Rhodoalgimonas zhirmunskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., a Marine Alphaproteobacterium Isolated from the Pacific Red Alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis: Phenotypic Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Maintenance
2.2. Phenotypic and Chemotaxonomic Characterization
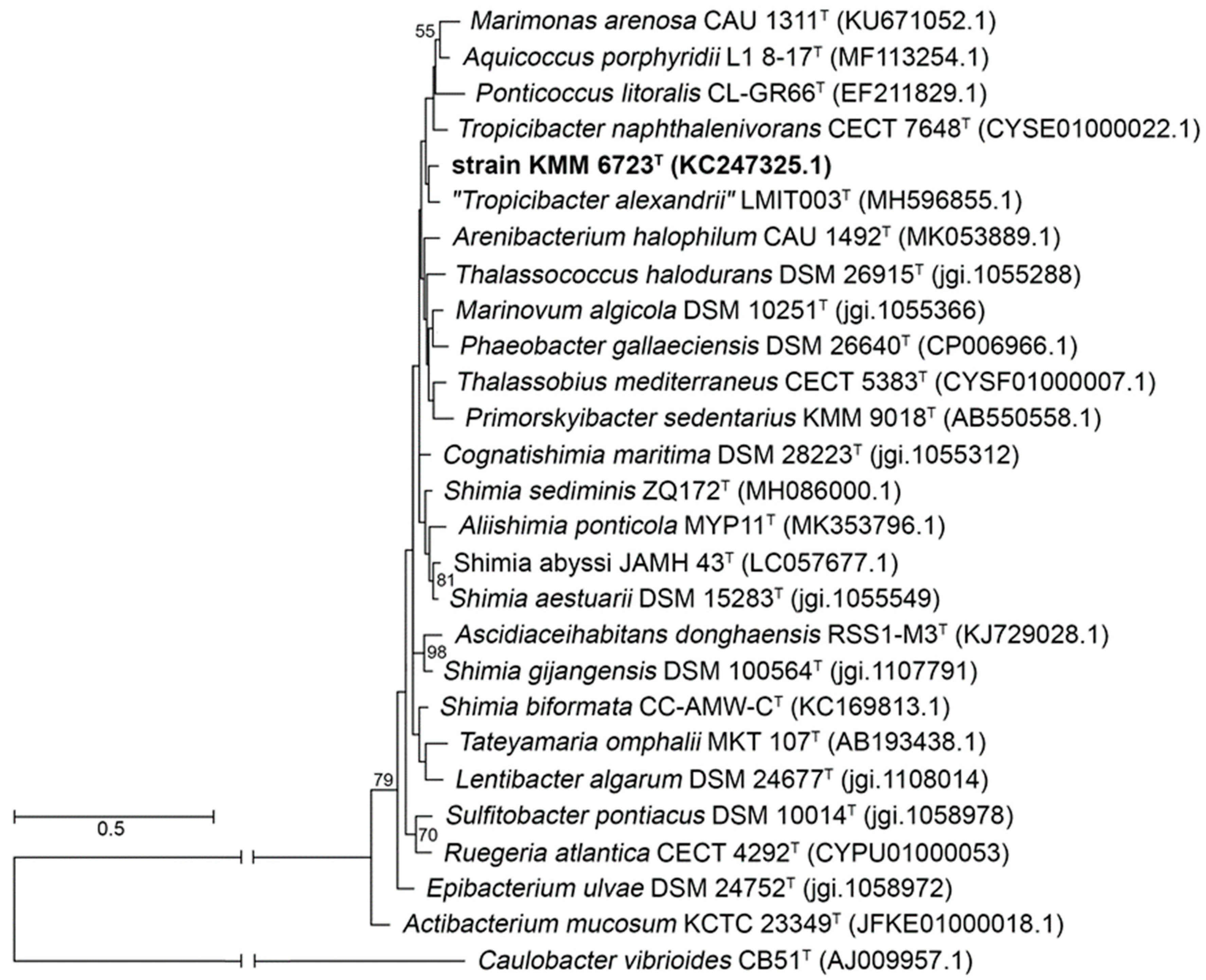
2.3. 16S rRNA and RpoC Sequences and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Genome-Based Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phylogenetic and Phylogenomic Analyses
3.2. Genomic Characteristics and Analysis of Genus-Related Features
3.3. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characteristics
3.4. Chemotaxonomy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbato, M.; Vacchini, V.; Engelen, A.H.; Patania, G.; Mapelli, F.; Borin, S.; Crotti, E. What lies on macroalgal surface: Diversity of polysaccharide degraders in culturable epiphytic bacteria. AMB Express 2022, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagasabhapathy, M.; Sasak, H. Phylogenetic identification of epibiotic bacteria possessing antimicrobial activities isolated from red algal species of Japan. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.N.; Hutchison, K. Diversity and abundance of the bacterial community of the red macroalga Porphyra umbilicalis: Did bacterial farmers produce macroalgae? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.T.; Song, S.L. The effect of grazing on the microbiome of two commercially important agarophytes, Gracilaria firma and G. salicornia (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chang, Y.Q. Algibacillus agarilyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the surface of the red algae Gelidium amansii. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.H.; Zhang, B.N. Comparative genomic analysis of the genus Marinomonas and taxonomic study of Marinomonas algarum sp. nov., isolated from red algae Gelidium amansii. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Xia, Y. Maribacter algarum sp. nov., a new member of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from the red alga Gelidium amansii. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3679–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Jeong, S.E. Maribacter algicola sp. nov., isolated from a marine red alga, Porphyridium marinum, and transfer of Maripseudobacter aurantiacus Chen et al. 2017 to the genus Maribacter as Maribacter aurantiacus comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.N.; Du, Z.Z. Marinomonas agarivorans sp. nov., an agar-degrading marine bacterium isolated from red algae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.H. Flagellimonas algicola sp. nov., isolated from a marine red alga, Asparagopsis taxiformis. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, X.Y.; Wang, K. Psychroserpens luteolus sp. nov., isolated from Gelidium, reclassification of Ichthyenterobacterium magnum as Psychroserpens magnus comb. nov., Flavihalobacter algicola as Psychroserpens algicola comb. nov., Arcticiflavibacter luteus as Psychroserpens luteus comb. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 279. [Google Scholar]
- Kristyanto, S.; Kim, K.R. Tenacibaculum aquimarinum sp. nov., isolated from a marine alga and sea-water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 5477. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, F.B.; Jiang, S. Thalassotalea algicola sp. nov., an alginate-utilizing bacterium isolated from a red al-ga. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, S.E. Hwanghaeella grinnelliae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine red alga. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3544–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Kurilenko, V.V. Characterization of Labrenzia polysiphoniae sp. nov. isolated from red alga Polysiphonia sp. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Kim, S.G. Aquimarina algiphila sp. nov., a chitin degrading bacterium isolated from the red alga Tichocarpus crinitus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Kukhlevskiy, A.D. Aureibaculum algae sp. nov. isolated from the Pacific red alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Balabanova, L.A.; Zhukova, N.V.; Kim, S.J.; Bakunina, I.Y.; Rhee, S.K. Flavobacterium ahnfeltiae sp. nov., a new marine polysaccharide-degrading bacterium isolated from a Pacific red alga. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Kim, S.G. Polaribacter staleyi sp. nov., a polysaccharide-degrading marine bacterium isolated from the red alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, P.; Murray, R.G.E.; Wood, W.A.; Krieg, N.R. Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos, M.L.; Toranzo, A.E. Modified medium for oxidation-fermentation test in the identification of marine bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 40, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smibert, R.M.; Krieg, N.R. Phenotypic characterization. In Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; Gerhardt, P., Murray, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., Krieg, N.R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 607–654. [Google Scholar]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Kim, S.B. Mesonia mobilis sp. nov., isolated from seawater, and emended description of the genus Mesonia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2433–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komagata, K.; Suzuki, K.I. Lipid and cell wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol. 1987, 19, 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomi-cally united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. Modelfinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattam, A.R.; Abraham, D.; Dalay, O.; Disz, T.L.; Driscoll, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; Gillespie, J.J.; Gough, R.; Hix, D.; Kenyon, R.; et al. PATRIC, the bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D581–D591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The enveomics collection: A toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Prepr. 2016, 4, e1900v1. [Google Scholar]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Thomas, A.M.; Beghini, F.; Mengoni, C.; Manara, S.; Manghi, P.; Zhu, Q.; Bolzan, M.; Cumbo, F.; May, U.; et al. Precise phylogenetic analysis of microbial isolates and genomes from meta-genomes using PhyloPhlAn 3.0. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dong, Z.; Fang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Y.Q.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Xia, Q.; et al. OrthoVenn2: A web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W52–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, F.; Luo, Y.; Bie, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y. OrthoVenn3: An integrated platform for exploring and visualizing orthologous data across genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 1, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yohe, T.; Huang, L.; Entwistle, S.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Busk, P.K.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y. dbCAN2: A meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W95–W101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. AntiSMASH 6.0: Improving Cluster Detection and Comparison Capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, J.S.; Whitman, W.B. Phylogenomic analyses of a clade within the roseobacter group suggest taxonomic reassignments of species of the genera Aestuariivita, Citreicella, Loktanella, Nautella, Pelagibaca, Ruegeria, Thalassobius, Thiobacimonas and Tropicibacter, and the proposal of six novel genera. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2393–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Thongphrom, C.; Kim, J.H. Marimonas arenosa gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from sea sand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Kim, K.H. Aquicoccus porphyridii gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a small marine red alga, Porphyridium marinum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qu, Z. Lentibacter algarum gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from coastal water during a massive green algae bloom. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colston, S.M.; Fullmer, M.S.; Beka, L.; Lamy, B.; Gogarten, J.P.; Graf, J. Bioinformatic genome comparisons for taxonomic and phylogenetic assignments using Aeromonas as a test case. mBio 2014, 5, e02136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. MyTaxa: An advanced taxonomic classifier for genomic and metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; da Costa, M.S.; Rooney, A.P.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.W.; De Meyer, S.; et al. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Lapina, M.C.; Bhushan, S.; Mueller-Cajar, O. Identification and characterization of multiple rubisco activases in chemoautotrophic bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceus, J.; Pinel, D.; Desmet, T. Glucosylglycerate phosphorylase, an enzyme with novel specificity involved in compatible solute vetabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01434-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, P.; Boos, W. Characteristics of a ugp-encoded and phoB-dependent glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase which is physically dependent on the ugp transport system of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 4125–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Feature | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly level | Contig | Contig | Contig | Contig |
| Genome size (bp) | 3,754,741 | 4,513,837 | 4,380,839 | 3,293,487 |
| Number of contigs | 73 | 256 | 38 | 21 |
| GC content (mol%) | 62.1 | 63.2 | 63 | 55.5 |
| N50 (bp) | 702,161 | 179,538 | 656,426 | 890,063 |
| L50 (bp) | 2 | 7 | 3 | 2 |
| Coverage | 19x | 100x | 90x | 311.0x |
| Total genes | 3609 | 4542 | 4299 | 3318 |
| Protein coding genes | 3535 | 4373 | 4205 | 3262 |
| rRNAs(5S/16S/23S) | 2/1/1 | 2/1/1 | 1/1/1 | 62/2/2 |
| tRNA | 41 | 42 | 44 | 44 |
| checkM completeness (%) | 98.24 | 100 | 99.42 | 99.69 |
| checkM contamination (%) | 0.04 | 2.6 | 0.34 | 0.31 |
| WGS project | JANFFA01 | VINQ01 | JANHAX01 | FNPR01 |
| Annotated genome assembly | ASM3084892v1 | ASM836910v1 | ASM3084894v1 | IMG-taxon 2693429861 |
| Submitted GenBank assembly | GCA_030848925.1 | GCA_008369105.1 | GCA_030848945.1 | GCA_900107355.1 |
| Number of Subsystems (RAST) | 300 | 324 | 315 | 285 |
| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source of isolation | Marine red alga | Marine red alga | Sea sand | Seawater |
| Colony color | Beige | Whitish | Beige | Whitish |
| Morphology | Rod | Coccus | Rod | Rod |
| Temperature range for growth (°C) *: | 4–40 | 20–40 | 20–37 | 22–28 |
| Salinity range for growth (% NaCl) *: | 0–5 | 0–7 | 0–6 | 3–9 |
| Nitrate reduction | - | - | - | + |
| Acetoin production (3-hydroxybutanone or acetyl methyl carbinol) | - | - | - | + |
| H2S production | - | + | - | - |
| Degradation of: | ||||
| Aesculin | W | - | - | + |
| Gelatin | - | - | + | - |
| Starch | W | - | - | - |
| Tweens 40 and 80 | + | - | - | + |
| Tyrosine | - | + | - | ND |
| Acid production from: | ||||
| D-fructose, D-glucose, maltose, sucrose, D-xylose | - | - | - | + |
| Utilization of: | ||||
| L-arabinose, maltose | + | + | - | + |
| D-cellobiose, D-fructose, | + | - | - | + |
| D-lactose, D-melibiose | + | - | - | ND |
| D-glucose, D-mannose | + | - | - | + |
| D-mannitol | + | - | + | + |
| N-acetylglucosamine | + | - | - | - |
| Adipate | + | - | + | - |
| Citrate | - | - | - | + |
| Gluconate | + | - | + | + |
| Malate | + | + | + | - |
| Phenylacetate | + | + | - | - |
| Susceptibility to: | ||||
| Ampicillin, carbenicillin | + | - | + | + |
| Gentamicin | + | - | + | - |
| Bensylpenicillin | + | - | - | + |
| Kanamycin | + | + | + | - |
| Oxacillin | + | - | - | - |
| Tetracycline | + | + | - | - |
| Vancomycin | + | + | - | + |
| Major polar lipids ** | PC, PG, PE, AL, PL, L | PC, PG, PE, AL, PL, L | PC, PG, PE, AL, GL | PC, PG, PE, AL, L |
| Fatty Acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight fatty acid | ||||
| C15:0 | 1.3 | tr | - | - |
| C16:0 | 8.2 | 7.7 | 4.5 | 12.0 |
| C17:0 | 1.6 | 1.5 | - | 2.0 |
| C18:0 | Tr | 2.3 | 3.9 | 20.0 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid | ||||
| C16:1 ω7c | 1.3 | tr | Tr | 1.0 |
| C18:1 ω7c | 82.1 | 81.8 | 80.6 | 60.0 |
| 11-methyl C18:1 ω7c | Tr | 4.3 | 4.1 | 2.0 |
| Hydroxy fatty acid | ||||
| C10:0 3-OH | - | - | - | 2.0 |
| C12:0 3-OH | 4.5 | 1.0 | 4.0 | - |
| C12:1 3-OH | - | 1.2 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nedashkovskaya, O.; Otstavnykh, N.; Balabanova, L.; Bystritskaya, E.; Kim, S.-G.; Zhukova, N.; Tekutyeva, L.; Isaeva, M. Rhodoalgimonas zhirmunskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., a Marine Alphaproteobacterium Isolated from the Pacific Red Alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis: Phenotypic Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102463
Nedashkovskaya O, Otstavnykh N, Balabanova L, Bystritskaya E, Kim S-G, Zhukova N, Tekutyeva L, Isaeva M. Rhodoalgimonas zhirmunskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., a Marine Alphaproteobacterium Isolated from the Pacific Red Alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis: Phenotypic Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(10):2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102463
Chicago/Turabian StyleNedashkovskaya, Olga, Nadezhda Otstavnykh, Larissa Balabanova, Evgenia Bystritskaya, Song-Gun Kim, Natalia Zhukova, Liudmila Tekutyeva, and Marina Isaeva. 2023. "Rhodoalgimonas zhirmunskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., a Marine Alphaproteobacterium Isolated from the Pacific Red Alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis: Phenotypic Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis" Microorganisms 11, no. 10: 2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102463
APA StyleNedashkovskaya, O., Otstavnykh, N., Balabanova, L., Bystritskaya, E., Kim, S.-G., Zhukova, N., Tekutyeva, L., & Isaeva, M. (2023). Rhodoalgimonas zhirmunskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., a Marine Alphaproteobacterium Isolated from the Pacific Red Alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis: Phenotypic Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis. Microorganisms, 11(10), 2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102463







