Seroprevalence, Direct Detection and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pigs in Serbia, and Influence of Biosecurity Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
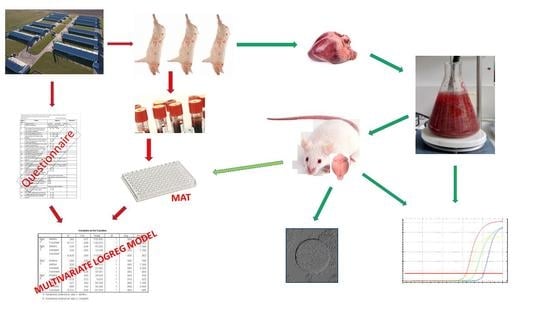
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Collection of Epizootiological Data
2.3. Serology
2.4. Trypsin Digestion
2.5. Biological Assay
2.6. DNA Extraction and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. T. gondii Seroprevalence and Risk Factors
3.2. Direct Detection of T. gondii and Viability Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Long-term persistence of Toxoplasma gondii in tissues of pigs inoculated with T. gondii oocysts and effect of freezing on viability of tissue cysts in pork. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Public health risks associated with food-borne parasites. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurković-Djaković, O.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; van der Giessen, J.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: Overview from a One Health perspective. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 12, e00054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO/WHO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization. Multicriteria-based ranking for risk management of food-borne parasites. Microbiol. Risk Assess. 2014, 23, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwknegt, M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Graham, H.; Robertson, L.J.; van der Giessen, J.; the Euro-FBP workshop participants. Prioritisation of food-borne parasites in Europe, 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapperud, G.; Jenum, P.A.; Stray-Pedersen, B.; Melby, K.K.; Eskild, A.; Eng, J. Risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnancy: Results of a prospective case-control study in Norway. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 144, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobić, B.; Jevremović, I.; Marinković, J.; Šibalić, D.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Risk factors for Toxoplasma infection in a reproductive age female population in the area of Belgrade, Yugoslavia. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 14, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.J.; Gilbert, R.E.; Buffolano, W.; Zufferey, J.; Petersen, E.; Jenum, P.A.; Foulon, W.; Semprini, A.E.; Dunn, D.T. Sources of toxoplasma infection in pregnant women: European multicentre case-control study. European Research Network on Congenital Toxoplasmosis. BMJ 2000, 321, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobić, B.; Nikolić, A.; Klun, I.; Vujanić, M.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Undercooked meat consumption remains the major risk factor for Toxoplasma infection in Serbia. Parassitologia 2007, 49, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra, A.; Jongert, E. Toxoplasma-safe meat: Close to reality? Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1994, 205, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Djurković-Djaković, O.; Bobić, B.; Klun, I.; Nikolić, A.; Dupouy-Camet, J. Pork as a source of human parasitic infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Comission. Pigmeat Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://agridata.ec.europa.eu/Reports/Pigmeat_Dashboard.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Eurostat. Statistic Explained. Agricultural Production—Livestock and Meat. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Agricultural_production-_livestock_and_meat&oldid=549389 (accessed on 3 April 2022).
- Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia (RZS). Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Serbia 2020. 2020, Volume 53, p. 222. Available online: https://publikacije.stat.gov.rs/G2020/Pdf/G20202053.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Guo, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Hill, D.; Buchanan, R.L.; Gamble, H.R.; Jones, J.L.; Pradhan, A.K. Prevalence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in meat animals and meat products destined for human consumption. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klun, I.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Katić-Radivojević, S.; Nikolić, A. Cross-sectional survey on Toxoplasma gondii infection in cattle, sheep and pigs in Serbia: Seroprevalence and risk factors. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 135, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrusfield, M. Surveys. In Veterinary Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 228–246. [Google Scholar]
- Klun, I.; Vujanić, M.; Year, H.; Nikolić, A.; Ivović, V.; Bobić, B.; Bradonjić, S.; Dupouy, J.C.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Toxoplasma gondii infection in slaughter pigs in Serbia: Seroprevalence and demonstration of parasites in blood. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia (RZS). 2018, Volume 32, pp. 1–2. Available online: https://publikacije.stat.gov.rs/G2018/Pdf/G20181032.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Opsteegh, M.; Schares, G.; Blaga, R.; van der Giessen, J.; on behalf of the Consortium. Experimental Studies of Toxoplasma gondii in the Main Livestock Species (GP/EFSA/BIOHAZ/2013/01). Final Report; European Food Safety Authority: Parma, Italy, 2016; 161p, Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.2903/sp.efsa.2016.EN-995 (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Farm Biosecurity. Available online: https://www.farmbiosecurity.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Piggery-Biosecurity-Audit-Checklist.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Desmonts, G.; Remington, J.S. Direct agglutination test for diagnosis of toxoplasma infection: Method for increasing sensitivity and specificity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 11, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzelac, A. Biological and Molecular Characterization of Lineage III Strains of Toxoplasma gondii Isolated in Serbia. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia, 30 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruca, L.; Klun, I.; Uzelac, A.; Nikolić, A.; Bobić, B.; Simin, S.; Lalošević, V.; Lalošević, D.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in naturally infected domestic pigs in Northern Serbia. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurković-Djaković, O.; Nikolić, A.; Bobić, B.; Klun, I.; Aleksić, A. Stage conversion of Toxoplasma gondii RH parasites in mice by treatment with atovaquone and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate. Microbes Infect. 2005, 7, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, W.L.; Vercammen, M.; De Braekeleer, J.; Verschueren, H. Identification of a 200- to 300-fold repetitive 529 bp DNA fragment in Toxoplasma gondii, and its use for diagnostic and quantitative PCR. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, M.; Fakhri, Y.; Riahi, S.M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Namroodi, S.; Taghipour, A.; Spotin, A.; Gamble, H.R.; Rostami, A. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 269, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villari, S.; Vesco, G.; Petersen, E.; Crispo, A.; Buffolano, W. Risk factors for toxoplasmosis in pigs bred in Sicily, Southern Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 161, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronesi, F.; Ranucci, D.; Branciari, R.; Miraglia, D.; Mammoli, R.; Fioretti, D.P. Seroprevalence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection on finishing swine reared in the Umbria region, central Italy. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bocanegra, I.; Simon-Grifé, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Casal, J.; Martín, G.E.; Cabezón, O.; Perea, A.; Almería, S. Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with Toxoplasma gondii in domestic pigs from Spain. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokic, V.; Blaga, R.; Aubert, D.; Durand, B.; Perret, C.; Geers, R.; Ducry, T.; Vallee, I.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Mzabi, A.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection in pork produced in France. Parasitology 2016, 143, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slany, M.; Reslova, N.; Babak, V.; Lorencova, A. Molecular charac-terization of Toxoplasma gondii in pork meat from different production systems in the Czech Republic. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2016, 238, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, O.; Marianne, S.; Hans, H.; Henrik, V.N.; Matt, D.; Tina, B.J.; Lis, A. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in sows and finishers from conventional and organic herds in Denmark: Implications for potential future serological surveillance. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 185, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Hill, D.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. All about Toxoplasma gondii infections in pigs: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 288, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Marangi, M.; Villa, L.; Ragona, M.E.; Olivieri, E.; Zanzani, S.A.; Giangaspero, A.; Manfredi, M.T. Toxoplasma gondii infection and biosecurity levels in fattening pigs and sows: Serological and molecular epidemiology in the intensive pig industry (Lombardy, Northern Italy). Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görlich, K. Toxoplasma-Infektionen bei Schweinen: Semi-automatisiertes Testsystem für Surveillance und Monitoring, Querschnittsstudie in Niedersachsen. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, L.; Gracia, M.J.; Pérez-Arquillué, C.; Lázaro, R.; Herrera, M.; Herrera, A.; Bayarri, S. Toxoplasma gondii: Pig seroprevalence, associated risk factors and viability in fresh pork meat. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 224, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limon, G.; Beauvais, W.; Dadios, N.; Villena, I.; Cockle, C.; Blaga, R.; Guitian, J. Cross-Sectional Study of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pig Farms in England. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, R.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Siegel, A.M.; Kitron, U.D.; Mannelli, A.; Mitchell, M.A.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E.; Thulliez, P.; Shen, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; et al. Risk factors for transmission of Toxoplasma gondii on swine farms in Illinois. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.; Chen, J.J. Tree-structured logistic model for over-dispersed binomial data with application to modeling developmental effects. Biometrics 1997, 53, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P.; Weigel, R.M.; Siegel, A.M.; Thulliez, P.; Kitron, U.D.; Mitchell, M.A.; Mannelli, A.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E.; Shen, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; et al. Sources and reservoirs of Toxoplasma gondii infection on 47 swine farms in Illinois. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klun, I.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Toxoplasma gondii in pork & pork products—Too much on our plate? Vet. Glas. 2021, 75, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Dubey, J.P. Foodborne Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, T.V.; Marlee, D.; Hyde, J.E.; Sims, P.F.G. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in commercial meat products as monitored by polymerase chain reaction—Food for thought? Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatsiros, V.G.; Athanasiou, L.V.; Kostoulas, P.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Tzika, E.; Billinis, C. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Swine: Implications for Public Health. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factor | Categories/Responses |
|---|---|
| Age group | Market-weight (<eight months); Adult/sows (≥eight months) |
| Type of husbandry | Farm; Backyard |
| Herd size | Large (>500); Medium (150–500); Small (<150) |
| Farm type | Farrow-to-finish; Smallholders’ finishing |
| Worker training | Yes; No |
| Work clothes | Yes; No |
| Multispecies farming | Yes; No |
| Presence of cats | Yes; No |
| Presence of dogs | Yes; No |
| Presence of rodents | Yes; No |
| Water supply | Draw well; Public water mains; Water mains and draw well |
| Water treatment and control | Yes; No |
| Closed feeding system | Yes; No |
| Disinfection barrier at farm entrance | Yes; No |
| Disinfection boot-dips at each barn | Yes; No |
| Rodent control | Professional; Professional and self-implemented; Self-implemented; None performed |
| Region | Northern Serbia; Western Serbia; Central & South-Eastern Serbia; Belgrade District |
| Factor | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | |||
| Market-weight (<eight months) | 1.00 | ||
| Adult/sows (≥eight months) | 4.197 | 2.104–8.374 | <0.0001 |
| Rodent control | |||
| Professional | 1.00 | 0.040 | |
| Professional and self-implemented | 4.550 | 1.564–13.237 | 0.005 |
| Self-implemented | 3.304 | 1.144–9.543 | 0.027 |
| None performed | 3.813 | 1.327–10.957 | 0.013 |
| Factor | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | |||
| Market-weight (<eight months) | 1.00 | ||
| Adult/sows (≥eight months) | 14.247 | 6.258–32.438 | <0.0001 |
| Farm type | |||
| Farrow-to-finish | 1.00 | ||
| Smallholders’ finishing | 4.508 | 2.160–9.406 | <0.0001 |
| Multispecies farming | |||
| No | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 3.092 | 1.480–6.459 | 0.003 |
| Disinfection boot-dips at each barn | |||
| Yes | 1.00 | ||
| No | 0.385 | 0.197–0.752 | 0.005 |
| Region | |||
| Northern Serbia | 1.00 | 0.001 | |
| Western Serbia | 4.014 | 1.777–9.070 | 0.001 |
| Central & South-Eastern Serbia | 2.264 | 1.051–4.877 | 0.037 |
| Belgrade District | 0.250 | 0.067–0.935 | 0.039 |
| Pig ID | MAT Titre (Pig Sera) | Real-Time PCR (Pig Heart Digest) | Mice with Cysts/Mice Examined (n) (Cyst Count) | Seropositive Mice/Mice Examined (n) (MAT Titre) | Real-Time PCR (Mouse Brain) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S5 | 1:50 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S10 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S14 | 1:100 | + | 1/1 a (820/mL) | 1/1 a (1:20,480) | 2/2 † |
| S16 | 1:50 | - | 1/2 (30/mL) | 1/2 (1:40,960) | 1/2 |
| S19 | 1:50 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S23 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S24 | 1:100 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 1/2 |
| S27 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S29 | 1:50 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S30 | 1:100 | - | 2/2 (30/mL; 10/mL) | 2/2 (1:5120; 1:2560) | 2/2 |
| S33 | 1:25 | + | 0/0 b | 0/0 b | 1/1 b,† |
| S34 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 1/2 (1:40) | 0/2 |
| S35 | 1:100 | - | 0/2 | 1/2 (1:20) | 0/2 |
| S36 | 1:200 | + | 0/1 c | 0/1 c | 0/1 c |
| S37 | 1:400 | + | 1/1 d (<10/mL *) | 1/1 d (1:40,960) | 1/1 d |
| S44 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S46 | 1:50 | + | 1/1 e (20/mL) | 1/1 e (1:20,480) | 1/1 e |
| S47 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S48 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S49 | 1:800 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S50 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S52 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S53 | 1:50 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S54 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S58 | 1:100 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S60 | 1:25 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 1/2 |
| S64 | 1:50 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| S65 | 1:400 | - | 0/2 | 0/2 | 1/2 |
| S66 | 1:100 | + | 1/2 (30/mL) | 2/2 (1:5120; 1:5120) | 2/2 |
| S68 | 1:100 | + | 1/2 (10/mL) | 2/2 (1:2560; 1:5120) | 2/2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Betić, N.; Karabasil, N.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Ćirković, V.; Bobić, B.; Branković Lazić, I.; Djordjević, V.; Klun, I. Seroprevalence, Direct Detection and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pigs in Serbia, and Influence of Biosecurity Measures. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051069
Betić N, Karabasil N, Djurković-Djaković O, Ćirković V, Bobić B, Branković Lazić I, Djordjević V, Klun I. Seroprevalence, Direct Detection and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pigs in Serbia, and Influence of Biosecurity Measures. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(5):1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051069
Chicago/Turabian StyleBetić, Nikola, Nedjeljko Karabasil, Olgica Djurković-Djaković, Vladimir Ćirković, Branko Bobić, Ivana Branković Lazić, Vesna Djordjević, and Ivana Klun. 2022. "Seroprevalence, Direct Detection and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pigs in Serbia, and Influence of Biosecurity Measures" Microorganisms 10, no. 5: 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051069
APA StyleBetić, N., Karabasil, N., Djurković-Djaković, O., Ćirković, V., Bobić, B., Branković Lazić, I., Djordjević, V., & Klun, I. (2022). Seroprevalence, Direct Detection and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pigs in Serbia, and Influence of Biosecurity Measures. Microorganisms, 10(5), 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051069