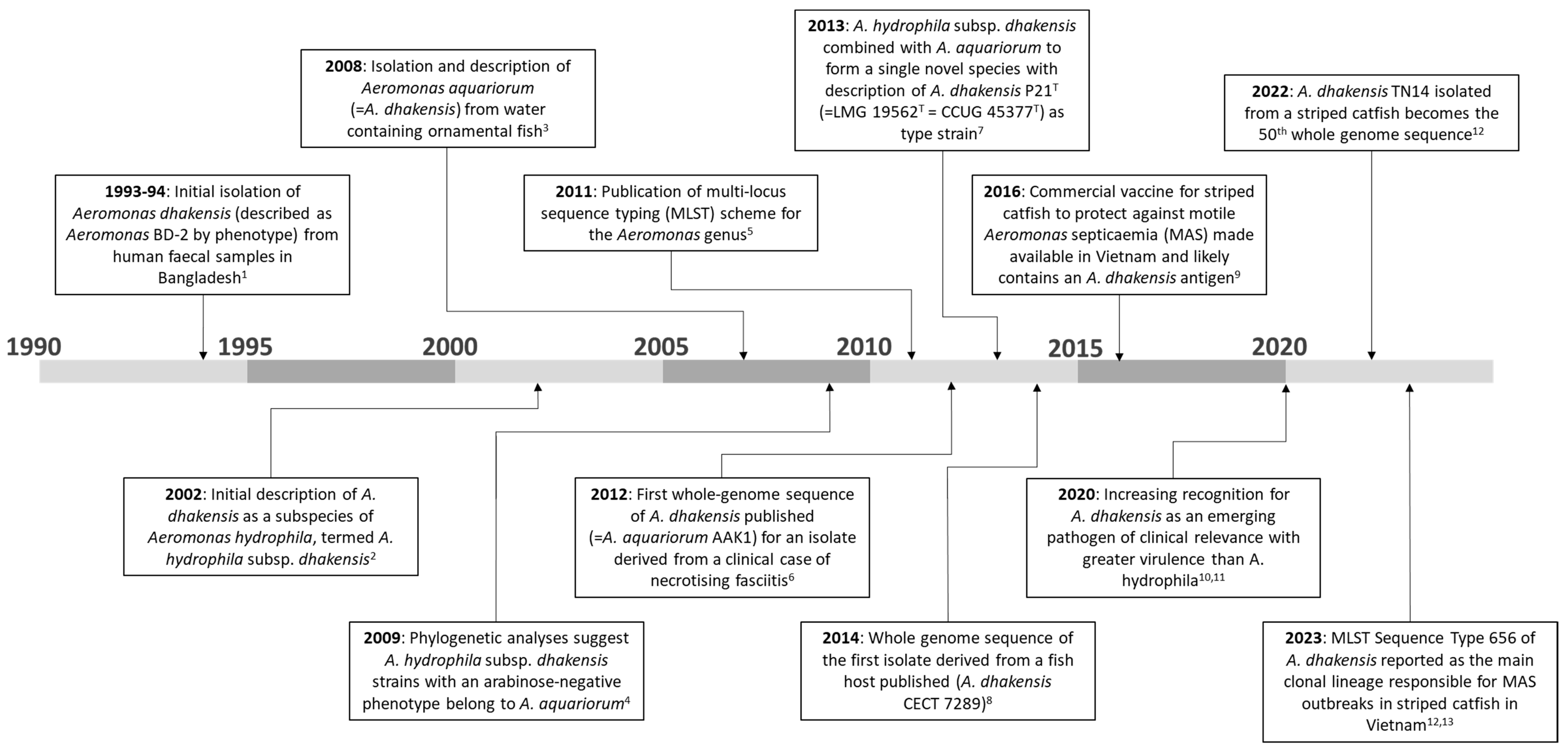
Aeromonas dhakensis: A Zoonotic Bacterium of Increasing Importance in Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
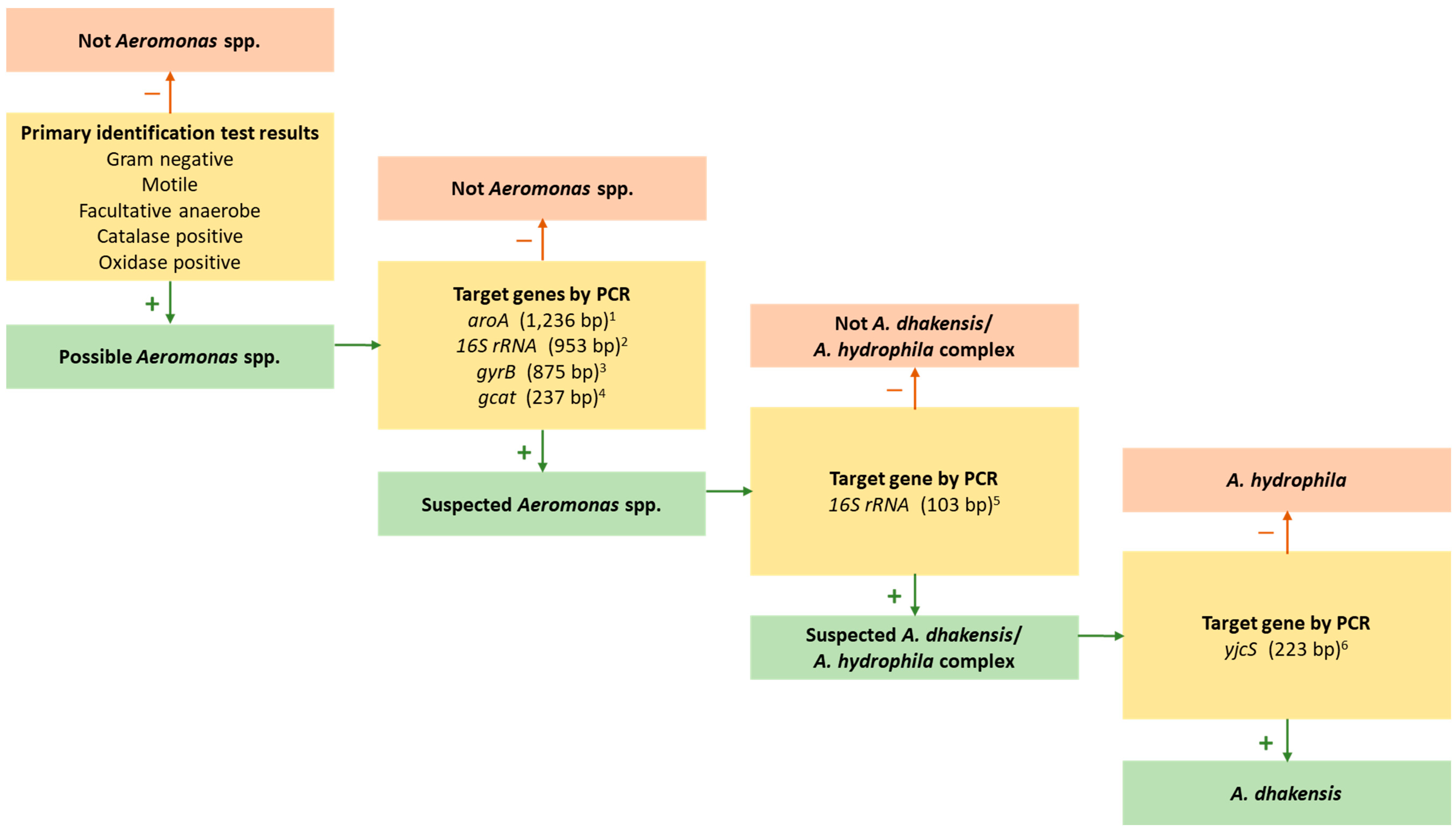
2. Taxonomy and Identification
2.1. Nomenclature and Classification
2.2. Isolation and Culture Conditions
2.3. Phenotypic Characteristics and Species Identification
2.4. PCR Approaches to Identification
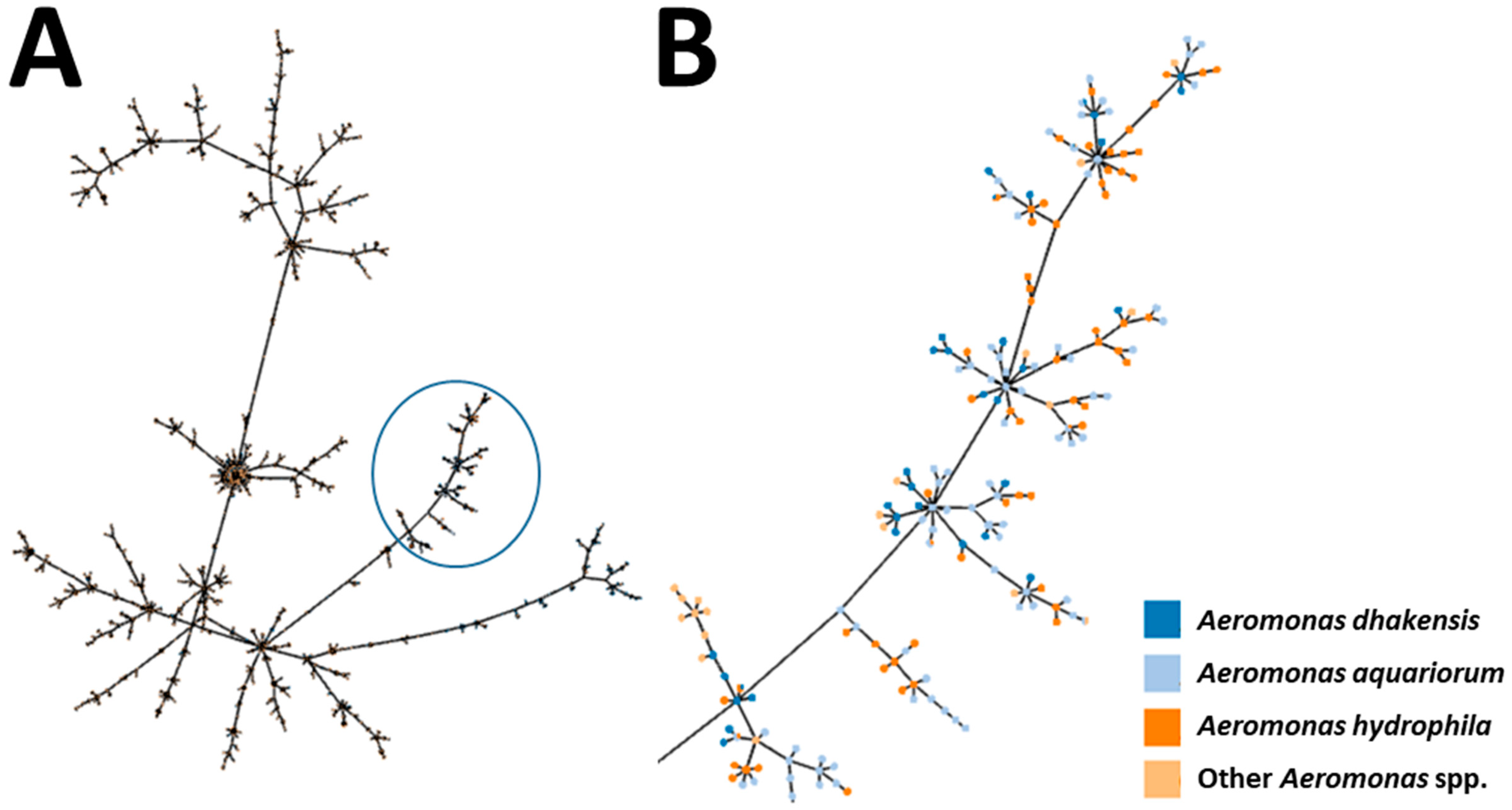
3. Phylogeny by Genetic Sequencing
3.1. Single-Gene Sequencing
3.2. Multi-Locus Approaches
3.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
4. Pathogenicity and Virulence of A. dhakensis
4.1. Comparative Virulence of A. dhakensis and A. hydrophila
4.2. Mechanisms of Virulence
4.3. Strains with Heightened Virulence
5. Prevention and Treatment of MAS Cases Caused by A. dhakensis
6. Antibiotic Resistance
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.-L.; Lamy, B.; Ko, W.-C. Aeromonas dhakensis, an Increasingly Recognized Human Pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An Update on the Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Abe, N.; Ui, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sakaguchi, A.; Suzuki, S.; Masuo, K.; Nakano, A.; et al. Comparison of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry and RpoB Gene Sequencing for the Identification of Clinical Isolates of Aeromonas spp. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, R.B.G.; Marques, D.S.C.; Lima, R.O.H.A.; Oliveira, M.B.M.; Lima, G.M.S.; Maciel de Carvalho, E.V.M.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Virulence Traits of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from the Tambaqui Fish (Colossoma macropomum). Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mzula, A.; Wambura, P.N.; Mdegela, R.H.; Shirima, G.M. Phenotypic and Molecular Detection of Aeromonads Infection in Farmed Nile Tilapia in Southern Highland and Northern Tanzania. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Mansour, E.S.; Monir, W. Isolation, Phenotypic Characterization and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Prevalent Bacterial Pathogens Implicating the Mortality of Cultured Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt. J. Aquac. 2020, 10, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanapala, P.M.; Kalupahana, R.S.; Kalupahana, A.W.; Wijesekera, D.P.H.; Kottawatta, S.A.; Jayasekera, N.K.; Silva-Fletcher, A.; de S. Jagoda, S.S.S. Characterization and Antimicrobial Resistance of Environmental and Clinical Aeromonas Species Isolated from Fresh Water Ornamental Fish and Associated Farming Environment in Sri Lanka. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Yusof, M.T.; Annas, S.; Najihah, M.Y.; Liles, M.R.; Monir, M.S.; Zaidi, Z.; Amal, M.N.A. The Prevalence, Putative Virulence Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Cultured Freshwater Fishes in Peninsular Malaysia. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharia, P.K.; Hussain, I.A.; Pokhrel, H.; Kalita, B.; Borah, G.; Yasmin, R. Prevalence of Motile Aeromonas Septicaemia (MAS) in Fish Culture Systems of the Central Brahmaputra Valley Zone of Assam, India. Aquac. Res. 2020, 52, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mursalim, M.F.; Budiyansah, H.; Raharjo, H.M.; Debnath, P.P.; Sakulworakan, R.; Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Yindee, J.; Piasomboon, P.; Elayaraja, S.; Rodkhum, C. Diversity and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Diseased Freshwater Fishes in Thailand. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legario, F.S.; Choresca, C.H.; Grace, K.; Turnbull, J.F.; Crumlish, M. Identification and Characterization of Motile Aeromonas Spp. Isolated from Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in the Philippines. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Rasmussen-Ivey, C.; Moen, F.S.; Fernández-Bravo, A.; Lamy, B.; Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Khan, C.D.; Escarpulli, G.C.; Salwany, I.; Figueras, M.J.; et al. A Global Survey of Hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila (vAh) Identified vAh Strains in the Lower Mekong River Basin and Diverse Opportunistic Pathogens from Farmed Fish and Other Environmental Sources. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03705-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, L.; Liles, M.; Hossain, M.; Griffin, M.; Hemstreet, W. Motile Aeromonas Septicemia. 2014. Available online: https://units.fisheries.org/fhs/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2017/08/1.2.9-Motile-Aeromonas-Septicemia-2014.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Bacterial Fish Pathogens—Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dien, L.T.; Ngo, T.P.H.; Thao, V.N.; Pattanapon, K.; Salin, K.R.; Mohan, C.V.; Channarong, R.; Ha, T.D. Non-antibiotic Approaches to Combat Motile Aeromonas Infections in Aquaculture: Current State of Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartie, K.L.; Ngo, T.P.H.; Bekaert, M.; Đặng, T.H.O.; Hoare, R.; Adams, A.; Desbois, A.P. Aeromonas hydrophila ST251 and Aeromonas dhakensis are Major Emerging Pathogens of Striped Catfish in Vietnam. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1067235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, V.I.; Khoi, L.M.; Hounmanou, Y.M.G.; Dung, T.T.; Phú, T.M.; Dalsgaard, A. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Aeromonas dhakensis and Aeromonas hydrophila from Diseased Striped Catfish Fingerlings Cultured in Vietnam. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1254781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.; Abarca, M.; Latif-Eugenín, F.; Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.; Domingo, M. Aeromonas dhakensis Pneumonia and Sepsis in a Neonate Risso’s Dolphin Grampus griseus from the Mediterranean Sea. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 116, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Guan, T.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Isolation, Identification and Virulence Gene Characterization of Aeromonas dhakensis Isolated from Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.R.; Lee, D.-H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.-S.; Lee, J.R.; Han, J.E.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, J.H. Wild Nutria (Myocastor coypus) is a Potential Reservoir of Carbapenem-Resistant and Zoonotic Aeromonas spp. In Korea. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriyanov, P.A.; Kashina, D.D.; Liskova, E.A.; Zhurilov, P.A.; Tutrina, A.I.; Ermolaeva, S.A.; Zakharova, O.I.; Blokhin, A.A. The First Detection of Two Aeromonas Strains in Mice of the Genus Apodemus. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W.; Guo, G.; Yang, N.; Li, Q.; Yin, F.; Wang, P.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, J. Three Species of Aeromonas (A. dhakensis, A. hydrophila and A. jandaei) Isolated from Freshwater Crocodiles (Crocodylus siamensis) with Pneumonia and Septicemia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qin, P.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Liang, Q.; He, W.; Peng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Z.; et al. Exploring Aeromonas dhakensis in Aldabra Giant Tortoises: A Debut Report and Genetic Characterization. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Tu, H.; Yao, X.; Lan, X.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, J.; Tang, Q.; Yi, S.; Xia, Z.; Yang, G. Isolation, Identification, and Virulence Gene Analysis of Pathogenic Aeromonas dhakensis in Macrobrachium rosenbergii and Histopathological Observation. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviad, S.; Halpern, M. Chironomids’ Relationship with Aeromonas Species. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okafor, A.C.; Ogbo, F.C.; Rosel, A.C.; Stöger, A.; Akharaiyi, F.C.; Prieto, B.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W. Genome Sequence of OXA-726-Encoding Aeromonas dhakensis Igbk (Sequence Type 1171) from an Edible Snail Traded in Nigeria. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e00343-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Du, X.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Qu, F.T.; Xie, G.L.; Zhou, H.J.; Hu, J.R.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kan, B.; et al. Comparative Study of the Genetic Diversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Pathogenicity of Aeromonas Isolates from Clinical Patients and Healthy Individuals. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve, C.; Alcaide, E.; Giménez, M.J. Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Aeromonas Recovered from the Metropolitan Area of Valencia (Spain): Diseases Spectrum and Prevalence in the Environment. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswaran, R.; Khandeparker, L. Seasonal Variation in β-Glucosidase-Producing Culturable Bacterial Diversity in a Monsoon-Influenced Tropical Estuary. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobral, M.; Barreto, C.; Bianco, K.; Sant’Anna, S.; Clementino, M.M. Virulence Determinants in Genetically Heterogeneous Populations of Aeromonads Recovered from an Urban Lagoon. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Singh, S.; Goyal, S.K. Effect of Seasonal Variation on Bacterial Inhabitants and Diversity in Drinking Water of an Office Building, Delhi. Air Soil Water Res. 2019, 12, 117862211988233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, K.; Shimoji, N.; Shimoji, S.; Tahara, R.; Uechi, A.; Tamaki, I.; Oshiro, H.; Komiyama, A.; Tedokon, M.; Hirai, I. Comparison of Species, Virulence Genes and Clones of Aeromonas Isolates from Clinical Specimens and Well Water in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 1515–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogry, F.A.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Haq, Q.M.R. Emergence of mcr-1 Conferred Colistin Resistance among Bacterial Isolates from Urban Sewage Water in India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 33715–33717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoel, S.; Vadstein, O.; Jakobsen, A.N. Species Distribution and Prevalence of Putative Virulence Factors in Mesophilic Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Fresh Retail Sushi. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.T.; Wang, W.Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.J.; Hu, J.R.; Du, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.Q.; Cui, Z.G.; Xie, G.L.; et al. Genetic Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Pathogenicity of Aeromonas Species from Food Products in Shanghai, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Storesund, J.E.; Lunestad, B.-T.; Hoel, S.; Lerfall, J.; Jakobsen, A.N. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Seafood: Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Factors. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1175304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, H.H.P.; Pham, M.Q.; Tran, Q.T.; Pham, Q.L.; Tran, K.C.; Bach, L.G.; Nguyen, T.L. Effects of Antibiotics on Vietnam Koi, Anabas Testudineus, Exposed to Aeromonas dhakensis as a Co-Infection. Acta Trop. 2022, 226, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.-W.; You, M.-J.; Cho, H.-S.; Lee, C.-S.; Kwon, J.-K.; Shin, G.-W. Molecular Characterization of Aeromonas Species Isolated from Farmed Eels (Anguilla japonica). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.; Adikesavalu, H.; Banerjee, S.; Abraham, T.J. Antibiotic Resistant Motile Aeromonads Induced Septicemia in Philippine Catfish Clarias batrachus (Linnaeus, 1758) fingerlings. Croat. J. Fish. 2015, 73, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulia, D.S.; Isnansetyo, A.; Pratiwi, R.; Asmara, W. Antibiotic Resistance of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Diseased Walking Catfish (Clarias sp.). Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2021, 22, 4839–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adah, D.A.; Saidu, L.; Oniye, S.J.; Adah, A.S.; Daoudu, O.B.; Ola-Fadunsin, S.D. Molecular Characterization and Antibiotics Resistance of Aeromonas Species Isolated from Farmed African Catfish Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Das, B.K.; Bera, A.K.; Borah, S.; Mohanty, D.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, J.; Koushlesh, S.K.; Chanu, T.N.; Panda, S.P.; et al. Co-Prevalence of Virulence and Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Aeromonas spp. from Diseased Fishes with In Silico Insight on the Virulent Protein Network. Life 2022, 12, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, M.; Saticioglu, I.B.; Janda, M.J.; Altun, S. The Determination of the Infectious Status and Prevalence of Motile Aeromonas Species Isolated from Disease Cases in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Aquarium Fish. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1843–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuñure, O.J.; Sandoval, C.N.; Estrella, O.M.; Ramos, E.F.; Herrera, R.A.; Valera, A.A.; Manchego, S.A. Identificación Y Caracterización de Aeromonas sp. Patógenas Aisladas de Truchas Arcoíris (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Clínicamente Enfermas Cultivadas En Piscigranjas Del Perú. Rev. De Investig. Vet. Del Perú 2021, 32, e20927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Cabanillas-Ramos, J.; Alcaraz, U.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Romalde, J.L. Identification and Virulence of Aeromonas dhakensis, Pseudomonas mosselii and Microbacterium paraoxydans Isolated from Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, Cultivated in Mexico. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preena, P.G.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Swaminathan, T.R. Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis of Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Freshwater Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Cultured in Kerala, India. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3278–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriero, M.M.; Maia; Luiz, R.; Henrique-Silva, F. Characterization of a New Strain of Aeromonas dhakensis Isolated from Diseased Pacu Fish (Piaractus mesopotamicus) in Brazil. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Murcia, A.J.; Saavedra, M.J.; Mota, V.R.; Maier, T.; Stackebrandt, E.; Cousin, S. Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov., Isolated from Aquaria of Ornamental Fish. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagoda, S.; Wijewardana, T.; Arulkanthan, A.; Igarashi, Y.; Tan, E.; Kinoshita, S.; Watabe, S.; Asakawa, S. Characterization and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Motile Aeromonads Isolated from Freshwater Ornamental Fish Showing Signs of Septicaemia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 109, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Morillo, M.; Sotil, G.; Arteaga, C.; Cordero, G.; Martins, M.L.; Murrieta-Morey, G.; Yunis-Aguinaga, J. Pathogenic Aeromonas spp. in Amazonian Fish: Virulence Genes and Susceptibility in Piaractus brachypomus, the Main Native Aquaculture Species in Peru. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, C.; Alcaide, E.; Blasco, M.D. Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis Isolated from Feces, Water and Fish in Mediterranean Spain. Microbes Environ. 2012, 27, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithin, M.S.; Kushala, K.B.; Girisha, S.K.; Dheeraj, S.B.; Harshitha, H.; Sowndarya, N.S.; Suresh, T.; Rakesh, K.; Vinay, T.N. First Evidence of Extensively Drug-Resistant Virulent Aeromonas dhakensis Isolated from Diseased Endemic Mascara Barb (Dawkinsia assimilis) in India. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiga, M.; Vaidyanathan, V.V.; Thayumanavan, T. Draft Genome Sequence of Aeromonas dhakensis Strain F2S2-1, Isolated from the Skin Surface of an Indian Oil Sardine (Sardinella longiceps). Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00494-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, R.B.G.; de Oliveira, W.F.; dos Santos Correia, M.T.; Fontes, A.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Aeromonas and Human Health Disorders: Clinical Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 868890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, I.; Albert, M.J.; Ansaruzzaman, M.; Bhuiyan, N.A.; Alabi, S.A.; Islam, M.S.; Neogi, P.K.; Huys, G.; Janssen, P.; Kersters, K.; et al. Characterization of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Humans with Diarrhea, from Healthy Controls, and from Surface Water in Bangladesh. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huys, G.; Denys, R.; Albert, M.J.; Swings, J.; Kühn, I.; Kämpfer, P. Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis subsp. nov., Isolated from Children with Diarrhoea in Bangladesh, and Extended Description of Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. hydrophila (Chester 1901) Stanier 1943 (Approved Lists 1980). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Murcia, A.; Monera, A.; Alperi, A.; Figueras, M.-J.; Saavedra, M.-J. Phylogenetic Evidence Suggests that Strains of Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis Belong to the Species Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Martínez-Murcia, A.; Figueras, M.J. Reclassification of Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis Huys et al. 2002 and Aeromonas aquariorum Martínez-Murcia et al. 2008 as Aeromonas dhakensis sp. nov. comb nov. and emendation of the species Aeromonas hydrophila. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colston, S.M.; Fullmer, M.S.; Beka, L.; Lamy, B.; Gogarten, J.P.; Graf, J. Bioinformatic Genome Comparisons for Taxonomic and Phylogenetic Assignments Using Aeromonas as a Test Case. mBio 2014, 5, e02136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Hossain, M.J.; Liles, M.R.; Figueras, M.J. Strategies to Avoid Wrongly Labelled Genomes Using as Example the Detected Wrong Taxonomic Affiliation for Aeromonas Genomes in the GenBank Database. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M. Taxonomic Update on Proposed Nomenclature and Classification Changes for Bacteria of Medical Importance, 2013–2014. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 83, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.E.; Fasolato, L.; Montemurro, F.; Rosteghin, M.; Manfrin, A.; Patarnello, T.; Novelli, E.; Cardazzo, B. Determination of Microbial Diversity of Aeromonas Strains on the Basis of Multilocus Sequence Typing, Phenotype, and Presence of Putative Virulence Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4986–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-J.; Wang, H.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Shu, H.-Y.; Kao, A.-W.; Chen, P.-L.; Ko, W.-C. Genome Sequence of a Novel Human Pathogen, Aeromonas aquariorum. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4114–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, V.T.; Phuong, T.D.; Phuong, L.T.K.; Phuc, N.T.; Nygaard, A.; Hungerholdt, L.B.; Klevan, L.A. Immunogenic Composition against Aeromonas hydrophila. 2014. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2014064217A1/en (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Shotts, E.B.; Rimler, R. Medium for the Isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl. Microbiol. 1973, 26, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernagozzi, M.; Bianucci, F.; Scerre, E.; Sacchetti, R. Assessment of Some Selective Media for the Recovery of Aeromonas hydrophila from Surface Waters. Zentralblatt Fur Hyg. Und Umweltmed. 1994, 195, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gobat, P.-F.; Jemmi, T. Comparison of Seven Selective Media for the Isolation of Mesophilic Aeromonas Species in Fish and Meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1995, 24, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, S.L.; Cheung, W.K.W.; Janda, J.M. The Genus Aeromonas: Biochemical Characteristics, Atypical Reactions, and Phenotypic Identification Schemes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igbinosa, I.H.; Igumbor, E.U.; Aghdasi, F.; Tom, M.; Okoh, A.I. Emerging Aeromonas Species Infections and Their Significance in Public Health. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 625023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedláček, I.; Krejčí, E.; Andělová, A.; Sedláčková, M.; Porazilová, I.; Holochová, P. Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis—A Causative Agent of Gastroenteritis Imported into the Czech Republic. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, R. The Genus Aeromonas: A General Approach. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, D.-D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.-A. VasH Contributes to Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila and is Necessary to the T6SS-Mediated Bactericidal Effect. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 793458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnahan, A.M.; Behram, S.; Joseph, S.W. Aerokey II: A Flexible Key for Identifying Clinical Aeromonas Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, G.; Pearson, M.D.; Kämpfer, P.; Denys, R.; Cnockaert, M.; Inglis, V.; Swings, J. Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. ranae subsp. nov., Isolated from Septicaemic Farmed Frogs in Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravena-Roman, M.; Chang, B.J.; Riley, T.V.; Inglis, T.J.J. Phenotypic Characteristics of Human Clinical and Environmental Aeromonas in Western Australia. Pathology 2011, 43, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Hossain, M.J.; Odom, S.E.; Terhune, J.S.; Hemstreet, W.G.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Zhang, D.; Xu, D.-H.; Griffin, M.J.; Liu, Y.-J.; et al. Classification of a Hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila Pathotype Responsible for Epidemic Outbreaks in Warm-Water Fishes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-L.; Wu, C.-J.; Chen, C.-S.; Tsai, P.-J.; Tang, H.-J.; Ko, W.-C. A Comparative Study of Clinical Aeromonas dhakensis and Aeromonas hydrophila Isolates in Southern Taiwan: A. dhakensis is More Predominant and Virulent. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O428–O434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.L.; Lee, T.F.; Wu, C.J.; Teng, S.H.; Teng, L.J.; Ko, W.C.; Hsueh, P.R. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Can Accurately Differentiate Aeromonas dhakensis from A. hydrophila, A. caviae, and A. veronii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2625–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Kan, B.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; et al. Comparison of the Multiple Platforms to Identify Various Aeromonas Species. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertran, X.; Rubio, M.; Gómez, L.; Llovet, T.; Muñoz, C.; Navarro, F.; Miro, E. Taxonomic Identification of Different Species of the Genus Aeromonas by Whole-Genome Sequencing and Use of Their Species-Specific β-Lactamases as Phylogenetic Markers. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Alperi, A.; Buján, N.; Romalde, J.L.; Figueras, M.J. Comparison of Phenotypical and Genetic Identification of Aeromonas Strains Isolated from Diseased Fish. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 33, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Pathogenicity, and Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciufo, S.; Kannan, S.; Sharma, S.; Badretdin, A.; Clark, K.; Turner, S.; Brover, S.; Schoch, C.L.; Kimchi, A.; DiCuccio, M. Using Average Nucleotide Identity to Improve Taxonomic Assignments in Prokaryotic Genomes at the NCBI. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Comparative Genome Analysis Provides Deep Insights into Aeromonas hydrophila Taxonomy and Virulence-Related Factors. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.J. Aeromonas spp. Whole Genomes and Virulence Factors Implicated in Fish Disease. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdella, B.; Abozahra, N.A.; Shokrak, N.M.; Mohamed, R.A.; El-Helow, E.R. Whole Spectrum of Aeromonas hydrophila Virulence Determinants and the Identification of Novel SNPs Using Comparative Pathogenomics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, T.T.V.; Tan, M.A.; Puthucheary, S.D.; Puah, S.-M.; Chua, K.-H. Genetic Relatedness and Novel Sequence Types of Clinical Aeromonas dhakensis from Malaysia. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.-L.; Roberts, R.J.; Ee, R.; Yin, W.-F.; Chan, K.-G. Complete Genome Sequence and Methylome Analysis of Aeromonas hydrophila Strain YL17, Isolated from a Compost Pile. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00060-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Kang, J.; Wu, B.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, L.; Mao, L.; Wang, S.; Yan, Q. Comparative Transcriptome and Phenotype Analysis Revealed the Role and Mechanism of ompR in the Virulence of Fish Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbiol. Open 2020, 9, e1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Cai, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhai, S.; Xu, X.; Lin, M. Comparative Genomics Analysis of the Multidrug-Resistant Aeromonas hydrophila MX16A Providing Insights into Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1042350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grim, C.J.; Kozlova, E.; Ponnusamy, D.; Fitts, E.C.; Sha, J.; Kirtley, M.L.; van Lier, C.J.; Tiner, B.L.; Erova, T.E.; Joseph, S.J.; et al. Functional Genomic Characterization of Virulence Factors from Necrotizing Fasciitis-Causing Strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4162–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Ma, Z.; Cai, Z.; Lin, G.; Zhou, J. Genome Sequence Analysis Reveals Evidence of Quorum-Sensing Genes Present in Aeromonas hydrophila Strain KOR1, Isolated from a Mangrove Plant (Kandelia obovata). Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01461-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, D.R.; Johnson, W.M.; Lior, H.; Tyler, S.D.; Rozee, K.R. Detection of the Aerolysin Gene in Aeromonas hydrophila by the Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2477–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-H.; Lu, C.-P. Multiplex PCR Assay for the Detection of Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Rathore, G.; Kapoor, D.; Mishra, B.N.; Lakra, W.S. Detection of Aerolysin Gene in Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Fish and Pond Water. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trakhna, F.; Harf-Monteil, C.; AbdelNour, A.; Maaroufi, A.; Gadonna-Widehem, P. Rapid Aeromonas hydrophila Identification by TaqMan PCR Assay: Comparison with a Phenotypic Method. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascón Soriano, A.; Anguita Castillo, J.; Hernanz Moral, C.; Sánchez Salazar, M.; Yugueros Marcos, J.; Naharro Carrasco, G. RFLP-PCR Analysis of the aroA Gene as a Taxonomic Tool for the Genus Aeromonas. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 156, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cho, J.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.-G.; Kim, S.-J. Distribution of Aeromonas spp. as Identified by 16S rDNA Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis in a Trout Farm. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, A.H. Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Rapid and Simultaneous Detection of Four Genera of Fish Pathogenic Bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif-Eugenín, F.; Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.J. A Culture Independent Method for the Detection of Aeromonas sp. From Water Samples. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2016, 5, 5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.J.; Goodwin, A.E.; Merry, G.E.; Liles, M.R.; Williams, M.A.; Ware, C.; Waldbieser, G.C. Rapid Quantitative Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila Strains Associated with Disease Outbreaks in Catfish Aquaculture. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, M.; Jiang, J.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kwok, A.H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Yao, H.; Lu, C.; Leung, F.C.; et al. Novel Insights into the Pathogenicity of Epidemic Aeromonas hydrophila ST251 Clones from Comparative Genomics. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, B.; Laurent, F.; Verdier, I.; Decousser, J.-W.; Lecaillon, E.; Marchandin, H.; Roger, F.; Tigaud, S.; de Montclos, H.; Kodjo, A. Accuracy of 6 Commercial Systems for Identifying Clinical Aeromonas Isolates. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 67, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.B.; Yoon, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, K. Comparison of MALDI-TOF MS, Housekeeping Gene Sequencing, and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing for Identification of Aeromonas Clinical Isolates. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozova, P.; Barker, M.; Austin, D.A.; Austin, B. Identification and Pathogenicity to Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) of some aeromonads. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küpfer, M.; Kuhnert, P.; Korczak, B.M.; Peduzzi, R.; Demarta, A. Genetic Relationships of Aeromonas Strains Inferred from 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoB Gene Sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2743–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñana-Galbis, D.; Aintzane Urbizu-Serrano, A.; Farfán, M.; Fusté, M.C.; Lorén, J.G. Phylogenetic Analysis and Identification of Aeromonas Species Based on Sequencing of the cpn60 Universal Target. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Martínez-Murcia, A. Phylogenetic Analyses of the Genus Aeromonas Based on Housekeeping Gene Sequencing and Its Influence on Systematics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bliss, C.M.; Bennett, J.S.; Bratcher, H.B.; Brehony, C.; Colles, F.M.; Wimalarathna, H.; Harrison, O.B.; Sheppard, S.K.; Cody, A.J.; et al. Ribosomal Multilocus Sequence Typing: Universal Characterization of Bacteria from Domain to Strain. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Gonçalves, B.; Francisco, A.P.; Vaz, C.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. PHYLOViZ Online: Web-Based Tool for Visualization, Phylogenetic Inference, Analysis and Sharing of Minimum Spanning Trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, A.; Suzuki, M.; Hayashi, K.; Doi, Y. Taxonomic Classification of Genus Aeromonas Using Open Reading Frame-Based Binarized Structure Network Analysis. Fujita Med. J. 2024, 10, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Salwany, I.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Salleh, A.; Liles, M.R.; Xu, T.; Noor, M.; Yusof, M.T. Draft Genome Sequence of Myo-Inositol Utilizing Aeromonas dhakensis 1P11S3 Isolated from Striped Catfish (Pangasianodon hypopthalmus) in a Local Fish Farm in Malaysia. Data Brief 2022, 41, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; Garcia-Gasca, M.T.; Abad-Rosales, S.M.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Ayala-Arellano, J. Virulence of the Fish Pathogen Aeromonas dhakensis: Genes Involved, Characterization and Histopathology of Experimentally Infected Hybrid Tilapia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 129, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, C.; Ahmed, A.; Li, H.; Wei, X.; Lian, Q.; Tastemel, M.; Xin, H.; Ge, M.; et al. The Microbiota Regulates Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Development by Mediating Inflammatory Signals in the Niche. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-J.; Chen, P.-L.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Chang, M.-C.; Tsai, P.-J.; Shih, H.-I.; Wang, H.-C.; Chou, P.-H.; Ko, W.-C. Clinical Implications of Species Identification in Monomicrobial Aeromonas Bacteremia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence Factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: In the Wake of Reclassification. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Potential Pathways of Exposure to ST251 Strains of Virulent Aeromonas hydrophila in Farmed Catfish. 2021. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/vah-potential-pathways-farmed-catfish.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Dong, J.; Ruan, J.; Xu, N.; Yang, Y.; Ai, X. Expression, Purification, and Characterization of Hemolytic Toxin from Virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 48, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, S.; Priyadarsini, S.; Paul, A.; Kumar, P.R.; Sahoo, P.K. Diversity of Virulence-Associated Genes in Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila Isolates and their In Vivo Modulation at Varied Water Temperatures. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Wang, S.-T.; Shu, C.-Y.; Tsai, P.-J.; Ko, W.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Chen, P.-L. Haemolysin Ahh1 Secreted from Aeromonas dhakensis Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Macrophages and Mediates Severe Soft Tissue Infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Heo, G.-J. Characterization of Virulence Properties and Multi-Drug Resistance Profiles in Motile Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.B.; Kumar, A.; Paria, A.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, K.P.; Rathore, G. Effect of Spatio-Temporal Variables, Host Fish Species and On-Farm Biosecurity Measures on the Prevalence of Potentially Pathogenic Aeromonas Species in Freshwater Fish Farms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Zhou, Y. Fur Functions as an Activator of T6SS-Mediated Bacterial Dominance and Virulence in Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1099611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.-T.V.; Puah, S.-M.; Tan, J.-A.M.A.; Merino, S.; Puthucheary, S.D.; Chua, K.-H. Flagellar Motility Mediates Biofilm Formation in Aeromonas dhakensis. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 177, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Yeh, W.-H.; Tang, H.-J.; Chen, J.-W.; Shu, H.-Y.; Su, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-T.; Kuo, C.-J.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; et al. UvrY Is Required for the Full Virulence of Aeromonas dhakensis. Virulence 2020, 11, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, N.; Zeng, J.; Guo, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Zeng, W.; Zheng, J. Response regulator KdpE contributes to Aeromonas dhakensis virulence. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Pei, T.-T.; Wang, Z.-H.; Xiong, W.; Wu, L.-L.; Xu, P.; Lin, S.; Dong, T.G. Characterization of Lysozyme-like Effector TseP Reveals the Dependence of Type VI Secretion System (T6SS) Secretion on Effectors in Aeromonas dhakensis Strain SSU. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00435-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Annas, S.; Yusof, M.T.; Monir, M.S.; Mohamad, A.; Muhamad-Sofie, M.H.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Chin, Y.K.; et al. Comparative Pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. in Cultured Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus). Biology 2021, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, M.E.; Fasolato, L.; Montemurro, F.; Novelli, E.; Cardazzo, B. Aeromonas spp.: Ubiquitous or Specialized Bugs? Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talagrand-Reboul, E.; Colston, S.M.; Graf, J.; Lamy, B.; Jumas-Bilak, E. Comparative and Evolutionary Genomics of Isolates Provide Insight into the Pathoadaptation of Aeromonas. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.P.H.; Vu, H.T.T.; Le, T.T.T.; Bui, H.C.N.; Liles, M.R.; Rodkhum, C. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila Strains from Striped Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Hu, X.; Miao, L.; Chen, J. Current Status and Development Prospects of Aquatic Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1040336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, A.; Phu, T.M.; Satapornvanit, K.; Min, J.; Shahabuddin, A.M.; Henriksson, P.J.G.; Murray, F.J.; Little, D.C.; Dalsgaard, A.; Van den Brink, P.J. Use of Veterinary Medicines, Feed Additives and Probiotics in Four Major Internationally Traded Aquaculture Species Farmed in Asia. Aquaculture 2013, 412–413, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, T.M.; Phuong, N.T.; Dung, T.T.; Hai, D.M.; Son, V.N.; Rico, A.; Clausen, J.H.; Madsen, H.; Murray, F.; Dalsgaard, A. An Evaluation of Fish Health-Management Practices and Occupational Health Hazards Associated with Pangasius Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Aquaculture in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2778–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, L.A.; Desbois, A.P.; Garza, M.; Wieland, B.; Mohan, C.V.; Häsler, B.; Tam, C.C.; Le, P.N.T.; Phuong, N.T.; Van, P.T.; et al. Identifying Hotspots for Antibiotic Resistance Emergence and Selection, and Elucidating Pathways to Human Exposure: Application of a Systems-Thinking Approach to Aquaculture Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter, M.; Sarter, S.; Caruso, D.; Avarre, J.C.; Combe, M.; Pepey, E.; Pouyaud, L.; Vega-Heredía, S.; de Verdal, H.; Gozlan, R.E. Aquaculture at the Crossroads of Global Warming and Antimicrobial Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Yu, T.; Yin, Z.; Wang, P.; Lu, X.; He, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Gao, B.; Mu, K. Uncovering the Hidden Threat: The Widespread Presence of Chromosome-Borne Accessory Genetic Elements and Novel Antibiotic Resistance Genetic Environments in Aeromonas. Virulence 2023, 14, 2271688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, A.; Du, P.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Kan, B.; et al. Distribution, Virulence-Associated Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance of Aeromonas Isolates from Diarrheal Patients and Water, China. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, B.; Baron, S.; Barraud, O. Aeromonas: The Multifaceted Middleman in the One Health World. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2022, 65, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.C.; LaMartina, E.L.; Lewis, J.R.; Dahl, A.J.; Nadig, N.; Szabo, A.; Newton, R.J.; Skwor, T.A. One Health and Global Health View of Antimicrobial Susceptibility through the “Eye” of Aeromonas: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, H.; Kannimuthu, D. Comparative Resistome Analysis of Aeromonas Species in Aquaculture Reveals Antibiotic Resistance Patterns and Phylogeographic Distribution. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.-W.; Chung, T.-H.; Joh, S.-J.; Park, C.; Park, B.-Y.; Shin, G.-W. High Prevalence of BlaCTX-M Group Genes in Aeromonas dhakensis Isolated from Aquaculture Fish Species in South Korea. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2014, 76, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.H.; Khare, K.; Saxena, P.; Debnath, P.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Yadav, D.A. Review on Colistin Resistance: An Antibiotic of Last Resort. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preena, P.G.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Kumar, R.; Swaminathan, T.R. Plasmid-Mediated Antimicrobial Resistance in Motile Aeromonads from Diseased Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Wimalasena, S.H.M.P.; Pathirana, H.N.K.S.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Heo, G.-J. Distribution of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Class 1 Integron Gene Cassette Arrays in Motile Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Goldfish (Carassius auratus). Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Wimalasena, S.H.M.P.; Pathirana, H.N.K.S.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Heo, G.-J. Characterization of Virulence Determinants and Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Motile Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Ornamental Goldfish (Carassius auratus). J. Exot. Pet Med. 2019, 29, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Indexing of Escherichia coli to Identify High-Risk Sources of Fecal Contamination of Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieseker, C.M.; Gaunt, P.S.; Hawke, J.P.; Crosby, T.C.; Hasbrouck, N.R.; Gao, D.X.; Stine, C.B.; Evans, E.R.; Grim, C.J. Epidemiological Cutoff Values for Standard Broth Microdilution and Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Fish. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.J.; Wang, H.-C.; Chen, P.L.; Chang, M.C.; Sun, H.S.; Chou, P.H.; Ko, W.C. AQU-1, a Chromosomal Class c β-Lactamase, among Clinical Aeromonas dhakensis Isolates: Distribution and Clinical Significance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Morinaga, Y.; Akamatsu, N.; Matsuda, J.; Uno, N.; Kosai, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Okada, M.; Moriuchi, H.; Yanagihara, K. The Rapid Induction of Carbapenem-Resistance in an Aeromonas dhakensis Blood Isolate. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 69, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Hilaire, S. Understanding Antibiotic Treatment Failures in Salmon Aquaculture. Asian Fish. Sci. 2020, 33, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, H.A.; Heney, C.; Sidjabat, H.E.; George, N.M.; Bergh, H.; Anuj, S.N.; Nimmo, G.R.; Paterson, D.L. Genotypic and Phenotypic Identification of Aeromonas Species and CphA-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance in Queensland, Australia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puah, S.M.; Khor, W.C.; Aung, K.T.; Tien, T.; Puthucheary, S.D.; Chua, K.H. Aeromonas dhakensis: Clinical Isolates with High Carbapenem Resistance. Pathogens 2022, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Bolivar, J.F.; Sinclair, H.A.; Sidjabat, H.E. Draft Genome Sequence of Aeromonas dhakensis, Isolated from a Patient with Fatal Necrotizing Fasciitis. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00009-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and Sequence Analysis Tools Services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Host or Sample Type | Country of Isolation | Year of Isolation a | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmed hosts | |||
| Anabas testudineus (Climbing perch) | Vietnam | 2019 | [37] |
| Anguilla japonica (Japanese eel) b | South Korea | [2013] | [38] |
| Clarias batrachus (Walking catfish) b | Philippines | 2013 | [39] |
| C. batrachus | Malaysia | 2019 | [8] |
| C. batrachus | Indonesia | [2021] | [40] |
| Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) | Nigeria | 2019–2020 | [41] |
| Colossoma macropomum (Tambaqui) | Brazil | [2020] | [4] |
| Labeo catla (Catla) | India | 2020 | [42] |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Giant freshwater prawn) | China | 2021 | [24] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss (Rainbow trout) | Turkey | 2013 | [43] |
| O. mykiss | Peru | [2021] | [44] |
| Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia) | Mexico | 2009 | [45] |
| O. niloticus | India | 2018–2019 | [46] |
| O. niloticus | India | [2020] | [46] |
| Oreochromis spp. (Tilapia) | Malaysia | 2019 | [8] |
| Piaractus mesopotamicus (Pacu) | Brazil | [2016] | [47] |
| Pangasianodon hypopthalmus (Striped catfish) | Vietnam | 2013–2019 | [16] |
| P. hypopthalmus | Vietnam | 2017–2021 | [17] |
| P. hypophthalmus | Malaysia | 2019 | [8] |
| Ornamental fish hosts | |||
| Aquaria of unspecified ornamental fish b | Portugal | 2004–2005 | [48] |
| Carassius auratus (Goldfish) | Turkey | 2014 | [43] |
| Cyprinus carpio (Koi) | Sri Lanka | 2007–2008 | [49] |
| Osphronemus goramy (Giant gourami) | Sri Lanka | 2007–2008 | [49] |
| Otocynclus affinis (Dwarf suckermouth catfish) | Peru | 2021 | [50] |
| Poecilia reticulata (Guppy) | Sri Lanka | 2020–2021 | [7] |
| Trachelyopterus galeatus (Driftwood catfish) | Peru | 2021 | [50] |
| Wild hosts | |||
| Anguillicola crassus (European eel) | Spain | 2004–2005 | [51] |
| Dawkinsia assimilis (Mascara barb) | India | 2018 | [52] |
| Ompok pabda (Pabda) | Bangladesh | [2023] | [12] |
| Sardinella longiceps (Indian oil sardine) | India | [2016] | [53] |
| Submitted Species Name | Isolate Name | Sample Type | Taxonomy Check Status | ANI against A. hydrophila ATCC 7966T (%) | ANI against A. dhakensis CIP 107500T (%) | Assembly Accession | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Records with apparent mismatch to original submitted species name | |||||||
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 116 | Human | Mismatch | 93.28 | 97.28 | GCF_000350405.1 | [87] |
| A. hydrophila | 187 | Human | Mismatch | 93.10 | 97.35 | GCF_000354635.1 | [87] |
| A. hydrophila | 14 | Human | Mismatch | 93.24 | 97.16 | GCF_000354655.1 | [84] |
| A. hydrophila | 259 | Human | Mismatch | 93.13 | 97.38 | GCF_000354695.1 | [84] |
| A. hydrophila | 145 | Human | Mismatch | 93.31 | 97.35 | GCF_000586035.1 | [87] |
| A. hydrophila | L14f | Lake water | Mismatch | 93.27 | 97.36 | GCF_000813465.1 | [84] |
| A. hydrophila | YL17 | Compost | Mismatch | 93.26 | 97.34 | GCF_000612075.2 | [88] |
| A. hydrophila | B11 | Anguilla japonica (Japanese eel) | Mismatch | 93.31 | 97.36 | GCA_013205705.1 | [89] |
| A. hydrophila | BB1457 | Hospital wastewater | Mismatch | 93.12 | 97.33 | GCA_903684605.1 | [90] |
| A. hydrophila | AYN7 | Heteropneustes fossilis (Asian stinging catfish) | Mismatch | 93.42 | 97.28 | GCA_028771245.1 | PRJNA911000 |
| Records with recently corrected species assignments | |||||||
| Aeromonas dhakensis | 173 | Human | Species match | N/A | 97.45 | GCF_000354675.1 | [87] |
| A. dhakensis | SSU | Human | Species match | N/A | 97.38 | GCF_000298055.1 | [91] |
| A. dhakensis | KOR1 | Kandelia obovate (Mangrove) | Species match | N/A | 97.41 | GCF_001306015.1 | [92] |
| Host or Sample Type | Isolate Name | Country of Isolation | Year of Isolation | Assembly Accession | Bioproject | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquarium water | CECT 7289 | Portugal | 2003 | GCF_000819705.1 | PRJEB7020 | [48] |
| Ancherythroculter nigrocauda (Cyprinid) | 202108B1 | China | 2021 | GCF_034143565.1 | PRJNA1009974 | |
| Ctenopharyngodon idella (Grass carp) | 202108C2 | China | 2021 | GCA_035658375.1 | PRJNA1060866 | |
| Danio rerio (Zebrafish) | b2-100 | China | 2019 | GCF_023920205.1 | PRJNA797204 | [115] |
| Ictalurus punctatus (Channel catfish) | OTH-19-VL-NY-MS-0027 | United States | 2019 | GCA_020765715.1 | PRJNA481355 | |
| Lates calcarifer (Asian seabass) | OTH-21-VL-ON-ON-0001 | Canada | 2021 | GCA_032496525.1 | PRJNA503849 | |
| Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia) | Aer_On15M | Brazil | 2009 | GCF_017163915.1 | PRJNA607226 | |
| O. niloticus | Aer_On24M | Brazil | 2009 | GCF_017310095.1 | PRJNA594314 | |
| O. niloticus | 26M | Brazil | 2009 | GCF_019348695.1 | PRJNA590952 | |
| O. niloticus | CAIM 1873 | Mexico | 2009 | GCF_003989145.1 | PRJNA422283 | [114] |
| O. niloticus | OnIF3 | Brazil | 2010 | GCF_018094765.1 | PRJNA591217 | |
| O. niloticus | IF_2 | Brazil | 2010 | GCF_019348645.1 | PRJNA590791 | |
| O. niloticus | Aer_OnIF1 | Brazil | 2010 | GCF_022703095.1 | PRJNA577584 | |
| Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Striped catfish) | 33 isolates, e.g., 12-AH41 | Vietnam | 2012-2022 | e.g., GCA_031915985.1 | PRJEB65955 | |
| P. hypophthalmus | 10 isolates, e.g., TN14 | Vietnam | 2013-2018 | e.g., GCF_905132925.1 | PRJEB41556 | [16] |
| P. hypophthalmus | 1P11S3 | Malaysia | 2019 | GCF_015666195.1 | PRJNA679132 | [113] |
| Phractocephalus hemioliopterus (Redtail catfish) | Aer_Pi12.1HTAS | Brazil | 2009 | GCF_025266835.1 | PRJNA595107 | |
| P. hemioliopterus | Pi16.2MC | Brazil | 2009 | GCF_018094645.1 | PRJNA591201 | |
| Sardinella longiceps (Indian oil sardine) | F2S2-1 | India | 2015 | GCF_001673685.1 | PRJNA312130 | [53] |
| Host | Challenge Material | Delivery | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anguilla anguilla (European eel) | Whole bacterial cells | Intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) | [51] |
| Danio rerio (Zebrafish) | Whole bacterial cells | i.p. | [72] a, [127] |
| Labeo rohita (Rohu) | Whole bacterial cells | i.p. | [52] |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Giant freshwater prawn) | Whole bacterial cells | Intramuscular injection (i.m.) | [24] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss (Rainbow trout) | Whole bacterial cells; Extracellular products (ECPs) | i.p.; i.m. | [105] |
| Oreochromis mossambicus (Mozambique tilapia) | Whole bacterial cells; ECPs | i.p | [45] |
| Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus (Hybrid tilapia) | Whole bacterial cells; ECPs | i.p. | [114] |
| O. niloticus × O. mossambicus | Whole bacterial cells | i.p. | [129] |
| Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Striped catfish) | Whole bacterial cells | i.p. | [64] |
| Piaractus brachypomus (Pacu) | Whole bacterial cells | i.p. | [47,50] |
| Solea vulgaris (Dover sole) | ECPs | i.p. | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartie, K.L.; Desbois, A.P. Aeromonas dhakensis: A Zoonotic Bacterium of Increasing Importance in Aquaculture. Pathogens 2024, 13, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060465
Bartie KL, Desbois AP. Aeromonas dhakensis: A Zoonotic Bacterium of Increasing Importance in Aquaculture. Pathogens. 2024; 13(6):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060465
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartie, Kerry L., and Andrew P. Desbois. 2024. "Aeromonas dhakensis: A Zoonotic Bacterium of Increasing Importance in Aquaculture" Pathogens 13, no. 6: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060465
APA StyleBartie, K. L., & Desbois, A. P. (2024). Aeromonas dhakensis: A Zoonotic Bacterium of Increasing Importance in Aquaculture. Pathogens, 13(6), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060465







