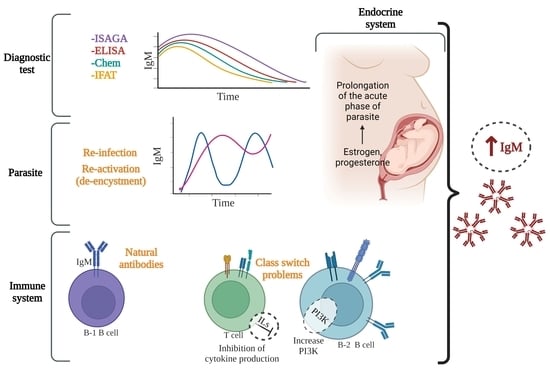
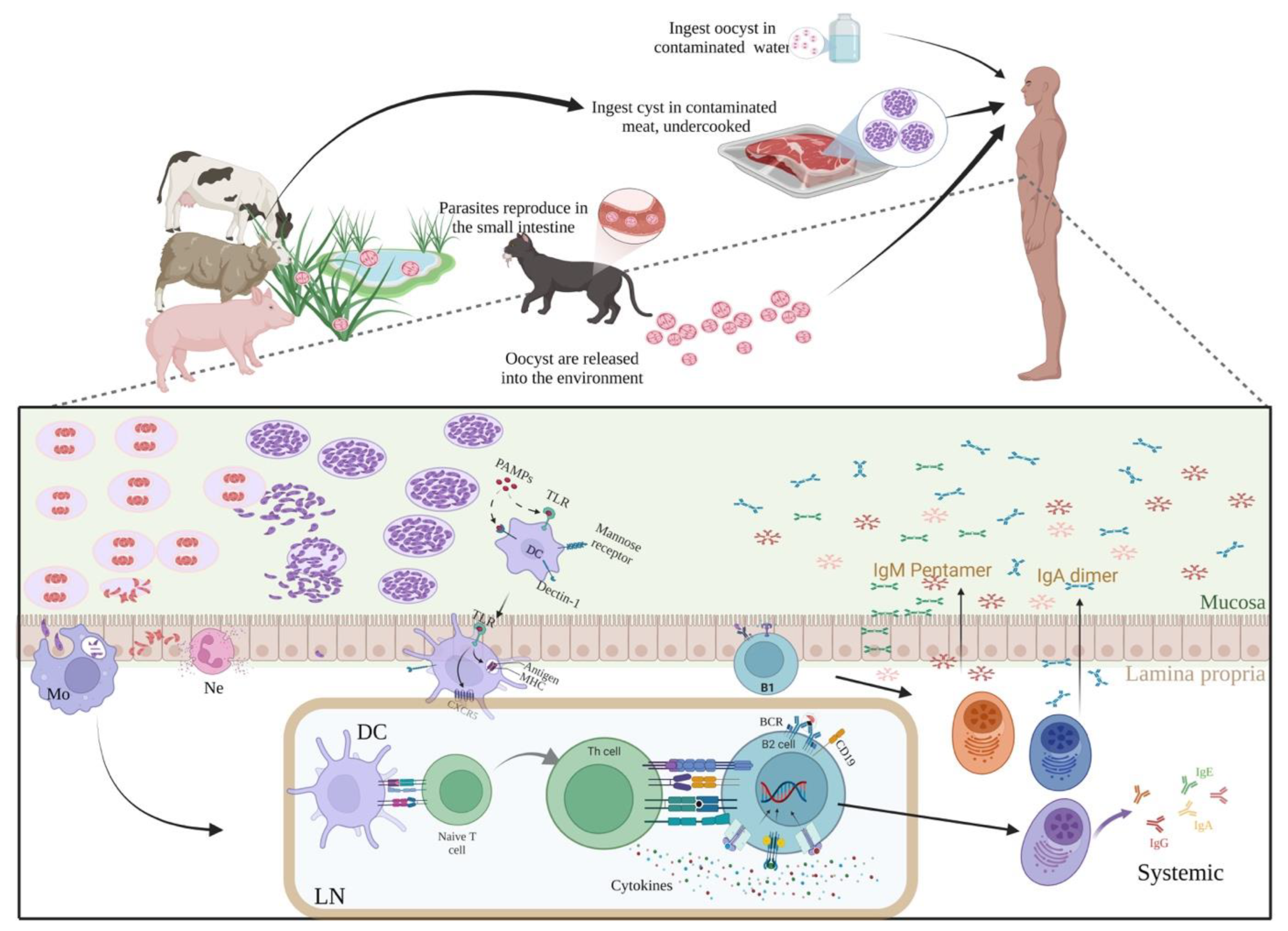
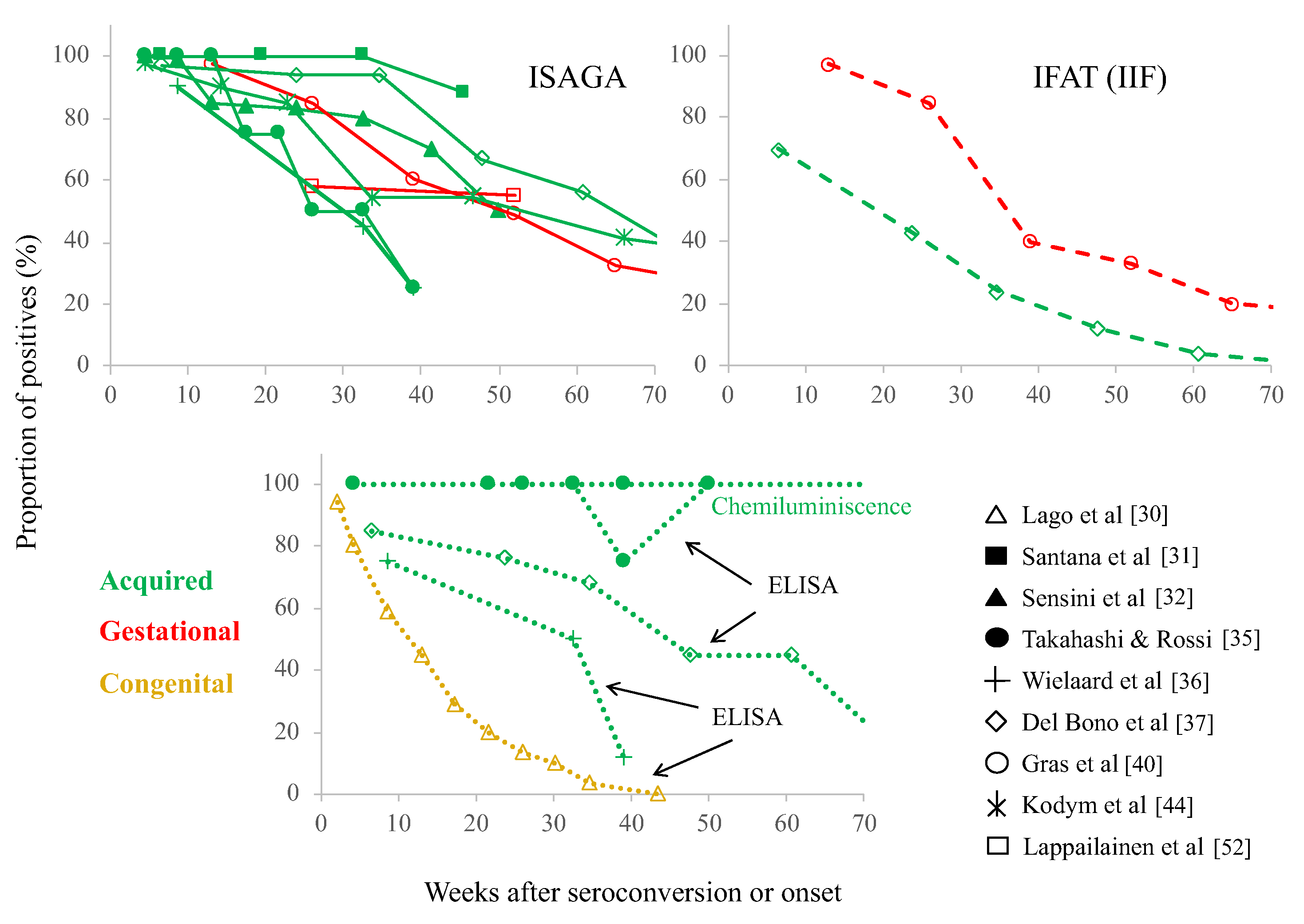
Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Is the “Chronic” IgM Phenomenon Occurring in A Specific Patient Group?
3. Specificity/Sensitivity Problems of Serological Tests
4. Explanations of the Chronic T. gondii-IgM Phenomenon
4.1. Dynamics of the Infection: Antigenic Variation
4.2. Long-Lasting Acute Infection or Continuous Stimulation by Cysts?
4.3. Reactivation/De-Encystment
4.4. Reinfection
4.5. Natural Antibodies, “Innate” B Cells, Microbiota and IgM Autoantibodies
4.6. Class-Switch Problems
5. Conclusions and Authors’ Viewpoints
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. History of the Discovery of the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.M.; Surveillance, D. Congenital toxoplasmosis. BMJ 1992, 305, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, D.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F.; Petersen, E.; Peckham, C.; Gilbert, R. Mother-to-child transmission of toxoplasmosis: Risk estimates for clinical counselling. Lancet 1999, 353, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sa, Q.; Ochiai, E.; Mullins, J.; Yolken, R.; Halonen, S.K. Toxoplasma gondii. In Toxoplasma gondii Model Apicomplexan Perspectives and Methods, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 755–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, A.; Tosh, K.; Jankovic, D. Innate recognition of Toxoplasma gondii in humans involves a mechanism distinct from that utilized by rodents. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Liesenfeld, O.; Heimesaat, M.M. Immunology of Toxoplasma gondii. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 240, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.D.; Christian, D.A.; Hunter, C.A. Immune response and immunopathology during toxoplasmosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkers, E.Y.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Regulation and function of T-cell-mediated immunity during Toxoplasma gondii infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Caballero-Ortega, H.; Rico-Torres, C.P. Congenital and acquired toxoplasmosis: Diversity and role of antibodies in different compartments of the host. Parasite Immunol. 2007, 29, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.B.; Denkers, E.Y. Border maneuvers: Deployment of mucosal immune defenses against Toxoplasma gondii. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Caballero-Ortega, H.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Rico-Torres, C.P.; Sahagún-Ruiz, A.; Medina-Escutia, M.E.; Correa, D. Congenital toxoplasmosis: Candidate host immune genes relevant for vertical transmission and pathogenesis. Genes Immun. 2010, 11, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyron, F.; Lobry, J.R.; Musset, K.; Ferrandiz, J.; Gomez-Marin, J.E.; Petersen, E.; Meroni, V.; Rausher, B.; Mercier, C.; Picot, S.; et al. Serotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in chronically infected pregnant women: Predominance of type II in europe and types I and III in Colombia (South America). Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaudaux, J.D.; Muccioli, C.; James, E.R.; Silveira, C.; Magargal, S.L.; Jung, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Jones, J.L.; Doymaz, M.Z.; Bruckner, D.A.; et al. Identification of an atypical strain of Toxoplasma gondii as the cause of a waterborne outbreak of toxoplasmosis in Santa Isabel do Ivai, Brazil. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobab, L.; Pleyer, U.; Johnsen, J.; Metzner, S.; James, E.R.; Torun, N.; Fay, M.P.; Liesenfeld, O.; Grigg, M.E. Toxoplasma serotype is associated with development of ocular toxoplasmosis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, A.W.; de-la-Torre, A.; Rochet, E.; Brunet, J.; Sabou, M.; Sauer, A.; Bourcier, T.; Gomez-Marin, J.E.; Candolfi, E. New clinical and experimental insights into old world and neotropical ocular toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Morales, E.; Taborda, L.; Cardona, N.; De-la-Torre, A.; Sepulveda-Arias, J.C.; Patarroyo, M.A.; Gomez-Marin, J.E. Th1 and Th2 immune response to P30 and ROP18 peptides in human toxoplasmosis. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 203, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, W.-W.; Elsheikha, H.M.; He, J.-J.; Li, F.-C.; Yang, W.-B.; Zhu, X.-Q. Transcriptomic analysis reveals Toxoplasma gondii strain-specific differences in host cell response to dense granule protein GRA15. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2785–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, R.; Boyer, K.M.; Lee, D.; Mui, E.; Wroblewski, K.; Karrison, T.; Noble, A.G.; Withers, S.; Swisher, C.N.; Heydemann, P.T.; et al. Prematurity and severity are associated with Toxoplasma gondii alleles (NCCCTS, 1981-2009). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicoténcatl-García, L.; Enriquez-Flores, S.; Correa, D. Testing new peptides from Toxoplasma gondii SAG1, GRA6, and GRA7 for serotyping: Better definition using GRA6 in mother/newborns pairs with risk of congenital transmission in Mexico. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chávez, F.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Flores-García, Y.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Gómez-Toscano, V.; López-Candiani, C.; Arce-Estrada, G.E.; Bonilla-Ríos, C.A.; et al. A proinflammatory immune response might determine Toxoplasma gondii vertical transmission and severity of clinical features in congenitally infected newborns. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chávez, F.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Flores-García, Y.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Mora-González, J.C.; Correa, D. Maternal immune response during pregnancy and vertical transmission in human toxoplasmosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico-Torres, C.P.; Vargas-Villavicencio, J.A.; Correa, D. Is Toxoplasma gondii type related to clinical outcome in human congenital infection? systematic and critical review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gras, L.; Gilbert, R.E.; Ades, A.E.; Dunn, D.T. Effect of prenatal treatment on the risk of intracranial and ocular lesions in children with congenital toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 30, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, N.J.; Furtado, J.M.; Winthrop, K.L.; Smith, J.R. Ocular toxoplasmosis II: Clinical features, pathology and management. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 41, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmonts, G.; Naot, Y.; Remington, J.S. Immunoglobulin M-immunosorbent agglutination assay for diagnosis of infectious diseases: Diagnosis of acute congenital and acquired Toxoplasma infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1981, 14, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertozzi, L.C.; Suzuki, L.A.; Rossi, C.L. Serological diagnosis of toxoplasmosis: Usefulness of IgA detection and IgG avidity determination in a patient with a persistent IgM antibody response to Toxoplasma gondii. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1999, 41, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobic, B.; Sibalic, D.; Djurkovix-Djakovic, O. High levels of IgM antibodies specific for Toxoplasma gondii in pregnancy 12 years after primary Toxoplasma infection. Gynecol. Obs. Investig. 1991, 31, 182–184. [Google Scholar]
- Raus, P.; Stalmans, P.; Demeuter, E.; Spileers, W.; Dralands, L. Unusual retinal vasculitis in a patient with protein S deficiency and systemic toxoplasmosis: A case report. Bull. Soc. Belge. Ophtalmol. 2001, 279, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lago, E.G.; Oliveira, A.P.; Bender, A.L. Presence and duration of anti-Toxoplasma gondii immunoglobulin M in infants with congenital toxoplasmosis. J. Pediatr. 2014, 90, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, S.S.; Silva, D.A.O.; Vaz, L.D.; Pirovani, C.P.; Barros, G.B.; Lemos, E.M.; Dietze, R.; Mineo, J.R.; Cunha-Junior, J.P. Analysis of IgG subclasses (IgG1 and IgG3) to recombinant SAG2A protein from Toxoplasma gondii in sequential serum samples from patients with toxoplasmosis. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 143, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensini, A. Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnancy: Opportunities and pitfalls of serological diagnosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensini, A.; Pascoli, S.; Marchetti, D.; Castronari, R.; Marangi, M.; Sbaraglia, G.; Cimmino, C.; Favero, A.; Castelletto, M.; Mottola, A. IgG avidity in the serodiagnosis of acute Toxoplasma gondii infection: A multicenter study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1996, 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulzer, A.J.; Franco, E.L.; Takafuji, E.; Benenson, M.; Walls, K.W.; Greenup, R.L. An oocyst-transmitted outbreak of toxoplasmosis: Patterns of immunoglobulin G and M over one year. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 35, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, E.E.; Rossi, C.L. IgM and IgA antibody responses in 12 cases of human acquired toxoplasmosis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1997, 39, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielaard, F.; van Gruijthuijsen, H.; Duermeyer, W.; Joss, A.W.; Skinner, L.; Williams, H.; van Elven, E.H. Diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis by an enzyme immunoassay for specific immunoglobulin M antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1983, 17, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bono, V.; Canessa, A.; Bruzzi, P.; Fiorelli, M.A.; Terragna, A. Significance of specific immunoglobulin M in the chronological diagnosis of 38 cases of toxoplasmic lymphadenopathy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 2133–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudrinier, F.; Villena, I.; Jaussaud, R.; Aubert, D.; Chemla, C.; Martinot, F.; Pinon, J.M. Clinical value of specific immunoglobulin E detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in cases of acquired and congenital toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgievski-Hrisoho, M.; Germann, D.; Matter, L. Diagnostic implications of kinetics of immunoglobulin M and A antibody responses to Toxoplasma gondii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, L.; Gilbert, R.E.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F.; Cortina-Borja, M. Duration of the IgM response in women acquiring Toxoplasma gondii during pregnancy: Implications for clinical practice and cross-sectional incidence studies. Epidemiol. Infect. 2004, 132, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbrink, P.; van Loon, A.M.; Rotmans, J.P.; van Knapen, F.; van Dijk, W.C. Interlaboratory evaluation of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunoblotting for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenum, P.A.; Stray-Pedersen, B. Development of specific immunoglobulins G, M, and A following primary Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, N.J.; Balfour, A.H. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting as “chronic active toxoplasmosis”. Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodym, P.; Machala, L.; Roháčová, H.; Širocká, B.; Malý, M. Evaluation of a commercial IgE ELISA in comparison with IgA and IgM ELISAs, IgG avidity assay and complement fixation for the diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, C.M.; Thulliez, P.; Remington, J.S.; Boothroyd, J.C. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasma infection by using polymerase chain reaction and amniotic fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Yen, D.O.; Joss, A.W.L.; Balfour, A.H.; Smyth, E.T.M.; Baird, D.; Chatterton, J.M.W. Use of the polymerase chain reaction to detect Toxoplasma gondii in human blood samples. J. Clin. Pathol. 1992, 45, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Bustos-Bahena, M.L.; González-Henkel, H.; Calderón-Segura, E.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Correa, D. Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy: Determination of IgM, IgG and avidity in filter paper-embedded blood. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Torres, C.P.; Valenzuela-Moreno, L.F.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Gómez-Toscano, V.; Hernández-Delgado, L.; Escobedo-Torres, M.P.; Correa, D. High heterogeneity, mixed infections and new genotypes in human congenital toxoplasmosis cases in the mega-metropolis of central Mexico. Acta Trop. 2018, 178, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Ortega, H.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Castañeda-Huitrón, A.L.; Murata, C.; Figueroa-Damián, R.; Correa Beltrán, M.D. Frequency of risk infections for congenital infection in pregnant women. Acta Pediátrica México 2021, 42, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naot, Y.; Guptil, D.R.; Remington, J. Duration of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii after acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 145, 94301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Bailly, S.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Dard, C.; Jean, D.; Coston, A.L.; Garnaud, C.; Pelloux, H. How to estimate time of infection with Toxoplasma gondii in pregnant women. Use of specific IgG and IgM kinetics by 7 techniques on 691 sera. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, M.; Koskela, P.; Koskiniemi, M.; Ämmälä, P.; Hiilesmaa, V.; Teramo, K.; Raivio, K.O.; Remington, J.S.; Hedman, K. Toxoplasmosis acquired during pregnancy: Improved serodiagnosis based on avidity of IgG. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naot, Y.; Barnett, E.V.; Remington, J.S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1981, 14, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondriska, F.; Catar, G.; Vozarova, G. The significance of complement fixation test in clinical diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2003, 104, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Oya, Y.; Futami, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Ishijima, K.; Umemiya, K.; Takizawa, F.; Imai, N.; Kitamura, H.; Matsumura, R. Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome following meningitis and systemic lymphadenopathy with persistent Toxoplasma immunoglobulin M: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, L.A.; Rocha, R.J.; Rossi, C.L. Evaluation of serological markers for the immunodiagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinni, M.P.; Scaletti, C.; Maggi, E.; Romagnani, S. Role of Hormone-controlled Th1-and Th2-type cytokines in successful pregnancy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 109, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyński, J.R. Th1/Th2 cytokines balance-yin and yang of reproductive immunology. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2005, 122, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chávez, F.; Correa, D.; Navarrete-Meneses, P.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S. NF-ΚB and its regulators during pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.W.; Cruickshank, S.M.; Alexander, J. Sex-determined resistance to Toxoplasma gondii is associated with temporal differences in cytokine production. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 2549–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Rafael, N.J. Desarrollo de un modelo de toxoplasmosis congénita en ratón que simule los cambios en la transmisión y daño fetal en humanos. Bachelor Thesis, Facultad de Estudios Superiores Zaragoza, UNAM, Ciudad de México, México, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Effects of Estradiol and progesterone-induced intracellular calcium fluxes on Toxoplasma gondii gliding, microneme secretion, and egress. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findal, G.; Stray-Pedersen, B.; Holter, E.K.; Berge, T.; Jenum, P.A. Persistent low toxoplasma IgG avidity is common in pregnancy: Experience from antenatal testing in Norway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.; Borobio, M.V.; Guy, E.; Liesenfeld, O.; Meroni, V.; Naessens, A.; Spranzi, E.; Thulliez, P. European multicenter study of the LIAISON automated diagnostic system for determination of Toxoplasma gondii-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM and the IgG avidity index. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flori, P.; Tardy, L.; Patural, H.; Bellete, B.; Varlet, M.N.; Hafid, J.; Raberin, H.; Sung, R.T.M. Reliability of immunoglobulin G antitoxoplasma avidity test and effects of treatment on avidity indexes of infants and pregnant women. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenum, P.A.; Stray-Pedersen, B.; Gundersen, A.G. Improved diagnosis of primary Toxoplasma gondii infection in early pregnancy by determination of antitoxoplasma immunoglobulin G avidity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.J.; Chan, J.A.; Handayuni, I.; Reiling, L.; Feng, G.; Hilton, A.; Kurtovic, L.; Oyong, D.; Piera, K.A.; Barber, B.E.; et al. IgM in human immunity to Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florini, F.; Visone, J.E.; Deitsch, K.W. Shared mechanisms for mutually exclusive expression and antigenic variation by protozoan parasites. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 852239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Pereira, S.; Jackson, A.P.; Figueiredo, L.M. Evolution of the variant surface glycoprotein family in African Trypanosomes. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, R.E.; McLeod, R.; Roberts, C.W. Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite interconversion. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, T.D.; Bathgate, T.; Mangan, J.; Johnson, J.D.; Holliman, R.E.; Butcher, P.D. Recognition of tissue cyst-specific antigens in reactivating toxoplasmosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 1997, 46, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadono, V.; Saccone, G.; Sarno, L.; Esposito, G.; Mazzarelli, L.L.; Sirico, A.; Guida, M.; Martinelli, P.; Zullo, F.; Maruotti, G.M. Association between lymphadenopathy after toxoplasmosis seroconversion in pregnancy and risk of congenital infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 41, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.; Siciliano, S.; Rocha, L.S.A.; Justa, M.T.R.; César, K.R.; Granato, C.F.H. Correlation between specific IgM levels and percentage IgG-class antibody avidity to Toxoplasma gondii. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2008, 50, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. B Cells in immunity and tolerance. In B Cells in Immunity and Tolerance; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1254, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Niewiadomski, A.; Schweickert, B.; Liesenfeld, O. Antiparasitic treatment suppresses production and avidity of Toxoplasma gondii -specific antibodies in a murine model of Acute infection. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 1, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.B.S.; Meurer, Y.S.R.; Andrade, J.M.A.; Costa, M.E.S.M.; Andrade, M.M.C.; Silva, L.A.; Lanza, D.C.F.; Vítor, R.W.A.; Andrade-Neto, V.F. Pathogenicity and phenotypic sulfadiazine resistance of Toxoplasma gondii isolates obtained from livestock in northeastern Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo. Cruz. 2016, 111, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Ramirez, M.L.; Madriz Elisondo, A.L.; Torres, C.P.R.; Luna-Pastén, H.; Pérez, L.R.R.; Rincón-Sánchez, A.R.; Franco, R.; Salazar-Montes, A.; Correa, D. Frequency of Toxoplasma gondii in pork meat in Ocotlan, Jalisco, Mexico. J. Food. Prot. 2010, 73, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.A.O.; Silva, N.M.; Mineo, T.W.P.; Pajuaba Neto, A.A.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Mineo, J.R. Heterologous antibodies to evaluate the kinetics of the humoral immune response in dogs experimentally infected with Toxoplasma gondii RH strain. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 107, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.N.; Choi, I.U.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, Y.H. Cytokine and antibody responses of reactivated murine toxoplasmosis upon administration of dexamathasone. Korean J. Parasitol. 2006, 44, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, B.J.; Remington, J.S. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Sterkers, Y.; Yera, H.; Accoceberry, I.; Menotti, J.; Cassaing, S.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Hennequin, C.; Delhaes, L.; Bonhomme, J.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients: A 3-year multicenter retrospective study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouin, F.; Pelloux, H. Prevention of toxoplasmosis in transplant patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Ramírez, M.L.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V.; Gutiérrez-Maldonado, A.F.; Pérez, L.R.R. Does Toxoplasma gondii infection impact liver transplantation outcomes? A systematic review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šibalić, D.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Bobić, B. Onset of ocular complications in congenital toxoplasmosis associated with immunoglobulin M Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1990, 9, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.D.C.; Camejo, A.; Melo, M.B.; Cordeiro, C.; Julien, L.; Grotenbreg, G.M.; Frickel, E.M.; Ploegh, H.L.; Young, L.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma gondii superinfection and virulence during secondary infection correlate with the exact ROP5/ROP18 allelic combination. MBio 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, G.L.; Costa, J.G.L.; Rêgo, W.M.F.; Baraviera, R.C.A.; Pinto, L.V.; Lopes, R.E.N.; Vitor, R.W.A. Tissue dissemination and humoral response after experimental reinfection with atypical Toxoplasma gondii strains obtained from congenital human toxoplasmosis in Brazil. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 207, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-L.; Zhang, N.-Z.; Li, T.-T.; He, J.-J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.-Q. Advances in the development of anti-Toxoplasma gondii vaccines: Challenges, opportunities, and perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.W.; McLeod, R.; Henriquez, F.L.; Alexander, J. Vaccination against toxoplasmosis: Current Status and Future Prospects. In Toxoplasma gondii; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmonts, G.; Couvreur, J. Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy and its transmission to the fetus. Bull. N. Y. Acad. Med. J. Urban Health 1974, 50, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavinet, M.F.; Robert, F.; Firtion, G.; Delouvrier, E.; Hennequin, C.; Maurin, J.R.; Tourte-Schaefer, C.; Dupouy-Camet, J. Congenital toxoplasmosis due to maternal reinfection during pregnancy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1276–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Moreno, L.F.; Méndez-Cruz, S.T.; Rico-Torres, C.P.; Cedillo-Peláez, C.; Correa, D.; Caballero-Ortega, H. SAG3 Toxoplasma gondii cloning reveals unexpected fivefold infection in the blood of feral cats in the Mexican Caribbean. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.; Winslow, G.M. IgM in microbial infections: Taken for granted? Immunol. Lett. 2009, 125, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.; Tokarz-Deptuła, B.; Deptuła, J.; Deptuła, W. Natural antibodies–facts known and unknown. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyneveld, G.I.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Parmentier, H.K. Current understanding of natural antibodies and exploring the possibilities of modulation using veterinary models. A review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzenberg, L.A. B-1 cells: The lineage question revisited. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 175, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgarth, N.; Waffarn, E.E.; Nguyen, T.T.T. Natural and induced B-1 cell immunity to infections raises questions of nature versus nurture. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1362, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, J.M.B.; Felippe, M.J.B. Development, phenotype, and function of non-conventional B cells. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 54, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, S.M.; Perry, H.M.; Gonen, A.; Prohaska, T.A.; Srikakulapu, P.; Grewal, S.; Das, D.; McSkimming, C.; Taylor, A.M.; Tsimikas, S.; et al. B-1b cells secrete Atheroprotective IgM and attenuate atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, e28–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, E. Naturally occurring antibodies that react with protozoan parasites. Parasitol. Today 1993, 9, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potasman, I.; Araujo, F.G.; Remington, J.S. Toxoplasma antigens recognized by naturally occurring human antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 24, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Takashima, Y.; Xuaun, X.; Igarashi, I.; Nagasawa, H.; Mikami, T.; Otsuka, H. Natural IgM antibodies in sera from various animals but not the cat kill Toxoplasma gondii by activating the classical complement pathway. Parasitology 2004, 128, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, C.B.; Black, C.M.; Phillips, D.J.; Logan, L.C.; Hunter, E.F.; Pender, B.J.; McGrew, B.E. The specificity of fetal IgM: Antibody or anti-antibody? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1975, 254, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, M.; Portela, R.W.D.; Snege, M.; Leser, P.G.; Camargo, M.E.; Mineo, J.R.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Immunoglobulin M (IgM)-glycoinositolphospholipid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: An immunoenzymatic assay for discrimination between patients with acute toxoplasmosis and those with persistent parasite-specific IgM antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesenfeld, O.; Press, C.; Montoya, J.G.; Gill, R.; Isaac-Renton, J.L.; Hedman, K.; Remington, J.S. False-positive results in immunoglobulin M (IgM) Toxoplasma antibody tests and importance of confirmatory testing: The Platelia Toxo IgM test. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuk, L.S.M.; Koch, M.A.; Slayden, L.C.; Lind, N.A.; Chu, S.; Savage, H.P.; Kantor, A.B.; Baumgarth, N.; Barton, G.M.B. Cell receptor and toll-like receptor signaling coordinate to control distinct B-1 responses to both self and the microbiota. Elife 2019, 8, e47015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, D.; Meissner, M. Toxoplasma as a novel system for motility. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2004, 16, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarovinsky, F.; Zhang, D.; Andersen, J.F.; Bannenberg, G.L.; Serhan, C.N.; Hayden, M.S.; Hieny, S.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Flavell, R.A.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Immunology: TLR11 activation of dendritic cells by a protozoan profilin-like protein. Science 2005, 308, 1626–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aosai, F.; Chen, M.; Kang, H.K.; Mun, H.S.; Norose, K.; Xun Piao, L.; Kobayashi, M.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Yano, A. Toxoplasma gondii-derived heat shock protein HSP70 functions as a B cell mitogen. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002, 7, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Aosai, F.; Norose, K.; Mun, H.; Yano, A. The role of anti-HSP70 autoantibody-forming VH1±JH1 B-1 cells in Toxoplasma gondii- infected mice. Japanese. Soc. Immunol. 2003, 15, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mun, H.S.; Piao, L.X.; Aosai, F.; Norose, K.; Mohamed, R.M.; Belal, U.S.; Fang, H.; Ahmed, A.K.; Kang, H.K.; et al. Induction of protective immunity by primed B-1 cells in Toxoplasma gondii-infected B cell-deficient mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 47, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Aosai, F.; Mun, H.S.; Norose, K.; Hata, H.; Yano, A. Anti-HSP70 autoantibody formation by B-1 cells in Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4893–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frickel, E.M.; Hunter, C.A. Lessons from Toxoplasma: Host responses that mediate parasite control and the microbial effectors that subvert them. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Gil, D.; Audebert, C.; Olivera-Ardid, S.; Pérez-Cruz, M.; Even, G.; Khasbiullina, N.; Gantois, N.; Shilova, N.; Merlin, S.; Costa, C.; et al. The formation of glycan-specific natural antibodies repertoire in galt-KO mice is determined by gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S.P.; Splitt, S.D.; Sanchez-Arcila, J.C.; Alvarez, J.A.; Wilson, J.N.; Wizzard, S.; Luo, Z.; Baumgarth, N.; Jensen, K.D.C. Genetic mapping reveals Nfkbid as a central regulator of humoral immunity to Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.; Caballero-Ortega, H.; Rico-Torres, C.P.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Ortiz-Alegría, L.B.; Becerra-Torres, E.; Olmedo-Hernández, M.; Medina-Escutia, M.E.; Murrieta, S. Immunobiology of congenital toxoplasmosis. In Advances in the Immunobiology of Parasitic Diseases; Terrazas, L., Ed.; Research Signpost: Thiruvananthapuram, India, 2007; pp. 199–224. [Google Scholar]
- Petakov, M.; Stojanović, N.; Jovčić, G.; Bugarski, D.; Todorović, V.; Djurcović-Djaković, O. Hematopoiesis during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Haematologia 2002, 32, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kugler, D.G.; Flomerfelt, F.A.; Costa, D.L.; Laky, K.; Kamenyeva, O.; Mittelstadt, P.R.; Gress, R.E.; Rosshart, S.P.; Rehermann, B.; Ashwell, J.D.; et al. Systemic Toxoplasma infection triggers a long-term defect in the generation and function of naive T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 3041–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavnezer, J.; Guikema, J.E.J.; Schrader, C.E. Mechanism and regulation of class switch recombination. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 261–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhamnani, R.D.; Nunes-Santos, C.J.; Bergerson, J.; Rosenzweig, S.D. Class-switch recombination (CSR)/hyper-IgM (HIGM) syndromes and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) defects. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.H. Signaling control of antibody isotype switching. Elsevier. Inc. 2019, 141, 105–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Jina, K.; Guk, S.-M.; Chang, Y.-P.; Yun, C.K. Experimental infection of murine splenic lymphocytes and granulocytes with Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. Korean J. Parasitol. 1997, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosowski, E.E.; Nguyen, Q.P.; Camejo, A.; Spooner, E.; Saeija, J.P.J. Toxoplasma gondii inhibits gamma interferon (IFN-γ)-and IFN-β-induced host cell STAT1 transcriptional activity by increasing the association of STAT1 with DNA. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chen, L.; Duan, Y. Toxoplasma gondii excreted-secreted antigens suppress Foxp3 via PI3K-AKT-MTOR signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 16044–16051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, P.; Sudarshana, D.M.; Gov, L.; Harker, K.S.; Lam, T.; Casali, P.; Boyle, J.P.; Lodoen, M.B. Type II Toxoplasma gondii induction of CD40 on infected macrophages enhances interleukin-12 responses. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4047–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgueta, R.; Benson, M.J.; De Vries, V.C.; Wasiuk, A.; Guo, Y.; Noelle, R.J. Molecular mechanism and function of CD40/CD40L engagement in the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vargas-Villavicencio, J.A.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Correa, D. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081659
Vargas-Villavicencio JA, Cañedo-Solares I, Correa D. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms? Microorganisms. 2022; 10(8):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081659
Chicago/Turabian StyleVargas-Villavicencio, José Antonio, Irma Cañedo-Solares, and Dolores Correa. 2022. "Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms?" Microorganisms 10, no. 8: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081659
APA StyleVargas-Villavicencio, J. A., Cañedo-Solares, I., & Correa, D. (2022). Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgM Long Persistence: What Are the Underlying Mechanisms? Microorganisms, 10(8), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081659