Structural and Functional Characterization of the Holliday Junction Resolvase RuvC from Deinococcus radiodurans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oligonucleotides
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. DNA Binding Assay
2.4. DNA Cleavage Assay
2.5. Crystallization, Data Collection and Structure Determination
2.6. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
3. Results
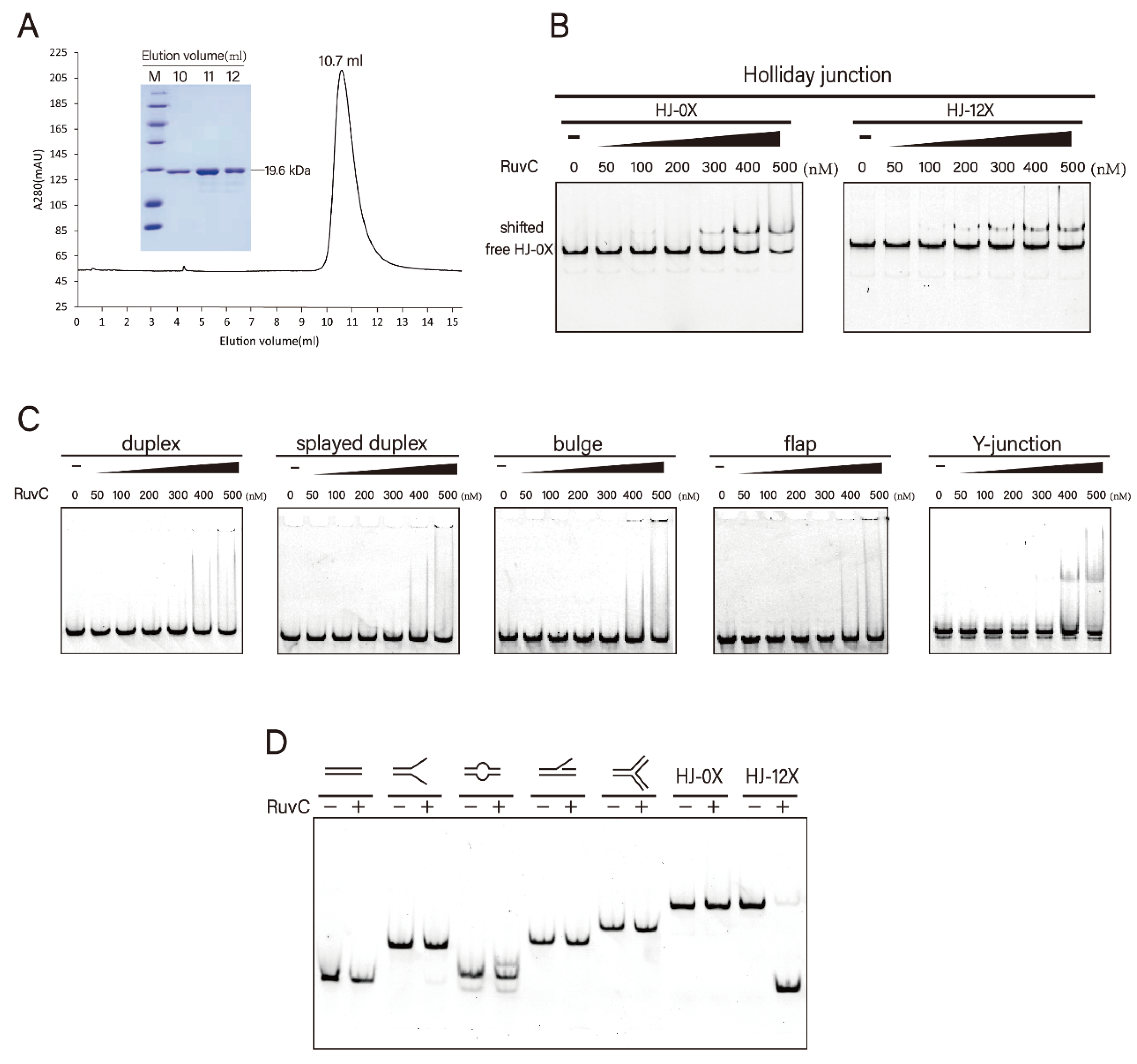
3.1. DrRuvC Is a Typical Holliday Junction Resolvase
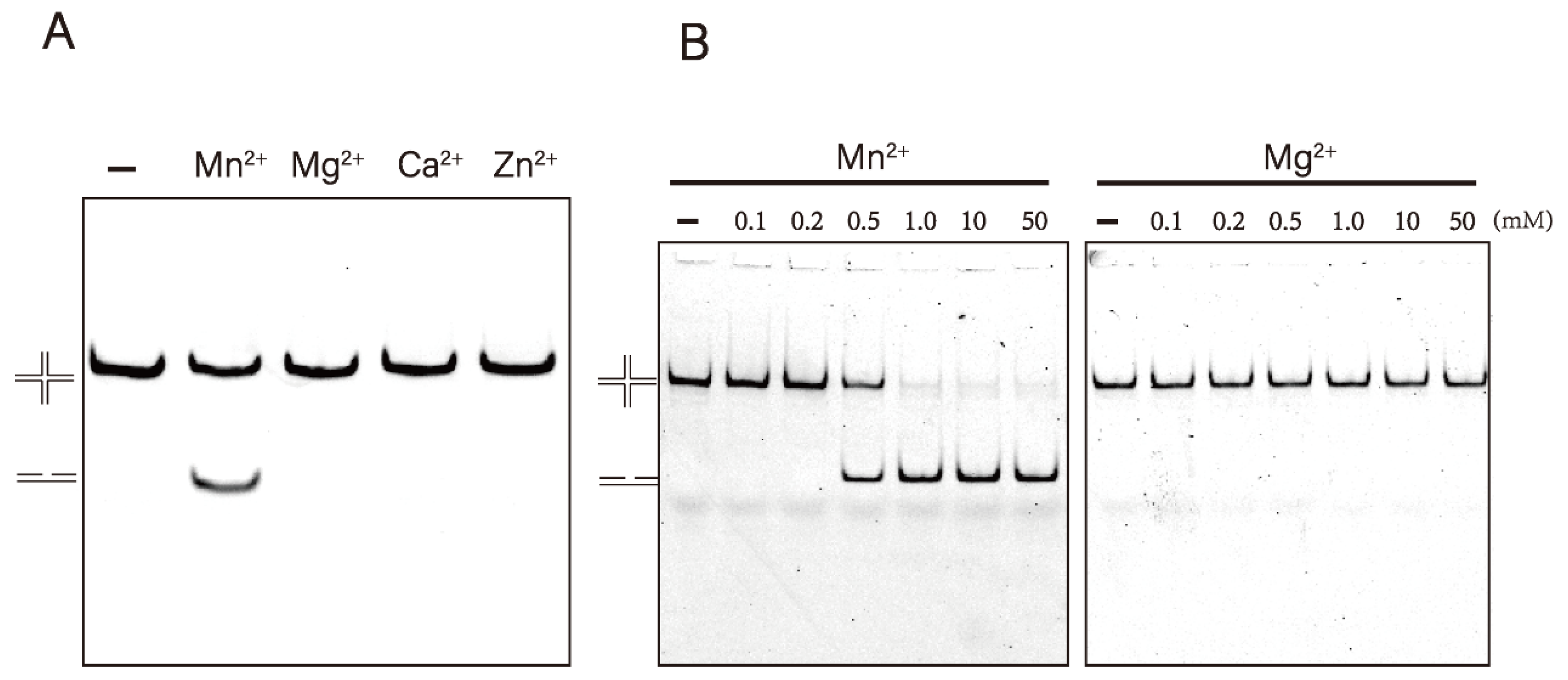
3.2. Mn2+ Is Essential for the Resolvase Activity of DrRuvC
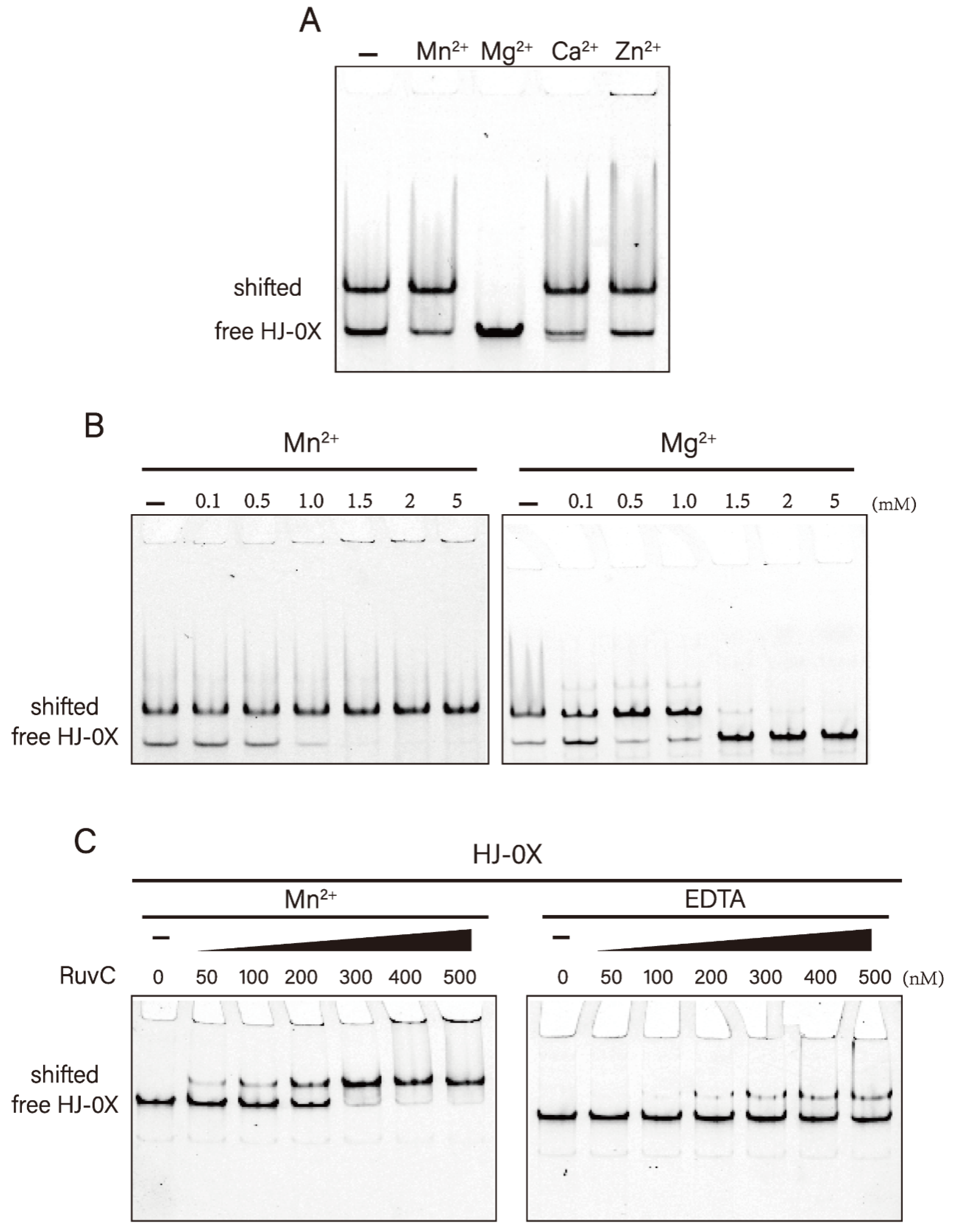
3.3. High Mg2+ Concentration Inhibits the Binding Activity of DrRuvC
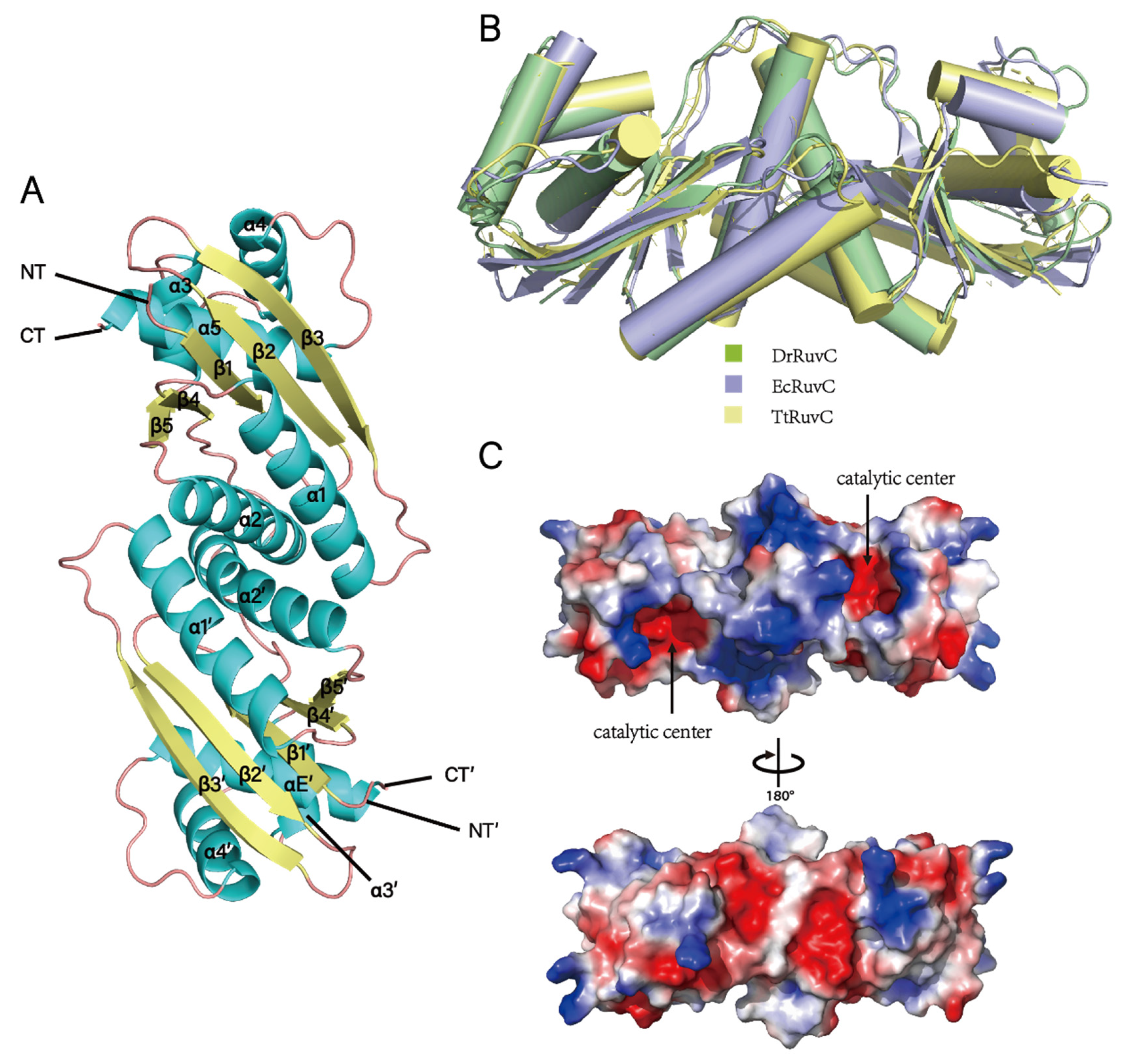
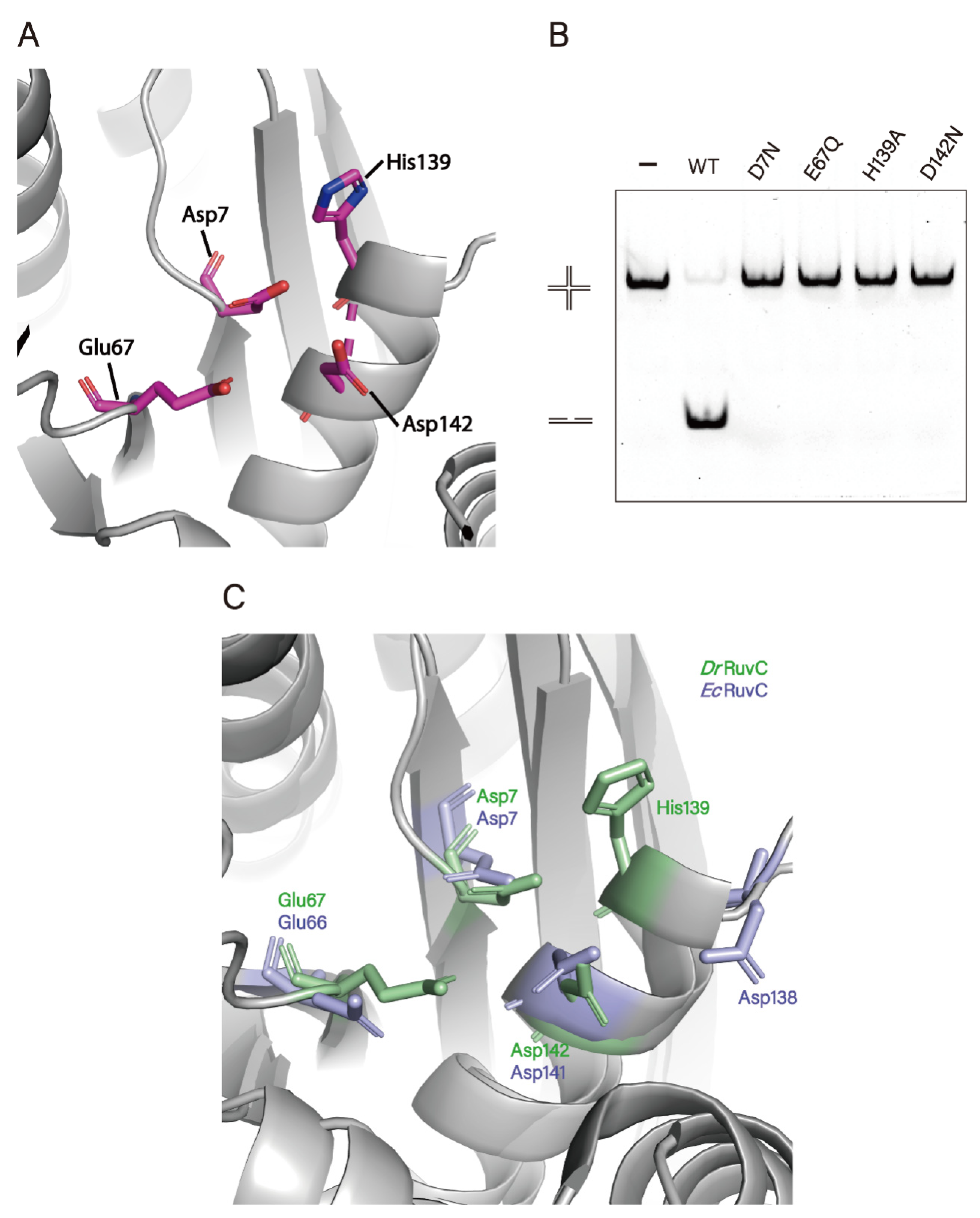
3.4. Crystal Structure of DrRuvC Reveals Its Essential Amino Acid Sites
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, W.D.; Shah, S.S.; Heyer, W.-D. Homologous recombination and the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10524–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Haber, J.E. Sources of DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Models of Recombinational DNA Repair. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, R. A mechanism for gene conversion in fungi (Reprinted). Genet. Res. 2007, 89, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, C.S.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Richard, D.; White, M.F.; Hunter, W.N. Structure of Hjc, a Holliday junction resolvase, from Sulfolobus solfataricus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5509–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, J.M.; Declais, A.-C.; Carr, S.B.; Lilley, D.M.J.; Phillips, S.E.V. The structural basis of Holliday junction resolution by T7 endonuclease. Nature 2007, 449, 621-U15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, J.J.; Cho, Y. Crystal structure of the Mus81-Eme1 complex. Acta Crystallogr.-Found. Adv. 2008, 64, C301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Komori, K.; Tsuchiya, D.; Ishino, Y.; Morikawa, K. Crystal structure of the archaeal Holliday Junction resolvase Hjc and implications for DNA recognition. Structure 2001, 9, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bizard, A.H.; Hickson, I.D. The Dissolution of Double Holliday Junctions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthei, K.A.; Keck, J.L. The BLM dissolvasome in DNA replication and repair. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4067–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.; Dunderdale, H.; West, S. Resolution of Holliday Junctions by Ruvc Resolvase—Cleavage Specificity and Dna Distortion. Cell 1993, 74, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunderdale, H.; Benson, F.; Parsons, C.; Sharples, G.; Lloyd, R.; West, S. Formation and Resolution of Recombination Intermediates by Escherichia-Coli Reca and Ruvc Proteins. Nature 1991, 354, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Takahagi, M.; Shiba, T.; Nakata, A.; Shinagawa, H. Escherichia-Coli Ruvc Protein Is an Endonuclease That Resolves the Holliday Structure. Embo J. 1991, 10, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggleston, A.K.; Mitchell, A.H.; West, S.C. In vitro reconstitution of the late steps of genetic recombination in E. coli. Cell 1997, 89, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Gool, A.J.; Shah, R.; Mézard, C.; West, S.C. Functional interactions between the holliday junction resolvase and the branch migration motor of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, T.N.; Mahdi, A.A.; Sharples, G.J.; Lloyd, R.G. Resolution of Holliday intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: Indirect suppression of ruvA, ruvB, and ruvC mutations. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4325–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, G.J.; Ingleston, S.M.; Lloyd, R.G. Holliday junction processing in bacteria: Insights from the evolutionary conservation of RuVABC, RecG, and RusA. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5543–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinagawa, H.; Iwasaki, H. Processing the Holliday junction in homologous recombination. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.; Stasiak, A.; Bennett, R.; West, S. Structure of a Multisubunit Complex That Promotes Dna Branch Migration. Nature 1995, 374, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, H.D.M.; West, S.C. Holliday Junction Resolvases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a023192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, J.R. Against all odds: The survival strategies of Deinococcus radiodurans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, A.-C.; Uivarosi, V.; Andries, A. Recent progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms of radioresistance in Deinococcus bacteria. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, D.; Radman, M. Oxidative Stress Resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 133–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Misumi, O.; Odahara, M.; Ishibashi, K.; Hirono, M.; Hidaka, K.; Endo, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Kuroiwa, T.; et al. Holliday junction resolvases mediate chloroplast nucleoid segregation. Science 2017, 356, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Hong, S.; Guan, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, D.; Yin, P. Structural insights into sequence-dependent Holliday junction resolution by the chloroplast resolvase MOC1. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Pan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Tian, B.; Wang, L.; Hua, Y. DRJAMM Is Involved in the Oxidative Resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 756867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, K.; Xu, H.; Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Hua, Y. Structural and Functional Characterization of a Unique AP Endonuclease From Deinococcus radiodurans. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; An, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Hua, Y. Biochemical characterization of a unique DNA polymerase A from the extreme radioresistant organism Deinococcus radiodurans. Biochimie 2021, 185, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, W.; Cymborowski, M.; Otwinowski, Z.; Chruszcz, M. HKL-3000: The integration of data reduction and structure solution —From diffraction images to an initial model in minutes. Acta Crystallogr. Sect.-Struct. Biol. 2006, 62, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Macromol. Crystallogr. Pt. A 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Hung, L.W.; Ioerger, T.R.; McCoy, A.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Read, R.J.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Sauter, N.K.; Terwilliger, T.C. PHENIX: Building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect.-Struct. Biol. 2002, 58, 1948–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect.-Struct. Biol. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R. Genetic recombination in E. coli: RuvC protein cleaves Holliday junctions at resolution hotspots in vitro. Cell 1994, 79, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.F.; Lilley, D.M.J. Characterization of a Holliday junction-resolving enzyme from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 6465–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- White, M.F.; Lilley, D.M.J. The Structure-selectivity and Sequence-preference of the Junction-resolving Enzyme CCE1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 257, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, Y.; Lin, Z. Biochemical and structural characterization of the Holliday junction resolvase RuvC from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, K.; Sakae, S.; Fujikane, R.; Morikawa, K.; Shinagawa, H.; Ishino, Y. Biochemical characterization of the Hjc Holliday junction resolvase of Pyrococcus furiosus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4544–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Takahagi, M.; Iwasaki, H.; Shinagawa, H. Structural requirements of substrate DNA for binding to and cleavage by RuvC, a Holliday junction resolvase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15132–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, K.; Yin, Z.; Aihara, H. Structural asymmetry in the Thermus thermophilus RuvC dimer suggests a basis for sequential strand cleavages during Holliday junction resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, D.; Zuo, K.; Yuan, C.; Li, J.; Huang, M.; Lin, Z. Structural basis of sequence-specific Holliday junction cleavage by MOC1. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górecka, K.M.; Komorowska, W.; Nowotny, M. Crystal structure of RuvC resolvase in complex with Holliday junction substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9945–9955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Iwasaki, H.; Shinagawa, H. Evidence that phenylalanine 69 in Escherichia coli RuvC resolvase forms a stacking interaction during binding and destabilization of a holliday junction DNA substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10432–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.C. Molecular views of recombination proteins and their control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, R. Mechanism for Gene Conversion in Fungi. Genet. Res. 1964, 5, 282–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hua, Y. PprI: The Key Protein in Response to DNA Damage in Deinococcus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 609714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R. The RuvC protein dimer resolves Holliday junctions by a dual incision mechanism that involves base-specific contacts. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Hua, Y. Structural basis for DNA 5′-end resection by RecJ. eLife 2016, 5, e14294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhou, C.; Xu, Q.; Ul Hussain Shah, A.M.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Hua, Y. Structural insights into catalysis and dimerization enhanced exonuclease activity of RNase J. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5550–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.M.D.; de Sanctis, D.; McSweeney, S.M. Structural and Functional Insights into DR2231 Protein, the MazG-like Nucleoside Triphosphate Pyrophosphohydrolase from Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 30691–30705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzi, A.T.; Zimanyi, C.M.; Nicoludis, J.M.; Lee, B.K.; Zhang, C.H.; Gaudet, R. Structures in multiple conformations reveal distinct transition metal and proton pathways in an Nramp transporter. eLife 2019, 8, e41124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, R.J.; Micossi, E.; McCarthy, J.; Moe, E.; Gordon, E.J.; Kozielski-Stuhrmann, S.; Leonard, G.A.; McSweeney, S. Structure of the manganese superoxide dismutase from Deinococcus radiodurans in two crystal forms. Acta Crystallograph. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2006, 62, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subinya, M.; Steudle, A.K.; Jurkowski, T.P.; Stubenrauch, C. Conformation and activity of lipase B from Candida antarctica in bicontinuous microemulsions. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2015, 131, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M.J.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Vasilenko, A.; Zhai, M.; Venkateswaran, A.; Hess, M.; Omelchenko, M.V.; Kostandarithes, H.M.; Makarova, K.S.; et al. Accumulation of Mn(II) in, Deinococcus radiodurans facilitates gamma-radiation resistance. Science 2004, 306, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Xu, G.; Zhan, H.; Chen, H.; Sun, Z.; Tian, B.; Hua, Y. Identification and evaluation of the role of the manganese efflux protein in Deinococcus radiodurans. Bmc Microbiol. 2010, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabares, L.C.; Un, S. In Situ Determination of Manganese(II) Speciation in Deinococcus radiodurans by High Magnetic Field EPR Detection of High Levels of Mn(II) Bound to Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 5050–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Bennett, B.; Daly, M.J.; Hoffman, B.M. Responses of Mn2+ speciation in Deinococcus radiodurans and Escherichia coli to gamma-radiation by advanced paramagnetic resonance methods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5945–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, L.; Nierzwicki, Ł.; Jinek, M.; Palermo, G. Catalytic Mechanism of Non-Target DNA Cleavage in CRISPR-Cas9 Revealed by Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 13596–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| DrRuvC | |
|---|---|
| Data collection | |
| Space group | P212121 |
| Cell dimensions | |
| a, b, c (Å) α, β, ɣ (°) | 40.02, 72.60, 113.90 90, 90, 90 |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.9793 |
| Resolution (Å) | 30.0–1.60 |
| Rsym (%) | 5.7 (41.1) |
| I/σI | 16.5 (4.3) |
| Completeness (%) | 94.8(98.6) |
| Redundancy | 3.7 (3.8) |
| Refinement | |
| Resolution (Å) | 30.0–1.60 (1.64–1.60) |
| No. reflections | 42,358 |
| Rwork/Rfree | 20.5/22.4 |
| No. atoms | |
| Protein | 2270 |
| Water | 151 |
| B-factors | |
| Protein | 30.7 |
| Water | 42.5 |
| R.m.s deviations | |
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.005 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.770 |
| Ramachandran statistics | |
| Favored (%) | 98.7 |
| Allowed (%) | 1.3 |
| Ourlier (%) | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, C.; Han, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Tian, B.; Wang, L.; Hua, Y. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Holliday Junction Resolvase RuvC from Deinococcus radiodurans. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061160
Qin C, Han W, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Xu H, Tian B, Wang L, Hua Y. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Holliday Junction Resolvase RuvC from Deinococcus radiodurans. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(6):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061160
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Chen, Wanchun Han, Ying Xu, Ye Zhao, Hong Xu, Bing Tian, Liangyan Wang, and Yuejin Hua. 2022. "Structural and Functional Characterization of the Holliday Junction Resolvase RuvC from Deinococcus radiodurans" Microorganisms 10, no. 6: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061160
APA StyleQin, C., Han, W., Xu, Y., Zhao, Y., Xu, H., Tian, B., Wang, L., & Hua, Y. (2022). Structural and Functional Characterization of the Holliday Junction Resolvase RuvC from Deinococcus radiodurans. Microorganisms, 10(6), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061160






