Galleria mellonella—A Model for the Study of aPDT—Prospects and Drawbacks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Characterization of G. mellonela and Significance for Microbiological Research
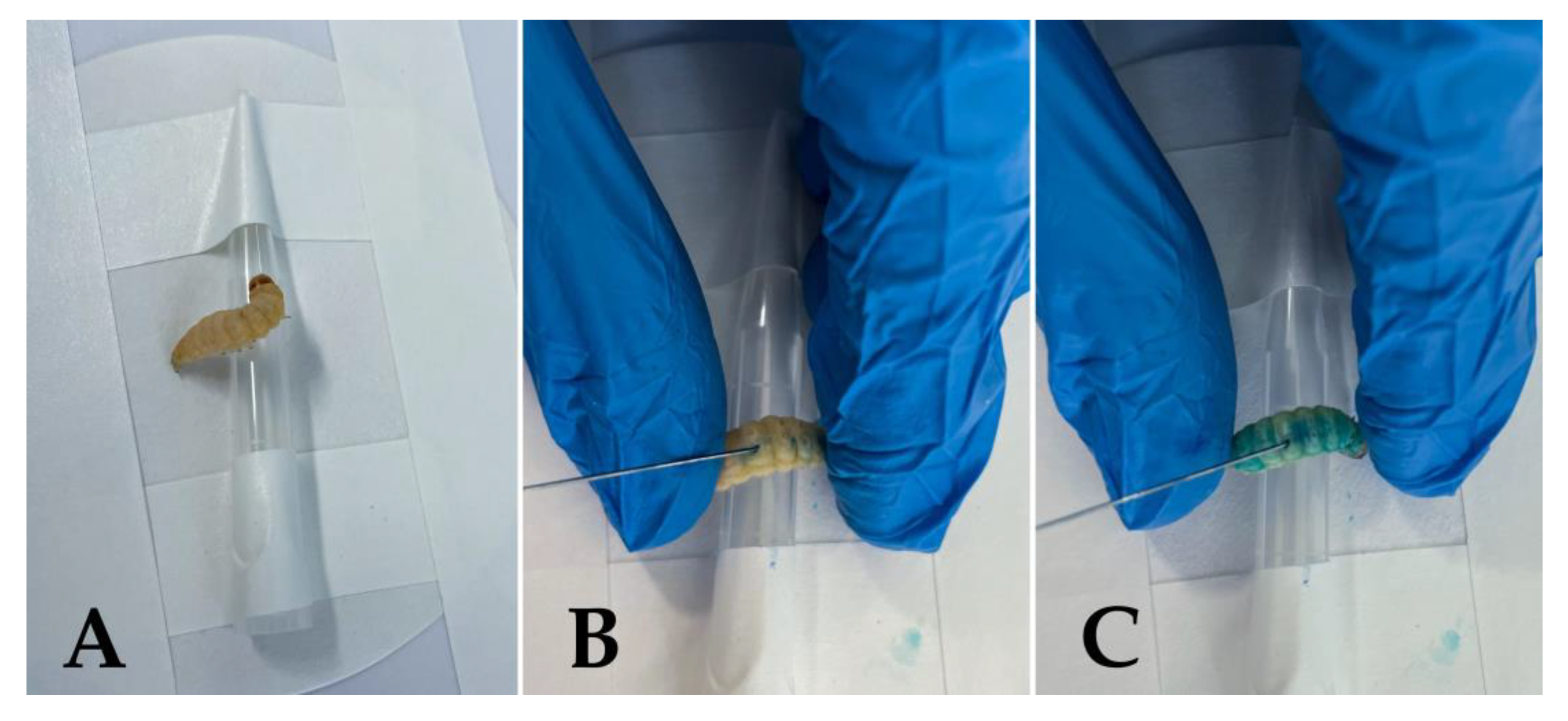
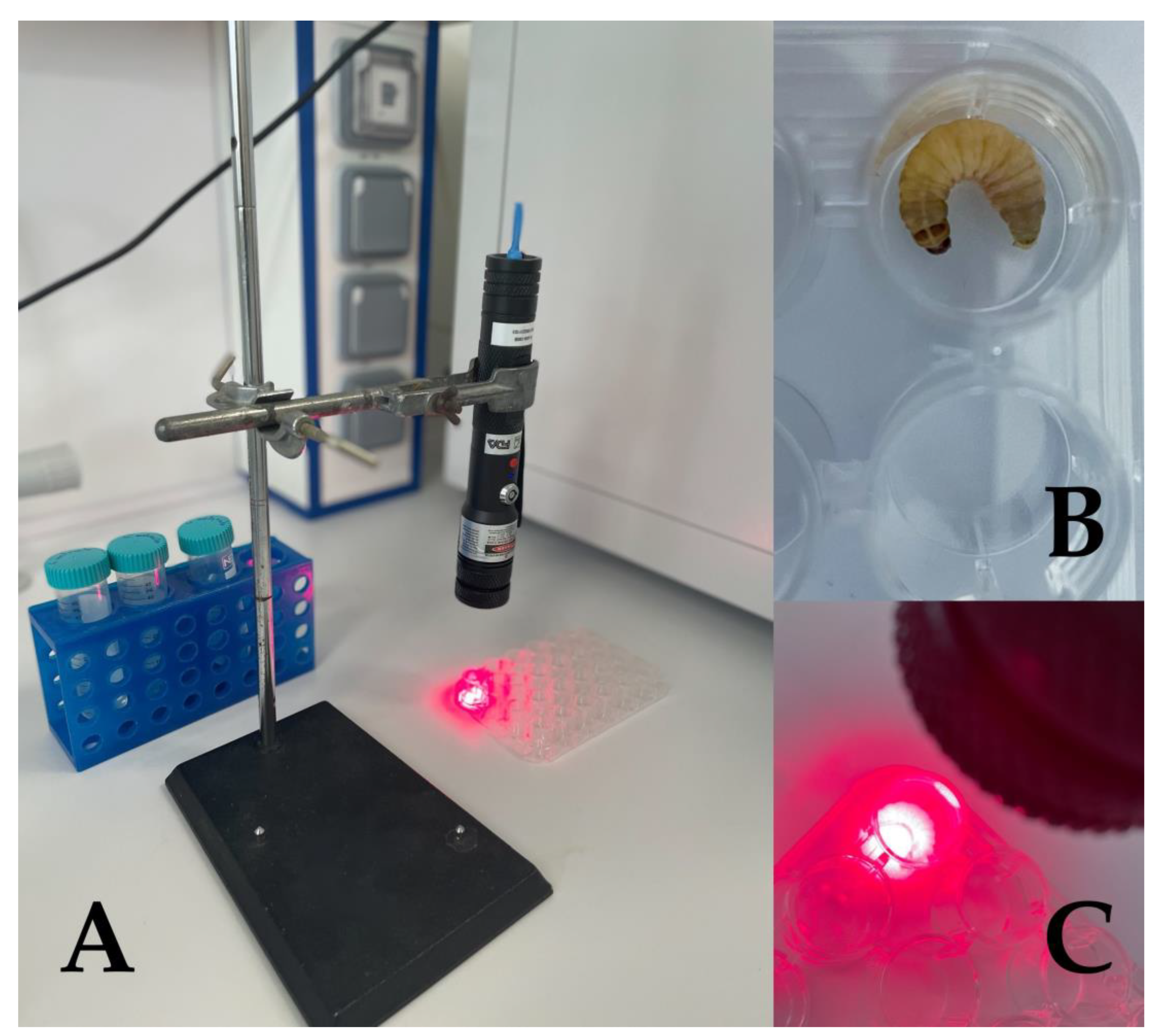
3. Principles of aPDT and the Use of G. mellonella in aPDT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lionakis, M.S. Drosophila and Galleria Insect Model Hosts: New Tools for the Study of Fungal Virulence, Pharmacology and Immunology. Virulence 2011, 2, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatek, M.; Sheehan, G.; Kavanagh, K. Galleria mellonella: The Versatile Host for Drug Discovery, In Vivo Toxicity Testing and Characterising Host-Pathogen Interactions. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, I.; Verdial, C.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. The Virtuous Galleria mellonella Model for Scientific Experimentation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, M.; Li, Y.; Newton, S.M.; Robertson, B.D.; Langford, P.R. Galleria mellonella—Intracellular Bacteria Pathogen Infection Models: The Ins and Outs. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, E.; Hörtnagl, C.; Lackner, M.; Grässle, D.; Naschberger, V.; Moser, P.; Segal, E.; Semis, M.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Binder, U. Galleria mellonella as a Model System to Study Virulence Potential of Mucormycetes and Evaluation of Antifungal Treatment. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, G.; Rouillon, A.; Cattoir, V.; Donnio, P.-Y. Galleria mellonella as a Suitable Model of Bacterial Infection: Past, Present and Future. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 782733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, E. European Science Foundation Policy Briefing: Use of Animals in Research. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2000, 28, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUR-Lex 32010L0063 EN EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32010L0063 (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Hubrecht, R.C.; Carter, E. Carter The 3Rs and Humane Experimental Technique: Implementing Change. Animals 2019, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, G.; Risi, G. Caenorhabditis elegans: Nature and Nurture Gift to Nematode Parasitologists. Parasitology 2018, 145, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Caenorhabditis Elegans as a Useful Model for Studying Aging Mutations. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 554994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolwinski, N. Introduction: Drosophila—A Model System for Developmental Biology. JDB 2017, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, S.; Lüersen, K.; Wagner, A.E.; Rimbach, G. Drosophila melanogaster as a Versatile Model Organism in Food and Nutrition Research. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3737–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teame, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Xie, M.; Gao, C.; Ye, Y.; Duan, M.; et al. The Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as Biomedical Models. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kang, H.; Kwon, B.; Lee, J.P.; Lee, J.; Choi, K. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a Model Organism for Screening Nephrotoxic Chemicals and Related Mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, E.; Titball, R.W.; Carter, J.; Champion, O.L. Galleria mellonella Larvae Allow the Discrimination of Toxic and Non-Toxic Chemicals. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Zambrano, L.J.; Bordallo-Cardona, M.Á.; Borghi, E.; Falleni, M.; Tosi, D.; Muñoz, P.; Escribano, P.; Guinea, J. Candida Isolates Causing Candidemia Show Different Degrees of Virulence in Galleria mellonella. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.A.; Garcia, M.T.; Pinto, J.G.; Ferreira-Strixino, J.; Faustino, E.G.; Pedroso, L.L.C.; Junqueira, J.C. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy Mediated by Fotenticine and Methylene Blue on Planktonic Growth, Biofilms, and Burn Infections of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legéňová, K.; Kovalčíková, M.; Černáková, L.; Bujdáková, H. The Contribution of Photodynamic Inactivation vs. Corsodyl Mouthwash to the Control of Streptococcus mutans Biofilms. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černáková, L.; Jordao, L.; Bujdáková, H. Impact of Farnesol and Corsodyl ® on Candida Albicans Forming Dual Biofilm with Streptococcus Mutans. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkerová-Chupáčová, J.; Borghi, E.; Morace, G.; Bujdáková, H. Up-Regulation of Antimicrobial Peptides Gallerimycin and Galiomicin in Galleria mellonella Infected with Candida Yeasts Displaying Different Virulence Traits. Mycopathologia 2018, 183, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singkum, P.; Suwanmanee, S.; Pumeesat, P.; Luplertlop, N. A Powerful in Vivo Alternative Model in Scientific Research: Galleria mellonella. AMicr 2019, 66, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, M.; Sheehan, G.; Li, Y.; Robertson, B.D.; Kavanagh, K.; Langford, P.R.; Newton, S.M. Innate Immune Responses of Galleria mellonella to Mycobacterium bovis BCG Challenge Identified Using Proteomic and Molecular Approaches. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 619981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojda, I.; Staniec, B.; Sułek, M.; Kordaczuk, J. The Greater Wax Moth Galleria mellonella: Biology and Use in Immune Studies. Pathog. Dis. 2020, 78, ftaa057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chupáčová, J.; Borghi, E.; Morace, G.; Los, A.; Bujdáková, H. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Antibody Directed against Surface Antigen Complement Receptor 3-Related Protein—Comparison of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, ftx127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, M.; Maisch, T.; Nonell, S.; Plaetzer, K.; Almeida, A.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Photoantimicrobials—Are We Afraid of the Light? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e49–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, H.; Hamblin, M.R. New Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieplik, F.; Deng, D.; Crielaard, W.; Buchalla, W.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Maisch, T. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy—What We Know and What We Don’t. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firacative, C.; Khan, A.; Duan, S.; Ferreira-Paim, K.; Leemon, D.; Meyer, W. Rearing and Maintenance of Galleria mellonella and Its Application to Study Fungal Virulence. JoF 2020, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.L. External Morphology of the Larva, Pupa, and Adult of the Wax Moth, Galleria mellonella L. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2023, 38, 287–310. [Google Scholar]
- Swamy, B.C.H. Bionomics and Biometrics of Greater Wax Moth Galleria mellonella Linnaeus. Asian J. Bio Sci. 2007, 3, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.D.; Graham, J.R.; Mortensen, A. Standard Methods for Wax Moth Research. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosamani, V.; Hanumantha Swamy, B.C.; Kattimani, K.N.; Kalibavi, C.M. Studies on Biology of Greater Wax Moth (Galleria mellonella L.). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2017, 6, 3811–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.V.; Siddhapara, M.R.; Patel, P.K.; Prajapati, A.P. Biology of Greater Wax Moth, Galleria mellonella L. on Artificial Diet. J. Exp. Zool. India 2019, 22, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, M.; Thomas, D.Y.; Whiteway, M.; Kavanagh, K. Correlation between Virulence of Candida albicans Mutants in Mice and Galleria mellonella Larvae. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.B.; Mylonakis, E. Using Non-Mammalian Hosts to Study Fungal Virulence and Host Defense. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, H.; Wright, C.L.; Jones, S.; da Silva, G.R.; McKillen, J.; Gilmore, B.F.; Kavanagh, O.; Green, B.D. Extracts of Sida Cordifolia Contain Polysaccharides Possessing Immunomodulatory Activity and Rosmarinic Acid Compounds with Antibacterial Activity. BMC Complement Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durieux, M.-F.; Melloul, É.; Jemel, S.; Roisin, L.; Dardé, M.-L.; Guillot, J.; Dannaoui, É.; Botterel, F. Galleria mellonella as a Screening Tool to Study Virulence Factors of Aspergillus fumigatus. Virulence 2021, 12, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Duma, L.; Rossez, Y. Galleria mellonella as a Good Model to Study Acinetobacter baumannii Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmquist, J.A.; Rogan, M.R.; McGillivray, S.M. Galleria mellonella as an Infection Model for Bacillus anthracis Sterne. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firacative, C.; Duan, S.; Meyer, W. Galleria mellonella Model Identifies Highly Virulent Strains among All Major Molecular Types of Cryptococcus gattii. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borman, A.M. Of Mice and Men and Larvae: Galleria mellonella to Model the Early Host-Pathogen Interactions after Fungal Infection. Virulence 2018, 9, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowlds, P.; Kavanagh, K. Effect of Pre-Incubation Temperature on Susceptibility of Galleria mellonella Larvae to Infection by Candida albicans. Mycopathologia 2008, 165, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S.A.; Gahan, C.G.M. Molecular Pathogenesis of Listeria Monocytogenes in the Alternative Model Host Galleria mellonella. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3456–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloezen, W.; van Helvert-van Poppel, M.; Fahal, A.H.; van de Sande, W.W. A Madurella mycetomatis Grain Model in Galleria mellonella Larvae. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, H.; Altincicek, B.; Glöckner, G.; Vilcinskas, A. A Comprehensive Transcriptome and Immune-Gene Repertoire of the Lepidopteran Model Host Galleria mellonella. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Schäfer, A.; Bender, A.; Steimle, A.; Beier, S.; Parusel, R.; Frick, J.-S. Galleria mellonella: A Novel Invertebrate Model to Distinguish Intestinal Symbionts from Pathobionts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Beier, S.; Huson, D.H.; Parusel, R.; Iglauer, F.; Frick, J.-S. Genome Sequence of Galleria mellonella (Greater Wax Moth). Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e01220-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.; Burne, A.; Casaro, S.; Brown, M.B.; Bisinotto, R.S.; Galvao, K.N. Establishing Galleria mellonella as an Invertebrate Model for the Emerging Multi-Host Pathogen Helcococcus Ovis. Virulence 2023, 14, 2186377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Sharma, K.K. Lepidopteran Insects: Emerging Model Organisms to Study Infection by Enteropathogens. Folia Microbiol. 2023, 68, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Pang, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Shi, D. Correlation Between Drug Resistance and Virulence of Candida Isolates from Patients with Candidiasis. IDR 2022, 15, 7459–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.B.; O’Brien, E.; El Khoury, J.B.; Mylonakis, E. Methods for Using Galleria mellonella as a Model Host to Study Fungal Pathogenesis. Virulence 2010, 1, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesketh-Best, P.J.; Mouritzen, M.V.; Shandley-Edwards, K.; Billington, R.A.; Upton, M. Galleria mellonella Larvae Exhibit a Weight-Dependent Lethal Median Dose When Infected with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pathog. Dis. 2021, 79, ftab003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuntaş, H.; Gwokyalya, R.; Bayram, N. Immunotoxic Effects of Force-Fed Ethephon on Model Organism Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemel, S.; Guillot, J.; Kallel, K.; Botterel, F.; Dannaoui, E. Galleria mellonella for the Evaluation of Antifungal Efficacy against Medically Important Fungi, a Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, J.; Duan, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Chang, W.; Lou, H. Hinokitiol Chelates Intracellular Iron to Retard Fungal Growth by Disturbing Mitochondrial Respiration. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 34, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempinski, P.; Smith, D.; Casadevall, A. Cryptococcus neoformans Virulence Assay Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Model System. Bio. Protoc. 2022, 12, e4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.A.; Menezes, R.T.; Carvalho, J.S.; Garcia, M.T.; Segundo, A.G.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Junqueira, J.C. Exploring the Galleria mellonella Model to Study Antifungal Photodynamic Therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 27, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntzel, P.; Nagel, C.; Weigelt, J.; Betts, J.W.; Pattrick, C.A.; Southam, H.M.; La Ragione, R.M.; Poole, R.K.; Schatzschneider, U. Biological Activity of Manganese(I) Tricarbonyl Complexes on Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: From Functional Studies to in Vivo Activity in Galleria mellonella. Metallomics 2019, 11, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, L.; Gustavo De Almeida, L.; Silva, F.R.O.; Cortez, M.; Taborda, C.P.; Spira, B. In Vivo Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Galleria mellonella. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, A.P.; Lee, M.; Megaw, J.; McEvoy, J.; Coulter, S.M.; Pentlavalli, S.; Laverty, G. Investigating the In Vivo Antimicrobial Activity of a Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel Using a Galleria mellonella Infection Model. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix-Fisher, E.; McLean, S. The Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Acetate against Acinetobacter baumannii in a Galleria mellonella Infection Model. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalfaro, C.; Iacobino, A.; Nardis, C.; Franciosa, G. Galleria mellonella as an in Vivo Model for Assessing the Protective Activity of Probiotics against Gastrointestinal Bacterial Pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moman, R.; O’Neill, C.A.; Ledder, R.G.; Cheesapcharoen, T.; McBain, A.J. Mitigation of the Toxic Effects of Periodontal Pathogens by Candidate Probiotics in Oral Keratinocytes, and in an Invertebrate Model. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Carpenter, C.E.; Broadbent, J.R. Organic Acid Exposure Enhances Virulence in Some Listeria Monocytogenes Strains Using the Galleria mellonella Infection Model. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 675241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, K.; Hain, T.; Fischer, R.; Chakraborty, T.; Vilcinskas, A. Brain Infection and Activation of Neuronal Repair Mechanisms by the Human Pathogen Listeria monocytogenes in the Lepidopteran Model Host Galleria mellonella. Virulence 2013, 4, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, M.; Lombardini, G.; Rizzo, S.; Scarafile, D.; Modesto, M.; Truzzi, E.; Benvenuti, S.; Elmi, A.; Bertocchi, M.; Fiorentini, L.; et al. Potential Applications of Essential Oils for Environmental Sanitization and Antimicrobial Treatment of Intensive Livestock Infections. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.; Edwards, J.; Brown, J.; Dixon, R. Galleria mellonella Infection Model Identifies Both High and Low Lethality of Clostridium Perfringens Toxigenic Strains and Their Response to Antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benthall, G.; Touzel, R.E.; Hind, C.K.; Titball, R.W.; Sutton, J.M.; Thomas, R.J.; Wand, M.E. Evaluation of Antibiotic Efficacy against Infections Caused by Planktonic or Biofilm Cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella kneumoniae in Galleria mellonella. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparecida Procópio Gomes, L.; Alves Figueiredo, L.M.; Luiza do Rosário Palma, A.; Corrêa Geraldo, B.M.; Isler Castro, K.C.; Ruano de Oliveira Fugisaki, L.; Jorge, A.O.C.; de Oliveira, L.D.; Junqueira, J.C. Punica granatum L. (Pomegranate) Extract: In Vivo Study of Antimicrobial Activity against Porphyromonas gingivalis in Galleria mellonella Model. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 8626987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázár, V.; Snitser, O.; Barkan, D.; Kishony, R. Antibiotic Combinations Reduce Staphylococcus aureus Clearance. Nature 2022, 610, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Monga, D.; Pillai, S.; Mylonakis, E.; Moellering, R.C.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Reduced Susceptibility to Vancomycin Influences Pathogenicity in Staphylococcus aureus Infection. J. Infect Dis. 2009, 199, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiblier, C.; Seidl, K.; Roschitzki, B.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Berger-Bächi, B.; Senn, M.M. Secretome Analysis Defines the Major Role of SecDF in Staphylococcus aureus Virulence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, A.P.; Coote, P.J. Wax Moth Larva (Galleria mellonella): An in Vivo Model for Assessing the Efficacy of Antistaphylococcal Agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Materazzi, A.; Bottai, D.; Campobasso, C.; Klatt, A.-B.; Cesta, N.; De Masi, M.; Trampuz, A.; Tavanti, A.; Di Luca, M. Phage-Based Control of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Galleria mellonella Model of Implant-Associated Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, G.; Dixon, A.; Kavanagh, K. Utilization of Galleria mellonella Larvae to Characterize the Development of Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Microbiology 2019, 165, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Khader, R.; Felix, L.O.; Frate, M.; Mylonakis, E.; Meschwitz, S.; Fuchs, B.B. A Substituted Diphenyl Amide Based Novel Scaffold Inhibits Staphylococcus aureus Virulence in a Galleria mellonella Infection Model. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 723133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.S.; Adenwalla, N.; Wiles, S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella Larvae as an Infection Model for Group A Streptococcus. Virulence 2013, 4, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.J.; Watkins, M.E.; Cantu, C.C.; Beres, S.B.; Musser, J.M. Virulence of Serotype M3 Group A Streptococcus Strains in Wax Worms (Galleria mellonella Larvae). Virulence 2011, 2, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.-Y.; Loh, J.M.S.; Proft, T. The Use of Galleria mellonella (Wax Moth) as an Infection Model for Group A Streptococcus. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2136, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, F.; Torfs, E.; Aizawa, J.; Vanhoutte, B.; Maes, L.; Caljon, G.; Delputte, P.; Cappoen, D.; Cos, P. Optimization and Characterization of a Galleria mellonella Larval Infection Model for Virulence Studies and the Evaluation of Therapeutics Against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.A.; Rozen, D.E. A Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection Model in Larvae of the Wax Moth Galleria mellonella. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2012, 31, 2653–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, J.T.; Primon-Barros, M.; de Carvalho Robaina, A.; Pizzutti, K.; Mott, M.P.; Trentin, D.S.; Dias, C.A.G. Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotype 19A from Carriers and Invasive Disease: Virulence Gene Profile and Pathogenicity in a Galleria mellonella Model. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2023, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, J.D.; de Oliveira Fugisaki, L.R.; Medina, R.P.; Scorzoni, L.; de Sá Alves, M.; de Barros, P.P.; Ribeiro, F.C.; Fuchs, B.B.; Mylonakis, E.; Silva, D.H.S.; et al. Streptococcus mutans Secreted Products Inhibit Candida albicans Induced Oral Candidiasis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.A.; Faustoferri, R.C.; Quivey, R.G. β-Phosphoglucomutase Contributes to Aciduricity in Streptococcus mutans. Microbiology 2014, 160, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, S.; de Mojana di Cologna, N.; Archer-Hartmann, S.; Rogers, A.M.; Samaddar, S.; Ganguly, T.; Black, I.M.; Glushka, J.; Ng, K.K.S.; Azadi, P.; et al. Involvement of the Streptococcus mutans PgfE and GalE 4-Epimerases in Protein Glycosylation, Carbon Metabolism, and Cell Division. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Mraheil, M.A.; Silva, S.; Müller, D.; Cemic, F.; Hemberger, J.; Hain, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Chakraborty, T. Anti-Listeria Activities of Galleria mellonella Hemolymph Proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4237–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Altincicek, B.; Hain, T.; Domann, E.; Vilcinskas, A.; Chakraborty, T. Galleria mellonella as a Model System for Studying Listeria Pathogenesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, S.L.; Casey, P.G.; Hill, C.; Diep, D.B.; Nes, I.F.; Brede, D.A. In Vivo Assessment of Growth and Virulence Gene Expression during Commensal and Pathogenic Lifestyles of LuxABCDE-Tagged Enterococcus faecalis Strains in Murine Gastrointestinal and Intravenous Infection Models. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3986–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, S.L.; Diep, D.B.; Nes, I.F.; Brede, D.A. Construction and Application of a LuxABCDE Reporter System for Real-Time Monitoring of Enterococcus faecalis Gene Expression and Growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7003–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, L.N.; Brunson, D.N.; Kajfasz, J.K.; Lemos, J.A. Methods for Using the Galleria mellonella Invertebrate Model to Probe Enterococcus faecalis Pathogenicity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2427, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieme, L.; Hartung, A.; Makarewicz, O.; Pletz, M.W. In Vivo Synergism of Ampicillin, Gentamicin, Ceftaroline and Ceftriaxone against Enterococcus Faecalis Assessed in the Galleria mellonella Infection Model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibebe Junior, J.; Fuchs, B.B.; Sabino, C.P.; Junqueira, J.C.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Gilmore, M.S.; Rice, L.B.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R.; et al. Photodynamic and Antibiotic Therapy Impair the Pathogenesis of Enterococcus faecium in a Whole Animal Insect Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, F.; Le Bras, F.; Reffuveille, F.; Ladjouzi, R.; Giard, J.-C.; Leclercq, R.; Cattoir, V. Galleria mellonella as a Model for Studying Enterococcus faecium Host Persistence. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradal, I.; Casado, A.; Del Rio, B.; Rodriguez-Lucas, C.; Fernandez, M.; Alvarez, M.A.; Ladero, V. Enterococcus Faecium Bacteriophage VB_EfaH_163, a New Member of the Herelleviridae Family, Reduces the Mortality Associated with an E. Faecium VanR Clinical Isolate in a Galleria mellonella Animal Model. Viruses 2023, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagatolla, C.; Mehat, J.W.; La Ragione, R.M.; Luzzati, R.; Di Bella, S. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies of Oritavancin and Fosfomycin Synergism against Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meir, M.; Grosfeld, T.; Barkan, D. Establishment and Validation of Galleria mellonella as a Novel Model Organism to Study Mycobacterium Abscessus Infection, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02539-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, M.; Bifani, P.; Barkan, D. The Addition of Avibactam Renders Piperacillin an Effective Treatment for Mycobacterium Abscessus Infection in an in Vivo Model. Antimicrob. Resist Infect Control 2018, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, M.; Li, Y.; Spiropoulos, J.; Cooley, W.; Everest, D.J.; Kendall, S.L.; Martín, C.; Robertson, B.D.; Langford, P.R.; Newton, S.M. Galleria mellonella as an Infection Model for the Virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Virulence 2022, 13, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Spiropoulos, J.; Cooley, W.; Khara, J.S.; Gladstone, C.A.; Asai, M.; Bossé, J.T.; Robertson, B.D.; Newton, S.M.; Langford, P.R. Galleria mellonella—A Novel Infection Model for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex. Virulence 2018, 9, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, M.; Li, Y.; Khara, J.S.; Gladstone, C.A.; Robertson, B.D.; Langford, P.R.; Newton, S.M. Use of the Invertebrate Galleria mellonella as an Infection Model to Study the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 148, e59703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffotaux, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, W.; Hui, Z.; Wang, X.; Gicquel, B.; Liu, S. A Hydrazine-Hydrazone Adamantine Compound Shows Antimycobacterial Activity and Is a Probable Inhibitor of MmpL3. Molecules 2022, 27, 7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Y.; Keddie, B.A. The Galleria mellonella-Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Model System: Characterization of Pathogen Virulence and Insect Immune Responses. J. Insect. Sci. 2021, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasastha Ram, V.; Yasur, J.; Abishad, P.; Unni, V.; Purushottam Gourkhede, D.; Nishanth, M.A.D.; Niveditha, P.; Vergis, J.; Singh Malik, S.V.; Kullaiah, B.; et al. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver with Entrapped Cinnamaldehyde against Multi-Drug-Resistant Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli in Galleria mellonella. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrieri, C.G.; Pereira, M.F.; Galdino, A.C.M.; Dos Santos, A.L.S.; Elias, W.P.; Schuenck, R.P.; Spano, L.C. Typical and Atypical Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Are Both Virulent in the Galleria mellonella Model. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, D.A.; Mills, G.; Johnson, J.R.; Porter, S.; Wiles, S. In Vivo Correlates of Molecularly Inferred Virulence among Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) in the Wax Moth Galleria mellonella Model System. Virulence 2014, 5, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, S.C.; Mil-Homens, D.; Fialho, A.M.; Arraiano, C.M. The Virulence of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium in the Insect Model Galleria mellonella Is Impaired by Mutations in RNase E and RNase III. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6124–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K.; Stasiłojć, M.; Grabowski, Ł.; Zdrojewska, K.; Węgrzyn, G.; Węgrzyn, A. Efficacy and Safety of Phage Therapy against Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhimurium and Enteritidis Estimated by Using a Battery of in Vitro Tests and the Galleria mellonella Animal Model. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 261, 127052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.; Card, R.; Nunes, C.; AbuOun, M.; Bagnall, M.C.; Nunez, J.; Mendonça, N.; Anjum, M.F.; da Silva, G.J. Virulence Characterization of Salmonella enterica by a New Microarray: Detection and Evaluation of the Cytolethal Distending Toxin Gene Activity in the Unusual Host S. Typhimurium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insua, J.L.; Llobet, E.; Moranta, D.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C.; Tomás, A.; Garmendia, J.; Bengoechea, J.A. Modeling Klebsiella kneumoniae Pathogenesis by Infection of the Wax Moth Galleria mellonella. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3552–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeçti, S. Pathophysiological Effects of Klebsiella kneumoniae Infection on Galleria mellonella as an Invertebrate Model Organism. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3509–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; MacDonald, U. The Galleria mellonella Infection Model Does Not Accurately Differentiate between Hypervirulent and Classical Klebsiella kneumoniae. mSphere 2020, 5, e00850-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Han, P.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Li, M.; An, X.; Song, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Characterization and Comparative Genomics Analysis of a New Bacteriophage BUCT610 against Klebsiella kneumoniae and Efficacy Assessment in Galleria mellonella Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.A.F.; Ahmed, F.A.; Elkhateeb, A.F.; Mahmoud, E.E.; Ahmed, M.I.; Ahmed, R.I.; Hosni, A.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Dablool, A.S.; et al. Virulence Characteristics of Biofilm-Forming Acinetobacter baumannii in Clinical Isolates Using a Galleria mellonella Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Shin, B.; Kang, M.; Yang, J.; Lee, T.K.; Park, W. A Novel Decoy Strategy for Polymyxin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Elife 2021, 10, e66988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, G.; Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, H.; Ye, Y.; Li, J. In Vivo Activity of Daptomycin/Colistin Combination Therapy in a Galleria mellonella Model of Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Goy, K.; She, R.; Spellberg, B.; Luna, B. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Performed in RPMI 1640 Reveals Azithromycin Efficacy against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Predicts In Vivo Outcomes in Galleria mellonella. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e0132022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelaus, J.; Lundmark, E.; Lindgren, P.; Sjödin, A.; Forsman, M. Galleria mellonella Reveals Niche Differences Between Highly Pathogenic and Closely Related Strains of Francisella Spp. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodmann, M.; Schnider, S.T.; Basler, M. Type VI Secretion System and Its Effectors PdpC, PdpD, and OpiA Contribute to Francisella Virulence in Galleria mellonella Larvae. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0057920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Propst, C.N.; Pylypko, S.L.; Blower, R.J.; Ahmad, S.; Mansoor, M.; van Hoek, M.L. Francisella philomiragia Infection and Lethality in Mammalian Tissue Culture Cell Models, Galleria mellonella, and BALB/c Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S. Demonstration of the Efficacy of Curcumin on Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Galleria mellonella Larvae Model. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, C.; Laforêt, F.; Blasdel, B.; Glonti, T.; Kutter, E.; Pirnay, J.P.; Mainil, J.; Delcenserie, V.; Thiry, D. Efficacy Assessment of PEV2 Phage on Galleria mellonella Larvae Infected with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Dog Otitis Isolate. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.A.; Scorzoni, L.; de Castro Santos, A.; Junqueira, J.C.; Anbinder, A.L. Galleria mellonella as an Experimental Model for Studying Periodontopathogens. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2020, 24, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, R.M.; Garcia, M.T.; Stossi, F.; de Barros, P.P.; Junqueira, J.C.; Anbinder, A.L. Effects of α and β-Adrenergic Signaling on Innate Immunity and Porphyromonas Gingivalis Virulence in an Invertebrate Model. Virulence 2022, 13, 1614–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowa-Jasiłek, A.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Stączek, S.; Wydrych, J.; Skrzypiec, K.; Mak, P.; Deryło, K.; Tchórzewski, M.; Cytryńska, M. Galleria mellonella Lysozyme Induces Apoptotic Changes in Candida albicans Cells. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, P.P.; Rossoni, R.D.; de Camargo Ribeiro, F.; Silva, M.P.; de Souza, C.M.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Junqueira, J.C. Two Sporulated Bacillus Enhance Immunity in Galleria mellonella Protecting against Candida albicans. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.; Mil-Homens, D.; Henriques, M.; Silva, S. Anti-EFG1 2′-OMethylRNA Oligomer Inhibits Candida albicans Filamentation and Attenuates the Candidiasis in Galleria mellonella. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 27, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskatepe, B.; Aslan Erdem, S.; Ozturk, S.; Safi Oz, Z.; Subasi, E.; Koyuncu, M.; Vlainić, J.; Kosalec, I. Antifungal and Anti-Virulent Activity of Origanum majorana L. Essential Oil on Candida albicans and In Vivo Toxicity in the Galleria mellonella Larval Model. Molecules 2022, 27, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins de Andrade, V.; Bardají, E.; Heras, M.; Ramu, V.G.; Junqueira, J.C.; Diane Dos Santos, J.; Castanho, M.A.R.B.; Conceição, K. Antifungal and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Designed Derivatives from Kyotorphin. Fungal. Biol. 2020, 124, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagle-Olmedo, T.; Andrade-Pavón, D.; Martínez-Gamboa, A.; Gómez-García, O.; García-Sierra, F.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C.; Villa-Tanaca, L. Inhibitors of DNA Topoisomerases I and II Applied to Candida dubliniensis Reduce Growth, Viability, the Generation of Petite Mutants and Toxicity, While Acting Synergistically with Fluconazole. FEMS Yeast Res. 2021, 21, foab023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, S.; Coutts, R.H.A. Aspergillus fumigatus Mycovirus Causes Mild Hypervirulent Effect on Pathogenicity When Tested on Galleria mellonella. Fungal. Genet. Biol. 2015, 76, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.; Walshe, K.; Kavanagh, K. Prolonged Subculturing of Aspergillus fumigatus on Galleria Extract Agar Results in Altered Virulence and Sensitivity to Antifungal Agents. Cells 2023, 12, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenman, H.C.; Duong, R.; Chan, H.; Tsue, R.; McClelland, E.E. Reduced Virulence of Melanized Cryptococcus neoformans in Galleria mellonella. Virulence 2014, 5, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.F.; Tansie, S.M.; Shahan, J.R.; Seipelt-Thiemann, R.L.; McClelland, E.E. Serial Passage of Cryptococcus neoformans in Galleria mellonella Results in Increased Capsule and Intracellular Replication in Hemocytes, but Not Increased Resistance to Hydrogen Peroxide. Pathogens 2020, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevijano-Contador, N.; Herrero-Fernández, I.; García-Barbazán, I.; Scorzoni, L.; Rueda, C.; Rossi, S.A.; García-Rodas, R.; Zaragoza, O. Cryptococcus neoformans Induces Antimicrobial Responses and Behaves as a Facultative Intracellular Pathogen in the Non Mammalian Model Galleria mellonella. Virulence 2015, 6, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.; Konings, M.; Parel, F.; Eadie, K.; Strepis, N.; Fahal, A.; Verbon, A.; van de Sande, W.W.J. Inhibiting DHN- and DOPA-Melanin Biosynthesis Pathway Increased the Therapeutic Value of Itraconazole in Madurella mycetomatis Infected Galleria mellonella. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, myac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, G.; Konings, M.; Lim, W.; Fahal, A.; Kavanagh, K.; van de Sande, W.W.J. Proteomic Analysis of the Processes Leading to Madurella mycetomatis Grain Formation in Galleria mellonella Larvae. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, K.; Parel, F.; Helvert-van Poppel, M.; Fahal, A.; van de Sande, W. Combining Two Antifungal Agents Does Not Enhance Survival of Galleria mellonella Larvae Infected with Madurella mycetomatis. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2017, 22, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, O.; Titball, R.; Bates, S. Standardization of G. mellonella Larvae to Provide Reliable and Reproducible Results in the Study of Fungal Pathogens. JoF 2018, 4, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, M.; Christian, P.; Marina, C.F.; Williams, T. A Comparison of Techniques for Detecting Invertebrate iridescent Virus 6. J. Virol. Methods 2001, 98, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossoni, R.D.; de Camargo Ribeiro, F.; Dos Santos, H.F.S.; Dos Santos, J.D.; de Sousa Oliveira, N.; Dutra, M.T.D.S.; de Lapena, S.A.B.; Junqueira, J.C. Galleria mellonella as an Experimental Model to Study Human Oral Pathogens. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 101, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Uçkan, F.; Er, A. Immunosuppressive Influence of Parasitoid Wasp Pimpla turionellae Calyx Fluid on Host Galleria mellonella Cell-Mediated Immune Response and Hemocyte Viability. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 112, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Haddad, L.; Angelidakis, G.; Clark, J.R.; Mendoza, J.F.; Terwilliger, A.L.; Chaftari, C.P.; Duna, M.; Yusuf, S.T.; Harb, C.P.; Stibich, M.; et al. Genomic and Functional Characterization of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci-Specific Bacteriophages in the Galleria mellonella Wax Moth Larvae Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Yong, D. Two Novel Bacteriophages Improve Survival in Galleria mellonella Infection and Mouse Acute Pneumonia Models Infected with Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02900-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, P.; Nachimuthu, R.; Lopes, B.S. The Therapeutic Potential of Bacteriophages Targeting Gram-Negative Bacteria Using Galleria mellonella Infection Model. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nale, J.Y.; Chutia, M.; Carr, P.; Hickenbotham, P.T.; Clokie, M.R.J. “Get in Early”; Biofilm and Wax Moth (Galleria mellonella) Models Reveal New Insights into the Therapeutic Potential of Clostridium Difficile Bacteriophages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sänger, P.-A.; Wagner, S.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.M.; Fuchs, T.M. Dissecting the Invasion of Galleria mellonella by Yersinia Enterocolitica Reveals Metabolic Adaptations and a Role of a Phage Lysis Cassette in Insect Killing. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.A.; Su, W.; Sergueev, K.V.; Kevorkian, R.T.; Snesrud, E.C.; Srijan, A.; He, Y.; Fouts, D.E.; Lurchachaiwong, W.; McGann, P.T.; et al. Design of a Bacteriophage Cocktail Active against Shigella Species and Testing of Its Therapeutic Potential in Galleria mellonella. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pu, M.; Han, P.; Li, M.; An, X.; Song, L.; Fan, H.; Chen, Z.; Tong, Y. Efficacy in Galleria mellonella Larvae and Application Potential Assessment of a New Bacteriophage BUCT700 Extensively Lyse Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04030-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasifar, R.; Kropinski, A.M.; Sabour, P.M.; Chambers, J.R.; MacKinnon, J.; Malig, T.; Griffiths, M.W. Efficiency of Bacteriophage Therapy against Cronobacter sakazakii in Galleria mellonella (Greater Wax Moth) Larvae. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, J.; Malik, S.; Pathak, R.; Kumar, M.; Ramanjaneya, S.; Kurkure, N.; Barbuddhe, S.B.; Rawool, D.B. Efficacy of Indolicidin, CAMA, Lactoferricin (17–30) and Their Combination against Multi-Drug Resistant Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, K.; Sheehan, G. The Use of Galleria mellonella Larvae to Identify Novel Antimicrobial Agents against Fungal Species of Medical Interest. JoF 2018, 4, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevijano-Contador, N.; Zaragoza, O. Immune Response of Galleria mellonella against Human Fungal Pathogens. JoF 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, G.; Rouillon, A.; Ghukasyan, G.; Emily, M.; Felden, B.; Donnio, P.-Y. Galleria mellonella Larvae as an Infection Model to Investigate SRNA-Mediated Pathogenesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 631710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junqueira, J.C. Galleria mellonella as a Model Host for Human Pathogens: Recent Studies and New Perspectives. Virulence 2012, 3, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.Y.; Keddie, B.A. Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Hemocytes Release Extracellular Traps That Confer Protection Against Bacterial Infection in the Hemocoel. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, N.; Heelan, M.; Kavanagh, K. An Analysis of the Structural and Functional Similarities of Insect Hemocytes and Mammalian Phagocytes. Virulence 2013, 4, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altincicek, B.; Stötzel, S.; Wygrecka, M.; Preissner, K.T.; Vilcinskas, A. Host-Derived Extracellular Nucleic Acids Enhance Innate Immune Responses, Induce Coagulation, and Prolong Survival upon Infection in Insects. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.L.; Kavanagh, O. Galleria mellonella as a Novel In Vivo Model to Screen Natural Product-Derived Modulators of Innate Immunity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, D.; Reeves, E.P.; Renwick, J.; Wientjes, F.B.; Kavanagh, K. Superoxide Production in Galleria mellonella Hemocytes: Identification of Proteins Homologous to the NADPH Oxidase Complex of Human Neutrophils. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 4161–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismuth, H.D.; Brasseur, G.; Ezraty, B.; Aussel, L. Bacterial Genetic Approach to the Study of Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Galleria mellonella During Salmonella Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 640112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepneva, I.A.; Glupov, V.V.; Sergeeva, S.V.; Khramtsov, V.V. EPR Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Hemolymph of Galleria mellonella and Dendrolimus superans sibiricus (Lepidoptera) Larvae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrońska, A.K.; Kaczmarek, A.; Kazek, M.; Boguś, M.I. Infection of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera) Larvae with the Entomopathogenic Fungus Conidiobolus coronatus (Entomophthorales) Induces Apoptosis of Hemocytes and Affects the Concentration of Eicosanoids in the Hemolymph. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 774086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, T.; de Barros, P.; Fugisaki, L.; Rossoni, R.; Ribeiro, F.; de Menezes, R.; Junqueira, J.; Scorzoni, L. Recent Advances in the Use of Galleria mellonella Model to Study Immune Responses against Human Pathogens. JoF 2018, 4, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcinskas, A. ANTI-Infective Therapeutics from the Lepidopteran Model Host Galleria mellonella. CPD 2011, 17, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordaczuk, J.; Sułek, M.; Mak, P.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Śmiałek, J.; Wojda, I. Cationic Protein 8 Plays Multiple Roles in Galleria mellonella Immunity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandra, R.M.; McCarron, P.; Viganor, L.; Fernandes, M.F.; Kavanagh, K.; McCann, M.; Branquinha, M.H.; Santos, A.L.S.; Howe, O.; Devereux, M. In Vivo Activity of Copper(II), Manganese(II), and Silver(I) 1,10-Phenanthroline Chelates Against Candida haemulonii Using the Galleria mellonella Model. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, F.E.; Rossoni, R.D.; de Barros, P.P.; Begnini, B.E.; Junqueira, J.C.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Leão, M.V.P.; de Oliveira, L.D. Immunomodulatory Effects and Anti-Candida Activity of Lactobacilli in Macrophages and in Invertebrate Model of Galleria mellonella. Microbial. Pathog. 2017, 110, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossoni, R.D.; Fuchs, B.B.; de Barros, P.P.; dos Santos Velloso, M.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Junqueira, J.C.; Mylonakis, E. Lactobacillus paracasei Modulates the Immune System of Galleria mellonella and Protects against Candida albicans Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, N.R.; Abdrahman, A.; Greig, C.; Mukherjee, K.; Thornton, C.; Ratcliffe, N.A.; Vilcinskas, A.; Butt, T.M. Myriocin Significantly Increases the Mortality of a Non-Mammalian Model Host during Candida Pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wu, G.; Lv, J.; Li, M. Eicosanoids Mediate Galleria mellonella Immune Response to Hemocoel Injection of Entomopathogenic Nematode Cuticles. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Namara, L.; Dolan, S.K.; Walsh, J.M.D.; Stephens, J.C.; Glare, T.R.; Kavanagh, K.; Griffin, C.T. Oosporein, an Abundant Metabolite in Beauveria caledonica, with a Feedback Induction Mechanism and a Role in Insect Virulence. Fungal. Biol. 2019, 123, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brivio, M.F.; Toscano, A.; De Pasquale, S.M.; De Lerma Barbaro, A.; Giovannardi, S.; Finzi, G.; Mastore, M. Surface Protein Components from Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria: Effects on Immune Responses of the Greater Wax Moth, Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): Immune-Depressive Role of Surface Components of Nematocomplexes. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolka, M.J. Immunosuppressive Effect of Cyclosporin A on Insect Humoral Immune Response. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 98, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcinskas, A.; Jegorov, A.; Landa, Z.; Götz, P.; Matha, V. Effects of Beauverolide L and Cyclosporin A on Humoral and Cellular Immune Response of the Greater Wax Moth, Galleria mellonella. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1999, 122, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zeng, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, D. An Insecticidal Protein from Xenorhabdus ehlersii Stimulates the Innate Immune Response in Galleria mellonella. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, G.; Margalit, A.; Sheehan, D.; Kavanagh, K. Proteomic Profiling of Bacterial and Fungal Induced Immune Priming in Galleria mellonella Larvae. J. Insect Physiol. 2021, 131, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.F.; de Almeida, D.R.Q.; Terra, L.F.; Baptista, M.S.; Labriola, L. Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer Treatment—An Update Review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Márquez, I.A.; Patiño-González, E.; Hernández-Villa, L.; Ortíz-Reyes, B.; Manrique-Moreno, M. Identification and Evaluation of Galleria mellonella Peptides with Antileishmanial Activity. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 546, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowlds, P.; Barron, A.; Kavanagh, K. Physical Stress Primes the Immune Response of Galleria mellonella Larvae to Infection by Candida albicans. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, J.P.; Troy, N.; Kavanagh, K. Pre-Exposure of Galleria mellonella Larvae to Different Doses of Aspergillus Fumigatus Conidia Causes Differential Activation of Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses. Virulence 2011, 2, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brivio, M.F.; Mastore, M.; Nappi, A.J. A Pathogenic Parasite Interferes with Phagocytosis of Insect Immunocompetent Cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, H.A.; Sehnal, F. Hemolin Expression in the Silk Glands of Galleria mellonella in Response to Bacterial Challenge and Prior to Cell Disintegration. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Shang, Y.; Cen, K.; Wang, C. Fungal Biosynthesis of the Bibenzoquinone Oosporein to Evade Insect Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11365–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.; Kavanagh, K. Caspofungin Primes the Immune Response of the Larvae of Galleria mellonella and Induces a Non-Specific Antimicrobial Response. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.P.; Entwistle, F.; Coote, P.J. Effective Immunosuppression with Dexamethasone Phosphate in the Galleria mellonella Larva Infection Model Resulting in Enhanced Virulence of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella kneumoniae. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 205, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Yao, Q.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, D.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z. Steinernema Glaseri Surface Enolase: Molecular Cloning, Biological Characterization, and Role in Host Immune Suppression. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yi, Y. Ultrastructural and Functional Characterization of Circulating Hemocytes from Galleria mellonella Larva: Cell Types and Their Role in the Innate Immunity. Tissue Cell 2016, 48, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazek, M.; Kaczmarek, A.; Wrońska, A.K.; Boguś, M.I. Conidiobolus coronatus Induces Oxidative Stress and Autophagy Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szurpnicka, A.; Wrońska, A.K.; Bus, K.; Kozińska, A.; Jabłczyńska, R.; Szterk, A.; Lubelska, K. Phytochemical Screening and Effect of Viscum album L. on Monoamine Oxidase A and B Activity and Serotonin, Dopamine and Serotonin Receptor 5-HTR1A Levels in Galleria mellonealla (Lepidoptera). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnul, C.; Turner, L.C.; Boyle, R.W. Immobilized Photosensitizers for Antimicrobial Applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Biol. 2015, 150, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolmans, D.E.J.G.J.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, K.; Goslinski, T. Photodynamic Therapy in Dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, T.J.; Gomer, C.J.; Henderson, B.W.; Jori, G.; Kessel, D.; Korbelik, M.; Moan, J.; Peng, Q. Photodynamic Therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 889–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.L.; Durães, C.P.; da Silva Menezes, A.S.; Tabosa, A.T.L.; Barbosa, C.U.; de Paulo Santiago Filho, A.; de Paula Souza, D.P.S.; Guimarães, V.H.D.; Santos, S.H.S.; de Paula, A.M.B.; et al. Comparison between Two Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy Protocols for Oral Candidiasis in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer: A Two-Arm, Single-Blind Clinical Trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 39, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, B.; Ali, D.; Ahmed, S.; Ibraheem, W.I.; Preethanath, R.S.; Vellappally, S.; Divakar, D.D. Role of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy in Reducing Subgingival Oral Yeasts Colonization in Patients with Peri-Implant Mucositis. Photodiagnosis. Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 38, 102803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Silva, E.G.; Arruda-Vasconcelos, R.; Louzada, L.M.; de-Jesus-Soares, A.; Ferraz, C.C.R.; Almeida, J.F.A.; Marciano, M.A.; Steiner-Oliveira, C.; Santos, J.M.M.; Gomes, B.P. Effect of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy on the Reduction of Bacteria and Virulence Factors in Teeth with Primary Endodontic Infection. Photodiagnosis. Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 41, 103292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Ozkiraz, S.; Akcan, A.B.; Canpolat, M. Low-Cost Home-Use Light-Emitting-Diode Phototherapy as an Alternative to Conventional Methods. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2015, 61, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockett, M.H.; Musbat, L.; Kjær, C.; Houmøller, J.; Toker, Y.; Rubio, A.; Milne, B.F.; Brøndsted Nielsen, S. The Soret Absorption Band of Isolated Chlorophyll a and b Tagged with Quaternary Ammonium Ions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 25793–25798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortik, N.; Steinbacher, P.; Maisch, T.; Spaeth, A.; Plaetzer, K. A Comparative Study on the Antibacterial Photodynamic Efficiency of a Curcumin Derivative and a Formulation on a Porcine Skin Model. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černáková, L.; Light, C.; Salehi, B.; Rogel-Castillo, C.; Victoriano, M.; Martorell, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Martins, N.; Rodrigues, C.F. Novel Therapies for Biofilm-Based Candida Spp. Infections. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1214, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Gomes, I.B.; Saavedra, M.J.; Simões, M. Photodynamic Therapy and Combinatory Treatments for the Control of Biofilm-Associated Infections. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štefánek, M.; Černáková, L.; Dekkerová, J.; Bujdáková, H. Photodynamic Inactivation Effectively Eradicates Candida auris Biofilm despite Its Interference with the Upregulation of CDR1 and MDR1 Efflux Genes. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, A.; Glueck, M.; Ckurshumova, W.; Liu, J.; Fefer, M.; Plaetzer, K. Breaking the Rebellion: Photodynamic Inactivation against Erwinia Amylovora Resistant to Streptomycin. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekrirad, Z.; Kashef, N.; Arefian, E. Photodynamic Inactivation Diminishes Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence Factor Production and Biofilm Formation of Serratia marcescens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangirolami, A.C.; Inada, N.M.; Bagnato, V.S.; Blanco, K.C. Biofilm Destruction on Endotracheal Tubes by Photodynamic Inactivation. Infect. Disord Drug Targets 2018, 18, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.F.; Iglesias, B.A.; Pinheiro, T.R.; Lacerda, L.E.; Sokolonski, A.R.; Pedreira, B.O.; Moreira, K.S.; Burgo, T.A.L.; Meyer, R.; Azevedo, V.; et al. Photodynamic Inactivation of Different Candida Species and Inhibition of Biofilm Formation Induced by Water-Soluble Porphyrins. Photodiagnosis. Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 42, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merigo, E.; Conti, S.; Ciociola, T.; Fornaini, C.; Polonelli, L.; Lagori, G.; Manfredi, M.; Vescovi, P. Effect of Different Wavelengths and Dyes on Candida albicans: In Vivo Study Using Galleria mellonella as an Experimental Model. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 18, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziani, M.H.; Tonani, L.; de Menezes, H.D.; Bachmann, L.; Wainwright, M.; Braga, G.Ú.L.; von Zeska Kress, M.R. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy with Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers in Non-Vertebrate Model Galleria mellonella Infected with Fusarium Keratoplasticum and Fusarium Moniliforme. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 25, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, C.V.G.; de Cássia Orlandi Sardi, J.; Terada, R.S.S.; Lazarini, J.G.; Freires, I.A.; Polaquini, C.R.; Torrezan, G.S.; Regasini, L.O.; Fujimaki, M.; Rosalen, P.L. Diacetylcurcumin: A New Photosensitizer for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy in Streptococcus mutans Biofilms. Biofouling 2019, 35, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcez, A.S.; Kaplan, M.; Jensen, G.J.; Scheidt, F.R.; Oliveira, E.M.; Suzuki, S.S. Effects of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy on Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 32, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibebe Junior, J.; Sabino, C.P.; Tan, X.; Junqueira, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Fuchs, B.B.; Jorge, A.O.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mylonakis, E. Selective Photoinactivation of Candida albicans in the Non-Vertebrate Host Infection Model Galleria mellonella. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černáková, L.; Chupáčová, J.; Židlíková, K.; Bujdáková, H. Effectiveness of the Photoactive Dye Methylene Blue versus Caspofungin on the Candida Parapsilosis Biofilm in Vitro and Ex Vivo. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRZP—Detail Kniha. Available online: https://opac.crzp.sk/?fn=detailBiblioFormChildA2KPL&sid=26764B43C57DF4A5B2DA947C556C&seo=CRZP-detail-kniha (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- dos Santos, J.D.; de Alvarenga, J.A.; Rossoni, R.D.; García, M.T.; Moraes, R.M.; Anbinder, A.L.; Cardoso Jorge, A.O.; Junqueira, J.C. Immunomodulatory Effect of Photodynamic Therapy in Galleria mellonella Infected with Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques Meccatti, V.; de Souza Moura, L.; Guerra Pinto, J.; Ferreira-Strixino, J.; Abu Hasna, A.; Alves Figueiredo-Godoi, L.M.; Campos Junqueira, J.; Marcucci, M.C.; de Paula Ramos, L.; Carvalho, C.A.T.; et al. Curcuma Longa L. Extract and Photodynamic Therapy Are Effective against Candida Spp. and Do Not Show Toxicity In Vivo. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 5837864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaetzer, K.; Krammer, B.; Berlanda, J.; Berr, F.; Kiesslich, T. Photophysics and Photochemistry of Photodynamic Therapy: Fundamental Aspects. Lasers Med. Sci. 2009, 24, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, M.C.A.; Manela-Azulay, M. Terapia Fotodinâmica: Revisão Da Literatura e Documentação Iconográfica. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2010, 85, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.R.; Downie, G.H.; Cuenca, R.; Hu, X.-H.; Childs, C.J.; Sibata, C.H. Photosensitizers in Clinical PDT. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2004, 1, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, P.; Kocher, T. Photodynamic Therapy for Periodontal Diseases: State of the Art. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Biol. 2005, 79, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grizante Barião, P.H.; Tonani, L.; Brancini, G.T.P.; Nascimento, E.; Braga, G.Ú.L.; Wainwright, M.; von Zeska Kress, M.R. In Vitro and in Vivo Photodynamic Efficacies of Novel and Conventional Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers against Multidrug-Resistant Candida auris. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, M.; Pan, W.; Wang, M.; Wu, X.; Dai, S.; Li, L.; Zeng, K. Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Responses of Photodynamic Therapy in Galleria mellonella Model. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de França, B.M.; Ghasemishahrestani, Z.; de Souza, G.F.M.; da Silva, R.N.; Queiroz, D.D.; Pierre, M.B.R.; Pereira, M.D.; Forero, J.S.B.; Corrêa, R.J. In Vitro Studies of Antitumor Effect, Toxicity/Cytotoxicity and Skin Permeation/Retention of a Green Fluorescence Pyrene-Based Dye for PDT Application. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 97, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigotto Caruso, G.; Tonani, L.; Marcato, P.D.; von Zeska Kress, M.R. Phenothiazinium Photosensitizers Associated with Silver Nanoparticles in Enhancement of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacarne, M.C.; Mastore, M.; Gariboldi, M.B.; Brivio, M.F.; Caruso, E. Preliminary Toxicity Evaluation of a Porphyrin Photosensitizer in an Alternative Preclinical Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, J.; Rahban, D.; Aghamiri, S.; Teymouri, A.; Bahador, A. Photosensitizers in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy: An Overview. Laser Ther. 2018, 27, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glueck, M.; Hamminger, C.; Fefer, M.; Liu, J.; Plaetzer, K. Save the Crop: Photodynamic Inactivation of Plant Pathogens I: Bacteria. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Richter, P.; Strauch, S.; Nasir, A.; Burkovski, A.; Antunes, C.; Meißgeier, T.; Schlücker, E.; Schwab, S.; Lebert, M. What an Escherichia coli Mutant Can Teach Us About the Antibacterial Effect of Chlorophyllin. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzeniene, A.; Juzenas, P.; Ma, L.-W.; Iani, V.; Moan, J. Effectiveness of Different Light Sources for 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Photodynamic Therapy. Lasers Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenleitner, M.; Plaetzer, K. In the Right Light: Photodynamic Inactivation of Microorganisms Using a LED-Based Illumination Device Tailored for the Antimicrobial Application. Antibiotics 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Gonzales, F.; Maisch, T. Photodynamic Inactivation for Controlling Candida albicans Infections. Fungal. Biol. 2012, 116, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcez, A.S.; Hamblin, M.R. Methylene Blue and Hydrogen Peroxide for Photodynamic Inactivation in Root Canal—A New Protocol for Use in Endodontics. Eur. Endod. J. 2017, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bispo, M.; Anaya-Sanchez, A.; Suhani, S.; Raineri, E.J.M.; López-Álvarez, M.; Heuker, M.; Szymański, W.; Romero Pastrana, F.; Buist, G.; Horswill, A.R.; et al. Fighting Staphylococcus aureus Infections with Light and Photoimmunoconjugates. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e139512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
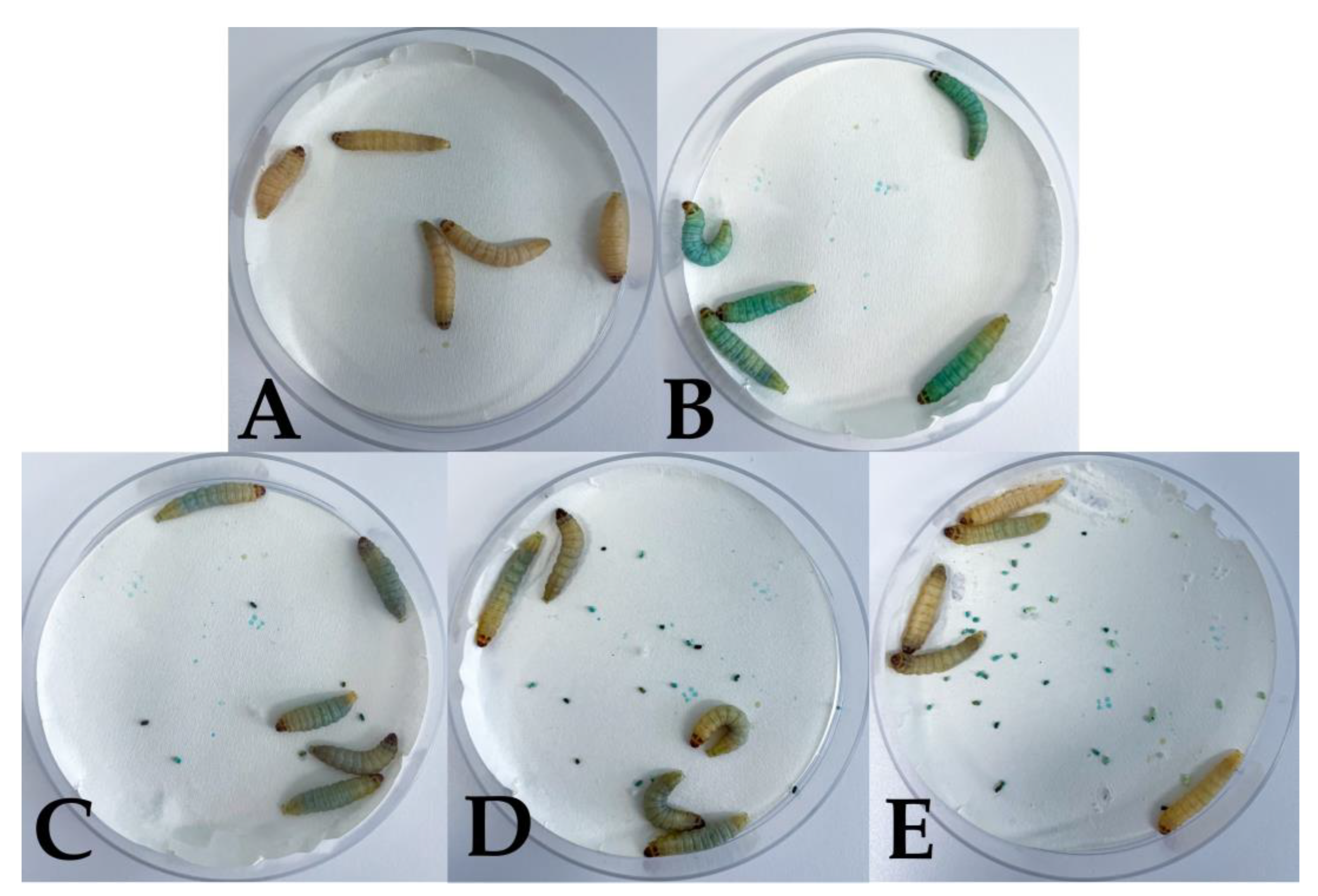

| Photosensitizer | Light Source | Energy | Microorganism | Authors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylene blue 0.2 mg/mL | 660 nm red light device composed of 48 LEDs | 30 J/cm2 | Acinetobacter baumannii | Figueiredo-Godoi et al. (2022) | [18] |
| Fotenticine 1.2 mg/mL | 660 nm red light device composed of 48 LEDs | 30 J/cm2 | Acinetobacter baumannii | Figueiredo-Godoi et al. (2022) | [18] |
| Methylene blue 75–600 μM | 660 nm red laser light | 6 J/cm2 and 15 J/cm2 | C. albicans | Figueiredo-Godoi et al. (2019) | [58] |
| Methylene blue 1 mM | 660 ± 15 nm broadband non-coherent red light source | 0.45–18 J/cm2 | Enterococcus faecium | Chibebe Junior et al. (2013) | [93] |
| Erythrosine 100 μM | 532 nm green diode laser | 10 J/cm2 | C. albicans | Merigo et al. (2017) | [209] |
| Curcumin 100 μM | 405 nm blue-violet diode laser | 10 J/cm2 | C. albicans | Merigo et al. (2017) | [209] |
| Toluidine blue 10 μM | 650 nm red diode laser | 10 J/cm2 | C. albicans | Merigo et al. (2017) | [209] |
| Methylene blue 750–3000 μM | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm and integrated irradiance from 570 to 670 nm | 15 J/cm2 | Fusarium keratoplasticum, F. moniliforme | Paziani et al. (2019) | [210] |
| New methylene blue N 100–400 μM | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm and integrated irradiance from 570 to 670 nm | 15 J/cm2 | Fusarium keratoplasticum, F. moniliforme | Paziani et al. (2019) | [210] |
| Pentacyclic phenothiazinium photosensitizer S137 100–400 μM | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm and integrated irradiance from 570 to 670 nm | 15 J/cm2 | Fusarium keratoplasticum, F. moniliforme | Paziani et al. (2019) | [210] |
| Curcumin 50 μg/mL | 440–480 nm LED source | 1.2 J/cm2 | Streptococcus mutants | Sanches et al. (2019) | [211] |
| Diacetylcurcumin 50 μg/mL | 440–480 nm LED source | 1.2 J/cm2 | Streptococcus mutants | Sanches et al. (2019) | [211] |
| Methylene blue 100 μM | 660 nm LED source | 3–18 J/cm2 | Escherichia coli | Garcez et al. (2020) | [212] |
| Methylene blue 1 mM | 660 ± 15 nm broadband non-coherent red light source | 0.45–18 J/cm2 | C. albicans | Chibebe Junior et al. (2013) | [213] |
| Methylene blue 600 mM | 660 nm red laser light | 15 J/cm2 | Porphyromonas gingivalis | Dos Santos et al. (2017) | [216] |
| Curcuma longa L. Extract 100 mg/mL | --- | --- | --- | Marques Meccatti et al. (2022) | [217] |
| Curcumin 200 μg/mL | --- | --- | --- | Marques Meccatti et al. (2022) | [217] |
| Methylene blue Concentration not specified | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm | 15 J/cm2 | C. albicans, C. auris | Grizante Barião et al. (2022) | [222] |
| New methylene blue N Concentration not specified | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm | 15 J/cm2 | C. albicans, C. auris | Grizante Barião et al. (2022) | [222] |
| Toluidine blue O Concentration not specified | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm | 15 J/cm2 | C. albicans, C. auris | Grizante Barião et al. (2022) | [222] |
| Pentacyclic phenothiazinium photosensitizer S137 Concentration not specified | An array of 96 light-emitting diodes with an emission peak at 635 nm | 15 J/cm2 | C. albicans, C. auris | Grizante Barião et al. (2022) | [222] |
| Methylene blue 10–500 mM | 630 nm red light-emitting diode device | Not specified | Fonsecaea monophora | Huang et al. (2020) | [223] |
| 5-aminolevulinic acid 10–500 mM | 630 nm red light-emitting diode device | Not specified | Fonsecaea monophora | Huang et al. (2020) | [223] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bugyna, L.; Kendra, S.; Bujdáková, H. Galleria mellonella—A Model for the Study of aPDT—Prospects and Drawbacks. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061455
Bugyna L, Kendra S, Bujdáková H. Galleria mellonella—A Model for the Study of aPDT—Prospects and Drawbacks. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061455
Chicago/Turabian StyleBugyna, Larysa, Samuel Kendra, and Helena Bujdáková. 2023. "Galleria mellonella—A Model for the Study of aPDT—Prospects and Drawbacks" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061455
APA StyleBugyna, L., Kendra, S., & Bujdáková, H. (2023). Galleria mellonella—A Model for the Study of aPDT—Prospects and Drawbacks. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061455






