In Vitro Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of Ophidian Serpentoviruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Establishing Reptile Cell Lines
2.2. Serpentovirus Isolation
2.3. Ball Python Nidovirus
2.4. Green Tree Python Serpentovirus
2.5. Antaresian Python Serpentovirus
2.6. Establishing a Median Tissue Culture Infectious Dose (TCID50) Assay
2.7. Freeze-Thaw Characterization
2.8. Environmental Stability
2.9. Single-Cycle Growth Kinetics
2.10. Multiple-Cycle Growth Kinetics
2.11. Epifluorescent Immunostaining to Assess Infection
2.12. Sanitizer Efficacy
2.13. Antiviral Test Compounds
2.14. Antiviral Efficacy
3. Results
3.1. Freeze-Thaw Stability
3.2. Environmental Stability
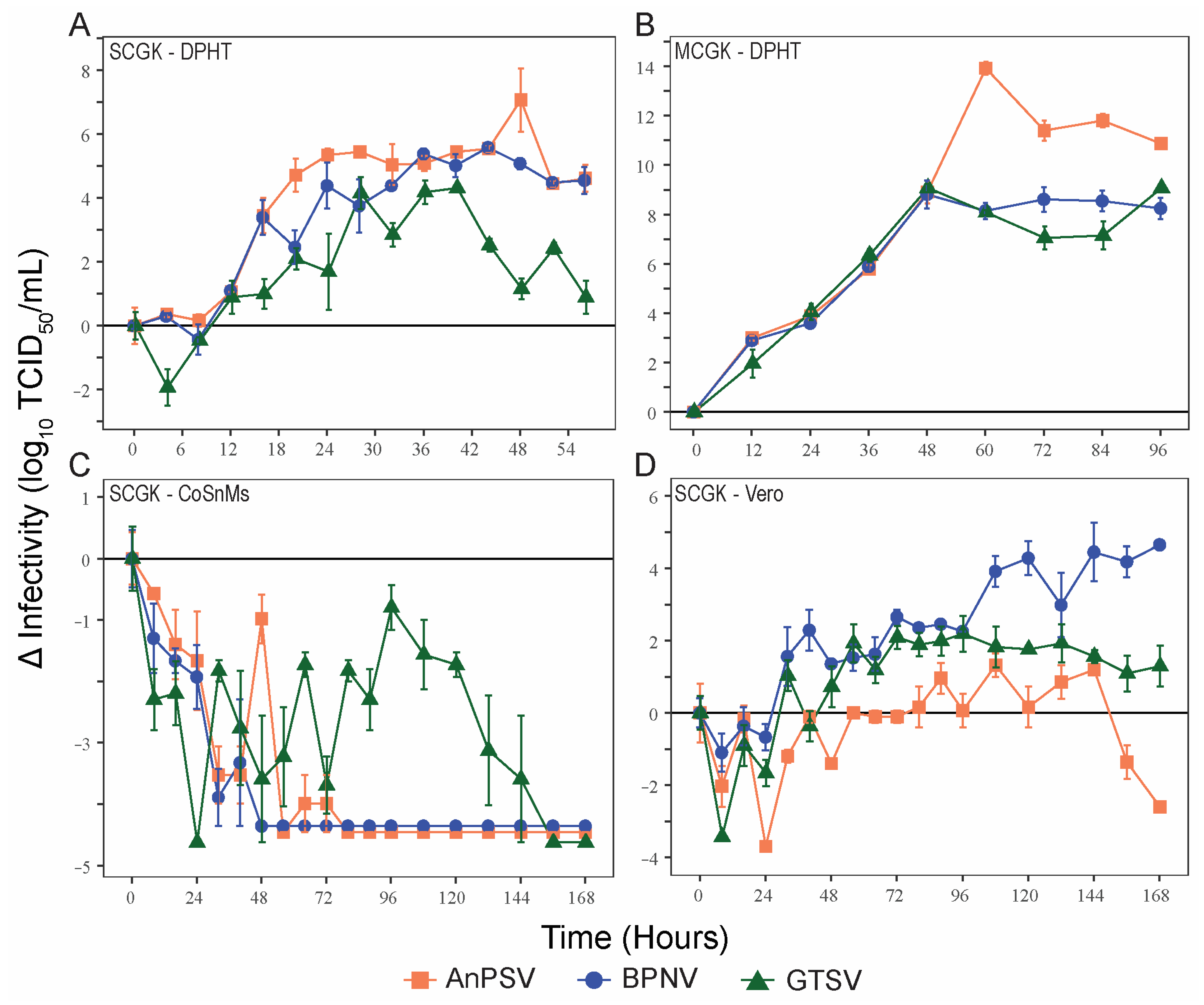
3.3. Growth Kinetics
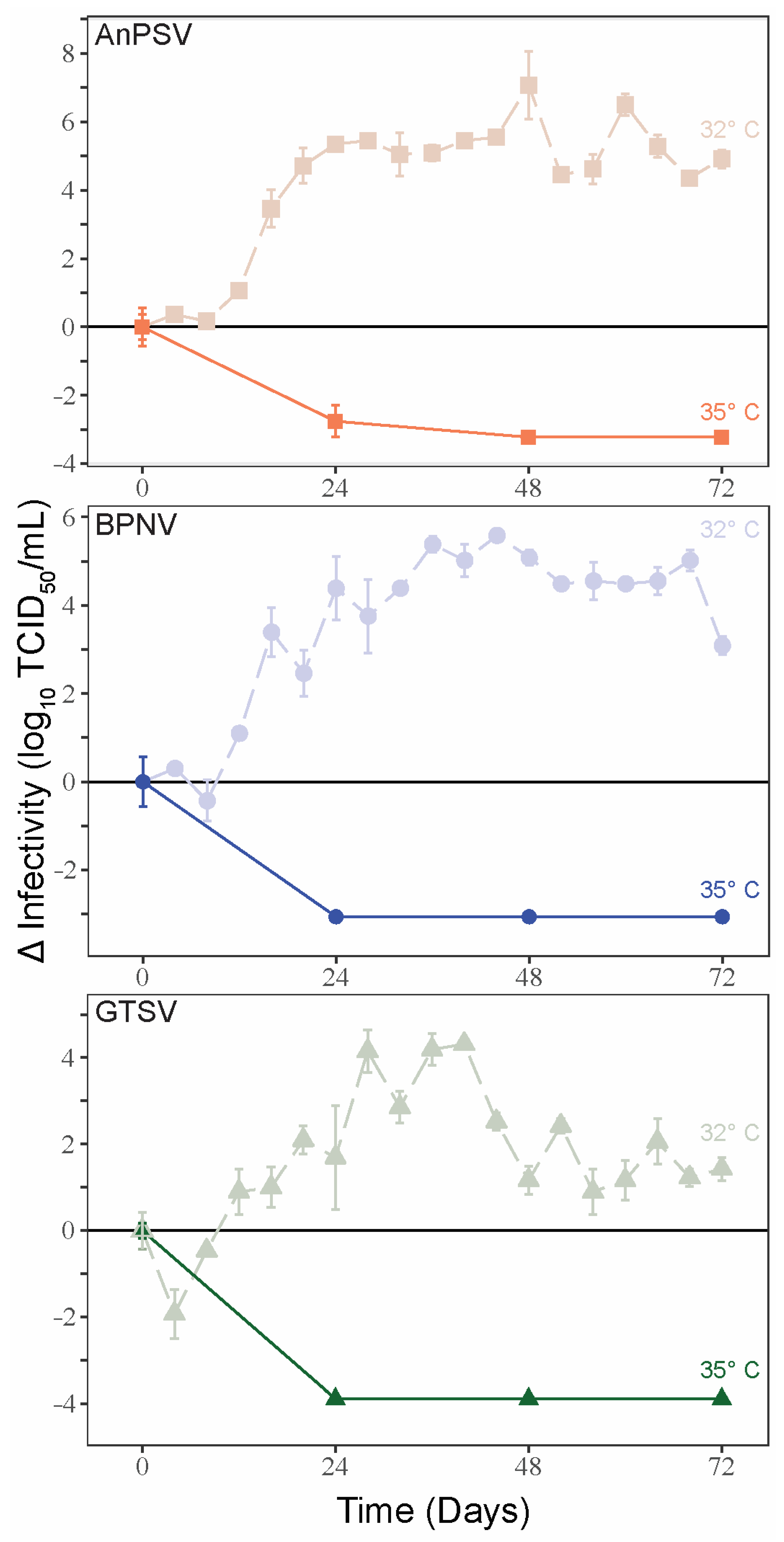
3.4. Temperature-Dependent Growth Kinetics
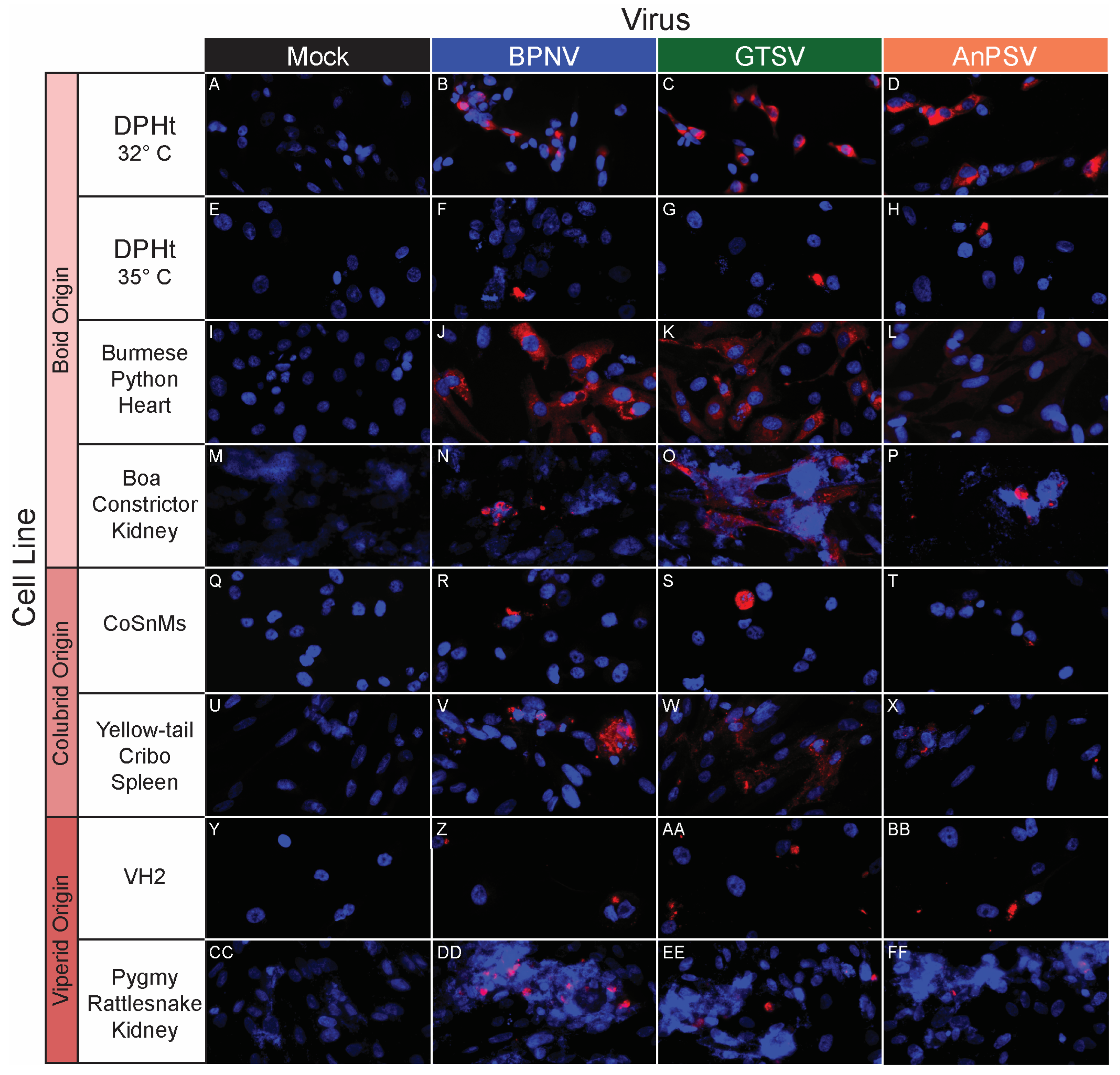
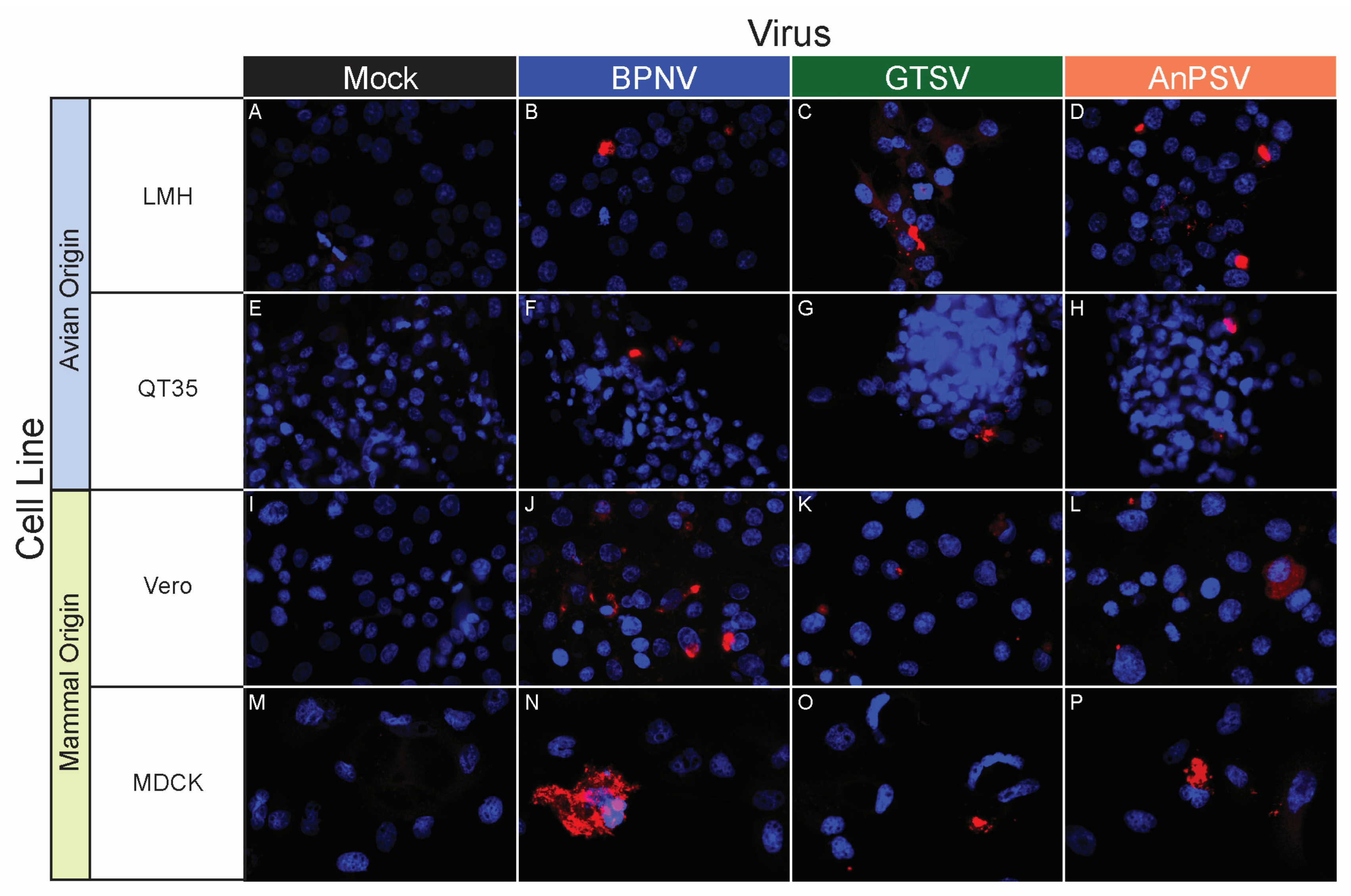
3.5. In Vitro Host Range Assessment by Epifluorescent Immunostaining
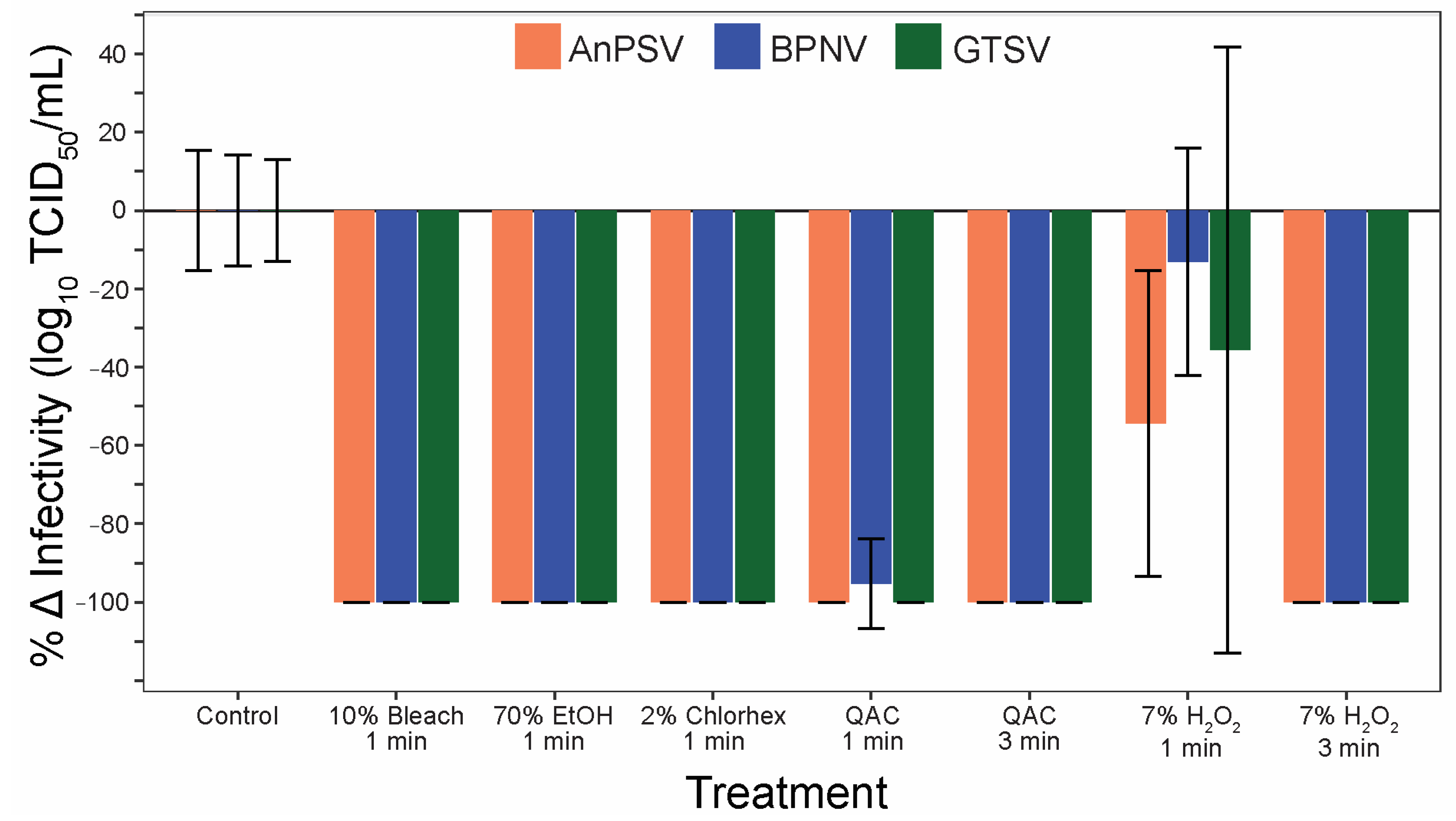
3.6. Sanitizer Efficacy
3.7. Antiviral Efficacy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stenglein, M.D.; Leavitt, E.B.; Abramovitch, M.A.; McGuire, J.A.; DeRisi, J.L. Genome Sequence of a Bornavirus Recovered from an African Garter Snake (Elapsoidea Loveridgei). Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00779-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, E.F.; Russo, A.G.; Yan, G.J.H.; Mercer, L.K.; White, P.A. Revealing the Uncharacterised Diversity of Amphibian and Reptile Viruses. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.F.; Lief, F.S.; Lunger, P.D.; Waters, D.; Leloup, P.; Foelsch, D.W.; Wyler, R.W. Fer de Lance Virus (FDLV): A Probable Paramyxovirus Isolated from a Reptile. J. Gen. Virol. 1979, 44, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintala, A.; Szirovicza, L.; Kipar, A.; Hetzel, U.; Hepojoki, J. Persistent Reptarenavirus and Hartmanivirus Infection in Cultured Boid Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0158522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenglein, M.D.; Sanders, C.; Kistler, A.L.; Graham Ruby, J.; Franco, J.Y.; Reavill, D.R.; Dunker, F.; DeRisia, J.L. Identification, Characterization, and in Vitro Culture of Highly Divergent Arenaviruses from Boa Constrictors and Annulated Tree Boas: Candidate Etiological Agents for Snake Inclusion Body Disease. MBio 2012, 3, e00180-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J. Respiratory Medicine of Reptiles. Vet. Clin. NA Exot. Pet 2011, 14, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J. Respiratory Diseases of Reptiles. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 1997, 6, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon-Hanks, L.L.; Layton, M.L.; Ossiboff, R.J.; Parker, J.S.L.; Dubovi, E.J.; Stenglein, M.D. Respiratory Disease in Ball Pythons (Python Regius) Experimentally Infected with Ball Python Nidovirus. Virology 2018, 517, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Finlaison, D.S.; Frost, M.J.; Gestier, S.; Gu, X.; Hall, J.; Jenkins, C.; Parrish, K.; Read, A.J.; Srivastava, M.; et al. Identification of a Novel Nidovirus as a Potential Cause of Large Scale Mortalities in the Endangered Bellinger River Snapping Turtle (Myuchelys Georgesi). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, M.A.; Jackson, B.; Jackson, C.; Xavier, P.; Warren, K. Discovery and Partial Genomic Characterisation of a Novel Nidovirus Associated with Respiratory Disease in Wild Shingleback Lizards (Tiliqua Rugosa). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon-Hanks, L.L.; Ossiboff, R.J.; Bartolini, P.; Fogelson, S.B.; Perry, S.M.; Stöhr, A.C.; Cross, S.T.; Wellehan, J.F.X.; Jacobson, E.R.; Dubovi, E.J.; et al. Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Sampling of Serpentovirus (Nidovirus) Infection in Captive Snakes Reveals High Prevalence, Persistent Infection, and Increased Mortality in Pythons and Divergent Serpentovirus Infection in Boas and Colubrids. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbalenya, A.; Samborskiy, D.; Junglen, S.; Lauber, C.; Neuman, B.; Ziebuhr, J. Create 47 New Taxa in the Order, Ranging from Subfamilies to Species (Nidovirales). 2021. Available online: https://ictv.global/ictv/proposals/2021.005S.R.Nidovirales.zip (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Hoon-Hanks, L.L.; Stöhr, A.C.; Anderson, A.J.; Evans, D.E.; Nevarez, J.G.; Díaz, R.E.; Rodgers, C.P.; Cross, S.T.; Steiner, H.R.; Parker, R.R.; et al. Serpentovirus (Nidovirus) and Orthoreovirus Coinfection in Captive Veiled Chameleons (Chamaeleo Calyptratus) with Respiratory Disease. Viruses 2020, 12, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillis, S.B.; Josimovich, J.M.; Miller, M.A.; Hoon-Hanks, L.L.; Hartmann, A.M.; Claunch, N.M.; Iredale, M.E.; Logan, T.D.; Yackel Adams, A.A.; Bartoszek, I.A.; et al. Divergent Serpentoviruses in Free-Ranging Invasive Pythons and Native Colubrids in Southern Florida, United States. Viruses 2022, 14, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leineweber, C.; Marschang, R.E. Detection of Nidoviruses in Samples Collected from Captive Snakes in Europe between 2016 and 2021. Vet. Rec. 2023, 192, e2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenglein, M.D.; Jacobson, E.R.; Wozniak, E.J.; Wellehan, J.F.X.; Kincaid, A.; Gordon, M.; Porter, B.F.; Baumgartner, W.; Stahl, S.; Kelley, K.; et al. Ball Python Nidovirus: A Candidate Etiologic Agent for Severe Respiratory Disease in Python Regius. MBio 2014, 5, e01484-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionie, O.; Courtillon, C.; Allee, C.; Maurel, S.; Queguiner, M.; Eterradossi, N. An Experimental Study of the Survival of Turkey Coronavirus at Room Temperature and +4 °C. Avian Pathol. 2013, 42, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenau, H.F.; Cinatl, J.; Morgenstern, B.; Bauer, G.; Preiser, W.; Doerr, H.W. Stability and Inactivation of SARS Coronavirus. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 194, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Sridhar, S.; Zhang, R.R.; Chu, H.; Fung, A.Y.F.; Chan, G.; Chan, J.F.W.; To, K.K.W.; Hung, I.F.N.; Cheng, V.C.C.; et al. Factors Affecting Stability and Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.S.; Dashti, M.; Tafuro, J.; Nasiri, M.; Muntean, E.A.; Wong, N.; Kemp, T.; Hills, G.; Mallen, C.D. Methods to Disinfect and Decontaminate SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review of in Vitro Studies. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 2049936121998548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.L.; Xiang, J.; MacKin, S.R.; Perlman, S.; Thorne, P.; O’Shaughnessy, P.; Strzelecki, B.; Aubin, P.; Ortiz-Hernandez, M.; Stapleton, J.T. Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus Virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Diverse RNA and DNA Viruses on Three-Dimensionally Printed Surgical Mask Materials. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.D.; Boucraut-baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-jones, T.; Hartmann, K.; Horzinek, M.C.; Hosie, M.J.; Lloret, A.; Lutz, H.; et al. Disinfectant Choices in Veterinary Practices, Shelters and Households ABCD Guidelines on Safe and Effective Disinfection for Feline Environments. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015, 17, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschang, R.E.; Gravendyck, M.; Kaleta, E.F. Herpesviruses in Tortoises: Investigations into Virus Isolation and the Treatment of Viral Stomatitis in Testudo Hermanni and T. Graeca. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1997, 44, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.P.; Chen, S.N.; Zou, P.F.; Huang, B.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, L.B.; Qin, Q.W.; Nie, P. IFN-γ in Turtle: Conservation in Sequence and Signalling and Role in Inhibiting Iridovirus Replication in Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle Pelodiscus Sinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 43, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer, J.; Killington, R. Virus Isolation and Quantitation. In Virology Methods Manual; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 26–46. ISBN 9780080543581. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, S.C.; Bounous, D.I.; Lee, M.D. Early Events in the Pathogenesis of Avian Salmonellosis. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersts, P.J. DotDotGoose; American Museum of Natural History, Center for Biodiversity and Conservation: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Blahak, S.; Jenckel, M.; Höper, D.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Schlottau, K. Investigations into the Presence of Nidoviruses in Pythons. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russmann, S.; Ignazio, G.; Piero, P.; Vincenzo, P.O.; Giuseppe, P. Ribavirin-Induced Anemia: Mechanisms, Risk Factors and Related Targets for Future Research. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3351–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkolova, E.; Dejmek, M.; Hřebabecký, H.; Šála, M.; Böserle, J.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E. Remdesivir Triphosphate Can Efficiently Inhibit the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Various Flaviviruses. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Leist, S.R.; Schäfer, A.; Won, J.; Brown, A.J.; Montgomery, S.A.; Hogg, A.; Babusis, D.; Clarke, M.O.; et al. Comparative Therapeutic Efficacy of Remdesivir and Combination Lopinavir, Ritonavir, and Interferon Beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julander, J.G.; Bunyan, E.; Jordan, R.; Porter, D.P. Remdesivir Efficacy against Yellow Fever in a Hamster Model. Antivir. Res. 2022, 203, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.L.; Schul, W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Gu, F.; Duraiswamy, J.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Niyomrattanakit, P.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Goh, A.; et al. An Adenosine Nucleoside Inhibitor of Dengue Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20435–20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brattstrom, B.H. Body Temperatures of Reptiles. Am. Midl. Nat. 1965, 73, 376–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, C. Ball Pythons, 1st ed.; TFH Publications Inc.: Neptune City, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, M.S.; Bennett, R.A.; Kinsel, M.J.; Mitchell, M.A. Evaluation of the Histologic Reactions to Commonly Used Suture Materials in the Skin and Musculature of Ball Pythons (Python Regius). Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, G.; Heatwole, H. Patterns of Heat Distribution within the Bodies of Some Australian Pythons. Am. Soc. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 1971, 1971, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.R.; Webb, G.J.W.; Johnson, C. Thermoregulation in Pythons: III. Thermal Ecology and Behavior of the Black-Headed Rock Python, Aspidites Melanocephalus. Herpetologica 1975, 31, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Shine, R.; Madsen, T. Is Thermoregulation Unimportant for Most Reptiles? An Example Using Water Pythons (Liasis Fuscus) in Tropical Australia. Physiol. Zool. 1996, 69, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobian, D.; Overgaard, J.; Wang, T. Oxygen Transport Is Not Compromised at High Temperature in Pythons. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 3958–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zaar, M.; Arvedsen, S.; Vedel-Smith, C.; Overgaard, J. Effects of Temperature on the Metabolic Response to Feeding in Python Molurus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002, 133, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, L.E.; Barnes, F.D.; Percy, D.H. Temperature as a Factor in Resistance of Young Puppies to Canine Herpesvirus. J. Infect. Dis. 1969, 120, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retallick, R.W.R.; Miera, V. Strain Differences in the Amphibian Chytrid Batrachochytrium Dendrobatidis and Non-Permanent, Sub-Lethal Effects of Infection. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2007, 75, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhams, D.C.; Alford, R.A.; Marantelli, G. Emerging Disease of Amphibians Cured by Elevated Body Temperature. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 55, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuring, W.L.; Poynter, B.M.; Wells, S.; Pessier, A.P. Successful Clearance of Chytrid Fungal Infection in Threatened Chiricahua Leopard Frog (Rana Chiricahuensis) Larvae and Frogs Using an Elevated Temperature Treatment Protocol. Salamandra 2021, 57, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Korzyukov, Y.; Iheozor-Ejiofor, R.; Levanov, L.; Smura, T.; Hetzel, U.; Szirovicza, L.; de la Torre, J.C.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Kipar, A.; Vapalahti, O.; et al. Differences in Tissue and Species Tropism of Reptarenavirus Species Studied by Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Pseudotypes. Viruses 2020, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monath, T.P.; Cropp, C.B.; Frazier, C.L.; Murphy, F.A.; Whitfield, S.G. Viruses Isolated from Reptiles: Identification of Three New Members of the Family Rhabdoviridae. Arch. Virol. 1979, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenburg, S.; Brennan, G. Species-Specific Host–Virus Interactions: Implications for Viral Host Range and Virulence. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigent, S.J.; McCauley, J.W. Influenza Type A in Humans, Mammals and Birds: Determinants of Virus Virulence, Host-Range and Interspecies Transmission. BioEssays 2003, 25, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Fung, T.S.; Chong, K.K.L.; Shukla, A.; Hilgenfeld, R. Accessory Proteins of SARS-CoV and Other Coronaviruses. Antiviral Res. 2014, 109, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.R.; Leibowitz, J.L. Coronavirus Pathogenesis, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 81, ISBN 9780123858856. [Google Scholar]
- Damas, J.; Hughes, G.M.; Keough, K.C.; Painter, C.A.; Persky, N.S.; Corbo, M.; Hiller, M.; Koepfli, K.P.; Pfenning, A.R.; Zhao, H.; et al. Broad Host Range of SARS-CoV-2 Predicted by Comparative and Structural Analysis of ACE2 in Vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22311–22322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Rasche, A.; Greenwood, A.D.; Osterrieder, K.; Drexler, J.F. Potential Zoonotic Sources of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Grouping | Common Name | Species | Origin Tissue | Commercial Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snake- | Diamond Python | Morelia spilota spilota | Heart | |
| Boid | Carpet Python | Morelia spilota ssp. | Heart, Kidney, Lung | |
| Burmese Python | Python bivittatus | Heart | ||
| Amethystine Python | Simalia amethistina | Spleen | ||
| Common Boa | Boa imperator | Heart, Kidney, Lung | ||
| Snake- | Yellowtail Cribo | Drymarchon corais | Spleen | |
| Colubrid | Smooth Greensnake | Opheodrys vernalis | Lung | |
| Trans-Pecos Ratsnake | Bogertophis subocularis | Kidney | ||
| Corn Snake | Pantherophis guttatus | Mass | ||
| Snake- | Venezuelan Rattlesnake | Crotalus durissus | Heart | |
| Viperid | Pygmy Rattlesnake | Sistrurus miliarius | Kidney | |
| Russell’s Viper | Daboia russelii | Heart | VH2 | |
| Lizard | Brown Anole | Anolis sagrei | Kidney | |
| Knight Anole | Anolis equestris | Kidney | ||
| Leopard Gecko | Eublepharis macularius | Spleen | ||
| Chelonian | Gopher Tortoise | Gopherus polyphemus | Spleen | |
| Galapagos Tortoise | Chelonoidis nigra | Liver | ||
| Diamondback Terrapin | Malaclemys terrapin | Lung | ||
| Yellowbelly Slider | Trachemys scripta | Heart | ||
| Crocodilian | Chinese Alligator | Alligator sinensis | Lung | |
| Saltwater Crocodile | Crocodylus porosus | Lung | ||
| Broad Snouted Caiman | Caiman latirostrus | Pancreas | ||
| Mammalian | Green Monkey | Chlorocebus sabaeus | Kidney | VERO E6 |
| Feline | Felis catus | Kidney | CRFK | |
| Canine | Canis lupus | Kidney | MDCK | |
| Avian | Japanese Quail | Coturnix japonica | Fibrosarcoma | QT-35 |
| Budgie | Melopsittacus undulatus | Lipomas | ||
| Chicken | Gallus gallus domesticus | Carcinoma | LMH |
| Virus | 32 °C (Infected/To.) | 35 °C (Infected/To.) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mock | 0% (0/1322) | 0% (0/513) | n/a |
| AnPSV | 27.9% (266/953) | 0.5% (4/805) | <2.2 × 10−16 * |
| BPNV | 11.6% (122/1053) | 0.5% (2/422) | <2.2 × 10−16 * |
| GTSV | 15.6% (64/410) | 0.4% (3/694) | <2.2 × 10−16 * |
| Compound | Virus | EC50 a (µg/mL) | EC90 b (µg/mL) | CC50 c (µg/mL) | SI50 d (µg/mL) | SI90 e (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ribavirin | AnPSV f | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 12 | >1000 | >500 | >83 |
| BPNV g | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.6 | >1000 | >1100 | >625 | |
| GTSV h | 7.9 ± 3.0 | 14 | >1000 | >127 | >71 | |
| Remdesivir | AnPSV | <0.022 ± 0.02 | <0.001 | 2.2 ± 1.6 | >100 | >1700 |
| BPNV | <0.022 ± 0.02 | <0.001 | 2.3 ± 1.8 | >105 | >1500 | |
| GTSV | <0.022 ± 0.02 | <0.001 | 2.2 ± 1.2 | >100 | >1700 | |
| NITD-008 | AnPSV | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.76 | 33 ± 9.0 | 55 | 53 |
| BPNV | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 1.5 | 37 ± 26 | 53 | 13 | |
| GTSV | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 4.8 | 55 ± 42 | 39 | 6.7 | |
| Favipiravir | AnPSV | >320 | ND | >320 | 0 | ND |
| BPNV | >320 | ND | >320 | 0 | ND | |
| GTSV | >320 | ND | >320 | 0 | ND | |
| Enviroximine | AnPSV | >0.24 | ND | 0.24 | 0 | ND |
| BPNV | >0.38 | ND | 0.38 | 0 | ND | |
| GTSV | >4.9 | ND | 4.9 | 0 | ND | |
| Pirodavir | AnPSV | 1.1 | ND | 7.3 | 6.6 | ND |
| BPNV | 2.6 | ND | >10 | >3.8 | ND | |
| GTSV | 0.86 | ND | >10 | >12 | ND | |
| Infergen | AnPSV | >0.01 | ND | 0.01 | 0 | ND |
| BPNV | >0.01 | ND | 0.01 | 0 | ND | |
| GTSV | >0.01 | ND | 0.01 | 0 | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tillis, S.B.; Holt, C.; Havens, S.; Logan, T.D.; Julander, J.G.; Ossiboff, R.J. In Vitro Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of Ophidian Serpentoviruses. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061371
Tillis SB, Holt C, Havens S, Logan TD, Julander JG, Ossiboff RJ. In Vitro Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of Ophidian Serpentoviruses. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061371
Chicago/Turabian StyleTillis, Steven B., Camille Holt, Spencer Havens, Tracey D. Logan, Justin G. Julander, and Robert J. Ossiboff. 2023. "In Vitro Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of Ophidian Serpentoviruses" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061371
APA StyleTillis, S. B., Holt, C., Havens, S., Logan, T. D., Julander, J. G., & Ossiboff, R. J. (2023). In Vitro Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of Ophidian Serpentoviruses. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061371






