Shiga Toxin Subtypes, Serogroups, Phylogroups, RAPD Genotypic Diversity, and Select Virulence Markers of Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli Strains from Goats in Mid-Atlantic US
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. STEC Isolates
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Evaluation of Shiga Toxin Subtypes in STEC
2.4. Screening for Presence of eae and hly in STEC
2.5. Determination STEC Serogroups
2.6. Characterization of Phylogenetic Groups
2.7. RAPD Genotyping of STEC
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
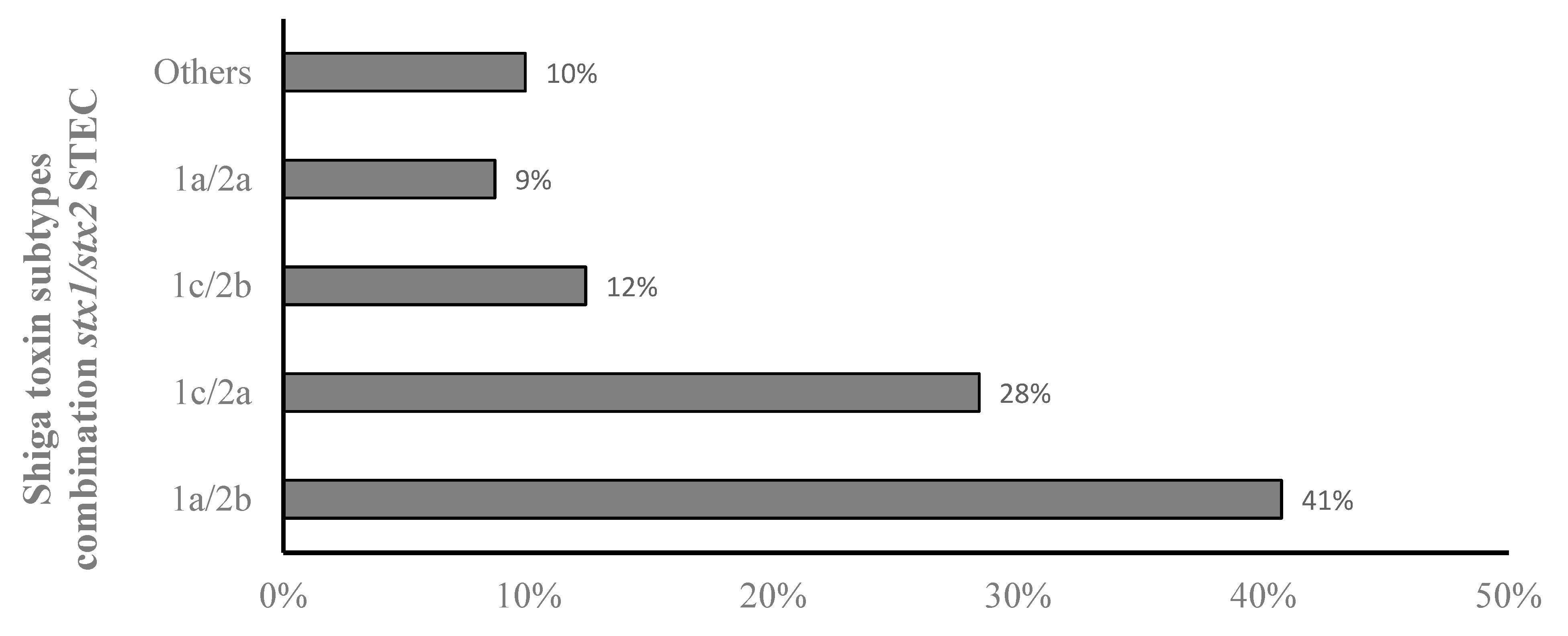
3.1. Prevalence of stx1 and stx2 Subtypes in STEC from Goats
3.2. Serogroups of STEC from Goats and Prevalence of Select Virulence Genes
3.3. Distribution of Shiga Toxin Types and Subtypes in the Different STEC Serogroups
3.4. Phylogroups of STEC from Goats
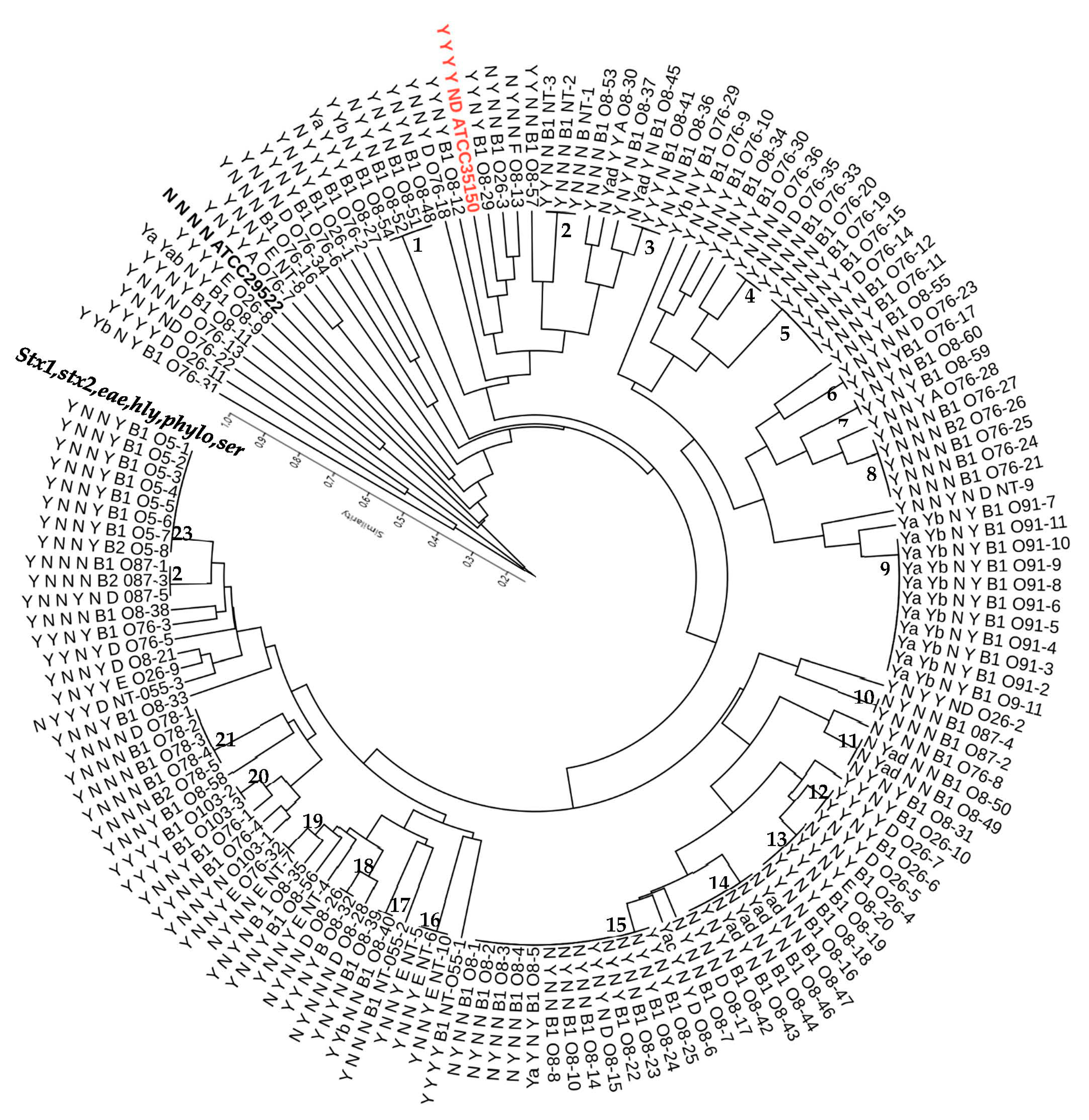
3.5. Genetic Diversity of STEC Strains from Goats as Revealed by M13 RAPD PCR
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croxen, M.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. Recent Advances in Understanding Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Gunther, N.W., IV. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 86, 145–197. [Google Scholar]
- Farrokh, C.; Jordan, K.; Auvray, F.; Glass, K.; Oppegaard, H.; Raynaud, S.; Thevenot, D.; Condron, R.; De Reu, K.; Govaris, A.; et al. Review of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and their significance in dairy production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 162, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.M. Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli (STEC). Clin. Lab. Med. 2010, 30, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergan, J.; Lingelem, A.B.D.; Simm, R.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K. Shiga toxins. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1085–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Römer, W. Shiga toxins—From cell biology to biomedical applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Piérard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of a Sequence-Based Protocol for Subtyping Shiga Toxins and Standardizing Stx Nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Lucchesi, P.M.A. Shiga toxins and stx phages: Highly diverse entities. Microbiology 2015, 161, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, D.; Grif, K.; Khan, A.B.; Naim, A.; Dierich, M.P.; Würzner, R. The Shiga toxin genotype rather than the amount of Shiga toxin or the cytotoxicity of Shiga toxin in vitro correlates with the appearance of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 59, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.A.; Pellino, C.A.; Flagler, M.J.; Strasser, J.; Weiss, A.A. Shiga Toxin Subtypes Display Dramatic Differences in Potency. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandal, L.T.; Wester, A.L.; Lange, H.; Løbersli, I.; Lindstedt, B.-A.; Vold, L.; Kapperud, G. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections in Norway, 1992–2012: Characterization of isolates and identification of risk factors for haemolytic uremic syndrome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melton-Celsa, A.R. Shiga Toxin (Stx) Classification, Structure, and Function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, K.; De Reu, K.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Piérard, D.; De Zutter, L.; Herman, L.; Robyn, J.; Heyndrickx, M. Genetic characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli O157, O26, O103, O111 and O145 isolates from humans, food, and cattle in Belgium. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Gierke, R.E.; Griffin, P.M.; Gould, L.H.; Herman, K.; Bopp, C.A.; Strockbine, N.; Mody, R.K. Outbreaks of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection: USA. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 2270–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, L.H.; Mody, R.K.; Ong, K.L.; Clogher, P.; Cronquist, A.B.; Garman, K.N.; Lathrop, S.; Medus, C.; Spina, N.L.; Webb, T.H.; et al. Increased recognition of non-O157 Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli infections in the United States during 2000–2010: Epidemiologic features and comparison with E. coli O157 infections. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Scallan, E.; Jones-Bitton, A.; Sargeant, J.M.; Stapleton, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Yeung, D.H.; Kirk, M.D. Global Incidence of Human Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli Infections and Deaths: A Systematic Review and Knowledge Synthesis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, L.; Vanstone, G.; Perry, N.T.; Launders, N.; Adak, G.K.; Godbole, G.; Grant, K.A.; Smith, R.; Jenkins, C. Epidemiology and microbiology of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli other than serogroup O157 in England, 2009–2013. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierz, L.; Cernela, N.; Hauser, E.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R. Characteristics of Shigatoxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains Isolated during 2010–2014 from Human Infections in Switzerland. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; Van Pelt, W.; Van Der Voort, M.; Heck, M.; Friesema, I.; Franz, E. Attribution of human infections with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) to livestock sources and identification of source-specific risk factors, The Netherlands (2010–2014). Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 65, e8–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, A.J.; Budimir, A.; Nashev, D.; Sá-Leão, R.; van Dijl, J.M.; Laurent, F.; Grundmann, H.; Friedrich, A.W.; on behalf of the ESCMID Study Group of Epidemiological Markers (ESGEM). Overview of molecular typing methods for outbreak detection and epidemiological surveillance. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.L.; Godfrey, P.A.; Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Feldgarden, M.; Frimodt-Møller, N. Selection of unique Escherichia coli clones by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD): Evaluation by whole genome sequencing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 103, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, B.G.; Souza, M.M.; Regua-Mangia, A.H.; Bittencourt, A.J. Genetic relationship between Escherichia coli strains isolated from dairy mastitis and from the stable fly Stomoxys calcitrans. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2016, 36, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marialouis, X.A.; Santhanam, A. Antibiotic resistance, RAPD-PCR typing of multiple drug resistant strains of Escherichia coli from urinary tract infection (UTI). J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, DC05–DC09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madico, G.; Akopyants, N.S.; Berg, D.E. Arbitrarily primed PCR DNA fingerprinting of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains by using templates from boiled cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, S.; Ling, O.W.; Rusul, G.; Karim, M.I.A.; Nishibuchi, M. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by multiplex PCR and their characterization by plasmid profiling, antimicrobial resistance, RAPD and PFGE analyses. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suardana, I.W.; Artama, W.T.; Widiasih, D.A.; Mahardika, I. Genetic diversity of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Int. Res. J. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ndegwa, E.; Alahmde, A.; Kim, C.; Kaseloo, P.; O’Brien, D. Age related differences in phylogenetic diversity, prevalence of Shiga toxins, Intimin, Hemolysin genes and select serogroups of Escherichia. coli from pastured meat goats detected in a longitudinal cohort study. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Rodgers, F.G. Detection in Escherichia coli of the genes encoding the major virulence factors, the genes defining the O157:H7 serotype, and components of the type 2 Shiga toxin family by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3613–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, C.; Roberts, E.; Fratamico, P.M. Detection of O antigens in Escherichia coli. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2011, 12, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, A.; Iyoda, S.; Seto, K.; Morita-Ishihara, T.; Scheutz, F.; Ohnishi, M. Escherichia coli O-Genotyping PCR: A Comprehensive and Practical Platform for Molecular O Serogrouping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelheim, K.A. The Non-O157 Shiga-Toxigenic (Verocytotoxigenic) Escherichia coli; Under-Rated Pathogens. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 33, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.E.; Foster, D.; Rogers, A.T.; Balcomb, C.C.; Shi, X.; Nagaraja, T.G. Evidence of Non-O157 Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli in the Feces of Meat Goats at a U.S. Slaughter Plant. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1626–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.; Samanta, I.; Munshi, Z.; Bhat, M.; Nishikawa, Y. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in healthy goats in India: Occurrence and virulence properties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Suárez, M.-E.; Otero, A.; García-López, M.-L.; Dahbi, G.; Blanco, M.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; Santos, J.A. Genetic characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) isolates from goat’s milk and goat farm environment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 236, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.; Mustafa, A.; Elhariri, M.; Abdelhamed, G. The distribution of Escherichia coli serovars, virulence genes, gene association and combinations and virulence genes encoding serotypes in pathogenic E. coli recovered from diarrhoeic calves, sheep and goat. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.; Ajuwape, A.; Otesile, E.; Owoade, A.; Oyekunle, M.; Adetosoye, A. Potentially zoonotic shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serogroups in the faeces and meat of food-producing animals in Ibadan, Nigeria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtaz, H.; Dehkordi, F.S.; Rahimi, E.; Ezadi, H.; Arab, R. Incidence of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serogroups in ruminant’s meat. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, T.; Saleha, A.; Mutalib, A.; Zunita, Z.; Murugaiyah, M. Occurrence and virulence gene of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from goats in Selangor, Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Animal Health and Human Safety, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 6–8 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, D.D.; Kumar, N.; Kumarsen, G.; Paul, S.; Kumar, A. Role of Bacterial and Parasitic Pathogens in Occurrence of Neonatal Diarrhoea in Goat-Kids. J. Anim. Res. 2020, 10, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanti, A.; Samanta, I.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Joardar, S.N. Molecular characterization and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of caprine Shiga toxin producing-Escherichia coli (STEC) isolates from India. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 16, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, C.; Pires, M.M.; Stoppe, N.C.; Hachich, E.M.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Amaral, L.A.; Ottoboni, L.M.M. Escherichia coli phylogenetic group determination and its application in the identification of the major animal source of fecal contamination. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, L.; Giraffa, G. Rapid identification of dairy lactic acid bacteria by M13-generated, RAPD-PCR fingerprint databases. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Vallvé, S.; Palau, J.; Romeu, A. Horizontal gene transfer in glycosyl hydrolases inferred from codon usage in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEDCALC®. MedCalc Comparison of Proportions Calculator. 2020. Available online: https://www.medcalc.org/calc/comparison_of_proportions.php (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Jajarmi, M.; Badouei, M.A.; Fooladi, A.A.I.; Ghanbarpour, R.; Ahmadi, A. Pathogenic potential of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains of caprine origin: Virulence genes, Shiga toxin subtypes, phylogenetic background and clonal relatedness. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Hu, B.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhao, A.; Ba, P.; Fu, S.; Fan, R.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Molecular and Phylogenetic Characterization of Non-O157 Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TayZar, A.C.; Saleha, A.A.; Rahim, A.M.; Murugaiyah, M.; Shah, A.H. Occurrence of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in healthy cattle and goats and distribution of virulence genes among isolates. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, S.; Llorente, M.T.; Echeita, M.A.; Herrera-León, S. Development of Three Multiplex PCR Assays Targeting the 21 Most Clinically Relevant Serogroups Associated with Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli Infection in Humans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézquita-López, B.A.; Quiñones, B.; Lee, B.G.; Chaidez, C. Virulence profiling of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli recovered from domestic farm animals in Northwestern Mexico. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, B.; Chen, M.; Guo, D.; Guo, X.; Liu, F.; Feng, L.; Wang, L. A multiplex PCR method to detect 14 Escherichia coli serogroups associated with urinary tract infections. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 82, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtaz, H.; Karimian, A.; Madani, M.; Dehkordi, F.S.; Ranjbar, R.; Sarshar, M.; Souod, N. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli in Iran: Serogroup distributions, virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance properties. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2013, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käppeli, U.; Hächler, H.; Giezendanner, N.; Beutin, L.; Stephan, R. Human Infections with Non-O157 Shiga Toxin–producing Escherichia coli, Switzerland, 2000–2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Mahanti, A.; Samanta, I.; Dutta, T.K.; Ghosh, M.K.; Bera, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Bhattacharya, D. Virulence repertoire of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) from diarrhoeic lambs of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, C.; Ludovico, M.; Valadares, G.F.; Gatti, M.S.V.; Leite, D.S. Detection of virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrheic and healthy feces of dairy calves in Brazil. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2012, 79, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Taku, A.; Malik, A.; Bhat, M.; Javed, R.; Badroo, G.; Kour, A. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial profiling of Escherichia coli isolates from diarrheic calves. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 87, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Vu-Khac, H.; Holoda, E.; Pilipcinec, E.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.; Dahbi, G.; Mora, A.; López, C.; González, E. Serotypes, virulence genes, intimin types and PFGE profiles of Escherichia coli isolated from piglets with diarrhoea in Slovakia. Vet. J. 2007, 174, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-M.; Liao, X.-P.; Liu, S.-G.; Zhang, W.-J.; Jiang, H.-X.; Zhang, M.-J.; Zhu, H.-Q.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, A.-X.; et al. Serotypes, virulence genes, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolates from pigs. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Dibarrat, J.; Enriquez-Gómez, E.; Talavera-Rojas, M.; Soriano-Vargas, E.; Navarro, A.; Morales-Espinosa, R. Characterization of commensal Escherichia coli isolates from slaughtered sheep in Mexico. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bingen, E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4555–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Condamine, B.; Dion, S.; Gordon, D.M.; Denamur, E. The E phylogroup of Escherichia coli is highly diverse and mimics the whole E. coli species population structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 7139–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghadosi, R.; Shakibaie, M.R.; Alizade, H.; Hosseini-Nave, H.; Askari, A.; Ghanbarpour, R. Serogroups, subtypes and virulence factors of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from human, calves and goats in Kerman, Iran. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2018, 11, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aflatoonian, M.R.; Alizade, H.; Jajarmi, M.; Ghanbarpour, R.; Shamsaddini Bafti, M.; Askari, A.; Adib, N.; Khatami, M. Phylotyping of antibiotic resistant, shiga toxin-producing and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from ovine and caprine carcasses in Iran. J. Biochem. Technol. 2018, s2, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.; Mao, L.; Li, J.; Hao, F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Li, W. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of pathogenic Escherichia coli from goats with respiratory disease in eastern China. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 166, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; López, C.; Dhabi, G.; López-Beceiro, A.M.; Fidalgo, L.E.; Díaz, E.A.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; Mamani, R.; Herrera, A.; Blanco, J.E.; et al. Seropathotypes, Phylogroups, Stx Subtypes, and Intimin Types of Wildlife-Carried, Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains with the Same Characteristics as Human-Pathogenic Isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2578–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coura, F.M.; De Araújo Diniz, S.; Mussi, J.M.S.; Silva, M.X.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B. Characterization of virulence factors and phylogenetic group determination of Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic and non-diarrheic calves from Brazil. Folia Microbiol. 2017, 62, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, N.-H.; Bae, W.-K.; Lim, J.-Y.; Koo, H.-C.; Kim, J.-M.; Noh, K.-M.; Jung, W.-K.; Park, K.-T.; et al. Isolation and identification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using different detection methods and molecular determination by multiplex PCR and RAPD. J. Vet. Sci. 2005, 6, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Padola, N.L.; Parma, A.E.; Lucchesi, P.M.A. Intraserotype diversity among Argentinian verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli detected by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahilah, A.; Audrey, L.; Ong, S.; Wan Sakeenah, W.; Safiyyah, S.; Norrakiah, A.; Aminah, A.; Ahmad Azuhairi, A. DNA profiling among egg and beef meat isolates of Escherichia coli by enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR (ERIC-PCR) and random amplified polymorphic DNA-PCR (RAPD-PCR). Int. Food Res. J. 2010, 17, 853–866. [Google Scholar]



| Target Size | Target Gene | Sequence | Primer Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 209 | stx1 | GTACGGGGATGCAGATAAATCGC | stx1-det-F1 | [7] |
| AGCAGTCATTACATAAGAACGYCCACT | stx1-det-R1 | |||
| 478 | stx1a | CCTTTCCAGGTACAACAGCGGTT | stx1a-F1 | “ |
| GGAAACTCATCAGATGCCATTCTGG | stx1a-R2 | |||
| 252 | stx1c | CCTTTCCTGGTACAACTGCGGTT | stx1c-F1 | “ |
| CAAGTGTTGTACGAAATCCCCTCTGA | stx1c-R1 | |||
| 203 | stx1d | CAGTTAATGCGATTGCTAAGGAGTTTACC | stx1d-F1 | “ |
| CTCTTCCTCTGGTTCTAACCCCATGATA | stx1d-R2 | |||
| 600 | stx2 (all except 2f) | GGCACTGTCTGAAACTGCTCCTGT | F4 | “ |
| stx2 (all except 2e and 2f) | ATTAAACTGCACTTCAGCAAATCC | R1 | ||
| stx2 (stx2f) | CGCTGTCTGAGGCATCTCCGCT | F4-f | ||
| stx2 (2e and2f) | TAAACTTCACCTGGGCAAAGCC | R1-e/f | ||
| 349 | stx2a | GCGATACTGRGBACTGTGGCC | stx2a-F2 | “ |
| CCGKCAACCTTCACTGTAAATGTG | stx2a-R3 | |||
| 347 | stx2a | GCCACCTTCACTGTGAATGTG | stx2a-R2 | “ |
| 251 | stx2b | AAATATGAAGAAGATATTTGTAGCGGC | stx2b-F1 | “ |
| CAGCAAATCCTGAACCTGACG | stx2b-R1 | |||
| 177 | stxc2 | GAAAGTCACAGTTTTTATATACAACGGGTA | stx2c-F1 | “ |
| CCGGCCACYTTTACTGTGAATGTA | stx2c-R2 | |||
| 179 | stx2d | AAARTCACAGTCTTTATATACAACGGGTG | stx2d-F1 | “ |
| TTYCCGGCCACTTTTACTGTG | stx2d-R1 | |||
| 235 | stx2d-055 | TCAACCGAGCACTTTGCAGTAG | stx2d-O55 | “ |
| 280 | stx2d | GCCTGATGCACAGGTACTGGAC | stx2d-R2 | “ |
| 411 | stx2e | CGGAGTATCGGGGAGAGGC | stx2e | “ |
| CTTCCTGACACCTTCACAGTAAAGGT | ||||
| 424 | stx2f | TGGGCGTCATTCACTGGTTG | stx2f | “ |
| TAATGGCCGCCCTGTCTCC | ||||
| 573 | stx2g | CACCGGGTAGTTATATTTCTGTGGATATC | stx2g | “ |
| GATGGCAATTCAGAATAACCGCT | ||||
| 248 | eaeA | ATGCTTAGTGCTGGTTTAGG | eaea-a | [28] |
| GCCTTCATCATTTCGCTTTC | eaea-b | |||
| 569 | hlyA | AGCTGCAAGTGCGGGTCTG | HlyA-a | “ |
| TACGGGTTATGCCTGCAAGTTCAC | HlyA-b | |||
| 152 | O26wzx | GCGCTGCAATTGCTTATGTA | Wzx-F | [29] |
| TTTCCCCGCAATTTATTCAG | Wzx-R | |||
| 527 | O45wzx | CCGGGTTTCGATTTGTGAAGGTTG | Wzx-F | “ |
| CACAACAGCCACTACTAGGCAGAA | Wzx-R | |||
| 321 | O103wzx | TTGGAGCGTTAACTGGACCT | Wzx-F | “ |
| GCTCCCGAGCACGTATAAG | Wzx-R | |||
| 925 | O126wzx | TTAGCTCTCGTAGAGGCTGGTGTT | Wzx-F | “ |
| ATGTCATTCCTGGGACGCGAATGT | Wzx-R | |||
| 640 | O146wzx | AGGGTGACCATCAACACACTTGGA | wzx-F | “ |
| AGTTCAATACTGTCGCAGCTCCTC | wzx-R | |||
| 566 | O5wzx | AGGGCAATCTTCCGTAATGA | Og5-PCR_F | [30] |
| CCTCTTGGGCTATAAACAACC | Og5-PCR_R | |||
| 448 | orf469 (O8) | CCAGAGGCATAATCAGAAATAACAG | Og8-PCR_F | “ |
| GCAGAGTTAGTCAACAAAAGGTCAG | Og8-PCR_R | |||
| 783 | O6wzy | GGATGACGATGTGATTTTGGCTAAC | Og6-PCR_F | “ |
| TCTGGGTTTGCTGTGTATGAGGC | Og6-PCR_R | |||
| 207 | O55wzy | TCCTTATTTGTGTCGGGGG | Og55-PCR_F | “ |
| CCAGGAAAGCTGCCAATTATC | Og55-PCR_R | |||
| 511 | O75wzy | GAGATATACATGGGGAGGTAGGCT | Og75-PCR_F | “ |
| ACCCGATAATCATATTCTTCCCAAC | Og75-PCR_R | |||
| 457 | O76wzy | TGGCTTTTATGGCGATATGTG | Og76-PCR_F | “ |
| TTGTGAGTATAAGCCCCCCAA | Og76-PCR_R | |||
| 992 | O78wzx | GGTATGGGTTTGGTGGTA | Og78-PCR_F | “ |
| AGAATCACAACTCTCGGCA | Og78-PCR_R | |||
| 167 | O87wzy | GGATGAATGGGGAAAAGCAA | Og87-PCR_F | “ |
| TCACGCGTAAATCTTCAATCC | Og87-PCR_R | |||
| 953 | O91wzy | GCCTGCGATACCAGTATCCTT | Og91-PCR_F | “ |
| CCCCCATAATTGGGATCATAT | Og91-PCR_R | |||
| 241 | O112wzy | CGGGTTAACAGCCCATTTTT | Og112ab-PCR_F | “ |
| CAGCCCCCATTTACCAGTAAT | Og112ab-PCR_R | |||
| 782 | O128wzy | ATGATTTCTTACGGAGTGC | Og128-PCR_F | “ |
| CTCTAACCTAATCCCTCCC | Og128-PCR_R | |||
| 193 | O121wzy | CAAATGGGCGTTAATACAGCC | Og121-PCR_F | “ |
| TTCCACCCATCCAACCTCTAA | Og121-PCR_R | |||
| 288 | ChuA | ATGGTACCGGACGAACCAAC | Chua Bf | [31] |
| TGCCGCCAGTACCAAAGACA | Chua BR | |||
| 211 | yjA | CAAACGTGAAGTGTCAGGAG | Yja BF | “ |
| AATGCGTTCCTCAACCTGTG | Yja BR | |||
| 152 | TspE4. C2 | CACTATTCGTAAGGTCATCC | TspE4.C2 BF | “ |
| AGTTTATCGCTGCGGGTCGC | TspE4.C2 BR | |||
| 400 | arpA | AACGCTATTCGCCAGCTTGC | arpA BF | “ |
| TCTCCCCATACCGTACGCTA | arpA BR | |||
| 301 | Grp E (arpA) | GATTCCATCTTGTCAAAATATGCC | arpA CF | “ |
| GAAAAGAAAAAGAATTCCCAAGAG | arpA CR | |||
| RAPD | M13 | GAGGGTGGCGGTTCT | M13 |
| Serogroups (343) | eae | hly | eae/hly |
|---|---|---|---|
| O8 (158) | 15 (9.5%) | 53 (34%) | 3 (1.8%)) |
| O76 (67) | 7 (10%) | 36 (54%) | 3 (4.5%) |
| O91 (42) | 2 (5%) | 42 (100%) | 2 (5%) |
| O5 (17) | - | 13 (76%) | - |
| O26 (18) | 5 (28%) | 14 (78%) | 5 (28%) |
| O78 (6) | - | - | - |
| O87 (4) | - | 1 (25%) | - |
| O103 (3) | 2 (67%) | 3 (100%) | 2 (67%) |
| O146 (2) | - | - | - |
| O121 (1) | - | 1 (100%) | - |
| Serogroups | Percentage | Stx1 | Stx2 | STX1/stx2 | stx1a | stx1c | stx1c/stx1a | stx2a | stx2b | stx2d | stx2d/2a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O8 (158) | 46% | 48 (30%)) | 107 (68%) | 34 (22%) | 2 (6%) | 46 (96%) | - | 75 (70%) | 5 (5%) | 2 (1.8%) | 18 (17%) |
| O76 (67) | 20% | 58 (87%) | 9 (13%) | 7 (10%) | 2 (3.4%) | 56 (95%) | 1 (1.7%) | 5 (56%) | 4 (44%) | - | - |
| O91 (42) | 12% | 42 (100%) | 42 (100%) | 42 (100%) | 42 (100%) | - | - | - | 42 (100%) | - | - |
| O5 (17) | 5% | 17 (100%) | - | - | - | 17 (100%) | - | - | - | - | - |
| O26 (18) | 5% | 13 (72%) | 12 (67%) | 5 (28%) | 3 (23%) | 10 (77% | - | 12 (100%) | - | - | - |
| O78 (6) | 2% | 6 (100%) | 1 (17%) | 1 (17%) | - | 6 (100%) | - | - | 1 (100%) | - | - |
| O87 (4) | 1% | 2 (50%) | 2 (50%) | - | - | 2 (100%) | - | - | 2 (100%) | - | - |
| O103 (3) | 1% | 3 (100%) | 2 (67%) | 2 (67%) | 1 (33%) | 3 (100%) | 1 (33%) | 2 (100%) | - | - | - |
| O146 (2) | 1% | 1 (50%) | 2 (100%) | - | - | 1 (100%) | - | 2 (100%) | - | - | - |
| O121 (1) | - | 1 (100%) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndegwa, E.; O’Brien, D.; Matthew, K.; Wang, Z.; Kim, J. Shiga Toxin Subtypes, Serogroups, Phylogroups, RAPD Genotypic Diversity, and Select Virulence Markers of Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli Strains from Goats in Mid-Atlantic US. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091842
Ndegwa E, O’Brien D, Matthew K, Wang Z, Kim J. Shiga Toxin Subtypes, Serogroups, Phylogroups, RAPD Genotypic Diversity, and Select Virulence Markers of Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli Strains from Goats in Mid-Atlantic US. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091842
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdegwa, Eunice, Dahlia O’Brien, Kwame Matthew, Zhenping Wang, and Jimin Kim. 2022. "Shiga Toxin Subtypes, Serogroups, Phylogroups, RAPD Genotypic Diversity, and Select Virulence Markers of Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli Strains from Goats in Mid-Atlantic US" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091842
APA StyleNdegwa, E., O’Brien, D., Matthew, K., Wang, Z., & Kim, J. (2022). Shiga Toxin Subtypes, Serogroups, Phylogroups, RAPD Genotypic Diversity, and Select Virulence Markers of Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli Strains from Goats in Mid-Atlantic US. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091842





