Therapeutic Potential of Engineered Virus-like Particles of Parvovirus B19
Abstract
1. Introduction
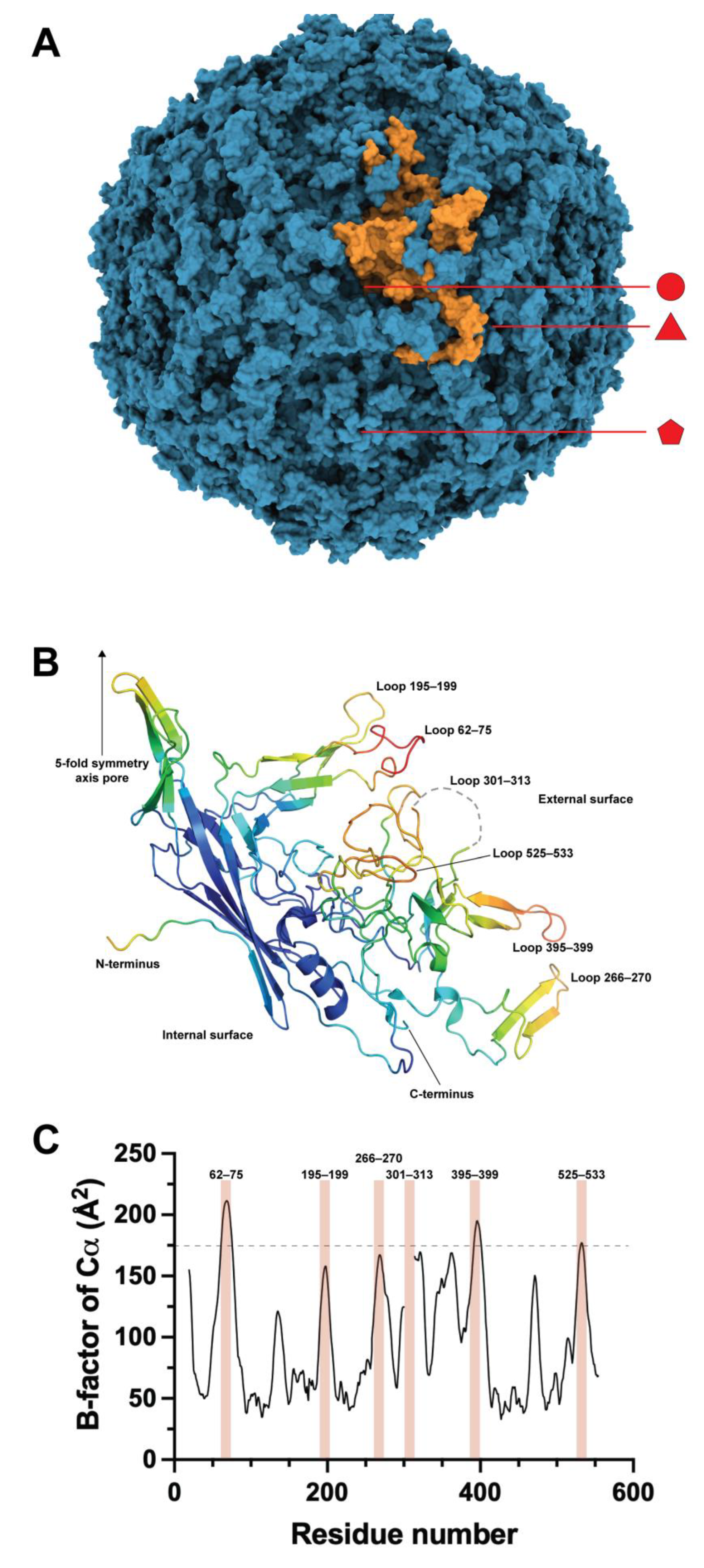
2. B19V Structural Proteins and Virus-like Particles
3. Engineering of the N-Terminal Region of VP2/VP1
4. VP2 Loop Engineering
5. VLP Vaccines against B19V
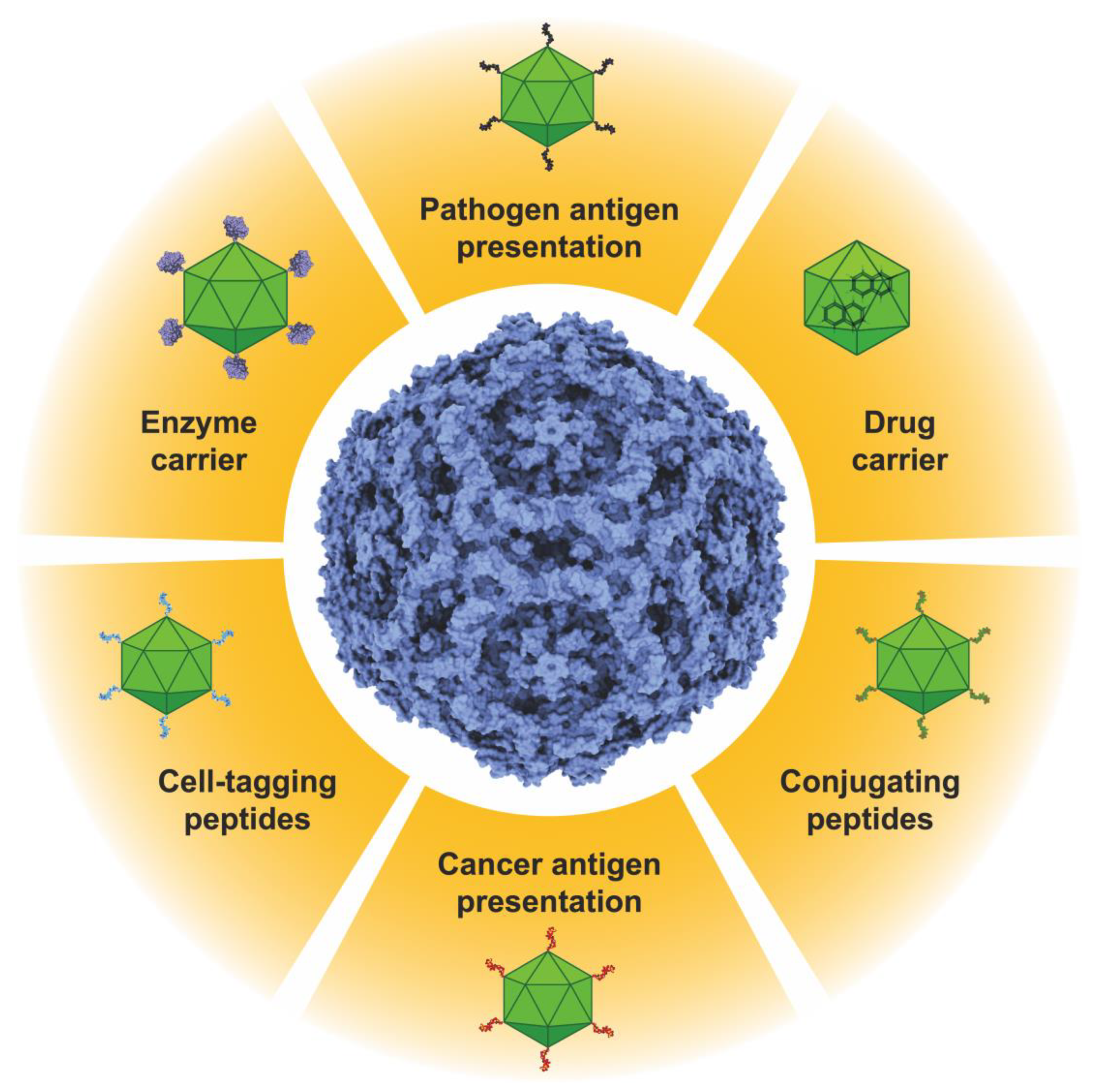
6. Conclusions and Expectations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mejía-Méndez, J.L.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Hernández, L.R.; Sánchez-Arreola, E.; Bach, H. Virus-like Particles: Fundamentals and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, G.P.; Bradel-Tretheway, B.; Piehowski, P.D.; Brewer, H.M.; Lee, B.N.R.; Usher, N.T.; Zamora, J.L.R.; Ortega, V.; Contreras, E.M.; Teuton, J.R.; et al. Nipah Virus-Like Particle Egress Is Modulated by Cytoskeletal and Vesicular Trafficking Pathways: A Validated Particle Proteomics Analysis. mSystems 2019, 4, e00194-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Bachmann, M.F. Virus-like Particle Vaccinology, from Bench to Bedside. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiding, Q.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Cui, W. Antigens-on-a-Ship: A New Journey to Solid Tumor Vaccines. Matter 2023, 6, 1680–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi Vahdat, M.; Hemmati, F.; Ghorbani, A.; Rutkowska, D.; Afsharifar, A.; Eskandari, M.H.; Rezaei, N.; Niazi, A. Hepatitis B Core-Based Virus-like Particles: A Platform for Vaccine Development in Plants. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 29, e00605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, H.; Batool, S.; Asif, S.; Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Virus-Like Particles: Revolutionary Platforms for Developing Vaccines Against Emerging Infectious Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 790121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.S.; Bose, R.J.; McCarthy, J.R.; Mat Azmi, I.D.; Madheswaran, T. Biomimetic Bacterial and Viral-Based Nanovesicles for Drug Delivery, Theranostics, and Vaccine Applications. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Steinmetz, N.F. Cisplatin Prodrug-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Physalis Mottle Virus for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; Baluk, P.; Morikawa, S.; McLean, J.W.; Thurston, G.; Roberge, S.; Jain, R.K.; McDonald, D.M. Openings between Defective Endothelial Cells Explain Tumor Vessel Leakiness. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor Angiogenesis: Causes, Consequences, Challenges and Opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Sek, M.W.; Lim, L.Y. Folic Acid-Conjugated Protein Cages of a Plant Virus: A Novel Delivery Platform for Doxorubicin. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockney, D.M.; Guenther, R.N.; Loo, L.; Overton, W.; Antonelli, R.; Clark, J.; Hu, M.; Luft, C.; Lommel, S.A.; Franzen, S. The Red Clover Necrotic Mosaic Virus Capsid as a Multifunctional Cell Targeting Plant Viral Nanoparticle. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Shukla, S.; Wu, M.; Ayat, N.R.; El Sanadi, C.E.; Wen, A.M.; Edelbrock, J.F.; Pokorski, J.K.; Commandeur, U.; Dubyak, G.R.; et al. Stealth Filaments: Polymer Chain Length and Conformation Affect the in Vivo Fate of PEGylated Potato Virus X. Acta Biomater. 2015, 19, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.; Scheideler, O.; Schaffer, D. Engineering the AAV Capsid to Evade Immune Responses. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 60, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, S.P.; Münch-Anguiano, L.; Echeverría, O.; Vázquez-Nin, G.; Mora-Pale, M.; Dordick, J.S.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Human Parvovirus B19 Virus-like Particles: In Vitro Assembly and Stability. Biochimie 2012, 94, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, A.; Señorale-Pose, M.; Marín, M. Inclusion Bodies: Not That Bad…. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heegaard, E.D.; Brown, K.E. Human Parvovirus B19. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinella, G. Parvovirus B19 Achievements and Challenges. ISRN Virol. 2013, 2013, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. Role of Capsid Proteins in Parvoviruses Infection. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajigaya, S.; Shimada, T.; Fujita, S.; Young, N.S. A Genetically Engineered Cell Line That Produces Empty Capsids of B19 (Human) Parvovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 7601–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.S.; Salimans, M.M.M.; Noteborn, M.H.M.; Weiland, H.T. Antigenic Parvovims B19 Coat Proteins VP1 and VP2 Produced in Large Quantities in a Baculovirus Expression System. Virus Res. 1990, 15, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowin, T.; Raab, U.; Schroeder, J.; Franssila, R.; Modrow, S. Parvovirus B19 VP2-Proteins Produced in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae: Comparison with VP2-Particles Produced by Baculovirus-Derived Vectors. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2005, 52, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Valerio, I.A.; Cayetano-Cruz, M.; Valadez-García, J.; Guadarrama, P.; Méndez, C.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. In Vitro Refolding of the Structural Protein VP1 of Parvovirus B19 Produces Virus-like Particles with Functional VP1 Unique Region. Virology 2022, 570, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Yang, S.; Tang, F.; Su, J.; et al. Recombinant Virus-like Particles of Human Parvovirus B19 with the Internal Location of VP1 Unique Region Produced by Hansenula Polymorpha. Viruses 2022, 14, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Noguchi, T.; Matsugu, N.; Suzuki, A.; Kimura, S.; Onishi, M.; Kosaka, M.; Miyazato, P.; Morita, E.; Ebina, H. Safety and Immunogenicity of Parvovirus B19 Virus-like Particle Vaccine Lacking Phospholipase A2 Activity. Vaccine 2022, 40, 6100–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Simpson, A.A.; Rossmann, M.G. The Structure of Human Parvovirus B19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11628–11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Sekiguchi, T.; Boonyakida, J.; Kato, T.; Park, E.Y. Display of Multiple Proteins on Engineered Canine Parvovirus-like Particles Expressed in Cultured Silkworm Cells and Silkworm Larvae. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1096363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán-Uribe, J.S.; Valadez-García, J.; Morán-García, A.d.C.; Santillán-Uribe, H.C.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Peptide Display on a Surface Loop of Human Parvovirus B19 VP2: Assembly and Characterization of Virus-like Particles. Virus Res. 2015, 201, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos-Jaimes, I.; Soto-Román, R.A.; Gutiérrez-Landa, I.A.; Valadez-García, J.; Segovia-Trinidad, C.L. Construction of Protein-Functionalized Virus-like Particles of Parvovirus B19. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 263, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Noguchi, T.; Kimura, S.; Suzuki, H.; Ebina, H.; Morita, E. Tracking of Human Parvovirus B19 Virus-Like Particles Using Short Peptide Tags Reveals a Membrane-Associated Extracellular Release of These Particles. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0163122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, J.; Chapman, M.S.; Agbandje, M.; Keller, W.; Smith, K.; Wu, H.; Luo, M.; Smith, T.J.; Rossmann, M.G.; Compans, R.W.; et al. The Three-Dimensional Structure of Canine Parvovirus and Its Functional Implications. Science 1991, 251, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Chipman, P.R.; Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Modrow, S.; Rossmann, M.G. Visualization of the Externalized VP2 N Termini of Infectious Human Parvovirus B19. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7306–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, M.; Momoeda, M.; Young, N.S.; Kajigaya, S. Most of the VP1 Unique Region of B19 Parvovirus Is on the Capsid Surface. Virology 1995, 211, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, C.; Gerber, M.; Kempf, C. Conformational Changes in the VP1-Unique Region of Native Human Parvovirus B19 Lead to Exposure of Internal Sequences That Play a Role in Virus Neutralization and Infectivity. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12017–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, K.; Zou, W.; Xu, P.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, E.Y.; Zhang-Chen, A.; Kleiboeker, S.; Qiu, J. Identification of AXL as a Co-Receptor for Human Parvovirus B19 Infection of Human Erythroid Progenitors. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade0869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Ning, K.; Xu, P.; Deng, X.; Cheng, F.; Kleiboeker, S.; Qiu, J. The N-Terminal 5-68 Amino Acids Domain of the Minor Capsid Protein VP1 of Human Parvovirus B19 Enters Human Erythroid Progenitors and Inhibits B19 Infection. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00466-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bönsch, C.; Zuercher, C.; Lieby, P.; Kempf, C.; Ros, C. The Globoside Receptor Triggers Structural Changes in the B19 Virus Capsid That Facilitate Virus Internalization. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11737–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisi, R.; Von Nordheim, M.; Ros, C.; Kempf, C. The VP1u Receptor Restricts Parvovirus B19 Uptake to Permissive Erythroid Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Momoeda, M.; Field, A.; Kajigaya, S.; Young, N.S. Formation of Empty B19 Parvovirus Capsids by the Truncated Minor Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 4690–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amexis, G.; Young, N.S. Parvovirus B19 Empty Capsids as Antigen Carriers for Presentation of Antigenic Determinants of Dengue 2 Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brown, C.S.; Welling-Wester, S.; Feijlbrief, M.; Van Lent, J.W.M.; Spaan, W.J.M. Chimeric Parvovirus B19 Capsids for the Presentation of Foreign Epitopes. Virology 1994, 198, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán-García, A.d.C.; Rivera-Toledo, E.; Echeverría, O.; Vázquez-Nin, G.; Gómez, B.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Peptide Presentation on Primate Erythroparvovirus 1 Virus-like Particles: In Vitro Assembly, Stability and Immunological Properties. Virus Res. 2016, 224, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, Y.; Amexis, G.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kajigaya, S.; Leppla, S.H.; Young, N.S. Recombinant Viral-like Particles of Parvovirus B19 as Antigen Carriers of Anthrax Protective Antigen. In Vivo 2006, 20, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Cayetano-Cruz, M.; Coffeen, C.F.; Valadez-García, J.; Montiel, C.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Decoration of Virus-like Particles with an Enzymatic Activity of Biomedical Interest. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.-L.; Lai, L.; Zhang, W.-B. Tuning SpyTag–SpyCatcher Mutant Pairs toward Orthogonal Reactivity Encryption. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6577–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desnick, R.J.; Schuchman, E.H. Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Lysosomal Diseases: Lessons from 20 Years of Experience and Remaining Challenges. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2012, 13, 307–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayetano-Cruz, M.; Valadez-García, J.; Méndez, C.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Virus-like Nanoparticles Derived from Parvovirus B19 Efficiently Internalize in Human Heptatocytes: A Biocompatible Delivery System for Peptides and Proteins. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6178–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paran, N.; Cooper, A.; Shaul, Y. Interaction of Hepatitis B Virus with Cells. Rev. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Is a Functional Receptor for Human Hepatitis B and D Virus. Elife 2012, 2012, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Tao, M.-H.; Huang, C. Entry of Hepatitis B Virus into Immortalized Human Primary Hepatocytes by Clathrin-Dependent Endocytosis. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9443–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, S.P.; Morán-García, A.d.C.; Bolonduro, O.; Dordick, J.S.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Enhanced Assembly and Colloidal Stabilization of Primate Erythroparvovirus 1 Virus-like Particles for Improved Surface Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, S.P.; Enrriquez-Avila, J.V.; Soto-Fajardo, J.M.; Peña-Montes, C.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. In Vitro Encapsulation of Heterologous DsDNA Into Human Parvovirus B19 Virus-Like Particles. Mol. Biotechnol. 2015, 57, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, K.; Kajigaya, S.; Momoeda, M.; Smith-Gill, S.J.; Young, N.S. Parvovirus Particles as Platforms for Protein Presentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Chávez, Á.D.J.; Moreno-Fierros, L.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Therapy with Multi-Epitope Virus-like Particles of B19 Parvovirus Reduce Tumor Growth and Lung Metastasis in an Aggressive Breast Cancer Mouse Model. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7256–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Skora, A.D.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Tam, A.J.; Blosser, R.L.; Diaz, L.A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; et al. Eradication of Metastatic Mouse Cancers Resistant to Immune Checkpoint Blockade by Suppression of Myeloid-Derived Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11774–11779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Jaiswal, P.; Goel, A. Survivin: A Molecular Biomarker in Cancer. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 141, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulaski, B.A.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Mouse 4T1 Breast Tumor Model. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2001, 39, 20.2.1–20.2.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Sandeep, N.; Mbbs, W.; Ahmedin, J. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-González, J.A.; Ruiz-Cruz, A.A.; Bustos-Jaimes, I.; Moreno-Fierros, L. Expression of Breast Cancer-Related Epitopes Targeting the IGF-1 Receptor in Chimeric Human Parvovirus B19 Virus-Like Particles. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuya, J.; Paz, I.B.; Maddux, B.A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Hefta, S.A.; Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y. Characterization of Human Placental Insulin-like Growth Factor-I/Insulin Hybrid Receptors by Protein Microsequencing and Purification. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 13531–13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrami, V.; Keyhanfar, M.; Mohabatkar, H.; Mahdavi, M.; Moreau, V. In Silico Prediction of B Cell Epitopes of the Extracellular Domain of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2016, 5, 201. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, M.; Moreau, V.; Kheirollahi, M. Identification of B and T Cell Epitope Based Peptide Vaccine from IGF-1 Receptor in Breast Cancer. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2017, 75, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvicini, F.; Filippone, C.; Manaresi, E.; Zerbini, M.; Musiani, M.; Gallinella, G. HepG2 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Are a Non-Permissive System for B19 Virus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 3034–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, G.P.; Hatfield, J.A.; Dunn, F.E.; Kramer, A.A.; Brady, F.; Riggin, C.H.; Collett, M.S.; Yoshimoto, K.; Kajigaya, S.; Young, N.S. Candidate Recombinant Vaccine for Human B19 Parvovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pédelacq, J.D.; Cabantous, S.; Tran, T.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Waldo, G.S. Engineering and Characterization of a Superfolder Green Fluorescent Protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 24, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.S.; Brown, K.E. Parvovirus B19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.L. Parvovirus B19. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajigaya, S.; Fujii, H.; Field, A.; Anderson, S.; Rosenfeld, S.; Anderson, L.J.; Shimada, T.; Young, N.S. Self-Assembled B19 Parvovirus Capsids, Produced in a Baculovirus System, Are Antigenically and Immunogenically Similar to Native Virions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4646–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, E.; Mason, M.R.; Cacciuttolo, M.A.; Bowen, S.H.; Folena-Wasserman, G. Production of Parvovirus B I 9 Vaccine in Insect Cells Co-Infected with Double Baculoviruses. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1996, 49, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, W.R.; Reed, J.L.; Noble, W.; Young, N.S.; Koenig, S. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Recombinant Parvovirus B19 Vaccine Formulated with MF59C.1. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Sahly, H.M.E.; Keitel, W.A.; Wolff, M.; Simone, G.; Segawa, C.; Wong, S.; Shelly, D.; Young, N.S.; Dempsey, W. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Candidate Parvovirus B19 Vaccine. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7357–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramouli, S.; Medina-Selby, A.; Coit, D.; Schaefer, M.; Spencer, T.; Brito, L.A.; Zhang, P.; Otten, G.; Mandl, C.W.; Mason, P.W.; et al. Generation of a Parvovirus B19 Vaccine Candidate. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3872–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Proteins | Expression System | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| VP1 + VP2 | Chinese Hamster Ovary cells | [20] |
| VP2 VP2 + VP1 | Spodoptera frugiperda Sf cells | [21] |
| VP2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | [22] |
| VP2 | Escherichia coli | [15] |
| VP1 VP1 + VP2 | Escherichia coli | [23] |
| VP1 + VP2 | Hansenula polymorpha | [24] |
| VP1 + VP2 | Human 293 T cells | [25] |
| Pathogen | Antigen Type | Antigen Length | Neutralizing Antibodies | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEN-2 | E-glycoprotein domain III and fragments of this domain | 12–100 aa | Yes, titer depends on the selected fragment | [40] |
| B. anthracis | Fragments of the PA subunit of the anthrax toxin | 27–173 aa | Yes, titer depends on the selected fragment | [43] |
| HSV-1 | Glycoprotein gD, epitope VII, residues 9–21 | 13 aa | Yes | [41] |
| MHV | Spike protein, Site A epitope | 12 aa | Yes | [41] |
| SRV | Fusion glycoprotein F, antigenic site II, antigenic sites IV-VI | 63 aa site II 57 aa sites IV-VI | N.D. | [42] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Moguel, I.; Montiel, C.; Bustos-Jaimes, I. Therapeutic Potential of Engineered Virus-like Particles of Parvovirus B19. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081007
Sánchez-Moguel I, Montiel C, Bustos-Jaimes I. Therapeutic Potential of Engineered Virus-like Particles of Parvovirus B19. Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Moguel, Ignacio, Carmina Montiel, and Ismael Bustos-Jaimes. 2023. "Therapeutic Potential of Engineered Virus-like Particles of Parvovirus B19" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081007
APA StyleSánchez-Moguel, I., Montiel, C., & Bustos-Jaimes, I. (2023). Therapeutic Potential of Engineered Virus-like Particles of Parvovirus B19. Pathogens, 12(8), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081007







