Parasite Diversity in a Freshwater Ecosystem
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
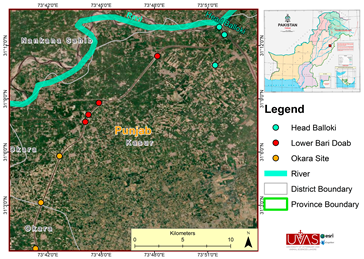
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Examination of Protozoan Parasites
2.3.1. Study of External Protozoan Parasites
2.3.2. Study of Internal Protozoan Parasites
2.4. Examination of Trematode Parasites
2.4.1. Detection of Metacercariae
- The muscle compression technique.
- The pepsin-HCL artificial digestion technique.
2.4.2. Muscle Compression
2.4.3. Pepsin-HCL Artificial Digestion Technique
2.5. Examination of Monogenean Trematodes
2.6. Identification of Parasites
2.7. Prevalence, Intensity, and Density of Parasites
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, M.K.; Ahmed, A.T.; Khan, M.H.; Rafiquzzaman, S.M.; Begum, F.; Islam, M.A. Distribution, prevalence and intensity of protozoan and monogenean parasites of carp fingerlings in selected nursery ponds. Bangladesh J. Fish. Res. 2007, 11, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dogiel, V. Parasitology of Fishes; Oliver and Boyd: London, UK, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, E.T.S.; Takemoto, R.M.; Alves, L.C.; Chellappa, S. First report of metazoan fish parasites with zoonotic potential in Scomberomorus brasiliensis and Trichiurus lepturus from the coastal waters of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2012, 5, e40. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.Y.; Murrell, K.D.; Lymbery, A.J. Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: Status and issues. Parasitol. Int. 2005, 35, 1233–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Seppala, O.; Karvonen, A.; Valtonen, E.T. Manipulation of fish host by eye flukes in relation to cataract formation and parasite infectivity. Anim. Behav. 2005, 70, 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Bedasso, G.T. Study on the prevalence and temporal abundance of parasites of fishes in Lake Elan. Int. J. Fish. Aquac. 2015, 3, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Moyle, P.B.; Cech, J.J. An Introduction to Ichthyology; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tasawar, Z.; Umer, K.; Hayat, C.S. Observations on lernaeid parasites of Catla catla from a fish hatchery in Muzaffargarh, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2007, 27, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Lom, J.; Dykova, I. Protozoan Parasites of Fishes. Dev. Aquac. Fish. Sci. 1992, 26, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J. The parasitology of teleosts. In Fish Pathology; W.B. Saunders: London, UK, 2001; pp. 254–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kayis, S.; Ozcelep, T.; Capkin, E.; Altinok, I. Protozoan and Metazoan Parasites of Cultured Fish in Turkey and their Applied Treatments. Isr. J. Aquac.—Bamidgeh 2009, 61, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Schaperclaus, W. Diseases caused by ciliates. In Fish Diseases; Amerind Publishing: New Delhi, India, 1991; pp. 702–725. [Google Scholar]
- Abowei, J.F.N.; Briyai, O.F.; Bassey, S.E. A Review of Some Basic Parasite Diseases in Culture Fisheries Flagellids, Dinoflagellides and Ichthyophthriasis, Ichtyobodiasis, Coccidiosis, Trichodiniasis, Heminthiasis, Hirudinea Infestation, Crustacean Parasite and Ciliates. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F.P.; Hoffman, G.L. Parasites of Freshwater Fishes; II, Protozoa 3. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis; Leaflet No. 2; U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Fish Disease: Washington, DC, USA, 1974.
- Li, K.; Clausen, J.H.; Murrell, K.D.; Liu, L.; Dalsgaard, A. Risks for fishborne zoonotic trematodes in Tilapia production systems in Guangdong province, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Furst, T.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. Global burden of human food-borne trematodiasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 210–221. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.W.; Kim, J.S.; Joo, H.S.; Kim, J. A human case of Clinostomum complanatum infection in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hechinger, R.F.; Lafferty, K.D. Host diversity begets parasite diversity: Bird final hosts and trematodes in snail intermediate hosts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol Sci. 2005, 272, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, T.T.K.; Murrell, K.D.; Madsen, H.; Khue, N.V.; Dalsgaard, A. Fishborne zoonotic trematodes in raw fish dishes served in restaurants in Nam Dinh Province and Hanoi, Vietnam. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 2394–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Sripa, J.; Kiatsopit, N.; Piratae, S. Prevalence of trematode larvae in intermediate hosts: Snails and fish in Ko Ae sub-district of Khueang Nai, Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health. 2016, 47, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thuy, D.T.; Kania, P.; Buchmann, K. Infection status of zoonotic trematode metacercariae in Sutchi catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) in Vietnam: Associations with season, management and host age. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pardeshi, P.R.; Hiware, C.J.; Wangswad, C. Histopathology of the liver of Mastacembelus armatus (Lecepede, 1800) due to trematode parasite, Allocreadium khami n. sp. J. Parasit. Dis. 2012, 36, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kearn, G.C. Monogeneans-the ultimate fish parasites. Monogenea 2011, 58, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sures, B.; Nachev, M.; Selbach, C.; Marcogliese, D.J. Parasite responses to pollution: What we know and where we go in ‘Environmental Parasitology. Parasit. Vectors. 2017, 10, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, K. Diseases of cultured marine fishes caused by Platyhelminthes (Monogenea, Digenea, Cestoda). Parasitology 2015, 142, 178–195. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Godoy, M. Fish host-monogenean parasite interactions, with special reference to Polyopisthocotylea. In Advances in the Immunobiology of Parasitic Disease; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2007; pp. 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.P. A new monogenean Hamatopeduncularia saketensisn. sp. from fresh water fish Wallago attu. Int. J. Adv. Multidiscip. Res. Dev. 2014, 1, 244–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, T.; Huang, C.; Sun, R.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Brown, C.L.; Yang, T. Mucosal immune response of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus during Gyrodactylus cichlidarum infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 106, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cable, J.; Scott, E.C.G.; Tinsley, R.C.; Harris, P.D. Behavior favoring transmission in the viviparous monogenean Gyrodactylus turnbulli. J. Parasitol. 2002, 88, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Paul, A.; Sahoo, M.K.; Pattanayak, S.; Kumar, P.; Das, B.K. Incidences of infectious diseases in freshwater aquaculture farms of eastern India: A passive surveillance based study from 2014–2018. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2020, 11, 579. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman. NWFHS Laboratory Manual. In Parasitology; Becky Lasee Lacrosse Fish Health Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Chapter 8; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, E.P., 3rd; Govett, P. Parasitology and necropsy of fish. Compend. Yardley PA 2009, 31, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, W.M. Fish-borne zoonotic trematode metacercariae in the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, E.E.P.; Sereemaspun, A.; Rocklov, J.; Nithikathkul, C. Discovery of Carcinogenic Liver Fluke Metacercariae in Second Intermediate Hosts and Surveillance on Fish-Borne Trematode Metacercariae Infections in Mekong Region of Myanmar. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. Public. Health. 2020, 17, 4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Sohn, W.M.; Na, B.K.; Park, J.B.; Jeoung, H.G.; Hoang, E.H.; Htoon, T.T.; Tin, H.H. Zoonotic trematode metacercariae in fish from Yangon, Myanmar and their adults recovered from experimental animals. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 631. [Google Scholar]
- Magda, A.A.; Amer, O.H.; Maysa, A.I.A.; Merwad, A.M.A.; Hassan, M.S.A. Role of Atherina fi sh in transmitting some trema todes of public health importance. In Proceedings of the 3rd Global Fisheries and Aquaculture Research Conference, Foreign Agricultural Relations (FAR), Cairo, Egypt, 29 November–1 December 2010; pp. 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Klinger, R.; Floyd, R.F. Introduction to Freshwater Fish Parasites; IFAS Extension, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1998; Volume 1, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shahawy, I.S.; El-Seify, M.O.; Metwally, A.M.; Fwaz, M.M. Survey on endoparasitic fauna of some commercially important fishes of the River Nile, southern of Egypt (Egypt). Rev. De Med. Vet. 2017, 168, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmawy, K.I.; Hiekal, F.A.; Abo-Akadda, S.S.; Laban, N.E. The inter-relationship of water quality parameters and fish parasite occurrence. Alexandr. J. Veter. Sci. 2018, 59, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Yadav, S.; Limbu, J.H. Identification of Ecto-parasites in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) at fishery development Center Bhairahawa, Rupandehi, Nepal. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Eyiseh, T.E.; Amos, S.O.; Thomas, I. Incidence of parasitic infection in adult and juvenile Clarias gariepinus in a private fish farm, Yola, Adamawa state. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2022, 10, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emere, M.C.; Egbe, N.E.L. Protozoan parasites of Synodonits clarias (a fresh water fish in river Kaduna). Best. J. 2006, 3, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, R.S.; Spira, D.T. Ichthyophthiriasis in the mirror carp Cyprinus carpio (L.). III. pathology. J. Fish Biol. 1974, 6, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, B.; Barzegar, M. Fish parasites in Zarivar Lake. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Barzegar, M.; Raeisi, M.; Bozorgnia, A.; Jalali, B. Parasites of the eyes of fresh and brackish water fishes in Iran. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 9, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Borji, H.; Naghibi, A.; Nasiri, M.R.; Ahmadi, A. Identification of Dactylogyrus spp. and other parasites of common carp in northeast of Iran. J. Paras. Dis. 2012, 36, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jalali, J.B. Parasites and Parasitic Diseases of Freshwater Fishes of Iran; Iranian Fisheries Organization Press: Tehran, Iran, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Raissy, M.; Ansari, M.; Moumeni, M.; Goudarzi, M.A.; Sohrabi, H.R.; Rashedi, M. An epizootic of Ichthyophthiriasis among fishes in Armand River, Iran. J. Cell Anim. Boil. 2010, 4, 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Omeji, S.; Solomon, S.G.; Idoga, E.S. A comparative study of the common protozoan parasites of Clarias gariepinus from the wild and cultured environments in Benue State, Nigeria. J. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 2011, 916489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.C. Introduction to Parasitology; Willey: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, E.R.; Noble, G.A. Parasitology: The biology of animal parasites. In Parasitology, 3rd ed.; Lea & Febiger: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Adebanjo, A.O. A Survey of Parasites of Clarias lazera in Dundaye area of Rima River; Sokoto, Project, Zoology Unit of Biological Science, Usman Danfodio University: Sokoto, Nigeria, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Rokicka, M.; Lumme, J.; Ziętara, M.S. Identification of Gyrodactylus ectoparasites in Polish salmonid farms by PCR-RFLP of the nuclear ITS segment of ribosomal DNA (Monogenea, Gyrodactylidae). Acta Parasitol. 2007, 52, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, G.; Gustinelli, A.; Fioravanti, M.L.; Hansen, H.; Shinn, A.P. The first report of Gyrodactylus salaris Malmberg, 1957 (Platyhelminthes, Monogenea) on Italian cultured stocks of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paperna, I. Parasites, Infections and Diseases of Freshwater Fishes in Africa; CIFA Technical Paper; Department of Fisheries, CIFA, FAO: Rome, Italy, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.Q.; Yu, S.H.; Chen, Y.D. Clonorchiasis sinensis in China. Parasitology 2005, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.J.; Cao, H.X.; Lv, G. The current prevalence of clonorchiasis in China. J. Hainan. Med. Uni. 2003, 9, 248–251. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, T.; Ditrich, O.; Giboda, M. Larval stages of medically important flukes (Trematoda) from Vientiane province, Laos Part 1. metacercariae. Ann. De Parasitol. Hum. Et Comp. 1990, 65, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, H.J.; Sohn, W.M.; Yong, T.S.; Eom, K.S.; Chai, J.Y.; Min, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hoang, E.H.; Phommasack, B.; Insisengmay, S. Fishborne trematode metacercariae detected in freshwater fish from Vientiane Municipality and Savannakhet Province, Lao PDR. Korean J. Parasitol. 2008, 46, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.T.; Shin, E.H.; Phommakorn, S.; Sengvilaykham, B.; Kim, J.L.; Rim, H.J.; Chai, J.Y. Centrocestus formosanus (Digenea: Heterophyidae) encysted in the freshwater fish, Puntius brevis, from Lao PDR. Korean J. Parasitol. 2008, 46, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.; Hong, S.J.; Pak, J.H.; Le, T.H.; Choi, S.H.; Na, B.K.; Sohn, W.M. High prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis and other zoonotic trematode metacercariae in fish from a local market in Yen Bai province, Northern Vietnam. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waruiru, R.M.; Mbuthia, P.G.; Wanja, D.W.; Mwadime, J.M. Prevalence, intensity and influence of water quality on parasites of farmed fish in Kirinyaga County, Kenya. Livest Res. Rural Devel. 2020, 32, 164. [Google Scholar]

| Identified Parasites | Host | Infection Site | Locality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protozoans | |||
| Microsporidia (Balbiani, 1882) | Labeo rohita | Liver | LBD Canal |
| Icthyophthirus multifillus (Foquet, 1876) | Intestine | ||
| Costia (Henneguy, 1883) | Cirrhinus mrigala | Kidney | |
| Ichthyobodo necator (Henneguy, 1883) | Cyprinus carpio | Liver | |
| Cryptobia (E. Nohynkova, 1984) | Labeo rohita | Intestine | Head Balloki |
| Chilodonella (Kiernik, 1909) | Skin | ||
| Entamoeba histolitica (Chatton, 1909) | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Liver | |
| Coccidia (WT. Johnson, 1892) | Labeo rohita | Gills | Okara |
| Ichthyophithirus | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Intestine | |
| Chilodonella | Skin | ||
| Piscinoodinium (Schaperclaus, 1954) | Intestine | ||
| Entamoeba histolitica | Wallagu attu | Liver | |
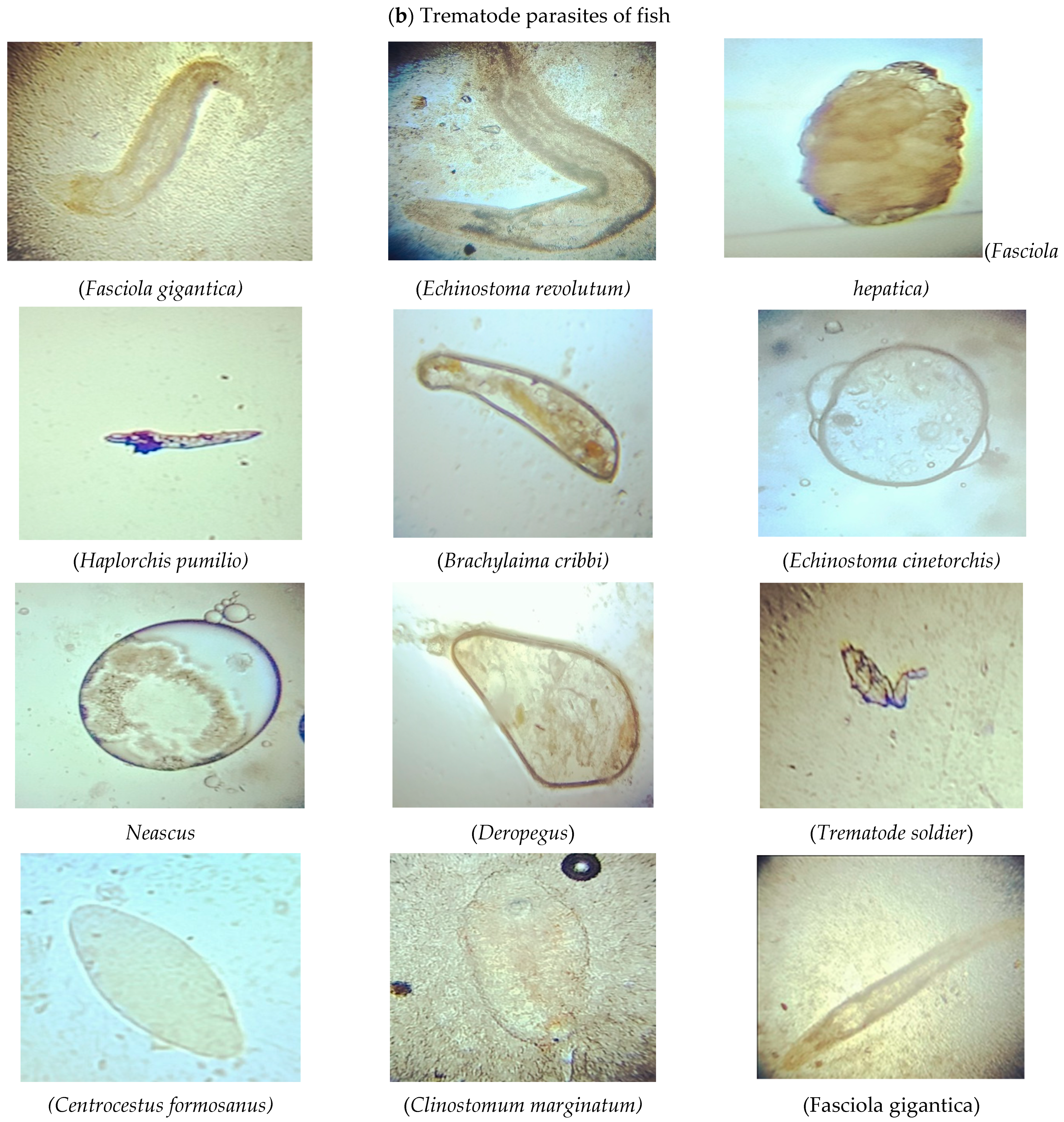
| Trematodes | |||
| Fasciola hepatica (Linnaeus, 1758) | Labeo rohita | Gills | LBD Canal |
| Trematode Soldier (Gibson, 1996) | Intestine | ||
| Haplorchis pumilio (Looss, 1896) | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Intestine | |
| Brachylaima cribbi (A.R. Butcher, 2003) | |||
| Echinostoma cinetorchis (Ando & Ozaki, 1923) | Labeo rohita | Gills | Head Balloki |
| Clinostomum marginatum (Rudolphi, 1819) | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Intestine | |
| Deropegus sp. (McCauley, 1961) | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Intestine | |
| Neascus (Hoffman, 1955) | |||
| Fasciola gigantica (Cobbold, 1853) | Labeo rohita | Gills | Okara |
| Echinostoma revolutum (Frohlich, 1802) | |||
| Centrocestus formosanus (Nishigori, 1924) | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Intestine | |
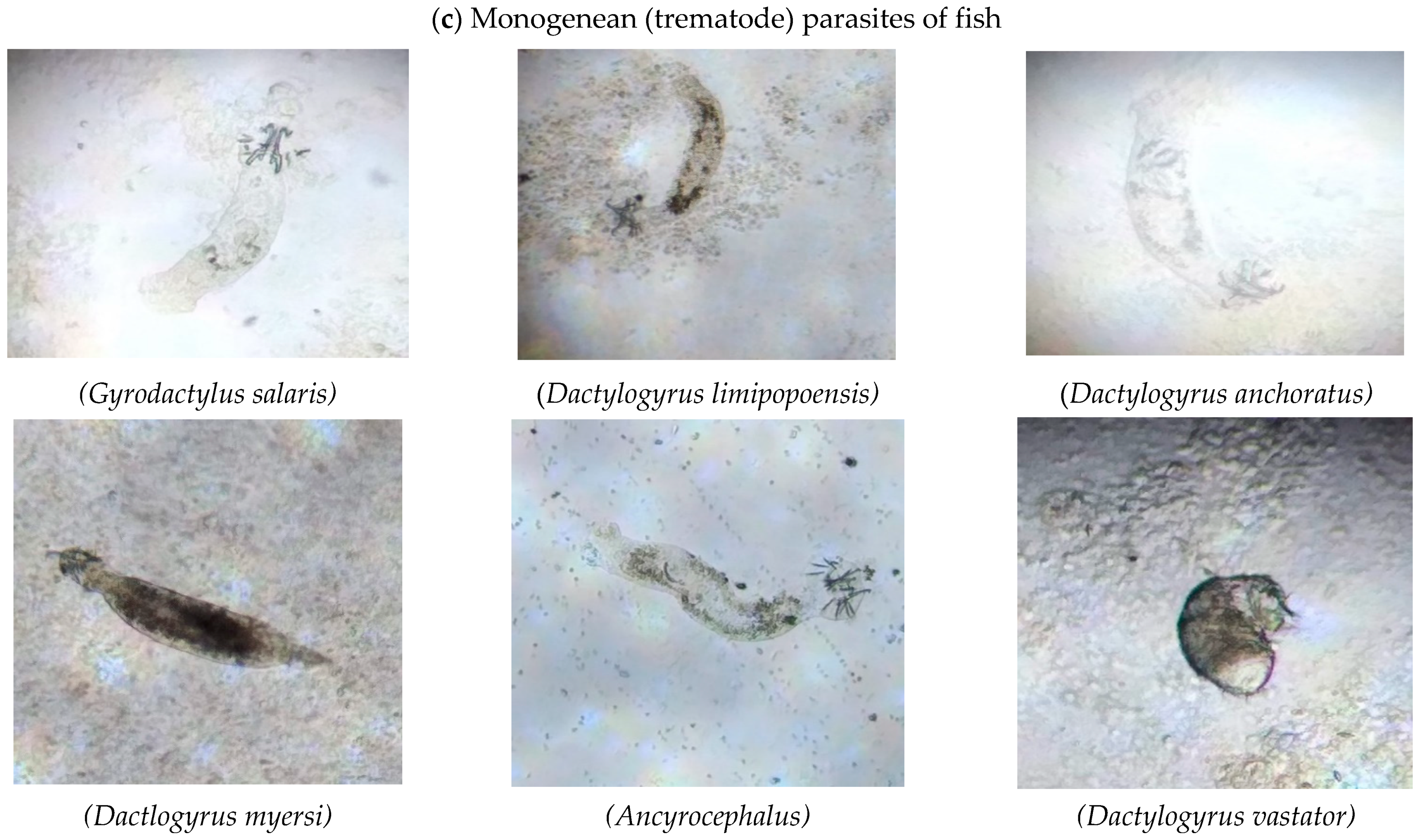
| Monogeneans | |||
| Gyrodactylus (Malmberg, 1957) | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Gills | LBD Canal |
| Dactylogyrus (Kulwiec, 1927) | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Fins | |
| Gyrodactylus | Oreochromis niloticus | Skin | |
| Dactylogyrus | Labeo rohita | Skin | Head Balloki |
| Dactylogyrus | Fin | ||
| Ancyrocephalus (Creplin, 1839) | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Gills | |
| Gyrodactylus | Cyprinus carpio | Gills | Okara |
| Dactylogyrus | Skin | ||
| Ancyrocephalus | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Gills | |
| Dactylogyrus | Oreochromis niloticus | Skin | |
| Study Site | Observed Parasites | Number | Infection Rate | Χ2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protozoans | |||||
| LBD | Microsporidia | 16 | 36% | 16.333 | 0.569 |
| Icthyophthirus multifillus | 12 | ||||
| Costia | 20 | ||||
| Ichthyobodo necator | 28 | ||||
| Head Balloki | Cryptobia | 16 | 21% | ||
| Chilodonella | 18 | ||||
| Entamoeba histolitica | 10 | ||||
| Okara | Coccidia | 20 | 43% | ||
| Ichthyophithirus | 10 | ||||
| Chilodonella | 20 | ||||
| Piscinoodinium | 32 | ||||
| Entamoeba histolitica | 8 | ||||
| Treematodes | |||||
| LBD | Fasciola hepatica | 15 | 34.5% | 22 | 0.341 |
| Trematode Soldier | 20 | ||||
| Haplorchis pumilio | 12 | ||||
| Brachylaima cribbi | 17 | ||||
| Head Balloki | Echinostoma cinetorchis | 20 | 30% | ||
| Clinostomum marginatum | 12 | ||||
| Deropegus sp. | 16 | ||||
| Neascus | 8 | ||||
| Okara | Fasciola gigantica | 23 | 35% | ||
| Echinostoma revolutum | 30 | ||||
| Centrocestus formosanus | 12 | ||||
| Monogeneans | |||||
| LBD | Gyrodactylus | 30 | 32.5% | 23 | 0.310 |
| Dactylogyrus | 28 | ||||
| Head balloki | Dactylogyrus | 20 | 25% | ||
| Ancyrocephalus | 25 | ||||
| Okara | Gyrodactylus | 20 | 42% | ||
| Dactylogyrus | 27 | ||||
| Ancyrocephalus | 28 | ||||
| Parasite | Host (n = 45/Species) | Infected Fish (%) | Parasite Number (N) | Prevalence of Infection (p) | Mean Intensity (MI) | Mean Abundance (MA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chilodonella | Labeo rohita | 10 (0.22) | 18 | 22.2 | 1.8 | 0.4 |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 8 (0.17) | 20 | 17.6 | 2.5 | 0.4 | |
| Coccidia | Labeo rohita | 15 (0.33) | 20 | 33.2 | 1.33 | 0.4 |
| Costia | Cirrhinus mrigala | 19 (0.42) | 20 | 42.2 | 1.05 | 0.4 |
| Cryptobia | Labeo rohita | 10 (0.22) | 16 | 22.2 | 1.6 | 0.35 |
| Entamoeba histolitica | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 10 (0.22) | 10 | 22.2 | 1 | 0.22 |
| Wallagu attu | 4 (0.08) | 8 | 48.8 | 2 | 0.17 | |
| Icthyophthirus multifillus | Labeo rohita | 15 (0.33) | 12 | 33.2 | 0.8 | 0.26 |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 5 (0.11) | 10 | 11 | 2 | 0.22 | |
| Microsporidia | Labeo rohita | 12 (0.26) | 16 | 26.9 | 1.3 | 0.35 |
| Piscinoodinium | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 25 (0.55) | 32 | 55.4 | 1.28 | 0.71 |
| Ichthyobodo necator | Cyprinus carpio | 18 (0.4) | 28 | 40 | 1.55 | 0.62 |
| Parasite | Host (n = 45/Species) | Infected Fish (%) | Parasite Number (N) | Prevalence of Infection (p) | Mean Intensity (MI) | Mean Abundance (MA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brachylaima cribbi | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 12 (0.26) | 17 | 26.6 | 1.41 | 0.36 |
| Centrocestus formosanus | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 10 (0.22) | 12 | 22.2 | 1.2 | 0.26 |
| Clinostomum marginatum | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 11 (0.24) | 12 | 24.4 | 1.09 | 0.26 |
| Deropegus sp. | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 14 (0.31) | 16 | 31 | 1.14 | 0.34 |
| Echinostoma cinetorchis | Labeo rohita | 18 (0.4) | 20 | 40 | 1.11 | 0.44 |
| Echinostoma revolutum | Labeo rohita | 26 (0.57) | 30 | 57.6 | 1.15 | 0.66 |
| Fasciola hepatica | Labeo rohita | 12 (0.26) | 15 | 26.6 | 1.25 | 0.32 |
| Fasciola gigantica | Labeo rohita | 19 (0.42) | 23 | 42.2 | 1.21 | 0.5 |
| Haplorchis pumilio | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 10 (0.22) | 12 | 22.2 | 1.2 | 0.26 |
| Neascus | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 7 (0.15) | 8 | 15.4 | 1.14 | 0.16 |
| Trematode Soldier | Labeo rohita | 15 (0.33) | 20 | 33.2 | 1.33 | 0.44 |
| Parasite | Host (n = 45/Species) | Infected Fish (%) | Parasite Number (N) | Prevalence of Infection (p) | Mean Intensity (MI) | Mean Abundance (MA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gyrodactylus | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 15 (0.33) | 12 | 33.3 | 0.8 | 0.26 |
| Ancyrocephalus | 15 (0.33) | 10 | 33.3 | 0.6 | 0.22 | |
| Dactylogyrus | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 38 (0.84) | 24 | 84.4 | 0.63 | 0.53 |
| Ancyrocephalus | 38 (0.84) | 20 | 84.4 | 0.5 | 0.44 | |
| Dactylogyrus | Labeo rohitaza | 40 (0.88) | 46 | 88.8 | 1.15 | 1 |
| Gyrodactylus | Cyprinus carpio | 23 (0.51) | 15 | 51 | 0.65 | 0.33 |
| Dactylogyrus | 23 (0.51) | 13 | 51 | 0.5 | 0.28 | |
| Gyrodactylus | Oreochromis Niloticus | 15 (0.33) | 10 | 33.3 | 0.6 | 0.22 |
| Dactylogyrus | 15 (0.33) | 8 | 33.3 | 0.53 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shafiq, A.; Abbas, F.; Hafeez-ur-Rehman, M.; Khan, B.N.; Aihetasham, A.; Amin, I.; Hmidullah; Mothana, R.A.; Alharbi, M.S.; Khan, I.; et al. Parasite Diversity in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081940
Shafiq A, Abbas F, Hafeez-ur-Rehman M, Khan BN, Aihetasham A, Amin I, Hmidullah, Mothana RA, Alharbi MS, Khan I, et al. Parasite Diversity in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081940
Chicago/Turabian StyleShafiq, Amana, Farzana Abbas, Muhammad Hafeez-ur-Rehman, Bushra Nisar Khan, Ayesha Aihetasham, Iffat Amin, Hmidullah, Ramzi A. Mothana, Mohammed S. Alharbi, Imran Khan, and et al. 2023. "Parasite Diversity in a Freshwater Ecosystem" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081940
APA StyleShafiq, A., Abbas, F., Hafeez-ur-Rehman, M., Khan, B. N., Aihetasham, A., Amin, I., Hmidullah, Mothana, R. A., Alharbi, M. S., Khan, I., Khalil, A. A. K., Ahmad, B., Mubeen, N., & Akram, M. (2023). Parasite Diversity in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Microorganisms, 11(8), 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081940









