ESBL- and Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae among Bivalves from Portuguese Shellfish Production Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bivalve Samples
2.2. Bacterial Isolates
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Molecular Analysis
2.5. Conjugation Experiments and Plasmid Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Description
3.2. Carriage of Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacterales
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Rodríguez, F.; Mercanoglu Taban, B. A state-of-art review on multi-drug resistant pathogens in foods of animal origin: Risk factors and mitigation strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.L.E.; Caniça, M.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Escherichia coli as commensal and pathogenic bacteria among food-producing animals: Health implications of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) production. Animals 2020, 10, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, B.J.; Rubin, J.E. Carbapenemase producing bacteria in the food supply escaping detection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkonsholm, F.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Svanevik, C.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Lunestad, B.T.; Marathe, N.P. Antibiotic sensitivity screening of Klebsiella spp. and Raoultella spp. isolated from marine bivalve molluscs reveal presence of CTX-M-producing K. pneumoniae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevskott, D.H.; Svanevik, C.S.; Sunde, M.; Wester, A.L.; Lunestad, B.T. Marine bivalve mollusks as possible indicators of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and other species of the Enterobacteriaceae family. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignaroli, C.; Di Sante, L.; Leoni, F.; Chierichetti, S.; Ottaviani, D.; Citterio, B.; Biavasco, F. Multidrug-resistant and epidemic clones of Escherichia coli from natural beds of Venus clam. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, Y.; Mansour, W.; Lupo, A.; Saras, E.; Bouallègue, O.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M. Spread of blaCTX-M-15-producing Enterobacteriaceae and OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii sequence type 2 in Tunisian seafood. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00727-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, Y.; Mansour, W.; Mammeri, H.; Denamur, E.; Saras, E.; Boujâafar, N.; Bouallègue, O.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M. KPC-3-producing ST167 Escherichia coli from mussels bought at a retail market in Tunisia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2403–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, M.; Mani, Y.; Saras, E.; Drapeau, A.; Grami, R.; Aouni, M.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M.; Mansour, W. Prevalence and characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase- and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales from Tunisian seafood. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roschanski, N.; Guenther, S.; Vu, T.T.T.; Fischer, J.; Semmler, T.; Huehn, S.; Alter, T.; Roesler, U. VIM-1 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli isolated from retail seafood, Germany 2016. Euro Surveill. 2017, 22, 17–00032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.S.; Nayak, B.B.; Kumar, S.H. High prevalence of multiple antibiotic-resistant, Escherichia coli in fresh seafood sold in retail markets of Mumbai, India. Vet Sci. 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijsman, J.W.M.; Troost, K. Global production of marine bivalves. Trends and challenges. In Goods and Services of Marine Bivalves, 1st ed.; Smaal, A.C., Ferreira, J.G., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, J.; Castilho, F.; Cunha, A.; Pereira, M.J. Bivalve harvesting and production in Portugal: An overview. J. Shellfish. Res. 2013, 32, 911–924. [Google Scholar]
- Rehnstam-Holm, A.S.; Hernroth, B. Shellfish and public health: A Swedish perspective. Ambio 2005, 34, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUR-Lex. Official Journal of the European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/627 of 15 March 2019. Available online: file:///Volumes/GoogleDrive/O%20meu%20disco/Marta/Publicac%CC%A7oes%20MAS/Artigos/Bivalves/CELEX_32019R0627_EN_TXT.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe—Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) 2020. 2021. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AER-EARS-Net-2020.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Diallo, O.O.; Baron, S.A.; Abat, C.; Colson, P.; Chaudet, H.; Rolain, J.M. Antibiotic resistance surveillance systems: A review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Ortiz de la Rosa, J.M.; Gonçalves, M.L.; Pereira, A.L.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a hospital, Portugal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Lopes, E.; Gonçalves, M.L.; Pereira, A.L.; Machado Costa, A.E.; de Lencastre, H.; Poirel, L. Intestinal carriage of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae at admission in a Portuguese hospital. Eur J Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, C.; Aires de Sousa, M.; Fuster Escriva, B.; Sales, L.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Epidemiology of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae among healthcare students, at the Portuguese Red Cross Health School of Lisbon, Portugal. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, C.; Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Occurrence of CTX-M-15- and MCR-1-producing Enterobacterales in pigs in Portugal: Evidence of direct links with antibiotic selective pressure. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2020, 55, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Fournier, C.; Lopes, E.; de Lencastre, H.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. High colonization rate and heterogeneity of ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae isolated from gull feces in Lisbon, Portugal. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro, V.; Reis, L.; Jo, M.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M. Assessing the bacterial community composition of bivalve mollusks collected in aquaculture farms and respective susceptibility to antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 12.0. 2022. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lartigue, M.F.; Zinsius, C.; Wenger, A.; Bille, J.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases of the CTX-M type now in Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.; Brisse, S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Bertini, A.; Villa, L.; Falbo, V.; Hopkins, K.L.; Threlfall, E.J. Identification of plasmids by PCR-based replicon typing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, Y.; Hagiya, H.; Akeda, Y.; Aye, M.M.; Myo Win, H.P.; Sakamoto, N.; Shanmugakani, R.K.; Takeuchi, D.; Nishi, I.; Ueda, A.; et al. Dissemination of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae harbouring blaNDM or blaIMI in local market foods of Yangon, Myanmar. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecko, N.; Martz, S.L.; Avery, B.P.; Daignault, D.; Desruisseau, A.; Boyd, D.; Irwin, R.J.; Mulvey, M.R.; Reid-Smith, R.J. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter spp. in retail seafood imported from Southeast Asia to Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1675–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manageiro, V.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M.; Manaia, C.M. GES-5 among the β-lactamases detected in ubiquitous bacteria isolated from aquatic environment samples. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 351, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Machado, E.; Pires, J.; Ramos, H.; Novais, Â.; Peixe, L. Increase of widespread A, B1 and D Escherichia coli clones producing a high diversity of CTX-M-types in a Portuguese hospital. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Safia Chenouf, N.; Cunha, R.; Martins, C.; Pimenta, P.; Pereira, A.R.; Martínez-Álvarez, S.; Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Igrejas, G.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance genes and diversity of clones among ESBL- and acquired AmpC-producing Escherichia coli isolated from fecal samples of healthy and sick cats in Portugal. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, S.; Silva, I.A.T.; Tacão, M.; Patinha, C.; Alves, A.; Henriques, I. Characterization of antibiotic resistant and pathogenic Escherichia coli in irrigation water and vegetables in household farms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 257, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Cunha, R.; Martins, C.; Martínez-Álvarez, S.; Safia Chenouf, N.; Pimenta, P.; Pereira, A.R.; Ramos, S.; Sadi, M.; Martins, Â.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance genes and diversity of clones among faecal ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from healthy and sick dogs living in Portugal. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, R.D.S.; Tacão, M.; Figueiredo, A.S.; Duarte, A.S.; Esposito, F.; Lincopan, N.; Manaia, C.M.; Henriques, I. Genotypic and phenotypic traits of blaCTX-M-carrying Escherichia coli strains from an UV-C-treated wastewater effluent. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, S.; Grilo, T.; Poirel, L.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. Urban pigeons (Columba livia) as a source of broad-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Lisbon, Portugal. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayeni, F.A.; Falgenhauer, J.; Schmiedel, J.; Schwengers, O.; Chakraborty, T.; Falgenhauer, L. Detection of blaCTX-M-27-encoding Escherichia coli ST206 in Nigerian poultry stocks. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3070–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cheng, P.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Molecular epidemiology and colistin-resistant mechanism of mcr-positive and mcr-negative Escherichia coli isolated from animal in Sichuan province, China. Front Microbiol. 2022, 13, 818548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qin, L.; Hao, Z. High prevalence and diversity characteristics of blaNDM, mcr, and blaESBLs harboring multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from chicken, pig, and cattle in China. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 755545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidad, S.; van der Putten, B.; van Houdt, R.; Schneeberger, C.; Kuil, S.D. Recurrent E. coli urinary tract infections in nursing homes: Insight in sequence types and antibiotic resistance patterns. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmen, S.; Métayer, V.; Gay, E.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M. Characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-carrying plasmids and clones of Enterobacteriaceae causing cattle mastitis in France. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadar, A.; Phelan, J.; Elias, R.; Modesto, A.; Caneiras, C.; Marques, C.; Lito, L.; Pinto, M.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Ferreira, H.; et al. Genomic epidemiological analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from portuguese hospitals reveals insights into circulating antimicrobial resistance. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Henriques, I.; Gomila, M.; Manaia, C.M. Common and distinctive genomic features of Klebsiella pneumoniae thriving in the natural environment or in clinical settings. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
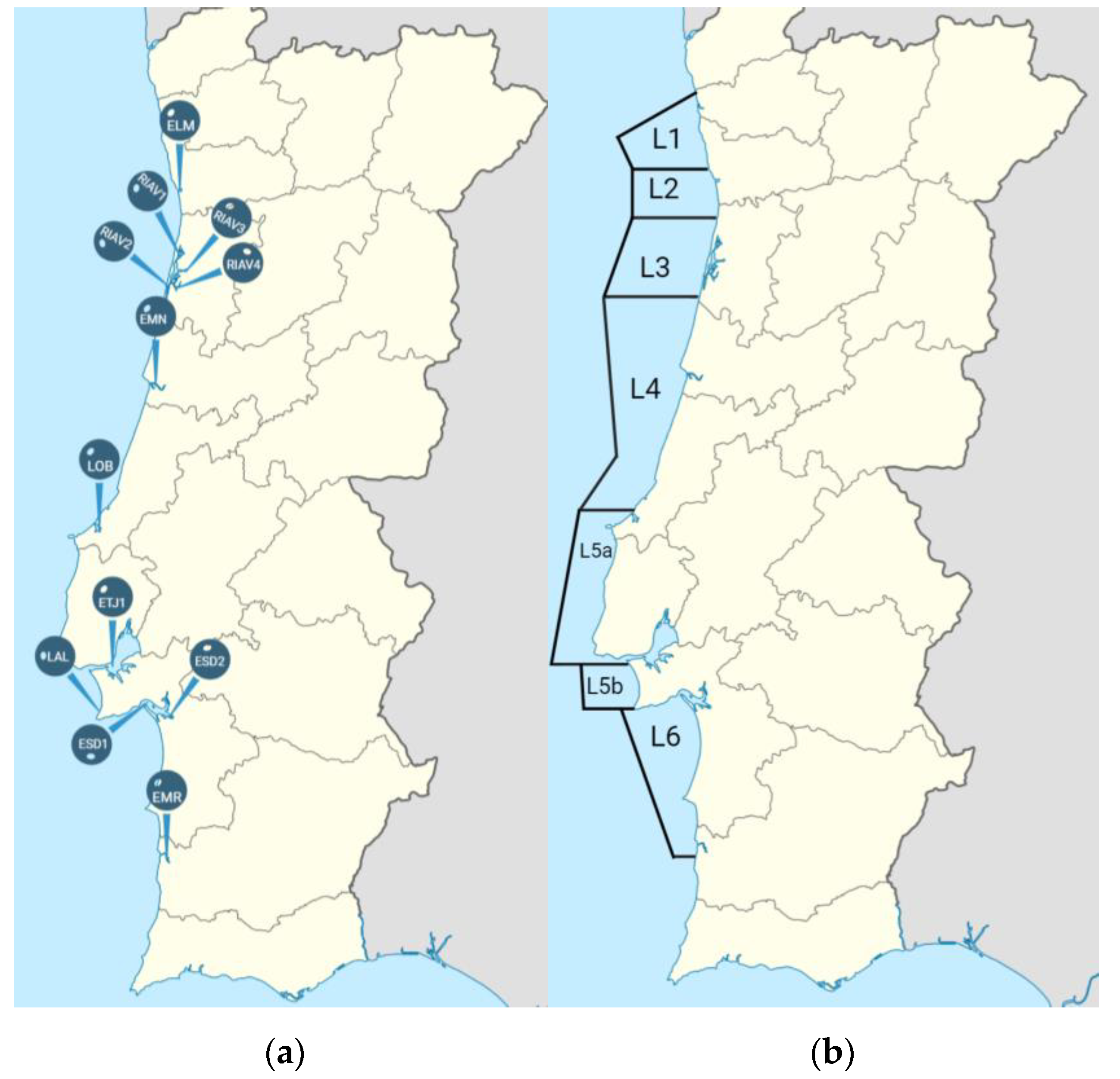
| Shellfish Production Area | No. of Screenings | Samples Recovered | Samples with E. coli Contamination 1 | ESBL Producers 2 | Carbapenemase Producers 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estuaries (n = 12) | ELM | 12 | 22 | 9 (41%) | 2 (22%) | - |
| RIAV1 | 29 | 51 | 23 (45%) | 1 (4%) | - | |
| RIAV2 | 23 | 35 | 15 (43%) | - | - | |
| RIAV3 | 20 | 33 | 13 (39%) | 1 (8%) | - | |
| RIAV4 | 18 | 32 | 14 (44%) | - | - | |
| EMN | 18 | 38 | 20 (53%) | 1 (5%) | 1 (5%) | |
| LOB | 10 | 58 | 25 (43%) | - | - | |
| ETJ1 | 19 | 28 | 14 (50%) | - | - | |
| LAL | 11 | 19 | 7 (37%) | - | - | |
| ESD1 | 25 | 27 | 12 (44%) | 1 (8%) | - | |
| ESD2 | 17 | 36 | 18 (50%) | 3 (17%) | - | |
| EMR | 8 | 16 | 4 (25%) | - | - | |
| Coastal waters (n = 7) | L1 | 14 | 14 | 1 (7%) | - | - |
| L2 | 12 | 16 | 1 (6%) | - | - | |
| L3 | 11 | 11 | 1 (9%) | - | - | |
| L4 | 7 | 7 | 1 (14%) | - | - | |
| L5a | 10 | 10 | 3 (30%) | - | - | |
| L5b | 18 | 24 | 10 (42%) | - | - | |
| L6 | 18 | 45 | 15 (33%) | - | - | |
| Total | 19 | 300 | 522 | 206 (39%) | 9 (4.4%) | 1 (0.5%) |
| Bivalve Species | Samples Recovered 1 | Samples with E. coli Contamination 2 | ESBL Producers 3 | Carbapenemase Producers 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clam | Venerupis corrugata | 43 (8%) | 21 (49%) | 2 (10%) | - |
| Clam | Ruditapes philippinarum | 38 (7%) | 17 (45%) | - | - |
| Clam | Ruditapes decussatus | 33 (6%) | 14 (42%) | - | - |
| Clam | Spisula solida | 31 (6%) | 3 (10%) | - | - |
| Clam | Scrobicularia plana | 15 (3%) | 10 (67%) | 1 (10%) | - |
| Clam | Donax trunculus | 11 (2%) | 4 (36%) | - | |
| Clam | Venus verrucosa | 9 (2%) | 2 (22%) | - | |
| Clam | Dosinia exoleta | 5 (1%) | 3 (60%) | - | - |
| Clam | Callista chione | 4 (1%) | - | - | - |
| Clam | Venus casina | 1 (<1%) | 1 (100%) | - | |
| Razor clam | Solen marginatus | 57 (11%) | 29 (51%) | 2 (7%) | - |
| Razor clam | Ensis siliqua | 16 (3%) | 7 (44%) | - | - |
| Oyster | Magallana gigas | 52 (10%) | 24 (46%) | 2 (8%) | - |
| Oyster | Magallana angulata | 28 (5%) | 11 (39%) | 2 (18%) | - |
| Oyster | Ostrea edulis | 9 (2%) | 2 (22%) | - | - |
| Cockle | Cerastoderma edule | 82 (16%) | 33 (40%) | - | 1 (3%) |
| Cockle | Glycymeris glycymeris | 14 (3%) | 1 (7%) | - | - |
| Cockle | Laevicardium crassum | 3 (1%) | 1 (33%) | - | - |
| Mussel | Mytilus galloprovincialis | 71 (14%) | 23 (32%) | - | - |
| Total | 19 | 522 | 206 (39%) | 9 (4%) | 1 (0.5%) |
| 8 | Isolate | ST | CC | ESBL/ Carbapenemase | TIC | AMC | CTX | CZD | TEM | FOX | CZA | ETP | IPM | MEM | ATM | CIP | SXT | TET | AKN | GMI | TMN | FOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | R6129 | 23 | 23 | CTX-M-15 | R | R | R | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | R | S | S | S | S |
| E. coli | R6130 | 746 | ND | CTX-M-32 | R | S | R | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S |
| E. coli | R6131 | SLV206 | 206 | CTX-M-14 | R | S | I | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| E. coli | R6132 | SLV2325 | ND | CTX-M-32 | R | S | R | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| E. coli | R6133 | 617 | 10 | CTX-M-32 | R | S | R | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | I | R | R | R | S | S | S | S |
| E. coli | R6134 | 10 | 10 | CTX-M-15 | R | S | R | I | I | S | S | S | S | S | R | I | R | R | S | S | S | S |
| E. coli | R6136 | 540 | ND | CTX-M-32 | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | S | R | R | S |
| K. pneumoniae | R6128 | 834 | ND | CTX-M-15 | R | R | R | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | R | R | R | S |
| K. pneumoniae | R6135 | 15 | ND | CTX-M-15 | R | R | R | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R | S | S | S | R | S |
| K. pneumoniae | R6137 | DLV644 | ND | GES-5 | R | R | S | R | I | R | S | R | I | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freire, S.; Grilo, T.; Rodrigues, B.; Oliveira, R.; Esteves, C.; Marques, A.; Poirel, L.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. ESBL- and Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae among Bivalves from Portuguese Shellfish Production Areas. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020415
Freire S, Grilo T, Rodrigues B, Oliveira R, Esteves C, Marques A, Poirel L, Aires-de-Sousa M. ESBL- and Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae among Bivalves from Portuguese Shellfish Production Areas. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020415
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreire, Samanta, Teresa Grilo, Bruna Rodrigues, Rui Oliveira, Carla Esteves, António Marques, Laurent Poirel, and Marta Aires-de-Sousa. 2023. "ESBL- and Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae among Bivalves from Portuguese Shellfish Production Areas" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020415
APA StyleFreire, S., Grilo, T., Rodrigues, B., Oliveira, R., Esteves, C., Marques, A., Poirel, L., & Aires-de-Sousa, M. (2023). ESBL- and Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae among Bivalves from Portuguese Shellfish Production Areas. Microorganisms, 11(2), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020415






