Abstract
The development of bacterial resistance is an insistent global health care issue, especially in light of the dwindled supply of new antimicrobial agents. This mandates the development of new innovative approaches to overcome the resistance development obstacle. Mitigation of bacterial virulence is an interesting approach that offers multiple advantages. Employing safe chemicals or drugs to mitigate bacterial virulence is an additive advantage. In the current study, the in vitro antivirulence activities of citrate were evaluated. Significantly, sodium citrate inhibited bacterial biofilm formation at sub-MIC concentrations. Furthermore, sodium citrate decreased the production of virulence factors protease and pyocyanin and diminished bacterial motility. Quorum sensing (QS) is the communicative system that bacterial cells utilize to communicate with each other and regulate the virulence of the host cells. In the present study, citrate in silico blocked the Pseudomonas QS receptors and downregulated the expression of QS-encoding genes. In conclusion, sodium citrate showed a significant ability to diminish bacterial virulence in vitro and interfered with QS; it could serve as a safe adjuvant to traditional antibiotic treatment for aggressive resistant bacterial infections such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
1. Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes broadly diverse pathogenesis and illness [1,2]. P. aeruginosa causes aggressive infections to almost all body systems; however, it causes serious surgical and burn wound infections, as well as infections of the lung, eye, bloodstream, and urinary tract [3,4]. This splendid capability of P. aeruginosa to invade, defeat, and establish infections in host tissues is owed to a huge arsenal of virulence factors. This virulence arsenal expands to involve the production of a wide array of virulent extracellular pigments and enzymes such as protease, elastase, hemolysins, and others for the formation of biofilms, motility, and resistance to oxidative stress [5,6,7]. In a magnificent manner, P. aeruginosa employs several systems to orchestrate its virulence factors and regulate its pathogenesis [4]. For instance, P. aeruginosa utilizes several types (types 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6) of secretion systems (SS). Although all types of secretion systems are involved in P. aeruginosa virulence, T3SS plays an important role in invasion and intracellular survival inside immune cells, as reviewed [8]. Furthermore, the P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing (QS) system plays a key role in controlling the production of virulence factors [9]. QS is the chemical language that bacterial cells use to communicate with each other in an inducer–receptor manner [10]. In general, in Gram-negative bacteria, autoinducers of the QS systems are produced by inducer synthetases that bind latterly to surface QS receptors forming inducer–receptor complexes, which have the ability to regulate the expression of virulence factors encoding genes [10,11]. It is well documented that QS controls biofilm formation, bacterial motilities, production of enzymes and pigments, resistance to oxidative stress, and other virulence factors [8,9]. There is growing evidence that targeting QS could guarantee mitigation of bacterial virulence [12,13].
Besides the vigorous virulence of P. aeruginosa, it develops phenotypic and/or genotypic resistance to almost all known antimicrobial classes [14]. This gives additional clinical importance to P. aeruginosa to be listed among the most important pathogenic microbes [15]. Indeed, resistance development to antibiotics is a major health issue, and the decrease in discovering new antibiotics worsens the situation, resulting in the need to discover new innovative solutions [16,17]. Attenuating bacterial virulence is a reasonable option that confers several advantages. First, mitigating bacterial virulence facilitates their eradication by the immune system and, at the same time, does not affect bacterial growth; hence, it does not induce resistance development [18,19,20]. The maximum benefit is accomplished by employing safe drugs or natural drugs to avoid any probable toxicological effects. In this direction, several drugs, chemical compounds, or natural products were screened for their antivirulence activities [12,21,22,23,24,25,26].
Sodium citrate is commonly used as an emulsifier for oils and is used in food industries as an acidity regulator and sanitizer by lowering the pH, providing unsuitable conditions for bacterial growth. It is also used in the collection of blood samples to prevent clotting in storage [27,28]. Furthermore, sodium citrate is used to neutralize excess acid in the urine and blood, as well as in the treatment of chronic kidney diseases and metabolic acidosis [28]. Importantly, it was shown that sodium citrate has antimicrobial activity, independent of pH, against oral Streptococcus pneumoniae and several oral bacteria such as Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus mutans [27]. Importantly, it was reported that sodium citrate (4%) could inhibit the formation of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms by 46.5% [29]. In another study, 4% sodium citrate in solution with 0.0015% nitroglycerin and 22% ethanol could eradicate biofilm formed by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE), vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, in addition to Candida albicans and Candida glabrata. Furthermore, sodium citrate at a concentration of 4% was able to prevent the biofilm formation of K. pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli [30,31,32,33]. In this context, the antibiofilm and antivirulence activities of sodium citrate were evaluated at concentrations of 4% and 5% against P. aeruginosa.
Taking into consideration that sodium citrate has no known toxicological reaction [28], this study aimed to evaluate the antivirulence activities of sodium citrate. In the current study, the antivirulence and anti-QS activities of sodium citrate against P. aeruginosa were investigated in vitro and in silico.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Bacterial Strains
All microbiological media were purchased from Oxoid (Hampshire, UK). All the used chemicals and sodium citrate were of pharmaceutical grade and purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). P. aeruginosa PAO1 was used in this study
2.2. Determination of Sodium Citrate Effect on Bacterial Growth
In order to ensure the antivirulence effect of sodium citrate is not due to the inhibition of bacterial growth, the effect of sodium citrate at tested concentrations on P. aeruginosa growth was assessed, as described previously [34]. Briefly, fresh P. aeruginosa cultures were inoculated overnight in LB broth provided with 4% or 5% sodium citrate at 37 °C for 24 h. The turbidites of P. aeruginosa cultures were measured at 600 nm, and viable bacterial cells were counted.
2.3. Evaluation of Antibiofilm Activities of Sodium Citrate
The inhibition of P. aeruginosa biofilm formation by sodium citrate was assessed by the crystal violet method [35]. One hundred microliter aliquots of P. aeruginosa suspension of an approximate cell inoculum of 1 × 106 CFU/mL were transferred to microtiter plate wells in the presence or absence of sodium citrate (4% and 5%). The nonadherent cells were washed out after 24 h incubation at 37 °C, and the biofilm-forming cells were fixed with methanol and stained with crystal violet (1%) for 20 min. The excess dye was washed out, plates were air-dried, adhered dye was extracted with 33% glacial acetic acid, and absorbances were measured at 590 nm using the Biotek Spectrofluorimeter (Winooski, VT, USA).
2.4. Assessment of Sodium Citrate Effect on P. aeruginosa Motility
The sodium citrate inhibition of P. aeruginosa swarming motility was performed as described previously [17,36]. LB agar plates containing 4% or 5% sodium citrate and control LB agar plates without sodium citrate were centrally inoculated with 5 µL of fresh P. aeruginosa PAO1 culture prepared from an overnight culture in tryptone broth, and the swarming zone was measured.
2.5. Determination of Sodium Citrate Effect on Pyocyanin Production
The virulent P. aeruginosa pyocyanin pigment was assayed in the presence or absence of sodium citrate, as previously shown [37,38]. Ten microliter aliquots of P. aeruginosa overnight cultures (adjusted to OD600 of 0.4) were mixed with 1 mL of LB broth provided with sodium citrate (4% or 5%). After 48 h incubation at 37 °C, the Eppendorf tubes were centrifuged, and the absorbances of pyocyanin pigment in the supernatants were measured at 691 nm.
2.6. Evaluation of Inhibitory Effect on Protease Activity
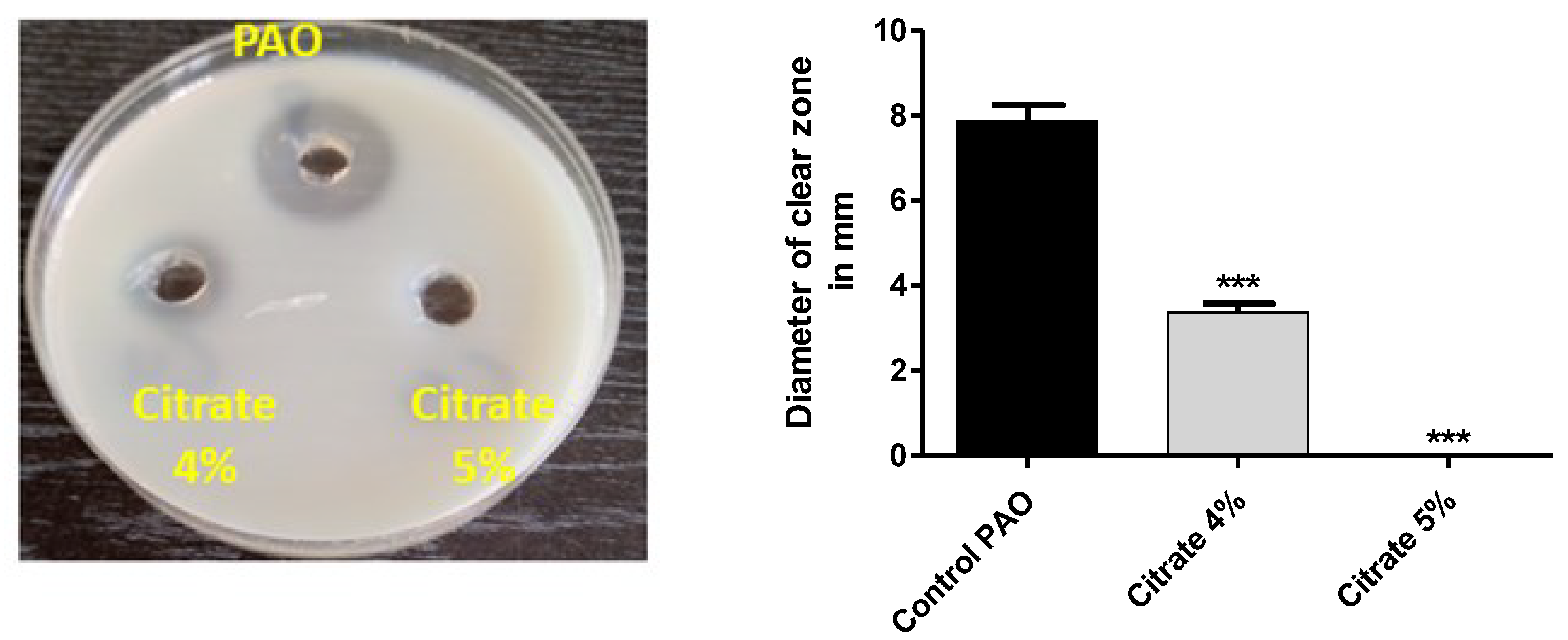
The skim milk agar method was used to assess the inhibitory effect of sodium citrate on the activity of protease [39]. P. aeruginosa overnight cultures in the presence or absence of sodium citrate (4% or 5%) were centrifuged to obtain the extracellular protease in the supernatants. One hundred microliters of the supernatants was placed in the wells prepared in skim milk (5%) agar plates. After 24 h incubation at 37 °C, the clear zones representing the proteolytic activity were measured.
2.7. Assessment of Sodium Citrate Effect on QS-Encoding Genes
A quantitative real-time PCR was performed to attest to the effect of sodium citrate on the expression of QS-encoding genes in P. aeruginosa. Citrate-treated and untreated overnight cultures of PAO1 at 37 °C were prepared, and the pellets were collected by centrifugation at 12,000× g for 2 min. The pellets were resuspended in Tris–EDTA buffer with lysozyme (100 µL) and incubated for 5 min at 25 °C. The lysis buffer with β-mercaptoethanol was added and mixed well. The RNA of P. aeruginosa cultures treated or not with sodium citrate 5% was extracted (Purification Kit Gene JET RNA, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and stored at −80 °C as described [40]. The expression levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene ropD, and the primers are listed in Table 1. The cDNA was synthesized using a high-capacity cDNA reverse transcriptase kit (Applied Biosystem, Waltham, MA, USA) and amplified using the SYBR Green I PCR Master Kit (Fermentas, Waltham, MA, USA) in a Step One instrument (Applied Biosystem, Waltham, MA, USA). A melting curve was established according to the manufacturer, and the relative expressions were calculated using the comparative threshold cycle (∆∆Ct) method [41].

Table 1.
Sequences of the used primers in this study [17].
2.8. In Silico Assessment of Sodium Citrate Ability to Bind P. aeruginosa QS Receptors
The P. aeruginosa LasR receptor (PDB ID: 2UV0) [42], RhlR receptor model (ID: P54292) [7], and citrate [43] were downloaded, then prepared using AutoDockTools [44] in accordance with our prior procedures [7]. AutoDock Vina [45] was used for docking, while Discovery studio [46] was used for both 3D visualization and 2D schematic presentation.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All the performed experiments were conducted in triplicates, and the data are expressed as means ± standard errors. One-way ANOVA test, followed by Tukey’s post-test, was used (unless mentioned) to test the statistical significance, where p ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Sodium Citrate at Concentrations of 4% or 5% Does Not Affect P. aeruginosa Growth
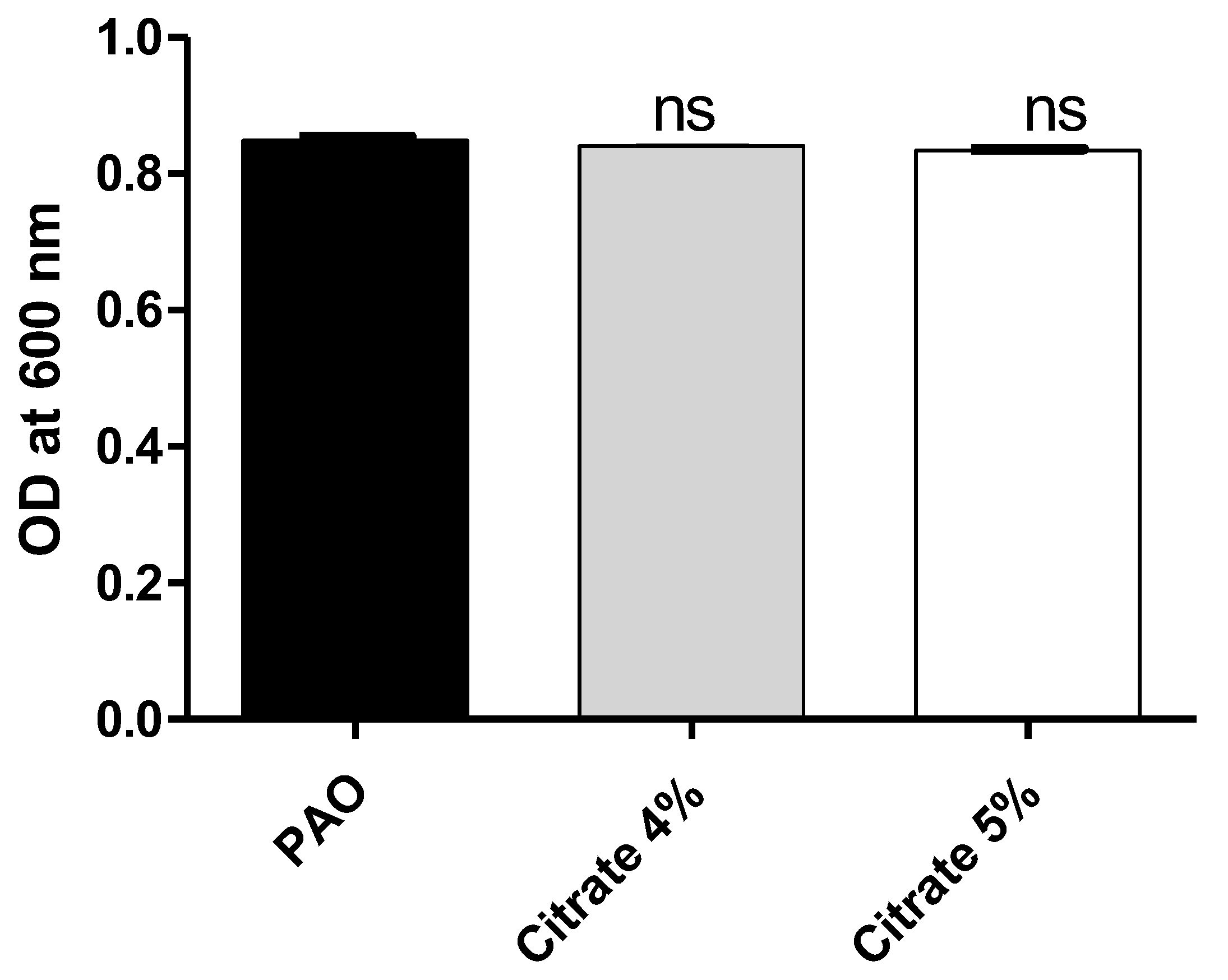
To exclude the effect of sodium citrate on bacterial growth, the optical densities of P. aeruginosa growth were measured in the presence or absence of 4% or 5% sodium citrate. There was no significant difference between bacterial growth in the presence or absence of sodium citrate (Figure 1). The bacterial cell count was performed, and there were no significant differences between counts of P. aeruginosa cultures treated or not with sodium citrate (Supplementary Figure S1).
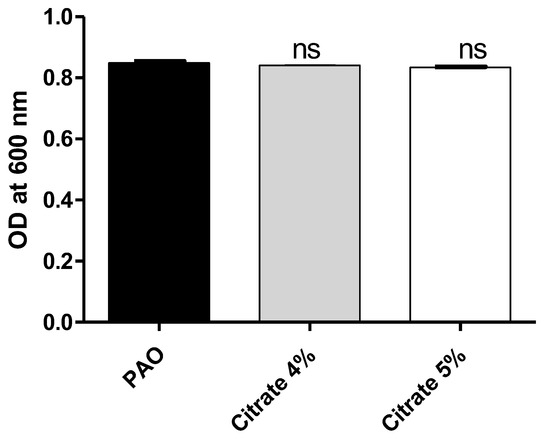
Figure 1.
Sodium citrate does not affect P. aeruginosa growth. The optical densities of P. aeruginosa growth were measured at OD600 after 24 h incubation in the presence and absence of 4% or 5% sodium citrate. ns: non-significant.
3.2. Sodium Citrate Inhibits P. aeruginosa Biofilm Formation
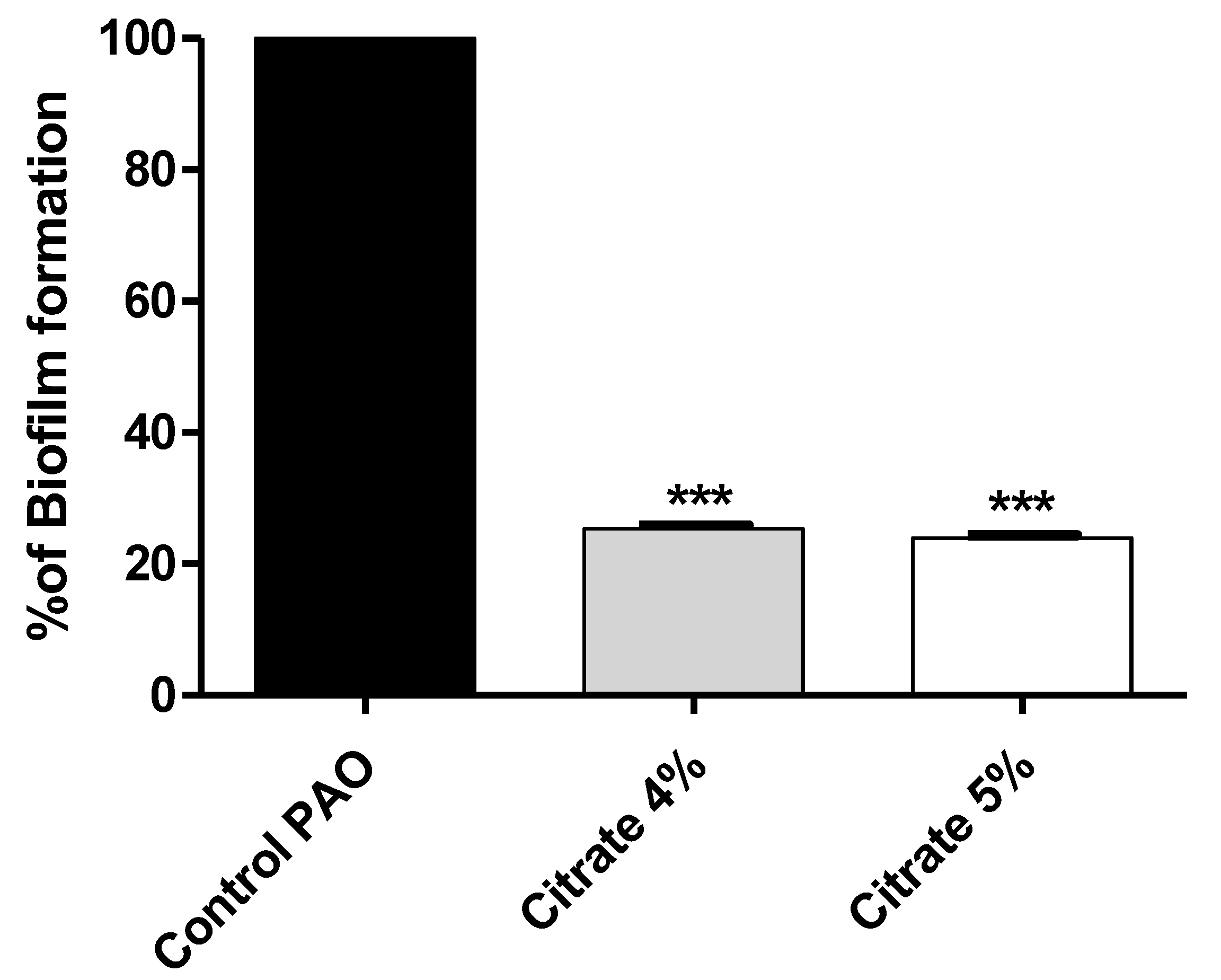
To assess the sodium citrate antibiofilm effect, the absorbances of stained biofilm-forming cells with crystal violet were measured in the presence or absence of 4% or 5% sodium citrate. The results were expressed as percentage change from untreated P. aeruginosa control. Sodium citrate in concentrations of 4% or 5% significantly decreased biofilm formation by 74.64% and 76.02%, respectively (Figure 2).
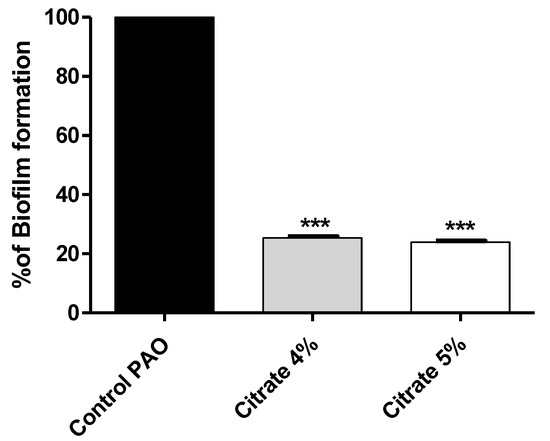
Figure 2.
Sodium citrate inhibits biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa. The absorbances of crystal-violet-stained biofilm-forming cells were measured. Sodium citrate in 4% or 5% significantly decreased biofilm formation (*** = p < 0.0001).
3.3. Sodium citrate Diminishes P. aeruginosa Motility
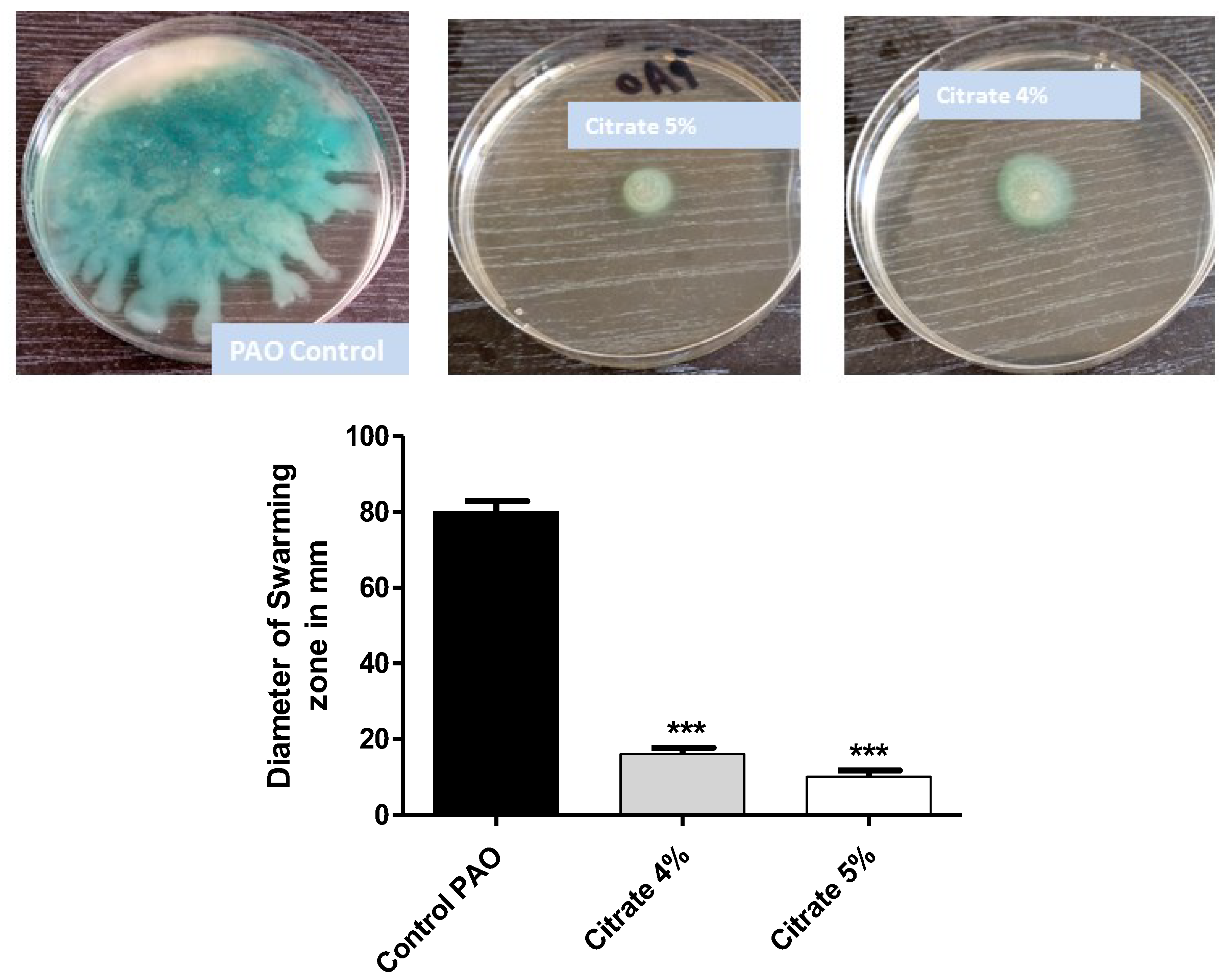
P. aeruginosa motility ensures its spread in the host tissues and enhances its pathogenicity [7]. The diameters of swarming motility of P. aeruginosa on agar plates provided with 4% or 5% sodium citrate were measured. Sodium citrate at concentrations of 4% or 5% significantly diminished bacterial motility by percentages of 80% and 87.6%, respectively (Figure 3).
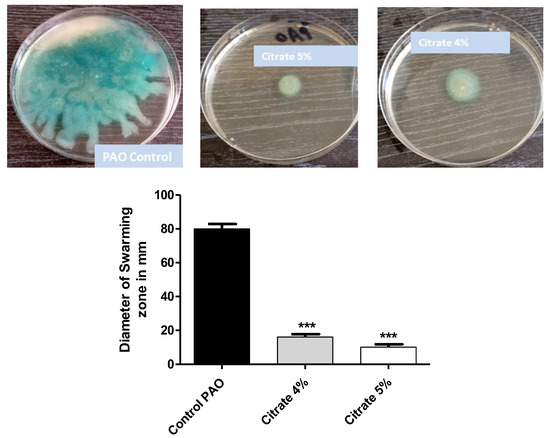
Figure 3.
Sodium citrate curtails P. aeruginosa motility. The diameters of P. aeruginosa swarming were measured in agar plates provided or not with 4% or 5% sodium citrate. Sodium citrate significantly diminished bacterial motility (*** = p < 0.0001).
3.4. Sodium Citrate Decreases the P. aeruginosa Pigment Pyocyanin
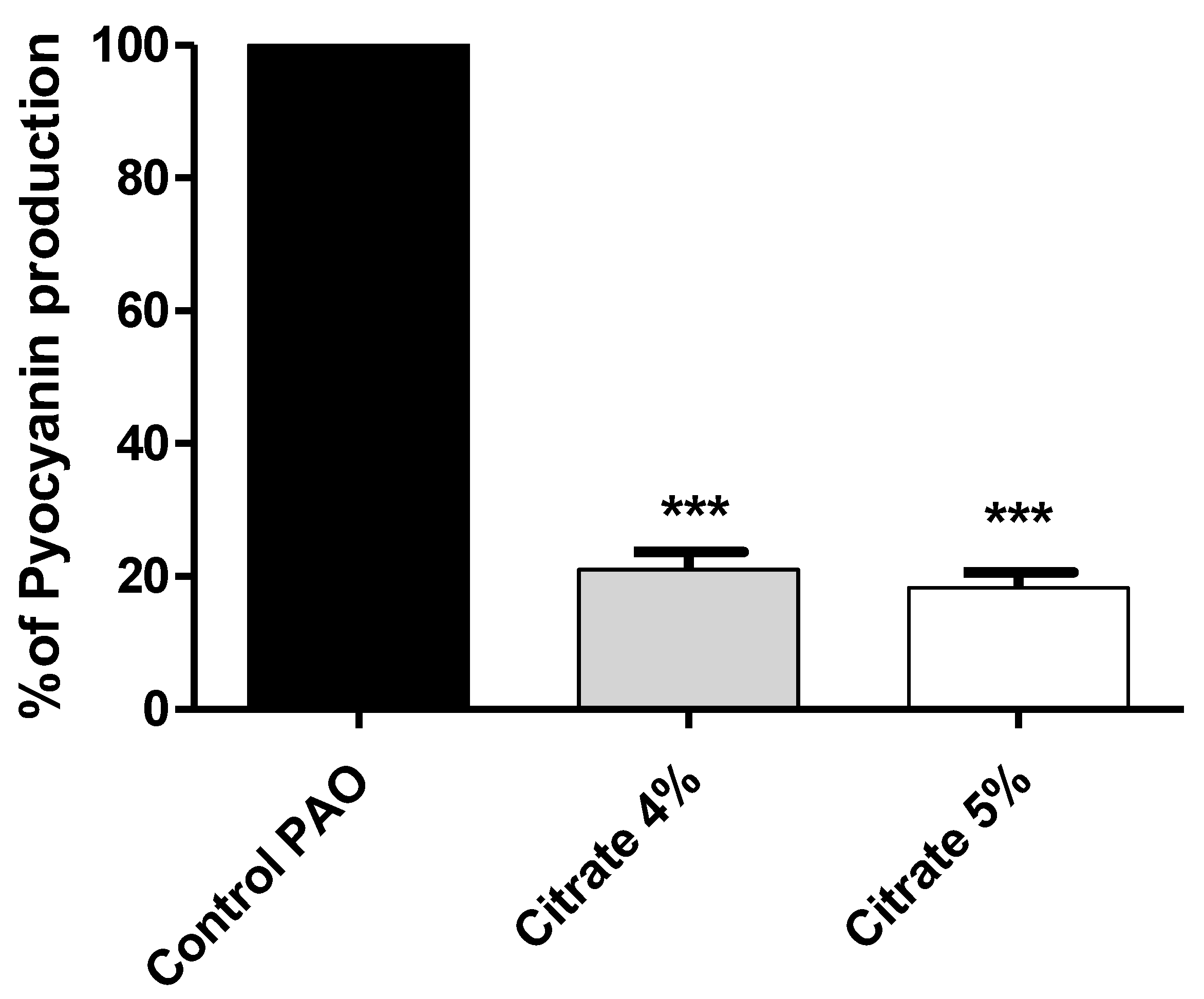
Pyocyanin, the bluish-green pigment produced by P. aeruginosa, has emerged as an important virulence factor that aids in killing host cells, as well as competitor microbes [47]. The absorbance of the produced pyocyanin was measured in P. aeruginosa treated or not with sodium citrate (4% or 5%). The data are presented as percentage change from untreated control. Sodium citrate significantly reduced pyocyanin production by 78.5% and 81.5% for concentrations of 4% and 5%, respectively (Figure 4).
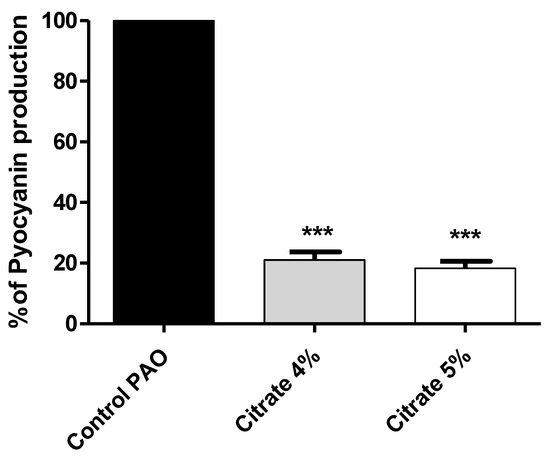
Figure 4.
Sodium citrate reduces the production of P. aeruginosa virulent pigment. The absorbances of produced pyocyanin were measured in cultures provided or not with 4% or 5% sodium citrate. Sodium citrate significantly reduced pyocyanin production (*** = p < 0.0001).
3.5. Sodium Citrate Decreases the Production of Protease
P. aeruginosa produces a wide array of extracellular virulent enzymes to establish and spread its infection into the host tissues. Protease facilitates the spread of bacterial infection, and the decrease in its production mitigates bacterial virulence [2]. The sim milk agar method was used to assess the effect of sodium citrate on protease activity. The extracellular protease collected from P. aeruginosa cultures treated with or without 4% or 5% sodium citrate was poured in wells made in skim milk agar plates, and the clear zones were measured. Sodium citrate significantly decreased the production of protease by 58.7% at a concentration of 4%, and protease inhibition was 100% at a concentration of 5% (Figure 5).
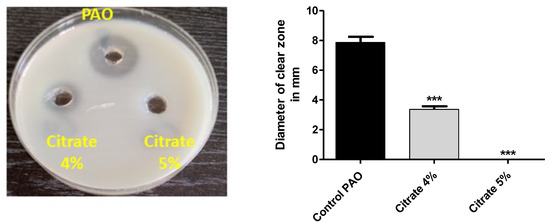
Figure 5.
Sodium citrate decreases the activity of protease. The clear zones due to proteolytic effects of collected protease from cultures provided or not with 4% or 5% sodium citrate on skim milk agar were measured. Sodium citrate significantly reduced protease production (*** = p < 0.0001).
3.6. Sodium Citrate Anti-QS Activities
3.6.1. Sodium Citrate Downregulates the P. aeruginosa QS Genes
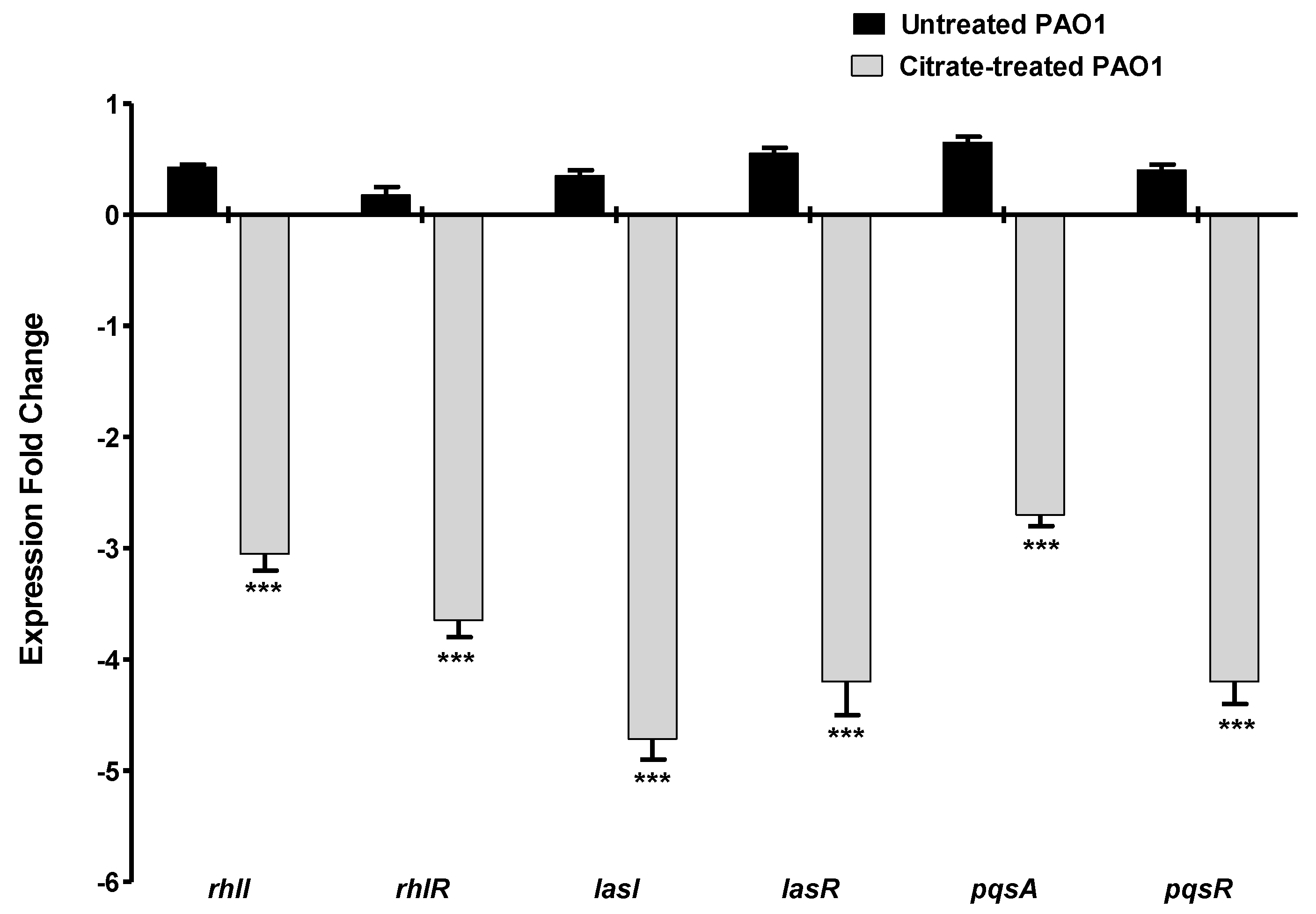
P. aeruginosa mainly utilizes three QS systems to regulate the production of its virulence factors [48]. The expression of the encoding genes of the autoinducer synthetases and their receptors in the three QS systems were quantified using RT-PCR in the presence or absence of 5% sodium citrate. The experiment was repeated in triplicate, the fold change of expression levels was represented as mean ± SD, and Student’s t-test was employed to attest to the significance. The current data revealed a significant reduction in the expression of all the QS-encoding genes in the presence of sodium citrate (Figure 6).
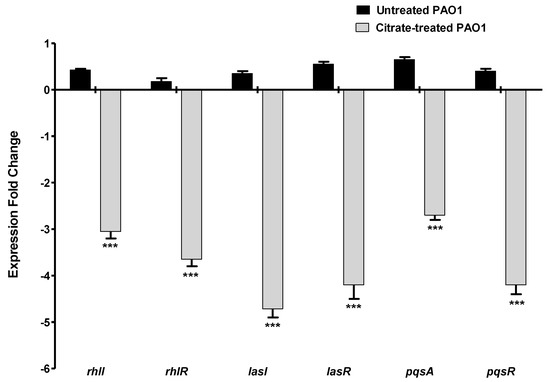
Figure 6.
Sodium citrate downregulates the expression of QS-encoding genes. The expressions of the encoding genes of the autoinducer synthetase and receptors of the main three QS systems in P. aeruginosa were quantified using RT−PCR and normalized to the expression level of housekeeping gene ropD. Sodium citrate significantly decreased the expression of all QS-encoding genes (*** = p < 0.0001).
3.6.2. Sodium Citrate Interferes with the Binding of Autoinducers to P. aeruginosa QS Receptors
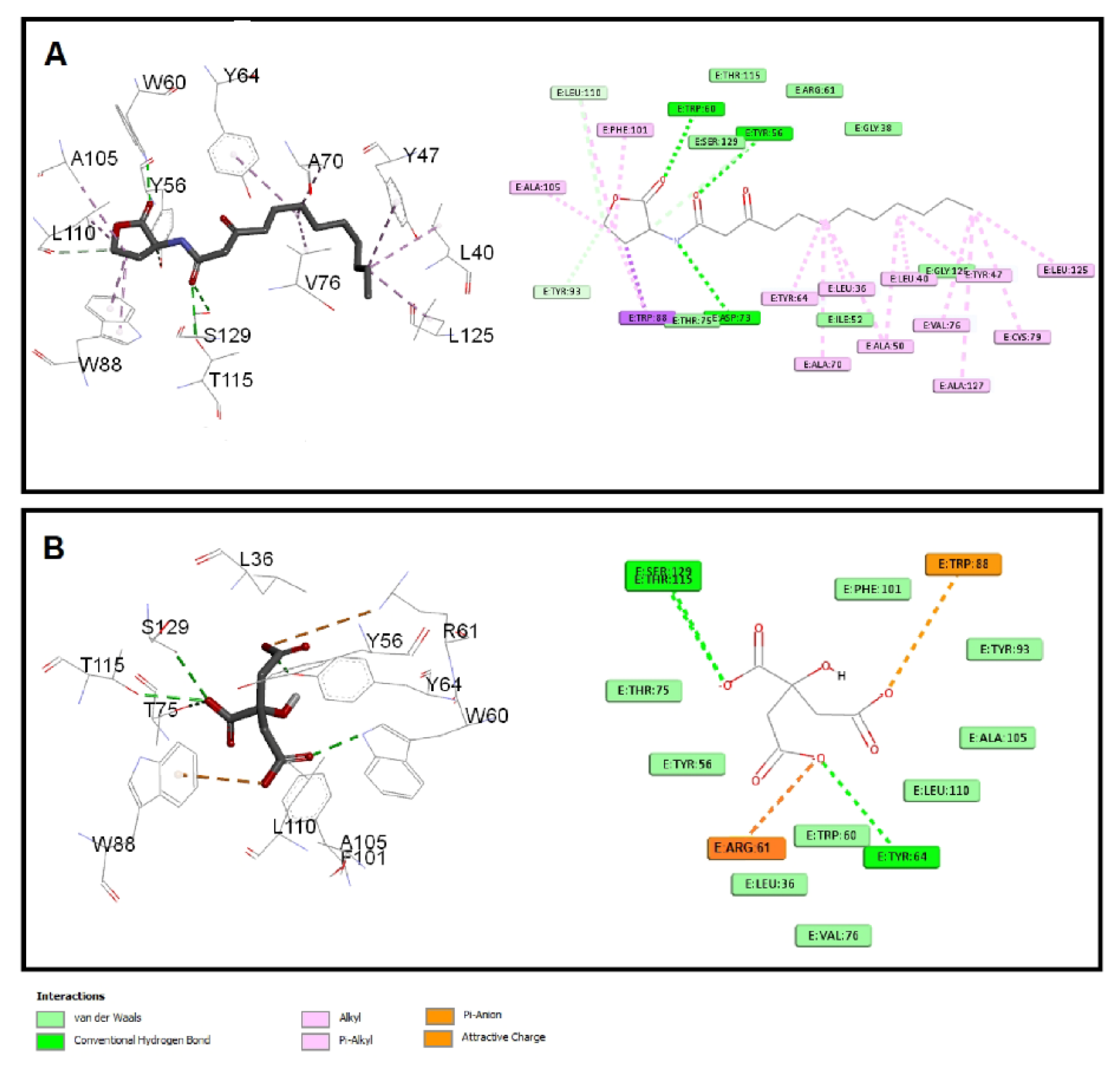
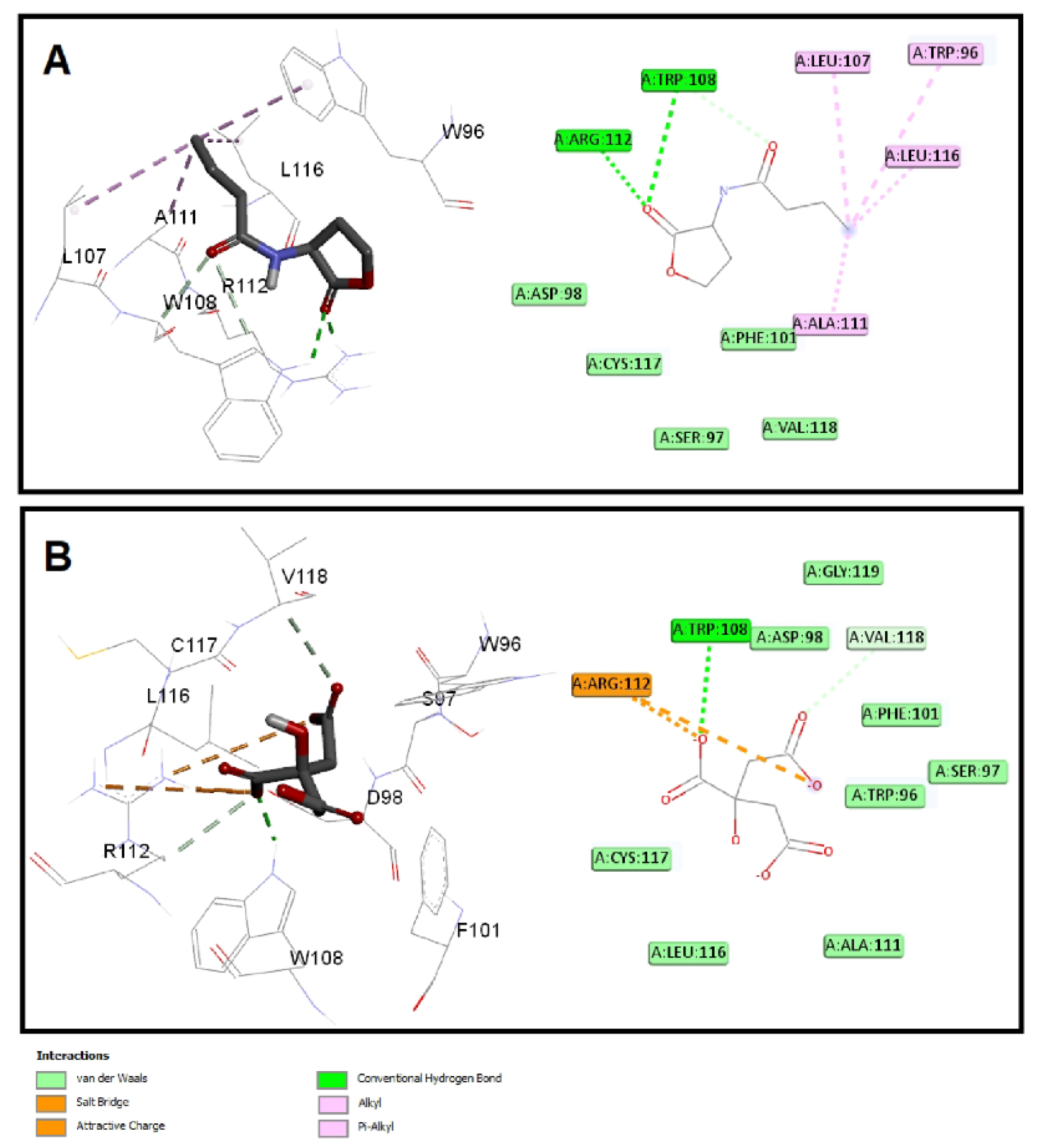
The quorum-sensing proteins LasR and RhlR were identified as potential targets for P. aeruginosa virulence inhibition [49]. A molecular docking investigation was performed to reveal the binding mechanism for citrate as a potential inhibitor for LasR and RhlR. Molecular docking demonstrated the good binding affinity of citrate for LasR (affinity = −5.9 Kcal/mol) that was comparable to the natural ligand (affinity = −6.1 Kcal/mol). Additionally, citrate had a respectable binding affinity to RhlR (affinity = −5.3 Kcal/mol) when related to C4-HSL (affinity = −5.8 Kcal/mol). The key interactions of citrate with LasR and RhlR are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively.
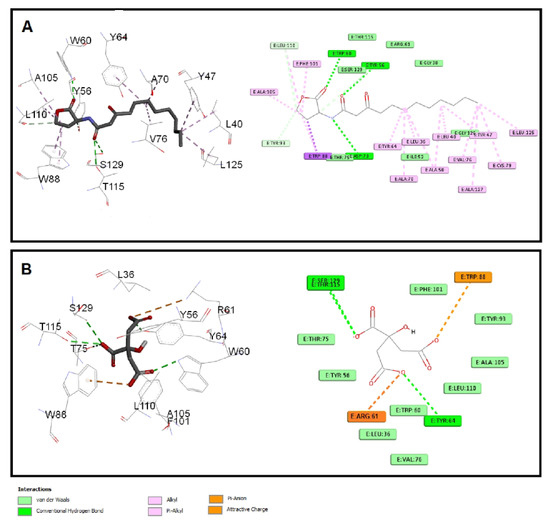
Figure 7.
Molecular docking of (A) citrate and (B) C12-HSL into the active site of LasR protein 3D representation (left) and 2D schematic interaction (right). Citrate could bind with the LasR receptor and interfere with the P. aeruginosa QS systems.
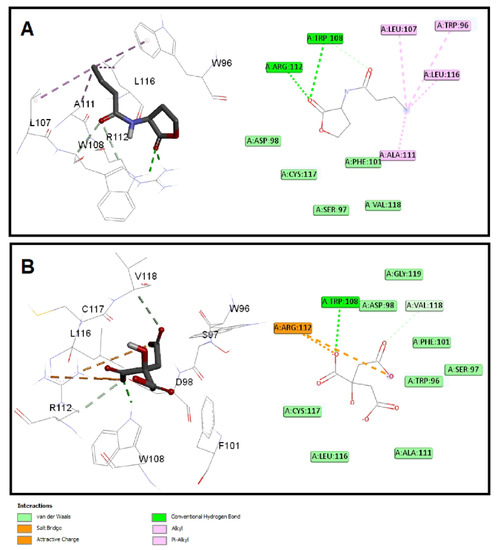
Figure 8.
Molecular docking of (A) citrate and (B) C4-HSL into the active site of RhlR protein 3D representation (left) and 2D Schematic interaction (right). Citrate could bind with the RhlR receptor and interfere with the P. aeruginosa QS systems.
Citrate had attractive charges with Arg61 and Arg112 for LasR and RhlR, respectively. Inside the LasR active site, citrate had a pi-anion interaction with Trp88. In addition, H-bonding with Tyr64, Thr115, and Ser129 was observed with the oxygen of the carboxylate groups of citrate into LasR, while only Trp108 formed an H-bond with citrate inside the active site of RhlR. All these mentioned interactions, besides the hydrophobic interactions, shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8 contributed to the affinity of citrate to LasR and RhlR targets as a potential quorum-sensing inhibitor.
4. Discussion
In this work, the antivirulence activity of sodium citrate against P. aeruginosa was assessed. P. aeruginosa is an excellent bacterial model to understand bacterial virulence, not only because of its arsenal of virulence factors but also its remarkable ability to develop resistance to different classes of antibiotics [2,4,15,50,51]. Antivirulence therapy is based on using a safe adjuvant to mitigate bacterial virulence without affecting bacterial growth. This approach is much less likely to lead to the emergence of resistance. Moreover, it enhances the immune system to eradicate microbial infection and augment antibiotic activity [9,17,52].
To exclude the probability that the antivirulence activity of sodium citrate is due to the inhibition of bacterial growth, the effect of sodium citrate at selected concentrations on P. aeruginosa growth was investigated, and sodium citrate did not interfere with bacterial growth. This means all subsequent antivirulence activities are not due to the inhibition of bacterial growth and are apart from the acidification influence of sodium citrate on the surrounding medium. The bacterial biofilms are additional obstacles to efficient antibiotic treatment, as observed in chronic and nosocomial infections, and so the biofilm eradication is a golden target in such infections [53,54]. The present findings showed the significant ability of sodium citrate to inhibit the biofilms formed by P. aeruginosa to more than 70% at concentrations of both 4% and 5%. Bacterial motility is an important structural virulence factor that eases the spread of bacterial infection and is associated with biofilm formation [20,29,54,55]. P. aeruginosa is peritrichous and can swim, swarm, and slide on solid surfaces [7,56]. Sodium citrate significantly prevented P. aeruginosa swarming at both selected concentrations.
P. aeruginosa pathogenesis is accomplished by employing diverse enzymes such as proteases, lipases, hemolysins, elastase, and others [4,17]. Protease aids bacteria to destroy the host tissue, conferring great ability for infection spread and conquering host defense [25,57]. Sodium citrate at 4% significantly diminished the activity of protease by P. aeruginosa; however, this inhibition was complete at a concentration of 5%. Besides enzymes, P. aeruginosa produces its characteristic bluish-green pigment pyocyanin, the roles of which in the virulence and survival of P. aeruginosa are well documented [37,47,58]. Our findings showed that sodium citrate at 4% or 5% could significantly reduce the production of pyocyanin.
Bacterial QS is used by bacterial cells to orchestrate the expression of virulence factors during the course of infection [5]. Both Gram-negative and -positive bacterial cells depend on QS systems to orchestrate the expression of virulence factors during the course of infection [24,59]. In Gram-negative, a wide array of autoinducers is produced and released to the surrounding niche, where they bind to their specific cognate receptors [26,60]. Then, the autoinducer–receptor complex binds to a specific DNA sequence to regulate the expression of virulence genes [34,60]. For instance, QS receptors LuxR, which are widely detected in different Gram-negative genera, bind to autoinducers to form complexes that bind to short DNA sequences on the bacterial chromosome called lux boxes to regulate their downstream virulent genes [61]. The QS system controls diverse P. aeruginosa virulence factors, including biofilm formation, motility and production of pyocyanin, and extracellular enzymes such as protease, as extensively documented [60,62,63,64]. The anti-QS activity of sodium citrate was assessed genotypically, and it significantly downregulated P. aeruginosa QS genes. Citrate downregulated the expression of the main three QS-receptor-encoding genes in P. aeruginosa lasR, rhlR, and pqsR, in addition to decreasing the production of inducer-synthetase-encoding genes lasI. rhlI, and pqsA. Furthermore, and in agreement with the above results, sodium citrate binds to P. aeruginosa QS receptors, competing with autoinducers in the in silico study.
These findings declare the antivirulence activities of sodium citrate at concentrations of 4% or 5%. The antivirulence and antibiofilm activities of sodium citrate could be owed to interference with QS systems, as sodium citrate binds to QS receptors and downregulates the expression of QS-encoding genes. As declared previously, sodium citrate was used efficiently alone or in combinations to eradicate the biofilms formed by different bacterial strains on inanimate objects or on living tissues [27]. The safety plus ability to diminish bacterial virulence at low concentrations indicates the possible application of sodium citrate as an adjuvant to traditional antibiotics in the treatment of aggressive bacterial infections caused by P. aeruginosa.
5. Conclusions
Conquering bacterial resistance requires looking for new approaches such as using efficient adjuvants to traditional antibiotics. These agents must possess some criteria, be safe, and not affect bacterial growth to avoid bacterial resistance development. This study evaluated the antivirulence activities of sodium citrate against P. aeruginosa. The present data showed the significant in vitro ability of sodium citrate to mitigate bacterial virulence, inhibiting biofilm formation and motility and reducing the production of P. aeruginosa pyocyanin pigment and the activity of the protease enzyme. The antivirulence activities of citrate were attributed to its ability to interfere with QS systems. This study proclaims the possible application of sodium citrate as an antivirulence agent and as an adjuvant to antibiotics. However, future work is needed to confirm the antivirulence activity in animal models.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms10051046/s1, Figure S1: Viable count of the bacterial cells in the presence or absence of citrate after several time intervals; Table S1: Mean absorbances of pyocyanin in citrate-treated and untreated culture supernatants at 691 nm; Table S2: Mean absorbances of biofilm cells in citrate-treated and untreated culture supernatants at 590 nm. Table S3: Fold expression of QS-encoding genes in the presence or absence of 5% citrate.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; methodology, M.T.K., H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; software, M.T.K., M.A.S. and K.A.M.; validation, T.S.I., A.N.K. and E.-S.K.; formal analysis, M.T.K., H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; investigation, K.A.M., M.A. and H.A.A.; resources, T.S.I., A.N.K., M.A. and M.T.K.; data curation, H.A.A., D.A.E.-d. and W.A.H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; writing—review and editing W.A.H.H.; visualization, A.N.K., T.S.I., D.A.E.-d., M.A. and E.-S.K.; supervision, H.A.A. and W.A.H.H.; project administration, H.A.A., M.T.K. and W.A.H.H.; funding acquisition, M.T.K., T.S.I. and A.N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University (KAU), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, has funded this project under Grant No. (RG-40-166-43). The authors, therefore, gratefully acknowledge the DSR for technical and financial support.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the DSR at King Abdulaziz University (KAU) for technical and financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Antonic, V.; Stojadinovic, A.; Zhang, B.; Izadjoo, M.J.; Alavi, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces pigment production and enhances virulence in a white phenotypic variant of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Drug Resist. 2013, 6, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellatly, S.L.; Hancock, R.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, V.I.; Stevenson, E.C.; Porter, S.L. Two-component systems required for virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Contreras, R. Is Quorum Sensing Interference a Viable Alternative to Treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.S.; Saqr, A.A.; Alalaiwe, A.; Abbas, H.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Goda, R.M. Tackling Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the Natural Furanone Sotolon. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filloux, A. Protein Secretion Systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Essay on Diversity, Evolution, and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, K.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing and the regulation of virulence gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 291, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elhady, S.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Darwish, K.M. Computational and Biological Evaluation of β-Adrenoreceptor Blockers as Promising Bacterial Anti-Virulence Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, H.; Swift, S.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing as an integral component of gene regulatory networks in Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Wang, L.H.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, L.H. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 2001, 411, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayyat, A.N.; Abbas, H.A.; Khayat, M.T.; Shaldam, M.A.; Askoura, M.; Asfour, H.Z.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Allam, A.N.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Secnidazole Is a Promising Imidazole Mitigator of Serratia marcescens Virulence. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morata, L.; Cobos-Trigueros, N.; Martinez, J.A.; Soriano, A.; Almela, M.; Marco, F.; Sterzik, H.; Nunez, R.; Hernandez, C.; Mensa, J. Influence of multidrug resistance and appropriate empirical therapy on the 30-day mortality rate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4833–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Montero, M.; Oliver, A.; Sorli, L.; Luque, S.; Gomez-Zorrilla, S.; Benito, N.; Grau, S. Epidemiology and Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00031-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernebro, J. Fighting bacterial infections-future treatment options. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer. Chemother. 2011, 14, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqr, A.A.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Shaldam, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. A Novel Use of Allopurinol as A Quorum-Sensing Inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat, A.N.; Abbas, H.A.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Youns, M.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Safo, M.K.; et al. Not Only Antimicrobial: Metronidazole Mitigates the Virulence of Proteus mirabilis Isolated from Macerated Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.H.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hwang, J.K. Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing by vanilla extract. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, H.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Targeting the virulence factors of Serratia marcescens by ambroxol. Roum. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 76, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Rajab, A.A.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Abbas, H.A. Anti-diabetics and antimicrobials: Harmony of mutual interplay. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1832–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Heydorn, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Parsek, M.R.; Rice, S.A.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Hoiby, N.; et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayyat, A.N.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Shaldam, M.A.; Mosbah, R.; Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khayat, M.T.; Khafagy, E.S.; Soliman, W.E.; Abbas, H.A. Xylitol Inhibits Growth and Blocks Virulence in Serratia marcescens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, Y.; Park, H.D. 6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Murata, S.; Kimura, K.; Mori, T.; Hojo, K. Antimicrobial activity of sodium citrate against Streptococcus pneumoniae and several oral bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urwin, C.S.; Snow, R.J.; Condo, D.; Snipe, R.; Wadley, G.D.; Carr, A.J. Factors Influencing Blood Alkalosis and Other Physiological Responses, Gastrointestinal Symptoms, and Exercise Performance Following Sodium Citrate Supplementation: A Review. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2021, 31, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Zhou, X.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Y. Inhibitory effect of trisodium citrate on biofilms formed by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob Resist. 2020, 22, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takla, T.A.; Zelenitsky, S.A.; Vercaigne, L.M. Effectiveness of a 30% ethanol/4% trisodium citrate locking solution in preventing biofilm formation by organisms causing haemodialysis catheter-related infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balestrino, D.; Souweine, B.; Charbonnel, N.; Lautrette, A.; Aumeran, C.; Traore, O.; Forestier, C. Eradication of microorganisms embedded in biofilm by an ethanol-based catheter lock solution. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitzel, R.A.; Rosenblatt, J.; Hirsh-Ginsberg, C.; Murray, K.; Chaftari, A.M.; Hachem, R.; Raad, I. In Vitro Assessment of the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Optimized Nitroglycerin-Citrate-Ethanol as a Nonantibiotic, Antimicrobial Catheter Lock Solution for Prevention of Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5175–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, J.; Reitzel, R.; Dvorak, T.; Jiang, Y.; Hachem, R.Y.; Raad, I.I. Glyceryl trinitrate complements citrate and ethanol in a novel antimicrobial catheter lock solution to eradicate biofilm organisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalca, Y.; Jansch, L.; Bredenbruch, F.; Geffers, R.; Buer, J.; Haussler, S. Quorum-sensing antagonistic activities of azithromycin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: A global approach. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic, S.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Savic, B.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.H.; Kornberg, A. Inorganic polyphosphate is needed for swimming, swarming, and twitching motilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Manefield, M. Pyocyanin promotes extracellular DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Taher, E.S.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Youns, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Al-Mahmoudy, A.M.M. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, Anti-Virulence and Anticancer Evaluation of New 5(4H)-Oxazolone-Based Sulfonamides. Molecules 2022, 27, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, P.; Vincent, S.G.P. A simple method for the detection of protease activity on agar plate using bromocresolgreen dye. J. Biochem. Technol. 2013, 4, 628–630. [Google Scholar]
- Youns, M.; Askoura, M.; Abbas, H.A.; Attia, G.H.; Khayyat, A.N.; Goda, R.M.; Almalki, A.J.; Khafagy, E.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Celastrol Modulates Multiple Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer via DDIT3 and ATF3 Up-Regulation and RRM2 and MCM4 Down-Regulation. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 3849–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottomley, M.J.; Muraglia, E.; Bazzo, R.; Carfì, A. Molecular Insights into Quorum Sensing in the Human Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the Structure of the Virulence Regulator LasR Bound to Its Autoinducer. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13592–13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pubchem. Citrate 3d struture. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/31348 (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA. Dassault Systèmes, [Discovery Studio client], [21.1.0.20298]; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.; McDermott, C.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; McFarland, A.J.; Forbes, A.; Perkins, A.V.; Davey, A.K.; Chess-Williams, R.; Kiefel, M.J.; Arora, D.; et al. Cellular Effects of Pyocyanin, a Secreted Virulence Factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, V. Regulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, C.T.; Miller, L.C.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, P.D.; Wolter, D.J.; Hanson, N.D. Antibacterial-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Clinical impact and complex regulation of chromosomally encoded resistance mechanisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 582–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B. Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: Lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skindersoe, M.E.; Alhede, M.; Phipps, R.; Yang, L.; Jensen, P.O.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Hoiby, N.; Givskov, M. Effects of antibiotics on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3648–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackman, G.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska, K.I.; Grudniak, A.M.; Rudnicka, Z.; Markowska, K. Genetic control of bacterial biofilms. J. Appl. Genet. 2016, 57, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.O.; Givskov, M.; Hoiby, N. Targeting quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: Current and emerging inhibitors. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voynow, J.A.; Fischer, B.M.; Zheng, S. Proteases and cystic fibrosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrodi, D.V.; Bonsall, R.F.; Delaney, S.M.; Soule, M.J.; Phillips, G.; Thomashow, L.S. Functional analysis of genes for biosynthesis of pyocyanin and phenazine-1-carboxamide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6454–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Youns, M.; Mosbah, R.; Soliman, W.E. Repurposing of antidiabetics as Serratia marcescens virulence inhibitors. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhas, M.; Eberl, L.; Tummler, B. Quorum sensing: The power of cooperation in the world of Pseudomonas. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing: Its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Li, M. Quorum sensing inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 867–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Ravindran, D.; Arunachalam, K.; Arumugam, V.R. Inhibition of quorum sensing-dependent biofilm and virulence genes expression in environmental pathogen Serratia marcescens by petroselinic acid. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).