Epidemiological Investigations and Molecular Characterization of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Grapevines, Weeds, Vectors and Putative Vectors in Western Sicily (Southern Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vineyard
2.2. Disease Assessment and Plant Sample Collection
2.3. Insect Sample Collection
2.4. DNA Extraction from Grapevines, Herbaceous Hosts and Insects
2.5. Phytoplasma Detection and Identification
2.6. Characterization of ‘Ca. P. solani’ Based on tuf Gene
2.7. Characterization of ‘Ca. P. solani’ Based on the vmp1 Gene
3. Results
3.1. Disease Assessment
3.2. Molecular Analysis According to the tuf Gene
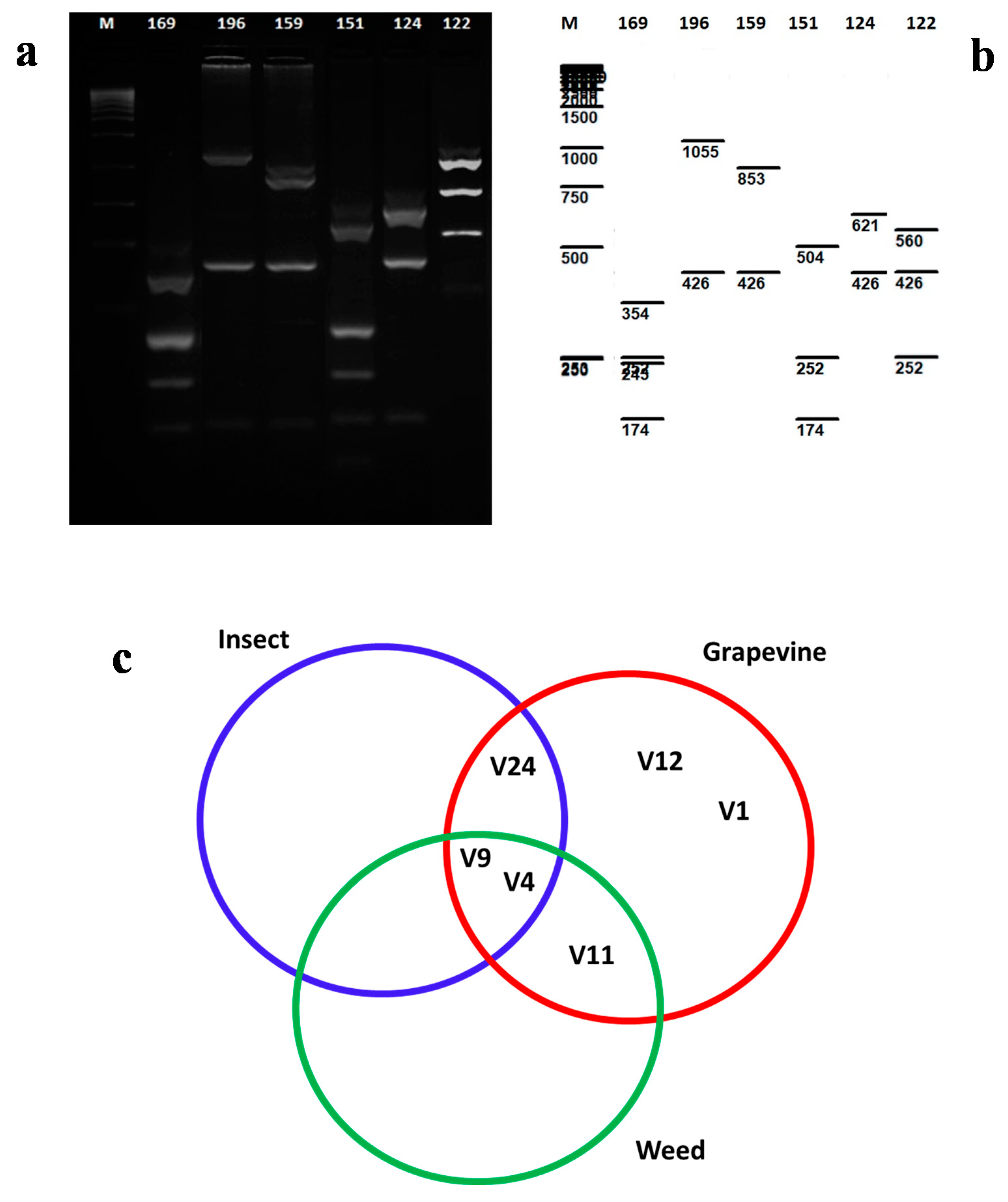
3.3. Analysis Based on the vmp1 Gene of ‘Ca. Phytoplasma solani’ Genotypes in Grapevines, Reservoir Plants, and Vectors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quaglino, F.; Zhao, Y.; Casati, P.; Bulgari, D.; Bianco, P.A.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’, a novel taxon associated with stolbur- and Bois noir-related diseases of plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2879–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maixner, M. Transmission of German grapevine yellows (Vergilbungskrankheit) by the planthopper Hyalesthes obsoletus (Auchenorrhyncha: Cixiidae). Vitis 1994, 33, 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cvrković, T.; Jović, J.; Mitrović, M.; Krstić, O.; Toševski, I. Experimental and molecular evidence of Reptalus panzeri as a natural vector of Bois noir. Plant Pathol. 2013, 63, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglino, F.; Sanna, F.; Moussa, A.; Faccincani, M.; Passera, A.; Casati, P.; Bianco, P.A.; Mori, N. Identification and ecology of alternative insect vectors of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ to grapevine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Quaglino, F.; Tessari, F.; Pozzebon, A.; Bulgari, D.; Casati, P.; Bianco, P. Investigation on ‘Bois noir’ epidemiology in north-eastern Italian vineyards through a multidisciplinary approach. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 166, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrátil, M.; Válová, P.; Fialová, R.; Lauterer, P.; Šafářová, D.; Starý, M. The incidence of stolbur disease and associated yield losses in vegetable crops in South Moravia (Czech Republic). Crop. Prot. 2009, 28, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murolo, S.; Mancini, V.; Romanazzi, G. Spatial and temporal stolbur population structure in a cv. Chardonnay vineyard according tovmp1gene characterization. Plant Pathol. 2013, 63, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, M.; Johannesen, J.; Michel, K.; Lux, B.; Seitz, A. Host plant specificity of Hyalesthes obsoletus and consequences for Bois noir epidemiology. Bull. Insectol. 2007, 60, 399–400. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, N.; Pavan, F.; Bondavalli, R.; Reggiani, N.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, A. Factors affecting the spread of Bois noir disease in north Italy vineyards. Vitis 2008, 47, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, F.; Mori, N.; Bressan, S.; Mutton, P. Control strategies for grapevine phytoplasma diseases: Factors influencing the profitability of replacing symptomatic plants. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2012, 51, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Murolo, S.; Garbarino, M.; Mancini, V.; Romanazzi, G. Spatial pattern of Bois noir: Case study of a delicate balance between disease progression and recovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, M.; Maixner, M. Molecular characterization of grapevine yellows associated phytoplasmas of the stolbur-group based on RFLP-analysis of non-ribosomal DNA. Vitis 2004, 43, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Aryan, A.; Brader, G.; Mörtel, J.; Pastar, M.; Riedle-Bauer, M. An abundant ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ tuf b strain is associated with grapevine, stinging nettle and Hyalesthes obsoletus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 140, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasova, B.; Jakovljevi, Ć.M.; Spasov, D.; Jović, J.; Mitrović, M.; Toševski, I.; Cvrković, T. The molecular epidemiology of bois noir grapevine yellows caused by ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in the Republic of Macedonia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 142, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosovac, A.; Radonjic, S.; Hrncic, S.; Krstić, O.; Toševski, I.; Jović, J. Molecular tracing of the transmission routes of Bois noir in Mediterranean vineyards of Montenegro and experimental evidence for the epidemiological role of Vitex agnus-castus (Lamiaceae) and associated Hyalesthes obsoletus (Cixiidae). Plant Pathol. 2015, 65, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, E.; Murolo, S.; Salehi, M.; Romanazzi, G. Sequence analysis of new Tuf molecular types of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Iranian Vineyards. Pathogens 2020, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimerman, A.; Pacifico, D.; Salar, P.; Marzachi’, C.; Foissac, X. Striking diversity of vmp1, a variable gene encoding a putative membrane protein of the stolbur phytoplasma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2951–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesen, J.; Foissac, X.; Kehrli, P.; Maixner, M. Impact of vector dispersal and host-plant fidelity on the dissemination of an emerging plant pathogen. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinovska, E.; Quaglino, F.; Mitrev, S.; Casati, P.; Bulgari, D.; Bianco, P.A. Multiple gene analyses identify distinct Bois noir phytoplasma genotypes in the Republic of Macedonia. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2014, 53, 300–310. [Google Scholar]
- Murolo, S.; Romanazzi, G. In-vineyard population structure of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ using multilocus sequence typing analysis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 31, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglino, F.; Maghradze, D.; Casati, P.; Chkhaidze, N.; Lobjanidze, M.; Ravasio, A.; Passera, A.; Venturini, G.; Failla, O.; Bianco, P.A. Identification and characterization of new ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ strains associated with Bois noir disease in Vitis vinifera L. cultivars showing a range of symptom severity in Georgia, the Caucasus Region. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, E.; Murolo, S.; Ravari, S.B.; Salehi, M.; Romanazzi, G. Molecular Typing of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Iranian Vineyards. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2412–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatti, S. Flora d’Italia; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 2003; Volume I–III. [Google Scholar]
- Marzachì, C.; Alma, A.; d’Aquilio, M.; Minuto, G.; Boccardo, G. Detection and identification of phytoplasmas infecting cultivated and wild plants in Liguria (Italian Riviera). J. Plant Pathol. 1999, 81, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Hiruki, C. Amplification of 16S rRNA genes from culturable and non-culturable mollicutes. J. Microbiol. Meth. 1991, 14, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, C.D.; Schneider, B.; Blomquist, C.L.; Guerra, L.J.; Harrison, N.A.; Ahrens, U.; Lorenz, K.H.; Seemüller, E.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Phytoplasma-specific PCR primers based on sequences of the 16S-23S rRNA spacer region. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-M.; Gundersen, D.E.; Hammond, R.W.; Davis, R.E. Use of mycoplasma-like organisms (MLO) group-specific oligonucleotide primers for nested-PCR assays to detect mixed-MLO infections in a single host plant. Phytopathology 1994, 84, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Marcone, C.; Kampmann, M.; Ragozzino, A.; Lederer, W.; Cousin, M.-T.; Seemüller, E. Characterization and classification of phytoplasmas from wild and cultivated plants by RFLP and sequence analysis of ribosomal DNA. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1997, 103, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialová, R.; Válová, P.; Balakishiyeva, G.; Danet, J.L.; Šafářová, D.; Foissac, X.; Navrátil, M. Genetic variability of stolbur phytoplasma in annual crop and wild plant species in south Moravia. J. Plant Pathol. 2009, 91, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- Romanazzi, G.; Murolo, S.; Feliziani, E. A new approach to manage phytoplasma diseases: Field treatments with resistance inducers to contain grapevine Bois noir. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Plant Health (PLH). Scientific Opinion on the pest categorisation of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panassiti, B.; Hartig, F.; Breuer, M.; Biedermann, R. Bayesian inference of environmental and biotic factors determining the occurrence of the grapevine disease ‘Bois noir’. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveillard, S.; Jollard, C.; Labroussaa, F.; Khalil, D.; Perrin, M.; Desqué, D.; Salar, P.; Razan, F.; Hévin, C.; Bordenave, L.; et al. Contrasting susceptibilities to Flavescence dorée in vitis vinifera, rootstocks and wild Vitis species. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, L.; Romanazzi, G. Seasonal variation of defense-related gene expression in leaves from bois noir affected and recovered grapevines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6628–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endeshaw, S.T.; Murolo, S.; Romanazzi, G.; Neri, D. Effects of Bois noir on carbon assimilation, transpiration, stomatal conductance of leaves and yield of grapevine (Vitis vinifera) cv. Chardonnay. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ember, I.; Bodor, P.; Zsófi, Z.; Pálfi, Z.; Ladanyi, M.; Pásti, G.; Deak, T.; Nyitrainé, D.S.; Bálo, B.; Szekeres, A.; et al. Bois noir affects the yield and wine quality of Vitis vinifera L. cv. ‘Chardonnay’. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 152, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G. Epidemic yellows in vineyards of cv Inzolia in Sicily. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 1985, 24, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Albanese, G.; Davis, R.E.; Granata, G.; Dally, E.L.; Santuccio, T.; Tessitori, M. DNA-based analysis to detect and phytoplasmas in yellows diseased grapevines in Sicily. Petria 1996, 6, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Belli, G.; Bianco, P.A.; Conti, M. Grapevine yellows in Italy: Past, present and future. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, 303–326. [Google Scholar]
- La Rosa, R.; Tessitori, M.; Pacifico, D.; Marzachì, C.; Cirvilleri, G.; Rapisarda, C.; D’Urso, V. Detection and characterization of grapevine phytoplasmas in Sicily (Italy). In Proceedings of the 15th Meeting ICVG 2006, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 3–7 April 2006; pp. 216–217. [Google Scholar]
- La Rosa, R.; Rapisarda, C.; Cavalieri, V.; Pacifico, D.; Tessitori, M. Monitoraggio ed epidemiologia dei giallumi della vite in Sicilia. Petria 2008, 18, 281–283. [Google Scholar]
- Pacifico, D.; Alma, A.; Bagnoli, B.; Foissac, X.; Pasquini, G.; Tessitori, M.; Marzachì, C. Characterization of Bois noir isolates by restriction fragment length polymorphism of a stolbur-specific putative membrane protein gene. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliveri, C.; Pacifico, D.; D′Urso, V.; La Rosa, R.; Marzachi’, C.; Tessitori, M. Bois noir phytoplasma variability in a Mediterranean vineyard system: New plant host and putative vectors. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2015, 44, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murolo, S.; Marcone, C.; Prota, V.; Garau, R.; Foissac, X.; Romanazzi, G. Genetic variability of the stolbur phytoplasma vmp1 gene in grapevines, bindweeds and vegetables. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissac, X.; Carle, P.; Fabre, A.; Salar, P.; Danet, J.L.; Ember, I. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ genome project and genetic diversity in the Euro-Mediterranean basin. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Bois Noir Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 20–21 March 2013; pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Delić, D.; Balech, B.; Radulović, M.; Lolić, B.; Karacić, A.; Vukosavljevic, V.; Đurić, G.; Cvetković, T.J. Vmp1 and stamp genes variability of ‘Candidatus phytoplasma solani’ in Bosnian and Herzegovinian grapevine. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 145, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavec, J.; Križanac, I.; Budinšćak, Ž.; Škorić, D.; Musić, M. Šeruga A case study of FD and BN phytoplasma variability in Croatia: Multigene sequence analysis approach. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 142, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, L.; Riolo, P.; Murolo, S.; Romanazzi, G.; Nardi, S.; Isidoro, N. Genetic variability of stolbur phytoplasma in Hyalesthes obsoletus (Hemiptera: Cixiidae) and its main host plants in vineyard agroecosystems. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Russo, A. Indagini su un giallume epidemico simile alla ‘Flavescenza dorata’. Vignevini 1990, 5, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Palermo, S.; Elekes, M.; Botti, S.; Ember, I.; Alma, A.; Orosz, A.; Bertaccini, A.; Kölber, M. Presence of Stolbur phytoplasma in Cixiidae from Hungarian grapevine growing areas. Vitis 2004, 43, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, L.; Isidoro, N.; Riolo, P. Natural phytoplasma infection of four phloem-feeding auchenorrhyncha across vineyard agroecosystems in central-eastern Italy. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, M.; Jović, J.; Cvrković, T.; Krstić, O.; Trkulja, N.; Toševski, I. Characterisation of a 16SrII phytoplasma strain associated with bushy stunt of hawkweed oxtongue (Picris hieracioides) in south-eastern Serbia and the role of the leafhopper Neoaliturus fenestratus (Deltocephalinae) as a natural vector. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 134, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Izadpanah, K.; Siampour, M. Characterization of a phytoplasma associated with cabbage yellows in Iran. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riolo, P.; Landi, L.; Nardi, S.; Isidoro, N. Relationships among Hyalesthes obsoletus, its herbaceous host plants and Bois noir phytoplasma strains in vineyard ecosystems in the Marche region (central-eastern Italy). Bull. Insectol. 2007, 60, 353–354. [Google Scholar]
- Minuz, R.L.; Isidoro, N.; Casavecchia, S.; Burgio, G.; Riolo, P. Sex-dispersal differences of four phloem-feeding vectors and their relationship to wild-plant abundance in vineyard agroecosystems. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2296–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, A.; Martínez, M.Á.; Laviña, A. Occurrence, distribution and epidemiology of grapevine yellows in Spain. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2000, 106, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafářová, D.; Lauterer, P.; Starý, M.; Válová, P.; Navrátil, M. Insight into epidemiological importance of phytoplasma vectors in vineyards in south Moravia, Czech Republic. Plant Prot. Sci. 2018, 54, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Duduk, B.; Perić, P.; Marčić, D.; Drobnjaković, T.; Picciau, L.; Alma, A.; Bertaccini, A. Phytoplasmas in carrots: Disease and potential vectors in Serbia. Bull. Insect. 2008, 61, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, M.; Raffone, E.; Santonastaso, M.; Priore, R.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, A.; Simeone, A.M. Phytoplasma detection in Empoasca decedens and Empoasca spp. and their possible role as vectors of European stone fruit yellows (16SrX-B) phytoplasma. XIX International Symposium on Virus and Virus-like Diseases of Temperate Fruit Crops-Fruit Tree Diseases. ISHS Acta Hort. 2004, 657, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetto, L.; Bosco, D.; Balestrini, R.; Genre, A.; Fletcher, J.; Marzachì, C. The major antigenic membrane protein of “Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris” selectively interacts with ATP synthase and actin of leafhopper vectors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cultivar | Total Plants (n) | Disease Incidence (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | ||
| Chardonnay | 600 | 5.0 (30) | 35.0 (210) |
| Nero d’Avola | 840 | 1.9 (16) | 4.0 (34) |
| Pinot noir | 840 | 1.4 (12) | 2.1 (18) |
| Total | 2280 | ||
| Sample Type | Grapevine Cultivar | Plants | Molecular Analysis (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Sampled (n) | 16Sr XII | tuf | vmp1 | |
| Grapevine | Chardonnay | 181 | 123 | 113 | 77 |
| Nero d’Avola | 42 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |
| Pinot noir | 29 | 4 | 3 | 2 | |
| Total | 252 | 131 | 120 | 81 | |
| Weed | Beta vulgaris | 4 | - | - | - |
| Convolvulus arvensis | 22 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
| Convolvulus tricolor | 30 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Diplotaxis erucoides | 3 | - | - | - | |
| Epilobium sp. | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | |
| Erigeron bonariensis | 1 | 1 | 1 | na | |
| Helminthotheca aculeata | 17 | 1 | - | - | |
| Malva sylvestris | 5 | - | - | - | |
| Solanum nigrum | 22 | 1 | 1 | - | |
| Total | 110 | 8 | 8 | 4 | |
| Family/Subfamily | Specimen Sample | RFLP Pattern 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Captured | DNA Extraction 1 | 16Sr RNA | tuf | vmp1 | ||
| Single (no.) | Pools (no.) | |||||
| Cicadellidae | ||||||
| Agalliinae | ||||||
| Anaceratagallia laevis (Ribaut, 1935) | 12 | - | 2 | 16Sr XII-A (1) | type-b (1) | - |
| Austroagallia sinuata (Mulsant and Rey, 1855) | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Deltocephalinae | ||||||
| Euscelis lineolatus Brullé, 1832 | 3 | 3 | - | - | - | - |
| Fieberiella florii (Stål, 1864) | 5 | 5 | - | - | - | - |
| Grypotes staurus Ivanoff, 1885 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| Neoaliturus fenestratus (Herrich-Schäffer, 1834) | 216 | 216 | - | 16Sr XII-A (3) | type-b (2) | V9 (2) |
| Psammotettix striatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Selachina apicalis (Matsumura, 1908) | 1 | 1 | - | 16Sr XII-A (1) | type-b (1) | - |
| Typhocybinae | ||||||
| Empoasca alsiosa Ribaut, 1933 | 91 | - | 18 | - | - | - |
| Empoasca decipiens Paoli, 1930 | 132 | - | 26 | 16Sr XII-A (1) | type-b (1) | V24 (1) |
| Empoasca vitis (Goethe, 1875) | 494 | - | 98 | 16Sr XII-A (1) | - | - |
| Eupteryx rostrata Ribaut, 1936 | 82 | - | 16 | - | - | - |
| Hauptidia provincialis Ribaut, 1931 | 30 | - | 6 | 16Sr XII-A (1) | na | na |
| Jacobiasca lybica (Bergevin and Zanon, 1922) | 48 | - | 9 | - | - | - |
| Liguropia juniperi (Lethierry, 1876) | 11 | - | 2 | - | - | - |
| Zygina rhamni Ferrari, 1882 | 184 | - | 37 | 16Sr XII-A (4) | type-b (2) | V4 (1) |
| Zyginidia serpentina (Matsumura, 1908) | 246 | - | 49 | 16Sr XII-A (1) | type-b (1) | na |
| Zyginidia servadeii Vidano, 1982 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Dictyopharidae | ||||||
| Dictyopharinae | ||||||
| Dictyophara europaea (Linnaeus, 1775) | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 1563 | 233 | 263 | 13 | 8 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conigliaro, G.; Jamshidi, E.; Lo Verde, G.; Bella, P.; Mondello, V.; Giambra, S.; D’Urso, V.; Tsolakis, H.; Murolo, S.; Burruano, S.; et al. Epidemiological Investigations and Molecular Characterization of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Grapevines, Weeds, Vectors and Putative Vectors in Western Sicily (Southern Italy). Pathogens 2020, 9, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110918
Conigliaro G, Jamshidi E, Lo Verde G, Bella P, Mondello V, Giambra S, D’Urso V, Tsolakis H, Murolo S, Burruano S, et al. Epidemiological Investigations and Molecular Characterization of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Grapevines, Weeds, Vectors and Putative Vectors in Western Sicily (Southern Italy). Pathogens. 2020; 9(11):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110918
Chicago/Turabian StyleConigliaro, Gaetano, Elham Jamshidi, Gabriella Lo Verde, Patrizia Bella, Vincenzo Mondello, Selene Giambra, Vera D’Urso, Haralabos Tsolakis, Sergio Murolo, Santella Burruano, and et al. 2020. "Epidemiological Investigations and Molecular Characterization of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Grapevines, Weeds, Vectors and Putative Vectors in Western Sicily (Southern Italy)" Pathogens 9, no. 11: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110918
APA StyleConigliaro, G., Jamshidi, E., Lo Verde, G., Bella, P., Mondello, V., Giambra, S., D’Urso, V., Tsolakis, H., Murolo, S., Burruano, S., & Romanazzi, G. (2020). Epidemiological Investigations and Molecular Characterization of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ in Grapevines, Weeds, Vectors and Putative Vectors in Western Sicily (Southern Italy). Pathogens, 9(11), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110918






