Abstract
The present study reports on serosurvey on the tick-borne encephalitis virus European subtype (TBEV; genus Flavivirus), and the tick-borne Kemerovo (KEMV) and Tribeč (TRBV) orbivirus (genus Orbivirus) infections in tick-infested and non-infested birds. No virus RNA was detected in the blood clots. Birds were infested mostly by Ixodes ricinus, but Haemaphysalis concinna and I. frontalis were observed too. TBEV, KEMV and TRBV neutralising antibodies (NAb) were detected in the screening microtitration neutralisation test (μVNT). Seropositive samples were further examined in simultaneous μVNT to distinguish TBEV infection from WNV and USUV. KEMV and TRBV infections were also further examined by μVNT against each other. The demonstrated results point to increased TBEV and TRBV seroprevalence in birds over the past several years. This is the first study on KEMV infection in the Slovak bird population, and seropositive juvenile birds suggest its occurrence in a new geographic area. The results indicate the significance of tick infestation rates, seropositivity and specific NAb titre. The reservoir role of birds for TBEV, KEMV and TRBV remains unclear. However, targeted monitoring of birds and vectors is an effective measure of surveillance of arbovirus introduction into new geographic areas.
1. Introduction
The autochthonous Central European bird species belong to the Palaearctic-Afrotropical migrants. Birds are frequently infested with ticks and can transmit them and tick-borne pathogens along the migratory routes [1,2].
Arboviruses (arthropod-borne viruses) are a group of viruses biologically transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods. To date, three species of tick-borne arboviruses have been identified in Slovakia: Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV; genus Flavivirus; family Flaviviridae) [3], Great Island virus (GIV; genus Orbivirus; family Sedoreoviridae) [4] and Uukuniemi uukuvirus (UUKV; genus Uukuvirus; family Phenuiviridae) [5]. Birds are considered potential reservoirs of TBEV, GIV and UUKV [6,7,8,9].
TBEV is the causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) and is considered the most important representative of arboviruses in Eurasia, of which the main vector is Ixodes ricinus [10]. Although rodents are its main reservoirs, the participation of birds in the natural transmission cycle of TBEV is becoming increasingly important. The magnitude of TBEV viremia in birds depends on the infected species [11]. No viremia was described in great tits (Parus major), common pheasants (Phasianus colchicus), common kestrels (Falco tinnunculus) and common buzzards (Buteo buteo); mild viremia was observed in house sparrows (Passer domesticus), common quails (Coturnix coturnix), mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) and common redpolls (Acanthis flammea) [12,13,14]. TBEV RNA has been detected in the brain of a buzzard [15]. Sporadically, TBEV was isolated from various bird species, such as redwings (Turdus iliacus), western jackdaws (Coloeus monedula), carrion crows (Corvus corone), Eurasian magpies (Pica pica), common starlings (Sturnus vulgaris) and other predominantly forest passerines; for more information see Hubálek and Rudolf (2012) [16]. The isolation of TBEV from eggs has been observed in redwing, fieldfare (Turdus pilaris), red-throated thrush (Turdus ruficollis), pale thrush (Turdus pallidus), brown shrikes (Lanius cristatus), chestnut-eared buntings (Emberiza fucata), Eurasian wrens (Troglodytes troglodytes) and northern goshawks (Accipiter gentilis) [17]. However, reservoir potential for TBEV was demonstrated only in fieldfares, bramblings (Fringilla montifringilla) and common redstarts (Phoenicurus phoenicurus), where a high prevalence (50%) of the TBEV RNA and antigen was confirmed [6].
The contribution of birds in the transmission of zoonotic GIV serotypes remains unknown. To date, two GIV serotypes have been reported in Slovakia—Tribeč virus (TRBV) and Lipovník virus (LIPV). I. ricinus is considered the main vector of TRBV and rodents as their reservoirs [18,19]. However, seroconversion has been reported in birds [20]. Kemerovo virus (KEMV) is another zoonotic serotype of GIV [21]. It was isolated from the blood of a common redstart caught in Egypt during migration. The bird was likely infected in Eurasia, where the main vector of KEMV, Ixodes persulcatus, is widely distributed [8].
Despite the reports on their neurotropic potential, tick-borne orbiviruses are neglected arboviruses, which do not receive much attention. TRBV-specific antibodies were detected in cases of febrile illness and aseptic meningitis [22]. KEMV was isolated from patients with meningitis and meningoencephalitis after tick bites [21]. Nonspecific symptoms make arboviral differential diagnosis problematic. The importance of tick-borne orbiviruses is also underlined by the fact that in Slovakia, between 2016 and 2018, 40% of viral central nervous system infections were diagnosed as unspecified viral encephalitis, meningitis or unspecified viral CNS infection [23].
Although animal diseases caused by TRBV and KEMV have not been reported yet, their role in the transmission cycle and maintenance in nature is not well understood. The aims of the present study build on previous results of arbovirus infection screening in wild birds captured in the model area Drienovská wetland [15,20]. Here, we examined wild living birds’ blood clots for TBEV, TRBV and KEMV RNA and serum samples for virus-specific NAb. Due to the high rate of serological cross-reaction among flaviviruses co-circulating in Central Europe (TBEV, West Nile virus and Usutu virus) and among orbiviruses of the GIV serogroup, the seropositive samples in the screening were further examined by simultaneous microtitration virus neutralization test (μVNT). The relationship between tick infestations and the prevalence and titre of specific NAb were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Model Area
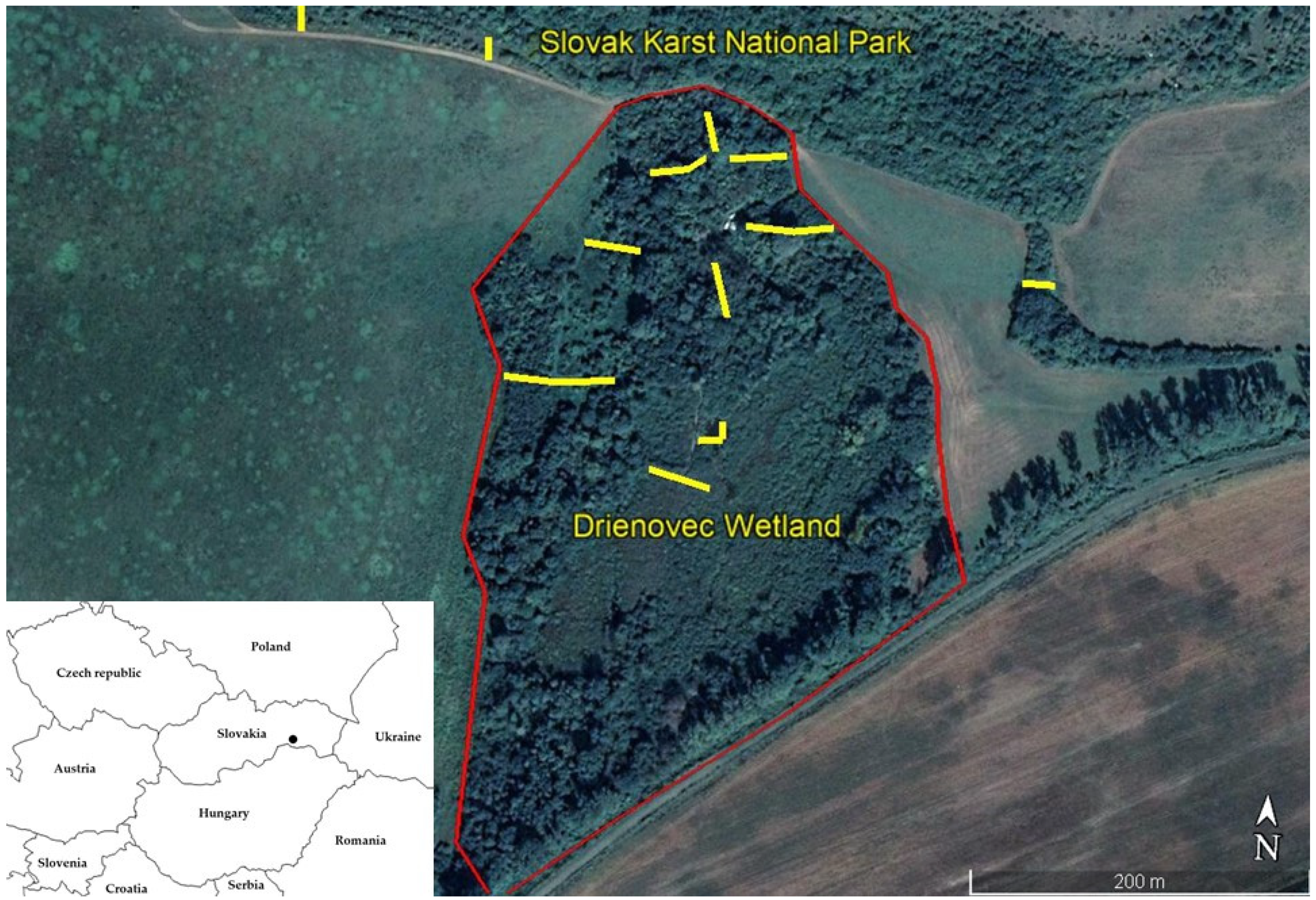
Drienovská wetland is located in the south-east of Slovakia, near the village Drienovec in Košice-okolie District, in the square DFS 7391, at an altitude of 190 m above sea level (Figure 1). In terms of altitudinal division, the wetland is in the lowland (planar stage). From the north, there is an immediate continuity with the hilly area of the Slovak Karst National Park. The wetland has an area of 7.7 ha. Orographically, it is located directly on the border of the Košice Basin and the Slovak Karst. The geographical coordinates of the site are 48°37′ N, 20°55′ E. Habitats surrounding the capture site within 500 metres are the following: 40% arable land, the most common cultivated crops are cereals and sunflower, a smaller part is made up of mown meadow and ruderal habitats, 20% xerothermic vegetation of the foothills of the plateau with shrub formations of pasture character, 20% oak forest, 15% willows (Salix sp.) and acrophytes (Phragmites australis) and 5% shrub and tree group habitats outside the forest [24].
Figure 1.
Location of Drienovská wetland and the distribution of mist nets. Legend Yellow lines depict the distribution of mist nets on the model area Drienovská wetland. Red lines depict the border of the model area. The insert in the left lower corner shows the location of Slovakia and its neighbouring countries in Central Europe.
The Drienovská wetland is known for its bird species richness and population density of migrating and nesting birds, and it is a core locality for the Drienovec Bird Ringing Station [15,20,25,26].
2.2. Capturing of Birds and Sample Collection
The birds were captured and handled by a licenced ornithologist (Ľ.K.) under exemption No. 3320/2019-6.3 from Act. No. 543/2002 of the code on nature and landscape protection, granted by the Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic.
Ornithological mist nets (Ecotone, Poland) were exposed in the northern part of the wetland in an area of approximately 2.5 ha. Blood samples were collected from transmigrating birds during spring and autumn ringing campaigns in 2019 and 2020. Samples from local breeders and hatched juveniles were collected during the 2019 and 2020 bird nesting seasons (May–July) using the Constant Effort Site (CES) Ringing method according to the British Trust for Ornithology [27] adapted according to [24]. We collected one blood sample per captured bird from fledged juveniles and adults.
For each captured bird, the species, age and, if possible, the sex were determined. All captured and sampled birds were ringed and weighed.
Blood samples were obtained by puncture of the right jugular vein according to [28]. Blood volume no higher than 0.8% of the body weight was collected from each bird. The puncture and blood collection were carried out using an insulin syringe BD Microfine Insulin 0.5 mL with a U-100 needle (Becton Dickinson & Comp., Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Immediately after sampling, birds were released at the capture site.
Ticks were removed from the birds using a tick removal spoon (Dr. Kapiller®, Budapest, Hungary) (Figure S1). We introduced the use of this tick removal spoon because it has a round shape and eliminates the risk of losing the tick immediately after removal from the bird.
2.3. Tick Diagnostics
Ticks were placed in tubes labelled with the host bird’s number and collection date and promptly transferred to the deep freezer (−80 °C). Morphological identification was performed by an SZO-4 stereomicroscope (Optika, Ponteranica, Italy) according to the morphological key [24,28].
2.4. Processing of Blood Samples
Blood samples collected during the first day of trapping according to CES Ringing methodology were stored overnight in the field at refrigerator temperature. Sera were separated by centrifugation using 3800 RCF at 4 °C for 30 min. The sera were collected into new tubes and stored with the blood clots at −80 °C until examination.
Blood clots were processed into a 10% (w/v) suspension in Eagle’s minimum essential medium (EMEM; Pan Biotech, Aidenbach, Germany). Suspensions were centrifuged at RCF 13,000 RCF at 4 °C for 10 min, and the supernatants were used for viral RNA isolation.
2.5. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR for Arbovirus Detection
Only blood clots of tick-infested individuals were tested for TBEV, TRBV and KEMV RNA. Nucleic acid was extracted using the NucleoSpin RNA virus kit (Macherey Nagel, GmbH & Co., Dueren, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and kept at −80 °C until use.
The complementary DNA was synthesised using LunaScript RT SuperMix (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The obtained cDNA was stored at −20 °C and used as a PCR template for the molecular detection of arboviruses.
Orbivirus RNA was detected by conventional PCR and flavivirus RNA was detected by hemi-nested PCR using the DreamTaqTM Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania). To detect TRBV and KEMV RNA, Orbi_GIV_serogr_F and Orbi_GIV_serogr_R primers amplifying a 770 bp PCR product in the sequence VP1 located on segment 1 were used [29]. PanFlavi-NS5-F [15] and cFD2 [30] primers used in the first flavivirus PCR amplify a 599 bp sequence in the NS5 protein. In the hemi-nested flavivirus PCR, the PanFlavi-NS5-F and PanFlavi-NS5-R [15] primers flanking a 360 bp PCR product were used. Each primer was used in a 400 nM final concentration. The thermal profiles of each PCR reaction are described in Table S1.
2.6. μVNT for Arbovirus NAb Screening
Serum samples were first screened by μVNT for TBEV, TRBV and KEMV seropositive individuals. Heat-inactivated samples (56 °C for 30 min) were diluted 1:5 in a volume of 25 μL. Diluted sera were mixed with 25 μL of the virus culture containing 100 TCID50, giving a final serum dilution of 1:10. Viruses used in the μVNT were the following: TBEV Hypr (kindly provided by Dr. Mária Takács, National Centre for Epidemiology, Budapest, Hungary), KEMV (kindly provided by Professor Gerhard Dobler, Institut für Mikrobiologie der Bundeswehr, München, Germany) and TRBV strain 16.C/16 [31]. After overnight incubation at 4 °C, 50 μL of the cell suspension containing 1 × 104 cells in Eagle’s Minimal Essential Medium (Biosera, Nuaillé, France) supplemented by 10% foetal bovine serum (Biosera) and antibiotics were added to each well. Vero E6 cells were used for KEMV and TRBV, and A549 cells for TBEV. Plates were incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere for three (TRBV and KEMV) and five (TBEV) days. Results were read by an inverted light microscope at 100–200× magnification.
2.7. Simultaneous μVNT for Differentiation of Arbovirus Infections
Due to the high serological cross-reaction among flaviviruses and GIV serogroup orbiviruses, the seropositive samples from the screening μVNT were further examined by simultaneous μVNT to differentiate the infection. Here, serum samples were 4-fold serially diluted to 1:10,240. The abovementioned orbiviruses were used for KEMV and TRBV infection differentiation. For the differentiation of flavivirus infections, TBEV strain Hypr, Usutu virus (USUV) strain 939/01 (kindly provided by Professor Norbert Nowotny, Veterinary University, Vienna, Austria) and West Nile virus (WNV) strain 291.B/2013/Velky Biel/SVK [32] were used. In cross-reactive serum samples, at least a 4-fold higher specific NAb titre was considered conclusive.
During each sample batch in the screening and simultaneous μVNTs, the virus inoculum was back-titrated in triplicates, and the average titre was considered the infective dose.
2.8. Quantitative Characteristics of the Captured Bird Population
Using the ecological index of dominance (IED%), we characterised the population of captured birds [33,34]:
IED—ecological index of bird species dominance, NPB—number of birds of a particular species, NB—total number of birds.
Birds were infested when at least one tick was attached. The prevalence of tick infestation in a bird species (PTI%) and the mean intensity of tick infestation in a certain species (MITB) were calculated according to previous studies [33,34,35]:
PTI—prevalence of tick infestation per bird species, NPBT—number of birds of a particular species infested with ticks, NPB—number of birds of a particular species.
MITB—mean intensity of tick infestation per bird, TNPB—number of all tick species collected from a particular bird species, NPBT—number of birds of a particular species infested with ticks.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
R software (libraries: stats, rstatix, tidyverse) version 4.2.2 was utilised for statistical analysis. Because of the confirmed non-normal distribution of dependent variables, nonparametric tests were used—specifically, Fisher’s exact test (when testing the infestation of birds) and the Kruskal–Wallis H test (when testing the prevalence of ticks). R script (File S1) documenting all statistical analysis and the data used (File S2) are available on request.
3. Results
3.1. Ornithological and Parasitological Findings
During 15 bird-trapping visits carried out in 2019 and 2020, a total of 393 birds belonging to 32 species were captured. Based on IED data, Eurasian blackcaps (Sylvia atricapilla) and European robins (Erithacus rubecula) dominated the bird species list (23.7%), followed by the great tit (18.3%; n = 72) and common blackbird (Turdus merula) (7.9%; n = 31). A detailed list of caught bird species is in Table S2.
Tick infestation was observed in 22.4% (n = 88) of caught birds belonging to nine species (Table 1 and Table S2). The most frequently infested species, according to PTI, was the common blackbird (87.1%; 27/31), followed by song thrush (53.8%; 7/13), dunnock (Prunella modularis) (40%; 2/5), common chaffinch (Fringilla coelebs) (27.3%; 3/11), great tit (25%; 18/72), European robin (24.7%; 23/93), hawfinch (Coccothraustes coccothraustes) (21.4%; 3/14) and the common nightingale (Luscinia megarhynchos) (20%; 18/72) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Tick infestation among the analysed bird species.
In total, 194 ticks were collected from birds. Ixodes ricinus was found in 95.9% (n = 186) of examined cases, followed by Haemaphysalis concinna in 1% (n = 2) and I. frontalis in 0.5% (n = 1). Due to the damage of ticks, 2.6% (n = 5) were recognised at the genus level as Ixodes spp. Nymphs were found in 71.1% (n = 138; I. ricinus, n = 134; I. frontalis, n = 1; Ixodes spp., n = 3), and the rest (28.9%; n = 56) were larvae (I. ricinus, n = 52; H. concinna, n = 2; Ixodes spp., n = 2) (Table 1).
The highest MITB was observed in blackbirds (3.44 ticks per bird), followed by hawfinches (2.3 ticks per bird), European robins (2.1 ticks per bird), common nightingales and dunnocks with equal MITB (2.0 ticks per bird) (Table 1).
We compared whether migratory status, species, sex, age, or feeding behaviour could influence tick prevalence using the Kruskal–Wallis H tests (Table 2). Data from nine species (Table 1 and File S2 avalaible on request) where at least one bird was infested with ticks were used for statistical analysis.

Table 2.
Results of Kruskal–Wallis H tests for tick prevalence in selected bird species where at least one bird was infested with ticks.
Migratory status was a significant factor determining tick prevalence, whether it was the total number of ticks (p ≤ 0.0000) or larvae (p ≤ 0.0177) or nymphs (p ≤ 0.0000). The highest number of ticks was observed for short-distance migrants (S), whereas the lowest number was observed in bird species in which some individuals are short-distance migrants and others are long-distance migrants (S/L). Pairwise comparisons also confirmed a significant difference between these groups (p ≤ 0.0000—total ticks and nymph prevalence; p ≤ 0.0082—larvae prevalence) (Table 2).
Another relevant factor determining the prevalence of ticks, larvae and nymphs was the feeding behaviour of the birds. We divided all infested species into two groups: Ground-feeding species (common blackbird, song thrush) and shrub-feeding species (hawfinch, European robin, common chaffinch, common nightingale, great tit, dunnock, common blackcap). Ground-feeding birds had a significantly higher prevalence of ticks (p ≤ 0.0000), larvae (p ≤ 0.0000) and nymphs (p ≤ 0.0000) than those feeding in shrubs (Table 2).
When comparing infestation in species, only hawfinches and common blackbirds showed a statistically significant difference in tick prevalence (p ≤ 0.0000) (Table 2).
The ages and sexes of birds were evaluated as factors not influencing tick prevalence (Table 2).
Fisher’s exact tests were used to determine the differences between tick-infested and non-infested birds within the selected nine species (the same species used for the Kruskal–Wallis H test). We investigated whether the infestation is influenced by migratory status, feeding behaviour, sex and age. A significant difference (p ≤ 0.0000) between groups was confirmed for migration status, where S migrants were more likely infested than S/L migrants, and feeding behaviour (p ≤ 0.0000), where ground-feeding birds were more likely infested than shrub-feeding birds. The effect of sex and age on infestation was not confirmed (Table 3).

Table 3.
Results of Fisher’s exact tests for determining the difference between tick-infested and non-infested birds in selected bird species where at least one bird was infested with ticks in sex, age, feeding behaviour and migration status.
3.2. Screening of Arbovirus Infections
None of the 88 blood clot samples collected from tick-infested birds were positive for the screened arbovirus RNA.
In total, 393 serum samples were included in the study, 305 from non-infested and 88 from tick-infested birds. However, due to haemolysis, three samples of non-infested and 14 samples of tick-infested bird sera were excluded from the neutralization assay. Overall, in the μVNT, 302 non-infested and 74 tick-infested serum samples were used in the screening for TBEV, KEMV and TRBV NAb at a serum dilution of 1:10 (Table S2). Due to the limited volume, not all the serum samples were screened for each arbovirus NAb.
TBEV NAb was detected in 9.8% (n = 37) of 376 tested sera, collected from 302 non-infested and 74 tick-infested birds (Table S2). Seropositivity was observed in 10.6% (n = 32) of the non-infested (common blackbird, n = 2; common nightingale, n = 1; Eurasian blackcap, n = 24; European robin, n = 5) and in 6.8% (n = 5) of tick-infested (common blackbird, n = 4; European robin, n = 1) individuals. Juveniles represented 40.5% (n = 15) of all TBEV NAb seropositive birds (common blackbird, n = 3; Eurasian blackcap, n = 11; European robin, n = 1).
KEMV NAb seroprevalence was detected in 7.5% (n = 24) of 318 tested sera collected from 244 non-infested and 74 tick-infested birds (Table S2). Seropositivity was observed in 6.6% (n = 16) of non-infested (common chaffinch, n = 2; Eurasian blackcap, n = 7; Eurasian jay, n = 2; European robin, n = 2; great tit, n = 2; marsh warbler, n = 1) and in 10.8% (n = 8) of tick-infested (common blackbird, n = 5; European robin, n = 1; great tit, n = 1; hawfinch, n = 1) individuals. Juveniles represented 33.3% (n = 8) of all KEMV NAb seropositive birds (common blackbird, n = 2; Eurasian blackcap, n = 3; European robin, n = 2; great tit, n = 1).
TRBV NAb seroprevalence was observed in 19.5% (n = 50) of 256 tested sera collected from 182 non-infested and 74 tick-infested birds (Table S2). Seropositivity was observed in 14.3% (n = 26) of the non-infested (common blackbird, n = 1; common chaffinch, n = 1; Eurasian blackcap, n = 4; Eurasian jay (Garrulus glandarius), n = 1; European robin, n = 6; great tit, n = 8; hawfinch, n = 2; marsh warbler (Acrocephalus palustris), n = 2; redwing, n = 1) birds. In the tick-infested group, TRBV NAb was detected in 32.4% (n = 24; common blackbird, n = 10; common chaffinch, n = 1; dunnock, n = 1; European robin, n = 4; great tit, n = 1; hawfinch, n = 3; song thrush, n = 4) individuals. Juveniles represented 42% (n = 21) of all TRBV NAb seropositive birds (common blackbird, n = 6; Eurasian blackcap, n = 1; European robin, n = 5; great tit, n = 7; song thrush, n = 2).
3.3. Determination of Arbovirus Infections by Simultaneous μVNT
Sufficient volume for simultaneous μVNT was available in 9 sera out of the 37 TBEV NAb positive samples (Table 4). A low TBEV NAb titre (1:10) was observed in five serum samples collected from non-infested birds. The remaining four samples were collected from tick-infested blackbirds, where the TBEV NAb titre reached 1:10–1:40. Two of these samples cross-reacted with WNV (86.B/19 and 118.B/19) and one with USUV (86.B/19). Sample 86.B/19 showed a 4-fold higher NAb titre (1:160) in favour of USUV, which might indicate USUV infection. In the case of serum 118.B/19, the differentiation of TBEV and WNV infections was not possible due to the equal titre of NAb (Table 4).

Table 4.
Determination of flavivirus infections by simultaneous μVNT.
The determination of orbivirus infection was possible in 27 serum samples. Eight samples were collected from non-infested and 19 from infested birds (Table 5).

Table 5.
Determination of TRBV and KEMV infections by simultaneous μVNT.
One non-infested Eurasian jay (49.B/20) tested positive only for KEMV with the 1:10 NAb titre (Table 5). Twenty-four birds tested positive for TRBV infection with NAb titres ranging from 1:10 to 1:10,240. In seven samples, the TRBV NAb titre ranged from 1:10 to 1:40, in ten birds from 1:40 to 1:640, and in seven birds, the titre was higher than 1:640. A cross-reaction with KEMV was observed in six samples, but in each case, the TRBV NAb titre was at least 4-fold higher.
Determination was not possible in two birds, a hawfinch (5.B/20) and a European robin (279.B/20). The hawfinch had equal TRBV and KEMV NAb titre (1:10), and in the latter sample, the endpoint titration of KEMV NAb was not possible due to the low volume of serum.
3.4. Simultaneous Occurrence of Flavivirus and Orbivirus NAb
Two serum samples collected from adult common blackbirds (86.B/19 and 216.B/19) contained NAb against flaviviruses and TRBV (Table 4 and Table 5). Namely, sample 86.B/19 was simultaneously positive for USUV NAb (1:160) and TRBV NAb (1:2560). Sample 216.B/19 tested positive for low TBEV NAb titre (1:10–1:40) and high titre of TRBV NAb (1:2560).
3.5. Statistical Evaluation of the Link between Tick Infestation, Seropositivity and Arbovirus NAb Titre
A difference between groups of tick-infested and non-infested birds in seropositivity (results from screening, Table S2) was statistically significant only in TRBV infection (p ≤ 0.0016, Table 6). Statistical results indicate that tick-infested birds were more likely to overcome TRBV infection than non-infested birds. Statistical significance between the NAb titre and tick infestation was observed in the case of the TBEV (1:10 or higher) titre (p ≤ 0.0119) and TRBV 1:160 or higher titre (p ≤ 0.0261), where tick-infested birds have a higher NAb titre than non-infested individuals (Table 6).

Table 6.
Results of Fisher’s exact tests for determination of the difference between tick-infested and non-infested birds in seroprevalence and antibody titre.
4. Discussion
The present study reports on the participation of birds in the transmission of TBEV, KEMV and TRBV infections and the link between tick infestation and arbovirus infections under natural conditions.
During 2019 and 2020, 393 birds were captured, of which 22.4% were infested with ticks. The most abundant (69.1%) ticks were I. ricinus nymphs. Similar to the abovementioned publications, in our study, the most infested were ground-feeding or medium-level foraging bird species (common blackbird, song thrush, dunnock, common chaffinch, great tit, European robin, hawfinch and the common nightingale). These results are comparable to previous studies from Slovakia [36,37], where nymphs feeding on birds were more common than larvae. However, in another study from Slovakia, the trend was in favour of larvae [38]. Except for I. ricinus, we also collected two tick species, H. concinna and I. frontalis, rarely obtained from birds in Slovakia [36,37,38].
Studies focusing on tick-borne arbovirus infections were carried out in autochthonous wild bird populations in Slovakia. Approximately 400 migratory, partially migratory and non-migratory birds of more than 20 species were tested for antibodies [15,20,25]. TBEV NAb was observed in an adult Eurasian blackcap, representing 1.1% seropositivity [20]. In comparison with our previous study [20], the present results show that TBEV NAb prevalence increased by almost 26% among the Eurasian blackcaps. Some individuals of the Eurasian blackcap population are short-distance migrants and others are long-distance migrants [39]. Thus, it is not possible to confirm that the birds seroconverted at the model area in the Drienovská wetland. Their nests are neat cups built low in brambles or scrubs close to the ground [40]. Indeed, adults and juveniles have a high probability of coming into contact with infected ticks.
Eleven TBEV NAb-positive Eurasian blackcaps were juveniles. The low TBEV NAb titre in the examined birds may be related to either developing the post-infectious antibody response or antibody decay of passively acquired maternal antibodies. Knowledge of post-infection antibody development and decay after flavivirus infections is limited. The nature and duration of the antibody response may vary between populations and bird species [41,42,43,44]. Haemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies were detected in Western capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus), willow ptarmigan (Lagopus lagopus) and rock ptarmigan (Lagopus muta) after louping ill virus (LIV) infection, a close relative virus to TBEV. LIV antibodies were detected (1:40–1:160) six days after infection, and in four days, reached high titre levels ranging from 1:640 to 1:10,240 [45]. In free-ranging birds, WNV NAb decreased by 0.188 log natural units per month. Most birds had an undetectable NAb titre two years following initial exposure to WNV, and juveniles had higher antibody decay rates than adults [46].
Other TBEV Nab-positive bird species included the European robin, common blackbird and a common nightingale. Several studies have described European robins and common blackbirds as potential TBEV reservoirs. Blackbirds in particular were highly infested in the present study. The presumption that these species could be reservoirs for TBEV stemmed mainly from the finding of virus-positive ticks on birds and TBEV NAb in blood samples [47,48,49,50]. However, isolation or detection of TBEV from bird blood is usually unsuccessful. In the present study, we also failed to detect virus RNA in the feeding ticks and in tick-infested bird blood clots. This result concurs with previous studies, where the prevalence of TBEV in endemic areas in questing ticks and ticks removed from hosts is less than 1% [51,52,53,54].
Both KEMV and TRBV are considered serotypes of GIV and are serologically close relatives. Differentiation of specific antibodies is possible based on the complement fixation test or neutralisation assay [55,56]. The main reservoirs of GIV are seabirds and small mammals of KEMV and TRBV [18]. The role of birds in the transmission of these viruses remains unclear. To date, there is only one report on the successful isolation of KEMV, the EgAn1169-61 strain, from the blood of a migrating redstart [8]. KEMV NAb was demonstrated in 37% sera of juvenile and adult wild birds caught near Romanovka village (Kemerovo region, Russia), where the original KEMV strains were recovered from I. persulcatus ticks. KEMV NAb specific to the R10 strain was detected in fieldfare, red-throated thrush, song thrush, carrion crow, common starling, tree pipit (Anthus trivialis), common buzzard and Eurasian magpie. The titre of NAb ranged from 1:6 to 1:8, and the highest seropositivity rate was noted in fieldfares [57]. Despite the high number of examined samples in our study, not all could be used for simultaneous μVNT due to the limited volume of sera, and KEMV infection was conclusively differentiated from TRBV infection only in one adult Eurasian jay. In one adult hawfinch, differentiation was not possible because of equal NAb titres.
The high seroprevalence in the study of Libíková et al. was likely caused by the origin of tested birds, which were caught in the area of the natural occurrence of KEMV [57]. KEMV NAb-seropositive adult Eurasian jay and dubious hawfinch caught in the Drienovská wetland may indicate that these birds migrated from endemic areas where they seroconverted earlier, or they become infected in Central Europe. However, reports of hawfinches ringed on the Drienovská wetland support the possibility of KEMV presence in Central Europe [58]. These birds migrate in the southwestern direction, which suggests the presence of KEMV along their migratory routes [59].
Until recently, it was believed that the distribution of KEMV is closely associated with Western Siberia. However, the latest molecular research indicates that KEMV circulates in areas thousands of miles apart (the Urals and certain areas in the European part of the Russian Federation) [60,61,62,63]. Multiple reassortments were observed among nine KEMV strains isolated in distinct parts of Russia. These results point to virus trafficking over long distances and support the assumption that birds are crucial in spreading the virus to new areas [62].
In the screening, nine sera of non-infested birds (marsh warbler, common chaffinch and Eurasian blackcaps) and one serum of infested great tit were positive only for KEMV NAb. Three of these birds were juvenile blackcaps. This may suggest previous KEMV infection of juveniles in Northeastern or Eastern Europe, where the virus is endemic. The birds may become seropositive by acquiring antibodies through eggs or infection in Central Europe. If the birds became infected in central Europe, that would suggest two hypotheses. First, the natural vector of KEMV I. persulcatus has already spread into a new area. According to the Tick maps of the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, there are no data on the presence of this tick species in Slovakia, Poland or Hungary. However, I. persulcatus was observed in the north of Ukraine [64]. Second, KEMV may have an alternative vector by which it is able to multiply and be transmitted to birds. A recent study showed, that an artificial feeding system allowed I. ricinus to acquire KEMV and transmit it transstadially, but the ticks could not transmit the virus to IFNAR-/- or BALB/c mice [65]. However, the transmission of KEMV by I. ricinus to birds is unknown.
The highest seropositivity among the screened arbovirus infections was observed in the case of TRBV. Most of the NAb-quantified samples had titres equal to or higher than 1:160, and some juvenile individuals fell into this group. Compared to previous research by Csank et al., where the prevalence of TRBV NAb was 7.4%, in the present research, it was 19.5% [20]. High NAb titres in adults and juveniles suggest an active transmission cycle of TRBV in the avifauna of the selected area, but also possible infection in other localities.
Circulation of TRBV and LIPV in the locality of Slovak karst has been reported before. In 1963, seven strains of LIPV were isolated from questing and half-engorged I. ricinus ticks [19]. Another three strains were isolated from half-engorged and engorged I. ricinus ticks [66]. In addition, in Western Slovakia, three further strains named Koliba were isolated from I. ricinus ticks [19]. Hence, in the case of samples with equal KEMV and TRBV NAb titres, it is safe to hypothesise that those sera may contain LIPV or Koliba NAb. Unfortunately, these strains are not kept at our disposal, and it is not possible to further examine the bird serum samples.
In two serum samples from adult blackbirds, simultaneous μVNT showed co-infection by flaviviruses and TRBV. Co-infection of flaviviruses and members of the former KEMV serogroup was described in the 1960s. TBEV and KEMV were detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient diagnosed with TBE [21]. Co-infection was also observed in ticks, and LIPV NAb were confirmed in 51% of 49 patients diagnosed with TBE [67]. Recently, we have demonstrated co-infection of WNV and TRBV at the model area in the Drienovská wetland [20]. The benefits of these viruses from co-infection remain unknown.
5. Conclusions
The demonstrated results indicate increased TBEV and TRBV seroprevalence in birds over the past several years. This is the first study investigating KEMV infection in the Slovak bird population. The high KEMV seropositivity in juveniles may indicate that the infection occurs in the model locality Drienovská wetland. However, at this stage, it is impossible to distinguish post-infectious seroconversion from passively acquired maternal antibodies. Hence, further research should be aimed at this field. Statistical analysis confirmed the significance of tick infestation rates in TRBV seroconversion. The relationship was demonstrated for both seropositivity and the NAb titre. In the case of TBEV, the infestation rate was associated with the amount of NAb. Although the role of birds as reservoirs of TBEV, KEMV and TRBV remains unclear, targeted monitoring of birds and vectors is an effective measure of the surveillance of zoonotic arbovirus introduction into new geographic areas.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms10122397/s1, Table S1: Thermal profiles of PCR used for the GIV serogroup orbivirus RNA and Flavivirus RNA detection; Table S2: The list of captured bird species and proportion of seropositive tick-infested and non-infested individuals in the screening and their migratory status. Figure S1: Tick removal spoon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—K.P., Ľ.K. and T.C.; methodology—K.P., Ľ.K., I.C.M., P.S., S.P. and T.C.; data curation—A.O., J.P., K.P. and T.C.; statistical analysis—A.L.; writing original draft—K.P. and T.C.; writing review and editing—K.P., Ľ.K. and T.C.; funding acquisition—K.P., A.O., J.P. and T.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovak Research and Development Agency, grant number APVV-19-0440; project implementation: “Open scientific community for modern interdisciplinary research in medicine (OPENMED)”, ITMS2014+: 313011V455 supported by the Operational Programme Integrated Infrastructure, funded by the ERDF; and by IGA UVLF 03/2020.
Data Availability Statement
File S1 R script and File S2 Data used for statistical analysis are available on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Boris Klempa (Biomedical Research Center of the Slovak Academy of Science, Bratislava, Slovakia) for access to the biosafety level 3 laboratory provided in the frame of the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program’s project EVA-GLOBAL (grant agreement number 871029). Project implementation: “Open scientific community for modern interdisciplinary research in medicine (OPENMED)”, ITMS2014+: 313011V455 supported by the Operational Programme Integrated Infrastructure, funded by the ERDF. The authors would like to thank David Idris Lewis for the English language correction.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hubalek, Z. An annotated checklist of pathogenic microorganisms associated with migratory birds. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 639–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.E. The Palaearctic-African Bird Migration Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Attoui, H.; Banyai, K.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Danthi, P.; Del Vas, M.; Dermody, T.S.; Duncan, R.; Fang, Q.; Johne, R.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Sedoreoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Adkins, S.; Alioto, D.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Avsic-Zupanc, T.; Ayllon, M.A.; Bahl, J.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. 2020 taxonomic update for phylum Negarnaviricota (Riboviria: Orthornavirae), including the large orders Bunyavirales and Mononegavirales. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 3023–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikryukova, T.P.; Moskvitina, N.S.; Kononova, Y.V.; Korobitsyn, I.G.; Kartashov, M.Y.; Tyuten Kov, O.Y.; Protopopova, E.V.; Romanenko, V.N.; Chausov, E.V.; Gashkov, S.I.; et al. Surveillance of tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild birds and ticks in Tomsk city and its suburbs (Western Siberia). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, M.A.; Barton, T.R.; Wanless, S.; Hails, R.S.; Harris, M.P.; Nuttall, P.A. Tick-borne Great Island Virus: (I) Identification of seabird host and evidence for co-feeding and viraemic transmission. Parasitology 2006, 132, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Shope, R.E. Kemerovo virus from a migrating common redstart of Eurasia. Acta Virol. 1971, 15, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, G.; Savji, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Guzman, H.; Yu, X.; Desai, A.; Rosen, G.E.; Hutchison, S.; Lipkin, W.I.; Tesh, R. Characterization of the Uukuniemi virus group (Phlebovirus: Bunyaviridae): Evidence for seven distinct species. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Mackenstedt, U.; Kahl, O.; Petney, T.N. Chapter 3: Transmission/Natural cycle. In The TBE Book, 2nd ed.; Dobler, G., Erber, W., Bröker, M., Schmitt, H.-J., Eds.; Global Health Press Pte Ltd: Singapore, 2019; pp. 62–86. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer, M.; Schmuck, H.M.; Leschnik, M. Chapter 8: TBE in animals. In The TBE Book, 2nd ed.; Dobler, G., Erber, W., Bröker, M., Schmitt, H.-J., Eds.; Global Health Press Pte Ltd: Singapore, 2019; pp. 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Kunze, U. Report of the 21st Annual Meeting of the International Scientific Working Group on Tick-Borne Encephalitis (ISW-TBE): TBE—record year 2018. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tongeren, H.A.E. Experimental infection of coots (Fulica atra) with Russian spring summer encephalitis virus. In Biology of Viruses of the Tick-Borne Encephalitis Complex: Proceedings; Libíková, H., Ed.; House of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Praha: Smolenice, Slovakia, 1962; pp. 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tongeren, H.A.E. Viraemia and antibody response of the mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) to infection with tick-borne encephalitis virus. J. Comp. Pathol. 1983, 93, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csank, T.; Bhide, K.; Bencurova, E.; Dolinska, S.; Drzewniokova, P.; Major, P.; Korytar, L.; Bockova, E.; Bhide, M.; Pistl, J. Detection of West Nile virus and tick-borne encephalitis virus in birds in Slovakia, using a universal primer set. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubalek, Z.; Rudolf, I. Tick-borne viruses in Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraminskiy, V.A.; Kraminskaya, N.N.; Brom, I.P.; Zhivolyapina, R.R.; Zonov, G.B.; Perevoznikov, V.A.; Sotnikova, A.N.; Soldatov, G.M. Transovarial (transembryonal) transmission of TBE virus in migratory birds. In Transcontinental Connections of Migratory Birds and Their Role in the Distribution of Arboviruses; Cherepanov, A.I.E.A., Ed.; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1972; pp. 274–276. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Grešíková, M.; Nosek, J.; Kožuch, O.; Ernek, E.; Lichard, M. Study on ecology of Tribeč virus. Acta Virol. 1965, 9, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Libíková, H.; Rehacek, J.; Ernek, E.; Gresikova, M.; Somogyio, J.; Kozuch, O. Cytopathic viruses isolated from Ixodes ricinus ticks in Czechoslovakia. Acta Virol. 1964, 8, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Csank, T.; Korytár, Ľ.; Pošiváková, T.; Bakonyi, T.; Pistl, J.; Csanády, A. Surveillance on antibodies against West Nile virus, Usutu virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus and Tribeč virus in wild birds in Drienovská wetland, Slovakia. Biologia 2019, 74, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, M.P. Report on the isolation from Ixodes persulcatus ticks and from patients in western Siberia of a virus differing from the agent of tick-borne encephalitis. Acta Virol. 1963, 7, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franková, V.; Marhoul, Z.; Duniewicz, M.; Pruklová, A. Meningoencephalitis associated with orbivirus infection. Sb. Lek. 1982, 84, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kerlik, J.; Pántiková Valachová, M.; Csank, T.; Avdičová, M. Výskyt západonílskej horúčky v Európe. In Proceedings of the VI. Ročník Vedeckého Kongresu Zoonózy, Alimentárne Nákazy a Nákazy z Vody—Spoločná Ochrana Zdravia Ľudí a Zvierat a XXIII, Červenkove Dni Preventívnej Medicíny, Banská Bystrica, Slovakia, 15–17 October 2018. (In Slovak). [Google Scholar]
- Olekšák, M.; Pjenčák, P.; Fulín, M.; Matis, Š. Bird nesting community of the Drienovec bird Ringing Station—CES pro-gramme. Tichodroma 2007, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Csank, T.; Drzewnioková, P.; Korytár, L.; Major, P.; Gyuranecz, M.; Pistl, J.; Bakonyi, T. A Serosurvey of Flavivirus Infection in Horses and Birds in Slovakia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reports from Bird Ringing Station Drienovec. Available online: https://brsdrienovec.webnode.sk/publikovanie/ (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Guidelines for Constant Effort Ringing. Available online: https://euring.org/files/documents/research/euro_ces_guidelines210904.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Hoysak, D.J.; Weatherhead, P.J. Sampling Blood from Birds: A Technique and an Assessment of Its Effect. Condor 1991, 93, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peňazziová, K.; Korytár, Ľ.; Pistl, J.; Ondrejková, A.; Csank, T. Detekcia arbovírusov z kliešťov u vtákov odchytených v Drienovskej mokradi. In Seminár Doktorandov Venovaný Pamiatke Akademika Boďu. Vedecké práce Doktorandov 2020: Zborník zo Seminára Doktorandov Venovaného Pamiatke Akademika Boďu; Slovenská Akadémia Vied, Centrum Biovied: Košice, Slovakia, 2020; pp. 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kuno, G. Universal diagnostic RT-PCR protocol for arboviruses. J. Virol. Methods 1998, 72, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzewniokova, P.; Csank, T.; Vargová, B.; Majláthová, V.; Pistl, J. Molecular detection of Tick-borne encephalitis virus and Tribeč virus from ticks in Eastern Slovakia. In Proceedings of the Czechoslovak Virology Conference, České Budějovice, Czech Republic, 16–17 February 2017; Biologické Centrum AV ČR: Branišovská, Czech Republic, 2017; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Drzewnioková, P.; Barzon, L.; Franchin, E.; Lavezzo, E.; Bakonyi, T.; Pistl, J.; Csank, T. The complete genome sequence analysis of West Nile virus strains isolated in Slovakia (central Europe). Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zając, Z.; Kulisz, J.; Kunc-Kozioł, R.; Woźniak, A.; Filipiuk, M.; Rudolf, R.; Bartosik, K.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. Tick Infestation in Migratory Birds of the Vistula River Valley, Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, L.; Esch, G.W.; Holmes, J.C.; Kuris, A.M.; Schad, G.A. The Use of Ecological Terms in Parasitology (Report of an Ad Hoc Committee of the American Society of Parasitologists). J. Parasitol. 1982, 68, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology Meets Ecology on Its Own Terms: Margolis et al. Revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taragel’ova, V.; Koci, J.; Hanincova, K.; Kurtenbach, K.; Derdakova, M.; Ogden, N.H.; Literak, I.; Kocianova, E.; Labuda, M. Blackbirds and song thrushes constitute a key reservoir of Borrelia garinii, the causative agent of borreliosis in Central Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitalska, E.; Literak, I.; Sparagano, O.A.; Golovchenko, M.; Kocianova, E. Ticks (Ixodidae) from passerine birds in the Carpathian region. Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2006, 118, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthova, L.; Slobodnik, V.; Slobodnik, R.; Oleksak, M.; Sekeyova, Z.; Svitalkova, Z.; Kazimirova, M.; Spitalska, E. The natural infection of birds and ticks feeding on birds with Rickettsia spp. and Coxiella burnetii in Slovakia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 68, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, D.; Perrins, C.M.; Gillmor, R. The Birds of the Western Palearctic (Concise); Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ferianc, O. Vtáky Slovenska 2; Veda: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1979; p. 472. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, F.; Magor, K.E.; Kaspers, B. Structure and evolution of avian immunoglobulins. In Avian Immunology; Davison, F., Kaspers, B., Schat, K.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kuno, G. Persistence of arboviruses and antiviral antibodies in vertebrate hosts: Its occurrence and impacts. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, W.; Lothrop, H.; Chiles, R.; Madon, M.; Cossen, C.; Woods, L.; Husted, S.; Kramer, V.; Edman, J. West Nile virus in California. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, W.K.; Kramer, L.D.; Chiles, R.E.; Green, E.G.; Martinez, V.M. Encephalitis virus persistence in California birds: Preliminary studies with house finches. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, H.W.; Moss, R.; Pow, I.; Buxton, D. The response of three grouse species (Tetrao urogallus, Lagopus mutus, Lagopus lagopus) to louping-ill virus. J. Comp. Pathol. 1980, 90, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, E.M.; Walker, E.D.; Anderson, T.K.; Kitron, U.D.; Brawn, J.D.; Krebs, B.L.; Newman, C.; Ruiz, M.O.; Levine, R.S.; Carrington, M.E.; et al. West Nile Virus Antibody Decay Rate in Free-Ranging Birds. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernek, E.; Kozuch, O.; Lichard, M.; Nosek, J. The role of birds in the circulation of tick-borne encephalitis virus in the Tribeč region. Acta Virol. 1968, 12, 468–470. [Google Scholar]
- Lommano, E.; Dvorak, C.; Vallotton, L.; Jenni, L.; Gern, L. Tick-borne pathogens in ticks collected from breeding and migratory birds in Switzerland. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikku, P. Blackbird, Turdus merula L., and tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus. Acta Virol. 1973, 17, 442. [Google Scholar]
- Waldenstrom, J.; Lundkvist, A.; Falk, K.I.; Garpmo, U.; Bergstrom, S.; Lindegren, G.; Sjostedt, A.; Mejlon, H.; Fransson, T.; Haemig, P.D.; et al. Migrating birds and tickborne encephalitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumann, R.; Muhlemann, K.; Strasser, M.; Beuret, C.M. High-throughput procedure for tick surveys of tick-borne encephalitis virus and its application in a national surveillance study in Switzerland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4241–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.H.O.; Golovljova, I.; Vene, S.; Jaenson, T.G.T. Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes ricinus ticks in northern Europe with particular reference to Southern Sweden. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanoff, P.; Pfeffer, M.; Hellenbrand, W.; Rogalska, J.; Rühe, F.; Makówka, A.; Michalik, J.; Wodecka, B.; Rymaszewska, A.; Kiewra, D.; et al. Virus detection in questing ticks is not a sensitive indicator for risk assessment of tick-borne encephalitis in humans. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsson, P.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Olsen, B.; Waldenström, J.; Lindgren, P.-E. Migratory birds as disseminators of ticks and the tick-borne pathogens Borrelia bacteria and tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus: A seasonal study at Ottenby Bird Observatory in South-eastern Sweden. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libíková, H.; Buckley, S.M. Serological characterization of Eurasian Kemerovo group viruses. II. Cross plaque neutralization tests. Acta Virol. 1971, 15, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Libíková, H.; Casals, J. Serological characterization of Eurasian Kemerovo group viruses. I. Cross complement fixation tests. Acta Virol. 1971, 15, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Libikova, H.; Mayer, V.; Kozuch, O.; Rehacek, J.; Ernek, E.; Albrecht, P. Isolation from Ixodes persulcatus ticks of cytopathic agents (Kemerovo virus) differing from tick-borne encephalitis virus and some of their properties. Acta Virol. 1964, 8, 289–301. [Google Scholar]
- Fulín, M.; Gálffyová, M.; Kiss, E.; Krišovský, P.; Olekšák, M. Personal Communication; Drienovec Bird Ringing Station, Slovak Karst National Park: Brzotín, Slovakia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cepák, J. Hawfinch. In Atlas Migrace Ptáku České a Slovenské Republiky; Cepák, J., Klvaňa, P., Škopek, J., Schropfer, L., Jelínek, L., Hořák, D., Formánek, J., Zárybnický, J., Eds.; Aventinum: Prague, Czech Republic, 2008; pp. 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Dedkov, V.G.; Markelov, M.L.; Gridneva, K.A.; Bekova, M.V.; Gmyl, A.P.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Karganova, G.G.; Romanova, L.; Pogodina, V.V.; Yakimenko, V.V.; et al. Prevalence of Kemerovo virus in ixodid ticks from the Russian Federation. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlova, T.V.; Khomyakova, T.I.; Dedkov, V.G.; Safonova, M.V.; Karan, L.S.; Grigoryeva, Y.E.; Kozlov, V.V.; Lopatin, A.A.; Ivanova, S.M.; Khomyakov, Y.N. The identification of new pathogens for focal infections in Ixodes ticks on the territory of Tula region. EIDj 2018, 23, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, M.V.; Gmyl, A.P.; Lukashev, A.N.; Speranskaya, A.S.; Neverov, A.D.; Fedonin, G.G.; Pimkina, E.V.; Matsvay, A.D.; Khafizov, K.F.; Karganova, G.G.; et al. Genetic diversity of Kemerovo virus and phylogenetic relationships within the Great Island virus genetic group. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachev, S.; Panov, V.; Dobler, G.; Tikunova, N. First detection of Kemerovo virus in Ixodes pavlovskyi and Ixodes persulcatus ticks collected in Novosibirsk region, Russia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Tick Maps. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/disease-vectors/surveillance-and-disease-data/tick-maps (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Migné, C.V.; Hönig, V.; Bonnet, S.I.; Palus, M.; Rakotobe, S.; Galon, C.; Heckmann, A.; Vyletova, E.; Devillers, E.; Attoui, H.; et al. Evaluation of two artificial infection methods of live ticks as tools for studying interactions between tick-borne viruses and their tick vectors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalek, Z.; Calisher, C.H.; Mittermayer, T. A new subtype (“Brezova”) of Tribec orbivirus (Kemerovo group) isolated from Ixodes ricinus males in Czechoslovakia. Acta Virol. 1987, 31, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Libíková, H.; Heinz, F.; Ujházyová, D.; Stünzner, D. Orbiviruses of the Kemerovo complex and neurological diseases. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1978, 166, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).