An Ultrasonic Vibration Scratch Tester for Studying the Scratch Characteristics of Materials under Ultrasonic Vibration Contact Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Ultrasonic Vibration Scratch Tester
3. Experiments and Discussion
3.1. Performance of the Ultrasonic Vibration Platform
3.2. UVAS Testing of AL1050
4. Conclusions
- (1)
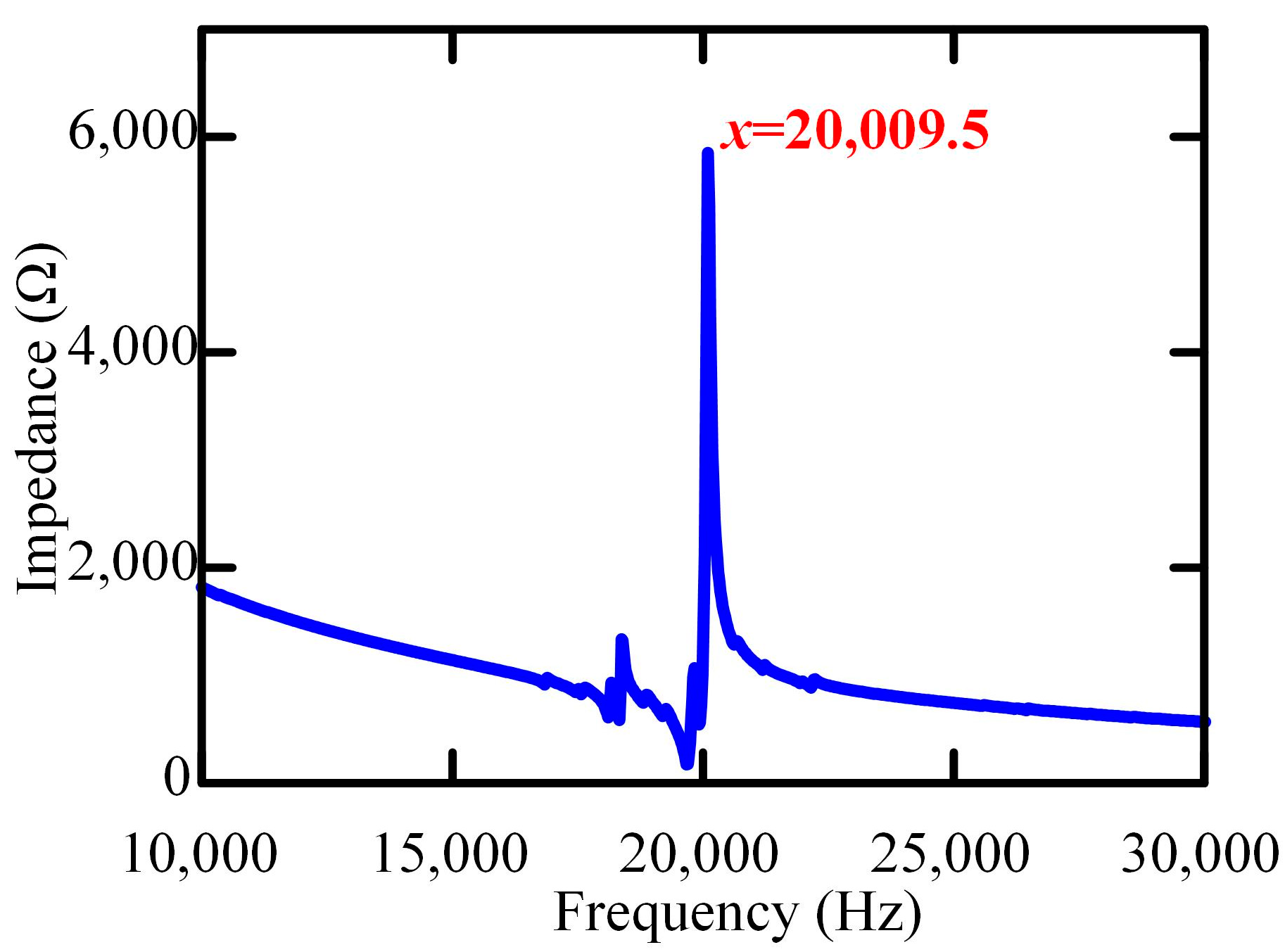
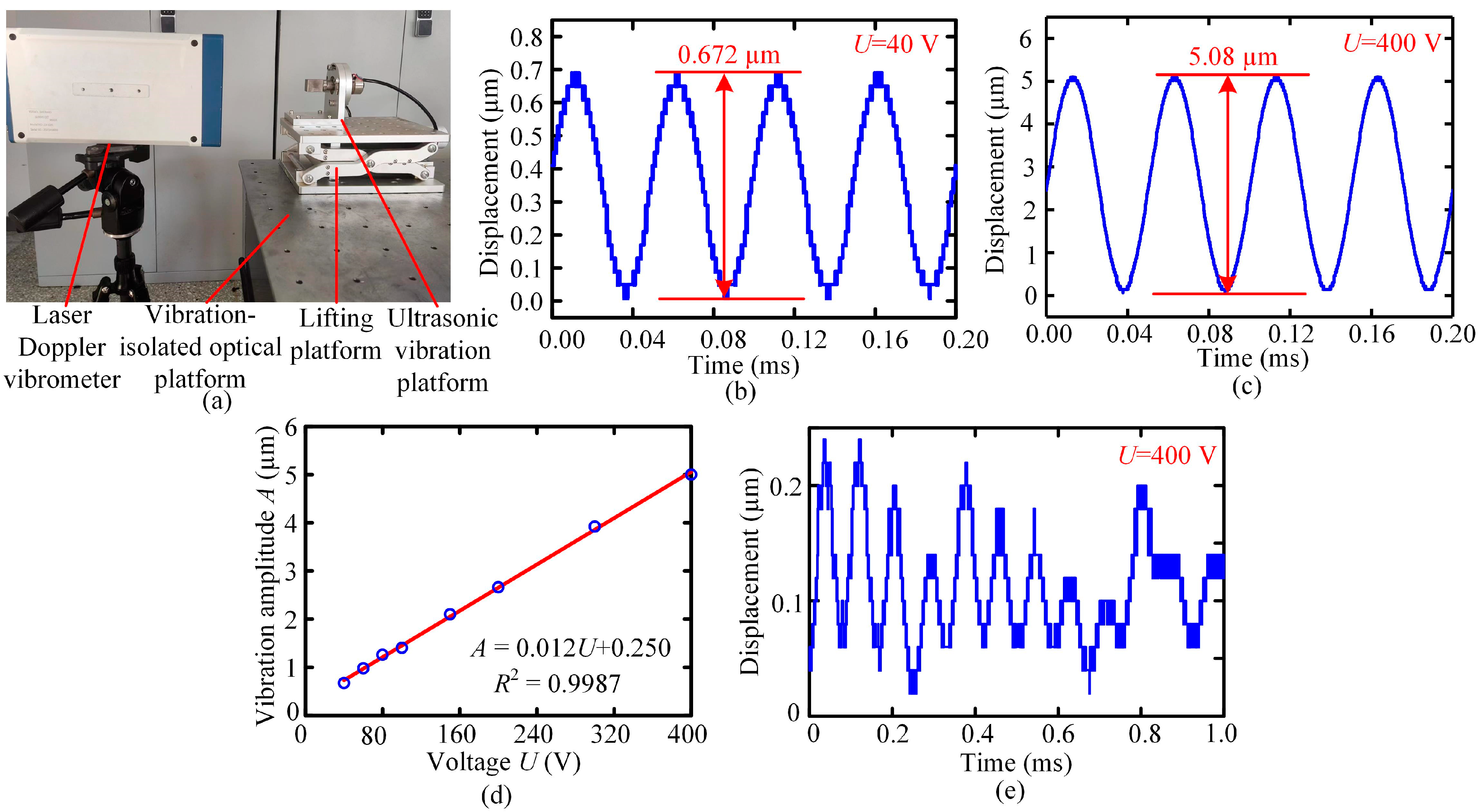
- The ultrasonic vibration platform could generate stable ultrasonic vibration at a frequency of 20 kHz within the amplitude range from 0.73 µm to 5.08 µm. The vibration amplitude had a good linear relationship with the excitation voltage.
- (2)
- The ultrasonic vibration scratch tester could perform ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratch (UVAS) testing of materials and simultaneously measure the normal force and lateral force.
- (3)
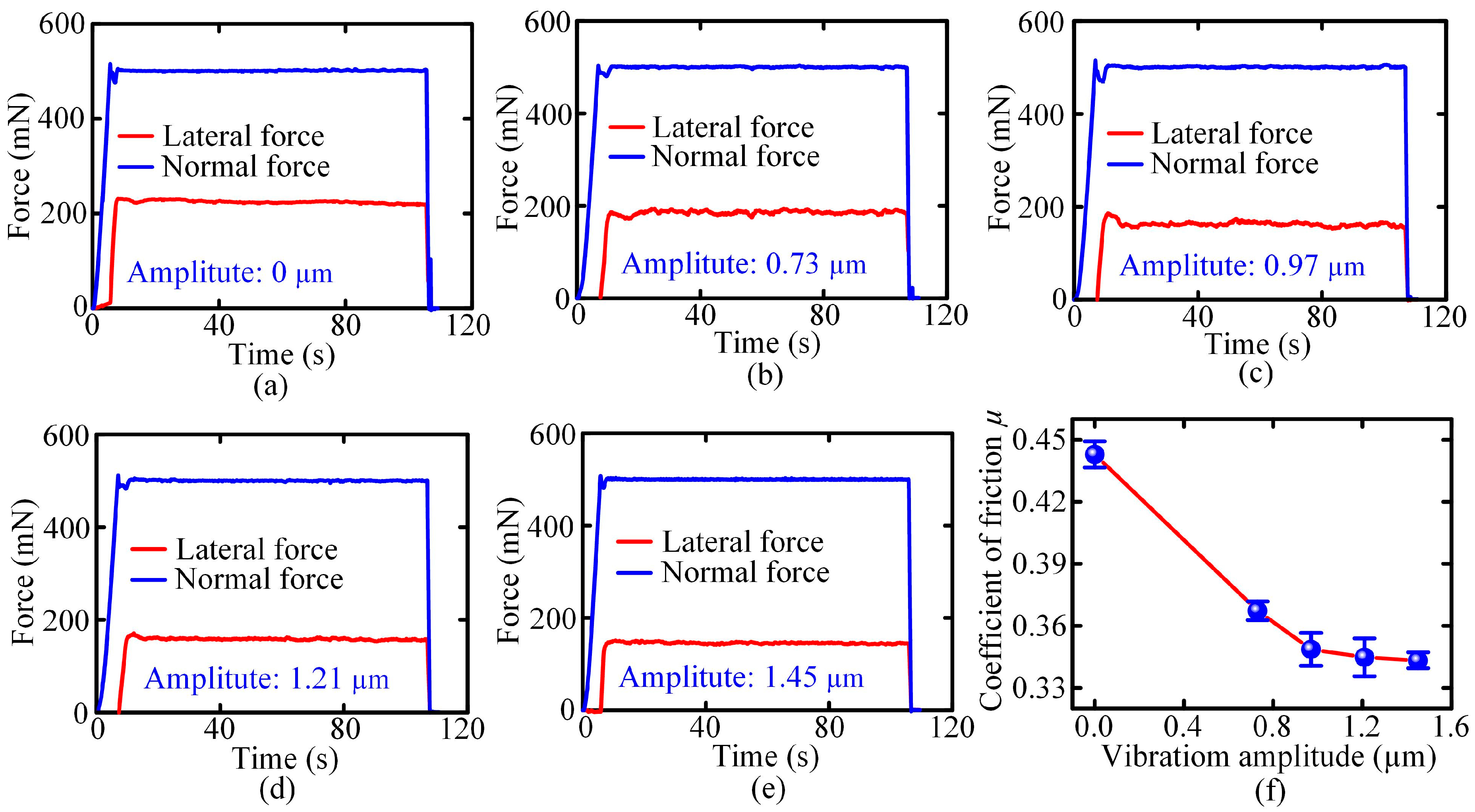
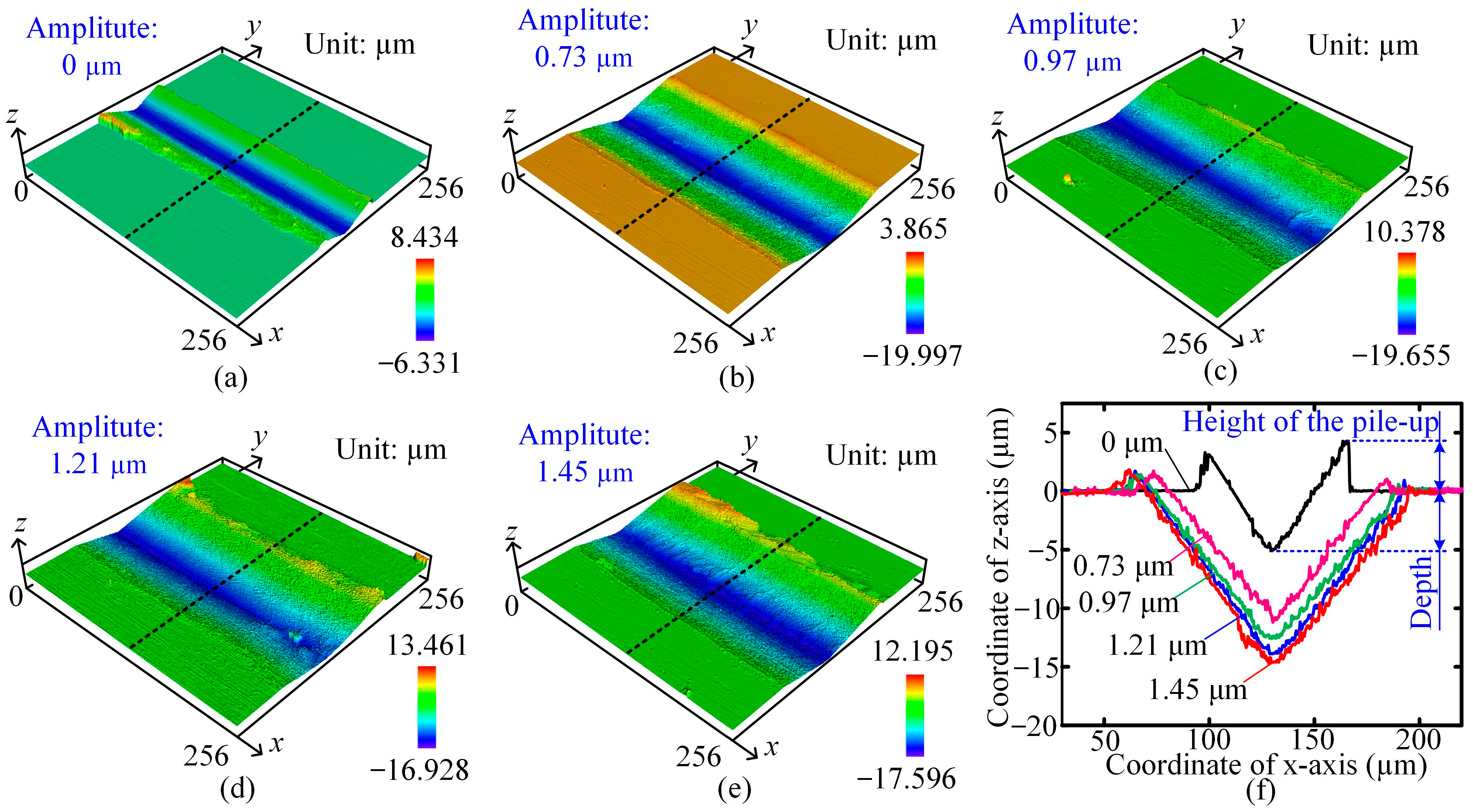
- Comparative experiments of AL1050 indicate that compared to conventional scratch (CS) testing, the introduction of ultrasonic vibration reduced the coefficient of friction, increased the depth of the residual scratch, and significantly reduced the height of the pile-up. These kinds of effects were dependent on the vibration amplitude. For the vibration amplitude of 1.45 μm, the coefficient of friction decreased by approximately 22.5%, and the depth of the residual scratch increased by approximately 175%.
- (4)
- SEM morphologies showed different material removal mechanisms of AL1050, plowing in the CS test, and cutting in the UVAS test. In addition, oxidation of the AL1050 occurred in the UVAS test, contributing to the different scratch characteristics listed above.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azarhoushang, B.; Tawakoli, T. Development of a novel ultrasonic unit for grinding of ceramic matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 57, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M. Effect of machining parameters in ultrasonic vibration cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babitsky, V.I.; Mitrofanov, A.V.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Ultrasonically assisted turning of aviation materials: Simulations and experimental study. Ultrasonics 2004, 48, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teimouri, R.; Amini, S.; Lotfi, M.; Alinaghian, M. Sustainable drilling process of 1045 steel plates regarding minimum energy consumption and desired work quality. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2019, 25, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zou, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X. Research on modeling of grinding force in ultrasonic vibration–assisted grinding of 304 stainless steel materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 3201–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zou, P.; Wei, S.; Fang, R.; Fang, L. Research on the formation mechanism of surface morphology in three-excitation ultrasonic spatial vibration-assisted turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 6851–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, B.; Yue, Y.; Ding, W.; Xu, J.; Guo, G. Developing a novel radial ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding device and evaluating its performance in machining PTMCs. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2023, 36, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, G.; Chen, B.; Zhuo, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, Y. Surface formation modeling and surface integrity research of normal ultrasonic assisted flexible abrasive belt grinding. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 80, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Geng, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X. Cutting performance and surface integrity for rotary ultrasonic elliptical milling of Inconel 718 with the ball end milling cutter. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 319, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujana, J.; Rivero, A.; Celaya, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Analysis of ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti6Al4V. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya, A.; Campa, F.J.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Marina, D.; Chinesta, F.; Chastel, Y.; El Mansori, M. The Effects of Ultrasonic Vibration Parameters on Machining Performance in Turning of Mild Steels. Int. Conf. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 1315, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Celaya, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Campa, F.J.; Lamikiz, A. Ultrasonic assisted turning of mild steels. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2010, 37, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; Veiga, F.; de Lacalle, L.N.L.; Polvorosa, R.; Lutze, S.; Wretland, A. Effects of Ultrasonics-Assisted Face Milling on Surface Integrity and Fatigue Life of Ni-Alloy 718. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 2, 5076–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Wu, H.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H. An in-situ scratch tester under the confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Vacuum 2024, 222, 113033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagała, I.; Gil, L.; Firlej, M.; Pieniak, D.; Selech, J.; Romek, D.; Biedziak, B. Statistical Comparison of the Hardness and Scratch-Resistance of the PMMA Polymers Used in Orthodontic Appliances. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2020, 14, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamplade, K.; Biermann, D. Examination of the Material Removal of unreinforced, thermoplastic Polymers by Scratch Tests. Prod. Eng. 2019, 13, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huang, H. A Novel Rotation-Structure Based Stick-Slip Piezoelectric Actuator with High Consistency in Forward and Reverse Motions. Actuators 2021, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, J.; Guo, W.; Huang, H.; Fan, H.; Liu, J.; Li, T. Design and Analysis of a Stepping Piezoelectric Actuator Free of Backward Motion. Actuators 2021, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Yu, D.; Chen, M.; Geier, N.; El Mansori, M. Investigation of material removal mechanisms and ductile-brittle transition zone of zirconia ceramics sintered at various temperatures. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 125, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; Wu, X.; Jiang, F.; Fang, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, C. Material removal and surface damage mechanisms in micro drilling of Nd:YAG material. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 90, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Piao, Y.; Meng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, F. Anisotropy dependence of material removal and deformation mechanisms during nanoscratch of gallium nitride single crystals on (0001) plane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 578, 152028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yan, J. Deformation behaviour of soft-brittle polycrystalline materials determined by nanoscratching with a sharp indenter. Precis. Eng. 2021, 72, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Yang, M.; Xia, K. Towards understanding the material removal mechanism on the effect of ultrasonic vibration and anisotropy for unidirectional CFRP by scratching. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 324, 118250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Shao, W.; Wen, J.; Huang, W. Study on scratch hardness in ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratching based on instantaneous contact analysis. Wear 2023, 528–529, 204991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Dong, Z.; Kang, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J. Analysis of material removal behavior in ultrasonically assisted scratching of RB-SiC from energy aspects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2257–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, H. Development of a Vibration-Assisted Micro/Nano Scratch Tester for Evaluating the Scratch Behaviors of Materials Under Vibration Environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Lu, X. Prediction and measurement for grinding force in wafer self-rotational grinding. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 258, 108530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J. Comparison of Vibration-Assisted Scratch Characteristics of SiC Polytypes (3C-, 4H- and 6H-SiC). Micromachines 2022, 13, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Y.; Yang, W.J.; Ma, L.L. Advances in Theoretical Investigation of Work Hardening for Metal Cutting. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 217–219, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Wen, D.H.; Yuan, J.L. PCBN Tool Wear Mechanism in Hard Turning Hardened Bearing Steel. Key Eng. Mater. 2006, 315–316, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Huang, H. An Ultrasonic Vibration Scratch Tester for Studying the Scratch Characteristics of Materials under Ultrasonic Vibration Contact Status. Actuators 2024, 13, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070262
Huang Y, Wu H, Yao Y, Zhao H, Huang H. An Ultrasonic Vibration Scratch Tester for Studying the Scratch Characteristics of Materials under Ultrasonic Vibration Contact Status. Actuators. 2024; 13(7):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070262
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yaming, Haoxiang Wu, Yuan Yao, Hongwei Zhao, and Hu Huang. 2024. "An Ultrasonic Vibration Scratch Tester for Studying the Scratch Characteristics of Materials under Ultrasonic Vibration Contact Status" Actuators 13, no. 7: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070262
APA StyleHuang, Y., Wu, H., Yao, Y., Zhao, H., & Huang, H. (2024). An Ultrasonic Vibration Scratch Tester for Studying the Scratch Characteristics of Materials under Ultrasonic Vibration Contact Status. Actuators, 13(7), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070262






