A Method for Isolation Bacteriophage Particles-Free Genomic DNA, Exemplified by TP-84, Infecting Thermophilic Geobacillus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Media and Reagent
2.2. Bacteriophage Propagation and Purification
2.2.1. TP-84 Cultivation
2.2.2. TP-84 Particles Purification
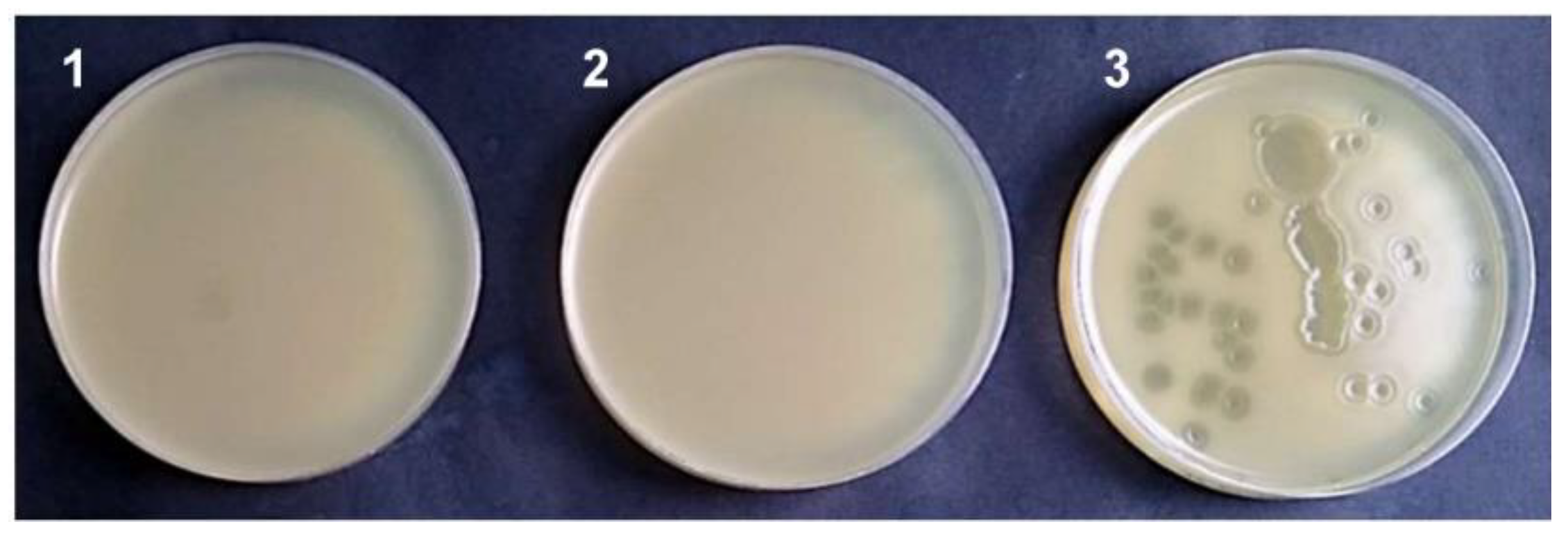
2.2.3. G. stearothermophilus Selection
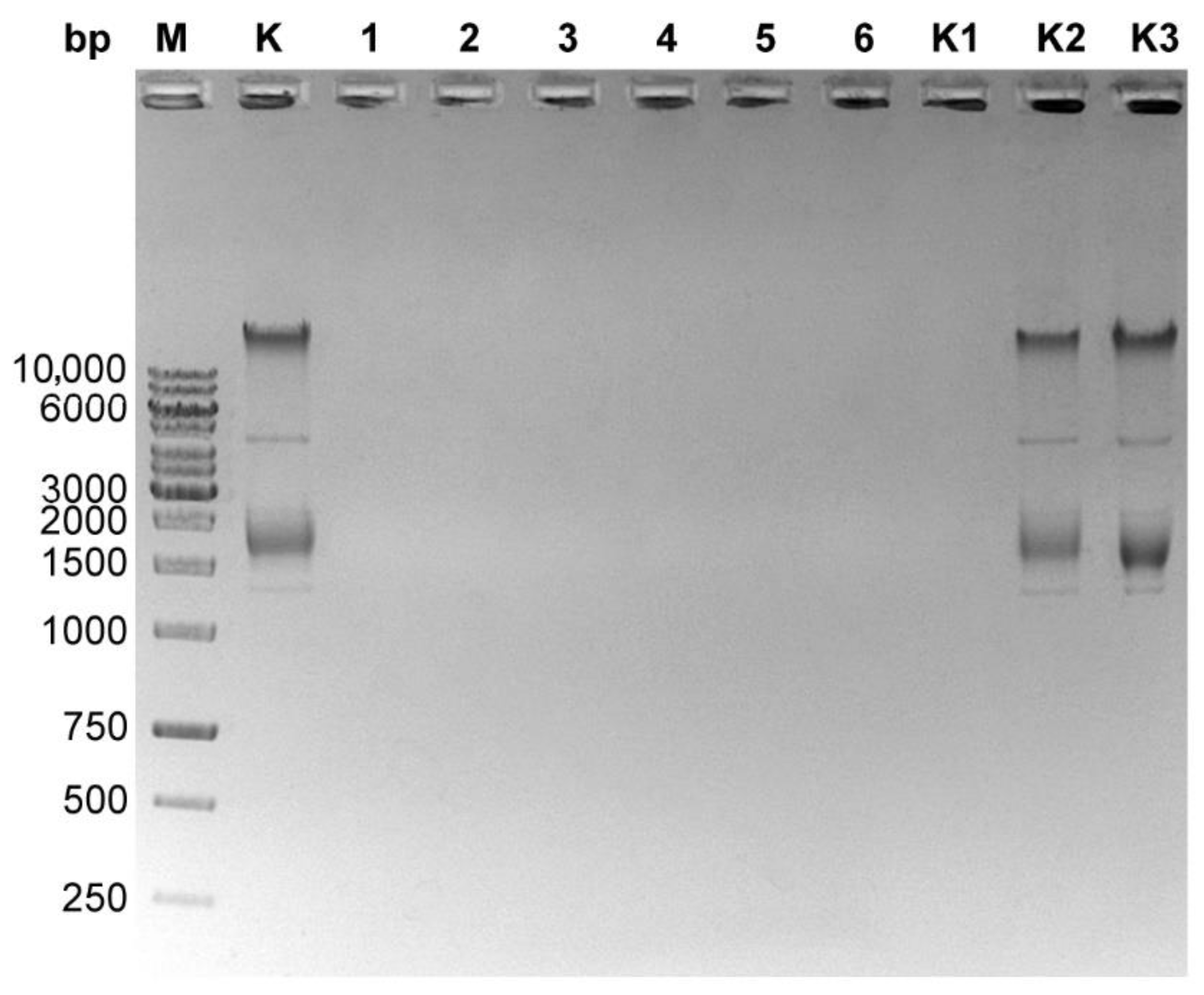
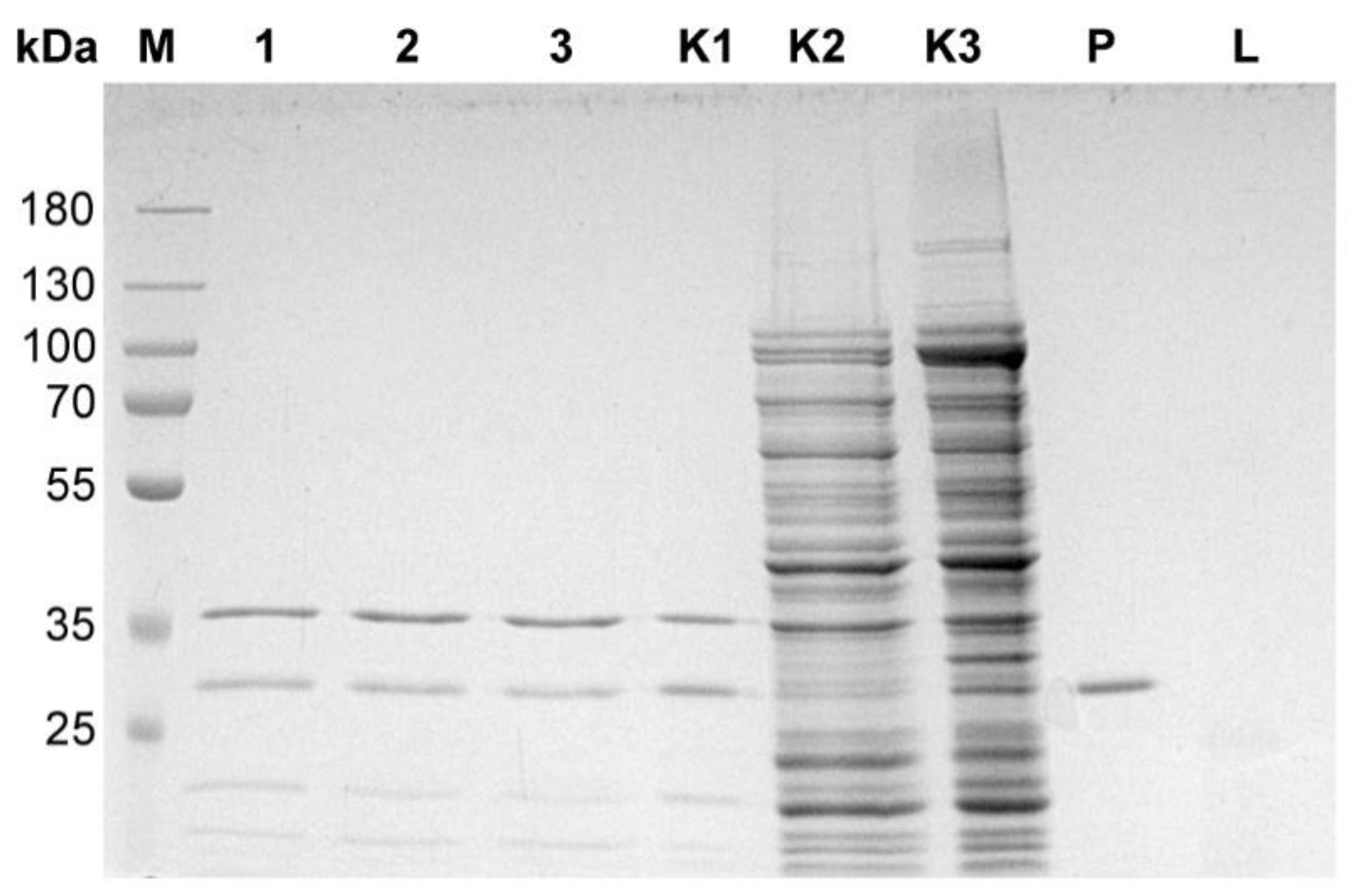
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development and Validation
3.2. Genomic DNA Contamination with Bacteriophage Particles Problem
3.3. Isolation of a Bacteriophage Particles-Free Bacteriophage Genomic DNA. Final Protocol
4. Conclusions
- A novel method for high purity genomic DNA isolation in a mini spin-format was developed and dedicated to concentrated CsCl preparations, as opposed to isolations performed directly for bacteriophage culture lysates used thus far.
- The method enables the fast and efficient purification of bacteriophage genomic DNA from concentrated bacteriophage preparations without removing concentrated CsCl solutions.
- The purified DNA is ready for further applications and analyzes without the need for precipitation or extraction with phenol.
- The protocol eliminates false ‘positives’ background during recombinant bacteriophages construction, such as when conducting phage display experiments.
- The preparations are free from alive bacteriophage particles, which is especially important in the case of highly resistant thermophilic bacteriophages that can survive the isolation procedures and contaminate the final DNA, ultimately leading to a contamination of laboratory surfaces and future host cultures.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harada, K.; Silva, E.C.; Campos, W.F.; del Fiol, F.S.; Vila, M.; Dąbrowska, K.; Krylov, V.N.; Balcão, V.M. Biotechnological applications of bacteriophages: State of the art. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 212–213, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łubkowska, B.; Jeżewska-Frąckowiak, J.; Sobolewski, I.; Skowron, P.M. Bacteriophages of Thermophilic ‘Bacillus Group’ Bacteria-A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, G.F.; Campbell, L.L. Characterization of a thermophilic bacteriophage for Bacillus stearothermophilus. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 91, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, G.F.; Campbell, L.L. Properties of the deoxyribonucleic acid of the thermophilic bacteriophage TP-84. Biochemistry 1965, 4, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, I.; Campbell, L.L. Production and purification of the thermophilic bacteriophage TP-84. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizer, P.E.; Saunders, G.F. Distribution of pyrimidine sequences in bacteriophage TP-84 deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowron, P.M.; Kropinski, A.M.; Zebrowska, J.; Janus, L.; Szemiako, K.; Czajkowska, E.; Maciejewska, N.; Skowron, M.; Łoś, J.; Łoś, M.; et al. Sequence, genome organization, annotation and proteomics of the thermophilic, 47.7-kb Geobacillus stearothermophilus bacteriophage TP-84 and its classification in the new Tp84virus genus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Mejía, J.L.; Muhammed, M.K.; Kot, W.; Neve, H.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Hansen, L.H.; Vogensen, F.K.; Nielsen, D.S. Optimizing protocols for extraction of bacteriophages prior to metagenomic analyses of phage communities in the human gut. Microbiome 2015, 3, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, M.; Hooper, L.V.; Duerkop, B.A. Evaluation of methods to purify virus-like particles for metagenomic sequencing of intestinal viromes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, N.; Barr, J.J. Phage on Tap: A Quick and Efficient Protocol for the Preparation of Bacteriophage Laboratory Stocks. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1838, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.R.; Alberts, B.M.; Benzinger, R.; Lawhorne, L.; Treiber, G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology 1970, 40, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasukawa, T.; Uchiyama, J.; Taharaguchi, S.; Ota, S.; Ujihara, T.; Matsuzaki, S.; Murakami, H.; Mizukami, K.; Sakaguchi, M. Virus purification by CsCl density gradient using general centrifugation. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3523–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, J.; Rashel, M.; Maeda, Y.; Takemura, I.; Sugihara, S.; Akechi, K.; Muraoka, A.; Wakiguchi, H.; Matsuzaki, S. Isolation and characterization of a novel Enterococcus faecalis bacteriophage φEF24C as a therapeutic candidate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachrach, U.; Friedmann, A. Practical procedures for the purification of bacterial viruses. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 22, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll-Portillo, A.; Coffman, C.N.; Varga, M.G.; Alcock, J.; Singh, S.B.; Lin, H.C. Standard Bacteriophage Purification Procedures Cause Loss in Numbers and Activity. Viruses 2021, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhwale, J.K.; Rohde, M.; Rohde, C.; Bunk, B.; Sproer, C.; Boga, H.I.; Klenk, H.-P.; Wittmann, J. Isolation, characterization and analysis of bacteriophages from the haloalkaline lake Elmenteita, Kenya. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beilstein, F.; Dreiseikelmann, B. Bacteriophages of freshwater Brevundimonas vesicularis isolates. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, D.J. Preparation of bacteriophage lysates and pure DNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 502, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, J.C.; Stowring, L.; Morales, M.F. Morales, The Effect of Structure-disrupting Ions on the Activity of Myosin and Other Enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Kojima, K.; Nakase, R.; Imai, S.; Yamasaki, T.; Takita, T.; Crouch, R.J.; Yasukawa, K. Effects of neutral salts and pH on the activity and stability of human RNase H2. J. Biochem. 2017, 162, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


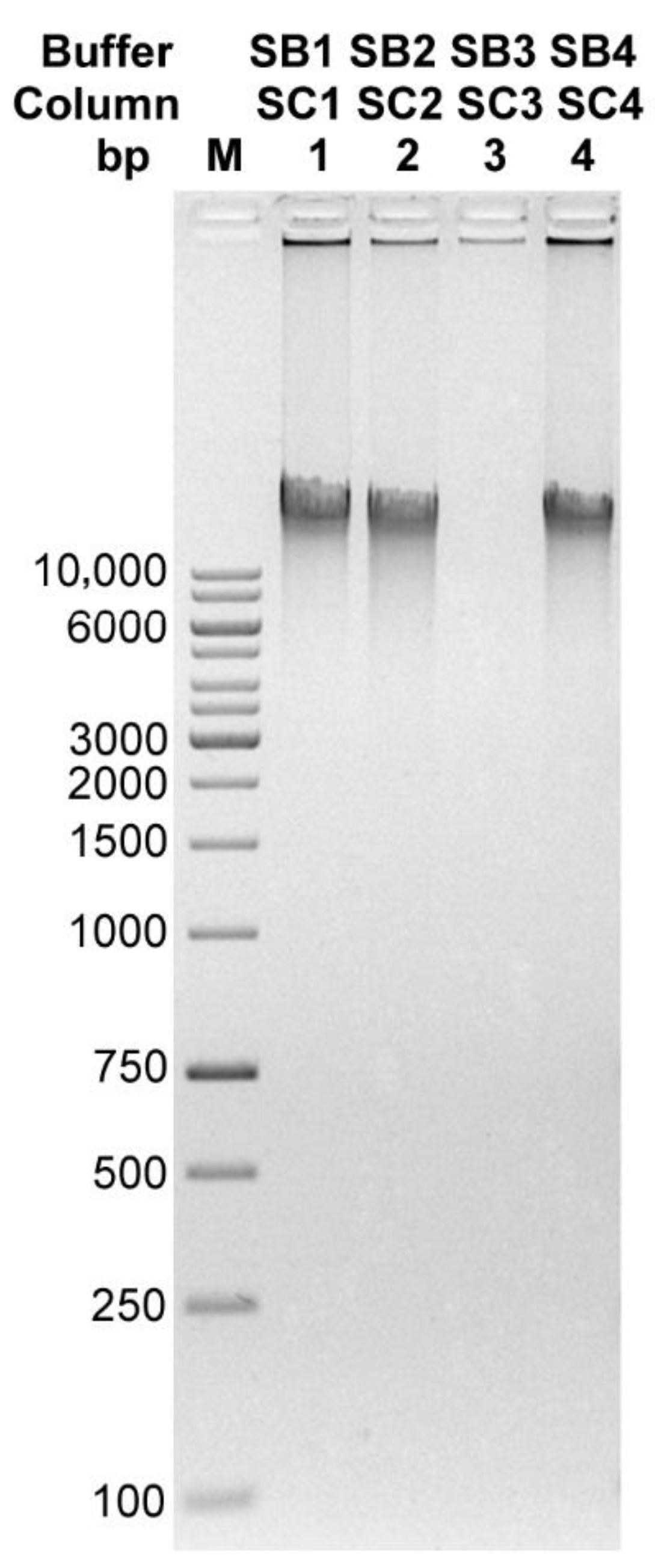
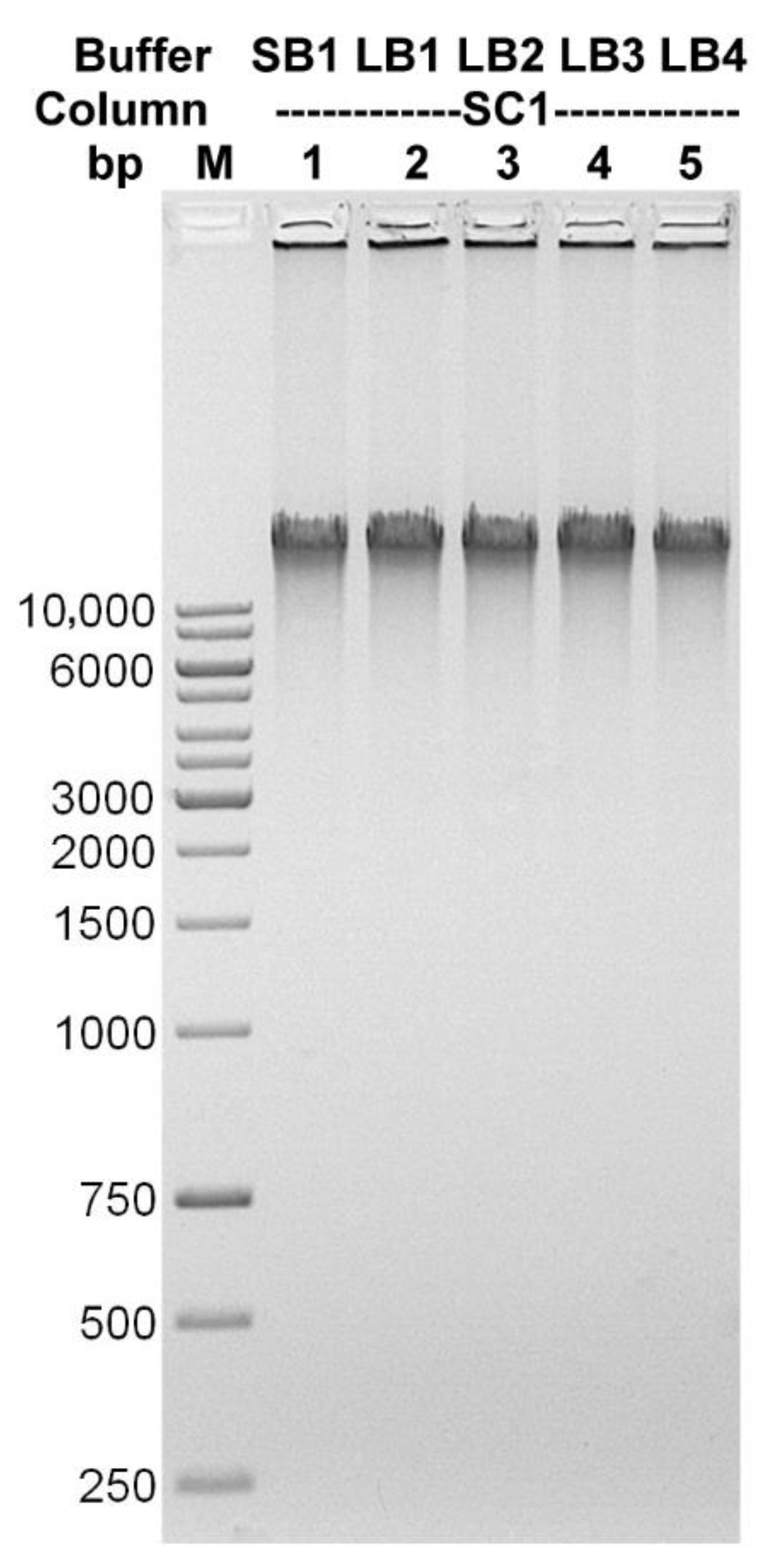
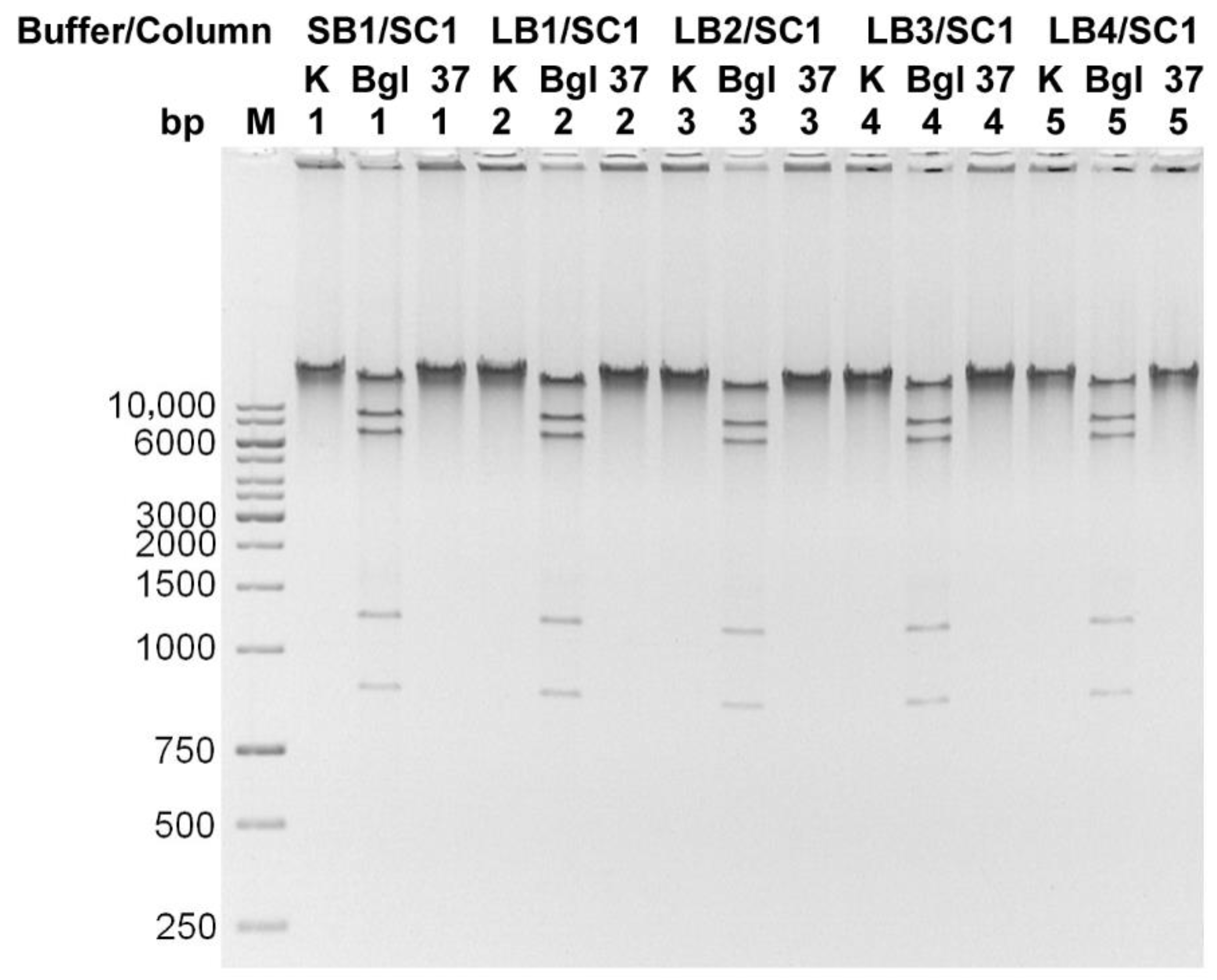

| Buffer/Column | DNA Concentration [ng/µL] | 260/280 | 260/230 | Amount of DNA Obtained [µg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB1/SC1 | 33.67 | 1.97 | 1.79 | 5.05 |
| SB2/SC2 | 26.41 | 1.77 | 2.36 | 3.96 |
| SB3/SC3 | 3.22 | 1.98 | 1.07 | 0.48 |
| SB4/SC4 | 33.3 | 1.76 | 1.99 | 4.99 |
| Lysis Buffer | DNA Concentration [ng/µL] | 260/280 | 260/230 | Amount of DNA Obtained [µg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB1 | 38.88 | 1.9 | 1.53 | 5.83 |
| LB1 | 37.85 | 1.9 | 1.75 | 5.68 |
| LB2 | 36.68 | 1.89 | 1.7 | 5.5 |
| LB3 | 35.81 | 1.89 | 1.74 | 5.37 |
| LB4 | 30.51 | 1.96 | 1.84 | 4.58 |
| Volume [µL] | |
|---|---|
| TP-84 after CsCl gradient | 50 |
| DNase I 10× buffer | 25 |
| DNase I (10 mg/mL) | 3 |
| RNase A (10 mg/mL) | 2 |
| H2O | 170 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobolewski, I.; Adamowicz, K.; Struck, A.; Zylicz-Stachula, A.; Skowron, P.M. A Method for Isolation Bacteriophage Particles-Free Genomic DNA, Exemplified by TP-84, Infecting Thermophilic Geobacillus. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091782
Sobolewski I, Adamowicz K, Struck A, Zylicz-Stachula A, Skowron PM. A Method for Isolation Bacteriophage Particles-Free Genomic DNA, Exemplified by TP-84, Infecting Thermophilic Geobacillus. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091782
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobolewski, Ireneusz, Katarzyna Adamowicz, Anna Struck, Agnieszka Zylicz-Stachula, and Piotr M. Skowron. 2022. "A Method for Isolation Bacteriophage Particles-Free Genomic DNA, Exemplified by TP-84, Infecting Thermophilic Geobacillus" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091782
APA StyleSobolewski, I., Adamowicz, K., Struck, A., Zylicz-Stachula, A., & Skowron, P. M. (2022). A Method for Isolation Bacteriophage Particles-Free Genomic DNA, Exemplified by TP-84, Infecting Thermophilic Geobacillus. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091782







