Effects of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Challenge on Jejunal Morphology and Microbial Community Profiles in Weaned Crossbred Piglets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Serum Parameters Analysis
2.5. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.6. Periodic Acid–Schiff Staining
2.7. 16S rDNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of ETEC Challenge on Growth Performance and Fecal Score
3.2. Effect of ETEC Challenge on Serum Biochemistry
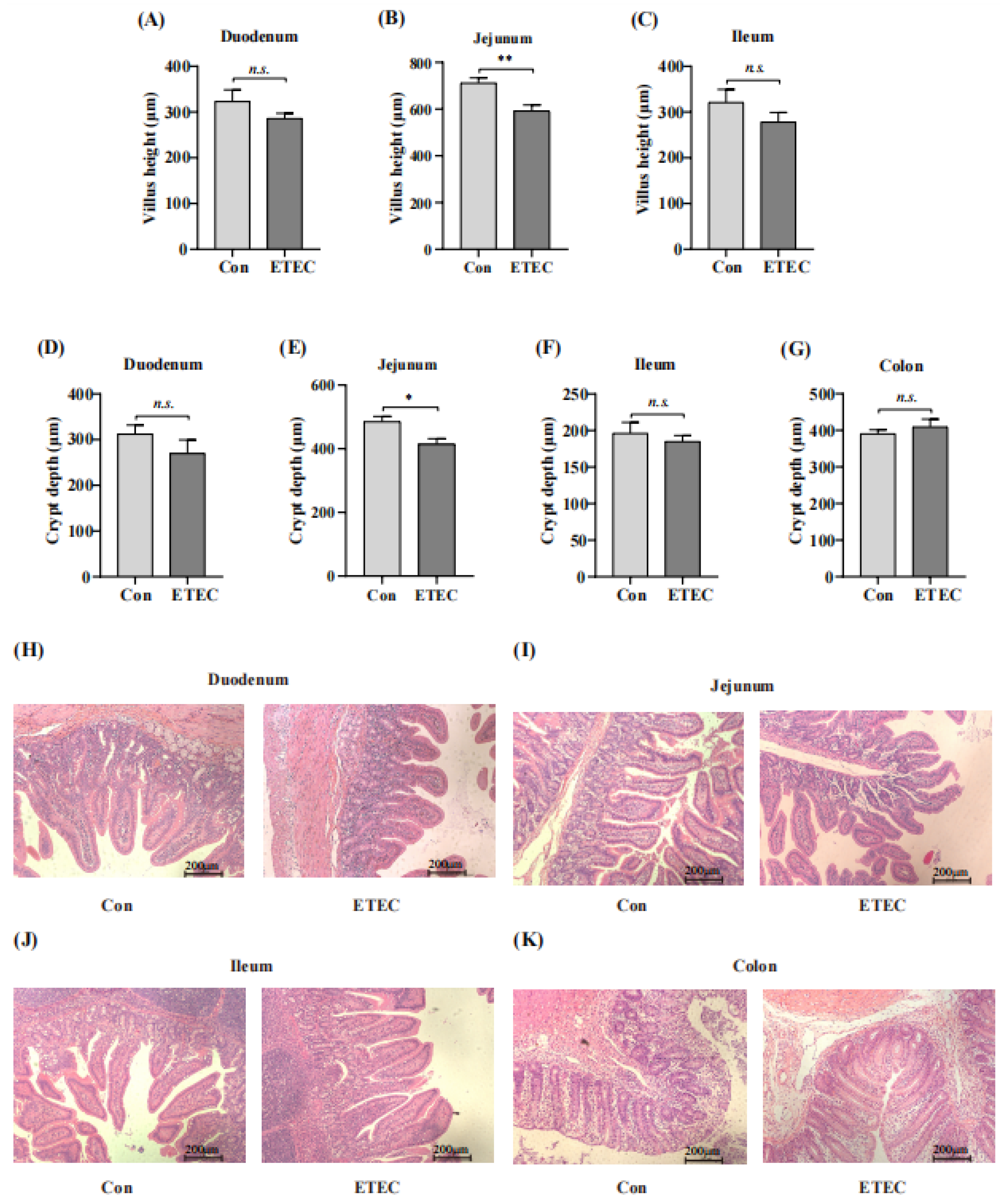
3.3. Effect of ETEC Challenge on Intestinal Segments
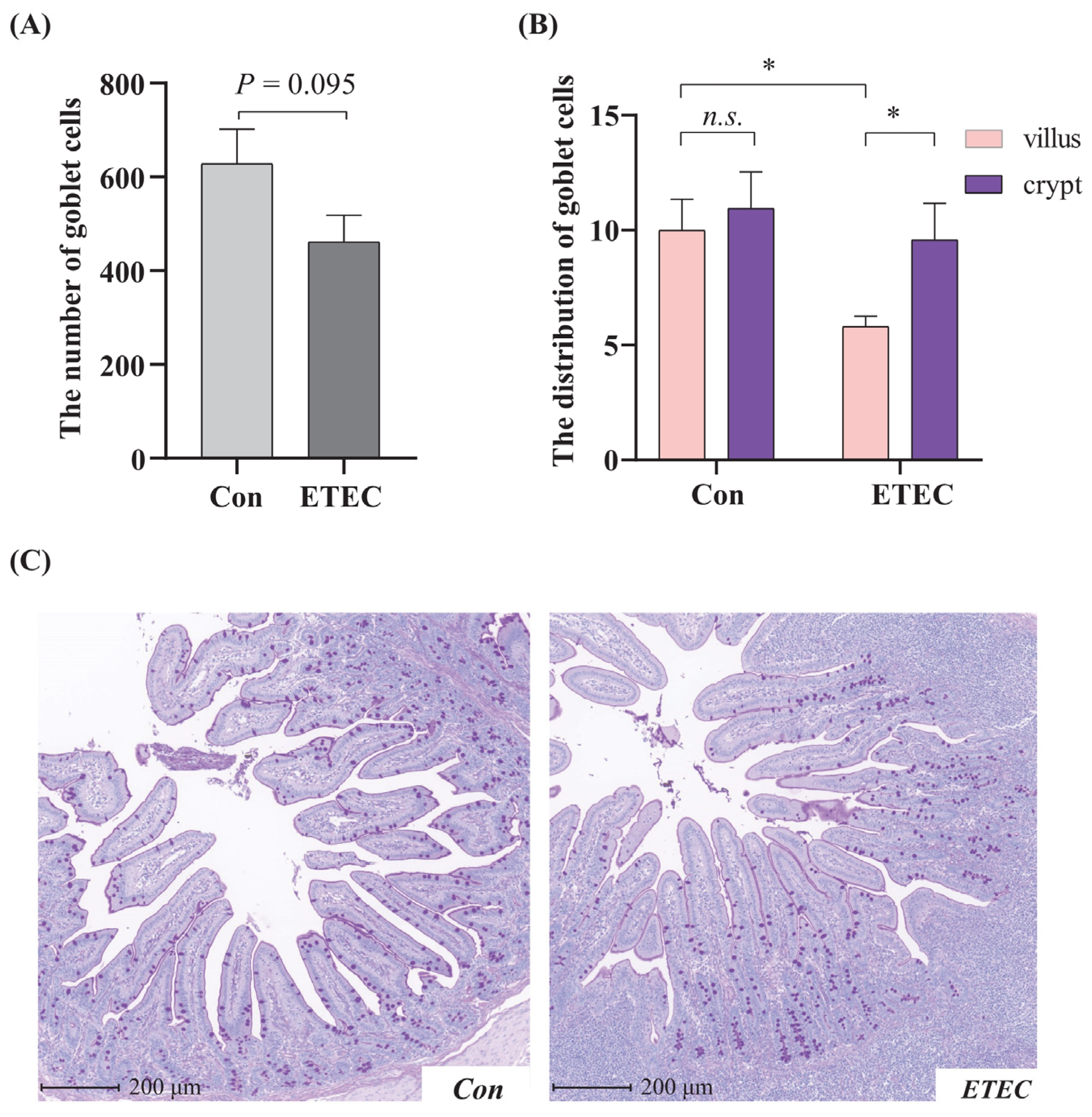
3.4. Effect of ETEC Challenge on Goblet Cell in Jejunum
3.5. Effect of ETEC Challenge on Jejunal Microbiome
4. Discussion
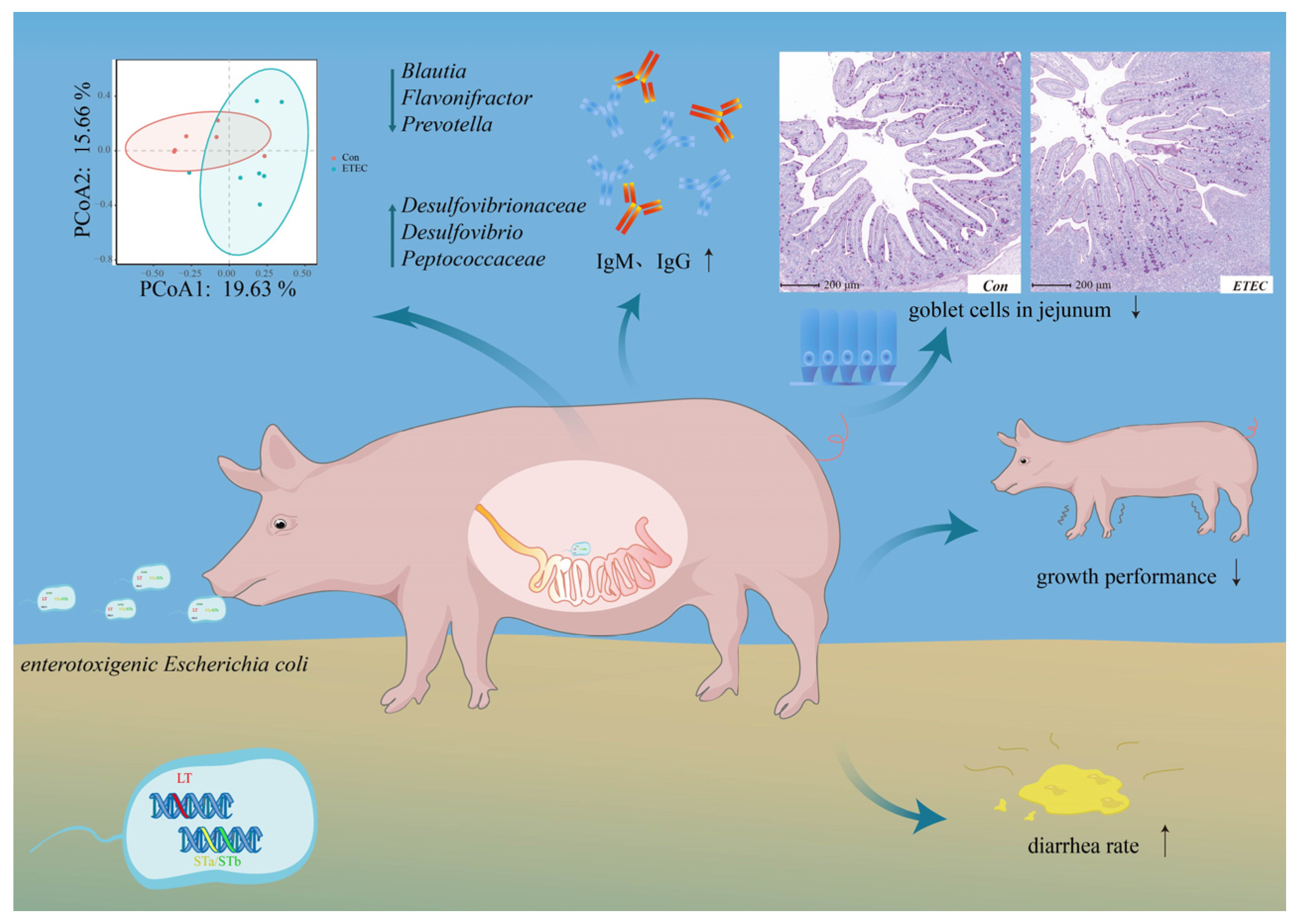
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Gao, L.M.; Liu, Y.L.; Xie, C.; Cai, L.; Xu, K.; Zhou, X.H. Maternal dietary uridine supplementation reduces diarrhea incidence in piglets by regulating the intestinal mucosal barrier and cytokine profiles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3709–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybschmann, G.; Ersbøll, A.; Vigre, H.; Baadsgaard, N.; Houe, H. Herd-level risk factors for antimicrobial demanding gastrointestinal diseases in Danish herds with finisher pigs: A register-based study. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 98, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujinaka, T.; Kishibuchi, M.; Iijima, S.; Yano, M.; Monden, M. Nucleotides and intestine. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1999, 23, S74–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjei, A.A.; Jones, J.T.; Enriquez, F.J.; Yamamoto, S. Dietary nucleosides and nucleotides reduce Cryptosporidium parvum infection in dexamethasone immunosuppressed adult mice. Exp. Parasitol. 1999, 92, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, J.M.; Nadeau, E.; Gyles, C.L. Escherichia coli in postweaning diarrhea in pigs: An update on bacterial types, pathogenesis, and prevention strategies. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2005, 6, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Faruque, A.; Sack, R.B. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in developing countries: Epidemiology, microbiology, clinical features, treatment, and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 465–483. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, D.; Yang, X.; Ju, W.; Huang, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, W. Molecular analysis and antimicrobial susceptibility of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from diarrheal patients. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 81, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Yin, J.; Chen, S.; Duan, J.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; Li, N.; Peng, Y.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y. Proteome analysis for the global proteins in the jejunum tissues of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-infected piglets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.; Mazumder, A. Prevalence of diarrhea-associated virulence genes and genetic diversity in Escherichia coli isolates from fecal material of various animal hosts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7371–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, A.; Gibellini, M.; Gin, T.; Vangroenweghe, F.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Bauerfeind, R.; Bonilauri, P.; Labarque, G.; Hidalgo, A. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoja-Don Juan, C.A.; Gomez-Verduzco, G.; Marquez-Mota, C.C.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Kwon, Y.M.; Cortes-Cuevas, A.; Arce-Menocal, J.; Martinez-Gomez, D.; Avila-Gonzalez, E. Productive Performance and Cecum Microbiota Analysis of Broiler Chickens Supplemented with beta-Mannanases and Bacteriophages—A Pilot Study. Animals 2022, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Yang, H.; Yin, Y. The relationship between villous height and growth performance, small intestinal mucosal enzymes activities and nutrient transporters expression in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Maclaren, O.J.; Fletcher, A.G.; Muraro, D.; Kreuzaler, P.A.; Byrne, H.M.; Maini, P.K.; Watson, A.J.; Pin, C. Cell proliferation within small intestinal crypts is the principal driving force for cell migration on villi. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.; Clark, J.E.; Overman, B.L.; Tozel, C.C.; Huang, J.H.; Rivier, J.E.; Blikslager, A.T.; Moeser, A.J. Early weaning stress impairs development of mucosal barrier function in the porcine intestine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G352–G363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, S.; Bin, P.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, G. Jejunal Metabolic Responses to Escherichia coli Infection in Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Interferes FATP4-Dependent Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake of Intestinal Epithelial Enterocytes via Phosphorylation of ERK1/2-PPARgamma Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Lu, P.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Lahaye, L.; Santin, E.; Liu, S.; Nyachoti, M. Effects of a microencapsulated formula of organic acids and essential oils on nutrient absorption, immunity, gut barrier function, and abundance of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 in weaned piglets challenged with E. coli F4. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, T.; Zhan, N.; Sun, T.; Shan, A. Effects of the antimicrobial peptide WK3 on diarrhea, growth performance and intestinal health of weaned piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Food Nutr. Res. 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Peng, X.; Xu, Q.; Xuan, Y.; Han, F.; Tian, G.; Fang, Z.; Lin, Y.; et al. Postnatal nutritional restriction affects growth and immune function of piglets with intra-uterine growth restriction. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Qi, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, T. Antioxidant potential of Pediococcus pentosaceus strains from the sow milk bacterial collection in weaned piglets. Microbiome 2022, 10, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.Y.; Ji, S.K.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, J.J.; Cao, Z.J.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, S.L. Dynamic change of the gastrointestinal bacterial ecology in cows from birth to adulthood. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.Y.; Fan, J.M.; Hu, A.K.; Su, H.Z.; Yang, J.H.; Huang, L.M.; Yan, F.R.; Zhang, H.P.; Zeng, Y.M. Disruption of sleep architecture in Prevotella enterotype of patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Brain. Behav. 2019, 9, e01287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Liu, G.; Yin, J.; Chen, S.; Li, T.; Kong, X.; Peng, Y.; Yin, Y.; Hardwidge, P.R. Draft Genome Sequence of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strain W25K. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00593-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, G.A.; Blavi, L.; Cross, T.L.; Lee, A.H.; Swanson, K.S.; Stein, H.H. Inclusion of the direct-fed microbial Clostridium butyricum in diets for weanling pigs increases growth performance and tends to increase villus height and crypt depth, but does not change intestinal microbial abundance. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skz372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Du, L.; Ding, B.; Hou, Y.; Gong, J.; Wu, T. Injury and mechanism of recombinant E. coli expressing STa on piglets colon. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeser, A.J.; Pohl, C.S.; Rajput, M. Weaning stress and gastrointestinal barrier development: Implications for lifelong gut health in pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhao, P.F.; Ma, X.K.; Shang, Q.H.; Xu, Y.T.; Long, S.F.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, F.M.; Piao, X.S. Probiotic supplementation protects weaned pigs against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 challenge and improves performance similar to antibiotics. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalles, J.P.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Stokes, C.R. Nutritional management of gut health in pigs around weaning. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.M.; Crenshaw, J.D.; Polo, J. The biological stress of early weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallès, J.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Stokes, C.R. Weaning—A challenge to gut physiologists. Livest. Sci. 2007, 108, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Wu, W.; Pang, S.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Coimmunization with Two Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Fimbrial Multiepitope Fusion Antigens Induces the Production of Neutralizing Antibodies against Five ETEC Fimbriae (F4, F5, F6, F18, and F41). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00217-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frydendahl, K. Prevalence of serogroups and virulence genes in Escherichia coli associated with postweaning diarrhoea and edema disease in pigs and a comparison of diagnostic approaches. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 85, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puno-Sarmiento, J.; Medeiros, L.; Chiconi, C.; Martins, F.; Pelayo, J.; Rocha, S.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, M.; Zanutto, M.; Kobayashi, R.; et al. Detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from dogs and cats in Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Munson, G.P.; Rasko, D.A.; Sommerfelt, H.; Steinsland, H. Molecular mechanisms of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. Microbes Infect 2010, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imberechts, H.; Bertschinger, H.U.; Stamm, M.; Sydler, T.; Pohl, P.; De Greve, H.; Hernalsteens, J.P.; Van Montagu, M.; Lintermans, P. Prevalence of F107 fimbriae on Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with oedema disease or postweaning diarrhoea. Vet. Microbiol. 1994, 40, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salajka, E.; Salajkova, Z.; Alexa, P.; Hornich, M. Colonization factor different from K88, K99, F41 and 987P in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from postweaning diarrhoea in pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 1992, 32, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Kumar, P.; Vickers, T.J.; Sheikh, A.; Lewis, W.G.; Rasko, D.A.; Sistrunk, J.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli secretes a highly conserved mucin-degrading metalloprotease to effectively engage intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Han, F.; Huang, X.; Rong, Y.; Yi, H.; Wang, Y. Changes in gut microbial populations, intestinal morphology, expression of tight junction proteins, and cytokine production between two pig breeds after challenge with Escherichia coli K88: A comparative study. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5614–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tan, B.; Xiong, X.; Li, F.; Ren, W.; Kong, X.; Qiu, W.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Yin, Y. Methionine deficiency reduces autophagy and accelerates death in intestinal epithelial cells infected with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meer, K.; Smolders, H.C.; Meesterburrie, J.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.; Voorbij, H.A.; Okken, A.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Kulik, W. A single food bolus stimulates albumin synthesis in growing piglets. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000, 31, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, X.; Ju, N.; Wang, Z.; Sui, L.; Wang, L.; Qiao, X.; Cui, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Immune Responses in Pregnant Sows Induced by Recombinant Lactobacillus johnsonii Expressing the COE Protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Provide Protection for Piglets against PEDV Infection. Viruses 2021, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, J.; Liao, S.; Duan, Y.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; He, X.; Fan, Z. Effects of Dietary Isomaltooligosaccharide Levels on the Gut Microbiota, Immune Function of Sows, and the Diarrhea Rate of Their Offspring. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 588986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) total RNA against ETEC challenge in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.; Rowe, J.C.; Kim, E.; Varikuti, S.; Steiner, H.E.; Zaghawa, A.; Hassan, H.; Cormet-Boyaka, E.; Satoskar, A.R.; Boyaka, P.N. Inhibitors of elastase stimulate murine B lymphocyte differentiation into IgG- and IgA-producing cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Sesquen, Y.E.; Tinajeros, F.; Bern, C.; Galdos-Cardenas, G.; Malaga, E.S.; Valencia Ayala, E.; Hjerrild, K.; Clipman, S.J.; Lescano, A.G.; Bayangos, T.; et al. The Immunoglobulin M-Shed Acute Phase Antigen (SAPA)-test for the Early Diagnosis of Congenital Chagas Disease in the Time of the Elimination Goal of Mother-to-Child Transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e477–e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breard, E.; Gorlier, A.; Viarouge, C.; Donnet, F.; Sailleau, C.; Schulz, C.; Hoffmann, B.; Comtet, L.; Beer, M.; Zientara, S.; et al. Evaluation of an IGM-specific ELISA for early detection of bluetongue virus infections in domestic ruminants sera. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, L.E.; Davis, M.J.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Amsen, D.; Dascher, C.C.; Ryffel, B.; Swanson, J.A.; Muller, M.; Blander, J.M. Detection of prokaryotic mRNA signifies microbial viability and promotes immunity. Nature 2011, 474, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbet, G.; Sander, L.E.; Geswell, M.; Leonardi, I.; Blander, J.M.J.I. Sensing Microbial Viability through Bacterial RNA Augments T Follicular Helper Cell and Antibody Responses. Immunity 2018, 48, 584–598.e5. [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado, P.; Peh, C.A. LL-37 promotes rapid sensing of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides by B lymphocytes and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z. Effect of dietary lactoferrin on the immune functions and serum iron level of weanling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wei, S.; Xu, B.; Hao, L.; Su, W.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y. Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium co-fermented feed regulates lactating sow’s performance, immune status and gut microbiota. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschetto, R.; Clemente, N.; Pagni, A.; Esposito, T.; Longhini, F.; Mercalli, F.; Boggio, E.; Boldorini, R.; Chiocchetti, A.; Dianzani, U.; et al. A double blind randomized experimental study on the use of IgM-enriched polyclonal immunoglobulins in an animal model of pneumonia developing shock. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Yin, C.; Comi, M.; Agazzi, A.; Perricone, V.; Li, X.; Jiang, X. Live Yeast Supplementation in Gestating and Lactating Primiparous Sows Improves Immune Response in Dams and Their Progeny. Animals 2022, 12, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elluru, S.R.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. The protective role of immunoglobulins in fungal infections and inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Tang, S.; Xiao, W.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, M.; Kang, J. Magnolol and honokiol regulate the calcium-activated potassium channels signaling pathway in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 755, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sole, F.; Babich, V.; Moe, O.W. The calcineurin homologous protein-1 increases Na(+)/H(+) -exchanger 3 trafficking via ezrin phosphorylation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Barber, D.L. A calcineurin homologous protein inhibits GTPase-stimulated Na-H exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12631–12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, T.; Su, X.; Wakabayashi, S.; Shigekawa, M.J. Calcineurin Homologous Protein as an Essential Cofactor for Na+/H+ Exchangers. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17367–17372. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Odle, J.; Lin, X.; Jacobi, S.K.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Z.; Hou, Y. Fish oil enhances intestinal integrity and inhibits TLR4 and NOD2 signaling pathways in weaned pigs after LPS challenge. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; He, J. Dietary chlorogenic acid supplementation affects gut morphology, antioxidant capacity and intestinal selected bacterial populations in weaned piglets. Food. Funct. 2018, 9, 4968–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibner, J.J.; Richards, J.D. The Digestive System: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2004, 13, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pluske, J.R.; Hampson, D.J.; Williams, I.H. Factors influencing the structure and function of the small intestine in the weaned pig: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1997, 51, 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, D.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, S.; Odle, J.; Lin, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, F.; Hou, Y.; Leng, W. Dietary supplementation of aspartate enhances intestinal integrity and energy status in weanling piglets after lipopolysaccharide challenge. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Ramsamooj, S.; Liang, R.J.; Katti, A.; Pozovskiy, R.; Vasan, N.; Hwang, S.K.; Nahiyaan, N.; Francoeur, N.J.; Schatoff, E.M.; et al. Dietary fructose improves intestinal cell survival and nutrient absorption. Nature 2021, 597, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCauley, H.A.; Guasch, G. Three cheers for the goblet cell: Maintaining homeostasis in mucosal epithelia. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ho, S.B. Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: Recent insights and progress. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, S.J.; Prince, L.S.; Weitkamp, J.H.; Reese, J.; Slaughter, J.C.; Polk, D.B. Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-dependent depletion of mucus in immature small intestine: A potential role in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G656–G666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Tang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection alters intestinal immunity in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jia, M.; Wong, E.A. Delayed access to feed affects broiler small intestinal morphology and goblet cell ontogeny. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5275–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Lee, J.J.; Gaskins, H.R.; Maddox, C.W.; Osuna, O.; Pettigrew, J.E. Escherichia coli challenge and one type of smectite alter intestinal barrier of pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zhou, D.; Wu, Q.; Song, D.; Dicksved, J.; Wang, J.F. Oral Administration of a Select Mixture of Bacillus Probiotics Affects the Gut Microbiota and Goblet Cell Function following Escherichia coli Challenge in Newly Weaned Pigs of Genotype MUC4 That Are Supposed to be Enterotoxigenic E. coli F4ab/ac Receptor Negative. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02747-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalath, S.; Magana-Arachchi, D. Dysbiosis of the Human Urinary Microbiome and its Association to Diseases Affecting the Urinary System. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guan, K.; Su, Q.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Kuang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, B. Change of Gut Microbiota in PRRSV-Resistant Pigs and PRRSV-Susceptible Pigs from Tongcheng Pigs and Large White Pigs Crossed Population upon PRRSV Infection. Animals 2022, 12, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, D.; Adams, S.; Zhao, B.; Qin, G.; Jiang, H. Effects of Dietary L-arginine Supplementation from Conception to Post- Weaning in Piglets. Curr. Protein. Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shao, M.; Fang, X.; Tang, W.; Zhou, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, K.P. Antipsychotic-induced gastrointestinal hypomotility and the alteration in gut microbiota in patients with schizophrenia. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2022, 99, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Schroyen, M.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Effect of Cephalosporin Treatment on the Microbiota and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Feces of Dairy Cows with Clinical Mastitis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, F.; Docherty, N.G.; Murphy, M.; Murphy, B.; Calvin Coffey, J.; O’Connell, P.R. Desulfovibrio bacterial species are increased in ulcerative colitis. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2010, 53, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.X.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Jin, B.Y.; Feng, B.C.; Zhai, Y.J.; Zheng, M.Q.; Kou, G.J.; et al. Melatonin Mitigates Oxazolone-Induced Colitis in Microbiota-Dependent Manner. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 783806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, S.; Yoshida, A.; Omata, Y.; Tsukada, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kamewada, H.; Koike, S.; Okuzumi, K.; Hishinuma, A.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Desulfovibrio desulfuricans bacteremia in a patient hospitalized with acute cerebral infarction: Case report and review. J. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 20, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Fei, N.; Pang, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; et al. A gut microbiota-targeted dietary intervention for amelioration of chronic inflammation underlying metabolic syndrome. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Sekhon, P.K.; Ambat, A.; Nelson, J.; Jose, D.; Bhat, G.J.; Scaria, J. Screening of Human Gut Bacterial Culture Collection Identifies Species That Biotransform Quercetin into Metabolites with Anticancer Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Sun, S.; Luo, Z.; Shi, B.; Shan, A.; Cheng, B. Maternal dietary resveratrol alleviates weaning-associated diarrhea and intestinal inflammation in pig offspring by changing intestinal gene expression and microbiota. Food. Funct. 2019, 10, 5626–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhao, S.; Sun, W.; Yan, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; et al. Structure and Function of the Fecal Microbiota in Diarrheic Neonatal Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, P.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, G. Intestinal microbiota mediates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Jia, Z.; Xiao, S.; Long, C.; Wang, L. Effects of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Challenge on Jejunal Morphology and Microbial Community Profiles in Weaned Crossbred Piglets. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112646
Xu J, Jia Z, Xiao S, Long C, Wang L. Effects of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Challenge on Jejunal Morphology and Microbial Community Profiles in Weaned Crossbred Piglets. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112646
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Juan, Zhen Jia, Shu Xiao, Cimin Long, and Leli Wang. 2023. "Effects of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Challenge on Jejunal Morphology and Microbial Community Profiles in Weaned Crossbred Piglets" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112646
APA StyleXu, J., Jia, Z., Xiao, S., Long, C., & Wang, L. (2023). Effects of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Challenge on Jejunal Morphology and Microbial Community Profiles in Weaned Crossbred Piglets. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112646



