Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of an Endophytic Fungus Alternaria sp. SPS-2 and Its Biosynthetic Potential of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain, Cultivation, and Crude Extracts Preparation
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
2.4. Gene Prediction and Annotation
2.5. Prediction of CAZymes
2.6. Analysis of Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Gene Clusters
2.7. Metabolomic Profiling of Strain SPS-2 Using LC–MS/MS
3. Results and Discussion
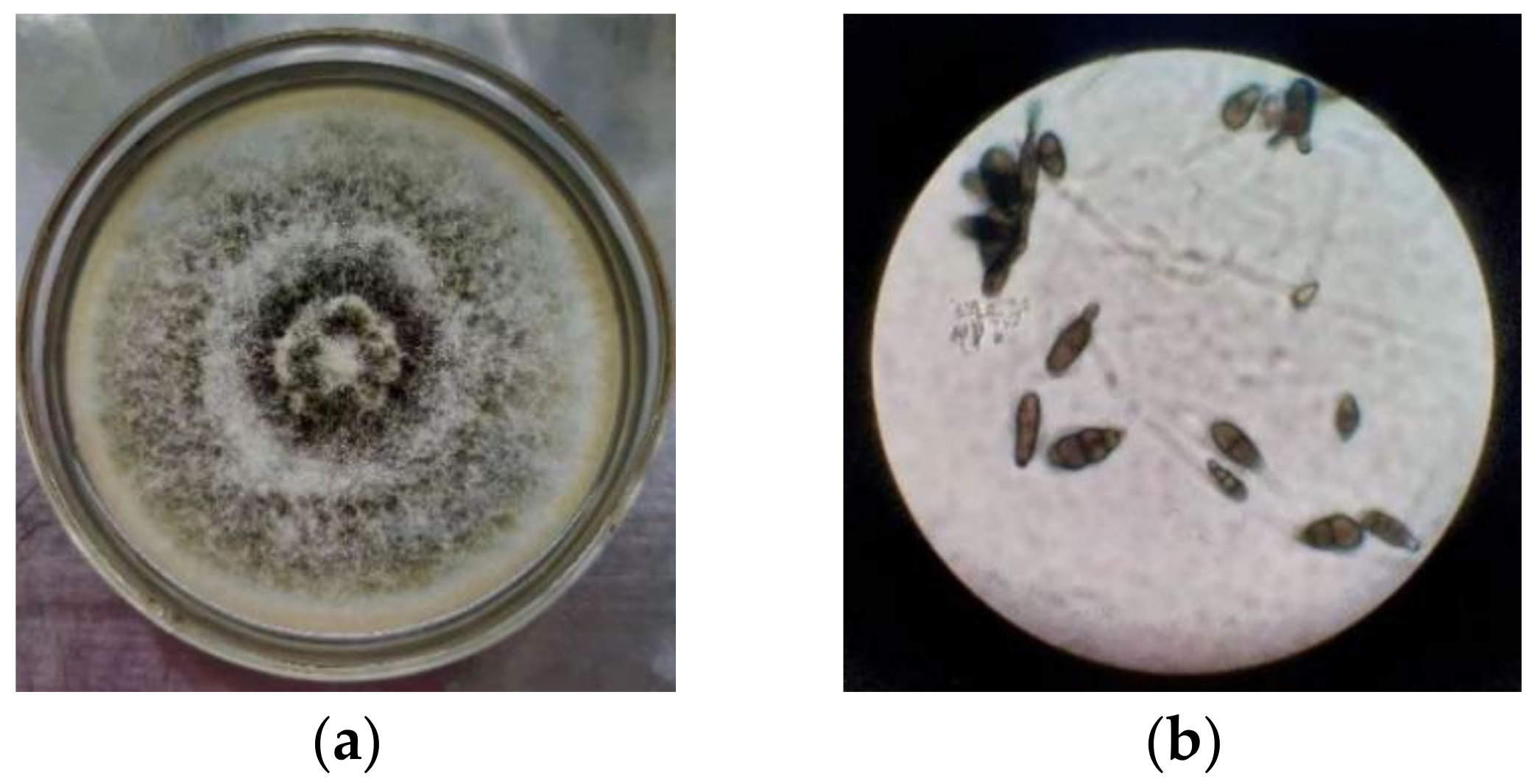
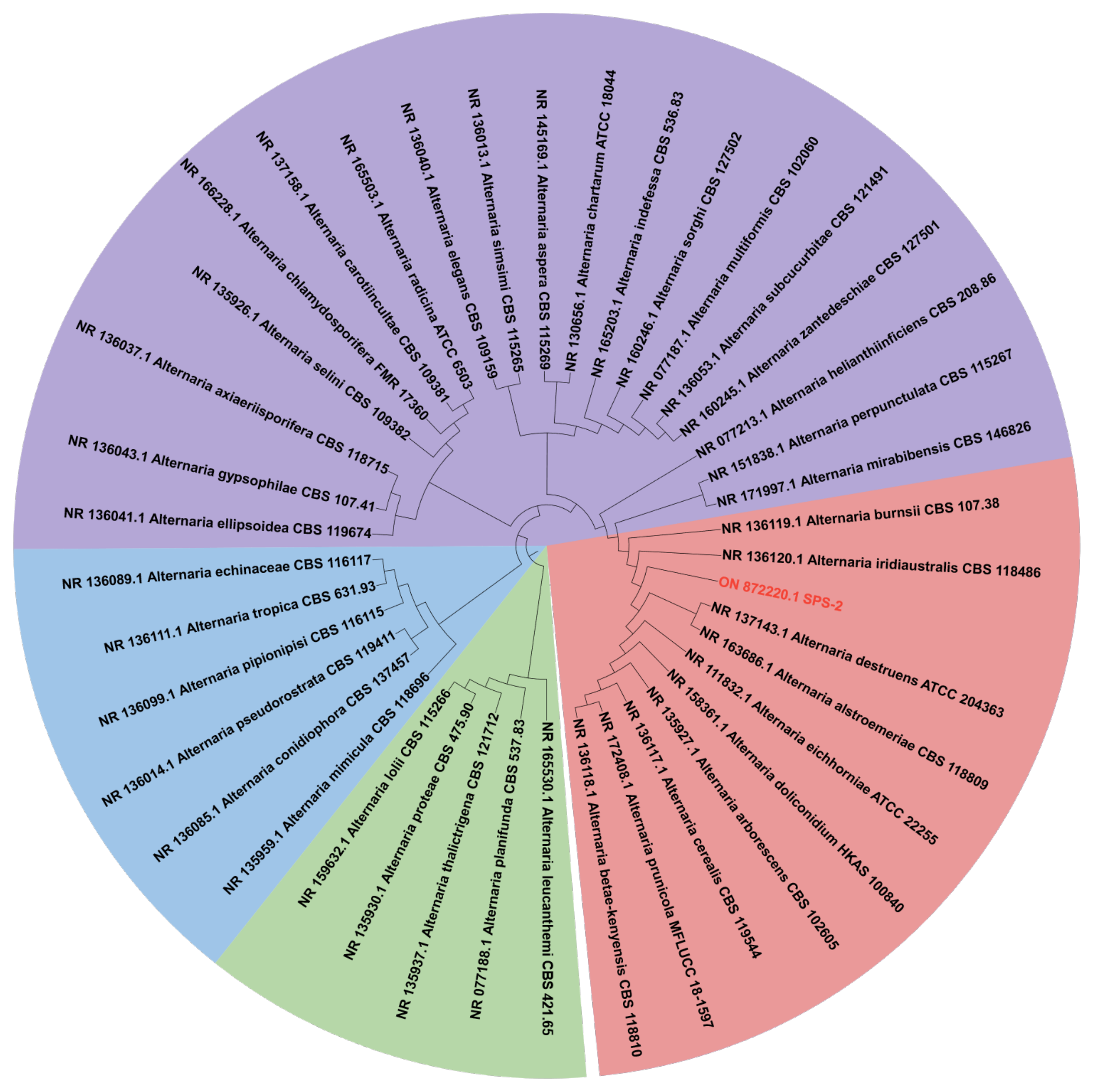
3.1. Morphology and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strain SPS-2
3.2. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
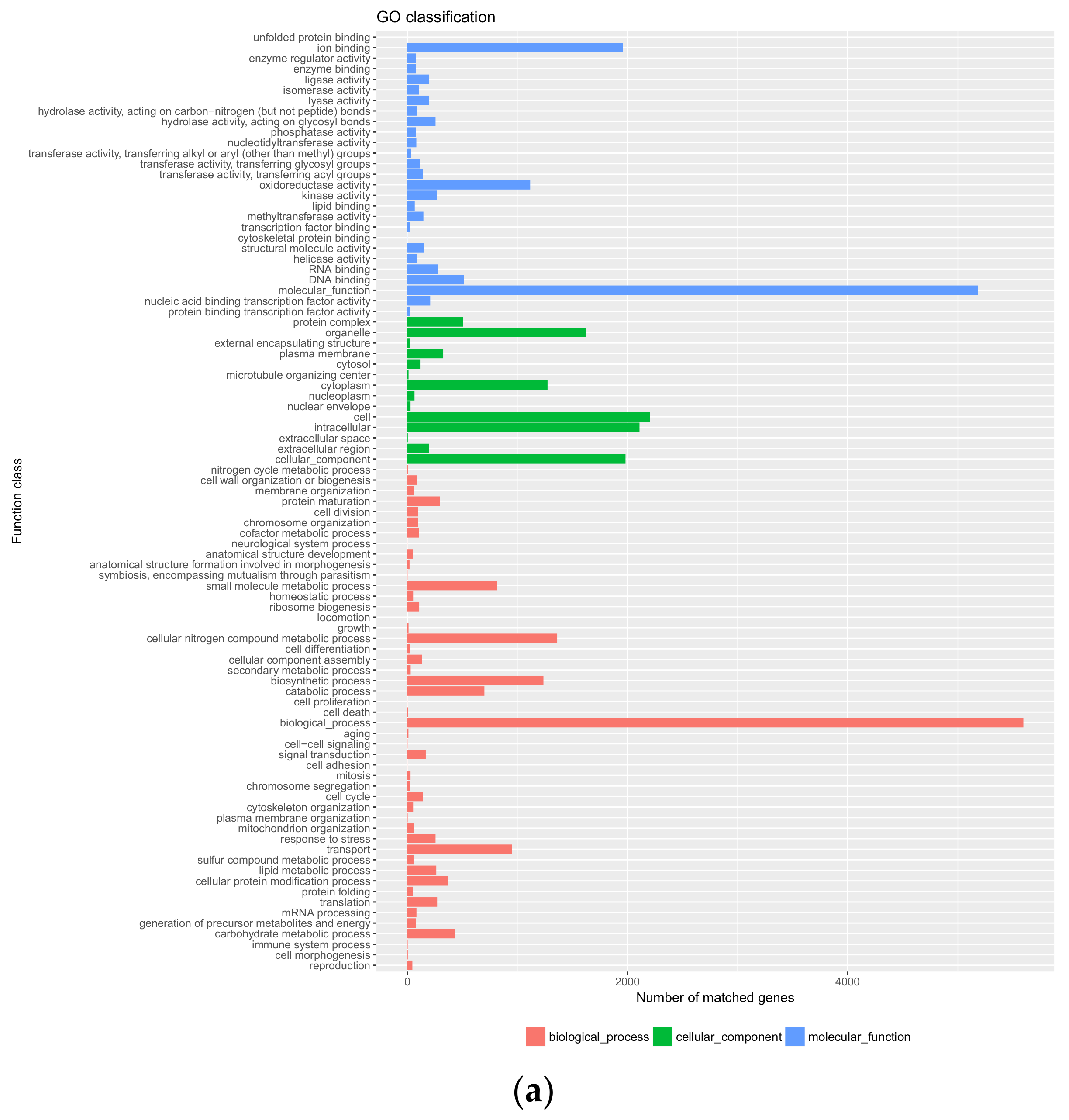
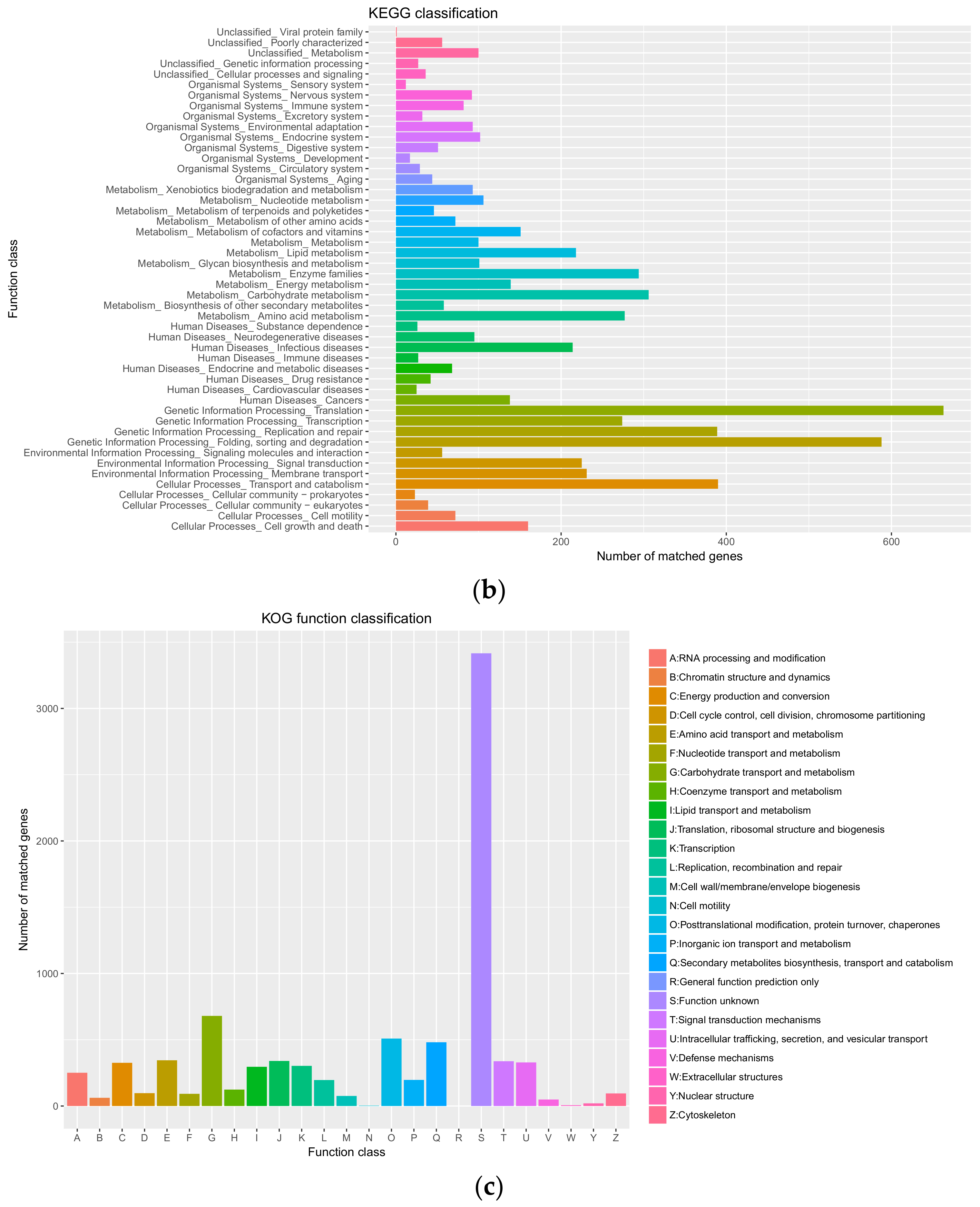
3.3. Genome Annotation
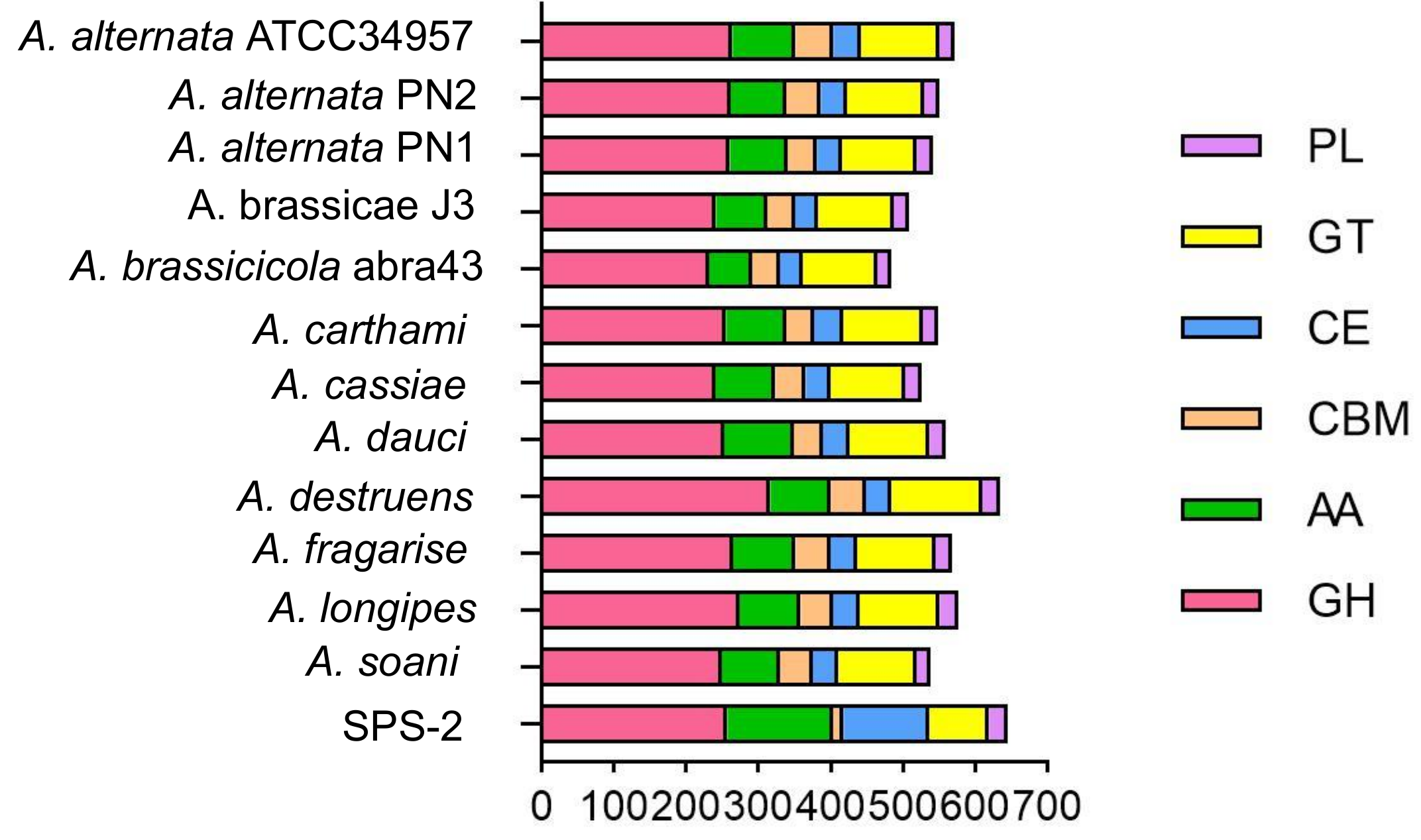
3.4. CAZyme Analysis
3.5. Analysis of Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Potential
3.6. Molecular Networking Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Natural products from plant-associated microorganisms: Distribution, structural diversity, bioactivity, and implications of their occurrence. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hridoy, M.; Gorapi, M.Z.H.; Noor, S.; Chowdhury, N.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Muscari, I.; Masia, F.; Adorisio, S.; Delfino, D.V.; Mazid, M.A. Putative anticancer compounds from plant-derived endophytic fungi: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L. Metabolites from Alternaria fungi and their bioactivities. Molecules 2013, 18, 5891–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su-shi, L.; Qian, L.; Jie-yu, Z.; Li, L.; Tao, W. Research progress on active secondary metabolites from Alternaria. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2021, 33, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.D.; Yi, T.F.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Chen, J.P.; Dai, H.F.; Wu, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.X. Biphenyl metabolites from the patchouli endophytic fungus Alternaria sp. PfuH1. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Ruan, C.F.; Bai, X.L. Isolation and antimicrobial effects of endophytic fungi from Edgeworthia chrysantha. Bangl. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, Y. Separation and determination of the effective components in the alabastrum of Edgeworthia chrysantha Lindl. by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lim, C.J.; Jeong, J.C.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J. Whole-genome sequence data and analysis of Saccharibacillus sp. ATSA2 isolated from Kimchi cabbage seeds. Data Brief 2019, 26, 104465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Lindgreen, S.; Orlando, L. AdapterRemoval v2: Rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Seppey, M.; Simao, F.A.; Manni, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Klioutchnikov, G.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO applications from quality assessments to gene prediction and phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinf. 2004, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanke, M.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS: A web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W465–W467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majoros, W.H.; Pertea, M.; Salzberg, S.L. TigrScan and GlimmerHMM: Two open source ab initio eukaryotic gene-finders. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2878–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R.J.N.a.r. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rodland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Moxon, S.; Marshall, M.; Khanna, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A. Rfam: Annotating non-coding RNAs in complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D121–D124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangrador-Vegas, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Chang, H.Y.; Yong, S.Y.; Finn, R.D. GO annotation in InterPro: Why stability does not indicate accuracy in a sea of changing annotations. Database 2016, 2016, baw027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H.J.N.m. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woudenberg, J.H.; Seidl, M.F.; Groenewald, J.Z.; de Vries, M.; Stielow, J.B.; Thomma, B.P.; Crous, P.W. Alternaria section Alternaria: Species, formae speciales or pathotypes? Stud. Mycol. 2015, 82, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Tang, J.; Zou, Y.; Sun, X.; Lan, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, P.; Wu, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, Q.; et al. Whole genome sequence of Alternaria alternata, the causal agent of black spot of Kiwifruit. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallister, E.; Gray, C.J.; Flitsch, S.L. Enzyme promiscuity of carbohydrate active enzymes and their applications in biocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2020, 65, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garron, M.L.; Henrissat, B. The continuing expansion of CAZymes and their families. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 53, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarammohan, S.; Paritosh, K.; Pental, D.; Kaur, J. Comparative genomics of Alternaria species provides insights into the pathogenic lifestyle of Alternaria brassicae—a pathogen of the Brassicaceae family. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, V.; Grothe, T.; Mayer-Bartschmid, A.; Endermann, R.; Geschke, F.U.; Henkel, T.; Stadler, M. Altersetin, a new antibiotic from cultures of endophytic Alternaria spp. taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, structure elucidation and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakule, T.B.; Sardar, D.; Lin, Z.; Schmidt, E.W. Two related pyrrolidinedione synthetase loci in Fusarium heterosporum ATCC 74349 produce divergent metabolites. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauers, G.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Berg, A.; Grafe, U.; Schachtele, C.; Totzke, F.; Finkenzeller, G.; et al. Anthraquinones and betaenone derivatives from the sponge-associated fungus Microsphaeropsis species: Novel inhibitors of protein kinases. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugai, T.; Minami, A.; Fujii, R.; Tanaka, M.; Oguri, H.; Gomi, K.; Oikawa, H. Heterologous expression of highly reducing polyketide synthase involved in betaenone biosynthesis. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1878–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Chung, K.-R. A nonribosomal peptide synthetase mediates siderophore production and virulence in the citrus fungal pathogen Alternaria alternata. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenderoth, M.; Garganese, F.; Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Soukup, S.T.; Ippolito, A.; Sanzani, S.M.; Fischer, R. Alternariol as virulence and colonization factor of Alternaria alternata during plant infection. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 112, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, M.A.F.; Love, S.K.; van der Helm, D. Nα-Dimethylcoprogens Three novel trihydroxamate siderophores from pathogenic fungi. Biol. Met. 1988, 1, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, J.; Moriwaki, A.; Ueno, M.; Tokunaga, T.; Arase, S.; Honda, Y. Cloning, functional analysis and expression of a scytalone dehydratase gene (SCD1) involved in melanin biosynthesis of the phytopathogenic fungus Bipolaris oryzae. Curr. Genet. 2004, 45, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, A.; Kihara, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Arase, S.; Honda, Y. Insertional mutagenesis and characterization of a polyketide synthase gene (PKS1) required for melanin biosynthesis in Bipolaris oryzae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 238, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jahns, C.; Hoffmann, T.; Muller, S.; Gerth, K.; Washausen, P.; Hofle, G.; Reichenbach, H.; Kalesse, M.; Muller, R. Pellasoren: Structure elucidation, biosynthesis, and total synthesis of a cytotoxic secondary metabolite from Sorangium cellulosum. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 5239–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, S.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Dong, B. Aqueous extract of sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) with potent activity against human cancer cells acts synergistically with doxorubicin. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Jiang, Z.E.; Song, L.Y.; Quan, Z.S.; Yu, H.L. Antidepressant and anxiolytic-like behavioral effects of erucamide, a bioactive fatty acid amide, involving the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 640, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.J.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Dethoup, T.; Cravo, S.; Mistry, S.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Kijjoa, A. A new meroterpene, a new benzofuran derivative and other constituents from cultures of the marine sponge-associated fungus Acremonium persicinum KUFA 1007 and their anticholinesterase activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Helw, E.A.E.; Morsy, A.R.I.; Hashem, A.I. Evaluation of some new heterocycles bearing2-oxoquinolylmoiety as immunomodulator against highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N8). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2021, 58, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Bai, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Exploring structural diversity of microbe secondary metabolites using OSMAC strategy: A literature review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Xu, J.; Wang, P. Recent advances in the heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene clusters for marine natural products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Keller, N.P. Transcriptional regulatory elements in fungal secondary metabolism. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

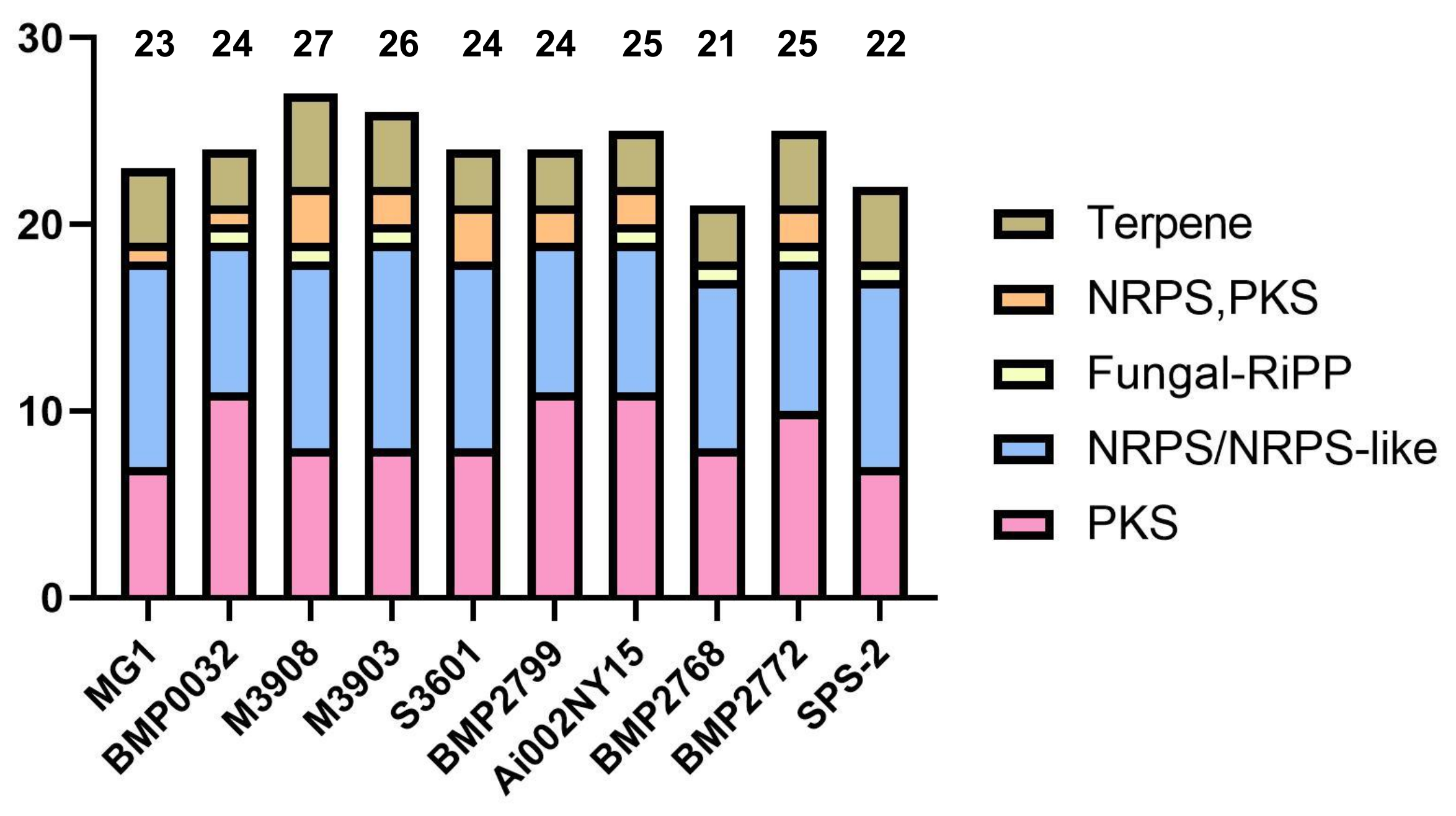

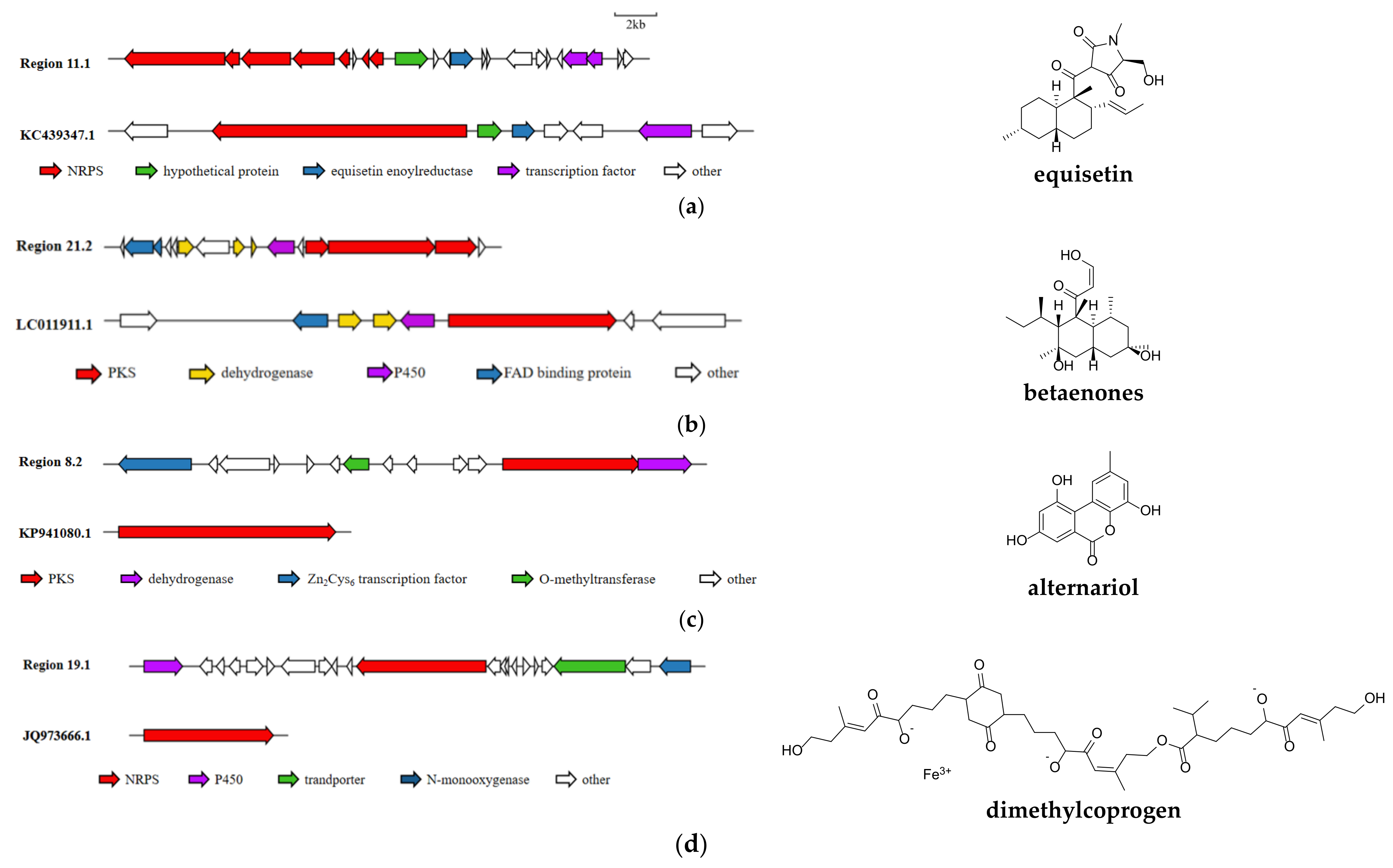

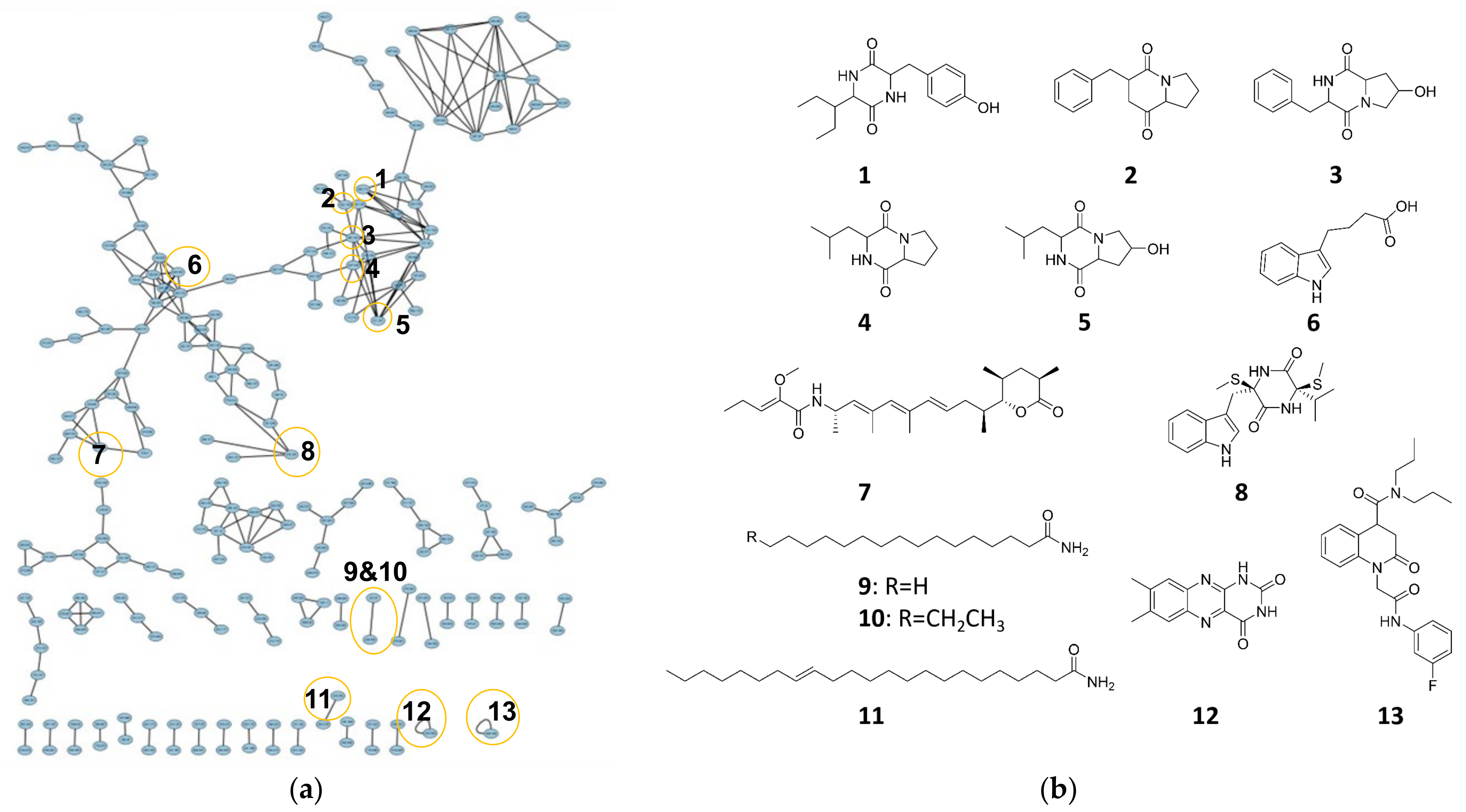
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Total length | 33,400,178 |
| Total sequence number | 38 |
| Max length | 4,684,119 |
| GC content | 51.0% |
| N50 | 2,610,814 |
| Total genes length | 14,826,936 |
| Total genes number | 9789 |
| Total CDSs length (bp) | 13,553,185 |
| CDSs percentage of genome | 40.58% |
| Strain | Genome Size (Mb) | GC% | Scaffolds | N50 (Mb) | Genes | Sequencing Technology | Assembly ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. arborescens FERA675 | 33.94 | 51.10 | 325 | - | 12,923 | Illumina MiSeq | GCA_004154835.1 |
| A. rosae MPI-PUGE-AT-0040 | 33.83 | 52 | 52 | 3.28 | 12,727 | PacBio SEQUEL | GCA_020736505.1 |
| A. longipes CBS 540.94 | 39.43 | 50.99 | 15 | 3.60 | - | Oxford Nanopore | GCA_019059555.1 |
| A. burnsii CBS107.38 | 32.96 | 50.9 | 67 | 1.49 | 11,314 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_013036055.1 |
| A. tenuissima FERA1166 | 35.7 | 51.1 | 22 | 2.58 | 13,575 | Illumina MiSeq | GCA_004156035.1 |
| A. alternata SRC1lrK2f | 32.99 | 51.4 | 79 | 1.1 | 13,577 | Illumina | GCA_001642055.1 |
| A. ethzedia BMP 0044 | 36.02 | 50.4 | 579 | 0.86 | 11,096 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023757985.1 |
| BMP 2799 | 36.4 | 50.2 | 225 | 1.0 | 11,159 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758145.1 |
| A. alternata EV-MIL-31 | 34.96 | 51 | 61 | 2.28 | 24,347 | Illumina MiSeq | GCA_016097525.1 |
| A. hordeiaustralica BMP2776 | 36.96 | 49.9 | 188 | 0.95 | 11,145 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758085.1 |
| A. novae-zelandiae BMP2774 | 37.57 | 49.5 | 204 | 1.24 | 11,027 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758075.1 |
| A. ventricosa BMP2768 | 34.69 | 51.4 | 89 | 1.33 | 11,061 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758065.1 |
| A. triticimaculans BMP 0046 | 36.79 | 49.9 | 236 | 1.67 | 11,104 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758025.1 |
| A. viburni BMP2772 | 36.35 | 50.3 | 188 | 1.05 | 11,586 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758015.1 |
| BMP0032 | 37.29 | 49.7 | 196 | 0.98 | 11,103 | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023758005.1 |
| A. panax BNCC115425 | 34.76 | 51 | 24 | 2.78 | 11,838 | Illumina HiSeq; PacBio | GCA_019702505.1 |
| M3908 | 33.77 | 51.1 | 118 | 0.77 | - | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023621335.1 |
| M3903 | 33.77 | 51.1 | 104 | 0.95 | - | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023621305.1 |
| S3601 | 34.24 | 50.9 | 75 | 1.30 | - | Illumina HiSeq | GCA_023621325.1 |
| MG1 | 34.7 | 49.9 | 130 | 1.66 | 13,440 | Illumina | GCA_003574525.1 |
| SPS-2 | 33.4 | 51 | 38 | 2.61 | 9789 | Illumina MiSeq | JAMXIG000000000 |
| Type | Repeat Number | Repeat Size | In Genome (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| rRNA | 12 | 6641 | 0.0199 |
| tRNA | 108 | 9657 | 0.0289 |
| ncRNA | 32 | 4218 | 0.0126 |
| LTR | 19 | 26,157 | 0.0008 |
| DNA | 29 | 12,782 | 0.0004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, J.; Bai, X.; Zeng, M.; Li, M.; Hu, Z.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, H. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of an Endophytic Fungus Alternaria sp. SPS-2 and Its Biosynthetic Potential of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091789
Tao J, Bai X, Zeng M, Li M, Hu Z, Hua Y, Zhang H. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of an Endophytic Fungus Alternaria sp. SPS-2 and Its Biosynthetic Potential of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091789
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Jianyun, Xuelian Bai, Mingyuan Zeng, Mengshi Li, Zhe Hu, Yunfen Hua, and Huawei Zhang. 2022. "Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of an Endophytic Fungus Alternaria sp. SPS-2 and Its Biosynthetic Potential of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091789
APA StyleTao, J., Bai, X., Zeng, M., Li, M., Hu, Z., Hua, Y., & Zhang, H. (2022). Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of an Endophytic Fungus Alternaria sp. SPS-2 and Its Biosynthetic Potential of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091789








