Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Candidate Key Virulence Genes of Vibrio harveyi at the Early Stage of Infection in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epinephelus polyphekadion × ♂ E. fuscoguttatus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Artificial Infection and Sampling
2.3. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.4. Sequencing Data Processing and Reads Mapping
2.5. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.6. Functional Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Quality Assessment
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Gene Expression between Groups
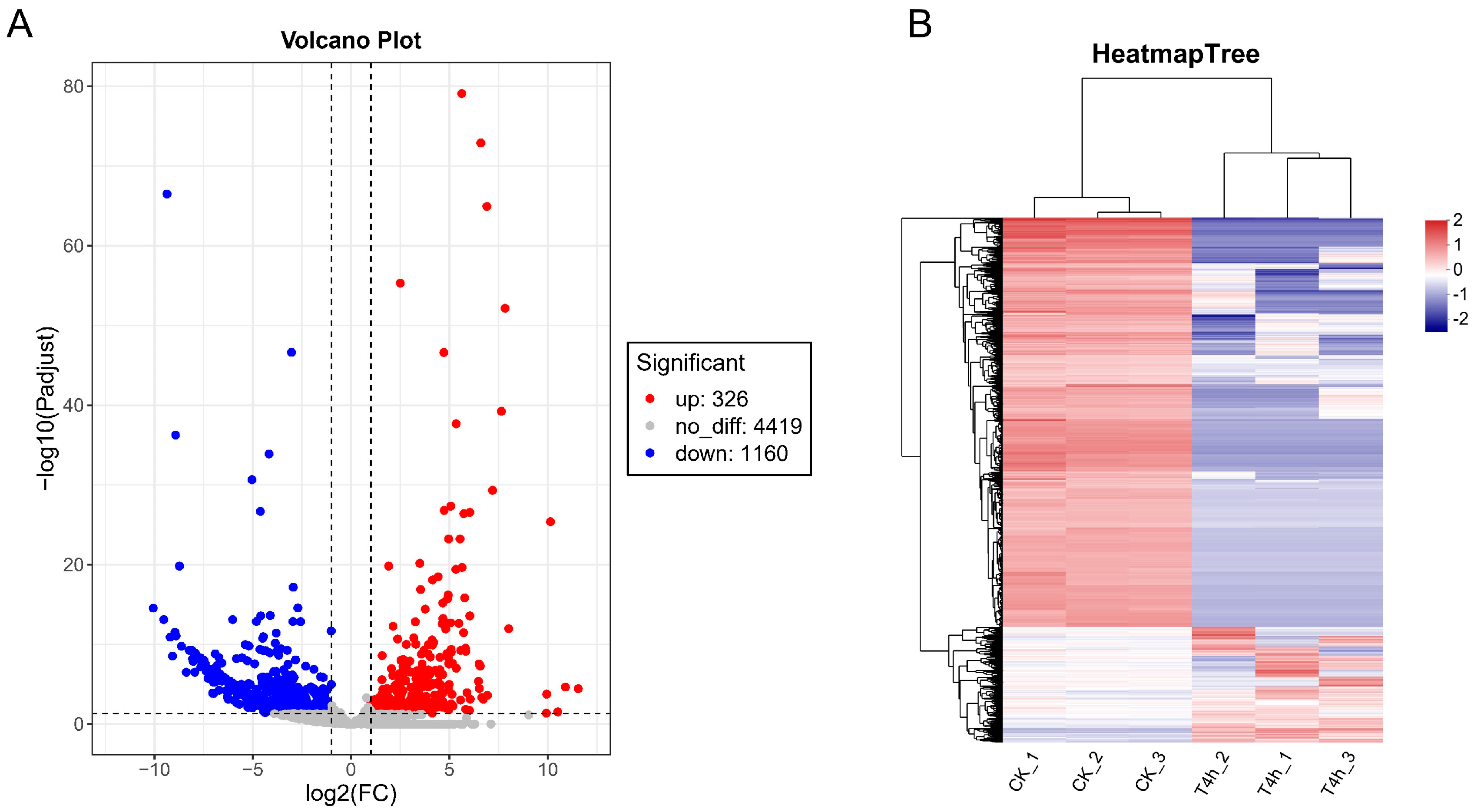
3.3. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
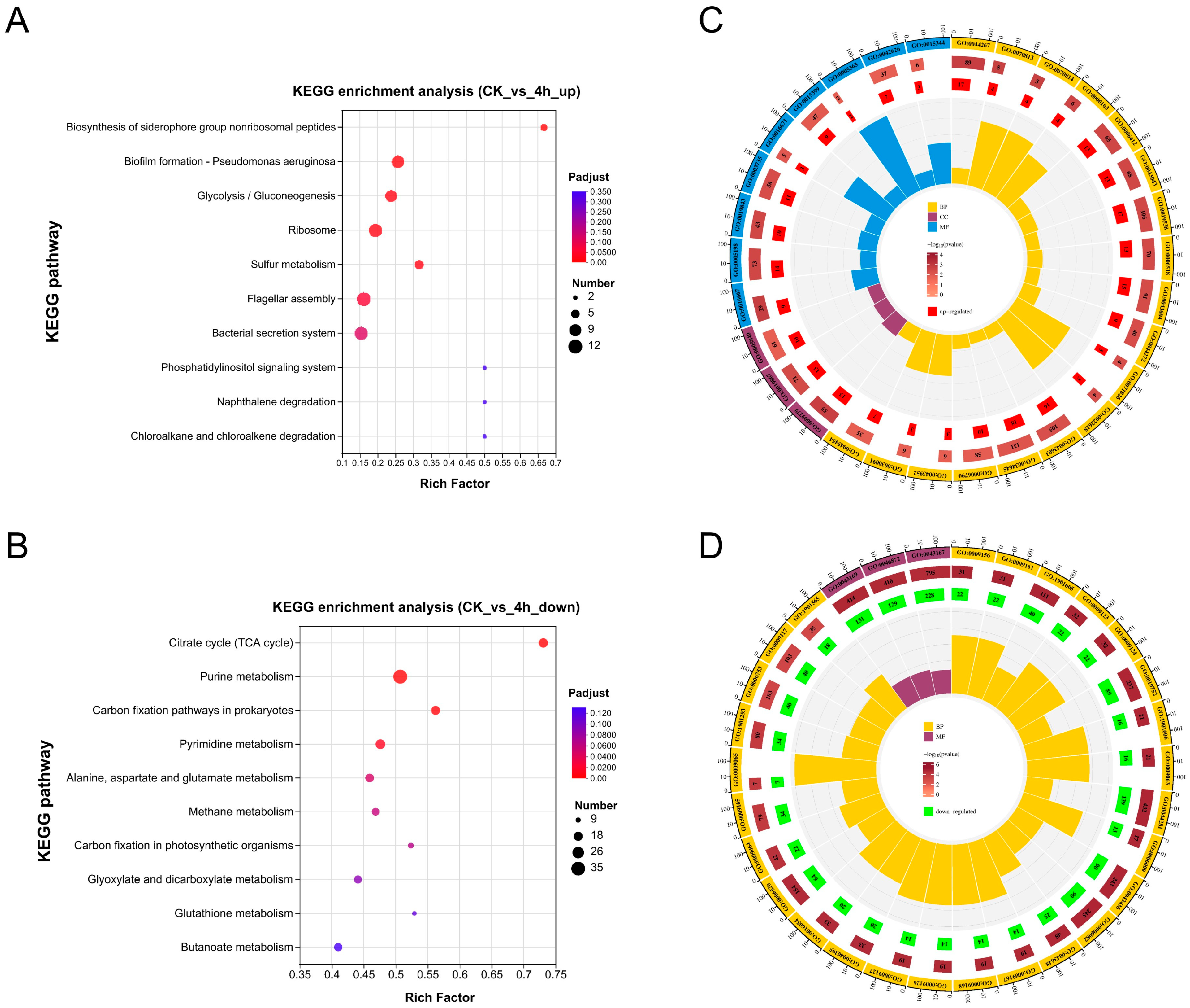
3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
3.5. Identification of Candidate Key Virulence Genes of V. harveyi at the Early Stage of Infection
3.5.1. Siderophore Biosynthesis and Transport
3.5.2. Type VI Secretion System (T6SS)
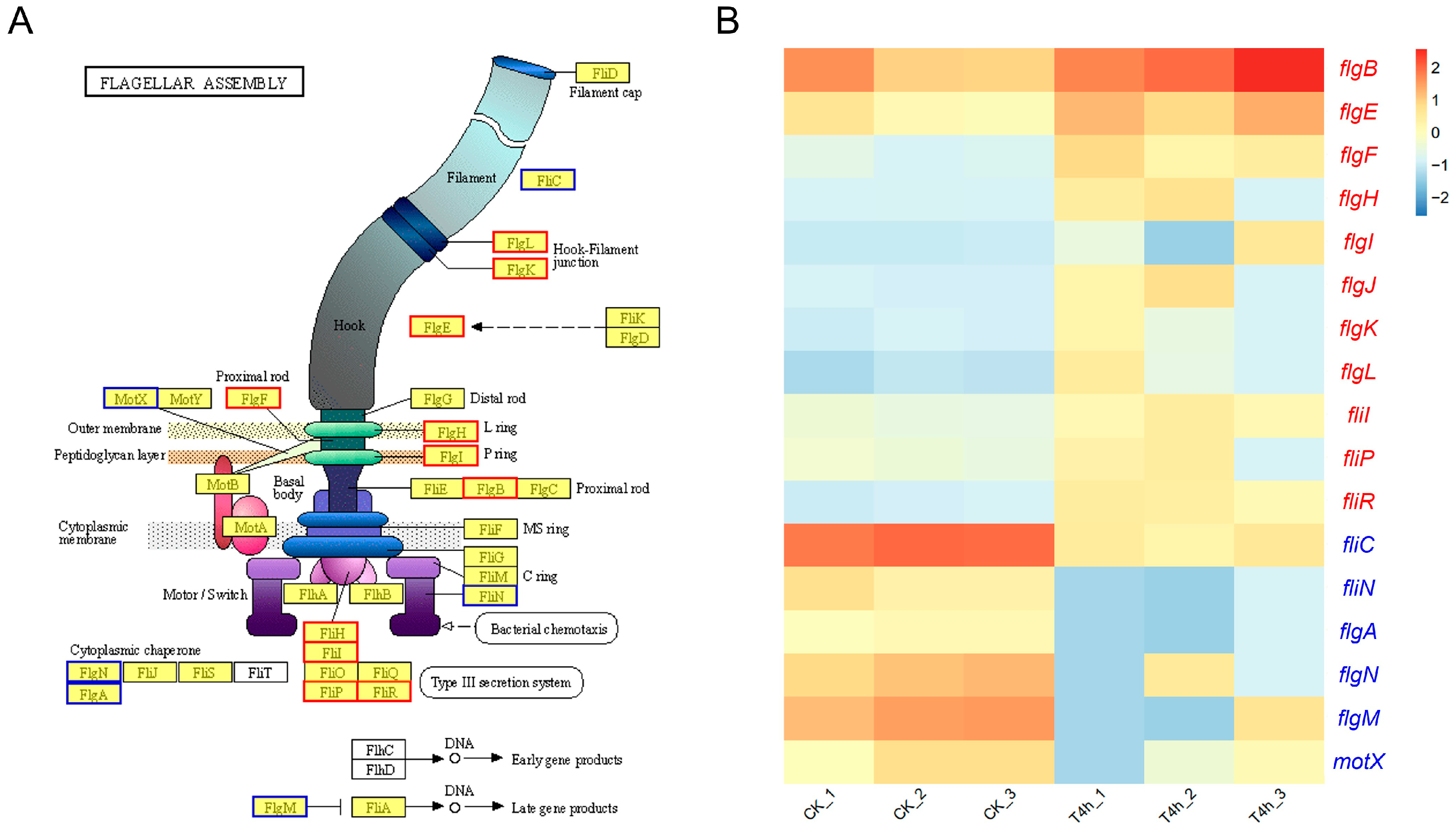
3.5.3. Flagellar Assembly
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.D.; Liu, K.F.; Wang, S.F.; Guo, W.L.; Xie, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.C. Identification of pathogenicity, investigation of virulent gene distribution and development of a virulent strain-specific detection PCR method for Vibrio harveyi isolated from Hainan Province and Guangdong Province, China. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; He, X.; Austin, B. Vibrio harveyi: A serious pathogen of fish and invertebrates in mariculture. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Dong, C.F.; Weng, S.P.; He, J.G. The high prevalence of pathogenic Vibrio harveyi with multiple antibiotic resistance in scale drop and muscle necrosis disease of the hybrid grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (♀) × E. lanceolatus (♂), in China. J. Fish. Dis. 2018, 41, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, C.; Ma, H.; Feng, J. Prevalence, virulence genes, and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio species isolated from diseased marine fish in South China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14329. [Google Scholar]
- Selvin, J.; Huxley, A.J.; Lipton, A.P. Pathogenicity, antibiogram and biochemical characteristics of luminescent Vibrio harveyi associated with ‘Black Shell Disease’ of Penaeus monodon. Fish. Technol. 2005, 42, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Fang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, S.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Qi, X.; Su, H.; Xie, L. A nonluminescent and highly virulent Vibrio harveyi strain is associated with “bacterial white tail disease” of Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.Y.; Long, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Cai, X.N.; Xie, Z.Y. Characterization of a pathogenic Vibrio harveyi strain from diseased Epinephelus coioides and evaluation of different methods to control its infection. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeng, Y.H.; Yin, W.L.; Lu, H.B.; Gong, X.X.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Long, H.; Ren, W.; Cai, X.N.; et al. Prevalence of Bacterial Coinfections with Vibrio harveyi in the Industrialized Flow-through Aquaculture Systems in Hainan Province: A Neglected High-Risk Lethal Causative Agent to Hybrid Grouper. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwandeepika, H.A.; Defoirdt, T.; Bhowmick, P.P.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Bossier, P. In vitro and in vivo expression of virulence genes in Vibrio isolates belonging to the Harveyi clade in relation to their virulence towards gnotobiotic brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana). Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Feng, J. Gut-Liver Immune Response and Gut Microbiota Profiling Reveal the Pathogenic Mechanisms of Vibrio harveyi in Pearl Gentian Grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × E. fuscoguttatus♀). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 607754. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Meaden, P.G.; Austin, B. Duplication of hemolysin genes in a virulent isolate of Vibrio harveyi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3161–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Roque, A.; Lizarraga-Partida, M.L.; Guerra-Flores, A.L.; Gomez-Gil, B. Virulence of luminous vibrios to Artemia franciscana nauplii. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 53, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morot, A.; El Fekih, S.; Bidault, A.; Le Ferrand, A.; Jouault, A.; Kavousi, J.; Bazire, A.; Pichereau, V.; Dufour, A.; Paillard, C.; et al. Virulence of Vibrio harveyi ORM4 towards the European abalone Haliotis tuberculata involves both quorum sensing and a type III secretion system. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5273–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, A.; Pirofski, L. Host-pathogen interactions: The attributes of virulence. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thänert, R.; Goldmann, O.; Beineke, A.; Medina, E. Host-inherent variability influences the transcriptional response of Staphylococcus aureus during in vivo infection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, A.J.; Barquist, L.; Vogel, J. Resolving host-pathogen interactions by dual RNA-seq. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Fu, Q.; Yan, Q. Dual RNA-Seq reveals the role of a transcriptional regulator gene in pathogen-host interactions between Pseudomonas plecoglossicida and Epinephelus coioides. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 87, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.Q.; Zhao, L.M.; Xu, X.J.; Huang, L.X.; Qin, Y.X.; Su, Y.Q.; Yan, Q.P. Dual RNA-Seq uncovers the function of an ABC transporter gene in the host-pathogen interaction between Epinephelus coioides and Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 92, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Liu, Z.X.; Zhao, L.M.; Huang, L.X.; Qin, Y.X.; Su, Y.Q.; Zheng, W.Q.; Wang, F.; Yan, Q.P. Dual RNA-seq provides novel insight into the roles of dksA from Pseudomonas plecoglossicida in pathogen-host interactions with large yellow croakers (Larimichthys crocea). Zool. Res. 2020, 41, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Sun, Y.; Huang, L.; Su, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Yan, Q. Time-resolved dual RNA-seq of tissue uncovers Pseudomonas plecoglossicida key virulence genes in host-pathogen interaction with Epinephelus coioides. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, P.; Hou, X.; Ma, J.; Yang, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; et al. Genetic characteristics and growth patterns of the hybrid grouper derived from the hybridization of Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (female) × Epinephelus polyphekadion (male). J. Fish. Biol. 2023, 102, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. Imeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, Y.; Benjamini, Y. More powerful procedures for multiple significance testing. Stat. Med. 1990, 9, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfenstein, D.V.; Zhang, L.; Pedersen, B.S.; Ramírez, F.; Warwick Vesztrocy, A.; Naldi, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Yunes, J.M.; Botvinnik, O.; Weigel, M.; et al. GOATOOLS: A Python library for Gene Ontology analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Ai, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y. Dual RNA-seq of spleens extracted from channel catfish infected with Aeromonas veronii reveals novel insights into host-pathogen interactions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Ai, X. Dual RNA-Seq of Trunk Kidneys Extracted from Channel Catfish Infected with Yersinia ruckeri Reveals Novel Insights into Host-Pathogen Interactions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 775708, Erratum in Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 982091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, J.; Özkaya, Ö.; Kümmerli, R. Bacterial siderophores in community and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serapio-Palacios, A.; Woodward, S.E.; Vogt, S.L.; Deng, W.; Creus-Cuadros, A.; Huus, K.E.; Cirstea, M.; Gerrie, M.; Barcik, W.; Yu, H.; et al. Type VI secretion systems of pathogenic and commensal bacteria mediate niche occupancy in the gut. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Kumari, K. Bacterial type VI secretion system (T6SS): An evolved molecular weapon with diverse functionality. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echazarreta, M.A.; Klose, K.E. Vibrio Flagellar Synthesis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavat, F.; Bidault, A.; Pichereau, V.; Paillard, C. Rapid and efficient protocol to introduce exogenous DNA in Vibrio harveyi and Pseudoalteromonas sp. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 154, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, R.; Zhang, X.D.; Lee, L.T.O.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M.; Peng, B.; Zheng, J. Organism dual RNA-seq reveals the importance of BarA/UvrY in Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7561–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddal, B.; Muzzi, A.; Censini, S.; Calogero, R.A.; Torricelli, G.; Guidotti, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Covacci, A.; Pizza, M.; Rappuoli, R.; et al. Dual RNA-seq of Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and Host Cell Transcriptomes Reveals Novel Insights into Host-Pathogen Cross Talk. mBio 2015, 6, e01765-15, Erratum in mBio 2016, 7, e00373-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepold, A.; Wagner, S. Assembly of the bacterial type III secretion machinery. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 802–822. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, B.C.; Garcia-Herrero, A.; Johanson, T.H.; Krewulak, K.D.; Lau, C.K.; Peacock, R.S.; Slavinskaya, Z.; Vogel, H.J. Siderophore uptake in bacteria and the battle for iron with the host; a bird’s eye view. Biometals 2010, 23, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnsen, J.; Raffatellu, M. Siderophores: More than Stealing Iron. mBio 2016, 7, e01906-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Pan, D.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Yu, D.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Z.; et al. Aerobactin-Mediated Iron Acquisition Enhances Biofilm Formation, Oxidative Stress Resistance, and Virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 699913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukatzki, S.; Ma, A.T.; Sturtevant, D.; Krastins, B.; Sarracino, D.; Nelson, W.C.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Mekalanos, J.J. Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, X. Beyond dueling: Roles of the type VI secretion system in microbiome modulation, pathogenesis and stress resistance. Stress. Biol. 2021, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; She, P.; Wu, Y. Composition, function, and regulation of T6SS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 172, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Osei-Adjei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Yang, H.; Yin, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhou, D. Transcriptional Regulation of the Type VI Secretion System 1 Genes by Quorum Sensing and ToxR in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2005, Erratum in Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 616153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losada, L.; Shea, A.A.; DeShazer, D. A MarR family transcriptional regulator and subinhibitory antibiotics regulate type VI secretion gene clusters in Burkholderia pseudomallei. Microbiology 2018, 164, 1196–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, H.C.; Rumbo, M.; Sirard, J.C. Bacterial flagellins: Mediators of pathogenicity and host immune responses in mucosa. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akahoshi, D.T.; Bevins, C.L. Flagella at the Host-Microbe Interface: Key Functions Intersect with Redundant Responses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 828758. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Q.; Du, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Y. Amino Acid-Induced Chemotaxis Plays a Key Role in the Adaptation of Vibrio harveyi from Seawater to the Muscle of the Host Fish. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnab, R.M. Type III flagellar protein export and flagellar assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1694, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | Clean Reads | Clean Q20 (%) | Clean Q30 (%) | Genome Mapped Reads (Ratio) | Uniq Mapped Reads (Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T4h_1 | 80,594,036 | 97.42 | 94.12 | 50,456 (0.06%) | 29,468 (0.04%) |
| T4h_2 | 73,525,504 | 97.46 | 94.09 | 53,577 (0.07%) | 28,826 (0.04%) |
| T4h_3 | 82,791,536 | 97.51 | 94.15 | 56,965 (0.07%) | 29,169 (0.04%) |
| CK_1 | 27,122,138 | 98.52 | 95.48 | 26,718,117 (98.51%) | 24,604,823 (90.72%) |
| CK_2 | 27,680,952 | 98.52 | 95.51 | 27,279,620 (98.55%) | 25,026,703 (90.41%) |
| CK_3 | 27,241,302 | 98.46 | 95.36 | 26,855,857 (98.59%) | 24,916,543 (91.47%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Y.-H.; Li, W.; Xu, H.; Gong, X.-X.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Long, H.; Xie, Z.-Y. Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Candidate Key Virulence Genes of Vibrio harveyi at the Early Stage of Infection in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epinephelus polyphekadion × ♂ E. fuscoguttatus). Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112113
Zeng Y-H, Li W, Xu H, Gong X-X, Zhang Y-M, Long H, Xie Z-Y. Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Candidate Key Virulence Genes of Vibrio harveyi at the Early Stage of Infection in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epinephelus polyphekadion × ♂ E. fuscoguttatus). Microorganisms. 2024; 12(11):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112113
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Yan-Hua, Wen Li, He Xu, Xiao-Xiao Gong, Yu-Mei Zhang, Hao Long, and Zhen-Yu Xie. 2024. "Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Candidate Key Virulence Genes of Vibrio harveyi at the Early Stage of Infection in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epinephelus polyphekadion × ♂ E. fuscoguttatus)" Microorganisms 12, no. 11: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112113
APA StyleZeng, Y.-H., Li, W., Xu, H., Gong, X.-X., Zhang, Y.-M., Long, H., & Xie, Z.-Y. (2024). Dual RNA-Seq Unveils Candidate Key Virulence Genes of Vibrio harveyi at the Early Stage of Infection in Hybrid Grouper (♀ Epinephelus polyphekadion × ♂ E. fuscoguttatus). Microorganisms, 12(11), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112113






