Metabarcoding the Bacterial Assemblages Associated with Toxopneustes roseus in the Mexican Central Pacific
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
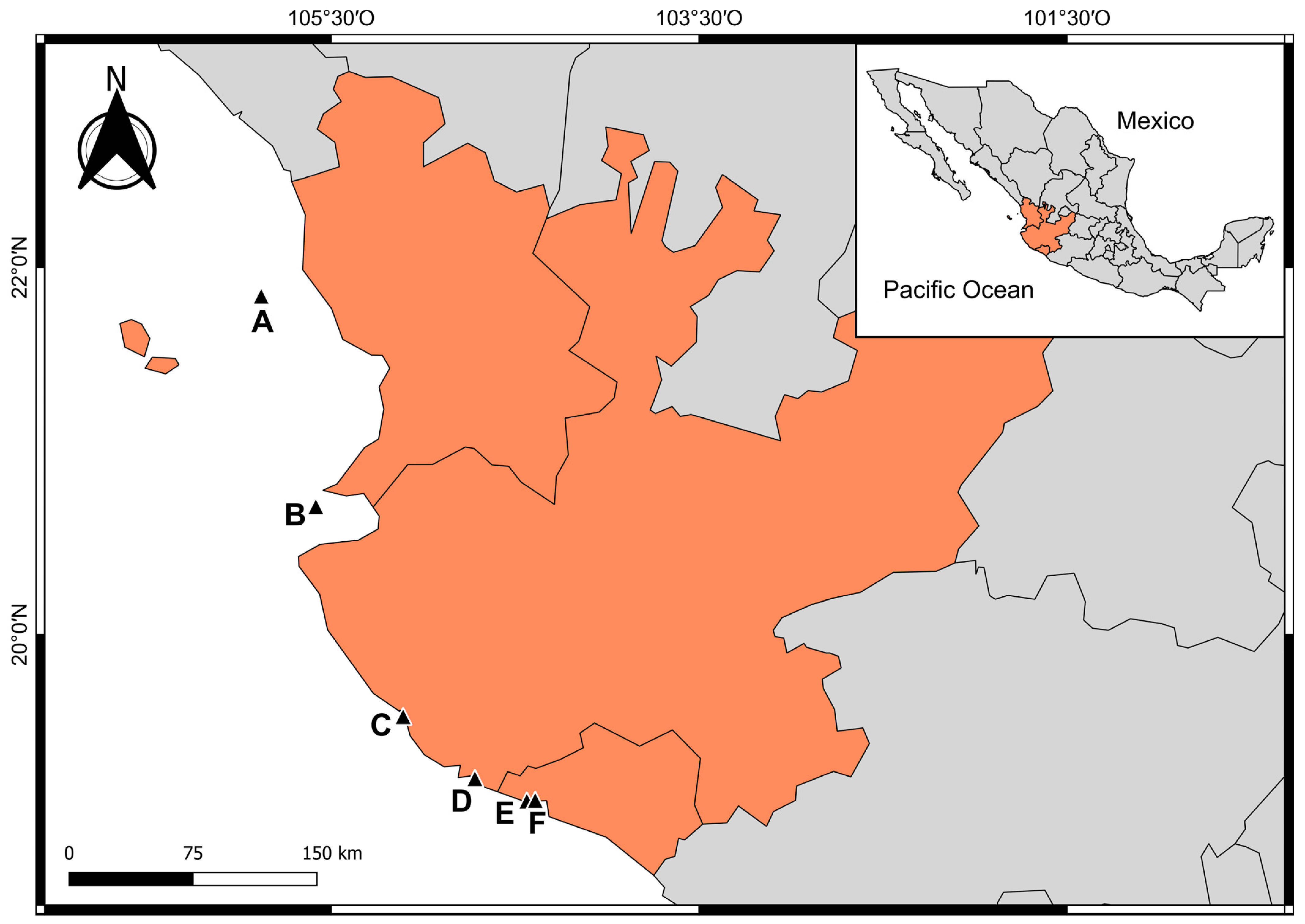
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Collection
2.3. Sequence Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
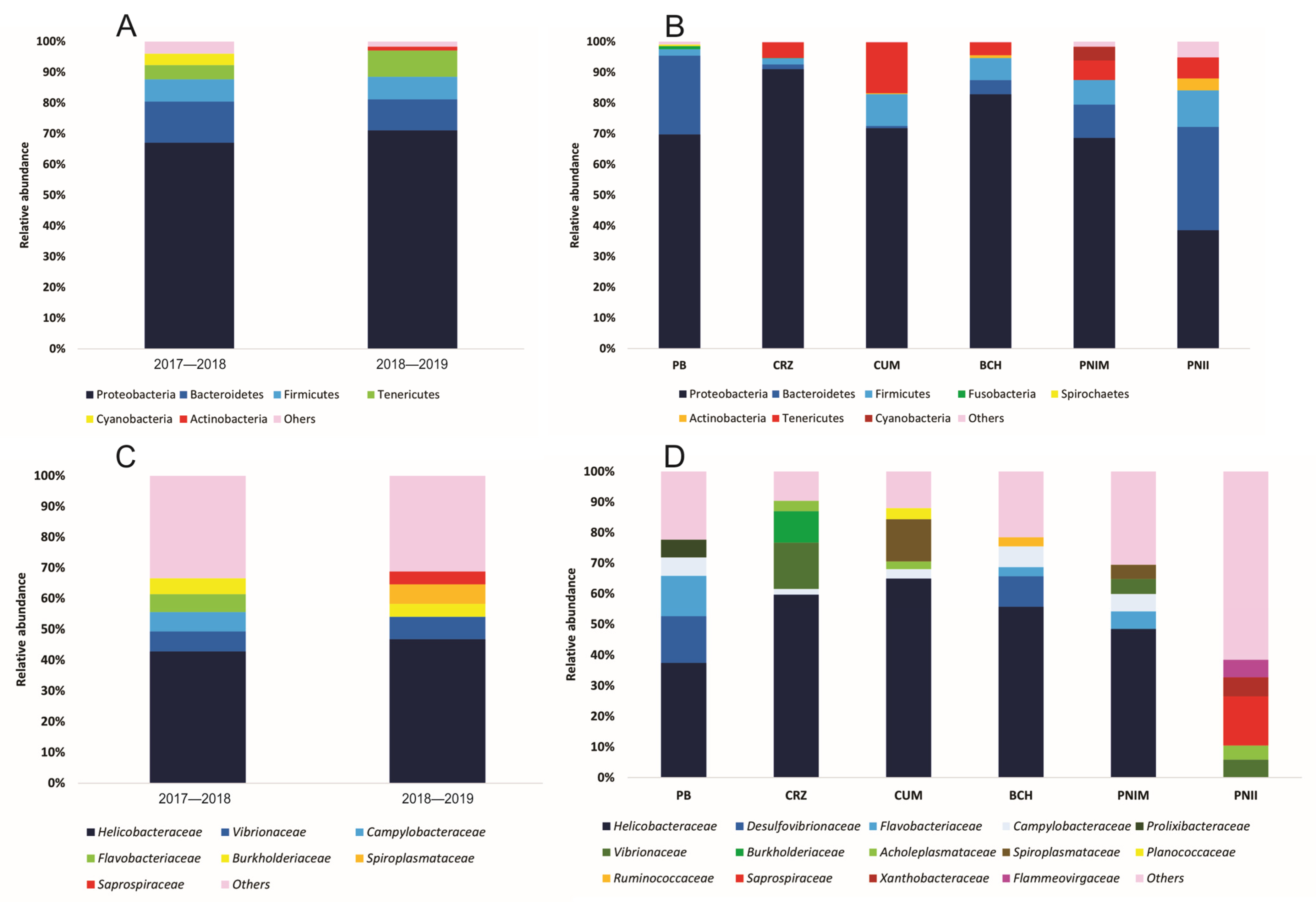
3.1. Characterization of the Bacterial Assembly of T. roseus
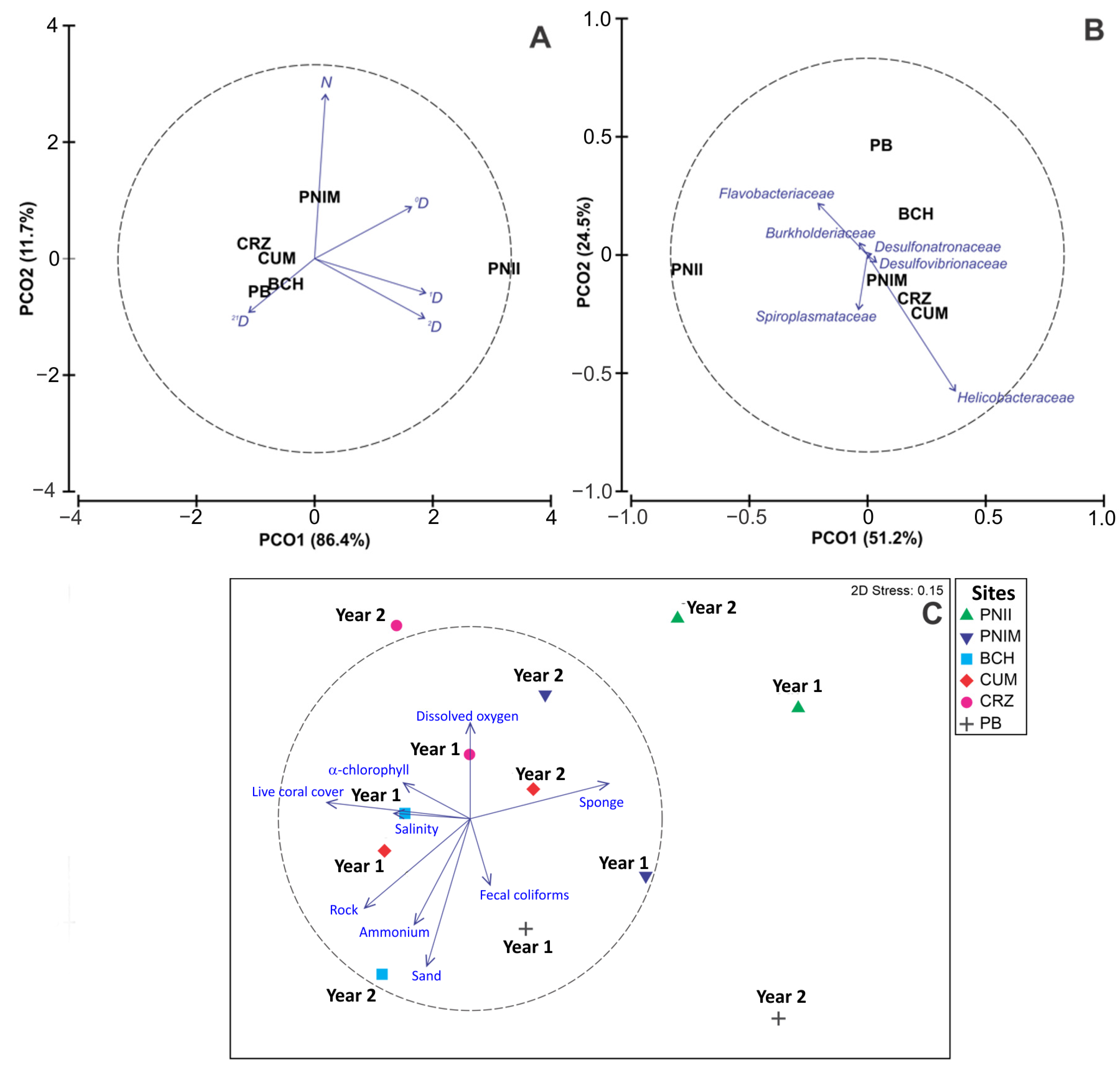
3.2. Alpha and Beta Diversity
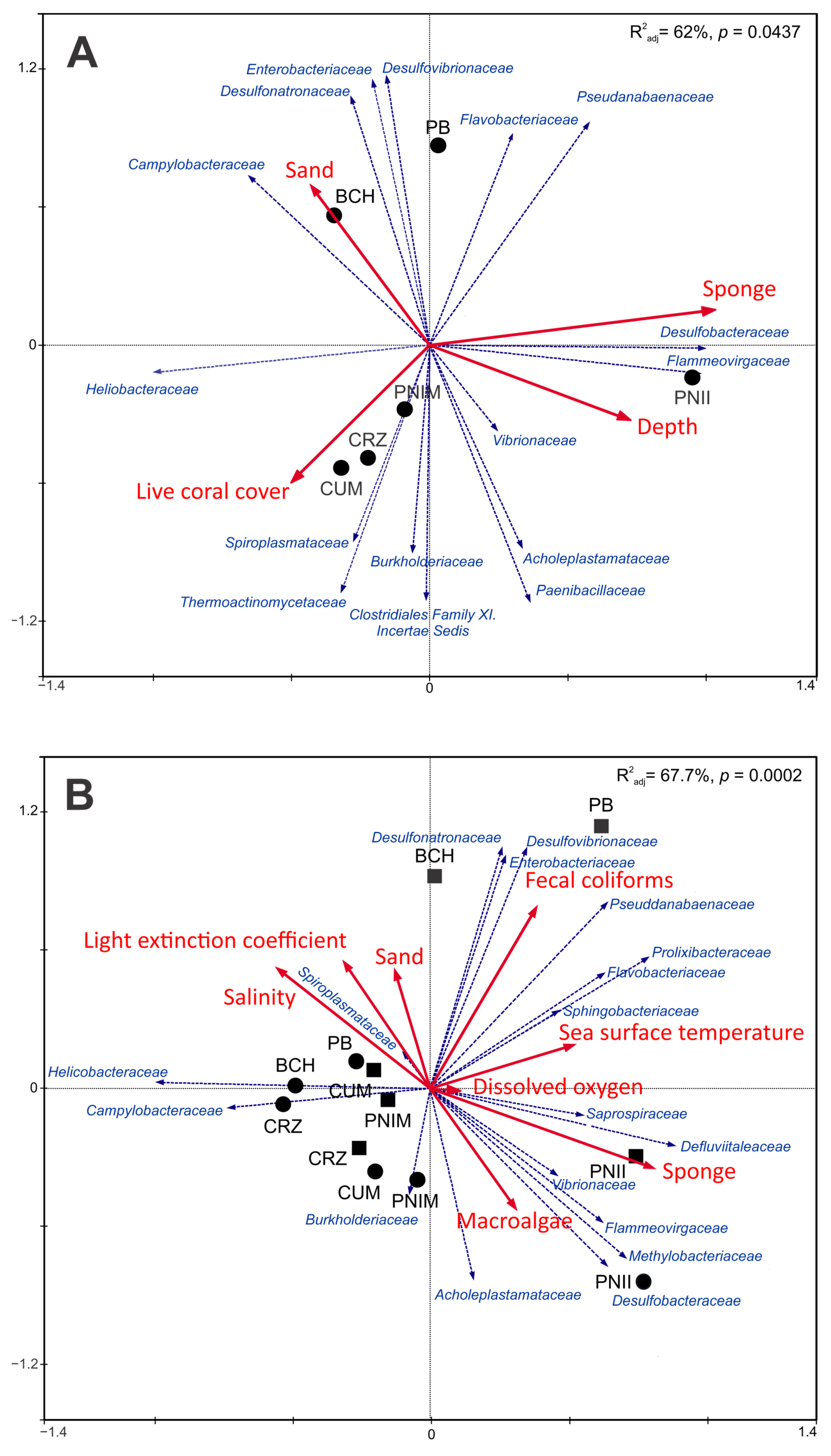
3.3. Relationship of Bacterial Assemblage and Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steele, J.A.; Countway, P.D.; Xia, L.; Vigil, P.D.; Beman, J.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Rose, J.M. Marine bacterial, archaeal and protistan association networks reveal ecological linkages. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttigieg, P.L.; Fadeev, E.; Bienhold, C.; Hehemann, L.; Offre, P.; Boetius, A. Marine microbes in 4D—Using time series observation to assess the dynamics of the ocean microbiome and its links to ocean health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 43, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, S.P.; Pelletreau, K.N.; Rumpho, M.E. 16S rDNA-based metagenomic analysis of bacterial diversity associated with two populations of the kleptoplastic sea slug Elysia chlorotica and its algal prey Vaucheria litorea. Biol. Bull. 2012, 223, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.; Knowlton, N.; Relman, D.A.; Rohwer, F.; Youle, M. Superorganisms and holobionts. Microbe 2013, 8, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.C.; Miller, D.J. The Holobiont Imperative; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cleary, D.F.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Huang, Y.M.; Swierts, T. Compositional variation between high and low prokaryotic diversity coral reef biotopes translates to different predicted metagenomic gene content. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 563–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostria-Hernández, M.L.; Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; Araya, R.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Ríos-Jara, E.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A. Core microbiome of corals Pocillopora damicornis and Pocillopora verrucosa in the north-eastern tropical Pacific. Mar. Ecol. 2022, 43, e12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Lau, N.S.; Amirul, A.A.A.; Bhubalan, K. Metagenomic data on bacterial diversity profiling of high-microbial-abundance tropical marine sponges Aaptos aaptos and Xestospongia muta from waters off terengganu, South China Sea. Data Brief 2020, 31, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; García-Maldonado, J.Q.; Nava-Martínez, G.G.; Salgado, M.A.G.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A. Bacterial assemblages associated with Acropora palmata affected by white band disease in the Mexican region of the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. J. Sea Res. 2022, 185, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosillo-Nuñez, B.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.; Ortiz, M.; Galván-Villa, C.; Cupul-Magaña, A. Effect of habitat structure on the most frequent echinoderm species inhabiting coral reef communities at Isla Isabel National Park (Mexico). Community Ecol. 2015, 16, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, J.A.; Koo, H.; Kumar, R.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Morrow, C.D.; Powell, M.L.; Watts, S.A.; Bej, A.K. The gut microbiome of the sea urchin, Lytechinus variegatus, from its natural habitat demonstrates selective attributes of microbial taxa and predictive metabolic profiles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, C.J.; Van Der Pol, W.J.; Morrow, C.D.; Hakim, J.A.; Koo, H.; McClintock, J.B. Ocean warming alters predicted microbiome functionality in a common sea urchin. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, M.; Rhode, C.; Macey, B.M.; Christison, K.W.; Roodt-Wilding, R. Metagenomic assessment of body surface bacterial communities of the sea urchin, Tripneustes gratilla. Mar. Genom. 2019, 47, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, J.A.; Schram, J.B.; Galloway, A.W.; Morrow, C.D.; Crowley, M.R.; Watts, S.A.; Bej, A.K. The Purple Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus demonstrates a compartmentalization of gut bacterial microbiota, predictive functional attributes, and taxonomic co-occurrence. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, P.T.; Samadi, S.; Zbinden, M.; Hoyoux, C.; Compère, P.; De Ridder, C. First insights into the gut microflora associated with an echinoid from wood falls environments. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2009, 50, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Tian, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y. Bacterial community in the intestine of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius during digestion of Macrocystis pyrifera. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2014, 47, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, M.S.; Wieland, A.; Ploug, H.; Kragelund, C.; Nielsen, P.H. Distribution, identity and activity of symbiotic bacteria in anoxic aggregates from the hindgut of the sea urchin Echinocardium cordatum. Ophelia 2003, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja-Fernández, R.; Maya-Alvarado, B.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L.; Troncoso, A.P.R.; Solís-Marín, F.A.; Sotelo-Casas, R.C. Echinoderms (Echinodermata) from the Central Mexican Pacific. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2021, 69, 219–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosillo-Núñez, B.B.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Ortiz, M.; Calderon-Aguilera, L.E.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L. Influence of the coral reef assemblages on the spatial distribution of echinoderms in a gradient of human impacts along the tropical Mexican Pacific. Biodivers. Conserv. 2016, 25, 2137–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Casas, R.C.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Solís-Marín, F.A.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P. Structural and environmental effects on an assemblage of echinoderms associated with a coral community. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, P.W. El Niño warming, coral mortality y reef framework destruction by echinoid bioerosion in the eastern Pacific. Galaxea 1988, 7, 129–160. [Google Scholar]
- James, D.W. Diet, movement, and covering behavior of the sea urchin Toxopneustes roseus in rhodolith beds in the Gulf of California, México. Mar. Biol. 2000, 137, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Hayashi, H.; Shinohara, M.; Ohura, K.; Tachikawa, E.; Kashimoto, T. Isolation of a novel lectin from the globiferous pedicellariae of the sea urchin Toxopneustes pileolus. Nat. Toxins 1996, 391, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, F.; Nakagawa, H.; Yamada, H.; Nagasaka, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Araki, Y.; Tomihara, Y.; Nozaki, M.; Sakuraba, H.; Ohshima, T.; et al. Fishing for bioactive substances from scorpionfish and some sea urchins. J. Nat. Toxins 2002, 11, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Edo, K.; Sakai, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Shinohara, M.; Ohura, K. Immunomodulatory activity of a pedicellarial venom lectin from the toxopneustid sea urchin Toxopneustes pileolus. Toxin Rev. 2012, 31, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, M.D.; Fox, H.E.; Allen, G.R.; Davidson, N.; Ferdaña, Z.A.; Finlayson, M.; Halpern, B.S.; Jorge, M.A.; Lombana, A.; Lourie, S.; et al. Marine ecoregions of the world: A bioregionalization of coastal and shelf areas. BioScience 2007, 57, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, M.F.; Castro, R.; Beier, E.; Godínez, V.M.; Amador, A.; Guest, P. SST, thermohaline structure, and circulation in the southern Gulf of California in June 2004 during the North American Monsoon Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C02025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja, D.A.; Marinone, S.G.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Gómez-Valdivia, F. Modelación numérica de la hidrografía y circulación estacional y de mesoescala en el Pacífico Central Mexicano. Cienc. Mar. 2012, 38, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-de Silva, C.V.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P. Temporal oceanographic variation using satellite imagery data in the central Mexican Pacific convergence zone. Cienc. Mar. 2023, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Rodriguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Araya, R.; Vargas, O.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.M.; Diaz-Perez, L.; Rios-Jara, E.; Ortiz, M. Multi-scale analysis of hermatypic coral assemblages at Mexican Central Pacific. Sci. Mar. 2017, 81, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; Galván-Villa, C.M.; Ayón-Parente, M.; Gómez-Petersen, P. Structure and spatial variation of the hermatypic coral assemblages of the southern coast of Jalisco, in the Mexican Central Pacific. J. Sea Res. 2021, 170, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. Determination of reactive nitrate. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1968, 167, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, H.H.; Atkins, W.R.G. Photo-electric measurement of submarine illumination troughout the year. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 1929, 16, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L.; Galván-Villa, C.M.; Ríos-Jara, E.; Ortiz, M.; Robles-Jarero, E.G.; Arias-González, J.E. Additive partitioning of reef fish diversity variation: A promising marine biodiversity management tool. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 1655–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroson, R.B.; Edmunds, P.J.; Precht, W.F.; Swanson, D.W.; Levitan, D.R. Large scale, long-term monitoring of Caribbean coral reefs: Simple, quick, inexpensive techniques. Atoll Res. Bull. 1994, 421, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, G.; Andersen, L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotelli, N.J.; Colwell, R.K. Quantifying biodiversity: Procedures and pitfalls in the measurement and comparison of species richness. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Chiu, C.H.; Jost, L. Unifying species diversity, phylogenetic diversity, functional diversity, and related similarity and differentiation measures through Hill numbers. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorely, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+Primer: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; Primer-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2008; Volume 214. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v6: User Manual/Tutorial; Primer-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Referent Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 5.0); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Araya, R.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Ceh, J.; Ríos-Jara, E.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A. First deep screening of bacterial assemblages associated with corals of the Tropical Eastern Pacific. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrtki, K. Oceanography of the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1966, 4, 33–68. [Google Scholar]
- Filonov, A.; Monzon, C.; Tereshschenko, I. On the conditions of internal tide wave generation along the west coast of Mexico. Cienc. Mar. 1996, 22, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, R.A.; Willis, B.L.; Pfeffer, C.; Bourne, D.G. Diversities of coral associated bacteria differ with location, but not species, for three acroporid corals on the Great Barrier Reef. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, C.; Torres, T.T.; Ottoboni, L. Bacterial communities and species-specific associations with the mucus of Brazilian coral species. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassarre, L.; Ying, H.; Reitzel, A.M.; Franzenburg, S.; Fraune, S. Microbiota mediated plasticity promotes thermal adaptation in the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, J.; van Oppen, M.J.H. A role for bacterial experimental evolution in coral bleaching mitigation? Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Jara, E.; Galván-Villa, C.M.; Solís-Marín, F.A. Equinodermos del Parque Nacional Isla Isabel, Nayarit, México. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2008, 79, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.I.; Herrera, M.; Liew, Y.J.; Aranda, M. Long-term temperature stress in the coral model Aiptasia supports the “Anna Karenina principle” for bacterial microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M.M.; Pespeni, M.H. Microbiome shifts with onset and progression of Sea Star Wasting Disease revealed through time course sampling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Xiao, Z.; Wei, Z.; Long, L. Bacterial communities associated with healthy and bleached crustose coralline alga Porolithon onkodes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Fang, X. The unusual 2014–2016 El Niño events: Dynamics, prediction and enlightenments. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwob, G.; Cabrol, L.; Poulin, E.; Orlando, J. Characterization of the gut microbiota of the Antarctic heart urchin (Spatangoida) Abatus agassizii. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.M.; Lamy, T.; Page, H.M.; Miller, R.J. Sea urchin microbiomes vary with habitat and resource availability. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2021, 6, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeker, K.J.; Bell, L.E.; Donham, E.M.; Hoshijima, U.; Lummis, S.; Toy, J.A.; Willis-Norton, E. Ecological change in dynamic environments: Accounting for temporal environmental variability in studies of ocean change biology. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantos, O.; Bongaerts, P.; Dennis, P.G.; Tyson, G.W.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Habitat-specific environmental conditions primarily control the microbiomes of the coral Seriatopora hystrix. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrattanapitak, N.; Pairohakul, S. Bacterial Community in Gut Contents of the Sea Urchin Diadema setosum (Leske, 1778) and the Ambient Sediments from Sichang Island using Metagenomics Approaches. NU Int. J. Sci. 2018, 15, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, T.J.; Dupont, S.; Reitzel, A.M. Geography, not food availability, reflects compositional differences in the bacterial communities associated with larval sea urchins. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Yu, K.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Qin, Z. The composition, diversity and predictive metabolic profiles of bacteria associated with the gut digesta of five sea urchins in Luhuitou fringing reef (northern South China Sea). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faddetta, T.; Ardizzone, F.; Faillaci, F.; Reina, C.; Palazzotto, E.; Strati, F.; De Filippo, C.; Spinelli, G.; Puglia, A.M.; Gallo, G.; et al. Composition and geographic variation of the bacterial microbiota associated with the coelomic fluid of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Casas, R.C.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A.; Solís-Marín, F.A.; Godínez-Domínguez, E.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L. Spatial-temporal variations in echinoderm diversity within coral communities in a transitional region of the northeast of the eastern pacific. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 227, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; Araya, R.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Ríos-Jara, E.; Ortiz, M.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A. Bacterial assemblages associated with coral species of the Mexican Central Pacific. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2017, 52, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.M.; Hassnien, F.S.; Abdel-Aal, M.M.; Zakar, A.H.; Elshfey, S.A. Enterobacteriaceae in some fresh and marine fish. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2018, 34, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, A.; Sims, J.A.; Grimes, M.; Howe-Kerr, L.I.; Grupstra, C.G.B.; Doyle, S.M.; Stadler, L.; Sylvan, J.B.; Shamberger, K.E.F.; Davies, S.W.; et al. On a reef far, far away: Offshore transport of floodwaters following extreme storms impacts sponge health and associated microbial communities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 8, 608036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Euan, H.; Rodríguez-Escamilla, Z.; Pérez-Rueda, E.; Escalante-Herrera, K.; Martínez-Núñez, M.A. Comparing Sediment Microbiomes in Contaminated and Pristine Wetlands along the Coast of Yucatan. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Heo, E.; Kang, H.; Adams, J. Changes in soil bacterial community structure with increasing disturbance frequency. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, H.K.; Hong, S.G.; Kim, O.S. Complete genome sequence of Pedobacter cryoconitis PAMC 27485, a CRISPR-Cas system-containing psychrophile isolated from Antarctica. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 226, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhong, L.; Qiu, L.; Chen, J. Shifts of microbial community structure in soils of a photovoltaic plant observed using tag-encoded pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barneah, O.; Ben-Dov, E.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Kushmaro, A. Characterization of black band disease in Red Sea stony corals. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt-Irwin, J.M.; Baum, J.K.; Garren, M.; Thurber, R.L.V. Responses of coral-associated bacterial communities to local and global stressors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | Pseudo-F | p | C.V.% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha diversity | |||
| Year | 2.0658 | 0.1336 | 14.4 |
| Site | 3.3813 | 0.0127 | 37.3 |
| Year × Site | 0.34989 | 0.9788 | 0.0 |
| Residuals | 48.3 | ||
| Beta diversity | |||
| Year | 0.89 | 0.0283 | 16.1 |
| Site | 0.62 | 0.0277 | 19.5 |
| Year × Site | 0.47 | 0.1463 | 17.9 |
| Residuals | 0.36 | 46.5 | |
| Environmental Variables | |||
| Year | 1.8421 | 0.1162 | 17.9 |
| Site | 2.0416 | 0.0032 | 34.4 |
| Residuals | 47.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Zulueta, J.; Rubio-Bueno, S.; Zamora-Tavares, M.d.P.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.A. Metabarcoding the Bacterial Assemblages Associated with Toxopneustes roseus in the Mexican Central Pacific. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061195
Hernández-Zulueta J, Rubio-Bueno S, Zamora-Tavares MdP, Vargas-Ponce O, Rodríguez-Troncoso AP, Rodríguez-Zaragoza FA. Metabarcoding the Bacterial Assemblages Associated with Toxopneustes roseus in the Mexican Central Pacific. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(6):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061195
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Zulueta, Joicye, Sharix Rubio-Bueno, María del Pilar Zamora-Tavares, Ofelia Vargas-Ponce, Alma Paola Rodríguez-Troncoso, and Fabián A. Rodríguez-Zaragoza. 2024. "Metabarcoding the Bacterial Assemblages Associated with Toxopneustes roseus in the Mexican Central Pacific" Microorganisms 12, no. 6: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061195
APA StyleHernández-Zulueta, J., Rubio-Bueno, S., Zamora-Tavares, M. d. P., Vargas-Ponce, O., Rodríguez-Troncoso, A. P., & Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F. A. (2024). Metabarcoding the Bacterial Assemblages Associated with Toxopneustes roseus in the Mexican Central Pacific. Microorganisms, 12(6), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061195








