Diversity of Culturable Bacteria from the Coral Reef Areas in the South China Sea and Their Agar-Degrading Abilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
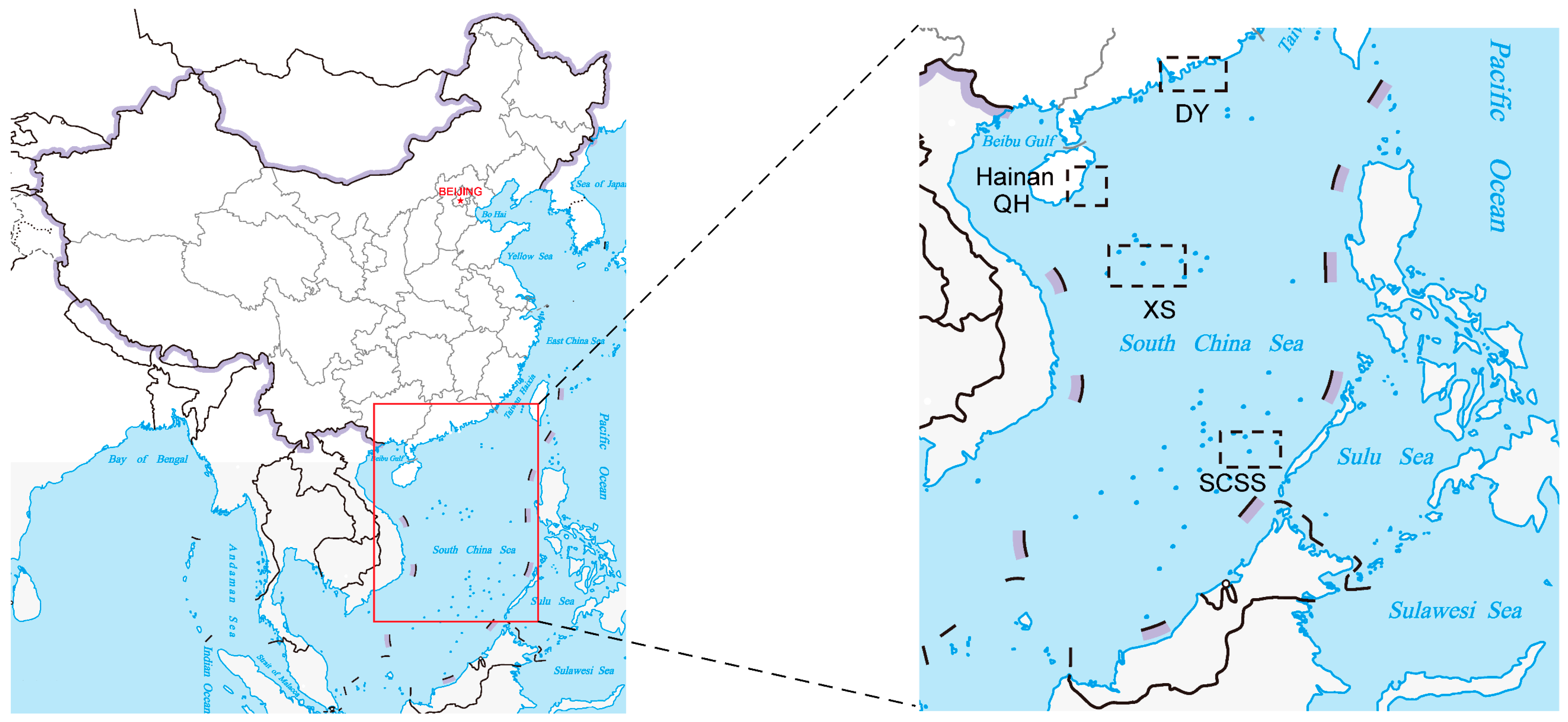
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.4. PCR Amplification for 16S rRNA Genes and Identification for Isolated Microbes
2.5. Genomic Sequencing, Assembly, and Functional Annotation
2.6. Detection of the Agar-Degrading Abilities of Microbes
2.7. Analysis of Agarases Based on Nucleotide and Amino Acid Sequences
3. Results
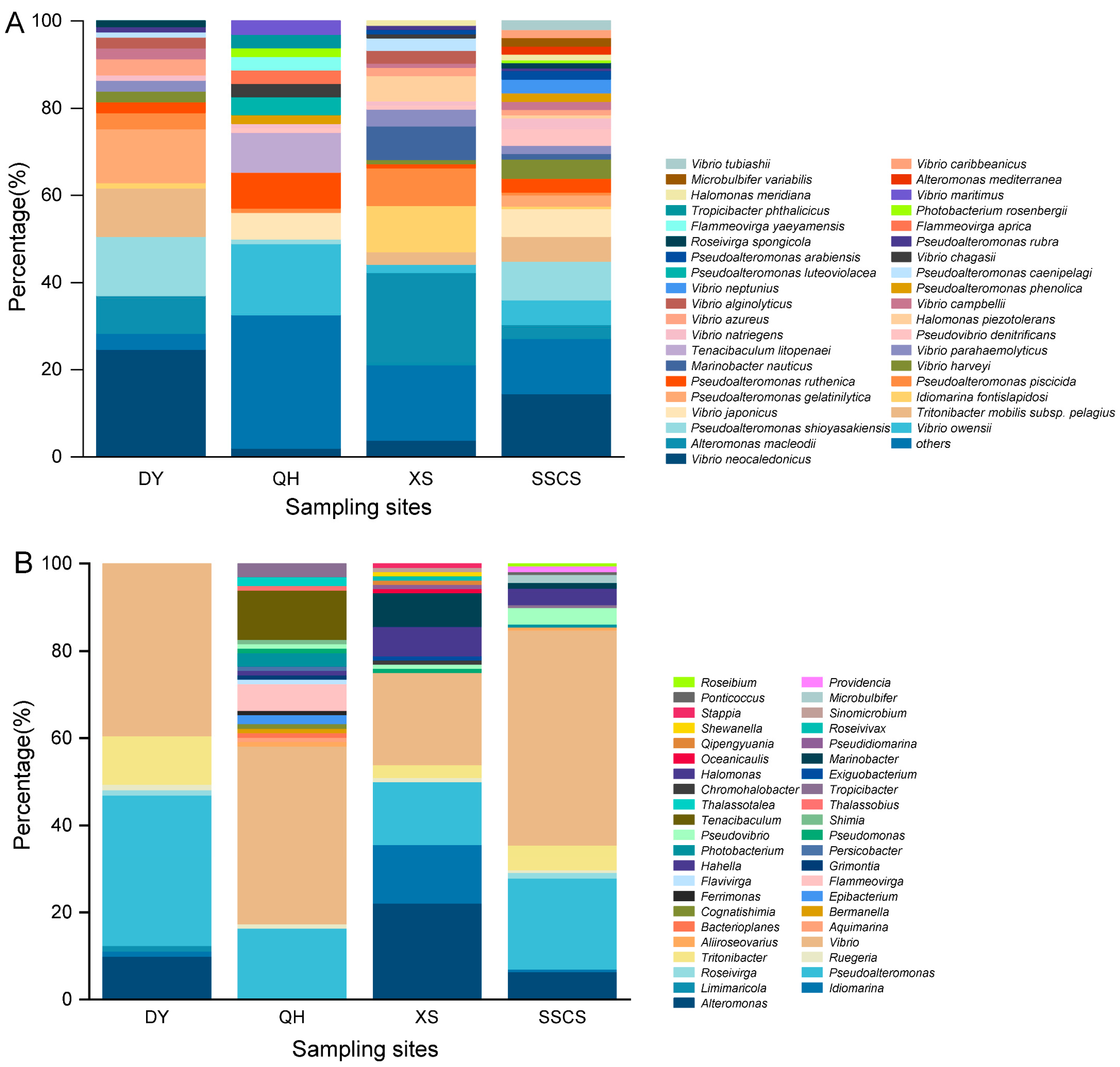
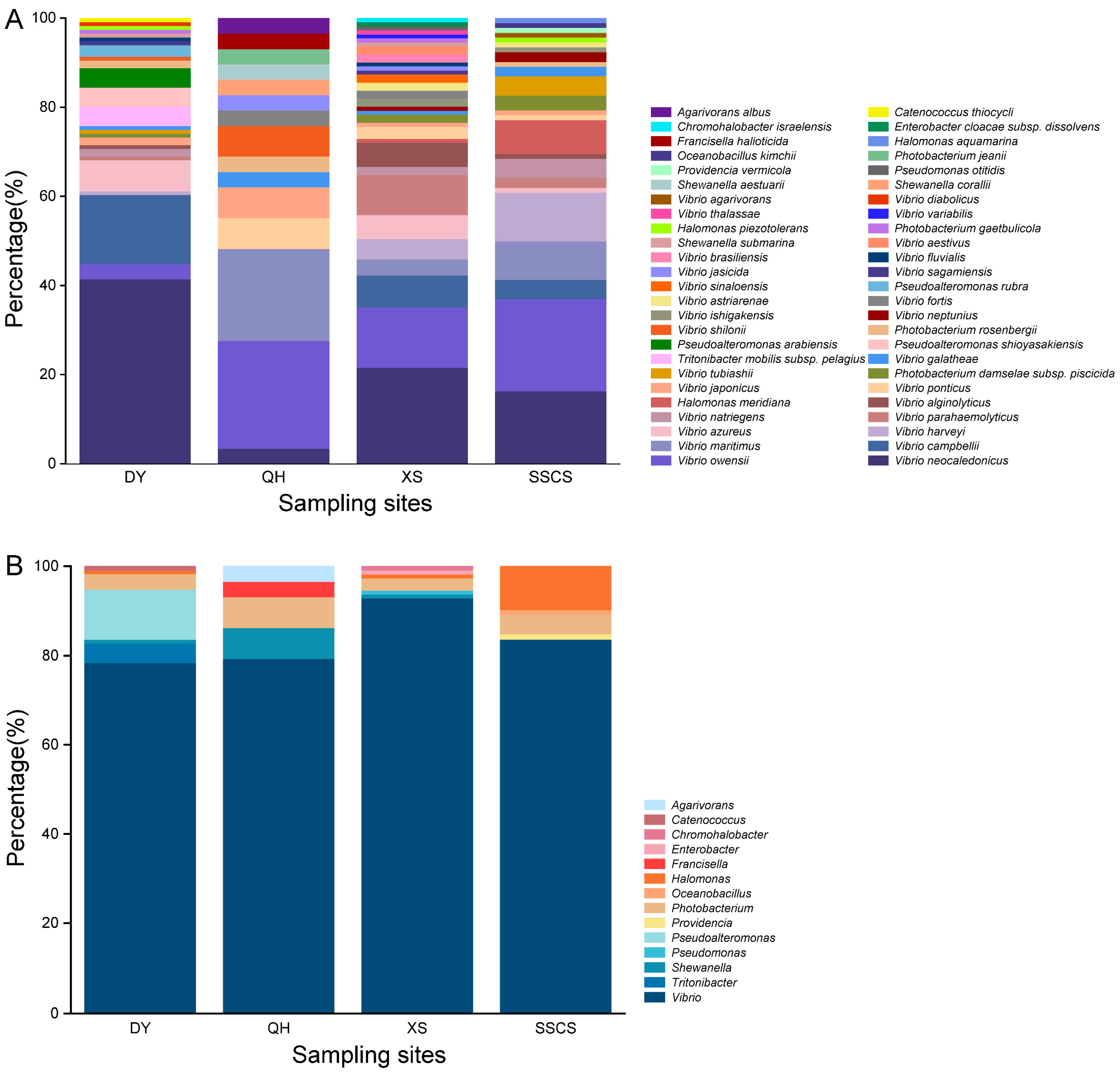
3.1. Diversity of Heterotrophic Bacteria among All Samples
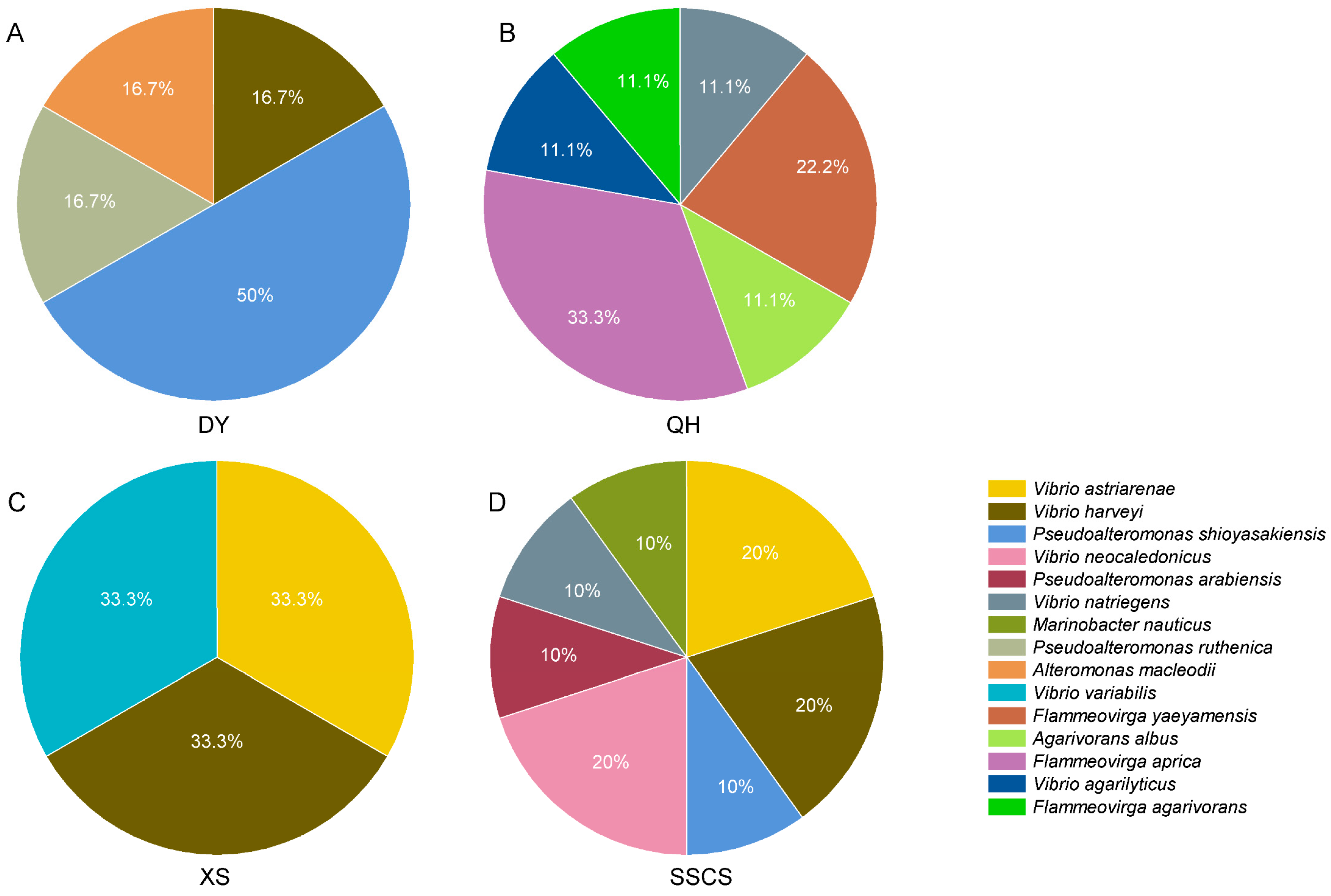
3.2. Differences of Heterotrophic Bacteria among Different Locations
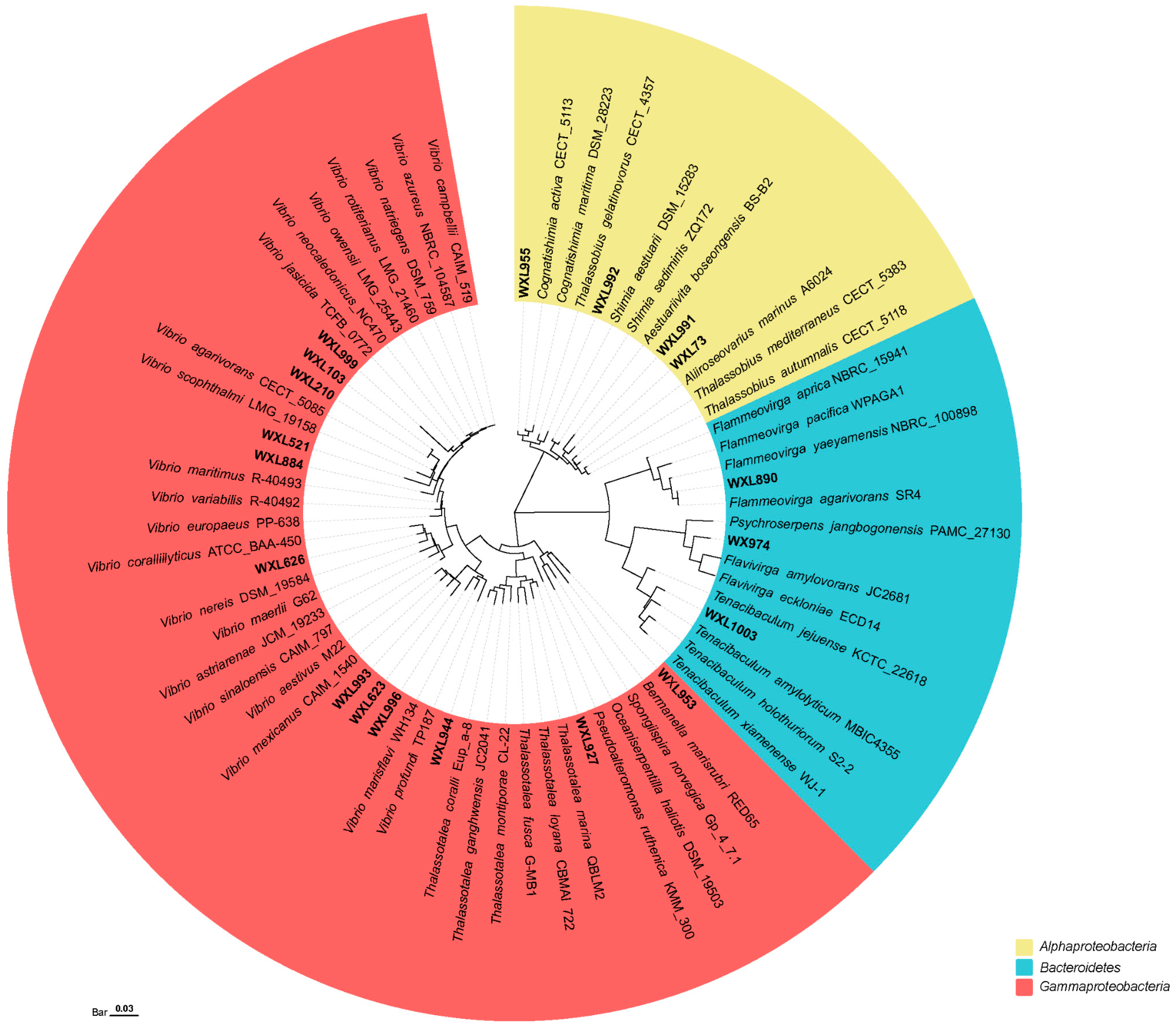
3.3. Potentially Novel Bacterial Species Isolated from the Coral Areas
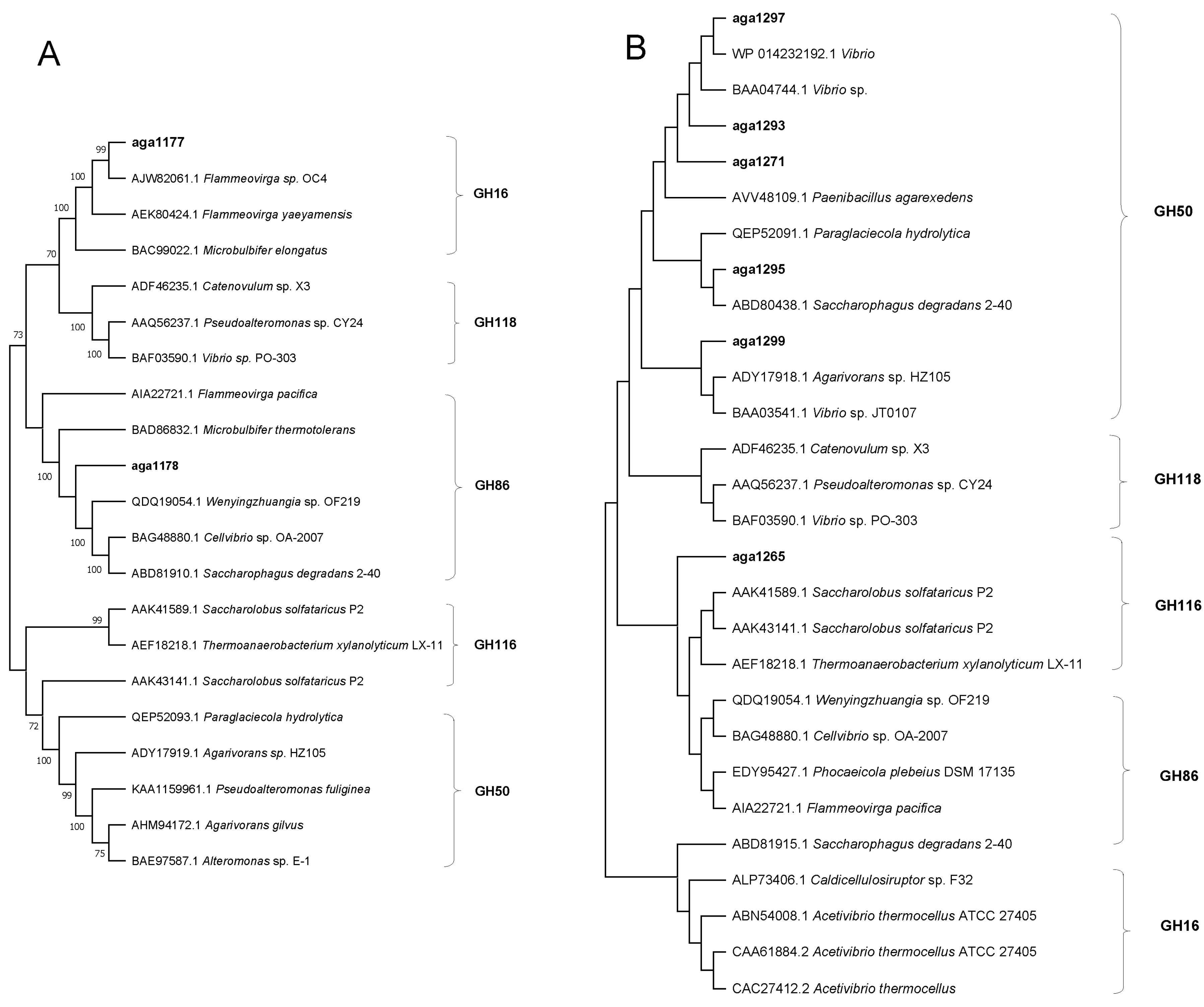
3.4. The Abilities of Bacterial Isolates to Agar-Degrading and the Phylogenetic of Agarases
4. Discussion
4.1. Highly Diverse Heterotrophic Bacteria Survived in the Coral Reef Areas
4.2. Coral Reef Areas May Be a Vast Treasure Trove of Novel Species and Agarases
4.3. Whether TCBS Agar Is a Suitable Medium for the Isolation of Vibrios?
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Recent Progress on Signalling Molecules of Coral-Associated Microorganisms. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Ling, J.; Yang, Q.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, C.C.; Sun, H.Y.; Feng, J.B.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wu, M.L.; et al. The Diversity of Coral Associated Bacteria and the Environmental Factors Affect Their Community Variation. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.; Gonzalez-Díaz, P.; Armenteros, M.; Apprill, A. The Coral Ecosphere: A Unique Coral Reef Habitat That Fosters Coral–Microbial Interactions. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 2373–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakayama, A.; Fuchinoue, Y.; Othman, B.H.R.; Toda, T. High Inorganic Phosphate Concentration in Coral Mucus and Its Utilization by Heterotrophic Bacteria in a Malaysian Coral Reef. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, X.; He, M.; Long, A.; Xu, J. Regulation of Bacterial Metabolic Activities and Community Composition by Temperature in a Fringing Coral Reef. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2022JC018823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, A.; Yoshida, T.; Hibino, K.; Eguchi, M. Community Structures of Actively Growing Bacteria Stimulated by Coral Mucus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 469, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, A.; Caldwell, J.M. Modes of coral disease transmission: How Do Diseases Spread Between Individuals and among Populations? Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Rosenberg, E. Bacteria Associated with the Bleached and Cave Coral Oculina patagonica. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, F.J.; Lamb, J.B.; van de Water, J.; Smith, H.A.; Schaffelke, B.; Willis, B.L.; Bourne, D.G. Reduced Diversity and Stability of Coral-Associated Bacterial Communities and Suppressed Immune Function Precedes Disease Onset in Corals. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barott, K.L.; Rodriguez-Brito, B.; Janouskovec, J.; Marhaver, K.L.; Smith, J.E.; Keeling, P.; Rohwer, F.L. Microbial Diversity Associated with Four Functional Groups of Benthic Reef Algae and the Reef-Building Coral Montastraea Annularis. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Gong, Y. Blooming of Bacteria and Algae is a Biokiller for Mass-Extinction of Devonian Coral-Stromatoporoid Reef Ecosystems. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Rosenberg, E. Bacterial Growth on Coral Mucus. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 56, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovaro, R.; Fonda Umani, S.; Pusceddu, A. Climate Change and the Potential Spreading of Marine Mucilage and Microbial Pathogens in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zeng, B.; Liu, D.; Wu, R.; Zhang, J.; Liao, B.; He, H.; Bian, F. Classification and Structural Insight into Vibriolysin-Like Proteases of Vibrio Pathogenicity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N., Jr.; Neto, O.S.; Silva, B.S.; De Moura, R.L.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Barreira, E.C.C.; Paranhos, R.; Bitner-Mathe, B.C.; Kruger, R.H.; Vicente, A.C.; et al. Diversity and Pathogenic Potential of Vibrios Isolated from Abrolhos Bank Corals. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldar, S.; Mody, K.H.; Jha, B. Abundance, Diversity and Antibiotics Resistance Pattern of Vibrio spp. in Coral Ecosystem of Kurusadai Island. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, J.; Ren, C.; Hu, C. Differences in Microbial Communities between Healthy and Bleached Coral Acropora Solitaryensis from Xisha Islands, South China Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2016, 12, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildemeister, O.S.; Zhu, B.C.R.; Laine, R.A. Chitovibrin: A Chitin-Binding Lectin from Vibrio parahemolyticus. Glycoconj. J. 1994, 11, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.N.; Padilla, P.I. Isolation and Characterization of Agar-Digesting Vibrio Species from the Rotten Thallus of Gracilariopsis Heteroclada Zhang et Xia. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 119, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimetto Tonon, L.A.; Silva, B.S.; Moreira, A.P.; Valle, C.; Alves, N., Jr.; Cavalcanti, G.; Garcia, G.; Lopes, R.M.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; de Moura, R.L.; et al. Diversity and Ecological Structure of Vibrios in Benthic and Pelagic Habitats along a Latitudinal Gradient in the Southwest Atlantic Ocean. PeerJ 2015, 3, e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.C.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, X.L.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Zhou, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.H. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Free-Living and Particle-Associated Vibrio Communities in the Northern Chinese Marginal Seas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Liang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.H. Spatial Heterogeneity of Vibrio spp. in Sediments of Chinese Marginal Seas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e03064-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, C.S.; Chua, K.H.; Thong, K.L. Simultaneous Differential Detection of Human Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Vibrio Species Using a Multiplex PCR Based on GyrB and PntA Genes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskin, I.P.; Farrimond, P.; Head, I.M. Identification of Novel Bacterial Lineages as Active Members of Microbial Populations in a Freshwater Sediment Using a Rapid RNA Extraction Procedure and RT-PCR. Microbiology 1999, 145, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.K.; Feng, G.; Al-Saari, N.; Meirelles, P.M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Mino, S.; Thompson, F.L.; Sawabe, T.; Sawabe, T. The First Temporal and Spatial Assessment of Vibrio Diversity of the Surrounding Seawater of Coral Reefs in Ishigaki, Japan. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.F.; Abd-Elgawad, A.; Cai, R.; Luo, Z.; Xu, C. The Bacterial Signature Offers Vision into the Machinery of Coral Fitness Across High-Latitude Coral Reef in the South China Sea. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2023, 15, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Tian, X.P.; Long, L.J. Highly Heterogeneous Bacterial Communities Associated with the South China Sea Reef Corals Porites lutea, Galaxea fascicularis and Acropora millepora. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Chen, L.R.; Liu, M.; Huang, K.Y.; Ding, Y.Q.; Xiao, J.G.; Tian, P.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Niu, W.T.; et al. Sedimentary Vibrio Blooms in the Xisha Islands May Associate with the 2020 Coral Bleaching Event. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Gu, K.; Ma, S.W.; Gao, W. Joint Chroma Downsampling and Upsampling for Screen Content Image. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 26, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the Quality of Microbial Genomes Recovered from Isolates, Single Cells, and Metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.B. ClustalW-MPI: ClustalW Analysis Using Distributed and Parallel Computing. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1585–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Diversity of Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria from Sediments of the Mariana Trench and Their Ability to Degrade Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP). Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2021, 61, 828–844. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kogure, K.; Zhang, X.-H. Diversity of Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria from the Mariana Trench and Their Ability to Degrade Macromolecules. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eakin, C.M.; Nim, C.; Brainard, R.; Aubrecht, C.; Elvidge, C.; Gledhill, D.; Muller-Karger, F.; Mumby, P.; Skirving, W.; Strong, A.; et al. Monitoring Coral Reefs from Space. Oceanography 2010, 23, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Wu, M.L.; Sun, C.C.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Cheng, H.; Fei, J. Bacterial Community Variations in the South China Sea Driven by Different Chemical Conditions. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Diao, X.; Yang, T.; Zeng, R.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H. Spatial and Interspecific Differences in Coral-Associated Bacterial Diversity in Hainan, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Gomez, C.; Duran-Riveroll, L.M.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Oliart-Ros, R.M.; Garcia-Casillas, A.M.; Cembella, A.D. Diversity of Bacterioplankton and Bacteriobenthos from the Veracruz Reef System, Southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Dennis, P.G.; Uthicke, S.; Soo, R.M.; Tyson, G.W.; Webster, N. Coral Reef Invertebrate Microbiomes Correlate with the Presence of Photosymbionts. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, R.A.; Willis, B.L.; Pfeffer, C.; Bourne, D.G. Diversities of Coral-Associated Bacteria Differ with Location, but Not species, for Three Acroporid Corals on the Great Barrier Reef. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.P.; Shimpi, G.G.; Haldar, S. A Comparative Account of Resistance and Antagonistic Activity of Healthy and Bleached Coral-Associated Bacteria as an Indicator of Coral Health Status. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Gao, B. Biodiversity and Nvironmental Adaptation of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Epsilon-Proteobacteria. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2017, 57, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, J.M. Agarolytic Pathway in the Newly Isolated Aquimarina sp. Bacterial Strain ERC-38 and Characterization of a Putative Beta-Agarase. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somboonna, N.; Wilantho, A.; Assawamakin, A.; Monanunsap, S.; Sangsrakru, D.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Tongsima, S. Structural and Functional Diversity of Free-Living Microorganisms in Reef Surface, Kra Island, Thailand. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, J.; Girvan, S.K.; Barkla, S.E.; Perez-Gonzalez, A.; Suggett, D.J.; Blackall, L.L.; van Oppen, M.J.H. Intracellular Bacteria Are Common and Taxonomically Diverse in Cultured and In Hospite Algal Endosymbionts of Coral Reefs. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2028–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampert, Y.; Kelman, D.; Dubinsky, Z.; Nitzan, Y.; Hill, R.T. Diversity of Culturable Bacteria in the Mucus of the Red Sea Coral Fungia Scutaria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 58, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.S.; Dong, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ling, J.; Wang, D.X.; Wu, M.L.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Z. Diversity Analysis of Diazotrophs Associated with Corals from Xisha and Sanya, South China Sea. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2015, 18, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodzori, F.A.; Saad, S.; Mansor, N.N.; Nasir, N.; Khalid, N.; Rawi, F.Z. Pathogenic Vibrio spp. Identified for White Syndrome Coral Disease in Tioman Island Marine Park, Malaysia. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2021, 17, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, G.M.; Bongiorni, L.; Gili, C.; Biavasco, F.; Danovaro, R. Vibrio Harveyi as a Causative Agent of the White Syndrome in Tropical Stony Corals. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.; Iida, Y.; Uthicke, S.; Smith-Keune, C. Changes in Coral-Associated Microbial Communities During a Bleaching Event. ISME J. 2008, 2, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tout, J.; Siboni, N.; Messer, L.F.; Garren, M.; Stocker, R.; Webster, N.S.; Ralph, P.J.; Seymour, J.R. Increased Seawater Temperature Increases the Abundance and Alters the Structure of Natural Vibrio Populations Associated with the Coral Pocillopora Damicornis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Tian, P.; Niu, W. Recent Deterioration of Coral Reefs in the South China Sea due to Multiple Disturbances. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnit-Orland, M.; Sivan, A.; Kushmaro, A. Antibacterial Activity of Pseudoalteromonas in the Coral Holobiont. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceh, J.; Kilburn, M.R.; Cliff, J.B.; Raina, J.-B.; van Keulen, M.; Bourne, D.G. Nutrient Cycling in Early Coral Life Stages:Pocillopora Damicornislarvae Provide Their Algal Symbiont (Symbiodinium) with Nitrogen Acquired from Bacterial Associates. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allers, E.; Niesner, C.; Wild, C.; Pernthaler, J. Microbes Enriched in Seawater after Addition of Coral Mucus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3274–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ling, J.; Yang, Q.; Wen, C.; Yan, Q.; Sun, H.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J. The Functional Gene Composition and Metabolic Potential of Coral-Associated Microbial Communities. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Tian, P.; Niu, W.; Zhang, X.-H.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Distinct Coral Environments Shape the Dynamic of Planktonic vibrio spp. Environ. Microbiome 2023, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Miyajima, T. Bacterial Decomposition of Coral Mucus as Evaluated by Long-Term and Quantitative Observation. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Long, L. Diversity and Distribution of Actinobacteria Associated with Reef Coral Porites Lutea. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, W.; Tang, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Phylogenetic Diversity of Actinobacteria Associated with Soft Coral Alcyonium Gracllimum and Stony Coral Tubastraea Coccinea in the East China Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Qiang, Y.A.N.; Ke-Fu, Y.U.; Ye-Hui, T.A.N. Recent Development in the Research of Carbon Cycle in Coral Reef Ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 6207–6215. [Google Scholar]
- Modolon, F.; Barno, A.R.; Villela, H.D.M.; Peixoto, R.S. Ecological and Biotechnological Importance of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Coral-Associated Bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Tanaka, M.; Nishikawa, S.; Mino, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Thompson, F.L.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Sawabe, T. Vibrio Clade 3.0: New Vibrionaceae Evolutionary Units Using Genome-Based Approach. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 79, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Suzuki, K.I.; Nakagawa, Y. Emendation of the genus Flammeovirga and Flammeovirga aprica with the Propsoal of Flammeovirga arenaria nom. rev., comb. nov and Flammeovirga yaeyamensis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Yu, P.; Liang, Q.Y.; Mu, D.S.; Du, Z.J. Inducible Expression of Agar-Degrading Genes in a Marine Bacterium Catenovulum Maritimus Q1(T) and Characterization of a Beta-Agarase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10541–10553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Kawahata, H. Carbon Budget of Coral Reef Systems: An Overview of Observations in Fringing Reefs, Barrier Reefs and Atolls in the Indo-Pacific Regions. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2003, 55, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, P. Biodiversity Analysis of Cultured Agar-Degrading Bacteria from Surfaces of Antarctic Macroalgae. Chin. J. Polar Res. 2020, 32, 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Morrice, L.M.; McLean, M.W.; Williamson, F.B.; Long, W.F. Beta-Agarases I and II from Pseudomonas atlantica. Purifications and Some Properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983, 135, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Park, J.H.; Yoon, S.C.; Kim, J.M.; Kong, I.S. Sequence Analysis of a β-agarase Gene (pjaA) from Pseudomonas sp. Isolated from Marine Environment. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2000, 89, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Lu, X.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Gu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chu, Y.; Han, F.; Gong, Q.; Yu, W. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel beta-agarase, AgaB, from marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. CY24. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3747–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.; Nikapitiya, C.; Lee, Y.; Whang, I.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, J. Cloning, Purification and Biochemical Characterization of Beta Agarase from the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. AG4. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mou, H.; Jiang, X.; Guan, H. Characterization of a Novel Beta-Agarase from Marine Alteromonas sp. SY37-12 and Its Degrading Products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Meulen, H.J.; Harder, W. Characterization of the Neoagarotetra-Ase and Neoagarobiase of Cytophaga flevensis. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek 1976, 42, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Tamaru, Y.; Araki, T. A Unique Beta-Agarase, AgaA, from a Marine Bacterium, Vibrio sp. Strain PO-303. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Mao, X.; Liu, N.; Qiu, Y.; Xue, C. Purification and Characterization of Two Agarases from Agarivorans albus OAY02. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.I.; Chen, L.C.; Shih, Y.Y.; Hsieh, C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, W.M.; Chen, C.C. Cloning and Characterization of Beta-Agarase AgaYT from Flammeovirga yaeyamensis strain YT. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.P.; Chen, X.L.; Chan, Z.H.; Zeng, R.Y. Expression and Characterization of a Thermostable and PH-Stable Beta-Agarase Encoded by a New Gene from Flammeovirga pacifica WPAGA1. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, L.; Chan, Z.; Zeng, R.; Lin, M.; Lin, H. One-Step Process for Environment-Friendly Preparation of Agar Oligosaccharides From Gracilaria lemaneiformis by the Action of Flammeovirga sp. OC4. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Ruan, L.W.; Shi, H. A Beta-Agarase with High PH Stability from Flammeovirga sp. SJP92. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 432, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasree, V.S.; Sobhana, K.S.; Jasmine, S.; Ranjith, L.; Kingsly, H.J.; Sreenath, K.R.; George, R.M.; Joshi, K.K.; Gopalakrishnan, A. Activity Optimisation of Extracellular Agarases Produced by Agarolytic Bacteria Flammeovirga yaeyamensis AM5.A, Aliagarivorans marinus AM17.E1 and Aliagarivorans taiwanensis A69.B2, Isolated from Coral Reef Ecosystems. Indian. J. Fish. 2021, 68, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Ruan, L.; Shi, H. Genome Sequence of a High Agarase-Producing Strain Flammeovirga sp. SJP92. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2017, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Qi, B.; Zhao, Y. Comparative Genomic and Secretomic Analysis Provide Insights into Unique Agar Degradation Function of Marine Bacterium Vibrio fluvialis A8 through Horizontal Gene Transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macián, M.C.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Pujalte, M.J.; Garay, E. Vibrio agarivorans sp. nov., a Novel Agarolytic Marine Bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, J.M.; Thompson, F.L.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Lorence, E.A.; Goreau, T.J.; Hayes, R.L.; Winiarski-Cervino, K.B.; Smith, G.W.; Hughen, K.; Bartels, E. The Vibrio Core Group Induces Yellow Band Disease in Caribbean and Indo-Pacific Reef-Building Corals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, K.M.; Westrich, J.R.; Alabady, M.S.; Edwards, M.L.; Lipp, E.K. Abundance and Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Vibrio Bacteria Associated with Diseased Elkhorn Coral (Acropora palmata) of the Florida Keys. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01035-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pinto, A.; Terio, V.; Novello, L.; Tantillo, G. Comparison Between Thiosulphate-Citrate-Bile Salt Sucrose (TCBS) Agar and CHRO Magar Vibrio for Isolating Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Control 2011, 22, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushmaro, A.; Banin, E.; Loya, Y.; Stackebrandt, E.; Rosenberg, E. Vibrio shiloi sp. nov., the Causative Agent of Bleaching of the Coral Oculina patagonica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinum, T.M.; Karataş, S.; Martinussen, N.T.; Meirelles, P.M.; Thompson, F.L.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Björkroth, J. Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Close Relatives Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio ordalii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5496–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.M.; Prachumwat, A.; Yu, C.P.; Yang, Y.T.; Promsri, S.; Liu, K.F.; Lo, C.F.; Lu, M.Y.J.; Lai, M.C.; Tsai, I.J.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Vibrio campbellii Strains and Core Species of the Vibrio Harveyi Clade. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyang, L.I.; Mingxia, C.; Tianling, Z.; Senlin, Z.; Bin, C. Relationship between TCBS Groups and Vibrios in Shenzhen Waters and Jiulongjiang River Estuary. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2011, 30, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavia, M.; Salamone, M.; Bennici, C.; Quatrini, P.; Cuttitta, A. A Modified Culture Medium for Improved Isolation of Marine Vibrios. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Azizah, R.N.; Kim, K.S. Comparative Evaluation of Three Agar Media-Based Methods for Presumptive Identification of Seafood-Originated Vibrio parahaemolyticus Strains. Food Control 2020, 116, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Yin, F.; Zhao, W.; Tian, P.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Huang, K.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, J.; Niu, W.; et al. Diversity of Culturable Bacteria from the Coral Reef Areas in the South China Sea and Their Agar-Degrading Abilities. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12010187
Liu M, Yin F, Zhao W, Tian P, Zhou Y, Jia Z, Huang K, Ding Y, Xiao J, Niu W, et al. Diversity of Culturable Bacteria from the Coral Reef Areas in the South China Sea and Their Agar-Degrading Abilities. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(1):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12010187
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Mei, Fu Yin, Wenbin Zhao, Peng Tian, Yi Zhou, Zhiyu Jia, Keyi Huang, Yunqi Ding, Jiaguang Xiao, Wentao Niu, and et al. 2024. "Diversity of Culturable Bacteria from the Coral Reef Areas in the South China Sea and Their Agar-Degrading Abilities" Microorganisms 12, no. 1: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12010187
APA StyleLiu, M., Yin, F., Zhao, W., Tian, P., Zhou, Y., Jia, Z., Huang, K., Ding, Y., Xiao, J., Niu, W., & Wang, X. (2024). Diversity of Culturable Bacteria from the Coral Reef Areas in the South China Sea and Their Agar-Degrading Abilities. Microorganisms, 12(1), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12010187





