A Simple In-Vivo Method for Evaluation of Antibiofilm and Wound Healing Activity Using Excision Wound Model in Diabetic Swiss Albino Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. In-Vitro Biofilm Formation
2.4. Preparation of Biofilm on the Coverslips and Its Determination
2.5. Induction of Type-II Diabetes in Mice
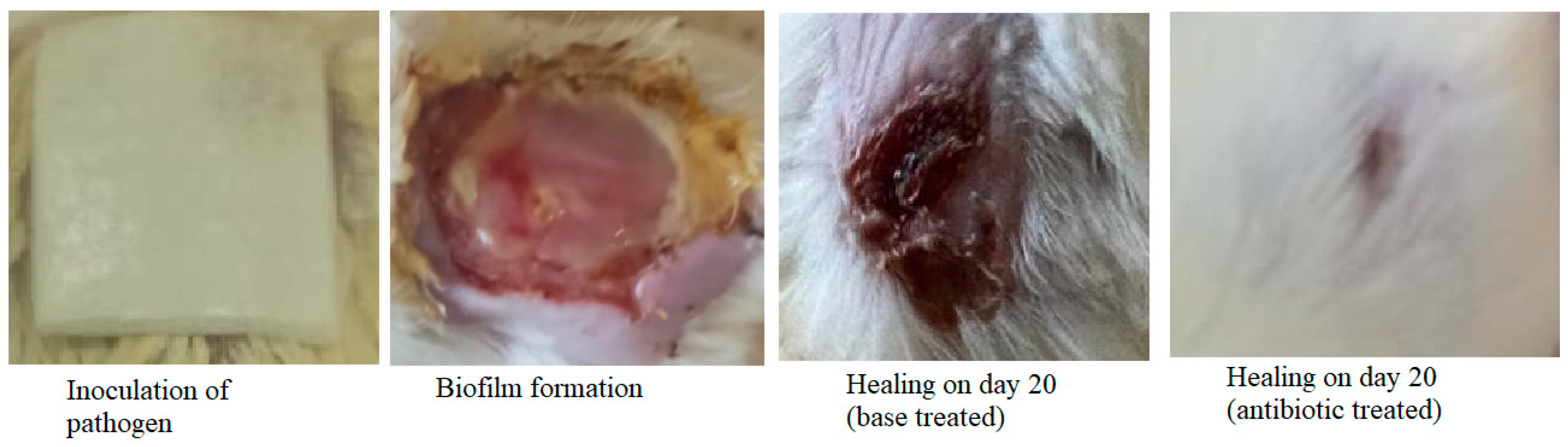
2.6. Excision Wound and Biofilm Formation
Staining
3. Results
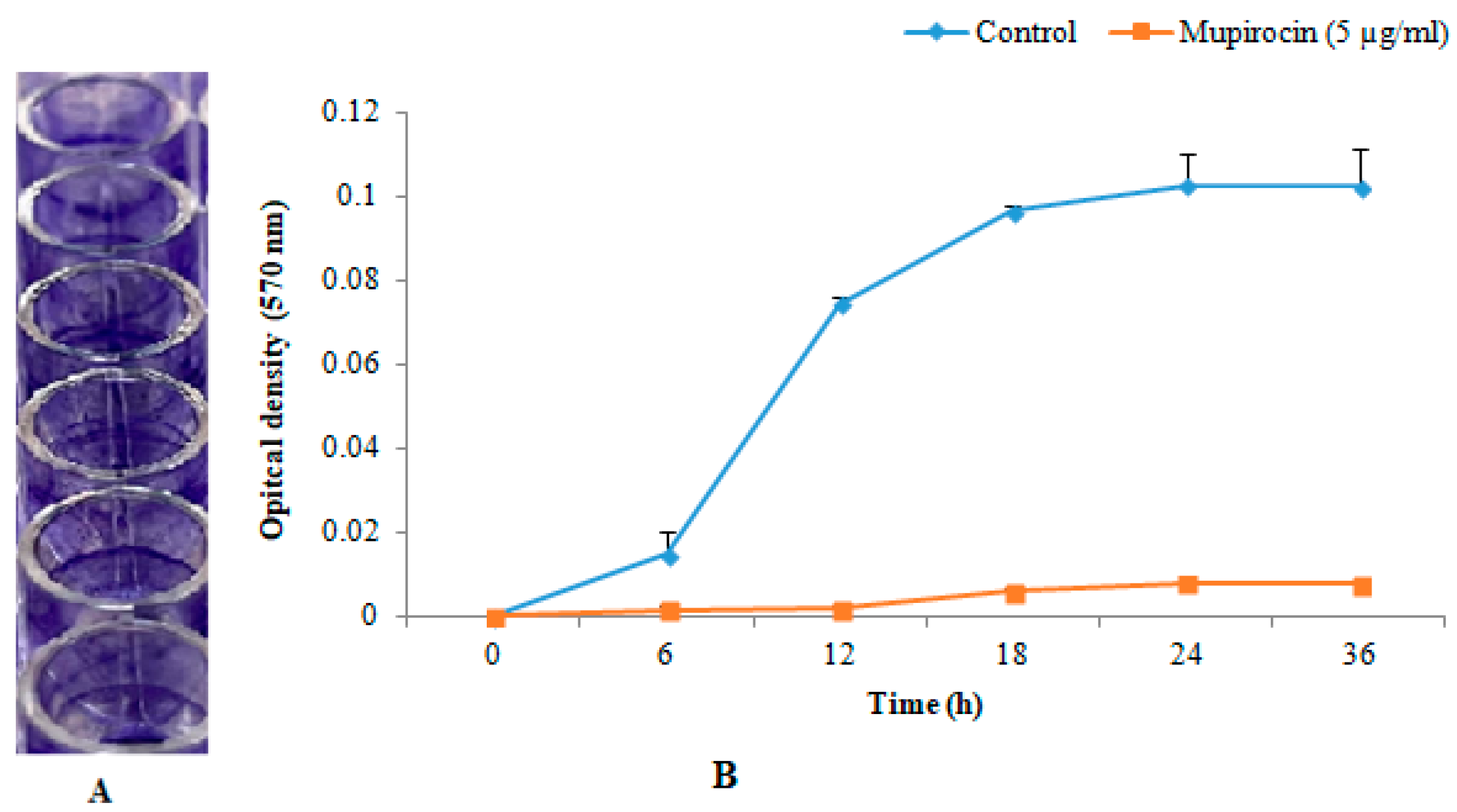
3.1. In-Vitro Biofilm Formation
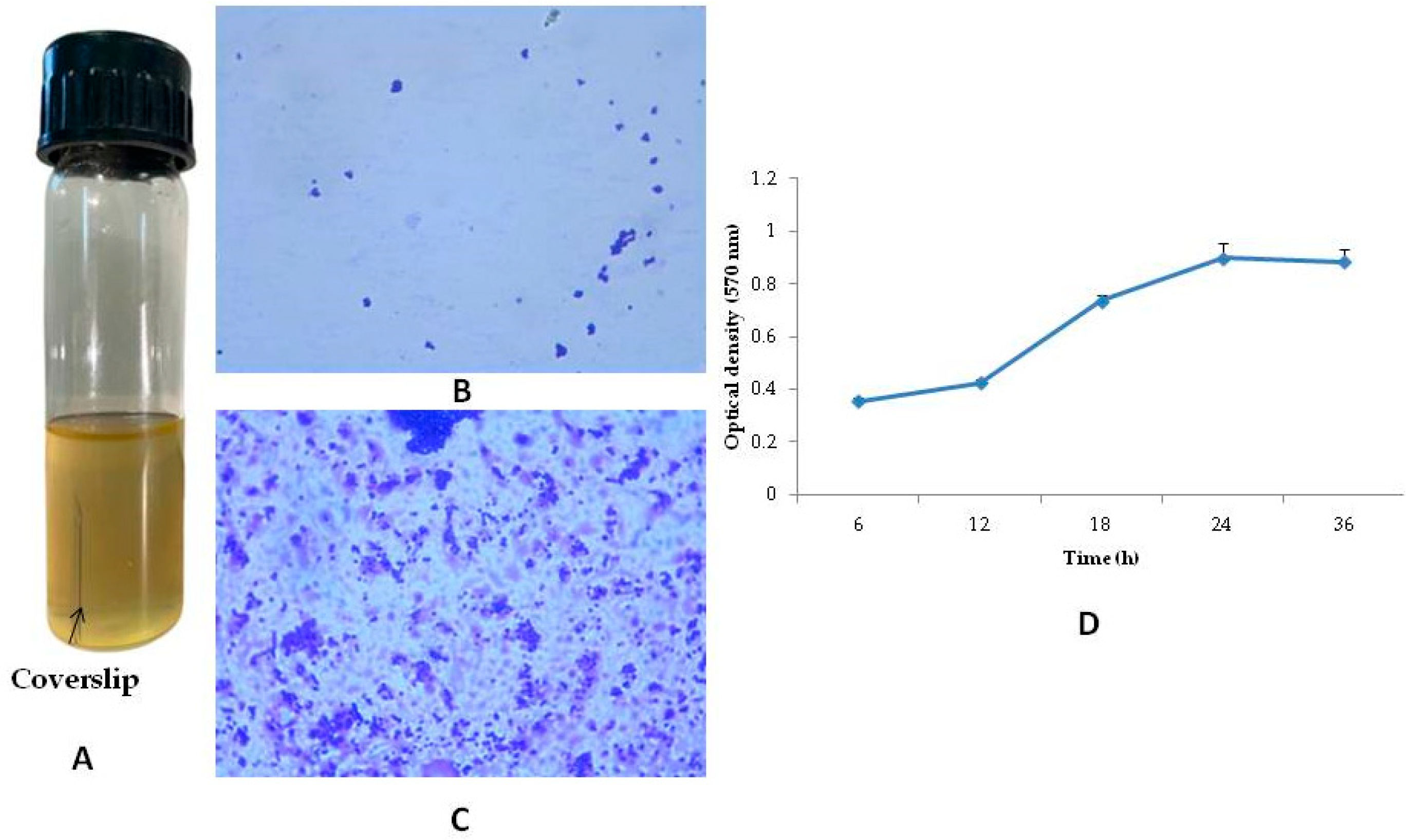
3.2. Biofilm Formation in Coverslip and Its Determination
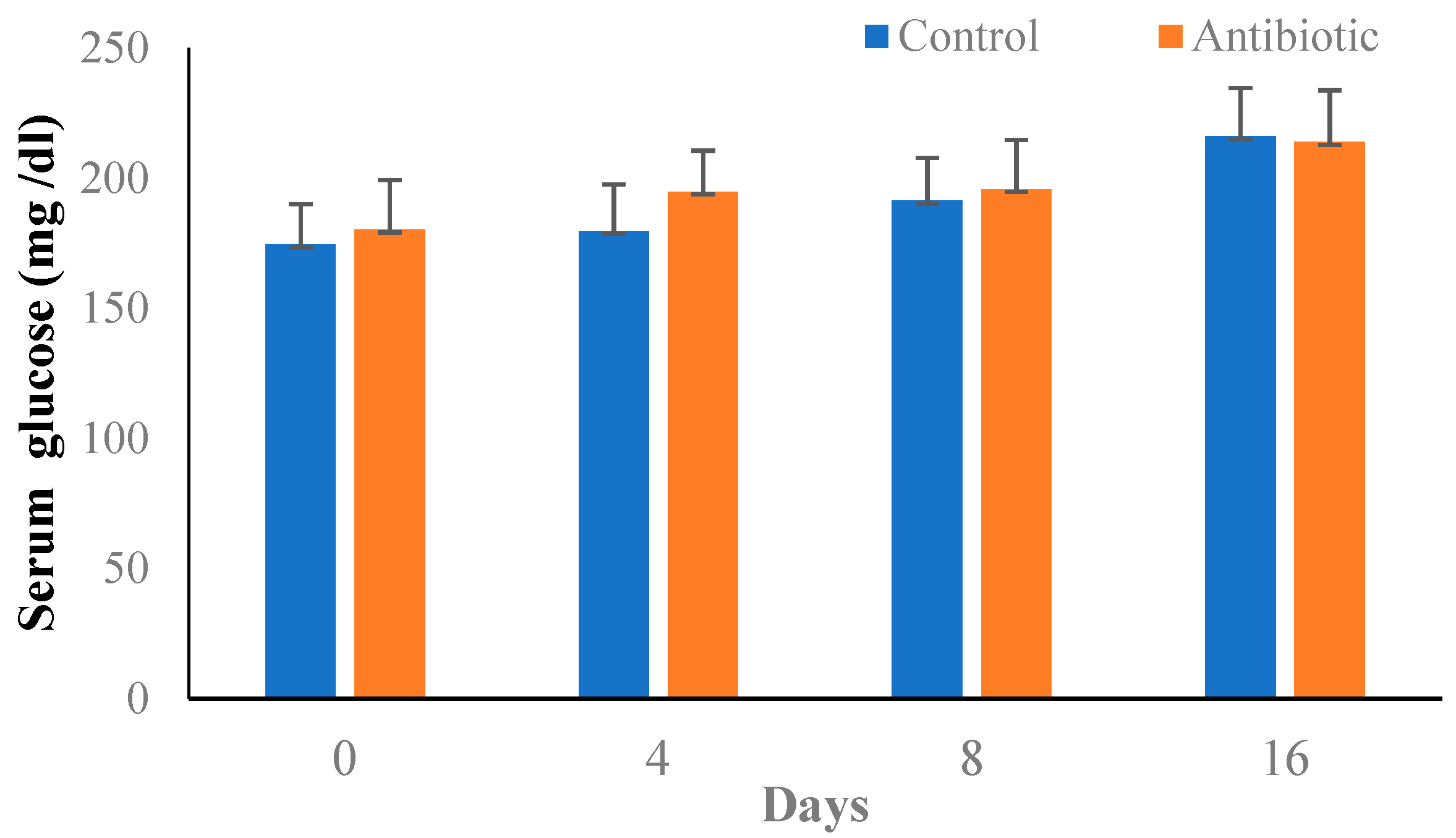
3.3. Induction of Type-II Diabetes in Mice
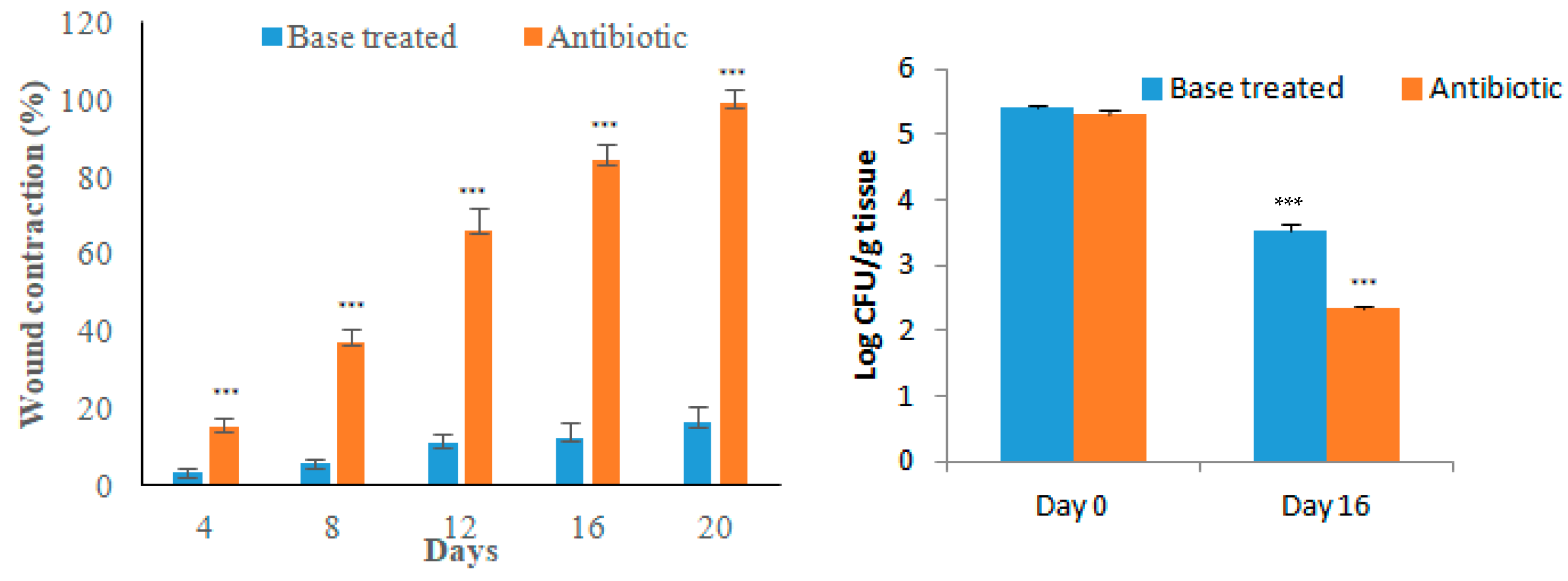
3.4. Excision Wound in Diabetic Animals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srinivasan, R.; Santhakumari, S.; Poonguzhali, P.; Geetha, M.; Dyavaiah, M.; Xiangmin, L. Bacterial Biofilm Inhibition: A Focused Review on Recent Therapeutic Strategies for Combating the Biofilm Mediated Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, B.A.R.N.; Pouget, C.; Magnan, C.; Molle, V.; Lavigne, J.P.; Dunyach-Remy, C. Bacterial Interactions in the Context of Chronic Wound Biofilm: A Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yrastorza, J.T.; Matis, M.; Cusick, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, G.; Xie, J. Biofilms: Formation, Research Models, Potential Targets, and Methods for Prevention and Treatment. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, K.; Sinha, M.; Mathew-Steiner, S.S.; Das, A.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Chronic Wound Biofilm Model. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyas, H.K.N.; Xia, B.; Mai-Prochnow, A. Clinically Relevant in Vitro Biofilm Models: A Need to Mimic and Recapitulate the Host Environment. Biofilm 2022, 4, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anju, V.T.; Busi, S.; Imchen, M.; Kumavath, R.; Mohan, M.S.; Salim, S.A.; Subhaswaraj, P.; Dyavaiah, M. Polymicrobial Infections and Biofilms: Clinical Significance and Eradication Strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, K.; Kobayashi, O.; Kishi, K.; Shirai, R.; Østrup Jensen, P.; Heydorn, A.; Hentzer, M.; Calum, H.; Christophersen, L.; Høiby, N.; et al. Animal Models of Chronic and Recurrent Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Lung Infection: Significance of Macrolide Treatment. APMIS 2022, 130, 458–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, K.; Stoodley, P.; Goeres, D.M.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Burmølle, M.; Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. The Biofilm Life Cycle: Expanding the Conceptual Model of Biofilm Formation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, K.M.; Nguyen, J.M.; Berg, L.J.; Townsend, S.D. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA): Antibiotic-Resistance and the Biofilm Phenotype. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Carbone, D.; Parrino, B.; Pecoraro, C.; Giovannetti, E.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P. Therapeutic Strategies To Counteract Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA Biofilm-Associated Infections. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Staphylococcus Aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, O.; Rizzetto, G.; Radi, G.; Molinelli, E.; Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Offidani, A. New Perspectives on Old and New Therapies of Staphylococcal Skin Infections: The Role of Biofilm Targeting in Wound Healing. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter Dish Biofilm Formation Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 47, e2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Hamed, M.I.; Panitch, A.; Seleem, M.N. Targeting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus with Short Salt-Resistant Synthetic Peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.N.; Horswill, A.R. A Coverslip-Based Technique for Evaluating Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm Formation on Human Plasma. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.J. The Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin Rodent Model of Type 2 Diabetes: Renal Pathophysiology and Redox Imbalance Features. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesthesia (Guideline)|Vertebrate Animal Research. Available online: https://animal.research.uiowa.edu/iacuc-guidelines-anesthesia (accessed on 13 February 2022).
- Becerra, S.C.; Roy, D.C.; Sanchez, C.J.; Christy, R.J.; Burmeister, D.M. An Optimized Staining Technique for the Detection of Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria within Tissue. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SOULSBY, J. The New Ointment Bases of the British Pharmocopoeia, 1948. Br. J. Dermatol. Syph. 1949, 61, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, T.; de Lencastre, H.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. Prevalence of Biocide Resistance Genes and Chlorhexidine and Mupirocin Non-Susceptibility in Portuguese Hospitals during a 31-Year Period (1985–2016). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 24, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining of Mouse Tissue Sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revision of the ARRIVE Guidelines|NC3Rs. Available online: https://www.nc3rs.org.uk/our-portfolio/revision-arrive-guidelines (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Schlafer, S.; Meyer, R.L. Confocal Microscopy Imaging of the Biofilm Matrix. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 138, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Pantel, A.; Schuldiner, S.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P. Biofilms in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Significance and Clinical Relevance. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watters, C.; Deleon, K.; Trivedi, U.; Griswold, J.A.; Lyte, M.; Hampel, K.J.; Wargo, M.J.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms Perturb Wound Resolution and Antibiotic Tolerance in Diabetic Mice. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 202, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szkudelski, T. Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Diabetes in the Rat. Characteristics of the Experimental Model. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 237, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Graff, F.T.; Fitzner, B.; Jaster, R.; Vollmar, B.; Zechner, D. Impact of Hyperglycemia on Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Regulatory T-Cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3120–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuard, W.L.; Titone, R.; Robertson, D.M. The IGF/Insulin-IGFBP Axis in Corneal Development, Wound Healing, and Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, T.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Tanaka, M.; Huang, Y.Y.; Bil de Arce, V.J.; Hamblin, M.R. Animal Models of External Traumatic Wound Infections. Virulence 2011, 2, 296–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Hochwalt, P.C.; Usui, M.L.; Underwood, R.A.; Singh, P.K.; James, G.A.; Stewart, P.S.; Fleckman, P.; Olerud, J.E. Delayed Wound Healing in Diabetic (Db/Db) Mice with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Challenge: A Model for the Study of Chronic Wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Mizuno, T.; Mitchell, S.H.; de Wit, H.; Curran, H.V.; Morgan, C.J.A.; Anagnostaras, S.G.; Sage, J.R.; Carmack, S.A.; et al. Db/Db Mouse. In Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2010; p. 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.; Goldsworthy, H.; Burton, S.; Lappin-Scott, H. Gene Expression of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and MRSA within a Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection Biofilm Model. Biosci. Horizons Int. J. Student Res. 2008, 1, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho Hunt, A.M.; Gibson, J.A.; Larrivee, C.L.; O’Reilly, S.; Navitskaya, S.; Busik, J.V.; Waters, C.M. Come to the Light Side: In Vivo Monitoring of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Infections in Chronic Wounds in a Diabetic Hairless Murine Model. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 2017, e55991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rais, N.; Ved, A.; Ahmad, R.; Parveen, K.; Gautam, G.K.; Bari, D.G.; Shukla, K.S.; Gaur, R.; Singh, A.P. Model of Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide Induced Type 2 Diabetes: A Comparative Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 18, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlow, J.; Bowler, P.G. Acute and Chronic Wound Infections: Microbiological, Immunological, Clinical and Therapeutic Distinctions. J. Wound Care 2022, 31, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, T.; Askri, Z.U.A.; Shahid, M.H.; Khan, A.Z.; Asif, S.; Ghumman, A.R.; Afzal, M.F. The Emergence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Culture Sensitivities of Post-Surgical Patients in Lahore General Hospital, Lahore. Cureus 2022, 14, e23212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, R.; Grande, R.; Butrico, L.; Rossi, A.; Settimio, U.F.; Caroleo, B.; Amato, B.; Gallelli, L.; De Franciscis, S. Chronic Wound Infections: The Role of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Staphylococcus Aureus. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, M.C.; Anderson, J.M.; Armstrong, A.S.; Gastineau, D.A.; Hiddinga, H.J.; Jahangir, A.; Eberhardt, N.L.; Kudva, Y.C. Single Dose Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes: Considerations for Study Design in Islet Transplantation Models. Lab. Anim. 2011, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrouji, M.; Kuriri, F.A.; Alqasmi, M.H.; AlSudais, H.; Alissa, M.; Alsuwat, M.A.; Asad, M.; Joseph, B.; Almuhanna, Y. A Simple In-Vivo Method for Evaluation of Antibiofilm and Wound Healing Activity Using Excision Wound Model in Diabetic Swiss Albino Mice. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030692
Alrouji M, Kuriri FA, Alqasmi MH, AlSudais H, Alissa M, Alsuwat MA, Asad M, Joseph B, Almuhanna Y. A Simple In-Vivo Method for Evaluation of Antibiofilm and Wound Healing Activity Using Excision Wound Model in Diabetic Swiss Albino Mice. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030692
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrouji, Mohammed, Fahd A. Kuriri, Mohammed Hussein Alqasmi, Hamood AlSudais, Mohammed Alissa, Meshari A. Alsuwat, Mohammed Asad, Babu Joseph, and Yasir Almuhanna. 2023. "A Simple In-Vivo Method for Evaluation of Antibiofilm and Wound Healing Activity Using Excision Wound Model in Diabetic Swiss Albino Mice" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030692
APA StyleAlrouji, M., Kuriri, F. A., Alqasmi, M. H., AlSudais, H., Alissa, M., Alsuwat, M. A., Asad, M., Joseph, B., & Almuhanna, Y. (2023). A Simple In-Vivo Method for Evaluation of Antibiofilm and Wound Healing Activity Using Excision Wound Model in Diabetic Swiss Albino Mice. Microorganisms, 11(3), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030692






