The Hormetic Effect Observed for Benzalkonium Chloride and Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride in Serratia sp. HRI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
2.2. Disinfectants
2.3. Inoculum and Shake Flask Preparation
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. 60-Min Growth Analysis with Cell Count
2.6. Absorbance Spectrum
3. Results
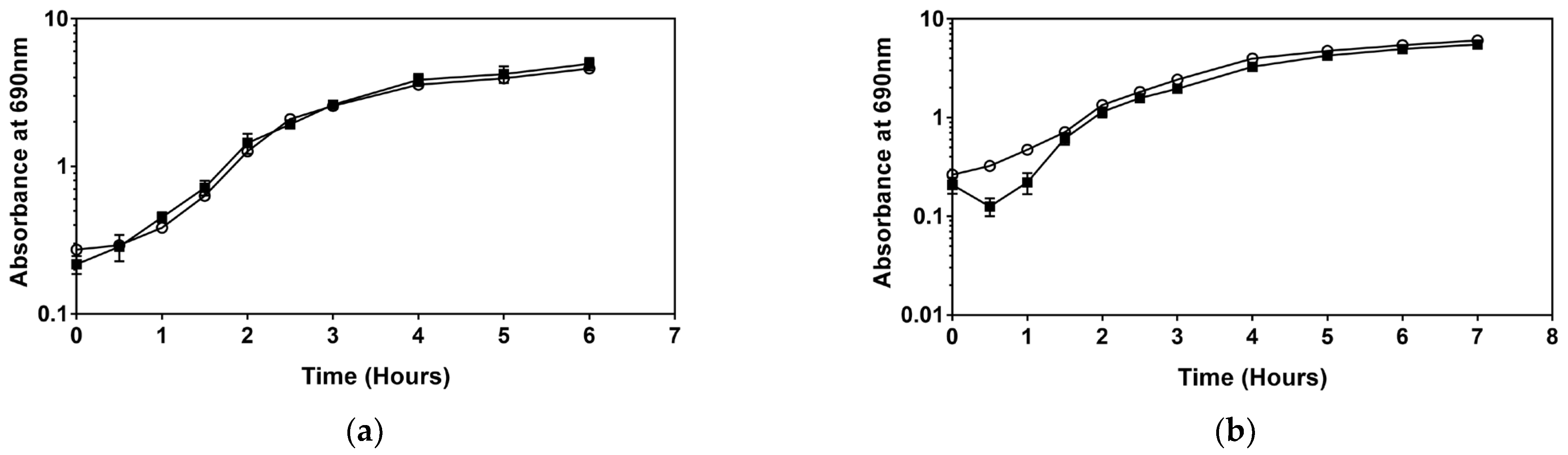
3.1. Growth Analysis of Serratia sp. in the Presence of Sub-MIC Level Disinfectants
3.2. Growth and Cell Count Analysis of Serratia sp. HRI and Serratia Marcescens ATCC 13880
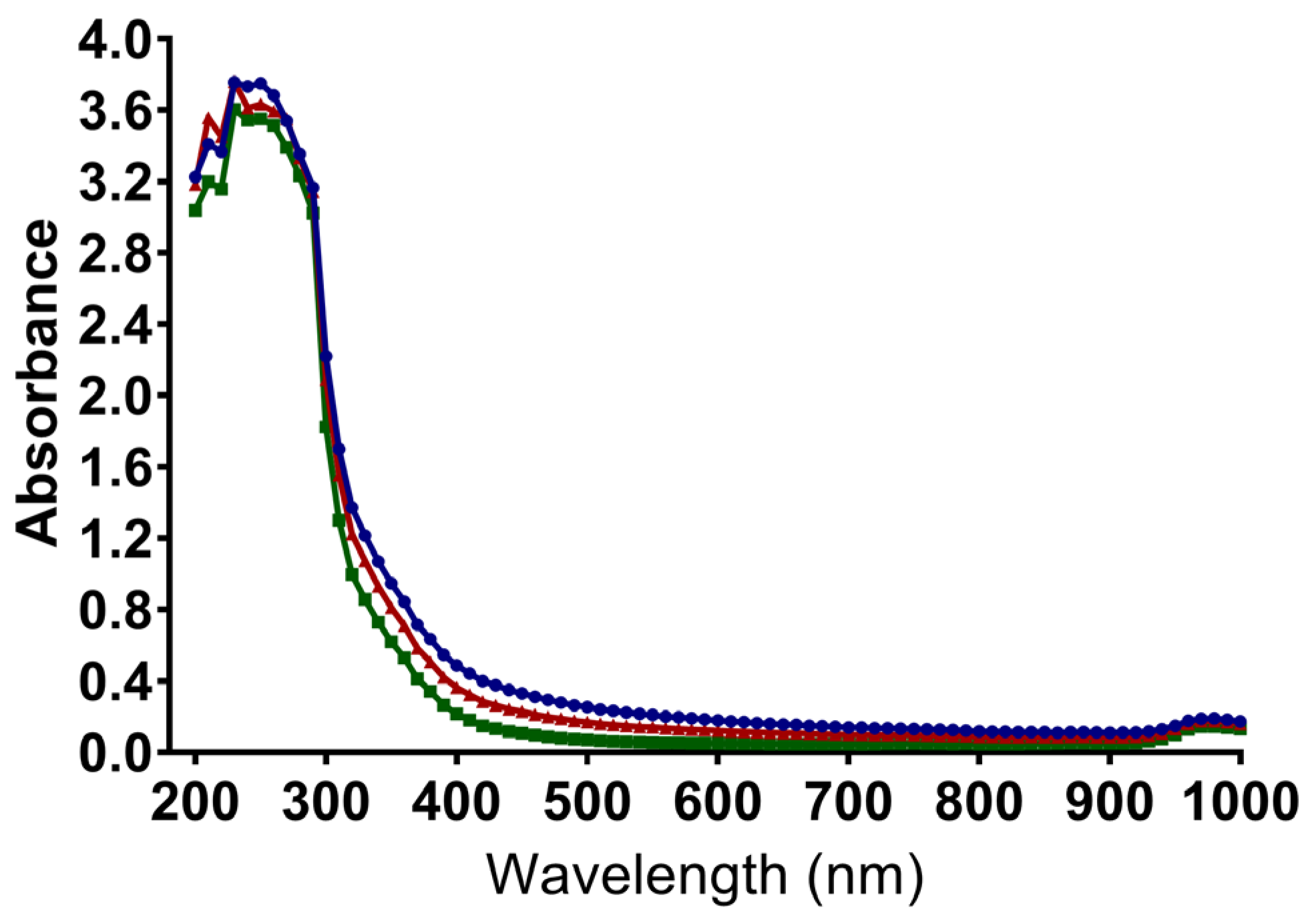
3.3. Absorbance Spectrum of QAC-Based Disinfectants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Haddix, P.L.; Jones, S.; Patel, P.; Burnham, S.; Knights, K.; Powell, J.N.; LaForm, A. Kinetic analysis of growth rate, ATP, and pigmentation suggests an energy-spilling function for the pigment prodigiosin of Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7453–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haddix, P.L.; Shanks, R.M.Q. Prodigiosin pigment of Serratia marcescens is associated with increased biomass production. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, K.; Janelle, S.; Schutz, K.; Hamilton, S.; Mayo, K.; Cichon, M.K.; Nyquist, A.-C.; Bamberg, W.M.; Dominguez, S.R. Outbreak of Serratia marcescens bacteremia in pediatric patients epidemiologically linked to pre-filled heparin flushes. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iosifidis, E.; Farmaki, E.; Nedelkopoulou, N.; Tsivitanidou, M.; Kaperoni, M.; Pentsoglou, V.; Pournaras, S.; Athanasiou-Metaxa, M.; Roilides, E. Outbreak of bloodstream infections because of Serratia marcescens in a pediatric department. Am. J. Infect. Control 2012, 40, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhne, C.; Chhatwal, P.; Peter, C.; Ebadi, E.; Hansen, G.; Schlüter, D.; Bange, F.-C.; Bohnhorst, B.; Baier, C. Detection of Serratia marcescens in neonatal intensive care units requires a rapid and comprehensive infection control response starting with the very first case. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2021, 16, Doc12. [Google Scholar]
- Soria, C.; Nieto, N.; Villacís, J.E.; Lainez, S.; Cartelle, M. Serratia marcescens outbreak in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Guayaquil, Ecuador. Rev. Chilena Infectol. 2016, 33, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millán-Lou, M.I.; López, C.; Bueno, J.; Pérez-Laguna, V.; Lapresta, C.; Fuertes, M.E.; Rite, S.; Santiago, M.; Romo, M.; Samper, S.; et al. Successful control of Serratia marcescens outbreak in a neonatal unit of a tertiary-care hospital in Spain. Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 40, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, T.; Costerton, J. Prolonged survival of Serratia marcescens in chlorhexidine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 42, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, T.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, L.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X. Inactivation and Subsequent Growth Kinetics of Listeria monocytogenes After Various Mild Bactericidal Treatments. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 646735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreira, A.; Vázquez, J.A.; García, M.R. Kinetics of Bacterial Adaptation, Growth, and Death at Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride sub-MIC Concentrations. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 758237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.; Morgan, N.; Humphreys, G.J.; Amézquita, A.; Mistry, H.; McBain, A.J. Loss of function in Escherichia coli exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of benzalkonium chloride. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02417-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, A.K.; Highsmith, A.K.; Martone, W.J. Survival of Serratia marcescens in benzalkonium chloride and in multiple-dose medication vials: Relationship to epidemic septic arthritis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Fernández, L.; Fernández-Crehuet, M.; Espigares, M.; Moreno, E.; Espigares, E. Study of the hormetic effect of disinfectants chlorhexidine, povidone iodine and benzalkonium chloride. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Mattson, M.P. How does hormesis impact biology, toxicology, and medicine? NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2017, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Z.; Liu, Y. Potential impacts of silver nanoparticles on bacteria in the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 191, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Guo, P.; Peng, X.; Wen, K. Effect of erythromycin exposure on the growth, antioxidant system and photosynthesis of Microcystis flos-aquae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Sato, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Ochi, K.; Hosaka, T. Lincomycin at Subinhibitory Concentrations Potentiates Secondary Metabolite Production by Streptomyces spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3869–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Migliore, L.; Rotini, A.; Thaller, M.C. Low Doses of Tetracycline Trigger the E. coli Growth: A Case of Hormetic Response. Dose-Response 2013, 11, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mc Carlie, S.; Hellmuth, J.; Newman, J.; Boucher, C.E.; Bragg, R.R. Genome Sequence of Resistant Serratia sp. Strain HRI, Isolated from a Bottle of Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride-Based Disinfectant. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00095-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.; Collier, P.; Brown, M. Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: Biofilms, cell cycle, dormancy, and stringent response. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 1865–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proctor, R.A.; von Eiff, C.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; McNamara, P.; Herrmann, M.; Peters, G. Small colony variants: A pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, R.H.; Padberg, F.T.; Smith, S.M.; Tan, E.N.; Cherubin, C.E. Bactericidal effects of antibiotics on slowly growing and nongrowing bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 1824–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Hatt, J.K.; Weigand, M.R.; Krishnan, R.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into how bacteria withstand high concentrations of benzalkonium chloride biocides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00197-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Weigand, M.R.; Oh, S.; Hatt, J.K.; Krishnan, R.; Tezel, U.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Widely Used Benzalkonium Chloride Disinfectants Can Promote Antibiotic Resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01201-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wessels, S.; Ingmer, H. Modes of action of three disinfectant active substances: A review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 67, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, A.C.; Melo, L.F.; Pereira, A. A Multi-Purpose Approach to the Mechanisms of Action of Two Biocides (Benzalkonium Chloride and Dibromonitrilopropionamide): Discussion of Pseudomonas fluorescens’ Viability and Death. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ginkel, C.G.; van Dijk, J.B.; Kroon, A.G. Metabolism of hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride in Pseudomonas strain B1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3083–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean-Raymond, D.; Alexander, M. Bacterial metabolism of quaternary ammonium compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langsrud, S.; Møretrø, T.; Sundheim, G. Characterization of Serratia marcescens surviving in disinfecting footbaths. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, P.A.; Sawant, A.D.; Wilson, L.A.; Ahearn, D.G. Adaptation and growth of Serratia marcescens in contact lens disinfectant solutions containing chlorhexidine gluconate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belter, B.; McCarlie, S.J.; Boucher-van Jaarsveld, C.E.; Bragg, R.R. Investigation into the Metabolism of Quaternary Ammonium Compound Disinfectants by Bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Tandukar, M.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Chain, P.S.G.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Microbial community adaptation to quaternary ammonium biocides as revealed by metagenomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2850–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezel, U.; Tandukar, M.; Martinez, R.J.; Sobecky, P.A.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Aerobic Biotransformation of n -Tetradecylbenzyldimethylammonium Chloride by an Enriched Pseudomonas spp. Community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8714–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezel, U.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Quaternary ammonium disinfectants: Microbial adaptation, degradation and ecology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauffenberger, A.; Fiumelli, H.; Almustafa, S.; Magistretti, P.J. Lactate and pyruvate promote oxidative stress resistance through hormetic ROS signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Sample | µmax (h−1) | Ave. µmax | Doubling Time (Td, h) | Ave. Td |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Disinfectant | ||||
| A1 | 1.06 | 1.07 ± 0.04 | 0.65 | 0.65 |
| A2 | 1.04 | 0.67 | ||
| A3 | 1.11 | 0.62 | ||
| H1 | 0.93 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 0.74 | 0.75 |
| H2 | 0.91 | 0.76 | ||
| H3 | 0.92 | 0.76 | ||
| Sub-MIC Level Benzalkonium Chloride | ||||
| A1 | 1.06 | 1.04 ± 0.04 | 0.52 | 0.67 |
| A2 | 1.00 | 0.73 | ||
| A3 | 1.07 | 0.76 | ||
| H1 | 1.61 | 1.75 ± 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.48 |
| H2 | 1.62 | 0.51 | ||
| H3 | 2.01 | 0.41 | ||
| A+ | 0.96 | N/A | 0.72 | N/A |
| H+ | 0.89 | N/A | 0.78 | N/A |
| Sub-MIC Level DDAC | ||||
| A1 | 0.90 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.77 | 0.7634 |
| A2 | 1.08 | 0.73 | ||
| A3 | 0.93 | 0.79 | ||
| H1 | 1.44 | 1.43 ± 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.5172 |
| H2 | 1.43 | 0.48 | ||
| H3 | 1.41 | 0.49 | ||
| A+ | 1.02 | N/A | 0.69 | N/A |
| H+ | 0.84 | N/A | 0.82 | N/A |
| Sub-MIC Level Virukill™ | ||||
| A1 | 1.09 | 1.14 ± 0.05 | 0.64 | 0.6075 |
| A2 | 1.16 | 0.60 | ||
| A3 | 1.18 | 0.59 | ||
| H1 | 0.93 | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.74 | 0.7353 |
| H2 | 0.91 | 0.76 | ||
| H3 | 0.99 | 0.70 | ||
| A+ | 1.12 | N/A | N/A | |
| H+ | 0.94 | N/A | N/A | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McCarlie, S.J.; Steyn, L.; du Preez, L.L.; Boucher, C.E.; Hernandez, J.C.; Bragg, R.R. The Hormetic Effect Observed for Benzalkonium Chloride and Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride in Serratia sp. HRI. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030564
McCarlie SJ, Steyn L, du Preez LL, Boucher CE, Hernandez JC, Bragg RR. The Hormetic Effect Observed for Benzalkonium Chloride and Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride in Serratia sp. HRI. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030564
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcCarlie, Samantha J., Laurinda Steyn, Louis L. du Preez, Charlotte E. Boucher, Julio Castillo Hernandez, and Robert R. Bragg. 2023. "The Hormetic Effect Observed for Benzalkonium Chloride and Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride in Serratia sp. HRI" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030564
APA StyleMcCarlie, S. J., Steyn, L., du Preez, L. L., Boucher, C. E., Hernandez, J. C., & Bragg, R. R. (2023). The Hormetic Effect Observed for Benzalkonium Chloride and Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride in Serratia sp. HRI. Microorganisms, 11(3), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030564






