Chronic Diarrhea Due to Aeromonas hydrophila in an Immunosuppressed Patient with a Pancreas–Kidney Transplant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
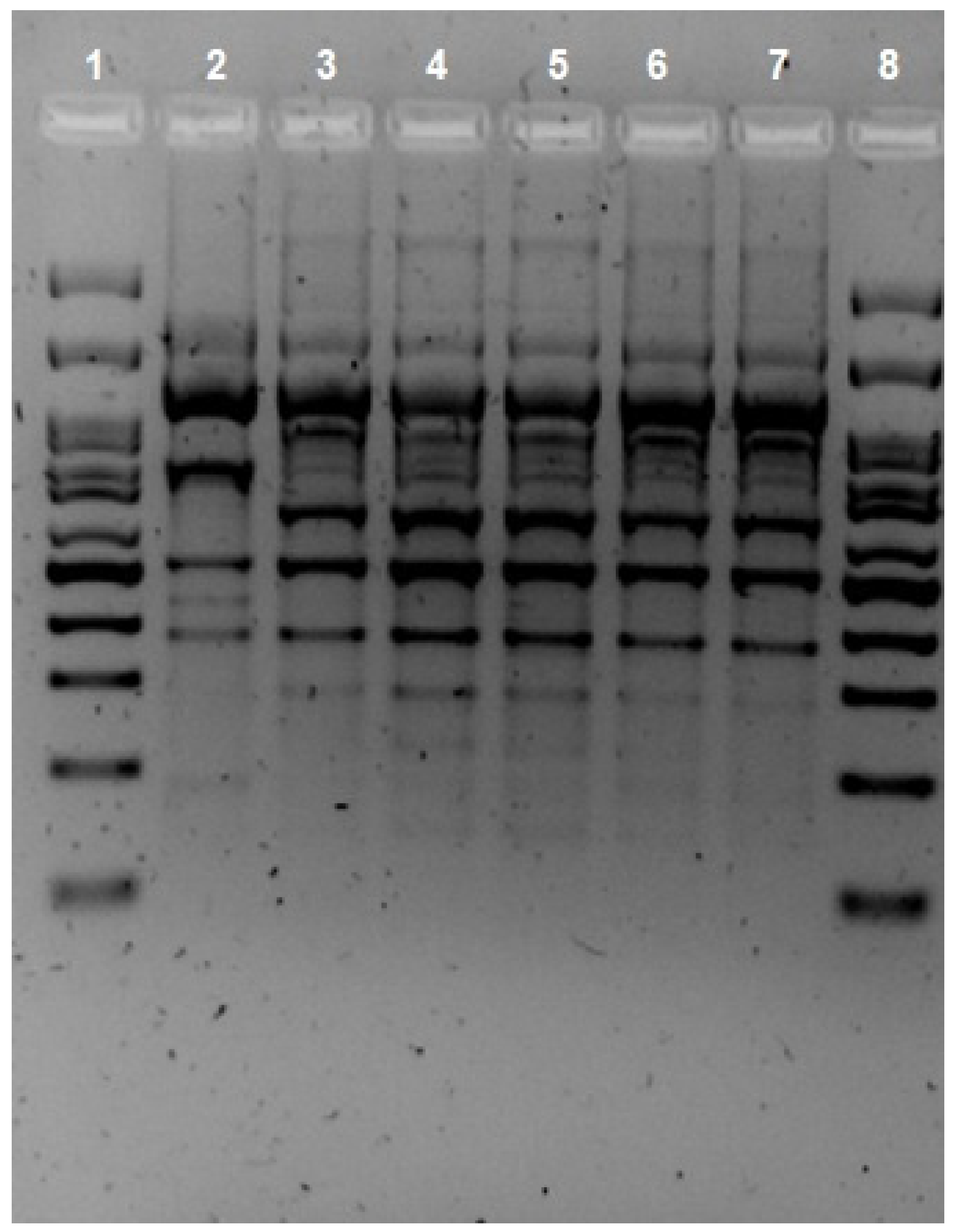
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselitz, F.H. How the Aeromonas story started in medical microbiology. Med. Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 5, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Bachhil, V.N.; Bhilegaonakar, K.N.; Agarwal, R.K. Occurrence of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas species in foods. J. Commun. Dis. 2000, 32, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, U.D.; Bhattacharjee, S. Bacteriological, Clinical and Virulence Aspects of Aeromonas-associated Diseases in Humans. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Shaw, J. Aeromonas spp. clinical microbiology and disease. J. Infect. 2011, 62, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citterio, B.; Biavasco, F. Aeromonas hydrophila virulence. Virulence 2015, 6, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.M.; Lai, C.C.; Tang, H.J.; Ko, W.C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Biliary tract infections caused by Aeromonas species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruíz de Alegría-Puig, C.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; Pintos-Fonseca, A. Epidemiology of Aeromonas spp. isolated from stool in a tertiary hospital in Cantabria, Northern Spain, in the last five years. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2021, 41, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhinh, D.T.; Le, D.V.; Van, K.V.; Giang, N.T.H.; Dang, L.T.; Hoai, T.D. Prevalence, Virulence Gene Distribution and Alarming the Multidrug Resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila Associated with Disease Outbreaks in Freshwater Aquaculture. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, S.; Al-Shuweli, S.; Yapici, S.; Jensen, J.N.; Olsen, K.E.P. Identification of clinical Aeromonas species by rpoB and gyrB sequencing and development of a multiplex PCR method for detection of Aeromonas hydrophila, A. caviae, A. veronii, and, A. media. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Marcos, M.A.; Jiménez de Anta, M.T. A comparative study of different PCR-based DNA fingerprinting techniques for typing of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-A. baumanii complex. J. Med. Microbiol. 1996, 44, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.L.; Ko, W.C.; Wu, C.J. Complexity of β-lactamases among clinical Aeromonas isolates and its clinical implications. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunniva Hoel, S.; Vadstein, O.; Jakobsen, A.N. Species Distribution and Prevalence of Putative Virulence Factors in Mesophilic Aeromonas spp. isolated from Fresh Retail Sushi. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, D.; Parlani, C.; Citterio, B.; Masini, L.; Leoni, F.; Canonico, C.; Sabatini, L.; Bruscolini, F.; Pianetti, A. Putative virulence properties of Aeromonas strains isolated from food, environmental and clinical sources in Italy: A comparative study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 144, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Hoel, S.; Lunestad, B.T.; Lerfall, J.; Jakobsen, A. Aeromonas spp. isolated from ready-to-eat seafood on the Norwegian market: Prevalence, putative virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 130, 1380–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, M.; Remacha, M.A.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; Santos, J.A.; Otero, A.; García-López, M.-L. Identity, virulence genes, and clonal relatedness of Aeromonas isolates from patients with diarrhea and drinking water. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 29, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.R.; Brokaw, J.M.; Zak, J.C.; Jeter, R.M. Natural transformation as a mechanism of horizontal gene transfer among environmental Aeromonas species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, I.Y.; Joh, K. Rapid detection of virulence factors of Aeromonas isolated from a trout farm by hexaplex-PCR. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gavin, R.; Merino, S.; Altarriba, M.; Canals, R.; Shaw, J.G.; Tomás, J.M. Lateral flagella are required for increased cell adherence, invasion and biofilm formation by Aeromonas spp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 224, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Gryllos, I.; Tomás, J.M.; Shaw, J.G. Motility and the polar flagellum are required for Aeromonas caviae adherence to HEp-2 cells. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinosa, I.H.; Igbinosa, E.O.; Okoh, A.I. Detection of antibiotic resistance, virulence gene determinants and biofilm formation in Aeromonas species isolated from cattle. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 17596–17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, C.; Sha, J.; Fadl, A.; Pillai, L.L.; Chopra, A.K. Host Immune Responses to Aeromonas Virulence Factors. Curr. Imm Rev. 2006, 2, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.J.; Ansaruzzaman, M.; Talukder, K.A.; Chopra, A.K.; Kuhn, I.; Rahman, M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Islam, M.S.; Sack, R.B.; Mollby, R. Prevalence of enterotoxin genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from children with diarrhea, healthy controls, and the environment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Ruiz, J.; Gallardo, F.; Vargas, M.; Soler, L.; Figueras, M.J.; Gascon, J. Aeromonas spp. and Traveler’s Diarrhea: Clinical Features and Antimicrobial Resistance. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.R.; Xu, X.J.; Houston, C.W.; Peterson, J.W.; Coppenhaver, D.H.; Popov, V.L.; Chopra, A.K. Hyperproduction, purification, and mechanism of action of the cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 4299–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, J.; Kozlova, E.V.; Fadl, A.A.; Olano, J.P.; Houston, C.W.; Peterson, J.W.; Chopra, A.K. Molecular characterization of a glucose-inhibited division gene, gidA, that regulates cytotoxic enterotoxin of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Lu, M.; Chopra, A.K. Regulation of the cytotoxic enterotoxin gene in Aeromonas hydrophila: Characterization of an iron uptake regulator. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6370–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, T.; Kozaki, S.; Kato, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Otsu, K.; Uemura, T.; Sakaguchi, G. Purification and characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 24, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.P.; Buckley, J.T. Membrane glycoprotein receptor and hole-forming properties of a cytolytic protein toxin. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Liu, C.; Pucknell, C.; Munro, C.K.; Kruk, T.M.A.C.; Caldeira, R.; Woodward, D.L.; Rodgers, F.G. Detection and characterization of the hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, J.M.; Kidd, S.P.; Schmidt, R. Secreted enzymes of Aeromonas. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 152, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, S.; Monteil, H. Purification and characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila beta-hemolysin. Toxicon 1989, 27, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Martínez, I.; Guerrero-Mandujano, A.; Ruiz-Ruiz, M.; Hernández-Cortez, C.; Molina-López, J.; Bocanegra-García, V.; Castro-Escarpulli, G. Active Shiga-like toxin produced by some Aeromonas spp., isolated in Mexico City. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperi, A.; Figueras, M.J. Human isolates of Aeromonas possess Shiga toxin genes (stx1 and stx2) highly similar to the most virulent gene variants of Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, A.; Santos-Pérez, J.L.; Navarro-Marí, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, J. Epidemiological data description of pediatric patients with diarrhea by Aeromonas spp. and the antibiotic susceptibility of this agent. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2020, 52, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Reed, J.; Shields, M.S.; Spiegel, K.M.; Farrell, L.D.; Sheridan, P.P. Phylogenetic analysis of Shiga toxin 1 and Shiga toxin 2 genes associated with disease outbreaks. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.Y.; Stevenson, R.M. Tn5-induced protease-deficient strains of Aeromonas hydrophila with reduced virulence for fish. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, H. Protection of atlantic salmon against motile aeromonad septicaemia with Aeromonas hydrophila protease. Microbios Lett. 1987, 36, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, T.; Seitz, R.; Dodt, J.; König, H. A secreted metallo protease from Aeromonas hydrophila exhibits prothrombin activator activity. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2004, 15, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; López-Fernández, L.; Figueras, M.J. The Metallochaperone Encoding Gene hypA Is Widely Distributed among Pathogenic Aeromonas spp. and Its Expression Is Increased under Acidic pH and within Macrophages. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, T.V.; Culotta, V.C. Metallochaperones, an intracellular shuttle service for metal ions. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25057–25060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, F.C.; Hu, H.Q.; Servetas, S.L.; Benoit, S.L.; Maier, R.J.; Maroney, M.J.; Merrell, D.S. Structure-function analyses of metal-binding sites of HypA reveal residues important for hydrogenase maturation in Helicobacter pylori. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Qin, Y.; Yan, Q.; Lin, G.; Huang, L.; Huang, B.; Huang, W. MinD plays an important role in Aeromonas hydrophila adherence to Anguilla japonica mucus. Gene 2015, 565, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, Z.; Li, A.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y. Contribution of nuclease to the pathogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila. Virulence 2015, 6, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, G.; Khajanchi, B.K.; Sierra, J.C.; Erova, T.E.; Sha, J.; Chopra, A.K. Actin cross-linking domain of Aeromonas hydrophila repeat in toxin A (RtxA) induces host cell rounding and apoptosis. Gene 2012, 506, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. Evolving concepts regarding the genus Aeromonas: An expanding panorama of species, disease presentations, and unanswered questions. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerdörffer, E.; Schwarzkopf-Steinhauser, G.; Ottenjann, R. New unusual forms of colitis. Report of four cases with known and unknown etiology. Hepatogastroenterology 1986, 33, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Block, K.; Braver, J.M.; Farraye, F.A. Aeromonas infection and intramural intestinal hemorrhage as a cause of small bowel obstruction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, 1902–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.C.; Ding, L.W.; Hsueh, P.R. Wound infection and septic shock due to Aeromonas trota in a patient with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1523–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, D.; Aspiroz, C.; Figueras, M.J.; González-Praetorius, A.; Aldea, M.J.; Alperí, A.; Bisquert, J. Surgical site infection due to Aeromonas species: Report of nine cases and literature review. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmaja, K.; Lakshmi, V.; Murthy, K.V.D. Sepsis due to Aeromonas hydrophila. Int. J. Infect. Control. 2013, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Hsu, W.-H.; Hsiao, C.-T.; Huang, Y.-K.; Li, Y.-Y.; Chen, J.-L.; Kuo, S.-F.; Hsiao, J.-C.; et al. Rational Use of Antibiotics and Education Improved Aeromonas Necrotizing Fasciitis Outcomes in Taiwan: A 19-Year Experience. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena-Román, M.; Inglis, T.J.; Henderson, B.; Riley, T.V.; Chang, B.J. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Aeromonas strains isolated from clinical and environmental sources to 26 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosse, T.; Giraud-Morin, C.; Madinier, I.; Labia, R. Sequence analysis and biochemical characterization of chromosomal CAV-1 (Aeromonas caviae), the parental cephalosporinase of plasmid-mediated AmpC ‘FOX’ cluster. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 222, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Lv, X.; Gao, Y. Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 13, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.M. Plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance: Acquisition and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153 (Suppl. 1), S347–S357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bisno, A.L.; Chambers, H.F.; Everett, E.D.; Dellinger, P.; Goldstein, E.J.C.; Gorbach, S.L.; Hirschmann, J.V.; Kaplan, E.L.; Montoya, J.G.; et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1373–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, T.L.; Janda, J.M. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Aeromonas jandaei, A. schubertii, A. trota, and, A. veronii biotype veronii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solís-Sánchez, P.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; Rodrigo-Calabia, E.; de Alegría-Puig, C.R. Chronic Diarrhea Due to Aeromonas hydrophila in an Immunosuppressed Patient with a Pancreas–Kidney Transplant. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091151
Solís-Sánchez P, Fernández-Martínez M, Rodrigo-Calabia E, de Alegría-Puig CR. Chronic Diarrhea Due to Aeromonas hydrophila in an Immunosuppressed Patient with a Pancreas–Kidney Transplant. Pathogens. 2023; 12(9):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091151
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolís-Sánchez, Pablo, Marta Fernández-Martínez, Emilio Rodrigo-Calabia, and Carlos Ruiz de Alegría-Puig. 2023. "Chronic Diarrhea Due to Aeromonas hydrophila in an Immunosuppressed Patient with a Pancreas–Kidney Transplant" Pathogens 12, no. 9: 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091151
APA StyleSolís-Sánchez, P., Fernández-Martínez, M., Rodrigo-Calabia, E., & de Alegría-Puig, C. R. (2023). Chronic Diarrhea Due to Aeromonas hydrophila in an Immunosuppressed Patient with a Pancreas–Kidney Transplant. Pathogens, 12(9), 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091151





