Abstract
Cancer cachexia is a multifactorial wasting syndrome associated with skeletal muscle and adipose tissue loss, as well as decreased appetite. It affects approximately half of all cancer patients and leads to a decrease in treatment efficacy, quality of life, and survival. The human microbiota has been implicated in the onset and propagation of cancer cachexia. Dysbiosis, or the imbalance of the microbial communities, may lead to chronic systemic inflammation and contribute to the clinical phenotype of cachexia. Though the relationship between the gut microbiome, inflammation, and cachexia has been previously studied, the oral microbiome remains largely unexplored. As the initial point of digestion, the oral microbiome plays an important role in regulating systemic health. Oral dysbiosis leads to the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and an imbalance in natural flora, which in turn may contribute to muscle wasting associated with cachexia. Reinstating this equilibrium with the use of prebiotics and probiotics has the potential to improve the quality of life for patients suffering from cancer-related cachexia.
1. Introduction
Only one of every two cells in the human body is human [1]. Of the remaining non-human cells, a significant portion is made up of bacteria and fungi. With each individual harboring 10 to 100 trillion microbial cells, these microorganisms play vital roles in maintaining a state of homeostasis [2]. The oral cavity contains the largest and most diverse collection of microorganisms in the body, second only to the gut microbiome [3,4]. Along with viruses and fungi, the oral microbiome is made up of over 700 different bacterial species that reside in the hard and soft palate, floor of the mouth, lips, tongue, teeth, gingiva, and the buccal mucosa [5]. At equilibrium, these microbiota function symbiotically with the human host. The oral microbiome contributes to metabolic, physiologic, and immunological functions that maintain the balance between human health and disease. These functions include digestion, nutrition, regulation of immune response, and prevention of disease-promoting microorganisms through maintenance of a mucosal barrier [6].
The microbial community of the oral cavity is complex and can be separated into core and variable microbiomes [4]. The core microbiome is composed of microflora that can be present throughout multiple organs in a person’s body when healthy [7]. This component of the oral microbiome is typically conserved across individuals [7]. For those in good states of health, the core microbiome should approximate the oral microbiome [8]. The concept of the core microbiome was explored in a study by Zaura et al. who capitalized on advances in sequencing techniques by performing 454 pyrosequencing of the oral microbiome in a group of healthy individuals. They found that even across several intra-oral microbial subcommunities including the dental surface, cheek, hard palate, tongue, and saliva, bacterial sequences of the oral microflora were for the most part homogenous [8]. Bik et al. also conducted a similar study in 2010 by amplifying bacterial sequences sourced from 26 distinct oral anatomic locations from 10 healthy individuals belonging to four discrete ethnicities [9]. They too, found identical bacterial sequences between their patients representative of the core microbiome. Specifically, they found evidence of the following genera’s presence in all their patients’ oral microbiomes: Actinomyces, Atopobium, Corynebacterium, Rothia, Campylobacter, Cardiobacterium, Haemophilus, Neisseria, Tm7, Fusobacterium, Bergeyelia, Capnocytophaga, Prevotella, Granulicatella, Streptococcus, and Veillonella. Notably, Bik et al. also found interindividual differences that were suggestive of the simultaneous presence of a distinct variable microbiome more specific to the individual.
The variable microbiome underlies the diversity in the oral microbiome seen between individuals [7]. This component is reflective of unique lifestyles, environments, and one’s own genotype [7].
The diet plays a prominent role in the variable oral microbiome composition [10]. Kato et al. explored the relationship between dietary composition and the oral microbiome through high-throughput 16S rRNA metagenomic sequencing. In their study, they identified correlations between alpha diversity indices (measuring variability between individuals) and saturated fatty acid [11]. Their sequencing analysis revealed that the abundance of betaproteobacteria and fusobacteria in the oral cavity was associated with dietary saturated fatty acid content. Additionally, they found that dietary glycemic load was positively correlated with Lactobacillaceae populations. A separate study examined the impact of vegan diets on the salivary microbiota. Broadly, Hansen et al. found significant differences between the oral microbiome of vegans and omnivores [12]. Analysis of patients’ primary dietary components showed that intake of fiber, medium chain fatty acids, piscine omega-11 mono-unsaturated fatty acids, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids was associated with salivary microbiota diversity. Dietary fiber was also associated with increased populations of Capnocytophaga and Neisseria subflava [12]. Together, these studies advocate for the recognition of another highly complex influence that the diet has on human health.
Ingestion of alcoholic beverages has also been postulated to have effects on the oral microbiome. Fan et al. sought to determine if differences in the oral flora existed between persons with different levels of alcohol use by performing 16S rRNA gene sequencing in 1044 American adults [13]. Between non-drinkers and heavy drinkers, the authors observed a significant difference in alpha and beta diversity. Furthermore, they noted significant differences in oral flora composition. Actinomyces, Leptotrichia, Cardiobacterium, and Neisseria were found to be greater in abundance in the heavy drinker group. Organisms belonging to the Lactobacillales order were found to be decreased in abundance when comparing heavy drinkers to non-drinkers. These differences persisted even after controlling for smoking status. Paralleling the findings of this study was a separate study of 150 healthy Chinese subjects comparing the microbiomes of those who drank alcohol and those who did not. Much like Fan et al.’s results, they also observed greater alpha diversity in alcohol drinkers and differences in the overall oral microbiome between drinkers and non-drinkers [14]. Their sequencing analysis uncovered that alcohol drinkers had greater organism populations of the Prevotella and Moryella genus as well as Prevotella melaninogenica and Prevotella tannerae species. On the other hand, Lautropia, Haeophilus, and Porphyromonas genera were diminished in the alcohol drinkers’ group. Decreased enrichment of Haemophilus parainfluenza populations was also observed. Interestingly, the enrichment of genera observed in the alcohol drinkers’ group was positively correlated with enhancement of anaerobic metabolic pathways and negatively correlated with the aerobic pyruvate metabolic pathway.
Cigarette smoking represents another environmental factor affecting the oral microbiome. A recent study of Jordanian subjects determined the existence of differences in the oral microbial communities of smokers and non-smokers. They specifically observed significant elevations in Streptococcus, Prevotella, and Veillonella genera and depression of Neisseria populations [15]. A similar study in the Chinese population reproduced the findings of enriched populations of Actinomyces and Veillonella in smokers [16]. The same experiment also found connections between cigarette use and Moryella, Bulleidia, and Moraxella genera as well as Prevotella melaninogenica, Rothia dentocariosa, Prevotella pallens, Bulleidia moorei, Rothia aeria, Actinobacillus parahaemolyticus, and Haemophilus parainfluenzae species. Further studies have added Streptococcus sobrinus and Eubacterium brachy as taxa also linked with positive smoking status [17]. These oral microbiome differences have led researchers to suggest the possible existence of a microbial signature able to differentiate smokers from non-smokers [15].
The increasing awareness of health disparities has led to the theorization of possible oral microbiome differences in persons of different socioeconomic statuses. A study conducted in a Danish cohort set out to test this hypothesis. To do this, Belstrøm et al. stratified patients into different socioeconomic statuses by scoring patients’ municipality of residence on various socioeconomic measures [17]. They then assessed saliva samples of their patients with a high throughput-based microarray platform. Bacterial probe assessment demonstrated significant differences in both presence and abundance of bacterial organisms between low and high socioeconomic status groups. Veillonella parvula taxa, Veillonella atypica taxa and Streptococcus parasanguinis clusters were highlighted to be different [17]. These effects of socioeconomic status can even be seen as early as five years of age. Boyce et al. studied dental health in kindergarten aged children of different upbringings residing in the San Francisco area to determine if a relationship between family socioeconomic status and oral microbiome composition existed [18]. Both socioeconomic status, measured by the parent-reported highest level of household education, and financial stress, measured by parental response to a 4-item questionnaire, were collected. These two variables were not surprisingly inversely related with each other. Importantly, socioeconomic status was associated with greater populations of cariogenic bacteria [18].These studies demonstrating differing microbiome composition in subjects of distinct socioeconomic classes offer a springboard for future investigations looking to elucidate the mechanisms of healthcare disparities.
Genetics are a non-modifiable factor known already to affect the gut microbiome with recent studies demonstrating similar effects on the oral microbiome as well. Characterization of monozygotic and dizygotic twin biofilm flora showed that oral microbiomes of monozygotic twins were more similar than those of dizygotic twins as measured by Bray–Curtis distances [19]. Highly hereditable oral flora identified in this study included Prevotella pallens, Veillonella taxon, Pasteurellaceae, Corynebacterium durum, Leptotrihcia, and Abiotrophia. A Colorado Twin Registry study produced similar results as they found greater beta diversity in dizygotic or unrelated individuals compared to monozygotic twins [20]. GWAS analysis was also performed and identified two loci, one located in proximity to the IMMPL2 gene on chromosome 7 and one near the INHBA0AS1 gene on chromosome 12, with the potential to determine oral microbiome phenotypes. Certainly, as demonstrated in these studies, understanding of both environment and genetic factors is critical in consideration of the variable microbiome.
When the balance of disease-preventing microbiota is tipped toward a disease-promoting microbial environment, previously inert bacteria may contribute to pathologic host response. Dysbiosis occurs when there is a shift in the composition or abundance of microbial communities deviating from homeostasis [21]. In this state, previously beneficial bacteria may lead to chronic and systemic inflammation in the body, resulting in disastrous health consequences. Oral dysbiosis has been implicated in numerous inflammatory diseases such as periodontitis, atherosclerosis, obesity, and cancer [22,23,24,25]. Although a direct mechanism has not been established between dysbiosis and the development of cancer, studies have continuously found that organisms from the oral cavity can influence a tumorigenic and inflammatory state [21,26]. This association has been studied extensively in malignancies of the abdominal cavity. In pancreatic cancer patients, increased populations of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Enterobacteriaceae, Lachnospiraceae G7, Bacteroidaceae, Granulicatella. adiacens, Leptotrichina, Streptococcus, and Staphylococcaceae have been observed in the oral microbiome [27]. Colorectal cancer, another abdominal malignancy, has been linked to greater prevalence of Peptostreptococcus, Parvimonas, and Fusobacterium [28]. Even precancerous gastric cancer lesions have been demonstrated by Salazar et al. to be associated with Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, Treponema denticola and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans colonization of dental plaque [29].
Cancer cachexia is a clinical manifestation of the inflammatory host response to carcinogenesis. It is a multifactorial syndrome resulting in skeletal muscle and adipose wasting, as well as anorexia [5]. Cancer cachexia’s reach can even extend beyond the musculoskeletal system to involve the heart, leading to cardiac muscle wasting and ultimately heart failure [30,31]. It is estimated that 2 million people die annually as a consequence of cancer cachexia [32]. Half of all cancer patients will eventually develop cancer cachexia and 20% will die as a result of this syndrome [33]. Research into therapeutic options for cancer cachexia is ongoing, with no cure or effective treatment yet found [34]. Cachectic patients are often left fatigued as well as immunosuppressed. This state leaves patients unable to tolerate chemotherapy and renders them poor candidates for surgical resection, thus contributing to advancement of the cancer [35]. This vicious cycle eventually leads to a lower quality of life and overall survival [36,37].
The immunosuppression that cachectic patients experience is due to subdued nutritional intake as well as a heightened inflammatory state. Cancer cachexia has been directly associated with the cytokines involved in the inflammatory response. In a study by Riccardi et al., patients with cancer cachexia were found to have increased levels of circulating TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 when compared with non-cachectic cancer patients and controls [38]. CRP, IL-1, IFN-γ, and proteolysis inducing factor (PIF) have also been found to be increased in cachectic patients [39]. Activation of metabolic pathways by these aforementioned molecules then sets in motion the processes that directly underlie cancer cachexia [33]. The heightened inflammatory state present in cachectic patients is also mediated by reactive oxygen species. In cancer patients, elevated levels of reactive oxygen species are produced by increased uncoupling of the electron transport chain and resulting loss of mitochondrial membrane potential [40]. TNF-α driven upregulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production as well as diminished antioxidant presence in muscle cells also contribute to the high levels of oxidative stress present in cancer patients [40]. Ensuing downstream upregulation of Ubiquitin Proteasome System activity, Calpain expression, and autophagic activation then proceed to induce muscle wasting [40,41,42,43].
Additionally, cancer cachexia has been associated with dysregulation of brain hypothalamic signals, leading to decreased appetite and metabolic changes which can contribute to lower quality of life [38]. Specifically, Braun et al., identified that the inflammatory marker IL-1 affects regulation of energy homeostasis in the central nervous system, leading to decreased food intake and anorexia [44]. These results indicate that central IL-1 production leads to malnutrition and increased resting energy expenditure that ultimately results in skeletal muscle catabolism [44]. Moreover, the resulting weight loss and fatigue from cancer cachexia devastates patient well-being. This relationship was highlighted in a secondary analysis of 405 cancer patients in a Swedish outpatient palliative care program [45]. In this analysis, Wallengren et al. found that weight loss above 2%, fatigue, BMI less than 20 kg/m2, and a CRP greater than 10 mg/L were significantly associated with adverse quality of life [45]. Weight loss above 2% and fatigue were additionally associated with shorter survival.
Currently, attempts to modify and increase nutritional intake are the primary treatment for cancer cachexia [36]. However, the use of nutritional supplements has not been shown to have clinical benefits of weight gain or improved function [46]. Palliative care and counseling is used secondarily to counteract weight loss and to reduce distress among the patient and their family. Pharmacologic therapies such as appetite stimulants, anabolic steroids, ghrelin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, psychiatric drugs, and thalidomide are being studied to treat cachexia, although side effects are prevalent and effectiveness is limited [46]. Interventions involving physical activity have also been investigated as a potential avenue of therapy in cancer cachexia. Yet, no clear benefit has been determined. While one randomized controlled study in cachectic pancreatic cancer patients concluded benefits of resistance training in the aspects of muscle strength, mobility and lean body mass, results of a meta-analysis were unable to draw conclusions in regard to efficacy or safety [47]. Clinical studies with promising results and minimal side effects are rare but generate excitement. One such study by Maccio et al. treated cachectic signs and symptoms with a combination of megestrol acetate, EPA, L-carnitine, and thalidomide. This combination was shown to improve appetite and performance status without increased risk of toxicity when compared to patients taking monotherapies [48]. While these therapies continue to be explored further, the only true cure for cachexia is to cure the underlying disease; a task difficult in late stage or advanced solid tumor cancer patients.
Given the limited treatment options available for cancer cachexia, additional research is needed to elucidate potential therapeutic targets. While the relationship between the gut microbiome and inflammatory response has been previously investigated, research involving the oral microbiome remains sparse. This review highlights the importance of the oral microbiome in systemic inflammation and in cancer cachexia. It further explores potential interventions for patients suffering from cancer cachexia.
2. The Oral Microbiome and Inflammation
Inflammation is intricately involved in the growth and development of malignancies. In addition to the activation and recruitment of the innate and adaptive immune system, inflammation is critical for tissue repair and regeneration [49]. As cancer progresses, local and systemic inflammation become dysregulated, promoting both tumorigenesis as well as cancer-related cachexia. The inflammatory response consists of a combination of different immune mediators, with cytokines contributing to the phenotypic changes seen in tissues [50,51].
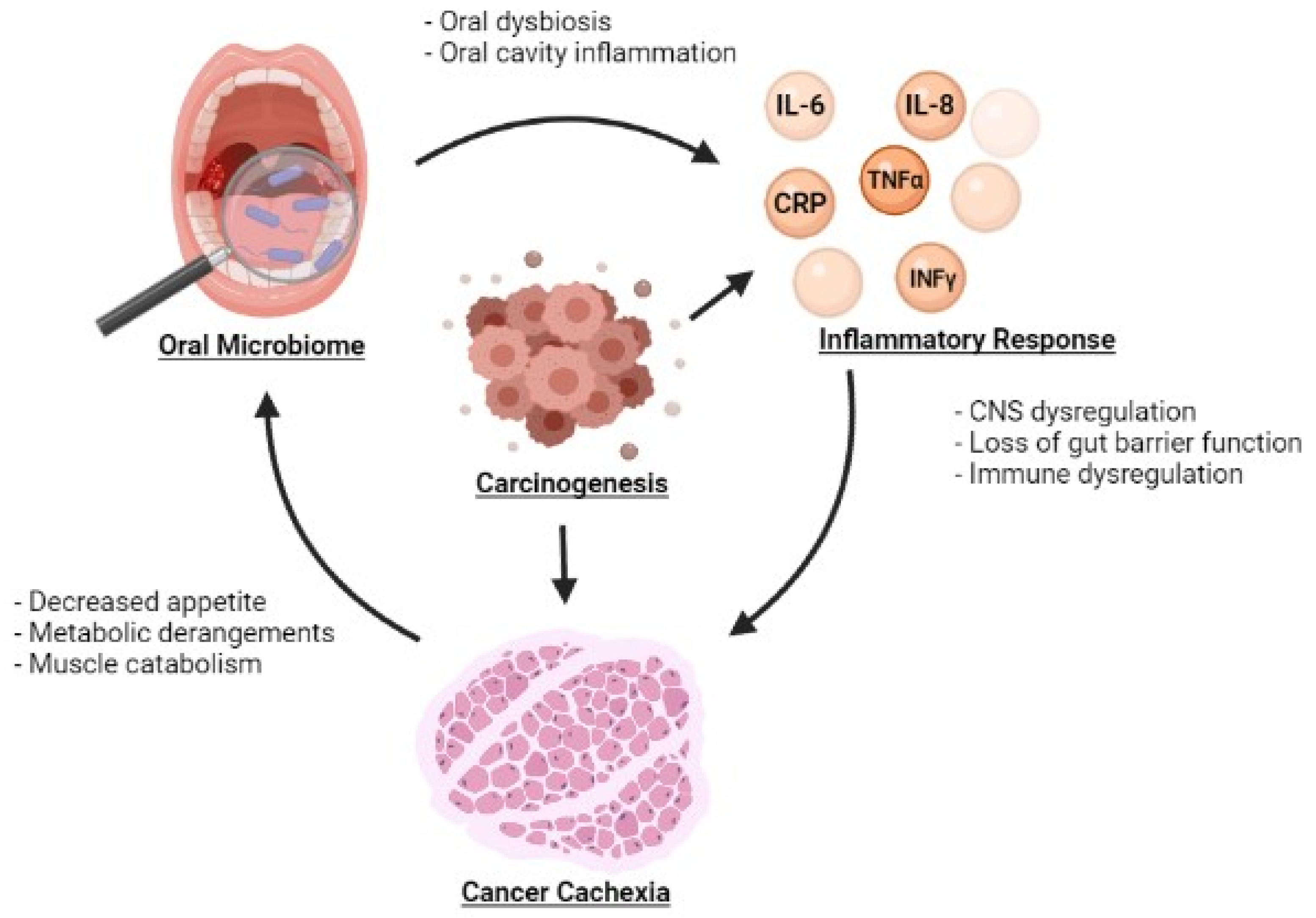
Oral dysbiosis is also implicated in systemic inflammation (Table 1). Changes in the oral microbiome may facilitate the development of systemic inflammation but also may be exacerbated by systemic inflammation, potentially leading to a vicious cycle (Figure 1).uIn a study by Sarkar et al., the oral microbiome was compared to the salivary levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8. Bacterial Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) belonging to Prevotella, SR1 and Ruminococcaceae were found to be associated with IL-1β whereas Prevotella and Granulicatella were associated with IL-8 [52]. Prevotella, in particular, is notable du eto its involvement in inflammatory diseases such as periodontitis, bacterial vaginosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and metabolic diseases [53]. The relationship between diurnal fluctuations in inflammatory markers and the oral microbiome was also explored in this study. Correlations in diurnal fluctuations were also observed with IL-1β and Prevotella, IL-6 and Prevotella, IL-6 and Neisseria, and IL-6 and Porphyromonas. Atarashi et al. separately demonstrated that oral bacteria were associated with the activation of a pro-inflammatory milieu by inoculating mice with the oral bacteria of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Significant inflammation was observed via activation of the Th1 immune signaling pathway [54]. The impact of the oral microbiome on systemic inflammation may also be mediated by bacterial products. Bacterial extracellular vesicles carry a variety of substrates including microbe-associated molecular patterns and molecules sourced from the bacteria where they were generated. Depending on the specific bacteria that these vesicles come from, their contents can exert various effects on the host including the activation of immunostimulatory pathways [55,56]. As such, these microbial products may provide another mechanism by which oral dysbiosis causes systemic inflammation. Kim et al. examined this process by studying bacterial extracellular vesicles derived from periodontal pathogens and oral commensal bacterium [57]. They hypothesized that these bacterial products could influence the differentiation of osteoclasts, a cell type derived from the macrophage-monocyte cell lineage [58]. Extracellular vesicles from the periodontal pathogens Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia as well as from the oral commensal bacterium Streptococcus oralis induced osteoclastogenesis through activation of Toll-like Receptor 2. Porphyromonas gingivalis uniquely has also been observed to produce a proinflammatory response through the same receptor pathway [59]. Indeed, these studies depict an interwoven relationship between dysbiosis and the onset of inflammation, a cornerstone to the beginning of systemic consequences.

Table 1.
The Oral Microbiome and Inflammation.
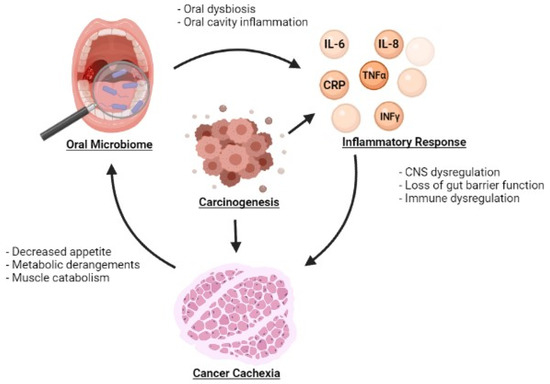
Figure 1.
Relationship between the oral microbiome, inflammatory markers, and development of cancer cachexia.
The inverse of this cycle may also take place when systemic disease precipitates an inflammatory state. An example is seen in the relationship between diabetes and periodontitis. Approximately 60% of patients with Type 1 Diabetes have periodontitis compared to only 15% found in a control population of patients without Type 1 Diabetes [60,61]. The pathogenesis of this may be explained by the diabetes-induced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-6 [62,63]. This cytokine production triggers a systemic innate immune response that involves the oral cavity. Over time, this can alter the natural flora of the oral microbiome, resulting in dysbiosis.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has similarly been examined in relation to inflammatory response and its effect on the oral microbiome. Jensen et al. first established this in the 1990 s by comparing bacterial loads in SLE and healthy subjects, ultimately finding that SLE patients had higher bacterial loads [64]. A study by Corrêa et al. built on these findings by sampling subgingival dental plaques of 52 SLE and 52 control patients to interrogate the relationship between SLE and subgingival bacterial community composition. They found that Prevotella nigrescens, Prevotella oulorum, Prevotella oris and Selenomomonas noxia species were enriched in healthy periodontal sites of SLE patients compared to non-SLE patients. At periodontitis sites, SLE patients exhibited significantly greater abundance of P.ouloorum, Fretibacterium fastidiosum and Anaeroglobus germinatusin in addition to Fusobacterium taxas 360 450 and TM7 taxon 437 [65].
Associations between the oral microbiome and mental health were recently discovered [66]. Using saliva samples obtained from students at the University of Florida, Ahrens et al. sought to establish a connection between salivary microbiota and recent suicidal ideation. Here, Alloprevotella rava was found in significantly higher relative abundance in those students with no suicidal ideation, particularly in the absence of the minor allele “G” at SNP rs10437629. Alloprevotella rava ferments glucose to succinate which is known to improve glucose oxidation in the brain and brain metabolism after injury [67,68,69,70,71].
The systemic inflammation of cancer cachexia is a result of similar mechanisms. Upregulation IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and IFN-γ may occur as a response to homeostatic shifts in the oral microbiota and lead to further amplification of inflammatory cytokines throughout the body. Resultant chronic inflammatory states may potentially stimulate cell proliferation and contribute to tumorigenesis [72]. In turn, tumor growth and metastasis leads to further increased inflammation (Figure 1). The systemic inflammatory state may then exacerbate oral immune dysregulation, potentially rendering the oral microbiome susceptible to pathogenic invasion. As found in diabetes and SLE, this dysbiosis has the potential to perpetuate an ongoing cycle of inflammation, worsening cancer cachexia. Though it may be difficult to distinguish the sequence of events, it is feasible that the reduction of inflammation may reduce dysbiosis.
3. The Microbiome and Cancer Cachexia
The relationship between the oral microbiome and cancer cachexia is a novel field of research that remains unexplored. However, the gut microbiome in the distal alimentary tract has been implicated in cancer cachexia [5]. Gut barrier dysfunction as well as an imbalance in the gut microbiome has been shown to lead to systemic inflammation, setting the stage for a cachectic response in cancer patients [5]. Jiang et al., specifically examined the role of bacterial translocation in the colon of patients with cancer cachexia. In this study, cachectic patients had a significantly higher prevalence of colonic bacterial translocation when compared to non-cachectic patients. Cachectic patients also exhibited increased concentrations of IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ in their venous blood samples from the middle colic vein. The study concluded that luminal bacterial overgrowth likely occurs secondary to immunosuppression, resulting in increased bacterial translocation. This induces a pro-inflammatory state, raising the metabolic rate and suppressing appetite. This cycle may result in further bacterial translocation which will then lead to a greater cytokine release eventually resulting in a cachectic state, a cycle similar to the one that may potentially be occurring in the oral microbiome [73].
The gut microbiome and cachexia were further explored in a 2018 study by Bindels et al. who investigated markers of gut barrier function by assessing mice injected with colon adenocarcinoma cells [74]. In these subjects, intestinal morphology was altered, renewal of cell lineages was decreased, and a decreased expression of the tight junctions responsible for binding the epithelium was observed [74]. These findings are supported by similar studies in leukemic mice with cachexia and a colorectal cancer mouse model of cachexia [75,76]. Both investigations indicated that gut barrier dysfunction was implicated in cachexia through its induction of a systemic inflammatory state. On a similar note, intestinal morphology is also altered by the binding of gut microbiota to gut epithelium with cadherin junctions, a type of adhesion molecule [77]. One such bacteria that illustrates this concept is Porphyromonas gingivalis, a bacterium that degrades cadherin junctions, leading to the translocation of Porphyromonas gingivalis and a state of systemic inflammation [78].
More knowledge of the relationship between the gut microbiome and cancer cachexia may be gleaned from interventional studies. Sakakida et al. studied the effects of partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG), a soluble dietary fiber, in a preclinical experiment [79]. They hypothesized that PHGG’s effect on the intestinal flora may counteract the pro-inflammatory intestinal state that leads to cancer cachexia. Utilizing a colon-26 murine cachexia model, they found that non-PHGG fed mice had decreased skeletal muscle mass compared to those with diets containing PHGG. Mice fed with PHGG also demonstrated increased Bifidobacterium, Akkermansia, and an unspecified S24-7 family populations with an associated preservation of gut barrier function. The resulting decrease in systemic levels of pro-inflammatory lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and IL-6 substantiates Jiang et al.’s, proposed role of gut permeability and bacterial translocation in the pathogenesis of cancer cachexia [74]. Interestingly, obesity and diabetes have been postulated to have similar elements in their pathology [80]. A separate investigation by Jia et al. has recently applied the anti-inflammatory effects of eggshell membranes observed in joint and connective tissue preservation to the field of cancer cachexia [81]. Its low-cost and its recognized ability to remedy intestinal dysbiosis make this modality an especially promising therapeutic candidate [81]. This multi-component investigation of eggshell membrane effects in an IL-10-knockout murine model of cachexia yielded a variety of key results. In particular, they found that the gut microbial make-up of mice receiving eggshell membranes differed from those who received non-supplemented diets. Bacteriodetes, Firmicutes, and Verrucomicrobia phyla, Bacteroidacae, Defferribacteraceae, Ruminococcaceae, and Porphyromonadacae families, and Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides acidifaciens, and Akkermansia Muciniphila species were among the microbiota whose population sizes increased to wild-type levels with eggshell membrane supplementation [82]. The restoration of Ruminococcaceae populations was of particular interest as this organism is known to have the potential to stimulate fermentation of short chain fatty acids which can induce wide-spread anti-inflammatory effects [82].
With regard to function and regulation, the oral and gut microbiome share many similarities. Both play a role in immune defense and house some of the largest stores of natural flora in the body [83,84]. The oral microbiome also serves as the introductory site for gut dysbiosis [84]. Inflammatory signals via cytokine signaling caused by bacteria in the oral cavity may be secreted down the digestive tract and influence the gut microbiome [85]. Additionally, oral dysbiosis has the potential to lead to foreign bacteria translocation to the gut, causing chronic and systemic inflammation [86]. While further studies are necessary, parallels between both cavities may indicate that, similar to the gut, the oral microbiome plays a significant role in the onset and perpetuation of inflammation leading to cancer cachexia.
4. Potential Therapeutic Agents
Biotherapeutics such as prebiotics and probiotics may be effective tools that have the potential to restore the balance of the oral microbiome. By re-establishing equilibrium among certain bacteria of the oral cavity, clinicians may effectively reduce the extent of muscle wasting seen in cancer cachexia.
Probiotics are defined as “viable micro-organisms that provide health benefits when taken in sufficient doses” [87]. At its essence, they are live bacteria used to displace pathogenic bacteria. Studies on the effects of probiotic administration on cancer cachexia through alteration of the oral microbiome are limited. However, the literature that exists regarding their effects on the oral cavity itself provides insight into their ability to impact local inflammation and perhaps oral microflora composition. Administration of probiotics in periodontal disease has been shown to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines in gingival crevicular fluid and myeloperoxidase activity [88,89]. Additional studies of their effects in dental caries and dental plaque have supported their ability to resolve these oral cavity diseases through the reduction of streptococcus mutans populations [90,91,92,93]. Similarly, growth of gingivalis and halitosis associated bacteria has been observed to be hampered through the inhibitory effects of probiotics on Porphyromonas gingivalis [94,95,96]. Even voice prosthetics have been found to have an increased lifespan due to probiotic use because of probiotics’ prohibiting effect on microorganism adhesion [97]. Mechanistically, these probiotic effects are made possible through competition for adhesion, production of anti-microbial compounds, and enhancement of host immune response [98].
Preclinical studies assessing the effects of probiotics on colorectal cancerous and precancerous lesions have also suggested an anticancer role. One such experiment reported that Pediococcus pentosaceus FP3, Lactobacillus salivarius FP25, L. salivarius FP35, and Enterococcus faecium FP51 inhibited cancer proliferation in an in vitro model of colorectal cancer [99]. The authors though believed that these anticancer properties were due to production of short chain fatty acids and did not note the alteration of the oral microbiome as an involved mechanism. However, another study conducted by Radaic et al. did indicate that probiotic effects in the oral microbiome served as the driver of anticancer activity [100]. Their investigation described the ability of the Lactococcus lactis probiotic to produce nisin, an antimicrobial substance active against Gram-positive and negative organisms [100]. Their findings in combination with nisin’s ability to increase apoptosis and survival in head and neck cancer models suggests an anticancer probiotic property mediated by oral microbiome modification [101].
Better studied are the effects of probiotics on the gut microbiome and its subsequent effects on systemic inflammation. Probiotics have previously been shown in studies analyzing intestinal inflammation from Crohn’s disease to have anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-8 and IL-1β [102]. Probiotic treatment can also maintain gut flora, improve flora defensive capabilities against pathogenic colonization, and improve intestinal barrier integrity [103]. One such study has been able to link these systemic effects to age related cachexia, a disease process with mechanisms that overlap with those of cancer cachexia. Chen et al. investigated the use of the probiotic Lactobacillus casei Shirota in SAMP8 mice models of age-related cachexia. They found that supplementation of Lactobacillus casei Shirota was associated with decreased inflammation, reduced age-related increases in reactive oxygen species, and altered gut microbiota composition. Importantly, key findings also included attenuated declines in muscle mass, strength, and mitochondrial function within the Lactobacillus casei Shirota supplemented group [104].
Prebiotics are a “non-viable food component that confer health benefits on the host associated with modulation of the microbiota” [105]. These substances act as nutritional sources for healthy bacteria and allow them to expand their population in the oral cavity. Recent studies have indicated applications of their utilization in the promotion of healthy oral flora. Slomka et al. studied the effects of 742 compounds on the respiratory activity in 16 oral bacteria [106]. Out of all the compounds studied, they identified beta-methyl-d-galactoside and N-acetyl-d-mannosamine as prebiotics with the ability to stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria in the oral microbiome [106]. Rosier et al. advocated for the classification of nitrate as a prebiotic after observing that its administration in in vitro biofilms increased levels of beneficial genera Neisseria and Rothia and decreased populations of the dental disease associated genera Streptococcus, Veillonella, Porphyromonas, Fusobacterium, Leptotrichia, Prevotella, Alloprevotella and Oribacterium [107]. Though their ability to affect cancer cachexia through the oral microbiome has never been established, prebiotic therapy has been shown to have beneficial effects in models of cancer cachexia via effects on the gut microbiome. Triterpine saponins and pectic oligosaccharides specifically are prebiotics named as being potentially therapeutic. In 2017, Huang et al. reported results of a study assessing the effects of ginsenoside-Rb3 and ginsenoside-Rd, specific types of triterpene saponins, in a mouse model of colorectal cancer [108]. Their analysis demonstrated that both triterpene saponins exerted anti-inflammatory effects on the mucosal cytokine profile. Strikingly, Dysgonomonas and Helicobacter, species of cancer cachexia associated bacteria, were decreased in prebiotic treated mice [108]. In a study with cachexia specific endpoints, Bindels et al. studied both inulin and pectic oligosaccharide prebiotics in the synbiotic treatment of a murine leukemia model. While inulin supplementation decreased leukemic invasion of the liver, pectic oligosaccharides were associated with increased Bifidobacterium, Roseburia and Bacteroides species in the gut. Most importantly, pectic oligosaccharide prebiotics delayed onset of cancer cachexia and decreased fat mass loss via modulation of genes involved in ß-oxidation [75].
Studies exploring interventions that alter the oral microbiome to potentially treat cancer cachexia are still in fledgling stages (Table 2). Agents that can re-establish and maintain oral symbiosis may also have properties to address the chronic and systemic inflammation associated with cancer cachexia.

Table 2.
The Microbiome and Cancer Cachexia.
5. Conclusions
The oral microbiota is a vast and diverse collection of bacteria that plays an important role in maintaining health. Composition of this microbial environment is complex and is determined by a variety of internal and external factors. Direct links between oral microbiota and inflammatory diseases remain largely unexplored, offering an exciting field of future study. Cancer cachexia is a devastating consequence of the systemic inflammation from tumorigenesis. While no therapeutic agents currently exist to treat this multifactorial syndrome, exploration of interventions targeting the gut microbiome have shown promise. Both prebiotic and probiotic agents are among the therapeutic modalities currently under investigation. Their reported ability to mitigate cancer cachexia through alterations in the gut microbiome suggests a role for not only gut flora but also oral flora as targets for future treatment. The effects of oral microbiome intervention and cancer cachexia, however, have yet to be explored and further study is needed to interrogate this potential relationship.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R.R., C.L. and K.M.H.; Funding Acquisition, J.G.T.; Investigation, S.R.R.; Project Administration, K.M.H. and J.G.T.; Resources, S.R.R., K.M.H. and A.N.R.; Supervision, K.M.H., A.N.R. and J.G.T.; Validation, S.R.R., K.M.H., A.N.R., V.V. and D.C.F.; Visualization, S.R.R. and K.M.H.; Writing—original draft, S.R.R.; Writing—review and editing, C.L., K.M.H., A.N.R., V.V., D.C.F., K.L.M., E.W.T. and J.G.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Authors are supported by the National Human Genome Research Institute (T32 HG008958 to KMH, ANR) and National Cancer Institute (T32 CA93423-13 to DCF R01 CA242003 to JGT, U54 CA233444 to JGT, and U54 CA233444-03S1 to ANR and JGT) of the National Institutes of Health and the Joseph and Ann Matella Fund for Pancreatic Cancer Research (JGT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Xu, T.; Huang, G.; Jiang, S.; Gu, Y.; Chen, F. Oral microbiomes: More and more importance in oral cavity and whole body. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, P.N.; Deshmukh, R. Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2019, 23, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herremans, K.M.; Riner, A.N.; Cameron, M.E.; Trevino, J.G. The Microbiota and Cancer Cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, M.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Hannig, M.; Marsh, P.D.; Meuric, V.; Pedersen, A.M.L.; Tonetti, M.S.; Wade, W.G.; Zaura, E. The oral microbiome–an update for oral healthcare professionals. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco, M.F.; Vess, T.J.; Ginsburg, G.S. The oral microbiome in health and disease and the potential impact on personalized dental medicine. Oral Dis. 2011, 18, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaura, E.; Keijser, B.J.F.; Huse, S.M.; Crielaard, W. Defining the healthy “core microbiome” of oral microbial communities. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, E.M.; Long, C.D.; Armitage, G.C.; Loomer, P.; Emerson, J.; Mongodin, E.F.; Nelson, K.E.; Gill, S.R.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Relman, D.A. Bacterial diversity in the oral cavity of 10 healthy individuals. ISME J. 2010, 4, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbor, T.A.; McCormick, B.A. Salmonella effectors: Important players modulating host cell function during infection. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1858–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, I.; Vasquez, A.; Moyerbrailean, G.; Land, S.; Djuric, Z.; Sun, J.; Lin, H.-S.; Ram, J.L. Nutritional Correlates of Human Oral Microbiome. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 36, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.H.; Kern, T.; Bak, E.G.; Kashani, A.; Allin, K.; Nielsen, T.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O. Impact of a vegan diet on the human salivary microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Freedman, N.D.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Pei, Z.; et al. Drinking alcohol is associated with variation in the human oral microbiome in a large study of American adults. Microbiome 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Tong, X.-T.; Jia, Y.-J.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Wu, Y.-X.; Xue, W.-Q.; He, Y.-Q.; Wang, T.-M.; Zheng, X.-H.; Zheng, M.-Q.; et al. The Effects of Alcohol Drinking on Oral Microbiota in the Chinese Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zyoud, W.; Hajjo, R.; Abu-Siniyeh, A.; Hajjaj, S. Salivary Microbiome and Cigarette Smoking: A First of Its Kind Investigation in Jordan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.-J.; Liao, Y.; He, Y.-Q.; Zheng, M.-Q.; Tong, X.-T.; Xue, W.-Q.; Zhang, J.-B.; Yuan, L.-L.; Zhang, W.-L.; Jia, W.-H. Association Between Oral Microbiota and Cigarette Smoking in the Chinese Population. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 658203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belstrøm, D.; Holmstrup, P.; Nielsen, C.H.; Kirkby, N.; Twetman, S.; Heitmann, B.L.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Paster, B.J.; Fiehn, N.-E. Bacterial profiles of saliva in relation to diet, lifestyle factors, and socioeconomic status. J. Oral Microbiol. 2014, 6, 23609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, W.T.; Besten, P.K.D.; Stamperdahl, J.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Adler, N.E.; Featherstone, J.D. Social inequalities in childhood dental caries: The convergent roles of stress, bacteria and disadvantage. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Espinoza, J.L.; Harkins, D.M.; Leong, P.; Saffery, R.; Bockmann, M.; Torralba, M.; Kuelbs, C.; Kodukula, R.; Inman, J.; et al. Host Genetic Control of the Oral Microbiome in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmitt, B.A.; Corley, R.P.; Huibregtse, B.M.; Keller, M.C.; Hewitt, J.K.; McQueen, M.B.; Knight, R.; McDermott, I.; Krauter, K.S. Genetic influences on the human oral microbiome. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakara, P.; Gupta, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Wilson, A. Oral Dysbiotic Communities and Their Implications in Systemic Diseases. Dent. J. 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Kong, C.; Yang, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, X.; Cai, G.; Ma, Y. Human oral microbiome dysbiosis as a novel non-invasive biomarker in detection of colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11595–11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benahmed, A.G.; Gasmi, A.; Doşa, A.; Chirumbolo, S.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Aaseth, J.; Dadar, M.; Bjørklund, G. Association between the gut and oral microbiome with obesity. Anaerobe 2020, 70, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietiäinen, M.; Liljestrand, J.M.; Kopra, E.; Pussinen, P.J. Mediators between oral dysbiosis and cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, L.J.; Garzón, H.; Arboleda, S.; Rodríguez, A. Oral Dysbiosis and Autoimmunity: From Local Periodontal Responses to an Imbalanced Systemic Immunity. A Review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Delgado, R.Z.R.; Frias-Lopez, J. The Oral Microbiome and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herremans, K.M.; Riner, A.N.; Cameron, M.E.; McKinley, K.L.; Triplett, E.W.; Hughes, S.J.; Trevino, J.G. The oral microbiome, pancreatic cancer and human diversity in the age of precision medicine. Microbiome 2022, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemer, B.; Warren, R.D.; Barrett, M.P.; Cisek, K.; Das, A.; Jeffery, I.B.; Hurley, E.; O‘Riordain, M.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. The oral microbiota in colorectal cancer is distinctive and predictive. Gut 2018, 67, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, C.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Francois, F.; Corby, P.; Perez, G.P.; Dasanayake, A.; Pei, Z.; Chen, Y. Association between Selected Oral Pathogens and Gastric Precancerous Lesions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi-Bajestani, S.M.R.; Becher, H.; Fassbender, K.; Chu, Q.; Baracos, V.E. Concurrent evolution of cancer cachexia and heart failure: Bilateral effects exist. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.T. The pathogenesis and treatment of cardiac atrophy in cancer cachexia. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H466–H477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burckart, K.; Beca, S.; Urban, R.J.; Sheffield-Moore, M. Pathogenesis of muscle wasting in cancer cachexia: Targeted anabolic and anticatabolic therapies. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, T.; Terracina, K.P.; Raza, A.; Matsubara, H.; Takabe, K. Cancer cachexia, mechanism and treatment. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 7, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Scott, A.M.; Hoogenraad, N.J.; Osellame, L.D. Mediators and clinical treatment for cancer cachexia: A systematic review. JCSM Rapid Commun. 2021, 4, 166–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulia, K.A.; Sarantis, P.; Antoniadou, D.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic Cancer and Cachexia—Metabolic Mechanisms and Novel Insights. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.E.; Makhijani, N.; Mace, T.A. Pancreatic Cancer–Induced Cachexia and Relevant Mouse Models. Pancreas 2018, 47, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, D.M.D.R.; Das Neves, R.X.; De Matos-Neto, E.M.; Camargo, R.G.; Lima, J.D.C.C.; Radloff, K.; Alves, M.J.; Costa, R.G.F.; Tokeshi, F.; Otoch, J.P.; et al. Plasma Lipid Profile and Systemic Inflammation in Patients With Cancer Cachexia. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, A. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment Cells in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ábrigo, J.; Elorza, A.A.; Riedel, C.A.; Vilos, C.; Simon, F.; Cabrera, D.; Estrada, L.; Cabello-Verrugio, C. Role of Oxidative Stress as Key Regulator of Muscle Wasting during Cachexia. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 2063179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, J.M.; Judge, A.R.; Talbert, E.; Powers, S.K. Calpain-1 is required for hydrogen peroxide-induced myotube atrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2009, 296, C363–C371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargelos, E.; Brulé, C.; Stuelsatz, P.; Mouly, V.; Veschambre, P.; Cottin, P.; Poussard, S. Up-regulation of calcium-dependent proteolysis in human myoblasts under acute oxidative stress. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Mofarrahi, M.; Kristof, A.S.; Nkengfac, B.; Harel, S.; Hussain, S.N. Reactive Oxygen Species Regulation of Autophagy in Skeletal Muscles. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Zhu, X.; Szumowski, M.; Scott, G.D.; Grossberg, A.; Levasseur, P.R.; Graham, K.; Khan, S.; Damaraju, S.; Colmers, W.F.; et al. Central nervous system inflammation induces muscle atrophy via activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2449–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallengren, O.; Lundholm, K.; Bosaeus, I. Diagnostic criteria of cancer cachexia: Relation to quality of life, exercise capacity and survival in unselected palliative care patients. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, R.; Wong, A.; Hui, D.; Bruera, E. The Evolving Approach to Management of Cancer Cachexia. Oncology 2017, 31, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bordignon, C.; dos Santos, B.S.; Rosa, D.D. Impact of Cancer Cachexia on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle: Role of Exercise Training. Cancers 2022, 14, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macciò, A.; Madeddu, C.; Gramignano, G.; Mulas, C.; Floris, C.; Sanna, E.; Cau, M.C.; Panzone, F.; Mantovani, G. A randomized phase III clinical trial of a combined treatment for cachexia in patients with gynecological cancers: Evaluating the impact on metabolic and inflammatory profiles and quality of life. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Wynn, T.A.; Martin, P. Inflammation and metabolism in tissue repair and regeneration. Science 2017, 356, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinstein, S.; Nelson, K.; Freire, M. Inflammatory Networks Linking Oral Microbiome with Systemic Health and Disease. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, C.L.; Kleckner, I.R.; Jatoi, A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Dunne, R.F. The Role of Systemic Inflammation in Cancer-Associated Muscle Wasting and Rationale for Exercise as a Therapeutic Intervention. JCSM Clin. Rep. 2018, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, J.; Zahra, A.; Venugopal, S.; Selvamani, T.Y.; Shoukrie, S.I.; Selvaraj, R.; Dhanoa, R.K.; Hamouda, R.K.; Mostafa, J. What Role Do Inflammatory Cytokines Play in Cancer Cachexia? Cureus 2022, 14, e26798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Kuehl, M.N.; Alman, A.C.; Burkhardt, B.R. Linking the oral microbiome and salivary cytokine abundance to circadian oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.M. The immune response toPrevotellabacteria in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Suda, W.; Luo, C.; Kawaguchi, T.; Motoo, I.; Narushima, S.; Kiguchi, Y.; Yasuma, K.; Watanabe, E.; Tanoue, T.; et al. Ectopic colonization of oral bacteria in the intestine drives T H 1 cell induction and inflammation. Science 2017, 358, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyofuku, M.; Nomura, N.; Eberl, L. Types and origins of bacterial membrane vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yin, S.; Wang, M. Extracellular vesicles of bacteria as potential targets for immune interventions. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 17, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Song, M.-K.; Lim, Y.; Jang, J.S.; An, S.-J.; Kim, H.-H.; Choi, B.-K. Effects of extracellular vesicles derived from oral bacteria on osteoclast differentiation and activation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatzky, K.F.; Uhle, F.; Eigenbrod, T. From macrophage to osteoclast–How metabolism determines function and activity. Cytokine 2018, 112, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielento, A.; Bereta, G.P.; Łagosz-Ćwik, K.B.; Eick, S.; Lamont, R.J.; Grabiec, A.M.; Potempa, J. TLR2 Activation by Porphyromonas gingivalis Requires Both PPAD Activity and Fimbriae. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popławska-Kita, A.; Siewko, K.; Szpak, P.; Król, B.; Telejko, B.; Klimiuk, P.A.; Stokowska, W.; Górska, M.; Szelachowska, M. Association between type 1 diabetes and periodontal health. Adv. Med. Sci. 2014, 59, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apoorva, S.M.; Sridhar, N.; Suchetha, A. Prevalence and severity of periodontal disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) patients in Bangalore city: An epidemiological study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.-A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetes: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Xiao, E.; Graves, D.T. Diabetes mellitus related bone metabolism and periodontal disease. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2015, 7, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.L.; Bergem, H.O.; Gilboe, I.-M.; Husby, G.; Axéll, T. Oral and ocular sicca symptoms and findings are prevalent in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2007, 28, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, J.D.; Calderaro, D.C.; Ferreira, G.A.; Mendonça, S.M.S.; Fernandes, G.R.; Xiao, E.; Teixeira, A.L.; Leys, E.J.; Graves, D.T.; Silva, T.A. Subgingival microbiota dysbiosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with periodontal status. Microbiome 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, A.P.; Sanchez-Padilla, D.E.; Drew, J.C.; Oli, M.W.; Roesch, L.F.W.; Triplett, E.W. Saliva microbiome, dietary, and genetic markers are associated with suicidal ideation in university students. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, J.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Wade, W.G. Description of Alloprevotella rava gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the human oral cavity, and reclassification of Prevotella tannerae Moore et al. 1994 as Alloprevotella tannerae gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.H. Sodium succinate; clinical use in respiratory depression. Curr. Res. Anesth. Analg. 1948, 27, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H.; Trautner, E.M.; Messer, M. Glucose, Glutamate and Succinate Oxidation in Brain. Nature 1951, 168, 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalloh, I.; Helmy, A.; Howe, D.J.; Shannon, R.J.; Grice, P.; Mason, A.; Gallagher, C.N.; Stovell, M.G.; Van Der Heide, S.; Murphy, M.; et al. Focally perfused succinate potentiates brain metabolism in head injury patients. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 37, 2626–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovell, M.G.; Mada, M.O.; Helmy, A.; Carpenter, T.A.; Thelin, E.P.; Yan, J.-L.; Guilfoyle, M.R.; Jalloh, I.; Howe, D.J.; Grice, P.; et al. The effect of succinate on brain NADH/NAD+ redox state and high energy phosphate metabolism in acute traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Zhan, X. Chronic inflammation: Key player and biomarker-set to predict and prevent cancer development and progression based on individualized patient profiles. EPMA J. 2019, 10, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Geng, C. The Altered Tight Junctions: An Important Gateway of Bacterial Translocation in Cachexia Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindels, L.B.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Loumaye, A.; Catry, E.; Walgrave, H.; Cherbuy, C.; Leclercq, S.; Van Hul, M.; Plovier, H.; Pachikian, B.; et al. Increased gut permeability in cancer cachexia: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18224–18238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Claus, S.P.; Le Roy, C.I.; Grangette, C.; Pot, B.; Martinez, I.; Walter, J.; Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. Synbiotic approach restores intestinal homeostasis and prolongs survival in leukaemic mice with cachexia. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppa, M.J.; White, J.P.; Sato, S.; Cairns, M.; Baynes, J.W.; Carson, J.A. Gut barrier dysfunction in the ApcMin/+ mouse model of colon cancer cachexia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, C.A.; Mezouar, S.; Mege, J.-L. The E-Cadherin Cleavage Associated to Pathogenic Bacteria Infections Can Favor Bacterial Invasion and Transmigration, Dysregulation of the Immune Response and Cancer Induction in Humans. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Sulijaya, B.; Yamada-Hara, M.; Tsuzuno, T.; Tabeta, K.; Yamazaki, K. Gingival epithelial barrier: Regulation by beneficial and harmful microbes. Tissue Barriers 2019, 7, e1651158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakakida, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Doi, T.; Morita, R.; Endo, Y.; Matsumura, S.; Ota, T.; Yoshida, J.; Hirai, Y.; Mizushima, K.; et al. Water-soluble dietary fiber alleviates cancer-induced muscle wasting through changes in gut microenvironment in mice. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Possemiers, S.; Van De Wiele, T.; Guiot, Y.; Everard, A.; Rottier, O.; Geurts, L.; Naslain, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Lambert, D.M.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009, 58, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Lyu, W.; Hirota, K.; Saito, E.; Miyoshi, M.; Hohjoh, H.; Furukawa, K.; Saito, K.; Haritani, M.; Taguchi, A.; et al. Eggshell membrane modulates gut microbiota to prevent murine pre-cachexia through suppression of T helper cell differentiation. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2088–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Hanate, M.; Aw, W.; Itoh, H.; Saito, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Hachimura, S.; Fukuda, S.; Tomita, M.; Hasebe, Y.; et al. Eggshell membrane powder ameliorates intestinal inflammation by facilitating the restitution of epithelial injury and alleviating microbial dysbiosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, I.; Yamazaki, K. Can oral bacteria affect the microbiome of the gut? J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1586422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghi, L.; DiMassa, V.; Harrington, A.; Lynch, S.V.; Kapila, Y.L. The oral microbiome: Role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontology 2000 2021, 87, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, S.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Hein, R.; Schmidt, T.M.; Kamada, N. The Bacterial Connection between the Oral Cavity and the Gut Diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, D.A.; Marsh, P.D. Prospects for the development of probiotics and prebiotics for oral applications. J. Oral Microbiol. 2009, 1, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twetman, S.; Derawi, B.; Keller, M.; Ekstrand, K.; Yucel-Lindberg, T.; Stecksén-Blicks, C. Short-term effect of chewing gums containing probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri on the levels of inflammatory mediators in gingival crevicular fluid. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2009, 67, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staab, B.; Eick, S.; Knöfler, G.; Jentsch, H. The influence of a probiotic milk drink on the development of gingivitis: A pilot study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S. Effect of Probiotic Curd on Salivary pH and Streptococcus mutans: A Double Blind Parallel Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanarat, O.; Makeudom, A.; Sastraruji, T.; Piwat, S.; Tianviwat, S.; Teanpaisan, R.; Krisanaprakornkit, S. Enhancement of salivary human neutrophil peptide 1–3 levels by probiotic supplementation. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, T.; Suzuki, N.; Yoneda, M.; Hirofuji, T. Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius-containing tablets on caries risk factors: A randomized open-label clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, L.C.; Huang, C.-S.; Ou-Yang, L.-W.; Lin, S.-Y. Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei effect on cariogenic bacterial flora. Clin. Oral Investig. 2010, 15, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Baek, D.-H. Effects of Streptococcus thermophilus on volatile sulfur compounds produced by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N.; Higuchi, T.; Nakajima, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Morita, H.; Yoneda, M.; Hanioka, T.; Hirofuji, T. Inhibitory Effect ofEnterococcus faeciumWB2000 on Volatile Sulfur Compound Production byPorphyromonas gingivalis. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 8241681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, H.; Nakka, S.S.; Sandén, C.; Svärd, A.; Hultenby, K.; Scherbak, N.; Aili, D.; Bengtsson, T. Antibacterial effects of Lactobacillus and bacteriocin PLNC8 αβ on the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwandt, L.Q.; Van Weissenbruch, R.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J.; Albers, F.W.J. Effect of dairy products on the lifetime of Provox2 voice prostheses in vitro and in vivo. Head Neck 2005, 27, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, P.; Dutt, R.; Sharma, A.; Bhagat, N.; Dhar, M.S. A critical appraisal of the effects of probiotics on oral health. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirabunyanon, M.; Hongwittayakorn, P. Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria of Human Origin Induce Antiproliferation of Colon Cancer Cells via Synergic Actions in Adhesion to Cancer Cells and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Bioproduction. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 169, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaic, A.; Ye, C.; Parks, B.; Gao, L.; Kuraji, R.; Malone, E.; Kamarajan, P.; Zhan, L.; Kapila, Y.L. Modulation of pathogenic oral biofilms towards health with nisin probiotic. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 12, 1809302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajan, P.; Hayami, T.; Matte, B.; Liu, Y.; Danciu, T.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Worden, F.; Kapila, S.; Kapila, Y. Nisin ZP, a Bacteriocin and Food Preservative, Inhibits Head and Neck Cancer Tumorigenesis and Prolongs Survival. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Díaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Vilchez-Padial, L.M.; Gil, A. Evidence of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Intestinal Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; McCartney, A.L.; Rastall, R.A. Prebiotics and resistance to gastrointestinal infections. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chang, S.; Chang, H.; Wu, C.; Pan, C.; Chang, C.; Chan, C.; Huang, H. Probiotic supplementation attenuates age-related sarcopenia via the gut–muscle axis in SAMP8 mice. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.R.; Naik, S.R.; Vakil, B.V. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, V.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Herrero, E.R.; Zaidel, L.; Bernaerts, K.; Boon, N.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Nutritional stimulation of commensal oral bacteria suppresses pathogens: The prebiotic concept. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosier, B.T.; Buetas, E.; Moya-Gonzalvez, E.M.; Artacho, A.; Mira, A. Nitrate as a potential prebiotic for the oral microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Khan, I.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Leong, W.; Ho, L.T.; Hsiao, W.L.W. Ginsenosides Rb3 and Rd reduce polyps formation while reinstate the dysbiotic gut microbiota and the intestinal microenvironment in ApcMin/+ mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).