national-omnibus (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Youssef, Enaam, Mervat Medhat, and Maryam Alserkal. 2024. Investigating the Effect of Social Media on Dependency and Communication Practices in Emirati Society. Social Sciences 13: 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Mi, and Weipeng Lin. 2016. Adaptability and Life Satisfaction: The Moderating Role of Social Support. Frontiers in Psychology 7: 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).