Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology
Abstract
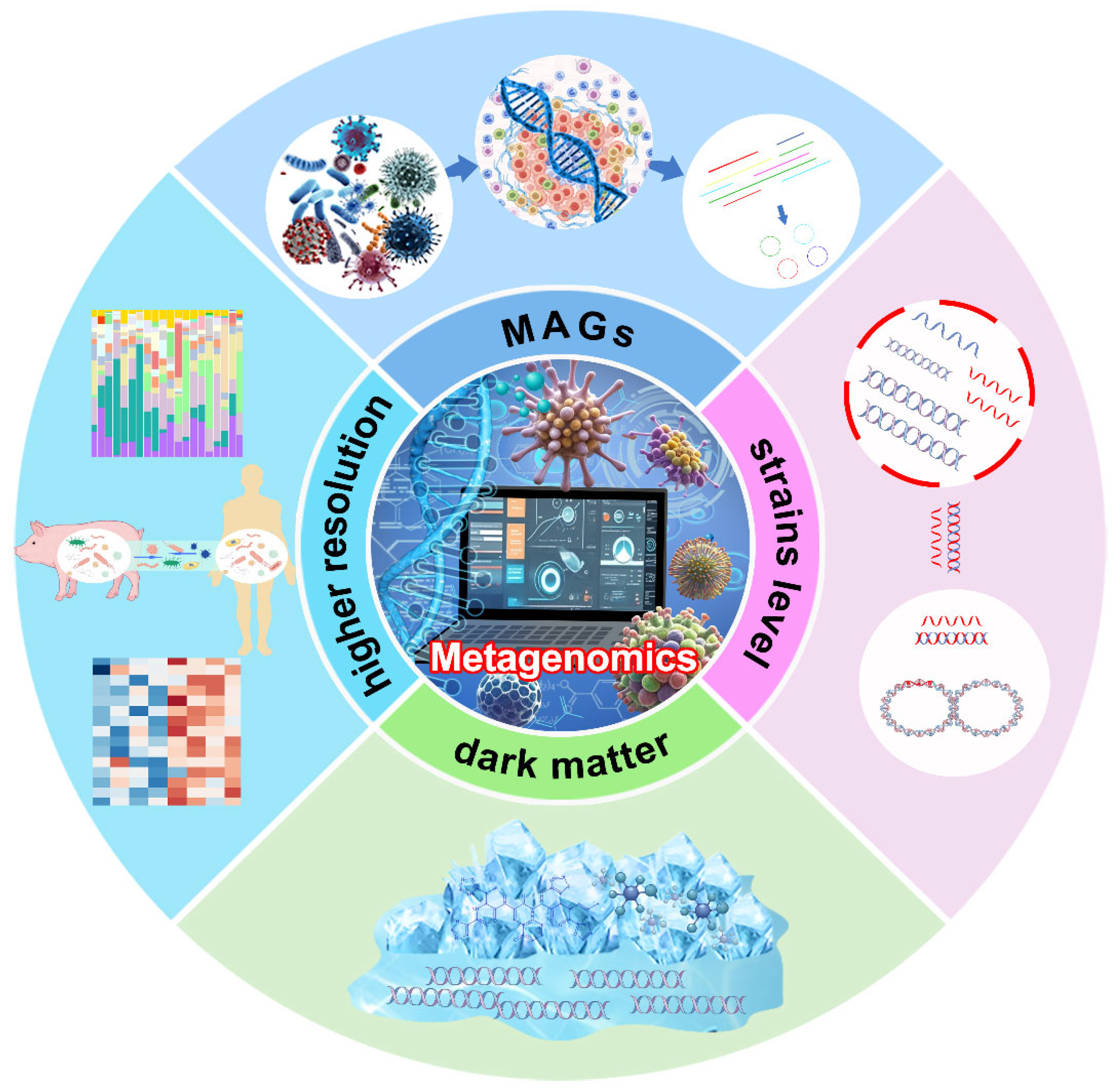
:1. Introduction
2. The Role and Applications of Metagenomics
3. Current Challenges in Metagenomics
4. Advantages of Long-Read Sequencing
5. Advantages of Pacbio HiFi Sequencing
6. Applications of HiFi Sequencing in Metagenomics
7. Other Applications of HiFi Sequencing in Metagenomics
7.1. Quantitative Microbial Analysis with HiFi Sequencing
7.2. Detection of Genetic Variations with HiFi Sequencing
7.3. Integration of Emerging Technologies with HiFi Sequencing
8. Future Applications of PacBio HiFi Sequencing Technology in Metagenomics
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Junkins, E.N.; Stevenson, B.S. Using Plate-Wash PCR and High-Throughput Sequencing to Measure Cultivated Diversity for Natural Product Discovery Efforts. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 675798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, A.L.; Pollard, K.S. Accurate and sensitive detection of microbial eukaryotes from whole metagenome shotgun sequencing. Microbiome 2021, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Kang, S.S.; Hyun, S.H. Next-Generation Sequencing Results Vary Between Cultured and Uncultured Microbes. Curr. Microbiol. Int. J. 2022, 79, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Qureshi, A.K.; Azhar, E.I. 16S amplicon sequencing of microbial communities in enriched and non-enriched sediments of non-volcanic hot spring with temperature gradients. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittleston, L.S. Connecting microbial community assembly and function. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 80, 102512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, R.; Xie, T.; Liu, X.; Chai, J.; Howe, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metagenomic and Meta-Transcriptomic Analysis Reveal the Colonization and Expression Profile of Probiotic Strains in Humans and Animals. Fermentation 2023, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, R.; Nesme, J.; Santos-Bay, L.; Koziol, A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Alberdi, A.; Aizpurua, O. A comparison of short-read, HiFi long-read, and hybrid strategies for genome-resolved metagenomics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03590-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; O’Neill, H.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Chatterjee, A.; Gupta, I. Advances in single-cell long-read sequencing technologies. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2024, 6, lqae047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Tan, S.; Zhang, Y.E. Chasing Sequencing Perfection: Marching Toward Higher Accuracy and Lower Costs. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2024, 22, qzae024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustinho, D.P.; Fu, Y.; Menon, V.K.; Metcalf, G.A.; Treangen, T.J.; Sedlazeck, F.J. Unveiling microbial diversity: Harnessing long-read sequencing technology. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Cui, K.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, N. Metagenomics reveals the temporal dynamics of the rumen resistome and microbiome in goat kids. Microbiome 2024, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.; Brown, N.; Rihtman, B.; Michniewski, S.; Redgwell, T.; Clokie, M.; Stekel, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Scanlan, D.J.; Hobman, J.L.; et al. The long and short of it: Benchmarking viromics using Illumina, Nanopore and PacBio sequencing technologies. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The human microbiome project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngara, T.R.; Zhang, H. Recent advances in function-based metagenomic screening. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.-Y.; Liu, L.; Hua, Z.-S.; Fang, B.-Z.; Zhou, E.-M.; Salam, N.; Hedlund, B.P.; Li, W.-J. Microbial dark matter coming to light: Challenges and opportunities. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, E.D.; McBride, S.G.; Strickland, M.S. Microbial dark matter could add uncertainties to metagenomic trait estimations. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lian, W.-H.; Han, J.-R.; Ali, M.; Lin, Z.-L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Jiang, X.-Z.; Li, W.-J.; et al. Capturing the microbial dark matter in desert soils using culturomics-based metagenomics and high-resolution analysis. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Baltoumas, F.A.; Liu, S.; Selvitopi, O.; Camargo, A.P.; Nayfach, S.; Azad, A.; Roux, S.; Call, L.; Ivanova, N.N.; et al. Unraveling the functional dark matter through global metagenomics. Nature 2023, 622, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Pratama, A.A.; Somasundaram, S.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Sullivan, M.B.; Yu, Z. Interrogating the viral dark matter of the rumen ecosystem with a global virome database. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, R.; Chai, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, F.; Li, Y. Metagenome-Assembled Genomes of Pig Fecal Samples in Nine European Countries: Insights into Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Viruses. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Rinke, C.; Chuvochina, M.; Chaumeil, P.-A.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Evans, P.N.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Recovery of nearly 8,000 metagenome-assembled genomes substantially expands the tree of life. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Xue, W.; Luo, G.; Deng, Z.; Qin, P.; Guo, R.; Sun, H.; Xia, Y.; Liang, S.; Dai, Y.; et al. 1520 reference genomes from cultivated human gut bacteria enable functional microbiome analyses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, S.C.; Kumar, N.; Anonye, B.O.; Almeida, A.; Viciani, E.; Stares, M.D.; Dunn, M.; Mkandawire, T.T.; Zhu, A.; Shao, Y.; et al. A human gut bacterial genome and culture collection for improved metagenomic analyses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A new genomic blueprint of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Jin, R.; Peng, Y.; Chai, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, F.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Exploring the Intestinal Microbial Community of Lantang Pigs through Metagenome-Assembled Genomes and Carbohydrate Degradation Genes. Fermentation 2024, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Moon, C.D.; Zheng, N.; Huws, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Opportunities and challenges of using metagenomic data to bring uncultured microbes into cultivation. Microbiome 2022, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzosa, E.A.; McIver, L.J.; Rahnavard, G.; Thompson, L.R.; Schirmer, M.; Weingart, G.; Lipson, K.S.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G.; Segata, N.; et al. Species-level functional profiling of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Míguez, A.; Beghini, F.; Cumbo, F.; McIver, L.J.; Thompson, K.N.; Zolfo, M.; Manghi, P.; Dubois, L.; Huang, K.D.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Extending and improving metagenomic taxonomic profiling with uncharacterized species using MetaPhlAn 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, N.; de Jong, A.E.; Li, Y.; Trubl, G.; Xue, Y.; Dove, N.C. Metagenomic tools in microbial ecology research. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 67, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Liang, W.; Wong, C.C.; Qin, H.; Gao, Y.; Liang, M.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum facilitates anti-PD-1 therapy in microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 1729–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Pei, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Akkermansia muciniphila and its outer protein Amuc_1100 regulates tryptophan metabolism in colitis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10184–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Ke, S.; He, M.; Fu, H.; et al. ABO genotype alters the gut microbiota by regulating GalNAc levels in pigs. Nature 2022, 606, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-F.; Liu, L.-R.; Pan, Y.-P.; Pan, J.; Li, M. Long-read assembled metagenomic approaches improve our understanding on metabolic potentials of microbial community in mangrove sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.C.; Hoff, J.; Olm, M.R.; West-Roberts, J.; Diamond, S.; Firek, B.A.; Morowitz, M.J.; Banfield, J.F. Using strain-resolved analysis to identify contamination in metagenomics data. Microbiome 2023, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, S.L.; Eren, A.M. Discovering new indicators of fecal pollution. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Hu, H.; Zhang, H.; Meng, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q.; et al. Investigating Possible Interspecies Communication of Plasmids Associated with Transfer of Third-Generation Cephalosporin, Quinolone, and Colistin Resistance Between Simultaneously Isolated Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0355422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, H.; Li, B.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L. Horizontal transfer potential of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment plants unraveled by microfluidic-based mini-metagenomics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärnänen, K.; Karkman, A.; Hultman, J.; Lyra, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.J.; Rautava, S.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.; Kumar, H. Maternal gut and breast milk microbiota affect infant gut antibiotic resistome and mobile genetic elements. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantseva, E.; Donmez, A.; Frolova, M.; Pop, M.; Kolmogorov, M. Strainy: Phasing and assembly of strain haplotypes from long-read metagenome sequencing. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olm, M.R.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Firek, B.A.; Morowitz, M.J.; Banfield, J.F. inStrain profiles population microdiversity from metagenomic data and sensitively detects shared microbial strains. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.T.; Tett, A.; Pasolli, E.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Microbial strain-level population structure and genetic diversity from metagenomes. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méheust, R.; Watson, A.K.; Lapointe, F.J.; Papke, R.T.; Lopez, P.; Bapteste, E. Hundreds of novel composite genes and chimeric genes with bacterial origins contributed to haloarchaeal evolution. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, R.; Grimm, D.G. Current challenges and best-practice protocols for microbiome analysis. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A new versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, I.L. Examining horizontal gene transfer in microbial communities. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayling, M.; Clark, M.D.; Leggett, R.M. New approaches for metagenome assembly with short reads. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.M.; Quick, J.C.; Tang, S.; Loman, N.J. Ultra-deep, long-read nanopore sequencing of mock microbial community standards. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richy, E.; Dobbler, P.T.; Tláskal, V.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Baldrian, P.; Kyselková, M. Pacbio HiFi Sequencing Sheds Light on Key Bacteria Contributing to Deadwood Decomposition Processes. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4181686/v1 (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Chen, L.; Zhao, N.; Cao, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X.; et al. Short-and long-read metagenomics expand individualized structural variations in gut microbiomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branton, D.; Deamer, D.W.; Marziali, A.; Bayley, H.; Benner, S.A.; Butler, T.; Di Ventra, M.; Garaj, S.; Hibbs, A.; Huang, X.; et al. The potential and challenges of nanopore sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A. Third generation DNA sequencing: Pacific biosciences’ single molecule real time technology. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 675–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bollas, A.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F. Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hon, T.; Mars, K.; Young, G.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Karalius, J.W.; Landolin, J.M.; Maurer, N.; Kudrna, D.; Hardigan, M.A.; Steiner, C.C.; et al. Highly accurate long-read HiFi sequencing data for five complex genomes. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, A.; Holmes, N.; Rakyan, V.; Loose, M. BulkVis: A graphical viewer for Oxford nanopore bulk FAST5 files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.M.; Peluso, P.; Rowell, W.J.; Chang, P.-C.; Hall, R.J.; Concepcion, G.T.; Ebler, J.; Fungtammasan, A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Olson, N.D.; et al. Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidane, N.; Rodrigues, C.; Bouchez, V.; Rethoret-Pasty, M.; Passet, V.; Brisse, S.; Crestani, C. Accurate genotyping of three major respiratory bacterial pathogens with ONT R10. 4.1 long-read sequencing. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Kang, L.; Qiu, X.; Xu, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Niu, Z.; Niu, B.; Bi, A.; et al. Structural variation discovery in wheat using PacBio high-fidelity sequencing. Plant J. 2023, 120, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, C.M.; Petriglieri, F.; Kristensen, J.M.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Michaelsen, T.Y.; Andersen, M.H.; Kondrotaite, Z.; Karst, S.M.; Dueholm, M.S.; Nielsen, P.H.; et al. Connecting structure to function with the recovery of over 1000 high-quality metagenome-assembled genomes from activated sludge using long-read sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T. Nanopore long-read-only metagenomics enables complete and high-quality genome reconstruction from mock and complex metagenomes. Microbiome 2022, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Shi, W.; Wang, L.; Qu, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wei, F. PandaGUT provides new insights into bacterial diversity, function, and resistome landscapes with implications for conservation. Microbiome 2023, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, E.L.; Maghini, D.G.; Bhatt, A.S. Complete, closed bacterial genomes from microbiomes using nanopore sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Han, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Chai, J.; Deng, L.; Wei, M.; Wu, K.; Zhao, H.; Yang, G.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in the giant panda gut. Imeta 2024, 3, e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Peng, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, M.; Wu, K.; Zhao, J.; et al. The unique gut microbiome of giant pandas involved in protein metabolism contributes to the host’s dietary adaption to bamboo. Microbiome 2023, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Nie, C.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T. Strategies and tools in illumina and nanopore-integrated metagenomic analysis of microbiome data. iMeta 2023, 2, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendure, J.; Balasubramanian, S.; Church, G.M.; Gilbert, W.; Rogers, J.; Schloss, J.A.; Waterston, R.H. DNA sequencing at 40: Past, present and future. Nature 2017, 550, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, B.; Ding, Y.; Niu, L.; Bai, X.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, C.-L. High accuracy methylation identification tools on single molecular level for PacBio HiFi data. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, E.L.; Naquin, D.; Gorrichon, K.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Ouazahrou, R.; Thermes, C.; Hernandez, C. Genomics in the long-read sequencing era. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, E.; van der Sanden, B.P.; O’Gorman, L.; Kwint, M.; Derks, R.; Wenger, A.M.; Lambert, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Baybayan, P.; Rowell, W.J.; et al. Comprehensive de novo mutation discovery with HiFi long-read sequencing. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfach, S.; Shi, Z.J.; Seshadri, R.; Pollard, K.S.; Kyrpides, N.C. New insights from uncultivated genomes of the global human gut microbiome. Nature 2019, 568, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikawa, K.; Ide, K.; Kogawa, M.; Saeki, T.; Yoda, T.; Endoh, T.; Matsuhashi, A.; Takeyama, H.; Hosokawa, M. Recovery of strain-resolved genomes from human microbiome through an integration framework of single-cell genomics and metagenomics. Microbiome 2021, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesker, T.R.; Durairaj, A.C.; Gálvez, E.J.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Baines, J.F.; Clavel, T.; Sczyrba, A.; McHardy, A.C.; Strowig, T. An integrated metagenome catalog reveals new insights into the murine gut microbiome. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2909–2922.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ren, H.; Zhong, H.; Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Han, M.; Li, M.; Madsen, L.; Kristiansen, K.; Xiao, L. An expanded gene catalog of mouse gut metagenomes. MSphere 2021, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, F.; Wang, T.; Gao, N.L.; Liu, Z.; Cui, K.; Duan, Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; et al. The microbiome of the buffalo digestive tract. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Jin, W.; Si, H.; Yuan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; et al. An integrated gene catalog and over 10,000 metagenome-assembled genomes from the gastrointestinal microbiome of ruminants. Microbiome 2021, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; He, C.; Wang, L.; Suo, L.; Guo, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Liu, G.; et al. Compendium of 5810 genomes of sheep and goat gut microbiomes provides new insights into the glycan and mucin utilization. Microbiome 2024, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, M.; Bi, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Ma, S.; Wan, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, G.; Gao, G.F. The multi-kingdom microbiome catalog of the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Biosaf. Health 2024, 6, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, H.; Xiong, X.; Fang, S.; Jiang, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Huang, L. Expanded catalog of microbial genes and metagenome-assembled genomes from the pig gut microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.D.; Treangen, T.J.; Hill, C.M.; Cepeda-Espinoza, V.; Ghurye, J.; Koren, S.; Pop, M. Metagenomic assembly through the lens of validation: Recent advances in assessing and improving the quality of genomes assembled from metagenomes. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.L.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Naquin, D.; Thermes, C. The third revolution in sequencing technology. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmohammadi, R.; Abouei, J.; Anpalagan, A. Error analysis of the PacBio sequencing CCS reads. Int. J. Biostat. 2023, 19, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedersoo, L.; Albertsen, M.; Anslan, S.; Callahan, B. Perspectives and benefits of high-throughput long-read sequencing in microbial ecology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00626-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Shen, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, A.; Xu, D.; Yuan, L.; Lei, L.; Chen, R.; et al. Recovery of metagenome-assembled microbial genomes from a full-scale biogas plant of food waste by pacific biosciences high-fidelity sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1095497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Xun, F.; Zhao, C.; Mao, Z.; Li, B.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q.L. Improved assembly of metagenome-assembled genomes and viruses in Tibetan saline lake sediment by HiFi metagenomic sequencing. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03328-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Ma, J.; Lee, I. HiFi metagenomic sequencing enables assembly of accurate and complete genomes from human gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, A.; Xu, D.; Fan, W. Improved microbial genomes and gene catalog of the chicken gut from metagenomic sequencing of high-fidelity long reads. GigaScience 2022, 11, giac116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, H. Evaluating and improving the representation of bacterial contents in long-read metagenome assemblies. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portik, D.M.; Brown, C.T.; Pierce-Ward, N.T. Evaluation of taxonomic classification and profiling methods for long-read shotgun metagenomic sequencing datasets. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedarko, M.W.; Kolmogorov, M.; Pevzner, P.A. Analyzing rare mutations in metagenomes assembled using long and accurate reads. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 2119–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickhart, D.M.; Kolmogorov, M.; Tseng, E.; Portik, D.M.; Korobeynikov, A.; Tolstoganov, I.; Uritskiy, G.; Liachko, I.; Sullivan, S.T.; Shin, S.B.; et al. Generating lineage-resolved, complete metagenome-assembled genomes from complex microbial communities. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; He, J.; Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, F. Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122482
Han Y, He J, Li M, Peng Y, Jiang H, Zhao J, Li Y, Deng F. Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122482
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yanhua, Jinling He, Minghui Li, Yunjuan Peng, Hui Jiang, Jiangchao Zhao, Ying Li, and Feilong Deng. 2024. "Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122482
APA StyleHan, Y., He, J., Li, M., Peng, Y., Jiang, H., Zhao, J., Li, Y., & Deng, F. (2024). Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122482





