Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is becoming an increasingly serious health problem in humans and animals. Probiotics can inhibit the development of IBD. Due to the specificity of the strains, the function and mechanism of action of different strains are still unclear. Here, a DSS-induced colitis mouse model was utilized to investigate the ability and mechanism by which Lacticaseibacillus casei IB1 alleviates colitis. Treatment with L. casei IB1 improved DSS-induced colitis in mice, as indicated by increased body weight, colon length, and goblet cell numbers and decreased disease activity index (DAI), proinflammatory factor (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) levels, and histopathological scores after intake of IB1. IB1 supplementation also improved the expression of tight junction proteins and inhibited the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways to alleviate intestinal inflammation. In addition, IB1 rebalanced the intestinal microbial composition of colitis mice by increasing the abundance of Faecalibaculum and Alistipes and decreasing the abundance of Bacteroides and Escherichia_Shigella. In summary, L. casei IB1 showed great potential for relieving colitis by regulating the microbiota and restoring the epithelial barrier. It can be used as a potential probiotic for the prevention and treatment of UC in the future.
1. Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), comprising ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) [1,2,3], is an idiopathic, chronic, and frequently recurrent condition impacting the gastrointestinal tract, with global implications for human health [4]. The main symptoms of UC are abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and bloody stool [5,6,7]. There are many pathogenic factors of UC. It is generally believed that heredity, diet, the immune system, the intestinal barrier, and microflora may be related to the development of UC [7,8,9,10]. In recent years, some studies have shown that intestinal flora imbalance [11,12,13,14,15] and intestinal epithelial barrier damage [14,15,16] are related to the occurrence of IBD.
The gut microbiota is strongly linked to the physiological function and immune ability of the host [14]. It has a significant impact on the host during homeostasis and disease [17,18]. An imbalance in the intestinal microflora leads to an increase in pathogens and abnormalities in the intestinal flora [17,19]. The integrity of the intestinal barrier is indispensable for human and animal health [20]. Tight junction proteins play an important role in maintaining the intestinal mucosal barrier. Studies have shown that in a model of inflammatory bowel disease, the level of tight junction proteins is increased after treatment with probiotics [21,22]. In addition, studies have shown that the pathogenic bacteria of the intestinal microflora are significantly increased and that the level of tight junction proteins is significantly decreased in IBD patients and animal models [23,24,25,26,27]. At present, the clinical drugs commonly used to treat IBD mainly contain antibiotics, aminosalicylic acid, steroids, and immune inhibitors [28,29]. However, these drugs have significant side effects on humans and animals and their application is greatly limited. Therefore, safe, effective drugs with no side effects are urgently needed to treat IBD.
Qinghai is one of the places in northwestern China where ethnic minorities gather. Dairy products are part of traditional food culture and thus are indispensable. Compared with modern techniques, the traditional approach to dairy production is more ecological and natural, and the types of probiotics produced are more abundant. IB1 is derived from herdsmen’s yogurt in Qinghai, China, with a safe source and long history. In a preliminary study, we chose L. casei IB1 for research, which has been proven to be acid-resistant, has a high survival rate in simulated gastrointestinal experiments, and has proved that IB1 has no toxic effect on mice in vivo. Probiotics are a class of living microorganisms that can have a healthy effect on the host when the intake is sufficient [30]; they are considered to promote the health of the host by producing related beneficial enzymes, organic acids, vitamins, and bacteriocins [31]. At present, commonly used probiotics are Lacticaseibacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterococcus, Bacillus, and Saccharomycetes [32]. Previous studies have shown that probiotics have antibacterial functions, regulating immune activity and antioxidation, improving the intestinal mucosal barrier, and regulating intestinal flora homeostasis [13,31,33,34]. However, probiotics have strain specificity, and the mechanism of action of different strains is still unclear [34]. The histological characteristics, clinical manifestations, location, and cytokine proliferation of the DSS-induced colitis model are very similar to those of human ulcerative colitis. The conditions and operation methods of the model are simple, low-cost, repeatable, and easy to master and promote [35,36]. Therefore, this study mainly used a DSS-induced colitis mouse model to explore the role and mechanism of L. casei IB1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of L. casei IB1
L. casei IB1 was preserved in our laboratory and subsequently cultured in MRS broth medium at 37 °C for 24 h and continuously oscillated at 120 rpm. After incubation, the concentration of IB1 reached 2.1 × 1010 CFU/mL. After centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 5 min, the cell supernatants were discarded and the cell pellets were collected. The cells were washed twice with PBS, diluted to 1 × 1010 CFU/mL, and stored at −80 °C for subsequent experiments.
2.2. Animal Experiment Design
Thirty male C57BL/6J mice (6 weeks old, 16–18 g) were bought from Youda Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). Dextran sodium sulfate (DSS, molecular weight: 36–50 kDa) was purchased from Dalian Meilun Biotechnology (Dalian, China). Throughout the animal experiment, all mice were kept in the Center of Animal Lab of Guangdong Ocean University at a temperature of 25 ± 2 °C and relative humidity of 50 ± 5%, with a 12 h light/dark cycle. The experimental process and technical route are shown in Figure 1. After 7 days of adaptation, the mice were randomly divided into 5 groups (n = 6): CON group, DSS model group, LOW group (DSS + L, 107 CFU/mL), MID group (DSS + M, 108 CFU/mL), and HIGH (DSS + H, 109 CFU/mL) group. The specific test scheme was as follows: a. Throughout the experimental period, the control group was provided standard food and drinking water, and 200 μL of PBS was given daily. b. The DSS model group was given standard food and drinking water during the experiment, 3% (w/v) DSS solution was used instead of drinking water in the last week of the experiment, and 200 μL of PBS was given daily during the experiment. c. The mice in the DSS + L, DSS + M, and DSS + H groups were given standard food and drinking water during the experiment, 3% (w/v) DSS solution was used instead of drinking water in the last week of the experiment, and 200 μL of the corresponding concentration of strain solution was given daily during the experiment. During the experiment, the weights of the mice were recorded, and fecal occult blood was observed. The DAI of each mouse was calculated daily in a previous study [37]. The DAI score was assessed according to the parameters (Table 1), with a maximum total score of 12 points.

Figure 1.
Experimental process and technical route. The mice were given 3% DSS in their drinking water for 7 days before being sacrificed. L. casei IB1 was administered daily by oral gavage (200 μL). Graphics created with BioRender. (www.biorender.com), accessed on 18 February 2024.

Table 1.
Disease activity index (DAI) scoring system.
2.3. Sample Collection
On the 15th day of the experiment, the eyeball blood of all mice was collected in a tube, and the serum was collected at 3000 rpm and 4 °C after 15 min and stored at −80 °C for subsequent experiments. Then, the anesthetized mice were killed by cervical dislocation. Colon contents were collected aseptically for microbiotomic analysis. In addition, the length of the colon was measured, and a portion of the colon (0.5 cm section) was quickly removed and soaked in 4% paraformaldehyde for histological evaluation. The remaining colon was rapidly frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C for further analysis.
2.4. Serum Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) were measured using commercially available ELISA kits (Jiangsu Meimian Industrial Co., Ltd., Yancheng, China).
2.5. Histopathological Examination of the Colon
Colon tissue samples were sent to Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China), for hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining. Histological changes in the colon were observed through a conventional light microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and images were taken digitally (Sony, Tokyo, Japan) for subsequent analysis according to Table 2.

Table 2.
Histological colitis scoring system.
2.6. Immunoblotting Analysis
Colon tissues were removed at −80 °C; total protein was extracted with RIPA lysis buffer (Strong), 1% protease inhibitor cocktail, and 1% phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Jiangsu CWBIO Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, China); and the protein concentration was determined with the Synergy HTX Multi-Mode Reader (Bio-Tek, Winooski, VT, USA) according to the instructions of a BCA kit (Yeasen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The protein samples were mixed with loading buffer, heated in a boiling water bath for 5 min, separated by SDS–PAGE (8%), and transferred to 0.22 μm polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). The membrane was blocked with 5% (w/v) skim milk in Tris-buffered saline containing 1% Tween 20 (TBST) at room temperature for 2 h and then washed three times with TBST for 10 min each time. After that, the PVDF membranes were incubated with the primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C: NF-κBP65 (8242S, CST, 1:1000), NF-κBP-p65 (3033S, CST, 1:1000), P38 (8690S, CST, 1:1000), P-p38 (4511S, CST, 1:1000), ERK1/2 (4695S, CST, 1:1000), P-ERK1/2 (4370S, CST, 1:1000), JNK (67096S, CST, 1:1000), P-JNK (4668S, CST, 1:1000), Occludin (27260, Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA, 1:1000), Claudin1 (37–4900, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), Claudin2 (AF0128, Affbiotech, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1:1000), and β-Actin (HC201, TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China, 1:1000). After washing three times for 10 min each with TBST buffer, the membrane was incubated with a horseradish peroxidase conjugate secondary antibody (TransGen Biotech, 1:5000) at room temperature for 2 h and then washed with TBST three times for 10 min each. Immunoblotting was performed on a Tanon 5200 chemiluminescence instrument (Tanon, Shanghai, China) using a Tanon High-sig ECL Western blotting substrate kit. ImageJ 1.53 software (National Institutes of Health, USA) was used to measure the density of each blot band.
2.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis
Colon tissue samples were sent to Wuhan Servicebio Technology Co., Ltd., for histological immunofluorescent analysis. The protein expression levels of ZO1 and Occludin in colon tissues were detected by immunofluorescence. The images were captured by an upright fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and processed by ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, USA).
2.8. 16S rRNA Sequencing of the Colon Microbiota
The colon contents were transported to Beijing Biomarker Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), on dry ice, with 5 biological replicates per group. Microbial sequencing (16S length) was completed by a company using the PacBio sequencing platform, and all microbiome data analysis was completed on the Biomarker Microbial Diversity analysis cloud platform (www.biocloud.net), accessed on 18 January 2024.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All the experimental results are from at least three independent experiments, and all the data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.). All the data were statistically significant according to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Student’s t-test in IBM SPSS Statistics 27. p < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. All figures and graphics were produced using GraphPad Prism 8.0 statistical software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. L. casei IB1 Alleviated DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice
To survey the alleviating effect of L. casei IB1 on colitis in mice, experimental colitis models were generated in mice induced with 3% DSS in their water for 7 days (Figure 1). Compared to that of the CON group, the body weight of the DSS group was significantly lower (p < 0.05) (Figure 2A). However, compared with those in the DSS group, after the oral administration of L. casei IB1, the weight loss of the mice in the MID group and the HIGH group was alleviated to some extent (p < 0.05). Compared with that in the CON group, the DAI in the DSS group was significantly greater (p < 0.05) (Figure 2B). In contrast, after treatment with L. casei IB1, the DAI scores of DSS-treated mice in the MID and HIGH groups were significantly greater than those of DSS-treated mice (p < 0.05). The colon length of the DSS treatment group was significantly shorter than that of the CON group (p < 0.05) (Figure 2C,D). Compared with DSS, the oral administration of L. casei IB1 efficiently prevented DSS-induced colon shortening (p < 0.05).
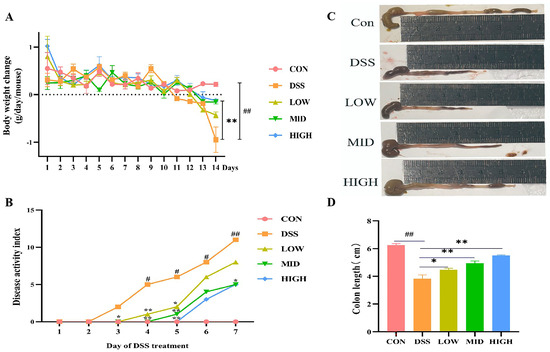
Figure 2.
L. casei IB1 alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice. (A) Body weight change. (B) The DAI score was measured. (C) Representative images of colons from mice. (D) Statistical analysis of colon length. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
3.2. Effect of L. casei IB1 on DSS-Induced Colon Histopathology
To observe the effect of L. casei IB1 on DSS-induced colon histopathology, we performed HE staining and PAS staining of colon tissue. As shown in Figure 3A–D, the colonic epithelial cells of the CON group were neatly arranged, the structure was complete, the villi were neat, the crypts were neatly arranged, there was a large number of goblet cells, and there was almost no inflammatory cell infiltration. After 7 days of DSS induction, compared with those in the CON group, the morphology of intestinal epithelial cells in the colon tissue of mice in the DSS group changed, the crypts were destroyed, the mucosal structure was unclear, the lamina propria and submucosa were infiltrated by a large number of inflammatory cells, and a large amount of connective tissue hyperplasia had occurred. In contrast, after treatment with L. casei IB1, compared to the DSS group, colon tissue injury was reduced in the MID and HIGH groups, the crypt structure was orderly, the mucosal structure was intact, and a large number of goblet cells were recovered (p < 0.01). Therefore, our results showed that L. casei IB1 had a certain preventive effect on DSS-induced colon injury.

Figure 3.
L. casei IB1 alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice. (A,B) Histopathology scores of the colitis mice post-treatment with L. casei IB1. (C,D) Periodic acid–Schiff staining and the number of goblet cells. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
3.3. Effect of L. casei IB1 on Serum Cytokine Levels
The levels of serum cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 I, and L-10) were measured by ELISA. As shown in Figure 4A–D, compared with those in the CON group, the levels of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 were significantly increased in the DSS group (p < 0.05), while the concentration of IL-10 was significantly decreased (p < 0.05). These results suggested that DSS treatment increased the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and correspondingly reduced the level of anti-inflammatory cytokines. After treatment with L. casei IB1, the levels of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 were significantly lower than those in the DSS group (p < 0.01), while the levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 were significantly increased (p < 0.01). The results showed that L. casei IB1 had anti-inflammatory effects on intestinal tissues.
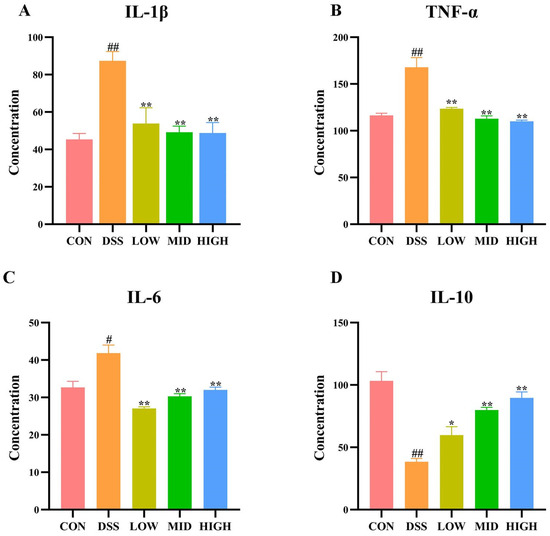
Figure 4.
Effect of L. casei IB1 on serum cytokine levels. (A–D) Serum cytokine levels after L. casei IB1 treatment. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
3.4. L. casei IB1 Upregulated Tight Junction Proteins to Improve Colonic Barrier Dysfunction in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
Intestinal epithelial tight junction (TJ) proteins play important roles in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. To study the changes in TJ proteins in DSS-induced colitis, Western blotting was used to detect changes in Claudin1, Claudin2, and Occludin in colon tissue. As shown in Figure 5A–C and Figure S1, after DSS induction, the protein levels of Occludin, Claudin1, and Cluaudin2 in the DSS group were significantly lower than those in the CON group (p < 0.01). Compared to the DSS group, the levels of the Occludin, Claudin1, and Claudin2 proteins increased after the oral administration of L. casei IB1, among which, those in the MID group and HIGH group increased most significantly (p < 0.01).

Figure 5.
L. casei IB1 upregulated tight junction proteins to improve colonic barrier dysfunction in DSS-induced colitis mice. (A–C) Statistical analysis of Occludin, Claudin1, and Claudin2 levels in the colon. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
In addition, the protein expression of ZO-1 and Occludin in colon tissue was detected by immunofluorescence to further evaluate the colonic barrier. As shown in Figure 6A–C, similar to the Western blot results, the expression of tight junction proteins in the DSS group was significantly lower than that in the CON group (p < 0.01). After treatment with IB1, the protein expression levels of ZO-1 and Occludin increased (p < 0.05). These results indicate that L. casei IB1 improves DSS-induced intestinal barrier damage by upregulating TJ proteins.
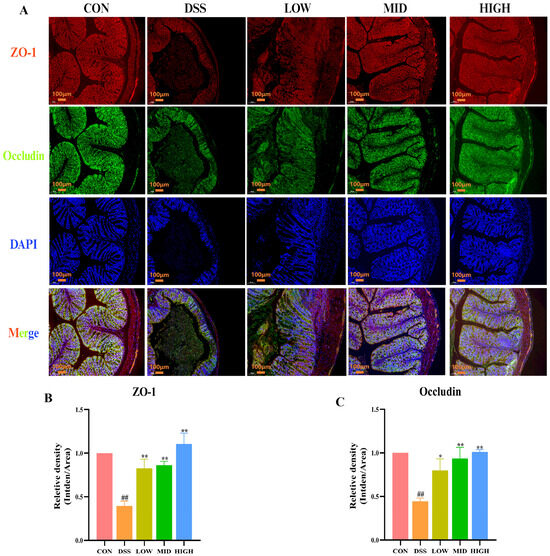
Figure 6.
L. casei IB1 upregulated tight junction proteins to improve colonic barrier dysfunction in DSS-induced colitis mice. (A) Immunofluorescence analysis of ZO-1 and Occludin levels in the colon. (B,C) Statistical analysis of ZO-1 and Occludin levels in the colon. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
3.5. L. casei IB1 Inhibits the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting the NF-κB- and MAPK-Mediated Signaling Pathways
To study the potential anti-inflammatory mechanism of L. casei IB1, we examined the effects of IB1 on the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. These signaling pathways are important key regulators of the inflammatory process and play an important part in intestinal inflammation. As shown in Figure 7A–D and Figure S2, after DSS treatment, the expression of key proteins in the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in the DSS group increased compared with that in the CON group (p < 0.01). Compared with that in the DSS group, the expression of the phosphorylated proteins P65 and P38 decreased after the oral administration of L. casei IB1 (p < 0.01). Interestingly, after the oral administration of L. casei IB1, only the protein levels of phosphorylated ERK and JNK in the MID group and the HIGH group decreased significantly, and there was no significant difference in the LOW group. These results suggest that L. casei IB1 may alleviate intestinal inflammation by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK.
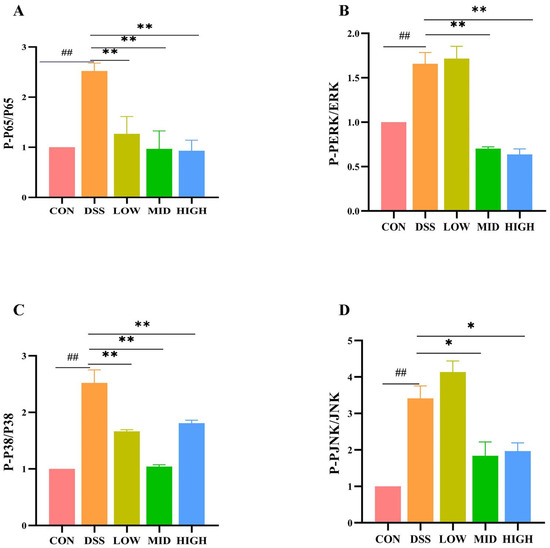
Figure 7.
L. casei IB1 inhibits the inflammatory response by inhibiting the NF-κB- and MAPK-mediated signaling pathways. (A–D) Statistical analysis of P65, P-P65, ERK1/2, P-ERK1/2, P38, P-P38, JNK, and P-JNK levels in the colon. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
3.6. Effects of L. casei IB1 on Microbial Diversity in the Colon
To explore the relationship between intestinal inflammation and intestinal microbial diversity, we collected the colonic contents of the mice and performed 16S rRNA sequencing. The colon microbiota diversity is shown in Figure 8A. There were 223 common OTUs in the colon of each experimental group. As shown in Figure 8B–E, the ACE and Chao1 indices measure species richness. The Simpson and Shannon indices are used to measure species diversity. There was no significant difference in the Chao1 index between the groups. Compared with that of the control group, the ACE index of the DSS group decreased significantly (p < 0.05). Compared to the DSS group, the ACE index of the LOW group and HIGH group increased significantly (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the Simpson index between the CON and DSS groups. Compared to the DSS group, those of the LOW and MID groups decreased significantly (p < 0.05). However, compared with those of the CON group, the Shannon indices of the DSS group increased significantly (p < 0.05), and the diversity of the microbial community significantly improved after the oral administration of L. casei IB1, which was similar to the CON group. The results showed that the oral administration of L. casei IB1 could regulate intestinal homeostasis. To further study the similarity between microbial communities, we performed beta diversity analysis based on weighted UniFrac to perform principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS). As shown in Figure 8F–G, there was a clear clustering separation between the DSS group and the CON group, indicating that the bacterial community composition differed between the two groups. However, after treatment with L. casei IB1, the bacterial colony composition overlapped with that of the CON group.
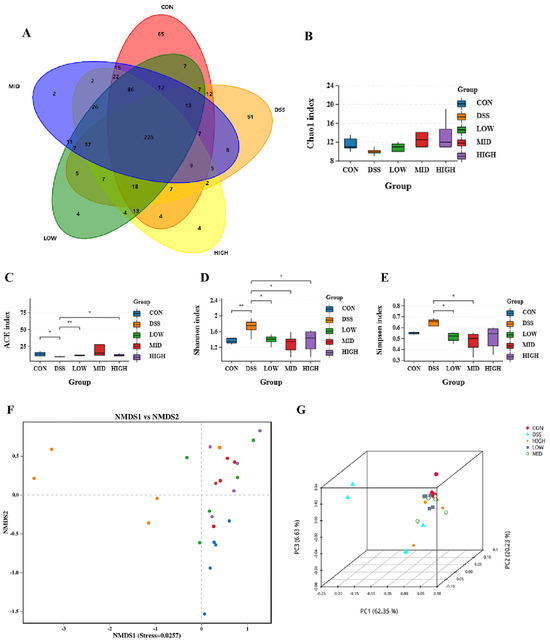
Figure 8.
The 16S rRNA sequencing results. (A) Shared OTU analysis of the content in the colon. (B–E) α-Diversity analysis using the ACE, Simpson, Shannon, and Chao1 indices. (F,G) β-Diversity analysis of PCoA and NMDS data. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
3.7. L. casei IB1 Changed the Structural Composition of Colon Microorganisms
As shown in Figure 9, the microbial flora of the five groups of colonic contents mainly consisted of five phyla, namely, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Verrucomicrobiota, and Patescibacteria, and nine genera, namely, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, unclassified Muribaculaceae, unclassified Clostridia_UCG_014, Bacteroides, uncultured Rumen_bacterium, Faecalibacterium, Escherichia_Shigella, Akkermansia, and Alistipes. At the phylum level, the contents of Verrucomicrobia, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Patescibacteria in the CON group were 51.80%, 41.37%, 1.32%, 0.78%, and 4.17%, respectively. Compared with those in the CON group, the contents of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Patescibacteria in the DSS group decreased to 31.82%, 31.69%, and 0.06%, respectively, while the contents of Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobiota increased to 20.69% and 12.67%, respectively. After treatment with L. casei IB1, the contents of Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia in the LOW group decreased to 3.38% and 0.62%, those in the MID group decreased to 2.42% and 1.72%, and those in the HIGH group decreased to 1.94% and 4.04%, respectively. At the genus level, the abundance of Faecalibaculum decreased after DSS treatment, while that of Escherichia_Shigella increased. Interestingly, after treatment with L. casei IB1, the abundance of Faecalibacterium increased, while the disruption of Escherichia_Shigella normalized.
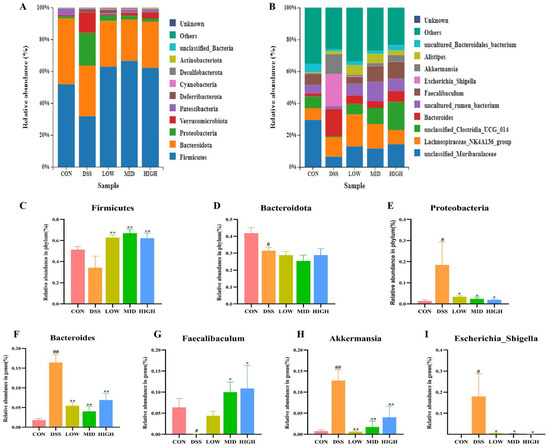
Figure 9.
L. casei IB1 changed the structural composition of colon microorganisms. (A,B) Histogram depicting the bacterial species distribution at the phylum and genus levels in the five mouse groups. (C–I) Statistical analysis of bacterial species at the phylum and genus levels. The data are shown as the means ± SEMs. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, compared to the CON group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the DSS group.
LEfSe and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) were used to analyze and compare the intestinal flora of each group to better understand the indicator bacteria of each group. As shown in Figure 10A,B, there were 21, 24, 11, 7, and 6 significant differences between the CON group, DSS group, LOW group, MID group, and HIGH group, respectively. The relative abundances of Muribaculaceae, Bacteroidota, Lactobacillaceae, Saccharimonadaceae and Prevotella in the CON group were greater than those in the DSS group. However, the bacterial diversity that affected the DSS group’s microbiome was distributed in different units. The abundance of potential pathogenic bacteria, such as Escherichia_Shigella at the genus level and Enterobacteriaceae at the family level, increased in the DSS group. After treatment with L. casei IB1, the abundance of potential pathogenic bacteria decreased to the lowest level. In the LOW group, the relative abundances of Clostridia at the class level and Erysipelatoclostridium and Alistipes at the genus level were greater. In the MID group, the relative abundances of Firmicutes at the phylum level and uncultured_rumen_bacterium and Turicibacter at the genus level were greater. In contrast, the relative abundances of unclassified _Clostridia _UCG _014 and Faecalibaculum at the genus level in the HIGH group were greater. In summary, treatment with L. casei IB1 alleviated DSS-induced colitis in mice by reducing the abundance of potential pathogenic bacteria and increasing the relative abundance of probiotics.
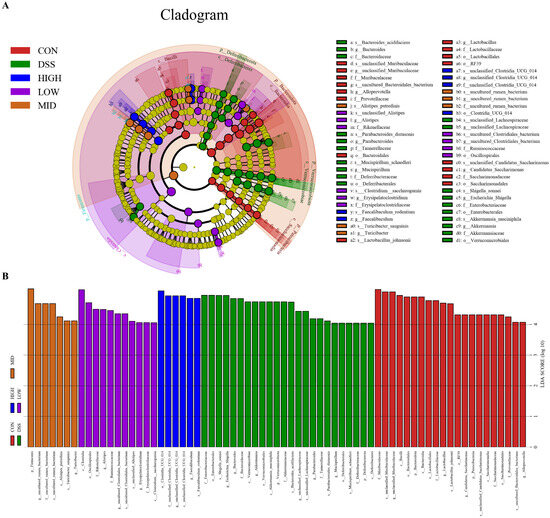
Figure 10.
Effects of L. casei IB1 on the gut microbiota. (A) LefSe multilevel species hierarchy tree. (B) The distribution histogram based on LDA.
4. Discussion
Recently, great progress has been made in the use of probiotics for the treatment of IBD. Probiotics mainly regulate the intestinal barrier [16,38] and the balance of the intestinal flora [39,40,41] to alleviate IBD. At present, the DSS-induced colitis mouse model is a useful tool for studying the efficacy and mechanism of probiotics in relieving acute IBD [33,35,36,42]. The mechanism of probiotic treatment for IBD may be related to reducing oxidative stress, repairing the intestinal barrier, regulating the intestinal flora balance, and modulating the intestinal immune response [43]. As one of the representative bacteria for probiotic-assisted therapy in IBD, multiple strains of Lactobacillus have been proven to alleviate intestinal damage and strengthen the intestinal immunological barrier, epithelial cell barrier, and mucus barrier [44]. Lactic acid bacteria are recognized as safe for use in food fermentation and dietary supplementation and are also thought to potentially colonize the human gastrointestinal tract [45]. Therefore, we used a DSS-induced mouse colitis model to study the effect of L. casei IB1 on colitis in C57BL/6 mice. After 7 days of 3% DSS treatment, the mice showed severe damage, and the clinical symptoms were weight loss, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding [23,46,47]. In addition, we confirmed that DSS significantly increased the DAI. On the contrary, the symptoms of colitis in mice treated with L. casei IB1 were significantly alleviated. Compared with the DSS group, treatment with L. casei IB1 significantly increased the colon length of the mice. Histopathological evaluation of the colon tissue revealed that L. casei IB1 treatment significantly reduced colonic mucosal damage, crypt injury, inflammatory cell infiltration, and local ulcers, thereby restoring the integrity of the intestinal epithelium. Goblet cells are glandular cells that secrete mucus, lubricate the surface of the epithelium, and protect the epithelium. They can perform lubrication and physical barrier functions to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from invading the host [48,49]. In this study, compared with that in the DSS group, the number of goblet cells increased after treatment with L. casei IB1, especially in the MID and HIGH groups. These results confirmed the therapeutic potential of L. casei IB1.
Cytokines have a wide range of biological activities. They modulate cell differentiation and growth by binding to corresponding receptors and regulating immune responses [50]. Previous studies have shown that the levels of proinflammatory factors increase and the levels of anti-inflammatory factors decrease in patients with ulcerative colitis and DSS-induced colitis in animal models [51,52,53]. Inflammatory factors such as IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α are the main immune response factors involved in the inflammatory response in IBD [54]. Some researchers believe that blocking IL-1β and IL-6 may be an important direction for the treatment of UC [55]. The concentration of cytokines in serum represents the systemic inflammatory response [55]. In this study, we measured the serum levels of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 using ELISA. Compared to the DSS group, the levels of pro-inflammatory factors were significantly decreased, while the level of IL-10 was markedly increased after treatment with L. casei IB1. These results suggest that L. casei IB1 may mitigate colitis by reducing proinflammatory factor levels and increasing anti-inflammatory factor levels.
The integrity of the gut barrier is mainly supported by the tight junctions of epithelial cells. The integrity of the intestinal barrier can prevent pathogens from entering the blood [47,56]. Studies have shown that DSS intervention can reduce the concentration of related tight junction proteins [57]. ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 are important epithelial TJ proteins [56,58]. In this study, Western blotting and immunofluorescence were used to detect related TJ proteins. Compared with those in the DSS group, the levels of related TJ proteins were greater after treatment with L. casei IB1, and the increase in the middle and high groups was the most significant. The results suggested that L. casei IB1 alleviated colitis by improving the expression of TJ proteins.
The NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways are involved in the pathogenesis of IBD [59,60]. Therefore, the inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK activation is considered to be an important target for the treatment of IBD [61]. The MAPK pathway, which includes the JNK, ERK, and p38 proteins, can regulate different physiological processes (apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation) in cells and is closely linked to intestinal mucosal injury [48]. These results suggest that L. casei IB1 may alleviate DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway-related proteins.
The intestinal microflora plays a very important role in maintaining human health, and the stability of the microbial community is conducive to the health of the host [62]. Intestinal microbial imbalances have been shown to be related to various diseases [63]. The gut microbiota has been identified as a key factor in the pathogenesis of IBD [47]. Therefore, the use of probiotics to prevent or treat IBD is a potential treatment strategy. In this study, 16S rRNA sequencing was used to explore the mechanism of action of L. casei IB1 on the intestinal microflora in DSS-induced colitis mice. As with previous studies [55], a wide range of gut microbiota disorders were observed, including a decrease in the number of OTUs and a disorder of β-diversity. The Chao1 and ACE indices measure species richness, that is, the number of species. The Shannon and Simpson indices are used to measure species diversity. The ACE and Chao1 indices decreased under the influence of DSS, while the Simpson and Shannon indices increased. However, these effects were reversed after treatment with L. casei IB1. Through PCoA and NMDS cluster analysis, it could be seen that the CON group and DSS group were obviously separated and, after treatment with L. casei IB1, the LOW group, MID group, and HIGH group overlapped with the CON group. In summary, L. casei IB1 alleviates colitis by regulating the abundance and diversity of microorganisms.
In UC patients, intestinal microbial diversity changes significantly, and intestinal microbial abundance decreases. When intestinal inflammation occurs, the proportion of Firmicutes that maintain intestinal health decreases and the abundance of Proteobacteria increases [52,61,64]. Consistent with the above reports, in our study, the proportion of Firmicutes was reduced and the abundance of Proteobacteria was increased in DSS-induced colitis mice. Escherichia_Shigella is a common pathogen that often increases in patients with colitis [65], and Alistipes has been shown to have the opposite relationship with a variety of inflammatory factors [62]. Bacteroides can produce succinic acid, which aggravates the inflammatory response in patients with ulcerative colitis [62,66]. Some studies have found that Faecalibaculum rodentium remodels retinoic acid signaling to govern eosinophil-dependent intestinal epithelial homeostasis [67]. Faecalibaculum was reported to protect the intestinal epithelial barrier by producing butyric acid [62,68]. Consistent with the above report, our study found that after treatment with IB1, the abundance of Faecalibaculum was upregulated, which may have led to the production of more butyric acid to mitigate colitis. Escherichia Shigella and Bacteroides exhibited a higher relative abundance in IBD individuals and further led to severe colitis [66,69]. Consistent with the above reports, the abundances of Escherichia Shigella and Bacteroides in the DSS group increased at the genus level compared with those in the CON group. However, after treatment with L. casei IB1, the proportions of Bacteroides and Escherichia Shigella decreased and the proportions of Faecalibacterium and Alistipes increased. The intestinal environment in vivo is more complex than the cell culture environment in vitro. There are interactions among microorganisms, microbial immune cells, and microbial intestinal epithelial cells in the intestinal tract [14]. IB1 may protect the intestinal barrier by interacting with other bacteria or influencing immune cells. It has been reported that the intestinal symbiotic flora can reduce the susceptibility of mice to experimental colitis through T-cell-derived IL-10 [70]. Therefore, L. casei IB1 promoted the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestine tract, especially beneficial microorganisms related to butyric acid production, and inhibited harmful microorganisms related to intestinal diseases. In this study, IB1 alleviated DSS-induced colitis in mice to a certain extent by improving the intestinal barrier, inhibiting the inflammatory response, and reshaping the intestinal microbiome structure. Further research is needed to investigate the mechanism of IB1 in the prevention and treatment of IBD.
5. Conclusions
In summary, L. casei IB1 can effectively improve DSS-induced colitis in mice. Its effects include alleviating the clinical symptoms caused by DSS, inhibiting the expression of proinflammatory factors, improving the expression of anti-inflammatory factors and tight junction proteins, inhibiting the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the intestine, and inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. This study provides a potential therapeutic strategy for the future treatment of IBD patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms12071379/s1, Figure S1: Western blot analysis of Occludin, Claudin1 and Claudin2 levels in the colon. Figure S2: Western blot analysis of P65, P-P65, ERK1/2, P-ERK1/2, P38, P-P38, JNK and P-JNK levels in the colon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.J. and Y.L. (Youquan Li); methodology, J.L. and Y.L. (Yin Li); software, X.Z.; validation, S.Y. and Z.W.; formal analysis, Y.Y.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L. and Y.L. (Yin Li); writing—review and editing, X.J. and Y.L. (Youquan Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the program for scientific research start-up funds of Guangdong Ocean University (060302052201), Datong County Science and Technology Planning Project (2022-ZB-4), Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (2022BBF03024), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32273077), Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research (2023B0303000014), Innovation Team Project of Guangdong Provincial Department of Education (2022KCXTD014), Guangdong Postgraduate Education Innovation Project (040510052201), and National Natural Science Foundation of ShenZhen (JCYJ20220530162008018).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal procedures adhered to the guidelines set by IACUC-Guangdong Ocean University, with the ethics approval number 2022-SCUEC-021. The animals were housed in the Animal Lab of Guangdong Ocean University, China. All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines provided by the National Research Council’s Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank A. M. Abd El-Aty for revising the manuscript and Zhi Li and Yanan Guo for sharing resources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kaplan, G.G. The global burden of IBD: From 2015 to 2025. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouillon, L.; Travis, S.; Bossuyt, P.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Head-to-head trials in inflammatory bowel disease: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.-F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.A.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Fornelos, N.; Haiser, H.J.; Reinker, S.; Vatanen, T.; Hall, A.B.; Mallick, H.; McIver, L.J.; et al. Gut microbiome structure and metabolic activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedian, S.S.; Nokhostin, F.; Malamir, M.D. A review of the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment methods of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Med. Life 2019, 12, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, J.P.; LeBlanc, J.-F.; Hart, A.L. Ulcerative colitis: An update. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindryckx, P.; Jairath, V.; D’Haens, G. Acute severe ulcerative colitis: From pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munyaka, P.M.; Rabbi, M.F.; Khafipour, E.; Ghia, J.-E. Acute dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis promotes gut microbial dysbiosis in mice. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiho, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Abe, S.; Nakazono, Y.; Murakami, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Fukawa, K.; Esaki, M.; Niina, Y.; Ogino, H. Promising biological therapies for ulcerative colitis: A review of the literature. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2015, 6, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Hwang, J.; Koh, H.-J.; Jang, K.; Lee, J.-D.; Choi, J.; Yang, C.-S. The targeted delivery of the c-Src peptide complexed with schizophyllan to macrophages inhibits polymicrobial sepsis and ulcerative colitis in mice. Biomaterials 2016, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfvarson, J.; Brislawn, C.J.; Lamendella, R.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Walters, W.A.; Bramer, L.M.; D’Amato, M.; Bonfiglio, F.; McDonald, D.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Dynamics of the human gut microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneishi, Y.; Furuya, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Picarelli, A.; Rossi, M.; Miyamoto, J. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xie, Q.; Yue, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, L.; Evivie, S.E.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of mixed lactobacilli in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5130–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, H.; Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Interaction Between the Microbiota, Epithelia, and Immune Cells in the Intestine. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.; Krug, S.M.; Siegmund, B.; Neurath, M.F.; Becker, C. Mend Your Fences: The Epithelial Barrier and its Relationship with Mucosal Immunity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 4, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Physiological Characteristics of Lactobacillus casei Strains and Their Alleviation Effects against Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Leung, R.K.-K.; Guan, W.; Au, W.W. Involvement of gut microbiome in human health and disease: Brief overview, knowledge gaps and research opportunities. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-H.; Zhu, C.-X.; Quan, Y.-S.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, W.-W.; Tan, B.; Wang, X.-Y. Relationship between intestinal microbiota and ulcerative colitis: Mechanisms and clinical application of probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citi, S. Intestinal barriers protect against disease. Science 2018, 359, 1097–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Vito, R.; Conte, C.; Traina, G. A Multi-Strain Probiotic Formulation Improves Intestinal Barrier Function by the Modulation of Tight and Adherent Junction Proteins. Cells 2022, 11, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. Tu1901 The Probiotic Mixture Alleviates Dextran-Sulfate Sodium(DSS)-Induced Colitis by Increasing the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins and Regulatory T Cells Proportion. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, S972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, X.; Deng, B.; Liao, Z.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Prevention of DSS-induced colitis in mice with water kefir microbiota via anti-inflammatory and microbiota-balancing activity. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 6813–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.-Y.; Yong, C.-C.; Oh, S. Regulatory Effect of Lactobacillus brevis Bmb6 on Gut Barrier Functions in Experimental Colitis. Foods 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Qiao, L.; Chang, J.; Yan, S.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, C. Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 and its metabolites alleviate dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through the NLRP3-(Caspase-1)/IL-1β pathway. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 12022–12035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.A.; Uppada, S.; Achkar, I.W.; Hashem, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Al-Naemi, H.A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S. Tight Junction Proteins and Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Inflammation: A Functional Crosstalk. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, M.B.; Dhawan, P.; Baumert, T.F. Tight junction proteins in gastrointestinal and liver disease. Gut 2019, 68, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscoli, S.; Febo, M.; Riccardi, C.; Migliorati, G. Glucocorticoid Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Practice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.N. Treatment of IBD: Where we are and where we are going. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Barnard, A.; Benoit, V.; Grimaldi, R.; Guyonnet, D.; Holscher, H.D.; Hunter, K.; Manurung, S.; Obis, D.; et al. Shaping the Future of Probiotics and Prebiotics. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Teng, W.; Fei, D.; Zhao, G.; Liu, W. Effects of Live Combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium on Gut Microbiota Composition in C57BL/6 Mice and in Humans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 821662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushelaibi, A.; Al-Mahadin, S.; El-Tarabily, K.; Shah, N.P.; Ayyash, M. Characterization of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria isolated from camel milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-K.; Han, D.H.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, S.; Jang, S.J.; Lee, G.; Han, H.S.; Ko, G. Alleviation of DSS-induced colitis via Lactobacillus acidophilus treatment in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Kuerman, M.; Cui, Q.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, H.; Gong, P.; Lin, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. Protective effects of Bifidobacterium bifidum FL-228.1 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced intestinal damage in mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 104, 15.25.1–15.25.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichele, D.D.; Kharbanda, K.K. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6016–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cai, J.; Fan, P.; Dong, X.; Zhang, N.; Tai, J.; Cao, Y. Salidroside alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by modulating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 7506–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, Q.; de Haan, B.J.; Faas, M.M.; Zhang, H.; de Vos, P. Protective effects of lactic acid bacteria on gut epithelial barrier dysfunction are Toll like receptor 2 and protein kinase C dependent. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, N.; Xia, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZJ316-fermented milk ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced chronic colitis by improving the inflammatory response and regulating intestinal microbiota. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 7352–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aindelis, G.; Ypsilantis, P.; Chlichlia, K. Alterations in Faecal Microbiota and Elevated Levels of Intestinal IgA Following Oral Administration of Lacticaseibacillus casei in mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Lv, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Z. The in vitro Effects of the Probiotic Strain, Lactobacillus casei ZX633 on Gut Microbiota Composition in Infants with Diarrhea. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 576185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W. Lactate-utilizing bacteria ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice. Life Sci. 2022, 288, 120179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, D.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Bao, C. Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence? Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peng, K.; Xiao, S.; Long, Y.; Yu, Q. The role of Lactobacillus in inflammatory bowel disease: From actualities to prospects. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Ma, S.; Li, X.; Lu, Y. Effect of Lactobacillus with Feruloyl Esterase-Producing Ability on Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14817–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Echave, P.; Martín-Cabrejas, I.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Langa, S.; Vezza, T.; Landete, J.M.; Hidalgo-García, L.; Algieri, F.; Mayer, M.J.; Narbad, A.; et al. Probiotic and Functional Properties of Limosilactobacillus reuteri INIA P572. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, N.; Fu, J.; Valencak, T.G.; Ren, D. Lactobacillus plantarum ZJUIDS04 alleviates DSS-induced colitis via modulating gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 109, 105794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Wu, Y.; Wusiman, A.; Gu, P.; Mao, N.; Xu, S.; Zhu, T.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D. Alhagi honey polysaccharides attenuate intestinal injury and immune suppression in cyclophosphamide-induced mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6863–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.K.; Johansson, M.E.V. The role of goblet cells and mucus in intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashant, C.; Arathi, N.; Ashok, P.; Jagneshwar, D.; Arup, S.; Bhaskar, S. A primer on cytokines. Cytokine 2021, 145, 155458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yi, L.; Pan, Y.; Long, X.; Mu, J.; Yi, R.; Zhao, X. Lactobacillus fermentum ZS40 Ameliorates Inflammation in Mice with Ulcerative Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 700217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Xia, C.; Liu, N.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P. Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting inflammation and regulating short-chain fatty acid levels and the gut microbiota in a mouse model. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3982–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mo, K.; Tian, G.; Zhou, J.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Huang, X. Shikimic Acid Regulates the NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota to Ameliorate DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8906–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.-W.; Wang, R.; Yao, L.-W.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Sun, P.-L.; Zheng, B.; Chen, Y.-F. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Mytilus coruscus Polysaccharide on RAW264.7 Cells and DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Ma, F.; An, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Q.; Zhao, C.; Sun, X.; Li, K.; Li, B.; et al. The Metabolites of Lactobacillus fermentum F-B9-1 Relieved Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Experimental Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 865925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: Implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Differential reinforcement of intestinal barrier function by various Lactobacillus reuteri strains in mice with DSS-induced acute colitis. Life Sci. 2023, 314, 121309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on Epithelial Tight Junctions of Mice with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Interferon. Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Sang, Y.; Dong, L. The improved effect and its mechanism of phytic acid on DSS-induced UC mice. Life Sci. 2022, 311, 121139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.H.; Ohigashi, H.; Murakami, A. Dextran sulfate sodium enhances interleukin-1 beta release via activation of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways in murine peritoneal macrophages. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Y. Eurotium cristatum, a Probiotic Fungus from Fuzhuan Brick Tea, and Its Polysaccharides Ameliorated DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2957–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Yaqian, L.; Xingyu, L.; Kaizhang, W.; Liuyang, Z.; Yuxuan, S.; Jihong, W.; Jie, G. Effect of potential postbiotics derived from food-isolated Lactobacillus parabuchneri on different enterotypes of human gut microbiome. LWT 2023, 182, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Qiao, L.; Dou, X.; Song, X.; Chang, J.; Zeng, X.; Xu, C. Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 combined with vasoactive intestinal peptide alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6 mice via NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ran, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Peng, M.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; et al. Deferasirox alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by inhibiting ferroptosis and improving intestinal microbiota. Life Sci. 2023, 314, 121312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Fang, X.; Wan, Y.; Yu, D.; Guo, Y. A tetrapeptide from maize combined with probiotics exerted strong anti-inflammatory effects and modulated gut microbiota in DSS-induced colitis mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12602–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ai, L. Probiotic yeast BR14 ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by restoring the gut barrier and adjusting the intestinal microbiota. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8386–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.G.; Bae, S.; Villarreal, J.; Moy, M.; Chun, E.; Michaud, M.; Lang, J.K.; Glickman, J.N.; Lobel, L.; Garrett, W.S. Faecalibaculum rodentium remodels retinoic acid signaling to govern eosinophil-dependent intestinal epithelial homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1295–1310.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lin, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Lu, H.; Gao, X.; Zhu, R.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Z. Microbiota metabolite butyrate constrains neutrophil functions and ameliorates mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1968257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, M.N.; Sergeant, M.; Kay, G.; Iqbal, T.; Chan, J.; Constantinidou, C.; Trivedi, P.; Ferguson, J.; Adams, D.H.; Pallen, M.; et al. The gut-adherent microbiota of PSC-IBD is distinct to that of IBD. Gut 2017, 66, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pils, M.C.; Bleich, A.; Prinz, I.; Fasnacht, N.; Bollati-Fogolin, M.; Schippers, A.; Rozell, B.; Müller, W. Commensal gut flora reduces susceptibility to experimentally induced colitis via T-cell-derived interleukin-10. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).