Effect of Biogas Slurry on the Soil Properties and Microbial Composition in an Annual Ryegrass-Silage Maize Rotation System over a Five-Year Period
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Field and Experimental Design
2.2. Analyses of the Soil Samples and Biogas Slurry
2.3. Extraction of the Soil Genomic DNA, Amplification of the 16S rRNA/ITS Genes, Sequencing, and Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
3.2. Diversity and Composition of the Soil Microbial Communities
3.3. Soil Microbial Community Composition
3.4. The Structure and Function of the Soil Microbial Community
3.5. Relationships between the Soil Microorganisms and Soil Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Biogas Slurry on the Soil’s Chemical Characteristics
4.2. Effects of the Biogas Slurry on the Soil Microbial Community
4.3. Sustainability of Soil Health with the Application of Biogas Slurry Compared to That of Chemical Fertilizer
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Mbatha, K.R.; Ward, D. The Effects of grazing, fFire, nitrogen and water availability on nutritional quality of grass in semi-arid Savanna, South Africa. J. Arid. Environ. 2010, 74, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.; van Ittersum, M.K.; Wang, G.; van der Putten, P.E.; van der Werf, W. Yield and yield components of wheat and maize in wheat–maize intercropping in the netherlands. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 76, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, P.; Duan, P.; Ji, C.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, F. Comparative proteomic analysis for assessment of the ecological significance of maize and peanut intercropping. J. Proteom. 2013, 78, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, I.; Uzun, F. Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization of rangelands affects yield, forage quality and the botanical composition. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Xing, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Ghimire, R.; Pradhan, G.P. Nitrogen fertilization I: Impact on crop, soil, and environment. Nitrogen Fixat. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Ruan, H. Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Wen, W.; Liu, H. Effects and potential of optimized fertilization practices for rice production in China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentinuzzi, F.; Cavani, L.; Porfido, C.; Terzano, R.; Pii, Y.; Cesco, S.; Marzadori, C.; Mimmo, T. The fertilising potential of manure-based biogas fermentation residues: Pelleted vs. liquid digestate. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debebe, Y.; Itana, F. Comparative Study on the Effect of Applying Biogas Slurry and Inorganic Fertilizer on Soil Properties, Growth and Yield of White Cabbage (Brassica oleracea Var. Capitata f. Alba). J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2016, 6, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Rahman, S.; Rahman, M.; Oh, D.; Ra, C. The effects of biogas slurry on the production and quality of maize fodder. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2010, 34, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Yu, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D. Effects of biogas slurry fertilization on fruit economic traits and soil nutrients of Camellia oleifera Abel. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, Z. Peanut-Shell Biochar and Biogas Slurry Improve Soil Properties in the North China Plain: A Four-Year Field Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xian, Y.; Wu, J.; Gu, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Peng, H.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, L. Effect of biogas slurry addition on soil properties, yields, and bacterial composition in the rice-rape rotation ecosystem over 3 years. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, K.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Ren, W.; Ding, Z. Cow manure application effectively regulates the soil bacterial community in tea plantation. BMC Microbioly 2020, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Zou, X.; Ruan, H.; Jin, F. Contrasting responses of fungal and bacterial communities to biogas slurry addition in rhizospheric soil of poplar plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, H.; Malghani, S. Incapability of biochar to mitigate biogas slurry induced N2O emissions: Field investigations after 7 years of biochar application in a poplar plantation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.A.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhan, X.; Li, G. Biogas slurry application could potentially reduce N2O emissions and increase crop yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Chapman, S.; Zou, P.; Ye, J.; Yu, Q.; Sun, W.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L. Soil microbial activity and community composition as influenced by application of pig biogas slurry in paddy field in Southeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2020, 18, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, X. From Large to Powerful: International Comparison, Challenges and Strategic Choices for China’s Livestock Industry. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Q. Evaluation of crop residues and manure production and their geographical distribution in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Dong, J.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhai, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, G. A large forage gap in forage availability in traditional pastoral regions in China. Fundam. Res. 2023, 3, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ning, J.; Zhu, P.; Zheng, Y.; Zhai, J. The conservation patterns of grassland ecosystem in response to the forage-livestock balance in North China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenyan, L.; Wei, Q.; Melse, R.W.; Lujun, L.; De Buisonjé, F.E.; Yajing, W.; Renjie, D. Patterns of dairy manure management in China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sanusi, I.A.; Wang, J.; Ye, X.; Kana, E.B.G.; Olaniran, A.O.; Shao, H. Developments and Prospects of Farmland Application of Biogas Slurry in China—A Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Jilani, G.; Arshad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Khalid, A. Bio-conversion of organic wastes for their recycling in agriculture: An overview of perspectives and prospects. Ann. Microbiolloy 2007, 57, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.C.; Reid, C.P.P.; Cole, C.V. Biological strategies of Nutrient Cycling in Soil Systems. In Advances in Ecological Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; Volume 13, pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Porazinska, D.L.; Bardgett, R.D.; Blaauw, M.B.; Hunt, H.W.; Parsons, A.N.; Seastedt, T.R.; Wall, D.H. Relationships at the Aboveground–Belowground Interface: Plants, Soil Biota, and Soil Processes. Ecol. Monogr. 2003, 73, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Lv, M.; Tian, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ge, S. Soil Fertility, Microbial Biomass, and Microbial Functional Diversity Responses to Four Years Fertilization in an Apple Orchard in North China. Hortic. Plant J. 2020, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yao, M.; Rui, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Soil bacterial community structure in Chinese wetlands. Geoderma 2019, 337, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M.; Qin, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shen, Z.; Shen, Q. Microbial communities of an arable soil treated for 8 years with organic and inorganic fertilizers. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tu, P.; Yang, Y.; Xue, X.; Feng, Z.; Dan, C.; Cheng, F.; Yang, Y.; Deng, L. Diversity of rice rhizosphere microorganisms under different fertilization modes of slow-release fertilizer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, J.I.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Curtis, T.P.; Ellis, R.J.; Firestone, M.K.; Freckleton, R.P.; Green, J.L.; Green, L.E.; Killham, K.; Lennon, J.J.; et al. The role of ecological theory in microbial ecology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Wu, K.; Yang, B.; Yin, F.; Zhang, W. Biogas slurry application alters soil properties, reshapes the soil microbial community, and alleviates root rot of Panax notoginseng. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Ullah, H.; Datta, A.; Attia, A.; Rakshit, A.; Molla, S.H. Application of Biogas Slurry in Combination with Chemical Fertilizer Enhances Grain Yield and Profitability of Maize (Zea mays L.). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 2501–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ji, L.; Wang, H.; Yao, L.; Lin, C. The Effect of Biogas Slurry Application on Biomass Production and Forage Quality of Lolium Multiflorum. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shi, K.; Ding, H.; Ding, C.; Yang, Z.; An, C.; Jin, C.; Liu, B.; Zhong, Z.; Xiao, X.; et al. The effect of biogas slurry application on biomass production and the silage quality of corn. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 36, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Knorr, M.; Parrent, J.L.; Simpson, R.T. Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Ji, L.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Yang, Q.; Ni, K.; Ruan, J. Long-term nitrogen fertilization indirectly affects soil Fungi community structure by changing soil and pruned litter in a subtropical tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Plantation in China. Plant Soil 2019, 444, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Grogan, P. Soil microbial biomass, nutrient availability and nitrogen mineralization potential among vegetation-types in a low arctic tundra landscape. Plant Soil 2010, 329, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Yuan, M.; Tang, L.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, S. Integrated microbiology and metabolomics analysis reveal responses of soil microorganisms and metabolic functions to phosphorus fertilizer on semiarid farm. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E.; Blomberg, S.; Bolker, B.; Brown, J.; Claude, J.; Cuong, H.S.; Desper, R.; Didier, G.; Durand, B.; Dutheil, J.; et al. Package ‘ape.’ Analyses of Phylogenetics and Evolution, Version 2019. Available online: https://cran.stat.unipd.it/web/packages/ape/ape.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Kolde, R.; Kolde, M.R. Package ‘Pheatmap.’; R Package: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; Volume 1, p. 790. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, M.K.; Labanya, R.; Joshi, H.C. Influence of Long-Term Chemical Fertilizers and Organic Manures on Soil Fertility-A Review. Univers. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen sddition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Zhang, W.J.; Xu, M.G.; Tong, X.G.; Sun, F.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Huang, S.M.; Zhu, P.; He, X.H. Long-term combined chemical and manure fertilizations increase soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in aggregate fractions at three typical cropland soils in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, B.; Sadet-Bourgeteau, S.; Cannavacciuolo, M.; Chauvin, C.; Flamin, C.; Haumont, A.; Jean-Baptiste, V.; Reibel, A.; Vrignaud, G.; Ranjard, L. Impact of biogas digestates on soil microbiota in agriculture: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3265–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Wu, L.; Brookes, P.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions under Integrated management systems in a low-productivity paddy soil given different organic amendments and chemical fertilizers. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Luo, L.; Carswell, A.; Misselbrook, T.; Shen, J.; Han, J. Changes in soil organic carbon status and microbial community structure following biogas slurry application in a wheat-rice rotation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Ristaino, J.B.; Hu, S. Soil microbial biomass and activity in organic tomato farming systems: Effects of organic inputs and straw mulching. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Niu, S. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Read, D.J. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thukral, A.K. A review on measurement of alpha diversity in biology. Agric. Res. J. 2017, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shamsi, I.H.; Xu, D.; Wang, G.; Lin, X.; Jilani, G.; Hussain, N.; Chaudhry, A.N. Chemical fertilizer and organic manure inputs in soil exhibit a vice versa pattern of microbial community structure. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; Hui, X.; Ran, J.; Ma, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Long-term high-P fertilizer input decreased the total bacterial diversity but not phoD-Harboring bacteria in wheat rhizosphere soil with available-P deficiency. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Bai, N.; Zhang, H.; Lv, W. Effects of biogas slurry combined with chemical fertilizer on doil bacterial and fungal community composition in a paddy field. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655515. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, D.R.; Ziv-El, M.; van Haren, J.; Park, J.G.; del Águila Pasquel, J.; Urquiza Muñoz, J.; Cadillo Quiroz, H. Methanogens and Methanotrophs Show Nutrient-Dependent Community Assemblage Patterns across Peatlands of the Pastaza-Marañón Basin, Peruvian Amazonia. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 00746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Ahmad, I.; Sayyed, R.Z.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Dailin, D.J.; Suriani, N.L. Recent Understanding of Soil Acidobacteria and Their Ecological Significance: A Critical Review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Reddy, G.B. Soil bacterial communities in constructed wetlands treated with swine wastewater using PCR-DGGE technique. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Zhan, G.; Qian, J.; Tao, Y. Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction by Pseudomonas Alcaliphila with an Electrode as the Sole Electron Donor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2904–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, B.; Li, J. Changes in the abundance and structure of bacterial communities in the greenhouse tomato cultivation system under long-term fertilization treatments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 121, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, L.; Xu, X.; Bi, R.; Xiong, Z. Biochar addition stabilized soil carbon sequestration by reducing temperature sensitivity of mineralization and altering the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable field. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; De Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.O.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH Determines Microbial Diversity and Composition in the Park Grass Experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, D.; Mhamdi, R. Microbial Inoculants and Their Impact on Soil Microbial Communities: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 863240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawarda, P.C.; Le Roux, X.; Dirk van Elsas, J.; Salles, J.F. Deliberate introduction of invisible invaders: A critical appraisal of the impact of microbial inoculants on soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Lin, X.; Fujii, T.; Morimoto, S.; Yagi, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J. Soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, bacterial community structure in response to long-term fertilizer management. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2971–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, B.; Lv, L.; Yang, D.; Zhou, L. Migration of heavy metals in vegetable farmlands amended with biogas slurry in the taihu basin, China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Liu, X.; Du, B.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Component analysis and risk assessment of biogas slurry from biogas plants. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 44, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
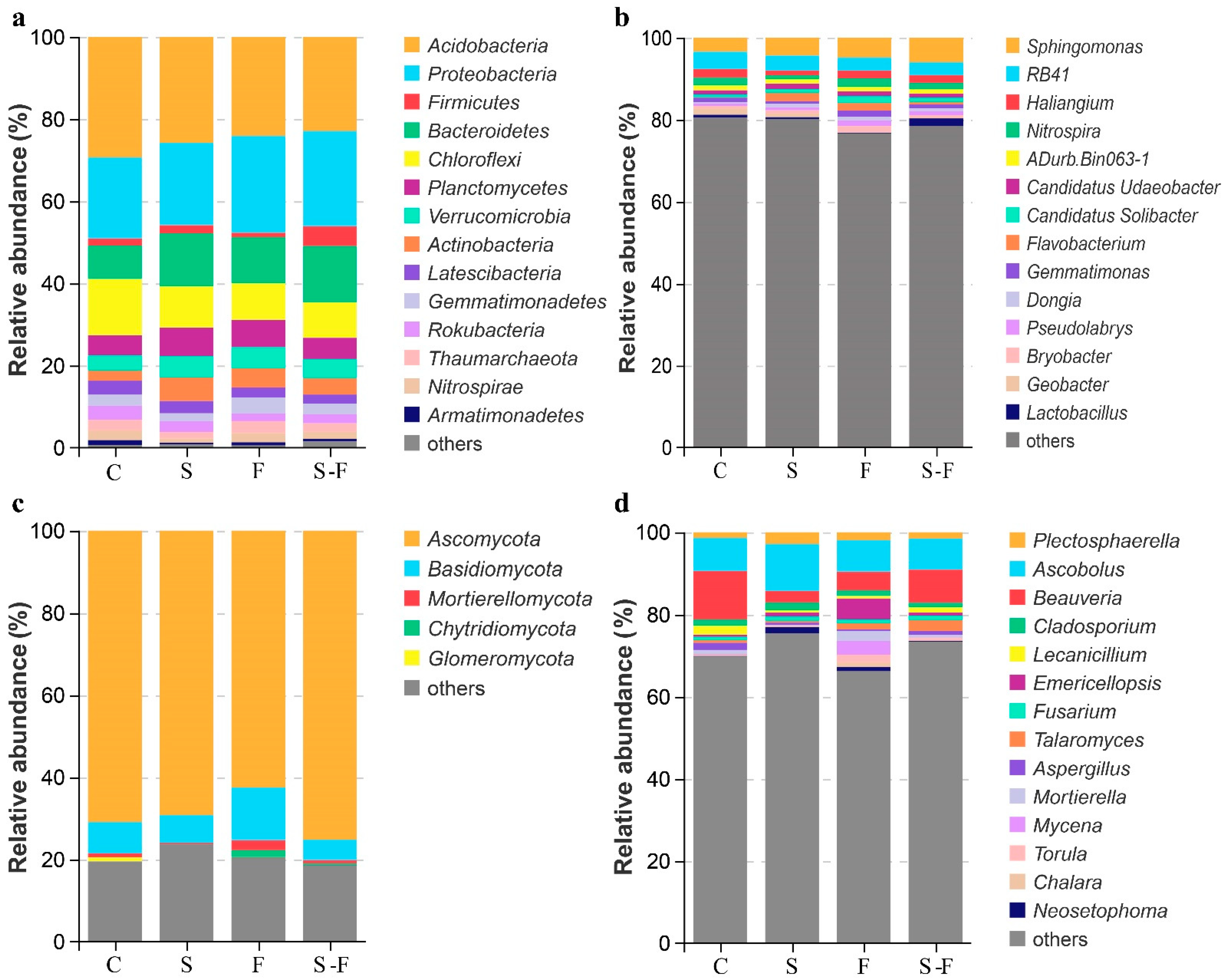
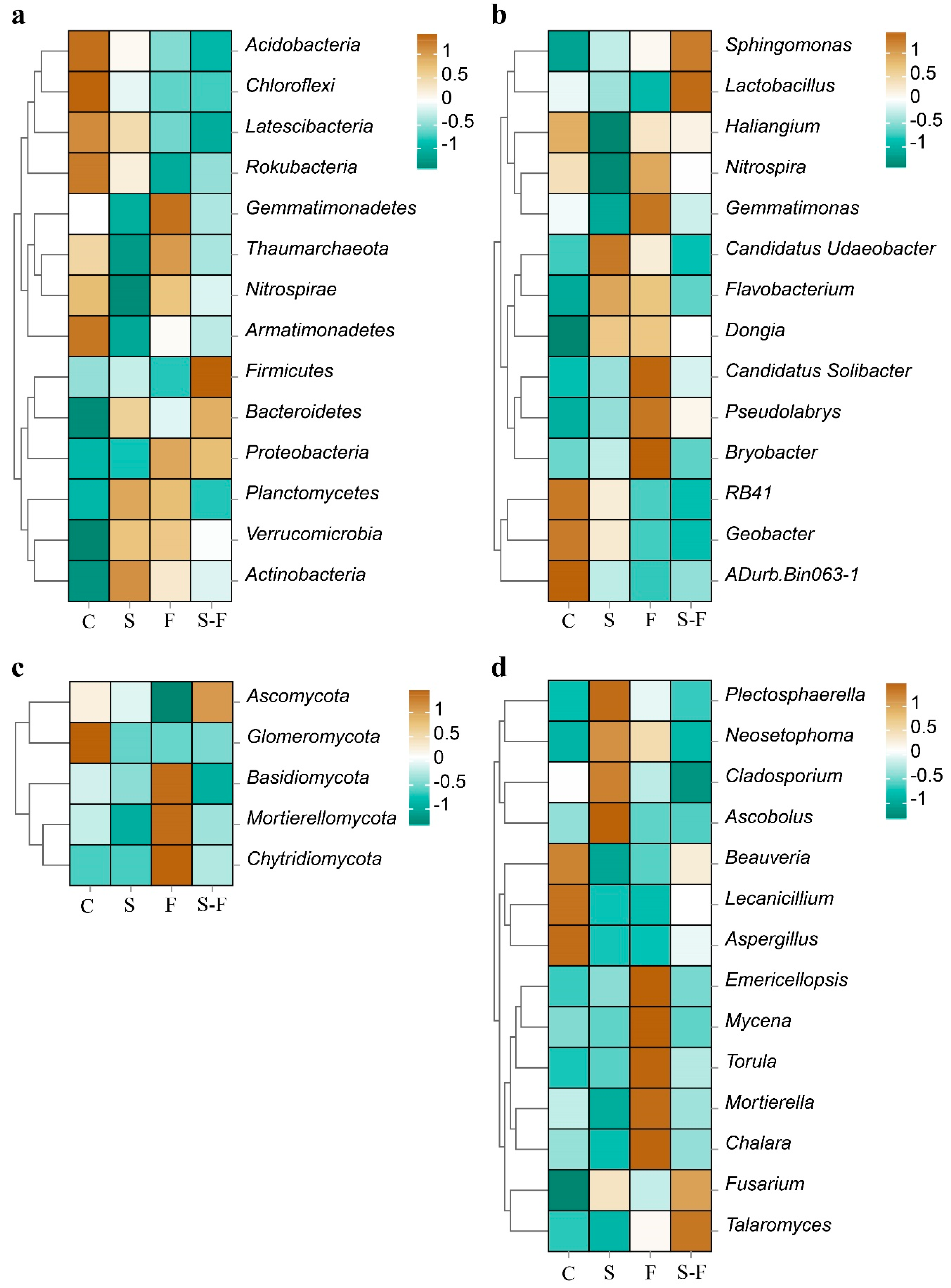
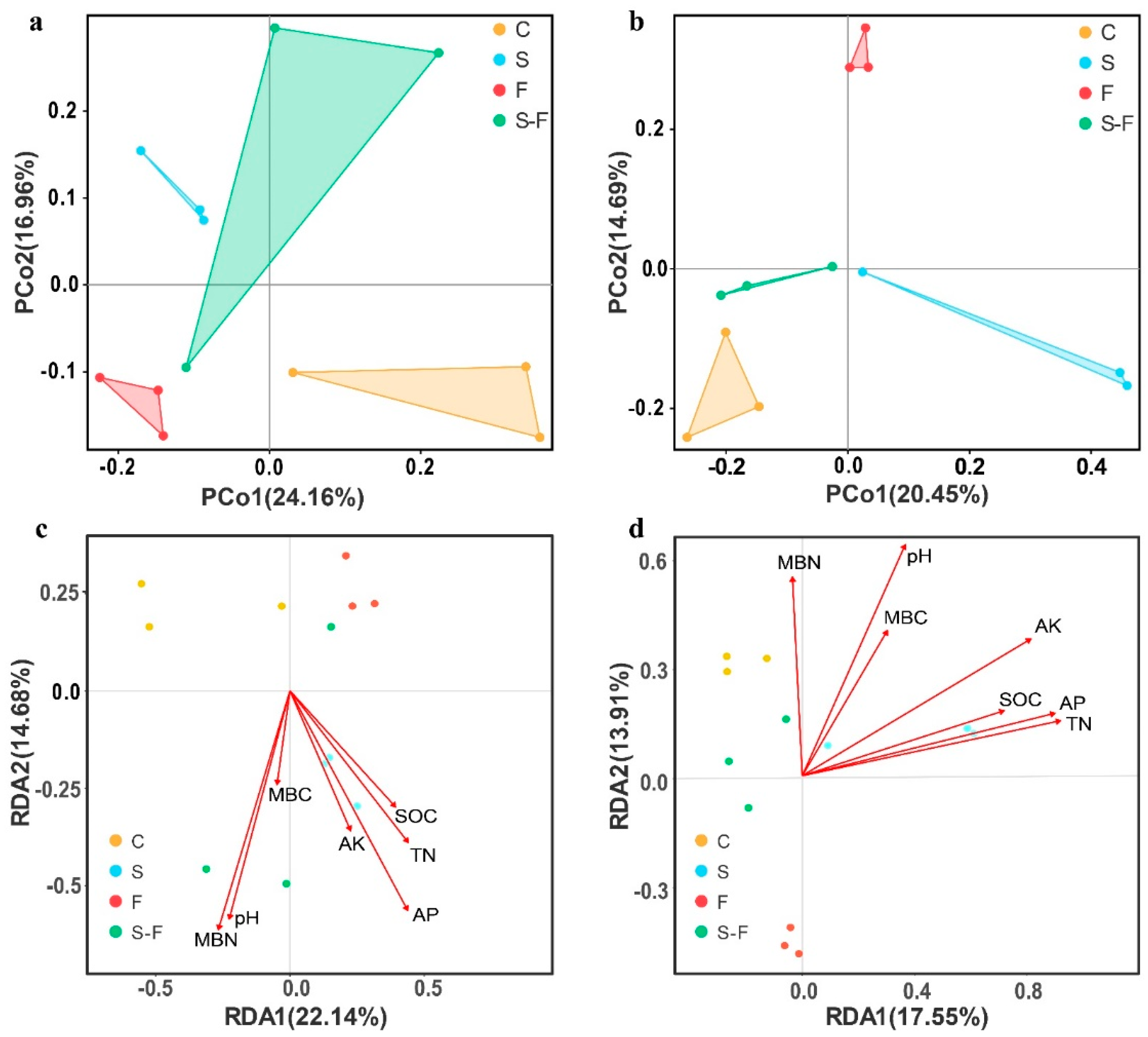
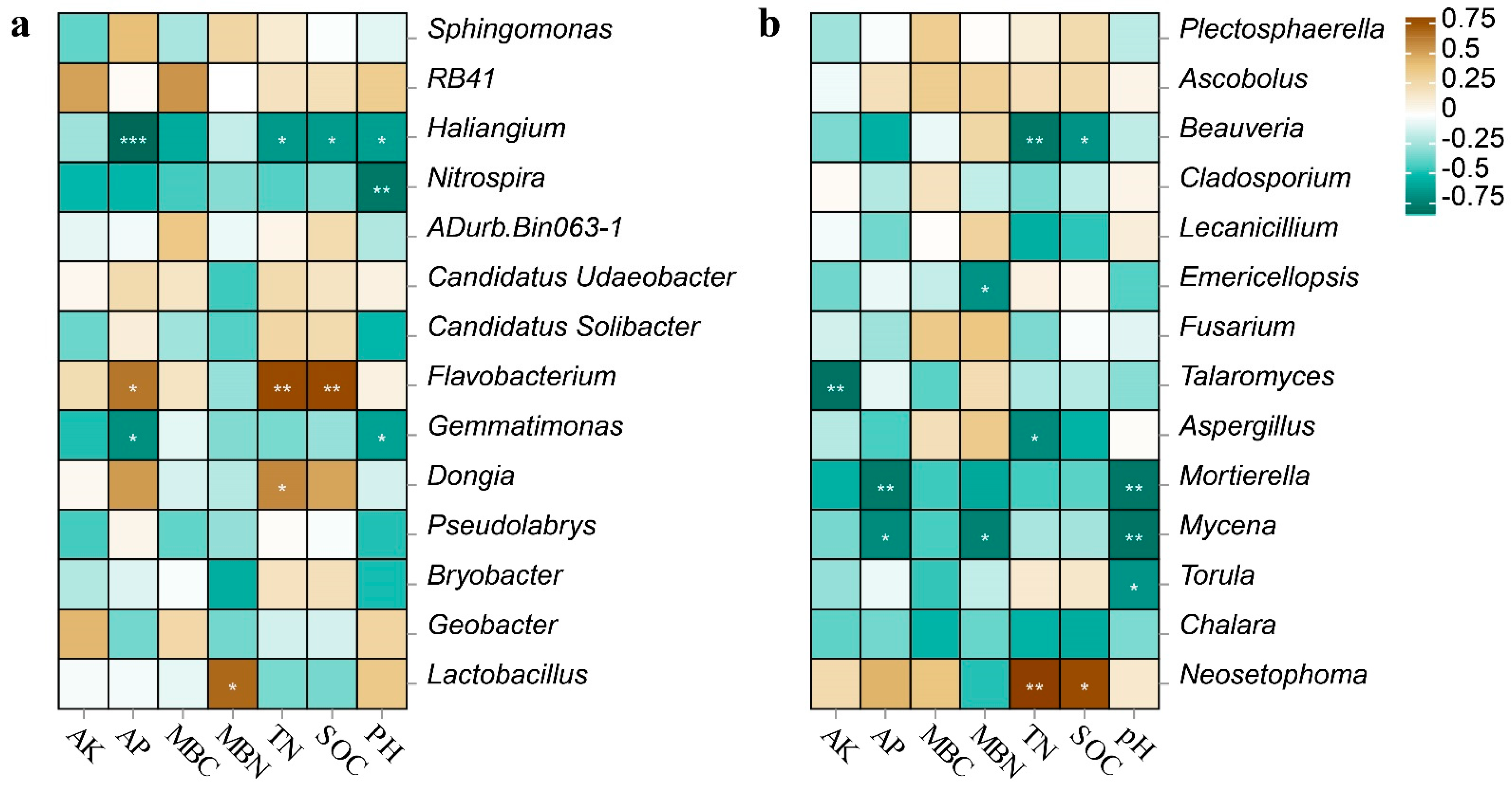
| Attribute | C | S | F | S-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (g/kg) | 14.15 ± 0.21 b | 20.65 ± 1.09 a | 14.4 ± 0.62 b | 13.81 ± 0.75 b |
| TN (g/kg) | 1.67 ± 0.04 b | 2.33 ± 0.06 a | 1.73 ± 0.06 b | 1.68 ± 0.04 b |
| C/N | 8.47 ± 0.10 a | 8.91 ± 0.70 a | 8.33 ± 0.09 a | 8.22 ± 0.28 a |
| AP (mg/kg) | 27.23 ± 4.18 b | 74.81 ± 6.19 a | 30.87 ± 3.83 b | 36.02 ± 1.83 b |
| AK (g/kg) | 0.13 ± 0.02 b | 0.34 ± 0.04 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.004 b |
| MBC (mg/kg) | 196.4 ± 12.13 ab | 228.78 ± 12.94 a | 171.37 ± 20.29 b | 196.13 ± 9.88 ab |
| MBN (mg/kg) | 17.10 ± 3.23 b | 20.32 ± 1.45 b | 6.65 ± 0.97 c | 31.81 ± 1.60 a |
| pH | 5.68 ± 0.02 b | 5.83 ± 0.02 a | 5.43 ± 0.05 c | 5.67 ± 0.02 b |
| Treatment | Observed Species | Chao1 | Shannon | ACE | Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | C | 1204 b | 1270.31 b | 6.43 a | 1282.35 b | 0.982 |
| S | 1246 ab | 1352.38 ab | 6.47 a | 1356.49 b | 0.977 | |
| F | 1357 a | 1498.41 a | 6.53 a | 1519.71 a | 0.970 | |
| S-F | 1188 b | 1287.23 b | 6.41 a | 1283.27 b | 0.979 | |
| p-value | * | * | ns | * | ||
| Fungi | C | 244 a | 262.63 a | 3.87 a | 261.84 a | 0.996 |
| S | 272 a | 296.04 a | 3.82 a | 295.14 a | 0.994 | |
| F | 270 a | 281.05 a | 4.28 a | 282.57 a | 0.996 | |
| S-F | 263 a | 281.73 a | 4.21 a | 276.43 a | 0.996 | |
| p-value | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, G.; Hao, F.; He, W.; Ran, Q.; Nie, G.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X. Effect of Biogas Slurry on the Soil Properties and Microbial Composition in an Annual Ryegrass-Silage Maize Rotation System over a Five-Year Period. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040716
Feng G, Hao F, He W, Ran Q, Nie G, Huang L, Wang X, Yuan S, Xu W, Zhang X. Effect of Biogas Slurry on the Soil Properties and Microbial Composition in an Annual Ryegrass-Silage Maize Rotation System over a Five-Year Period. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040716
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Guangyan, Feixiang Hao, Wei He, Qifan Ran, Gang Nie, Linkai Huang, Xia Wang, Suhong Yuan, Wenzhi Xu, and Xinquan Zhang. 2024. "Effect of Biogas Slurry on the Soil Properties and Microbial Composition in an Annual Ryegrass-Silage Maize Rotation System over a Five-Year Period" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040716
APA StyleFeng, G., Hao, F., He, W., Ran, Q., Nie, G., Huang, L., Wang, X., Yuan, S., Xu, W., & Zhang, X. (2024). Effect of Biogas Slurry on the Soil Properties and Microbial Composition in an Annual Ryegrass-Silage Maize Rotation System over a Five-Year Period. Microorganisms, 12(4), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040716








