Rhizosphere Signaling: Insights into Plant–Rhizomicrobiome Interactions for Sustainable Agronomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rhizosphere: A Pool of Plant–Microbe Signaling
2.1. Inter- or Intraspecies Signaling among Microorganisms
2.2. Interkingdom Signaling
2.2.1. Microbe–Plant Signaling
2.2.2. Plant–Microbe Signaling
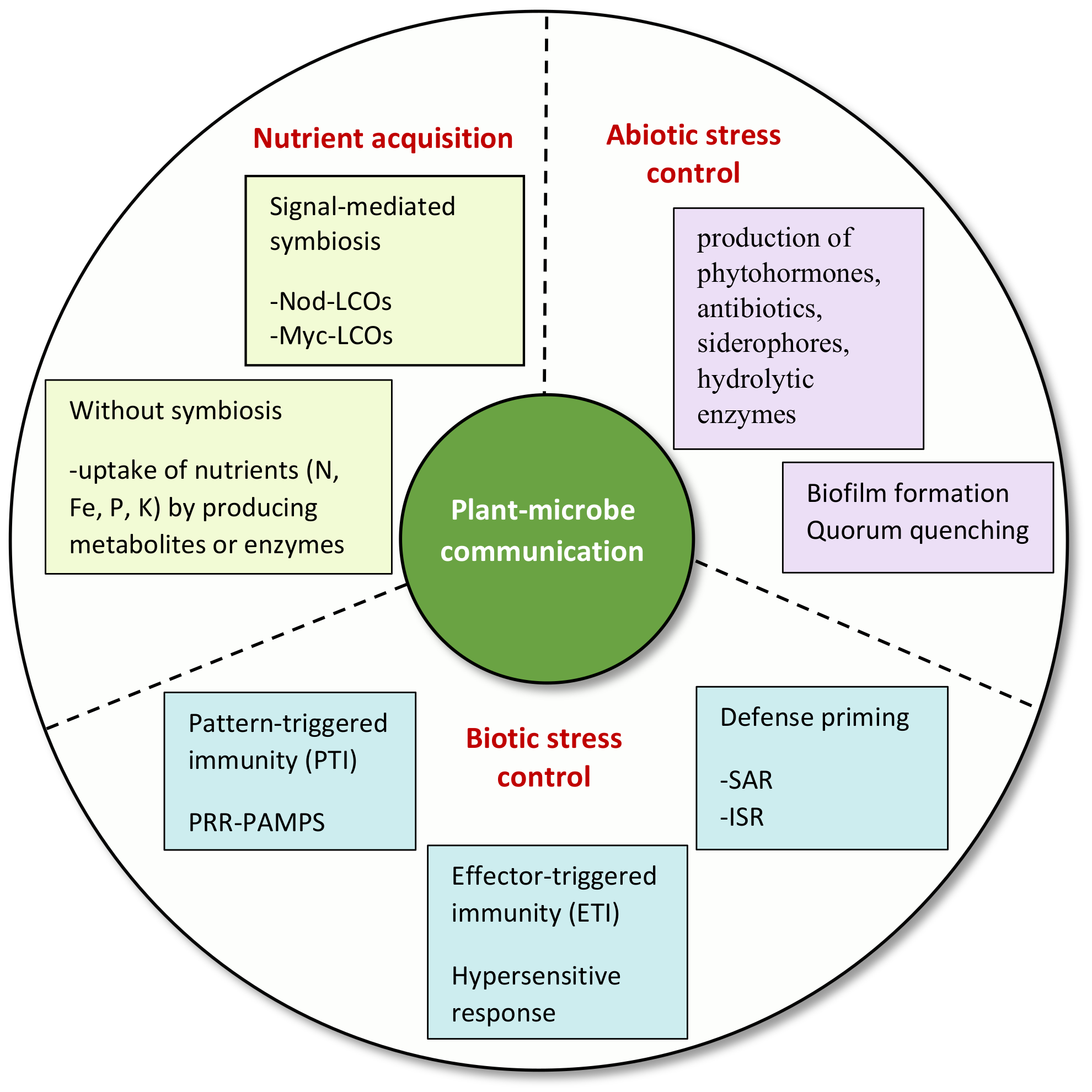
3. Significance of Signaling in Plant–Rhizomicrobiome Interaction
3.1. Nutrient Acquisition for Phytostimulation
3.1.1. Signal-Mediated Symbiosis
- Rhizobia–legume symbiotic interactions
- Mycorrhizal symbiotic interactions
3.1.2. Nutrient Acquisition without Symbiosis
3.2. Regulation of Plant Immunity against Phytopathogens
3.2.1. Pattern-Triggered Immunity (PTI)
3.2.2. Effector-Triggered Immunity (ETI)
3.3. Defense Priming
- Systemic acquired resistance (SAR)
- Induced systemic resistance (ISR)
3.4. Regulation of Plant Defenses against Abiotic Stresses
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PGPR | Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria |
| N-AHL | N-Acyl homoserine lactone |
| AIs | Autoinducers |
| QS | Quorum sensing |
| Quorum quenching | |
| VOC | Volatile organic compound |
| MAMP | Microbe-associated molecular pattern |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| DSF | Diffusible factor |
| ITC | Isothiocyanate |
| GLS | Glucosinolates |
| AMF | Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus |
| Nod | Nodulation |
| LCOs | Lipo-chitooligosaccharides |
| BF | Branching factor |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| CDPKs | Calcium-dependent protein kinases |
| PTI | Pattern-triggered immunity |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ETS | Effector-triggered susceptibility |
| ETI | Effector-triggered immunity |
| NB-LRRs | Nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat domains |
| HR | Hypersensitive response |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| NPR1 | Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related genes |
| SAR | Systemic acquired resistance |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| ET | Ethylene |
| MeJA | Methyl jasmonate |
| AzA | Azelaic acid |
| Pip | Pipecolic acid |
| ISR | Induced systemic resistance |
| ACC | 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| AOX | Alternative oxidases |
| COX | Cytochrome oxidase |
| GA | Gibberellin |
| SOS | Salt overly sensitive |
References
- Checcucci, A.; Marchetti, M. The Rhizosphere Talk Show: The Rhizobia on Stage. Front. Agron. 2020, 2, 591494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Schmid, M.; Van Tuinen, D.; Berg, G. Plant-Driven selection of microbes. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.D.; Schwab, E. Current Usage of Symbiosis and Associated Terminology. Int. J. Biol. 2013, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolla, G.; Badri, D.V.; Bakker, M.; Manter, D.K.; Vivanco, J.M. Soil microbiomes vary in their ability to confer drought tolerance to Arabidopsis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, G.; Panneerselvam, P.; Ganeshamurthy, A.N. Bacterial mediated alleviation of abiotic stress in crops. In Bacteria in Agrobiology: Stress Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Kruijt, M.; de Bruijn, I.; Dekkers, E.; Van Der Voort, M.; Schneider, J.H.; Piceno, Y.M.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Bakker, P.A.; et al. Deciphering the rhizosphere microbiome for disease-suppressive bacteria. Science 2011, 332, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, B.K.; Yadav, S.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, H.B. Microbial consortium-mediated plant defense against phytopathogens: Readdressing for enhancing efficacy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, V.; Fuqua, C. Chemical signalling between plants and plant-pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareen, A.; Burton, F.; Schäfer, P. Plant root-microbe communication in shaping root microbiomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, V.; Keel, C. Signaling in the rhizosphere. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, C.; Oldroyd, G.E.D. Plant signalling in symbiosis and immunity. Nature 2017, 543, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, F.O.; Pessotti, R.D.C.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Pupo, M.T. Chemical signaling involved in plant–microbe interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1652–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhat, S.; Imran, A.; Javaid, S.; Shahid, M.; Majeed, A.; Naqqash, T. Communication of plants with microbial world: Exploring the regulatory networks for PGPR mediated defense signaling. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 238, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldroyd, G.E.D. Speak, friend and enter: Signalling systems that promote beneficial symbiotic associations in plants. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Simões, M. Quorum Sensing Inhibition by marine bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Ma, A.; Zhuang, G.; Fray, R. Exogenous N-acyl-homoserine lactones enhance the expression of flagella of Pseudomonas syringae and activate defence responses in plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, S.T.; Hernández-Reyes, C.; Samans, B.; Stein, E.; Neumann, C.; Schikora, M.; Reichelt, M.; Mithöfer, A.; Becker, A.; Kogel, K.H.; et al. N-acyl-homoserine lactone primes plants for cell wall reinforcement and induces resistance to bacterial pathogens via the salicylic acid/oxylipin pathway. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2708–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, R.; Peukert, M.; Succurro, A.; Koprivova, A.; Kopriva, S. The Role of Soil Microorganisms in plant mineral nutrition—Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Park, S.-W.; Weir, T.L.; Callaway, R.M.; Vivanco, J.M. How plants communicate using the underground information superhighway. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, T.; Czymmek, K.J.; Paré, P.W.; Bais, H.P. Root-Secreted malic acid recruits beneficial soil bacteria. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauch-Mani, B.; Baccelli, I.; Luna, E.; Flors, V. Defense priming: An adaptive part of induced resistance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 485–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, M.; Schmülling, T. Stress priming, memory, and signalling in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, P.A.H.M.; Berendsen, R.L.; Doornbos, R.F.; Wintermans, P.C.A.; Pieterse, C.M.J. The rhizosphere revisited: Root microbiomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.B.; Oldroyd, G.E.D. The role of diffusible signals in the establishment of rhizobial and mycorrhizal symbioses. In Signalling and Communication in Plant Symbiosis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van der Ent, S.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Networking by small-molecule hormones in plant immunity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Ayangbenro, A.S.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O.; Ayangbenro, A. Plant health: Feedback effect of root exudates-rhizobiome interactions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, A.A.; Terpstra, J.; de Oliveria, A.L.M.; Salles, J.F. The Role of Rhizosphere Bacteriophages in Plant Health. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.S.; Nayak, S.; Malhotra, S.; Karmakar, S.; Sharma, M.; Raiping, S.; Mishra, V. Rhizosphere provides a new paradigm on the prevalence of lysogeny in the environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, W.; Chen, G.; Xu, H. Dynamics of Bacterial and Viral Communities in Paddy Soil with Irrigation and Urea Application. Viruses 2019, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.-C.; Marchesi, J.; Mougel, C.; Selosse, M.-A. Host-Microbiota interactions: From holobiont theory to analysis. Microbiome 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasse, J.; Martinoia, E.; Northen, T. Feed Your Friends: Do plant exudates shape the root microbiome? Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommer, L.; Kirkegaard, J.; van Ruijven, J. Root–Root Interactions: Towards a rhizosphere framework. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosier, A.; Bishnoi, U.; Lakshmanan, V.; Sherrier, D.J.; Bais, H.P. A perspective on inter-kingdom signaling in plant–beneficial microbe interactions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.W.; Wolfe, G.V.; Blee, K.A. Comparison of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities in Arabidopsis thaliana mutants for systemic Acquired Resistance. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaeppi, K.; Bulgarelli, D. The Plant Microbiome at Work. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Crowley, D.E. Rhizosphere microbial community structure in relation to root location and plant iron nutritional status. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malusà, E.; Pinzari, F.; Canfora, L. Efficacy of biofertilizers: Challenges to improve crop production. In Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Garcia, B.; Furches, A.; Tuskan, G.A.; Jacobson, D. Plant host-associated mechanisms for microbial selection. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Garbeva, P.; Raaijmakers, J.M. The rhizosphere microbiome: Significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 634–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Müller, D.B.; Srinivas, G.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Potthoff, E.; Rott, M.; Dombrowski, N.; Münch, P.C.; Spaepen, S.; Remus-Emsermann, M.; et al. Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.W.; Koh, C.L.; Sam, C.-K.; Yin, W.-F.; Chan, K.-G. Quorum Quenching Revisited—From Signal Decays to Signalling Confusion. Sensors 2012, 12, 4661–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, Y.; Chernin, L. Silencing the mob: Disrupting quorum sensing as a means to fight plant disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikora, A.; Schenk, S.T.; Hartmann, A. Beneficial effects of bacteria-plant communication based on quorum sensing molecules of the N-acyl-homoserine lactone group. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Shaaban, M.I.; Bar, F.A.; El-Mahdy, A.; Shokralla, S. Quorum sensing inhibiting activity of Streptomyces coelicoflavus Isolated from Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W. Role of the quorum-sensing system in biofilm formation and virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 5819–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing and social networking in the microbial world. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendeville, A.; Winzer, K.; Heurlier, K.; Tang, C.M.; Hardie, K. Making ‘sense’ of metabolism: Autoinducer-2, LUXS and pathogenic bacteria. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 3, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, K. Bacterial cell-to-cell communication: Sorry, can’t talk now—Gone to lunch! Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, C. Exploiting Quorum Sensing Interfering Strategies in Gram-negative bacteria for the enhancement of environmental applications. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferluga, S.; Steindler, L.; Venturi, V. N-acyl homoserine lactone quorum sensing in Gram-negative rhizobacteria. In Secondary Metabolites in Soil Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.S.; Sehrawat, A.; Sharma, R.; Dahiya, A.; Khandelwal, A. Belowground microbial crosstalk and rhizosphere biology. In Plant-Microbe Interactions in Agro-Ecological Perspectives; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 695–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigle, B.; Corre, C. Waking up Streptomyces Secondary Metabolism by Constitutive Expression of Activators or Genetic Disruption of Repressors. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 517, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, K.; Kube, M.; Becker, R.; Schneck, V.; Ulrich, A. Genomic analysis of the endophytic Stenotrophomonas strain 169 reveals features related to plant-growth promotion and stress tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R. Quorum sensing signal autoinducer-2 promotes root colonization of Bacillus velezensis SQR9 by affecting biofilm formation and motility. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7177–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Cao, X.-Y.; Jia, Z.-H.; Song, S.-S. N-3-oxo-hexanoyl-homoserine lactone, a bacterial quorum sensing signal, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis and wheat. Bot. Stud. 2020, 61, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.K.; Khan, A.R.; Hong, S.-J.; Park, G.-S.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeon, H.-J.; Khan, M.A.; Waqas, M.; Lee, I.-J.; et al. Quorum sensing activity of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Serratia glossinae GS2 isolated from the sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) rhizosphere. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bimerew, M.; Ma, Y.; Müller, H.; Ovadis, M.; Eberl, L.; Berg, G.; Chernin, L. Quorum-Sensing signaling is required for production of the antibiotic pyrrolnitrin in a rhizospheric biocontrol strain of Serratia plymuthica. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 270, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, J.; Solano, B.R.; Fray, R.G.; Cámara, M.; Hartmann, A.; Mañero, F.J.G. Transgenic tomato plants alter quorum sensing in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.-M.; Choi, H.K.; Lee, C.-H.; Murphy, J.F.; Lee, J.-K.; Kloepper, J.W. Modulation of Quorum Sensing in Acyl-homoserine Lactone-Producing or -Degrading Tobacco Plants Leads to Alteration of Induced Systemic Resistance Elicited by the Rhizobacterium Serratia marcescens 90–166. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 29, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jia, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, Z. N-butyryl-homoserine lactone, a bacterial quorum-sensing signaling molecule, induces intracellular calcium elevation in Arabidopsis root cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.; Saadalla, M.J.A.; Khan, S.-U.; Mirza, M.S.; Malik, K.A.; Hafeez, F.Y. Ochrobactrum sp. Pv2Z2 exhibits multiple traits of plant growth promotion, biodegradation and N-acyl-homoserine-lactone quorum sensing. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, P.; Müller, H.; Cardinale, M.; Zachow, C.; Sanchez, M.B.; Martinez, J.L.; Berg, G. The DSF Quorum Sensing System Controls the Positive Influence of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia on Plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sordi, L.; Mühlschlegel, F.A. Quorum sensing and fungal-bacterial interactions inCandida albicans: A communicative network regulating microbial coexistence and virulence. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009, 9, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, F.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Musetti, R.; Perazzolli, M.; Pertot, I.; Puopolo, G. The rhizosphere signature on the cell motility, biofilm formation and secondary metabolite production of a plant-associated Lysobacter strain. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 234, 126424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Schikora, A. Quorum Sensing of Bacteria and Trans-Kingdom Interactions of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactones with Eukaryotes. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinton, A.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Interspecies and Interkingdom Signaling via Quorum Signals. Isr. J. Chem. 2016, 56, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitas, V.; Kim, H.-S.; Bennett, J.W.; Kang, S. Sniffing on Microbes: Diverse Roles of Microbial Volatile Organic Compounds in Plant Health. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchiswamy, C.N.; Malnoy, M.; Maffei, M. Bioprospecting bacterial and fungal volatiles for sustainable agriculture. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, M.; Effmert, U.; Piechulla, B. Bacterial-Plant-Interactions: Approaches to Unravel the Biological Function of Bacterial Volatiles in the Rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyc, O.; Zweers, H.; de Boer, W.; Garbeva, P. Volatiles in Inter-Specific Bacterial Interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audrain, B.; Farag, M.A.; Ryu, C.-M.; Ghigo, J.-M. Role of bacterial volatile compounds in bacterial biology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Cordovez, V.; de Boer, W.; Raaijmakers, J.; Garbeva, P. Volatile affairs in microbial interactions. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraud, N.; Schleheck, D.; Klebensberger, J.; Webb, J.S.; Hassett, D.J.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms Mediates Phosphodiesterase Activity, Decreased Cyclic Di-GMP Levels, and Enhanced Dispersal. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 7333–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.; Garafola, C.; Monchy, S.; Newman, L.; Hoffman, A.; Weyens, N.; Barac, T.; Vangronsveld, J.; van der Lelie, D. Genome Survey and Characterization of Endophytic Bacteria Exhibiting a Beneficial Effect on Growth and Development of Poplar Trees. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, D.; Lorv, J.; Patten, C.L.; Rose, D.; Glick, B.R. Indole-3-acetic acid in plant–microbe interactions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 85–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, S.; Hussain, S.; Bano, A.; Saud, S.; Hassan, S.; Shan, D.; Khan, F.A.; Khan, F.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. Potential role of phytohormones and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in abiotic stresses: Consequences for changing environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4907–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, A.; Shaposhnikov, A.; Belimov, A.A.; Dodd, I.C.; Ali, B. Auxin production by rhizobacteria was associated with improved yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under drought stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.R.; Dai, L.; Xu, G.F.; Wang, H.S. A strain of Phoma species improves drought tolerance of Pinus tabulaeformis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Weller, D.M.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced Systemic Resistance by Beneficial Microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, I.A.; Pieterse, C.; Van Wees, S. Costs and benefits of hormone-regulated plant defences. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamioudis, C.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Modulation of Host Immunity by Beneficial Microbes. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Rad, U.; Klein, I.; Dobrev, P.I.; Kottova, J.; Zazimalova, E.; Fekete, A.; Hartmann, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Durner, J. Response of Arabidopsis thaliana to N-hexanoyl-dl-homoserine-lactone, a bacterial quorum sensing molecule produced in the rhizosphere. Planta 2008, 229, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, A.; Nizampatnam, N.R.; Kondreddy, A.; Pradhan, B.B.; Chatterjee, S. Xanthomonas campestriscell–cell signalling molecule DSF (diffusible signal factor) elicits innate immunity in plants and is suppressed by the exopolysaccharide xanthan. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6697–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral-Lugo, A.; Daddaoua, A.; Ortega, A.; Espinosa-Urgel, M.; Krell, T. Rosmarinic acid is a homoserine lactone mimic produced by plants that activates a bacterial quorum-sensing regulator. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Rothballer, M.; Hense, B.A.; Schröder, P. Bacterial quorum sensing compounds are important modulators of microbe-plant interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; van Gennip, M.; Phipps, R.K.; Shanmugham, M.S.; Christensen, L.D.; Alhede, M.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Friedrich, K.; Uthe, F.; et al. Ajoene, a Sulfur-Rich Molecule from Garlic, Inhibits Genes Controlled by Quorum Sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganin, H.; Rayo, J.; Amara, N.; Levy, N.; Krief, P.; Meijler, M.M. Sulforaphane and erucin, natural isothiocyanates from broccoli, inhibit bacterial quorum sensing. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, T.; Bais, H.P. Curcumin, a Known Phenolic from Curcuma longa, Attenuates the Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in Whole Plant and Animal Pathogenicity Models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Hentzer, M.; Kristoffersen, P.; Köte, M.; Nielsen, J.; Eberl, L.; Givskov, M. Screening for Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors (QSI) by Use of a Novel Genetic System, the QSI Selector. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, W.D.; Mathesius, U. Plant responses to bacterial quorum sensing signals. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Production of Substances by Medicago truncatula that Affect Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusari, P.; Kusari, S.; Spiteller, M.; Kayser, O. Implications of endophyte-plant crosstalk in light of quorum responses for plant biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5383–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teplitski, M.; Mathesius, U.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Perception and Degradation of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone Quorum Sensing Signals by Mammalian and Plant Cells. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Ye, T.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Quorum Quenching in a Novel Acinetobacter sp. XN-10 Bacterial Strain against Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, D.M.; Mavrodi, D.V.; Van Pelt, J.A.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van Loon, L.C.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced Systemic Resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana Against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato by 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol-Producing Pseudomonas fluorescens. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenhagen, U.; Baumgartner, R.; Bailly, A.; Gardiner, A.; Eberl, L.; Schulz, S.; Weisskopf, L. Production of Bioactive Volatiles by Different Burkholderia ambifaria Strains. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, M.; Haustein, M.; Molina, F.; Petri, A.; Scholz, B.; Piechulla, B. Bacterial volatiles and their action potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 81, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.-M.; Farag, M.A.; Hu, C.-H.; Reddy, M.S.; Wei, H.-X.; Paré, P.W.; Kloepper, J.W. Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, C.; Yang, X.; Weston, L.A. The role of root exudates and allelochemicals in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Bouwmeester, H.J. Engineering the plant rhizosphere. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, J.A. The roles of extracellular proteins, polysaccharides and signals in the interactions of rhizobia with legume roots. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.; Pascual, J.; Guillen, M.; Lopez-Martinez, A.; Carvajal, M. Influence of foliar Methyl-jasmonate biostimulation on exudation of glucosinolates and their effect on root pathogens of broccoli plants under salinity condition. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 282, 110027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Effects of different plant root exudates and their organic acid components on chemotaxis, biofilm formation and colonization by beneficial rhizosphere-associated bacterial strains. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Montaño, F.; Alias-Villegas, C.; Bellogín, R.A.; del Cerro, P.; Espuny, M.R.; Jiménez-Guerrero, I.; López-Baena, F.J.; Ollero, F.; Cubo, T. Plant growth promotion in cereal and leguminous agricultural important plants: From microorganism capacities to crop production. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudareva, N.; Negre, F.; Nagegowda, D.A.; Orlova, I. Plant Volatiles: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2006, 25, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmann, S.; Köllner, T.G.; Degenhardt, J.; Hiltpold, I.; Toepfer, S.; Kuhlmann, U.; Gershenzon, J.; Turlings, T.C.J. Recruitment of entomopathogenic nematodes by insect-damaged maize roots. Nature 2005, 434, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, P.; Ramachandran, V.; Terpolilli, J. Rhizobia: From saprophytes to endosymbionts. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczarek, M.; Rachwał, K.; Marzec, A.; Grządziel, J.; Palusińska-Szysz, M. Signal molecules and cell-surface components involved in early stages of the legume–rhizobium interactions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 85, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Mathesius, U. The role of flavonoids in root-rhizosphere signalling: Opportunities and challenges for improving plant-microbe interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3429–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerouge, P.; Roche, P.; Faucher, C.; Maillet, F.; Truchet, G.; Promé, J.C.; Dénarié, J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature 1990, 344, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldroyd, G.E.; Murray, J.D.; Poole, P.S.; Downie, J.A. The Rules of Engagement in the Legume-Rhizobial Symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpens, E.; van Zeijl, A.; Geurts, R. Lipochitooligosaccharides Modulate Plant Host Immunity to Enable Endosymbioses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L.; Gravel, V.; Yergeau, E. Editorial: Signaling in the Phytomicrobiome. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.L.; Praslickova, D.; Ilangumaran, G. Inter-organismal signaling and management of the phytomicrobiome. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, B.; Brière, C.; Bécard, G.; Dénarié, J.; Gough, C. Nod factors and a diffusible factor from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi stimulate lateral root formation in Medicago truncatula via the DMI1/DMI2 signalling pathway. Plant J. 2005, 44, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.L.; Hamayun, M.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kang, S.-M.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, I.-J. Gibberellins producing endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus sp. LH02 influenced endogenous phytohormonal levels, isoflavonoids production and plant growth in salinity stress. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J. Early interactions between legumes and rhizobia: Disclosing complexity in a molecular dialogue. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabood, F.; Souleimanov, A.; Khan, W.; Smith, D. Jasmonates induce Nod factor production by Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 44, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjelloun, I.; Alami, I.T.; El Khadir, M.; Douira, A.; Udupa, S. Co-Inoculation of Mesorhizobium ciceri with Either Bacillus sp. or Enterobacter aerogenes on Chickpea Improves Growth and Productivity in Phosphate-Deficient Soils in Dry Areas of a Mediterranean Region. Plants 2021, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.M.; Harrison, M.J. Signaling events during initiation of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyter-Spira, C.; Al-Babili, S.; van der Krol, S.; Bouwmeester, H. The biology of strigolactones. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldie, T.; McCulloch, H.; Leyser, O. Strigolactones and the control of plant development: Lessons from shoot branching. Plant J. 2014, 79, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschuk, G.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Giller, K.E.; Alberton, O.; Hungria, M.; Kuyper, T.W. Responses of legumes to rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: A meta-analysis of potential photosynthate limitation of symbioses. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phour, M.; Sehrawat, A.; Sindhu, S.S.; Glick, B.R. Interkingdom signaling in plant-rhizomicrobiome interactions for sustainable agriculture. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 241, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangelisti, A.; Natali, L.; Bernardi, R.; Sbrana, C.; Turrini, A.; Hassani-Pak, K.; Hughes, D.; Cavallini, A.; Giovannetti, M.; Giordani, T. Transcriptome changes induced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) roots. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, F.; Poinsot, V.; André, O.; Puech-Pagès, V.; Haouy, A.; Gueunier, M.; Cromer, L.; Giraudet, D.; Formey, D.; Niebel, A.; et al. Fungal lipochitooligosaccharide symbiotic signals in arbuscular mycorrhiza. Nature 2011, 469, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, A.M.; Bravo, A.; Harrison, M.J. Plant Signaling and Metabolic Pathways Enabling Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2319–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Laouane, R.; Meddich, A.; Bechtaoui, N.; Oufdou, K.; Wahbi, S. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Rhizobia Symbiosis on the Tolerance of Medicago Sativa to Salt Stress. Gesunde Pflanz. 2019, 71, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Xie, W.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus Improves Rhizobium–Glycyrrhiza Seedling Symbiosis under Drought Stress. Agronomy 2019, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-T.; Xie, M.-M.; Chen, S.-M.; Zhang, S.-M.; Wu, Q.-S. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Rhizobia on Physiological Activities in White Clover (Trifolium repens). Biotechnology 2019, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sui, X.-L.; Zhang, T.; Tian, Y.-Q.; Xue, R.-J.; Li, A.-R. A neglected alliance in battles against parasitic plants: Arbuscular mycorrhizal and rhizobial symbioses alleviate damage to a legume host by root hemiparasitic Pedicularis species. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Ogiwara, N.; Kaji, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ueno, M.; Sonoda, M.; Matsui, A.; Ishida, J.; Tanaka, M.; Totoki, Y.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of soybean (Glycine max) root genes differentially expressed in rhizobial, arbuscular mycorrhizal, and dual symbiosis. J. Plant Res. 2019, 132, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, A.; Thangavel, K.; Uthandi, S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus intraradices) and diazotrophic bacterium (Rhizobium BMBS) primed defense in blackgram against herbivorous insect (Spodoptera litura) infestation. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 231, 126355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiańska, I.; Gerlach, N.; Almario, J.; Bucher, M. Plant-mediated effects of soil phosphorus on the root-associated fungal microbiota in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 2123–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbon, E.H.; Trapet, P.L.; Stringlis, I.; Kruijs, S.; Bakker, P.A.; Pieterse, C.M. Iron and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Medina, A.; Van Wees, S.C.; Pieterse, C.M. Airborne signals from Trichoderma fungi stimulate iron uptake responses in roots resulting in priming of jasmonic acid-dependent defences in shoots of Arabidopsis thaliana and Solanum lycopersicum. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamioudis, C.; Korteland, J.; Van Pelt, J.A.; Hamersveld, M.; Dombrowski, N.; Bai, Y.; Hanson, J.; Van Verk, M.C.; Ling, H.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; et al. Rhizobacterial volatiles and photosynthesis-related signals coordinate MYB 72 expression in Arabidopsis roots during onset of induced systemic resistance and iron-deficiency responses. Plant J. 2015, 84, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, K.; Gerlach, N.; Sacristan, S.; Nakano, R.T.; Hacquard, S.; Kracher, B.; Neumann, U.; Ramirez, D.; Bucher, M.; O’Connell, R.J.; et al. Root Endophyte Colletotrichum tofieldiae Confers Plant Fitness Benefits that Are Phosphate Status Dependent. Cell 2016, 165, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Alikhani, H.A.; Pourbabaee, A.A.; Etesami, H.; Motasharezadeh, B.; Sarmadian, F. Consortium of endophyte and rhizosphere phosphate solubilizing bacteria improves phosphorous use efficiency in wheat cultivars in phosphorus deficient soils. Rhizosphere 2020, 14, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.M.; Uroz, S.; Barker, D.G. Ancestral alliances: Plant mutualistic symbioses with fungi and bacteria. Science 2017, 356, eaad4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nain, L. Microorganisms in the Conversion of Agricultural Wastes to Compost. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Rahman, S.; Hasan, M.; Paul, N.; Sajib, A.A. Microbial degradation of lignocellulosic biomass: Discovery of novel natural lignocellulolytic bacteria. BioTechnologia 2018, 99, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, W.M.; Abouziena, H.F.; Abd-El-Kreem, F.; El Habbasha, S. Agriculture biotechnology for management of multiple biotic and abiotic environmental stress in crops. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 882–889. [Google Scholar]
- Balmer, A.; Pastor, V.; Gamir, J.; Flors, V.; Mauch-Mani, B. The ‘prime-ome’: Towards a holistic approach to priming. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selosse, M.-A.; Bessis, A.; Pozo, M.J. Microbial priming of plant and animal immunity: Symbionts as developmental signals. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edenancé, N.; Esánchez-Vallet, A.; Egoffner, D.; Emolina, A. Disease resistance or growth: The role of plant hormones in balancing immune responses and fitness costs. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.S.; Singh, S.; Babu, C.S.V.; Shanker, K.; Srivastava, N.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Kalra, A. Fungal endophytes of Catharanthus roseus enhance vindoline content by modulating structural and regulatory genes related to terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, G.; Boudsocq, M.; Sheen, J. Protein kinase signaling networks in plant innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Zeier, J. Long-distance communication and signal amplification in systemic acquired resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Hormonal Modulation of Plant Immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Chini, A.; Solano, R. How Microbes Twist Jasmonate Signaling around Their Little Fingers. Plants 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, P.N.; Rathjen, J.P. Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant–pathogen interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, D.; Zipfel, C. Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Meng, X.; Shan, L.; He, P. Transcriptional Regulation of Pattern-Triggered Immunity in Plants. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clay, N.K.; Adio, A.M.; Denoux, C.; Jander, G.; Ausubel, F.M. Glucosinolate Metabolites Required for an Arabidopsis Innate Immune Response. Science 2009, 323, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, M.; Mbengue, M.; Barascud, M.; Navaud, O.; Raffaele, S. Small RNAs from the plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum highlight host candidate genes associated with quantitative disease resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1279–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetz, U.; Martinoia, E. Root exudates: The hidden part of plant defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Hébrard, C.; Deville, M.-A.; Cordelier, S.; Dorey, S.; Aziz, A.; Crouzet, J. Deciphering the Role of Phytoalexins in Plant-Microorganism Interactions and Human Health. Molecules 2014, 19, 18033–18056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rin, S.; Mizuno, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Fushimi, M.; Katou, S.; Sato, I.; Chiba, S.; Kawakita, K.; Takemoto, D. EIN2-Mediated signaling is involved in pre-invasion defense in Nicotiana benthamiana against potato late blight pathogen, Phytophthora infestans. Plant Signal. Behav. 2017, 12, e1300733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pel, M.J.C.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Microbial recognition and evasion of host immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; He, S.Y. Innate Immunity in Plants: An Arms Race between Pattern Recognition Receptors in Plants and Effectors in Microbial Pathogens. Science 2009, 324, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Mitsuhara, I.; Seo, S.; Imai, T.; Koga, J.; Okada, K.; Yamane, H.; Ohashi, Y. Phytoalexin Accumulation in the Interaction Between Rice and the Blast Fungus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, S.R.; McLellan, H.; Boevink, P.C.; Armstrong, M.R.; Bukharova, T.; Sukarta, O.; Win, J.; Kamoun, S.; Birch, P.R.; Banfield, M.J. Phytophthora infestans RXLR Effector PexRD2 Interacts with Host MAPKKKε to Suppress Plant Immune Signaling. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boevink, P.C.; Wang, X.; McLellan, H.; He, Q.; Naqvi, S.; Armstrong, M.R.; Zhang, W.; Hein, I.; Gilroy, E.M.; Tian, Z.; et al. A Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector targets plant PP1c isoforms that promote late blight disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Medina, A.; Flors, V.; Heil, M.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Pieterse, C.; Pozo, M.J.; Ton, J.; van Dam, N.M.; Conrath, U. Recognizing Plant Defense Priming. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.; Matthes, M.C.; Napier, J.A.; Pickett, J.A. Stressful “memories” of plants: Evidence and possible mechanisms. Plant Sci. 2007, 173, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. SOS—Too many signals for systemic acquired resistance? Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádám, A.L.; Nagy, Z.; Kátay, G.; Mergenthaler, E.; Viczián, O. Signals of Systemic Immunity in Plants: Progress and Open Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, G.J.M.; Spoel, S.H. Fine-Tuning Plant Defence Signalling: Salicylate versus Jasmonate. Plant Biol. 2006, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chu, J.Y.; Boyle, P.; Wang, Y.; Brindle, I.D.; De Luca, V.; Després, C. The Arabidopsis NPR1 protein is a receptor for the plant defense hormone salicylic acid. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, C.; Tsai, C.; Unsicker, S.B.; Xue, L.; Reichelt, M.; Gershenzon, J.; Hammerbacher, A. Salicylic acid activates poplar defense against the biotrophic rust fungus Melampsora larici-populina via increased biosynthesis of catechin and proanthocyanidins. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoodee, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Songnuan, W.; Boonchird, C.; Thitamadee, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Narangajavana, J. Phytohormone priming elevates the accumulation of defense-related gene transcripts and enhances bacterial blight disease resistance in cassava. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitti, A.; Pellegrini, E.; Nali, C.; Lovelli, S.; Sofo, A.; Valerio, M.; Scopa, A.; Nuzzaci, M. Trichoderma harzianum T-22 Induces Systemic Resistance in Tomato Infected by Cucumber mosaic virus. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwantisari, S.; Priyatmojo, A.; Sancayaningsih, R.P.; Kasiamdari, R.S.; Budihardjo, K. Systemic inducing resistance against late blight by applying antagonist Trichoderma Viride. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1025, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doornbos, R.F.; Geraats, B.P.J.; Kuramae, E.E.; Van Loon, L.C.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Effects of Jasmonic Acid, Ethylene, and Salicylic Acid Signaling on the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Ryu, C.-M. Dynamic Chemical Communication between Plants and Bacteria through Airborne Signals: Induced Resistance by Bacterial Volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C.-M. Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittel, P.; Robatzek, S. Microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) probe plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Solano, R. Molecular players regulating the jasmonate signalling network. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dahl, C.C.; Baldwin, I.T. Deciphering the Role of Ethylene in Plant–Herbivore Interactions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.K.; Johri, B.N. Interactions of Bacillus spp. and plants—With special reference to induced systemic resistance (ISR). Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, J.; Jia, X.; Ke, P.; He, L.; Cao, A.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. The role of wheat jasmonic acid and ethylene pathways in response to Fusarium graminearum infection. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 80, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, D.; Gautam, J.K.; Nandi, A.K. RSI1/FLD is a positive regulator for defense against necrotrophic pathogens. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 107, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic-Ekici, O.; Yuen, G.Y. Comparison of strains of Lysobacter enzymogenes and PGPR for induction of resistance against Bipolaris sorokiniana in tall fescue. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Gu, C.; Niu, D.-D.; Liu, H.-X.; Wang, Y.-P.; Guo, J.-H. Induction of Drought Tolerance in Cucumber Plants by a Consortium of Three Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacterium Strains. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, J.; Hernández, J.A.; Caravaca, F.; Roldán, A. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi modify alleviation biochemical mechanisms in water-stressed plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Parihar, S.S.; Ahirwar, N.K.; Snehi, S.K.; Singh, V. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Current and future prospects for development of sustainable agriculture. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 096–102. [Google Scholar]
- Beneduzi, A.; Ambrosini, A.; Passaglia, L.M. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Their potential as antagonists and biocontrol agents. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.P.; Uhl, J.; Grosch, R.; Alquéres, S.; Pittroff, S.; Dietel, K.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Borriss, R.; Hartmann, A. Cyclic Lipopeptides of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum Colonizing the Lettuce Rhizosphere Enhance Plant Defense Responses Toward the Bottom Rot Pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, D.; Trost, E.; Mayer, K.F.; Vlot, A.C.; Heller, W.; Schmid, M.; Hartmann, A.; Rothballer, M. Systemic Responses of Barley to the 3-hydroxy-decanoyl-homoserine Lactone Producing Plant Beneficial Endophyte Acidovorax radicis N35. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Bheemaraddi, M.C.; Shivannavar, C.T.; Gaddad, S.M. Biocontrol activity of siderophore producing Bacillus subtilis CTS-G24 against wilt and dry root rot causing fungi in chickpea. IOSR J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2014, 7, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, C.; Crowley, J.J.; Moënne-Loccoz, Y.; Dowling, D.N.; Bruijn, S.; O’Gara, F. Biological control of Pythium ultimum by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia W81 is mediated by an extracellular proteolytic activity. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3921–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Ding, J.; He, Q.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, K. The investigation of nematocidal activity in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia G2 and characterization of a novel virulence serine protease. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Jousset, A.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Friman, V.-P. Phage combination therapies for bacterial wilt disease in tomato. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enebe, M.C.; Babalola, O.O. The impact of microbes in the orchestration of plants’ resistance to biotic stress: A disease management approach. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 103, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Verma, J.P. Does plant—Microbe interaction confer stress tolerance in plants: A review? Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, K.K.; Sorty, A.M.; Bitla, U.M.; Choudhary, K.; Gupta, P.; Pareek, A.; Singh, D.P.; Prabha, R.; Sahu, P.K.; Gupta, V.K.; et al. Abiotic Stress Responses and Microbe-Mediated Mitigation in Plants: The Omics Strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorty, A.M.; Meena, K.K.; Choudhary, K.; Bitla, U.M.; Minhas, P.S.; Krishnani, K.K. Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria Associated with Halophytic Weed (Psoralea corylifolia L.) on Germination and Seedling Growth of Wheat Under Saline Conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sathya, A.; Vijayabharathi, R.; Varshney, R.K.; Gowda, C.L.; Krishnamurthy, L. Plant growth promoting rhizobia: Challenges and opportunities. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.; Sawant, K. Drought stress adaptation: Metabolic adjustment and regulation of gene expression. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.M.; Flexas, J.; Pinheiro, C. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: Regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaka, D.; Nakashima, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Toward understanding transcriptional regulatory networks in abiotic stress responses and tolerance in rice. Rice 2012, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, F.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Achievements and Challenges in Understanding Plant Abiotic Stress Responses and Tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Singh, P.; Tiwari, R.; Meena, K.K.; Yandigeri, M.; Singh, D.P.; Arora, D.K. Salt-tolerant rhizobacteria-mediated induced tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum) and chemical diversity in rhizosphere enhance plant growth. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, N.J.; Lilley, C.J.; Urwin, P.E. Identification of Genes Involved in the Response of Arabidopsis to Simultaneous Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasch, C.M.; Sonnewald, U. Simultaneous Application of Heat, Drought, and Virus to Arabidopsis Plants Reveals Significant Shifts in Signaling Networks. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1849–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, R.; Watanabe, Y.; Leyva-Gonzalez, M.A.; Van Ha, C.; Fujita, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Seki, M.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; et al. Arabidopsis AHP2, AHP3, and AHP5 histidine phosphotransfer proteins function as redundant negative regulators of drought stress response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4840–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, Z.; Blumwald, E. Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Lee, H.; Ishitani, M.; Zhu, J.-K. Regulation of Osmotic Stress-responsive Gene Expression by theLOS6/ABA1 Locus inArabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8588–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzarrini, S. Cross-talk in Plant Hormone Signalling: What Arabidopsis Mutants Are Telling Us. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Halo, B.A.; Khan, A.L.; Waqas, M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Hussain, J.; Ali, L.; Adnan, M.; Lee, I.-J. Endophytic bacteria (Sphingomonas sp. LK11) and gibberellin can improve Solanum lycopersicum growth and oxidative stress under salinity. J. Plant Interact. 2015, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnawal, D.; Bharti, N.; Pandey, S.S.; Pandey, A.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Kalra, A. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance wheat salt and drought stress tolerance by altering endogenous phytohormone levels and TaCTR1/TaDREB2 expression. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 161, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-M.; Shahzad, R.; Bilal, S.; Khan, A.L.; Park, Y.-G.; Lee, K.-E.; Asaf, S.; Khan, M.A.; Lee, I.-J. Indole-3-acetic-acid and ACC deaminase producing Leclercia adecarboxylata MO1 improves Solanum lycopersicum L. growth and salinity stress tolerance by endogenous secondary metabolites regulation. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, N.; Pandey, S.S.; Barnawal, D.; Patel, V.K.; Kalra, A. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-M.; Khan, A.L.; Waqas, M.; You, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-G.; Hamayun, M.; Lee, I.-J. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria reduce adverse effects of salinity and osmotic stress by regulating phytohormones and antioxidants in Cucumis sativus. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Effects of phosphate solubilization and phytohormone production of Trichoderma asperellum Q1 on promoting cucumber growth under salt stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Niu, S.; Yang, D.; Ren, W.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Q.; Paré, P.W.; Zhang, J. Two PGPR strains from the rhizosphere of Haloxylon ammodendron promoted growth and enhanced drought tolerance of ryegrass. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, M.; McWilliams, K.; Borrego, E.J.; Kolomiets, M.V.; Niu, G.; Pierson, E.A.; Jo, Y.-K. Bioprospecting Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria That Mitigate Drought Stress in Grasses. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saakre, M.; Baburao, T.M.; Salim, A.P.; Ffancies, R.M.; Achuthan, V.P.; Thomas, G.; Sivarajan, S.R. Identification and Characterization of Genes Responsible for Drought Tolerance in Rice Mediated by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.; Wang, L.; Ahmad, H.; Akhtar, K.; Roy, R.; Khan, M.I.; Zhao, T. Co-inoculation of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and the Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Improve Growth and Photosynthesis in Tobacco Under Drought Stress by Up-Regulating Antioxidant and Mineral Nutrition Metabolism. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 83, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, P.; Kanagendran, A.; Samaddar, S.; Pazouki, L.; Sa, T.-M.; Niinemets, Ü. Influence of Brevibacterium linens RS16 on foliage photosynthetic and volatile emission characteristics upon heat stress in Eucalyptus grandis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Smith, D.; Sultan, T.; Seleiman, M.F.; Alsadon, A.A.; Amna; Ali, S.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Solieman, T.H.I.; et al. Mitigation of Heat Stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. by ACC-deaminase and Exopolysaccharide Producing Bacillus cereus: Effects on Biochemical Profiling. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkasem, P.; Kurniawan, A.; Kao, T.-C.; Chuang, H.-W. A multifaceted rhizobacterium Bacillus licheniformis functions as a fungal antagonist and a promoter of plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 155, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J.; Chakraborty, B.; Chakraborty, U. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Protect Wheat Plants Against Temperature Stress Through Antioxidant Signalling and Reducing Chloroplast and Membrane Injury. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 37, 1396–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daim, I.A.A.; Bejai, S.; Meijer, J. Bacillus velezensis 5113 Induced Metabolic and Molecular Reprogramming during Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Wheat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Prasad, V.; Chauhan, P.S.; Lata, C. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Confers Tolerance to Various Abiotic Stresses and Modulates Plant Response to Phytohormones through Osmoprotection and Gene Expression Regulation in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradonia, F.; Francia, E.; Morcia, C.; Ghizzoni, R.; Moulin, L.; Terzi, V.; Ronga, D. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Avoid Processing Tomato Leaf Damage during Chilling Stress. Agronomy 2019, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Jacquard, C.; Villaume, S.; Michel, J.; Rabenoelina, F.; Clément, C.; Barka, E.A.; Dhondt-Cordelier, S.; Vaillant-Gaveau, N. Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN reduces impact of freezing temperatures on photosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, K.; Mitra, S.; Sarkar, A.; Maiti, T.K. Alleviation of phytotoxic effects of cadmium on rice seedlings by cadmium resistant PGPR strain Enterobacter aerogenes MCC 3092. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 351, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar-Ul-Hye, M.; Naeem, M.; Danish, S.; Khan, M.J.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R.; Brtnicky, M.; Kintl, A.; Hussain, G.S.; El-Esawi, M.A. Effect of Cadmium-Tolerant Rhizobacteria on Growth Attributes and Chlorophyll Contents of Bitter Gourd under Cadmium Toxicity. Plants 2020, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, S.; Shahzad, R.; Imran, M.; Jan, R.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, I.-J. Synergistic association of endophytic fungi enhances Glycine max L. resilience to combined abiotic stresses: Heavy metals, high temperature and drought stress. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 143, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa-Marín, J.; Del-Saz, N.F.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Pajuelo, E.; Ribas-Carbó, M.; Mateos-Naranjo, E. PGPR Reduce Root Respiration and Oxidative Stress Enhancing Spartina maritima Root Growth and Heavy Metal Rhizoaccumulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gururani, M.A.; Upadhyaya, C.P.; Baskar, V.; Venkatesh, J.; Nookaraju, A.; Park, S.W. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Enhance Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Solanum tuberosum Through Inducing Changes in the Expression of ROS-Scavenging Enzymes and Improved Photosynthetic Performance. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz, A.L.; Talano, M.A.; Nicotra, M.F.O.; Escudero, L.; Breser, M.L.; Porporatto, C.; Agostini, E. Impact of double inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum E109 and Azospirillum brasilense Az39 on soybean plants grown under arsenic stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Usha; Rizvi, S.M.H.; Sonia; Jaiwal, P.K. Genetic Engineering for Enhancing Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynkiewicz, K.; Zloch, M.; Kowalkowski, T.; Baum, C.; Niedojadło, K.; Buszewski, B. Strain-Specific bioaccumulation and intracellular distribution of Cd2+ in bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere, ectomycorrhizae, and fruitbodies of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3055–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Lata, C.; Tiwari, S.; Chauhan, A.S.; Mishra, S.K.; Agrawal, L.; Chakrabarty, D.; Nautiyal, C.S. Transcriptional alterations reveal Bacillus amyloliquefaciens -rice cooperation under salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Naveed, M.; Nawaz, S. Mitigation of salinity-induced negative impact on the growth and yield of wheat by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in naturally saline conditions. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type of Microbe | Rhizo-Microorganisms | Quorum Sensing Molecules | Type of Communication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | Bacillus subtilis | ComX pheromone | Inter- and intraspecies | [6] |
| Streptomyces spp. | Gamma-butyrolactones (A-factor) and methylenomycin furans (MMF1) | Interspecies | [55] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Circular oligopeptide | Interspecies | [16] | |
| Stenotrophomonas chelatiphaga | DSF (diffuse signal factor) | Interkingdom (poplar plant) | [56] | |
| Bacillus velezensis | AI-2 synthetase (2-methyl-2,3,3,4-tetrahydroxytetrahydrofuran (THMF)) | Interkingdom (maize plant) | [57] | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | Burkholderia sp. | N-3-oxo-hexanoyl-homoserine lactone (3OC6-HSL) | Interkingdom (wheat and arabidopsis plant) | [58] |
| Serratia glossinae | N-hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (m/z 200) and N-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (m/z 228) | Interkingdom (rice plant) | [59] | |
| Serratia plymuthica | N-butanoyl-HSL, N-hexanoyl-HSL, and N-3-oxo-hexanoyl-HSL (OHHL) | Interkingdom (oil seed rape) | [60] | |
| Burkholderia graminis M12 and B. graminis M14 | N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL or OC12-HSL (where “O” indicates an oxo substitution at the third carbon atom)) and 3-oxo-C14-HSL (OC14-HSL) | Interkingdom (tomato plant) | [61] | |
| Serratia marcescens | N-3-oxo-hexanoyl-homoserine lactone (3OC6-HSL) | Intraspecies and interkingdom (tobacco plant) | [62] | |
| Burkholderia sp. and Pseudomonas sp. | N-butyryl-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL) | Interkingdom (arabidopsis plant) | [63] | |
| Ochrobactrum sp. | 3O-C7-HSL and 3OH-C7-HSL | Interkingdom (bean plant) | [64] | |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | DSF (diffuse signal factor) | Interkingdom (oil seed rape) | [65] | |
| Serratia glossinae | N-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone and N-hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone | Interkingdom (sesame plant) | [59] | |
| Fungi | Candida albicans | Tyrosol, γ-butyrolactone, and farnesol | Intraspecies | [66] |
| Stress Type | Host Plant | Rhizo-Microorganisms | Signaling Pathways | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Triticum aestivum | Arthrobacter protophormiae (SA3) and Dietzia natronolimnaea (STR1) | IAA, ET | [218] | |
| Lycopersicum esculentum | Leclercia adecarboxylata | IAA | [219] | ||
| Triticum aestivum | Dietzia natronolimnaea | SOS, ABA | [220] | ||
| Cucumis sativus | Burkholdera cepacia, Promicromonospora sp., and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus | GA, ABA, SA | [221] | ||
| Cucumis sativus | Trichoderma asperellum | IAA, ABA, GA | [222] | ||
| Drought | Lolium multiflorum | Bacillus sp. and Pseudomonas sp. | ABA | [223] | |
| Triticum aestivum, Zea mays | Bacillus sp. and Enterobacter sp. | IAA, SA | [224] | ||
| Oryza sativa | Pseudomonas fluorescens | ABA | [225] | ||
| Nicotiana tabacum | Glomus versiforme (AMF) and Bacillus methylotrophicus | ABA, IAA | [226] | ||
| Heat | Eucalyptus grandis | Brevibacterium linens | ET | [227] | |
| Lycopersicum esculentum | Bacillus cereus | ET | [228] | ||
| Arabidopsis | Bacillus licheniformis | JA, ABA | [229] | ||
| Triticum aestivum | Bacillus safensis and Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense | ROS | [230] | ||
| Low temperature | Triticum aestivum | Bacillus velezensis | ROS, ABA | [231] | |
| Oryza sativa | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | ABA, SA, JA, ET | [232] | ||
| Solanum lycopersicum | Funneliformis mosseae and Paraburkholderia graminis | ROS | [233] | ||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Burkholderia phytofirmans | ROS | [234] | ||
| Heavy metals | Cd | Oryza sativa | Enterobacter aerogenes | IAA, ET | [235] |
| Momordica charantia | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Agrobacterium fabrum | ET | [236] | ||
| Ni, Cd, and Al | Glycine max | Paecilomyces formosus and Penicillium funiculosum | IAA, GA | [237] | |
| Cd, Cu, Pb, and Ni | Spartima maritima | Bacillus methylotrophicus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus aryabhattai | COX, AOX | [238] | |
| Solanum tuberosum | Bacillus sp. | ROS | [239] | ||
| As | Glycine max | Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Azospirillum brasilense | IAA | [240] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamil, F.; Mukhtar, H.; Fouillaud, M.; Dufossé, L. Rhizosphere Signaling: Insights into Plant–Rhizomicrobiome Interactions for Sustainable Agronomy. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050899
Jamil F, Mukhtar H, Fouillaud M, Dufossé L. Rhizosphere Signaling: Insights into Plant–Rhizomicrobiome Interactions for Sustainable Agronomy. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(5):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050899
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamil, Fatima, Hamid Mukhtar, Mireille Fouillaud, and Laurent Dufossé. 2022. "Rhizosphere Signaling: Insights into Plant–Rhizomicrobiome Interactions for Sustainable Agronomy" Microorganisms 10, no. 5: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050899
APA StyleJamil, F., Mukhtar, H., Fouillaud, M., & Dufossé, L. (2022). Rhizosphere Signaling: Insights into Plant–Rhizomicrobiome Interactions for Sustainable Agronomy. Microorganisms, 10(5), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050899









