Healthcare Equipment and Personnel Reservoirs of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Epidemic Clones in Intensive Care Units in a Tunisian Hospital
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Wards
2.2. Bacteria Cultivation
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
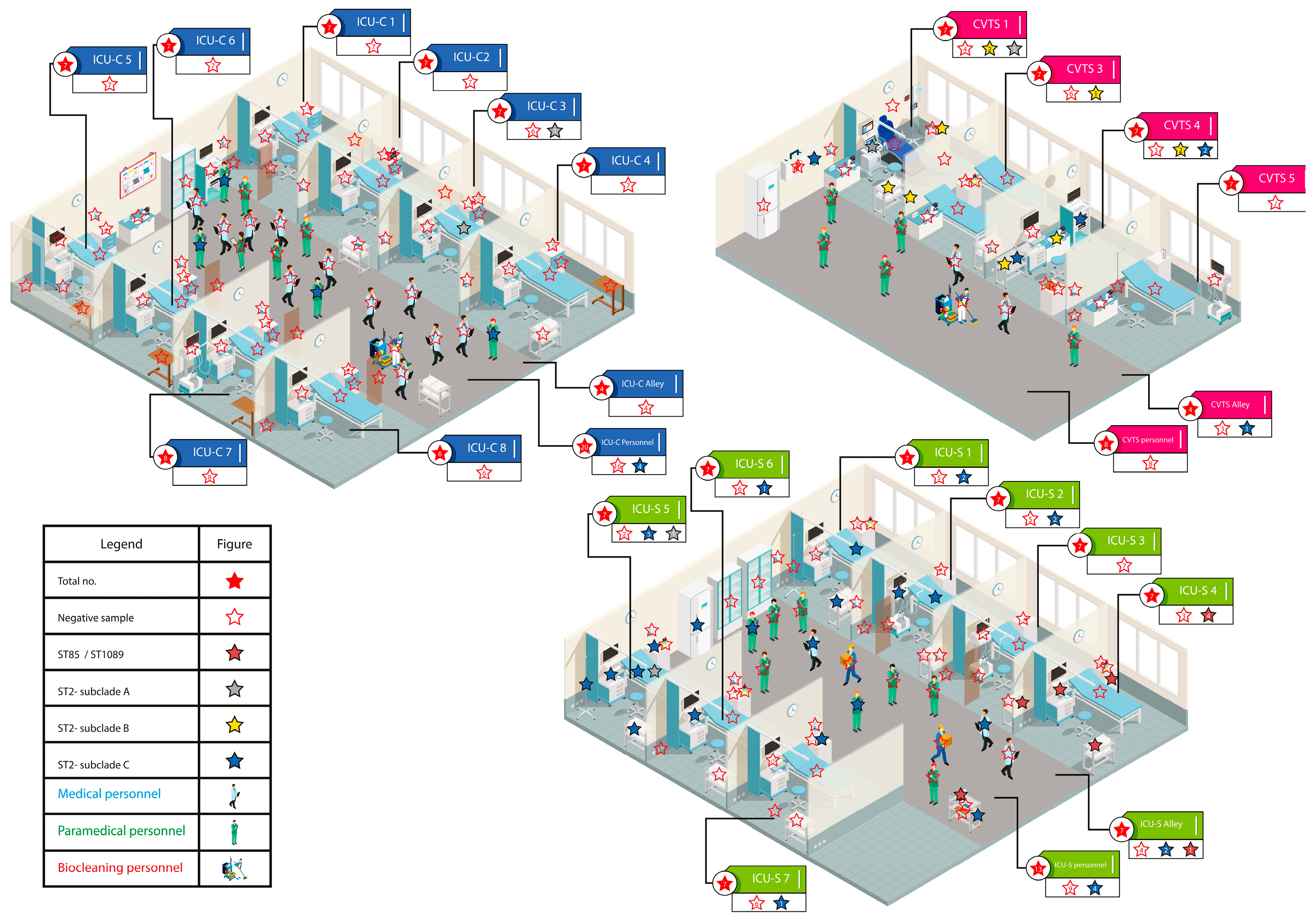
3.1. CRAB Prevalence in ICUs Wards
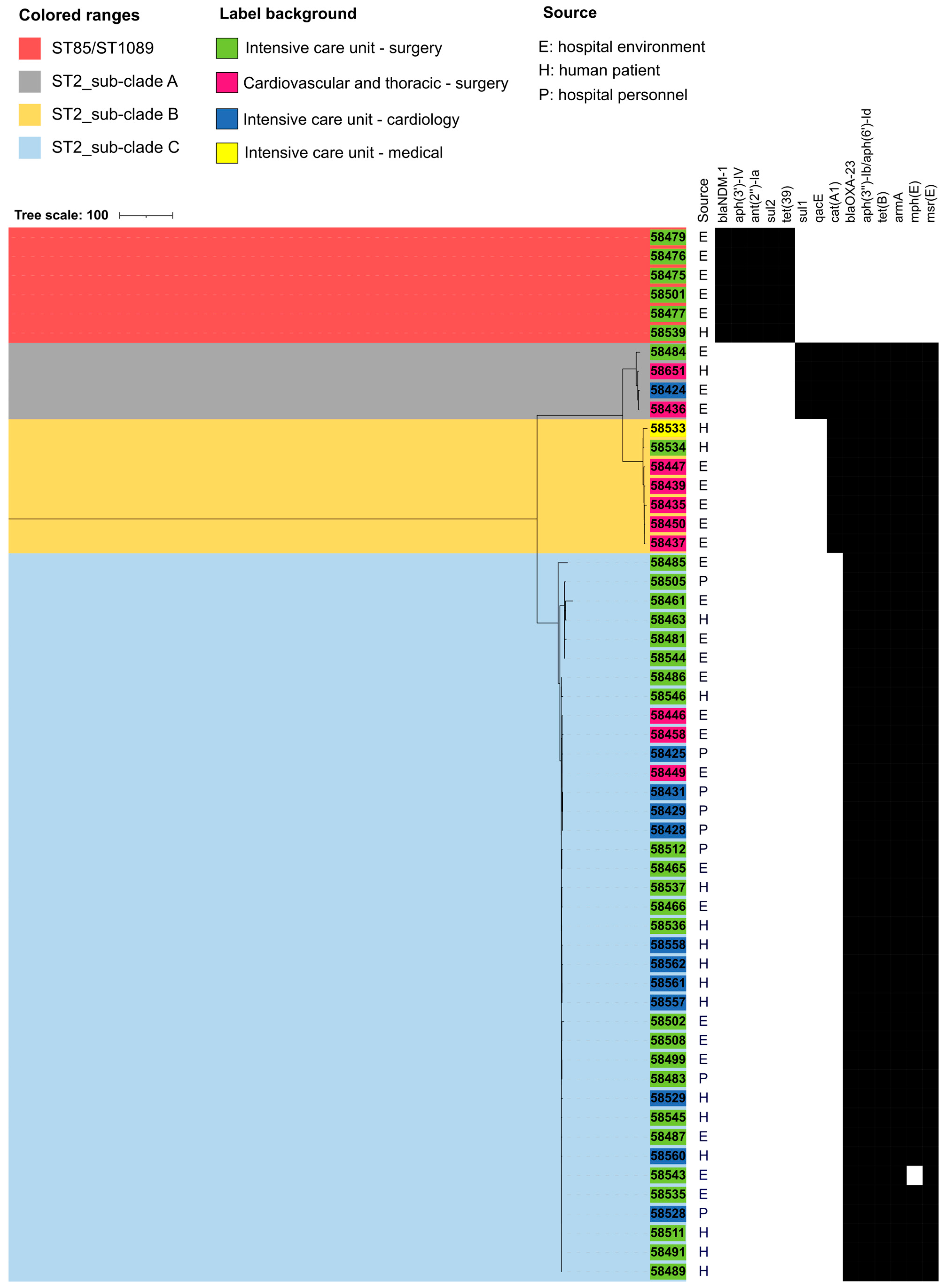
3.2. PyMLST of CRAB Isolates from Hospital Environment, Personnel and Patients
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of CRAB Strains and Antibiotic Resistance Genes
3.4. Genetic Elements Carrying Acquired Antibiotic Resistance Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaidane, N.; Naas, T.; Mansour, W.; Radhia, B.B.; Jerbi, S.; Boujaafar, N.; Bouallegue, O.; Bonnin, R.A. Genomic analysis of in vivo acquired resistance to colistin and rifampicin in Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jian, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A challenge in the intensive care unit. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, J.; Pachon, J. Therapeutic options for Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, K.E.; Maciel, W.G.; Croda, J.; Cayo, R.; Ramos, A.C.; de Sales, R.O.; Kurihara, M.N.L.; Vasconcelos, N.G.; Gales, A.C.; Simionatto, S. A high mortality rate associated with multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ST79 and ST25 carrying OXA-23 in a Brazilian intensive care unit. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Higgins, P.G.; Dammhayn, C.; Hackel, M.; Seifert, H. Global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidian, M.; Nigro, S.J. Emergence, molecular mechanisms and global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogou, V.; Pournaras, S.; Giannouli, M.; Voulgari, E.; Piperaki, E.T.; Zarrilli, R.; Tsakris, A. Evolution of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clonal lineages: A 10 year study in Greece (2000–09). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2767–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathlouthi, N.; Ben Lamine, Y.; Somai, R.; Bouhalila-Besbes, S.; Bakour, S.; Rolain, J.M.; Chouchani, C. Incidence of OXA-23 and OXA-58 Carbapenemases Coexpressed in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in Tunisia. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawfal Dagher, T.; Al-Bayssari, C.; Chabou, S.; Antar, N.; Diene, S.M.; Azar, E.; Rolain, J.M. Investigation of multidrug-resistant ST2 Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from Saint George hospital in Lebanon. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principe, L.; Piazza, A.; Giani, T.; Bracco, S.; Caltagirone, M.S.; Arena, F.; Nucleo, E.; Tammaro, F.; Rossolini, G.M.; Pagani, L.; et al. Epidemic diffusion of OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in Italy: Results of the first cross-sectional countrywide survey. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3004–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apisarnthanarak, A.; Apisarnthanarak, P.; Warren, D.K.; Fraser, V.J. Is central venous catheter tips’ colonization with multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii a predictor for bacteremia? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaladchalam, S.; Diraphat, P.; Utrarachkij, F.; Suthienkul, O.; Samakoses, R.; Siripanichgon, K. Bed rails and endotracheal tube connectors as possible sources for spreading Acinetobacter baumannii in ventilator-associated pneumonia patients. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, T.N.; Lee, S.H.; Huang, C.H.; Lee, C.L.; Chen, W.Y. Risk factors and impact of nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections in the adult intensive care unit: A case-control study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitiriga, V.; Bakalis, J.; Theodoridou, K.; Kanellopoulos, P.; Saroglou, G.; Tsakris, A. Lower risk of bloodstream infections for peripherally inserted central catheters compared to central venous catheters in critically ill patients. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuotto, C.; Grosso, F.; Longo, F.; Balice, M.P.; de Barros, M.C.; Peixe, L.; Donelli, G. Biofilm-Forming Ability and Clonality in Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from Urine Samples and Urinary Catheters in Different European Hospitals. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1057, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschopp, C.; Schneider, A.; Longtin, Y.; Renzi, G.; Schrenzel, J.; Pittet, D. Predictors of Heavy Stethoscope Contamination Following a Physical Examination. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J.; Rutala, W.A.; Miller, M.B.; Huslage, K.; Sickbert-Bennett, E. Role of hospital surfaces in the transmission of emerging health care-associated pathogens: Norovirus, Clostridium difficile, and Acinetobacter species. Am. J. Infect. Control 2010, 38, S25–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, K.A.; Johnson, J.K.; Lee, M.S.; Harris, A.D. Environmental contamination because of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii surrounding colonized or infected patients. Am. J. Infect. Control 2011, 39, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernards, A.T.; Harinck, H.I.; Dijkshoorn, L.; van der Reijden, T.J.; van den Broek, P.J. Persistent Acinetobacter baumannii? Look inside your medical equipment. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2004, 25, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, M.; Quelle, L.S.; Jeric, P.E.; Di Martino, A.; Maimone, S.M. Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on bed rails during an outbreak and during sporadic cases. J. Hosp. Infect. 1999, 42, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Broek, P.J.; Arends, J.; Bernards, A.T.; De Brauwer, E.; Mascini, E.M.; van der Reijden, T.J.; Spanjaard, L.; Thewessen, E.A.; van der Zee, A.; van Zeijl, J.H.; et al. Epidemiology of multiple Acinetobacter outbreaks in The Netherlands during the period 1999–2001. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Betchen, M.; Giovinco, H.M.; Curry, M.; Luu, J.; Fraimow, H.; Carabetta, V.J.; Nahra, R. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Hospital Antiseptics on Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Understanding the Relationship between Microbicide and Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, F.L.; Liu, Q.; Shah, B.; Clift, H.E.; Naidu, V.; Li, L.; Prity, F.T.; Mabbutt, B.C.; Hassan, K.A.; Paulsen, I.T. The Acinetobacter baumannii disinfectant resistance protein, AmvA, is a spermidine and spermine efflux pump. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, A.M.; Alsultan, A.A.; Ansari, M.A.; Alnimr, A.M. Biofilm-Formation in Clonally Unrelated Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates. Pathogens 2020, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.; Imperi, F.; Carattoli, A.; Visca, P. Deciphering the multifactorial nature of Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenicity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Seifert, H.; Snelling, A.M.; Heritage, J.; Hawkey, P.M. Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on dry surfaces: Comparison of outbreak and sporadic isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1938–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cole, C.G.; DuPai, C.D.; Davies, B.W. Protein Aggregation is Associated with Acinetobacter baumannii Desiccation Tolerance. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, L.; Tao, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J. High DNA Uptake Capacity of International Clone II Acinetobacter baumannii Detected by a Novel Planktonic Natural Transformation Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, S.; O’Connor, J.A.; Lucey, B.; Sleator, R.D. Hospital Reservoirs of Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter Species—The Elephant in the Room! Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Health Care Facilities. 2017, p. 74. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/259462 (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- CLSI/EUCAST; The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Recommendations for MIC Determination of Colistin (Polymyxin E) as Recommended by the Joint CLSI-EUCAST Polymyxin Breakpoints Working Group; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, P.G.; Prior, K.; Harmsen, D.; Seifert, H. Development and evaluation of a core genome multilocus typing scheme for whole-genome sequence-based typing of Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Sadek, M.; Nordmann, P. Contribution of PER-Type and NDM-Type beta-Lactamases to Cefiderocol Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0087721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillot, S.; Oueslati, S.; Vuillemenot, J.B.; Bour, M.; Iorga, B.I.; Triponney, P.; Plesiat, P.; Bonnin, R.A.; Naas, T.; Jeannot, K.; et al. Genomic characterization of an NDM-9-producing Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolate and role of Glu152Lys substitution in the enhanced cefiderocol hydrolysis of NDM-9. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1253160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, T.; Gerbaud, G.; Bouvet, P.; Vieu, J.F.; Courvalin, P. Dissemination of amikacin resistance gene aphA6 in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, V.; Salamov, A.A. Automatic Annotation of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomic Sequences. In Metagenomics and Its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine and Environmental Studies; Li, R.W., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, D.R.; Cox, G.; D’Erasmo, M.P.; Shakya, T.; Meck, C.; Mohd, N.; Wright, G.D.; Murelli, R.P. Inhibition of the ANT(2″)-Ia resistance enzyme and rescue of aminoglycoside antibiotic activity by synthetic alpha-hydroxytropolones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4943–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, N.; Blokesch, M. Pilus Production in Acinetobacter baumannii Is Growth Phase Dependent and Essential for Natural Transformation. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e00034-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaras, A.P.; Dorsey, C.W.; Edelmann, R.E.; Actis, L.A. Attachment to and biofilm formation on abiotic surfaces by Acinetobacter baumannii: Involvement of a novel chaperone-usher pili assembly system. Microbiology 2003, 149, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, S.; Hall, R.M. Distribution of the blaOXA-23-containing transposons Tn2006 and Tn2008 in Australian carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2409–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, S.J.; Hall, R.M. Antibiotic resistance islands in A320 (RUH134), the reference strain for Acinetobacter baumannii global clone 2. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, G.A.; Holt, K.E.; Bentley, S.D.; Hsu, L.Y.; Hall, R.M. Variants of AbGRI3 carrying the armA gene in extensively antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from Singapore. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Boulanger, A.; Schrenzel, J.; Kaase, M.; Nordmann, P. Tn125-related acquisition of blaNDM-like genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Koong, J.; Holt, K.E.; Hall, R.M.; Hamidian, M. Detection and Typing of Plasmids in Acinetobacter baumannii Using rep Genes Encoding Replication Initiation Proteins. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0247822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, F.; Endimiani, A.; Bonomo, R.A. Why are we afraid of Acinetobacter baumannii? Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2008, 6, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, U.; Amir, O.; Rodriguez-Bano, J. Healthcare-associated infections in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis of point prevalence studies. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 2022, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghnieh, R.A.; Kanafani, Z.A.; Tabaja, H.Z.; Sharara, S.L.; Awad, L.S.; Kanj, S.S. Epidemiology of common resistant bacterial pathogens in the countries of the Arab League. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e379–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, W.; Bouallegue, O.; Jeday, S.; Naija, W.; Boujaafar, N. Clinical and epidemiological characterization of infections due to imipenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii at the university hospital Sahloul, Tunisia. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2007, 65, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, W.; Bouallegue, O.; Dahmen, S.; Boujaafar, N. Characterization of the resistance mechanism to beta-lactams in Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated in the university hospital Sahloul in Tunisia (2005). Pathol. Biol. 2008, 56, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Othman, A.; Zribi, M.; Masmoudi, A.; Abdellatif, S.; Ben Lakhal, S.; Fendri, C. Multiresistance and endemic status of acinetobacter baumannii associated with nosocomial infections in a tunisian hospital: A critical situation in the intensive care units. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, A.; Achour, W.; Cherif, A.; Hmida, H.B.; Afif, F.B.; Jabnoun, S.; Khrouf, N.; Hassen, A.B. Outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii in a neonatal intensive care unit: Antimicrobial susceptibility and genotyping analysis. Ann. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrouk, A.; Grosso, F.; Botelho, J.; Achour, W.; Ben Hassen, A.; Peixe, L. GES-14-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Tunisia Are Associated with a Typical Middle East Clone and a Transferable Plasmid. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00142-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrouk, A.; Chebbi, Y.; Raddaoui, A.; Krir, A.; Messadi, A.A.; Achour, W.; Thabet, L. Clonal spread of PER-1 and OXA-23 producing extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii during an outbreak in a burn intensive care unit in Tunisia. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2020, 67, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellouli, A.; Maamar, B.; Bouzakoura, F.; Messadi, A.A.; Thabet, L. Colonisation et infection à Acinetobacter Baumannii dans une unité de réanimation des brûlés en Tunisie. Ann. Burn. Fire Disasters 2021, 34, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Maamar, E.; Alonso, C.A.; Ferjani, S.; Jendoubi, A.; Hamzaoui, Z.; Jebri, A.; Saidani, M.; Ghedira, S.; Torres, C.; Boubaker, I.B. NDM-1- and OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from intensive care unit patients in Tunisia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjani, S.; Kanzari, L.; Maamar, E.; Hamzaoui, Z.; Rehaiem, A.; Ferjani, A.; Boutiba-Ben Boubaker, I. Extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii co-producing VIM-2 and OXA-23 in intensive care units: Results of a one-day point prevalence in a Tunisian hospital. Infect. Dis. Now 2022, 52, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, H.B.; Domingues, S.; Silveira, E.; Kadri, Y.; Rosario, N.; Mastouri, M.; Da Silva, G.J. Molecular characterization of carbapenemases of clinical Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex isolates from a University Hospital in Tunisia. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Cuzon, G.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clone, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 822–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, K.; Urrutikoetxea-Gutierrez, M.; Vidal-Garcia, M.; Diaz de Tuesta Del Arco, J.L.; Sanchez-Urtaza, S.; Wille, J.; Seifert, H.; Higgins, P.G.; Gallego, L. First report of New Delhi Metallo-beta-Lactamase-6 (NDM-6) in a clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolate from Northern Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafer, M.M.; Hussein, A.F.A.; Al-Agamy, M.H.; Radwan, H.H.; Hamed, S.M. Genomic characterization of extensively drug-resistant NDM-producing Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates with the emergence of novel blaADC-257. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 736982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Leptihn, S.; Yu, Y.; Hua, X.; Fu, Y. Description of a rare pyomelanin-producing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strain coharboring chromosomal OXA-23 and NDM-1. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0214422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, J.; Nordmann, P.; Bouvier, M.; Kerbol, A.; Poirel, L. Dissemination of ArmA- and OXA-23-co-producing Acinetobacter baumannii Global Clone 2 in Switzerland, 2020–2021. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracquadanio, S.; Bonomo, C.; Marino, A.; Bongiorno, D.; Privitera, G.F.; Bivona, D.A.; Mirabile, A.; Bonacci, P.G.; Stefani, S. Acinetobacter baumannii and cefiderocol, between cidality and adaptability. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0234722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Cai, Y. Resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam and underlying mechanisms. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain | Ward | Original Ward | Pathology | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58546 | ICU-S | ER | Head trauma | IMI, COL, VAN | Transferred |
| 58534 | ICU-S | - | - | - | - |
| 58535 | ICU-S | Surgery | Septic shock | IMI, AMI, FLUC | Died |
| 58536 | ICU-S | ER | Head/chest trauma | AMC, GEN | Transferred |
| 58537 | ICU-S | Surgery | Post-surgery sepsis | CTX, GEN, TAZ, AMI, MEM, VAN | Died |
| 58539 | ICU-S | - | - | - | - |
| 58543 | ICU-S | ER | Hemoperitoneum | TAZ, CIP, IMI, COL, VAN, AMC | Died |
| 58544 | ICU-S | ER | Pneumothorax | AMC | Dismissed |
| 58545 | ICU-S | ER | Polytrauma | IMI, COL, VAN | Dismissed |
| 58557 | ICU | COVID unit | ARD | IMI, COL, VAN | Dismissed |
| 58558 | ICU | ER | ARD | IMI, COL | Died |
| 58560 | ICU | Nabeul Hospital | ARD | IMI, COL | Died |
| 58561 | ICU | COVID unit | ARD | IMI, COL | Died |
| 58562 | ICU | COVID unit | ARD | COL, AZI | - |
| 58651 | CVTS | Cardiology | Surgical valve replacement | IMI, COL, AMI | Dismissed |
| 58528 | M-ICU | ER | ARD | TAZ, CIP, TEC | Dismissed |
| 58529 | M-ICU | - | - | - | - |
| 58533 | Orthopedics | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azaiez, S.; Haenni, M.; Cheikh, A.B.; Chalbi, M.S.; Messaoudi, A.; Tilouch, L.; Bahri, S.; Drapeau, A.; Saras, E.; Mtibâa, M.; et al. Healthcare Equipment and Personnel Reservoirs of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Epidemic Clones in Intensive Care Units in a Tunisian Hospital. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112637
Azaiez S, Haenni M, Cheikh AB, Chalbi MS, Messaoudi A, Tilouch L, Bahri S, Drapeau A, Saras E, Mtibâa M, et al. Healthcare Equipment and Personnel Reservoirs of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Epidemic Clones in Intensive Care Units in a Tunisian Hospital. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112637
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzaiez, Sana, Marisa Haenni, Asma Ben Cheikh, Mohamed Sahbi Chalbi, Aziza Messaoudi, Lamia Tilouch, Sana Bahri, Antoine Drapeau, Estelle Saras, Mariem Mtibâa, and et al. 2023. "Healthcare Equipment and Personnel Reservoirs of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Epidemic Clones in Intensive Care Units in a Tunisian Hospital" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112637
APA StyleAzaiez, S., Haenni, M., Cheikh, A. B., Chalbi, M. S., Messaoudi, A., Tilouch, L., Bahri, S., Drapeau, A., Saras, E., Mtibâa, M., Zouaoui, R., Said, H., Madec, J.-Y., Lupo, A., & Mansour, W. (2023). Healthcare Equipment and Personnel Reservoirs of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Epidemic Clones in Intensive Care Units in a Tunisian Hospital. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112637







