Impacts of Japanese Larch Invasion on Soil Bacterial Communities of the Giant Panda Habitat in the Qinling Mountains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
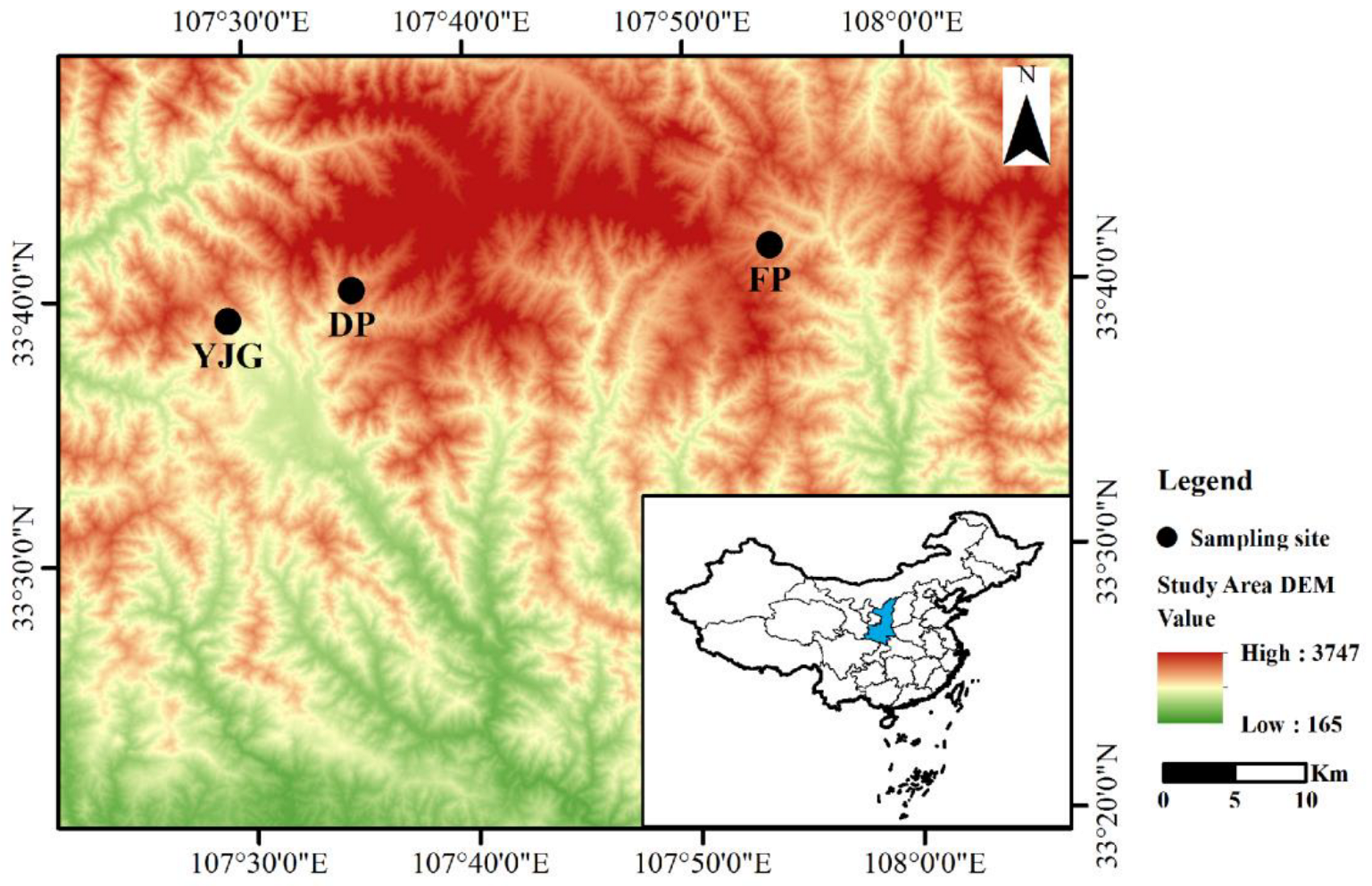
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Chemical Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Illumina HiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Processing of Sequencing Data
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Network Analysis
2.7. Functional Prediction Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
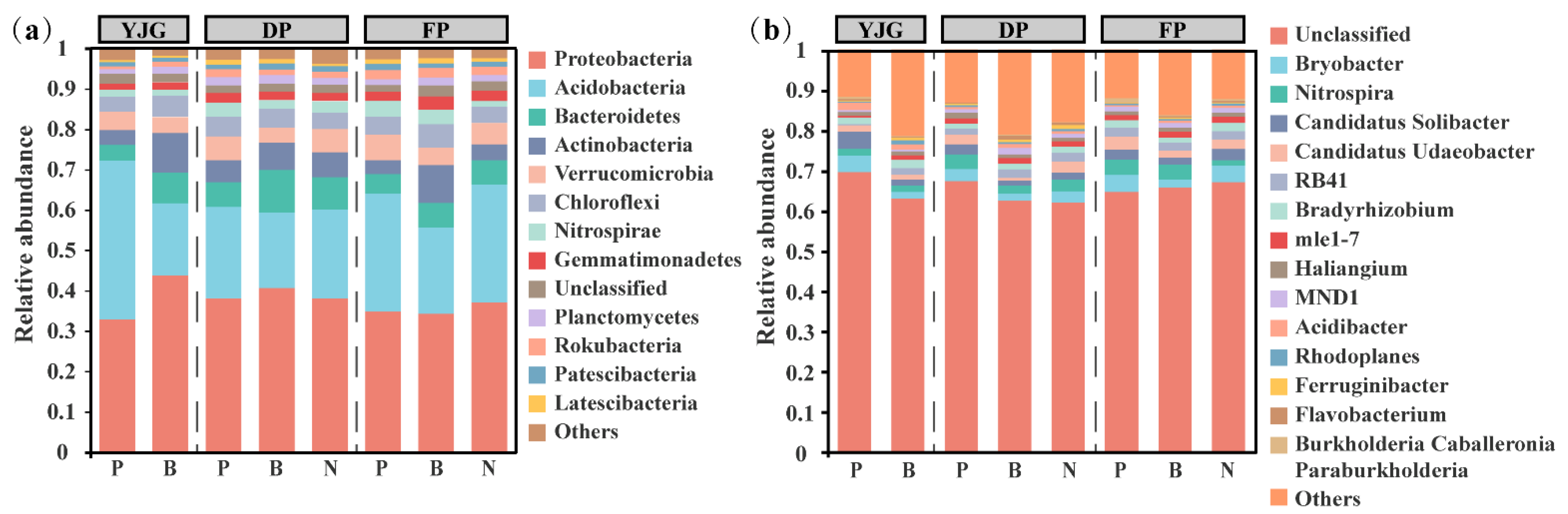
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity
3.3. Identifying Indicator Taxa among Different Forest Types and Sites
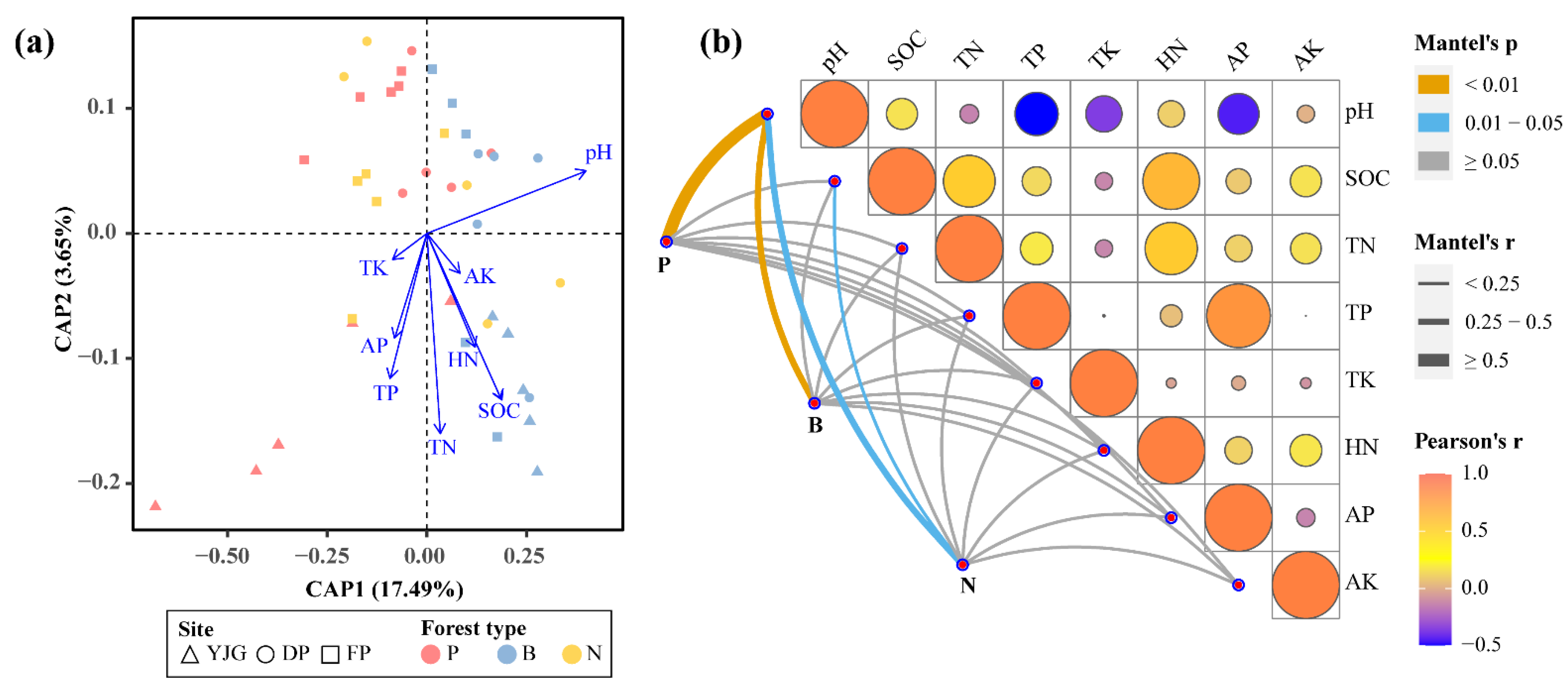
3.4. Key Factors Shaping Soil Bacterial Communities
3.5. Potential Functional Capabilities of Bacterial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. pH as the Primary Soil Physical Factor Driving Bacterial Community
4.2. Changes in Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity
4.3. Comparison of Functional Features between Planted and Native Forests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fierer, N. Embracing the Unknown: Disentangling the Complexities of the Soil Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagg, C.; Schlaeppi, K.; Banerjee, S.; Kuramae, E.E.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Fungal-Bacterial Diversity and Microbiome Complexity Predict Ecosystem Functioning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; van Straalen, N.M. The Unseen Majority: Soil Microbes as Drivers of Plant Diversity and Productivity in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Zeng, W.; Wang, W. Latitudinal and Depth Patterns of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Grasslands of an Agro-pastoral Ecotone. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3833–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ni, Y.; Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Chu, H. Distinct Soil Bacterial Communities along a Small-Scale Elevational Gradient in Alpine Tundra. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The Diversity and Biogeography of Soil Bacterial Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladygina, N.; Hedlund, K. Plant Species Influence Microbial Diversity and Carbon Allocation in the Rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, S.M.; Buckley, H.L.; Case, B.S.; Curran-Cournane, F.; Taylor, M.; Lear, G. Bacteria as Emerging Indicators of Soil Condition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02826-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, D.; Wang, X.; Settles, M.L.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Dong, P.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z. Soil Bacterial Communities of Different Natural Forest Types in Northeast China. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogberg, P.; Read, D. Towards a More Plant Physiological Perspective on Soil Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Wei, M.; Rong, X.; Li, Y.; Du, D. Ecological Restoration Treatments Enhanced Plant and Soil Microbial Diversity in the Degraded Alpine Steppe in Northern Tibet. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, P.; Zhou, R.; Li, C.; Dun, X.; Niu, X. Changing Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Soil Microbial Community during Litter Decomposition in a Mixed Quercus acutissima Carruth. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forest in Northern China. Catena 2021, 196, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareen, A.; Burton, F.; Schäfer, P. Plant Root-Microbe Communication in Shaping Root Microbiomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, P.; Shao, X.; Songer, M.; Cai, Q.; Zhu, Y.; He, X. Spatiotemporally Monitoring Forest Landscape for Giant Panda Habitat through a High Learning-Sensitive Neural Network in Guanyinshan Nature Reserve in the Qinling Mountains, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. The Status Quo and Conservation Management Planning of Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) Population and Habitat in Qinling Mountains, Shaanxi Province. Chin. J. Wildl. 2021, 42, 663–674. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, M.; Yuan, S.; Yang, Z.; Hong, M.; Yang, X.; Gu, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of Microhabitats and Foraging Strategies between the Captive-Born Zhangxiang and Wild Giant Pandas: Implications for Future Reintroduction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15089–15096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Duan, L.; Li, J. Habitat Use by Giant Panda in Relation to Man-Made Forest in Wanglang Nature Reserve of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13440–13445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Fei, Y.; Yang, H.; Gu, X.; Songer, M. Giant Panda National Park, a Step towards Streamlining Protected Areas and Cohesive Conservation Management in China. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiu, Q.; Meng, X. The pandas of Qinling—The 4th Survey Report on Giant Pandas in Shaanxi Province; Shaanxi Science and Technology Press: Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X. Report on the Comprehensive Scientific Study of Changqing National Nature Reserve in Shaanxi; Shaanxi Science and Technology Press: Xi’an, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D. History of the Development of Foping Nature Reserve; Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University Press: Xianyang, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Raubenheimer, D.; Elser, J.J.; Wei, W.; Wei, F. Obligate Herbivory in an Ancestrally Carnivorous Lineage: The Giant Panda and Bamboo from the Perspective of Nutritional Geometry. Funct. Ecol. 2015, 29, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly Accurate OTU Sequences from Microbial Amplicon Reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of RRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, M.; Cong, J.; Qi, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Cong, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Soil pH Exerts Stronger Impacts than Vegetation Type and Plant Diversity on Soil Bacterial Community Composition in Subtropical Broad-Leaved Forests. Plant Soil 2020, 450, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Weisenhorn, P.; Gilbert, J.A.; Shi, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chu, H. Soil pH correlates with the co-occurrence and assemblage process of diazotrophic communities in rhizosphere and bulk soils of wheat fields. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Lin, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of forest conversion on soil bacterial community composition and diversity in subtropical forests. Catena 2019, 175, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Inagaki, Y.; Sugihara, S.; Funakawa, S.; Toyota, K. Impacts of conversion from natural forest to cedar plantation on the structure and diversity of root-associated and soil microbial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wu, L.; Du, A. The Shifts in Soil Microbial Community and Association Network Induced by Successive Planting of Eucalyptus Plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 505, 119877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Kim, M.; Singh, D.; Lee-Cruz, L.; Lai-Hoe, A.; Ainuddin, A.N.; Go, R.; Rahim, R.A.; Husni, M.H.A.; Chun, J.; et al. Tropical Soil Bacterial Communities in Malaysia: pH Dominates in the Equatorial Tropics Too. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Soil pH as a Predictor of Soil Bacterial Community Structure at the Continental Scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Imamura, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Tateno, R. Does Conversion from Natural Forest to Plantation Affect Fungal and Bacterial Biodiversity, Community Structure, and Co-Occurrence Networks in the Organic Horizon and Mineral Soil? For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 446, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Li, C.; Wu, L. Effects of the Successive Planting of Eucalyptus Urophylla on Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Structure, Diversity, Microbial Biomass, and Enzyme Activity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, P.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Xu, J.; Dun, X. Effects of soil microbial community on the litter decomposition in mixed Quercus acutissima Carruth. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. forest. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, C.E.; Zabek, L.M.; Staley, C.L.; Kabzems, R. Decomposition of Broadleaf and Needle Litter in Forests of British Columbia: Influences of Litter Type, Forest Type, and Litter Mixtures. Can. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiang, W.; Wu, H.; Ouyang, S.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Tree Species Identity Surpasses Richness in Affecting Soil Microbial Richness and Community Composition in Subtropical Forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 130, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, L.; Dou, Y.; An, S. Comparison of Soil Microbial Community between Planted Woodland and Natural Grass Vegetation on the Loess Plateau. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 460, 117817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Song, Q.; Yu, D.; Yang, G.; Qi, H.; Shi, J. Strategy of fine root expansion of Phyllostachys pubescens population into evergreen broad-leaved forest. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.I.; Roccotelli, A.; Petrovičovà, B.; Romeo, M.; Badagliacca, G.; Monti, M.; Gelsomino, A. Temporal Dynamics of Total and Active Prokaryotic Communities in Two Mediterranean Orchard Soils Treated with Solid Anaerobic Digestate or Managed under No-Tillage. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 837–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.T.; Bates, S.T.; Eilers, K.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Caporaso, J.G.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. The Under-Recognized Dominance of Verrucomicrobia in Soil Bacterial Communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gong, F.; Zheng, B.; Chen, D.; Ma, L. Physical and Chemical Properties of the Soil for Larch Plantations. J. Northeast For. Univ. 1997, 03, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Klenk, H.-P.; Clément, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Miao, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, F.; Jiang, L.; Hui, D.; Wan, S. Soil Microbial Community Composition and Respiration along an Experimental Precipitation Gradient in a Semiarid Steppe. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Shen, L.; Wen, C.; Yan, Q.; Ning, D.; Qin, Y.; Xue, K.; Wu, L.; He, Z.; et al. Temperature Mediates Continental-Scale Diversity of Microbes in Forest Soils. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wang, G. Decoupling of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Dynamics along a Temperature Gradient on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2021, 396, 115084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Jiao, F.; Shi, X.; Sardans, J.; Maestre, F.T.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Peñuelas, J. Experimental and Observational Studies Find Contrasting Responses of Soil Nutrients to Climate Change. eLife 2017, 6, e23255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Yue, S.; Tian, J.; Chen, H.; Jiang, H.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Zhan, A.; Fang, Q.; Yu, Q. Soil Microbial Community and Network Changes after Long-Term Use of Plastic Mulch and Nitrogen Fertilization on Semiarid Farmland. Geoderma 2021, 396, 115086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Lin, Q.; Tang, Z.; Liu, F. Vertical Distribution of Soil Bacterial Communities in Different Forest Types Along an Elevation Gradient. Microb. Ecol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbrell, A.J.; Nelson, M.; Helgason, T.; Dytham, C.; Fitter, A.H. Relative Roles of Niche and Neutral Processes in Structuring a Soil Microbial Community. ISME J. 2010, 4, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjard, L.; Dequiedt, S.; Chemidlin Prévost-Bouré, N.; Thioulouse, J.; Saby, N.P.A.; Lelievre, M.; Maron, P.A.; Morin, F.E.R.; Bispo, A.; Jolivet, C.; et al. Turnover of Soil Bacterial Diversity Driven by Wide-Scale Environmental Heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Geng, M.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Investigating the Effect of Microbial Inoculants Frankia F1 on Growth-Promotion, Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties, and Bacterial Community of Ginseng. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 172, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Shaw, T.I.; Oladeinde, A.; Glenn, T.C.; Oakley, B.; Molina, M. Rapid Microbiome Changes in Freshly Deposited Cow Feces under Field Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Mo, X.; Kong, W.; Song, Y. Soil Bacterial Diversity, Structure, and Function of Suaeda Salsa in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils in Various Habitats in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Yan, P.; Zhao, X.; Bai, X. Reconstruction and functional recovery of soil microbial community after fumigation of metam-sodium. Plant Prot. 2021, 47, 44–53. [Google Scholar]



| Treatments | pH | SOC (%) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | TK (%) | HN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YJG | P | 4.87 ± 0.21 Bb | 5.62 ± 1.15 Ba | 4.1 ± 0.28 Aa | 0.43 ± 0.09 Aa | 1.14 ± 0.23 Aab | 252.42 ± 74.73 Aab | 10.12 ± 1.94 Aa | 195.8 ± 25.25 Aa |
| B | 6.11 ± 0.24 Aa | 12.4 ± 1.69 Aa | 4.54 ± 0.56 Aa | 0.3 ± 0.05 Ba | 0.99 ± 0.16 Aa | 410.93 ± 153.2 Aa | 7.12 ± 1.57 Ba | 193.2 ± 22.73 Aa | |
| DP | P | 5.61 ± 0.1 Ca | 6.62 ± 1.85 Aa | 3.77 ± 0.63 Aab | 0.29 ± 0.12 Aab | 1.35 ± 0.2 Aa | 362.9 ± 112.93 Aa | 7.84 ± 2.71 Aab | 195 ± 17.89 Aa |
| B | 6.1 ± 0.07 Aa | 5.63 ± 3.54 Ab | 3.42 ± 0.53 Ab | 0.28 ± 0.08 Aa | 1.05 ± 0.28 Aa | 214.52 ± 99.17 Ab | 6.02 ± 1.55 Aa | 205.8 ± 22.2 Aa | |
| N | 5.83 ± 0.19 Ba | 4.18 ± 1.83 Aa | 3.5 ± 0.43 Aa | 0.26 ± 0.09 Aa | 1.07 ± 0.39 Aa | 262.5 ± 47.92 Aa | 7.32 ± 1.87 Aa | 177.4 ± 9.53 Aa | |
| FP | P | 5.77 ± 0.15 Ba | 2.84 ± 0.52 Ab | 3.2 ± 0.35 Ab | 0.2 ± 0.05 Bb | 0.96 ± 0.06 Ab | 112.47 ± 60 Bb | 5.4 ± 1.28 Bb | 186.8 ± 16.15 Aa |
| B | 6.09 ± 0.18 Aa | 3.67 ± 1.24 Ab | 3.43 ± 0.28 Ab | 0.33 ± 0.04 Aa | 0.94 ± 0.16 Aa | 207.33 ± 28.48 Ab | 8.02 ± 1.25 Aa | 183 ± 17.09 Aa | |
| N | 5.66 ± 0.18 Ba | 3.83 ± 1.53 Aa | 3.53 ± 0.43 Aa | 0.24 ± 0.03 Ba | 1.16 ± 0.21 Aa | 184.18 ± 53.6 ABb | 6.46 ± 0.99 ABa | 188 ± 18.8 Aa | |
| Two-way ANOVA | |||||||||
| Forest type | *** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Site | *** | *** | *** | * | NS | *** | * | NS | |
| Forest type × Site | *** | *** | NS | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H.; Ye, X. Impacts of Japanese Larch Invasion on Soil Bacterial Communities of the Giant Panda Habitat in the Qinling Mountains. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091807
Zhuang Y, Xu Y, Yang M, Zhao H, Ye X. Impacts of Japanese Larch Invasion on Soil Bacterial Communities of the Giant Panda Habitat in the Qinling Mountains. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091807
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Yuqi, Yadong Xu, Meiling Yang, Huiru Zhao, and Xinping Ye. 2022. "Impacts of Japanese Larch Invasion on Soil Bacterial Communities of the Giant Panda Habitat in the Qinling Mountains" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091807
APA StyleZhuang, Y., Xu, Y., Yang, M., Zhao, H., & Ye, X. (2022). Impacts of Japanese Larch Invasion on Soil Bacterial Communities of the Giant Panda Habitat in the Qinling Mountains. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091807






