Evaluating Ammonia Toxicity and Growth Kinetics of Four Different Microalgae Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Species and Growth Conditions
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Biomass Concentration Estimation and Measurement
2.4. Growth Kinetics Modeling
2.5. Inhibition Kinetics Modeling
2.6. Determination of Nitrogen Removal Parameters
2.7. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
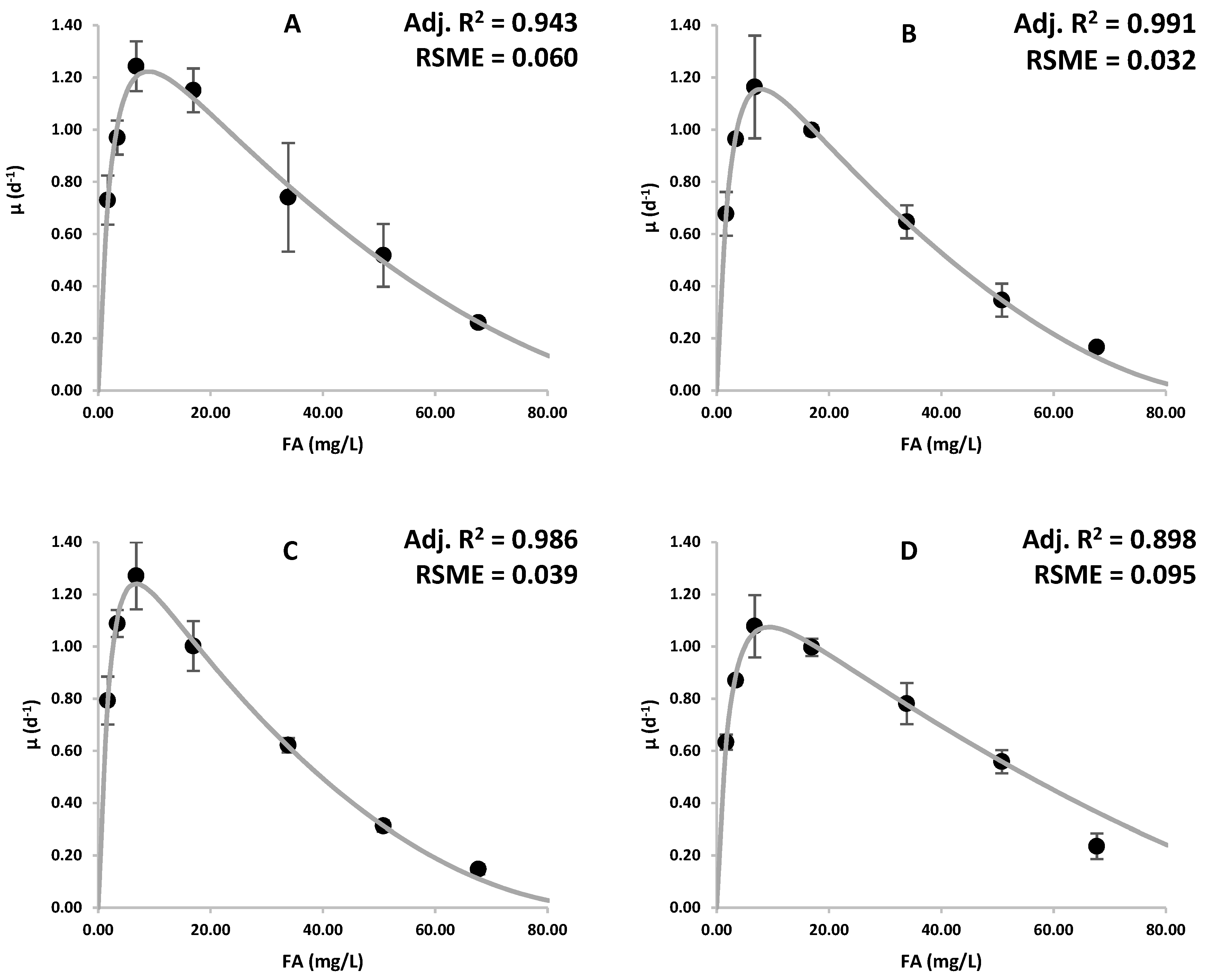
3.1. Effects of Ammonia on Growth
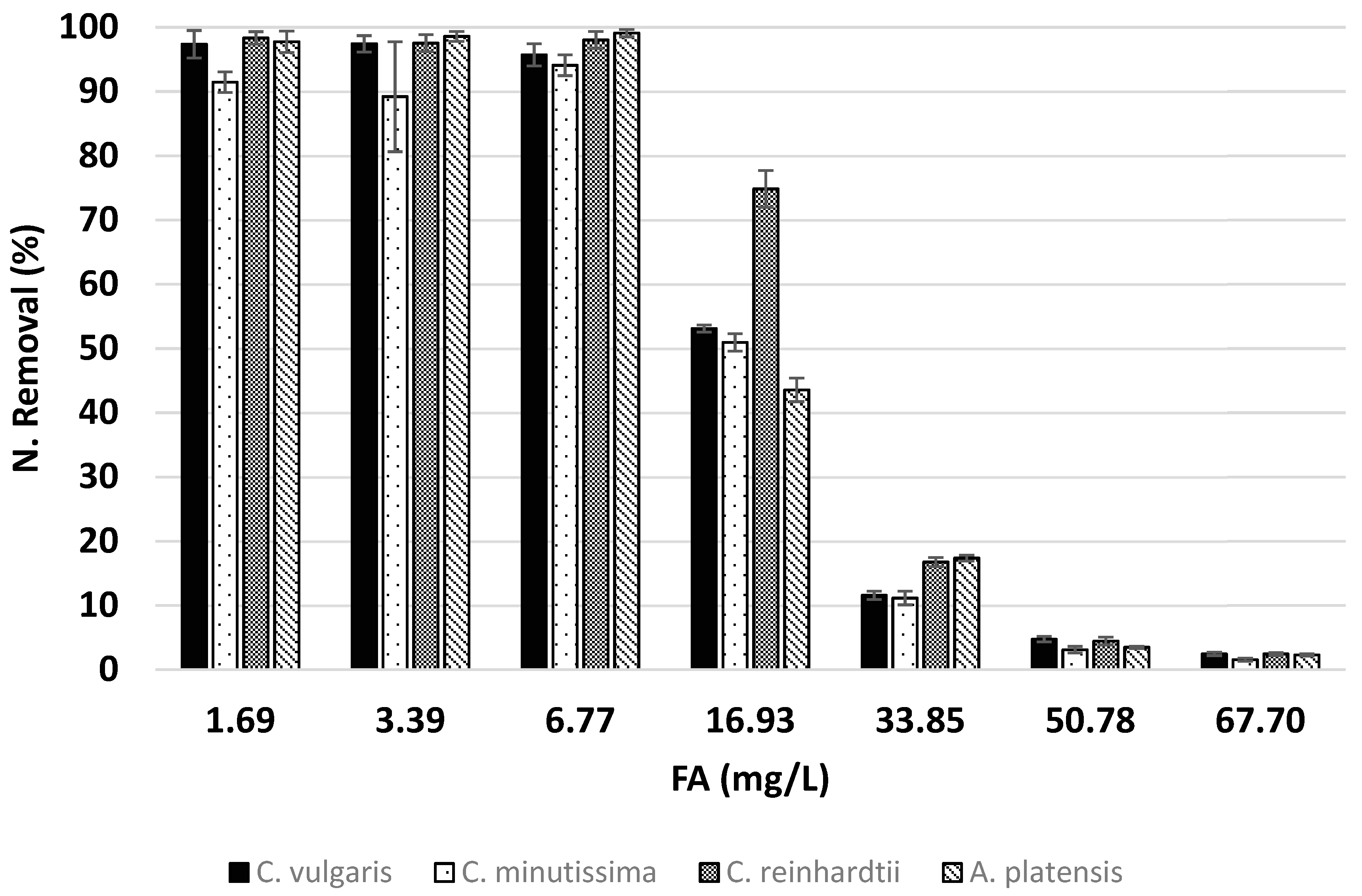
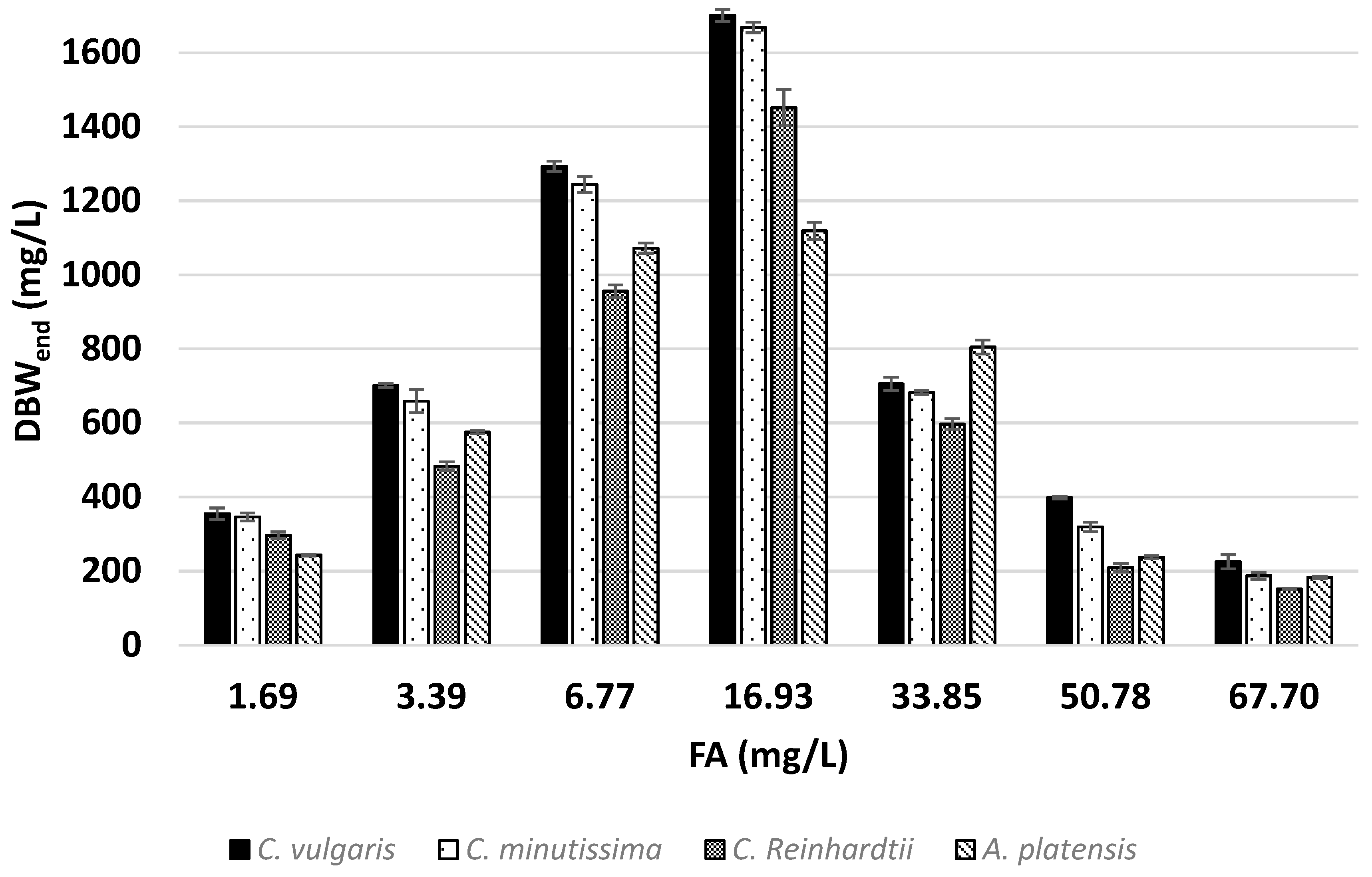
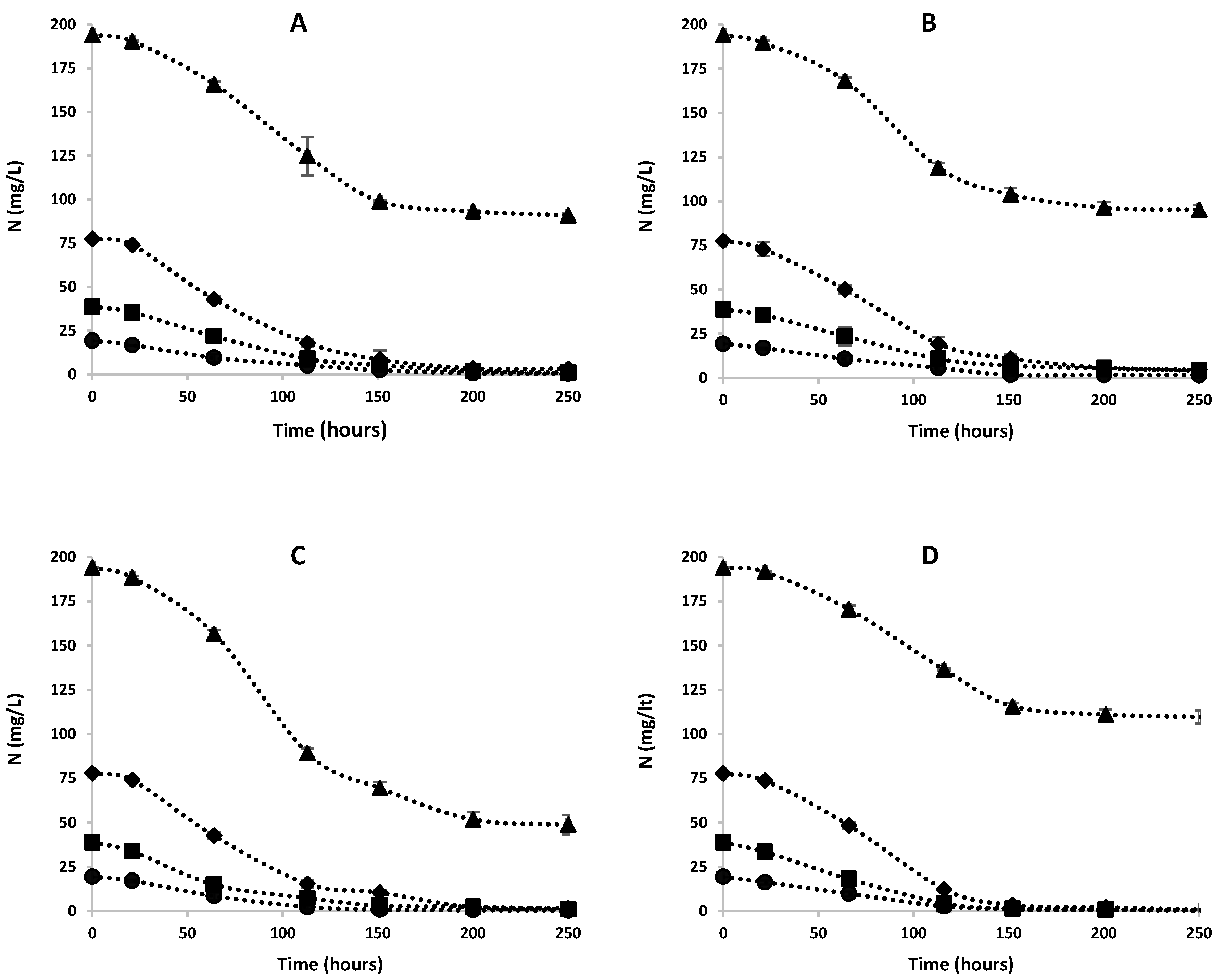
3.2. Effects of Ammonia on Nitrogen Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Chen, Y.; Vaidyanathan, S. Simultaneous assay of pigments, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids in microalgae. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 776, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L. Biorefinery as a promising approach to promote microalgae industry: An innovative framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Yap, J.Y.; Show, P.L.; Suan, N.H.; Juan, J.C.; Ling, T.C.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Microalgae biorefinery: High value products perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, L.; Qi, Y. Enhancing the productivity of microalgae cultivated in wastewater toward biofuel production: A critical review. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, S.S.; Goyal, D. Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4222–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar-Bermudez, S.P.; Aleman-Nava, G.S.; Chandra, R.; Garcia-Perez, J.S.; Contreras-Angulo, J.R.; Markou, G.; Muylaert, K.; Rittmann, B.E.; Parra-Saldivar, R. Nutrients utilization and contaminants removal. a review of two approaches of algae and cyanobacteria in wastewater. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidart, C.; Fröhling, M.; Schultmann, F. Electricity and substitute natural gas generation from the conversion of wastewater treatment plant sludge. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Vandamme, D.; Muylaert, K. Ammonia inhibition on Arthrospira platensis in relation to the initial biomass density and pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Vandamme, D.; Muylaert, K. Microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation: The supply of nutrients. Water Res. 2014, 65, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Moheimani, N.R. Sustainable biofuels from algae. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2013, 18, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Kwan, T.A.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Peccia, J. Ammonia inhibition in oleaginous microalgae. Algal Res. 2016, 19, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Qin, L.; Feng, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S. The joint effect of ammonium and pH on the growth of Chlorella vulgaris and ammonium removal in artificial liquid digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Jho, E.H.; Jang, H.S.; Hwang, S.J. Inhibition Effects of free ammonia (FA) on the rates of growth, photosynthesis and respiration of Chlorella vulgaris. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Liu, C.; Dong, H.; Zhu, Z. Effect of ammonium nitrogen concentration on the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria community in a membrane bioreactor for the treatment of anaerobically digested swine wastewater. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: Status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collos, Y.; Harrison, P.J. Acclimation and toxicity of high ammonium concentrations to unicellular algae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 80, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, P.; Guo, Y.; Kang, H.; Lefebvre, C.; Loh, K.C. Enhancing microalgae cultivation in anaerobic digestate through nitrification. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qiu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Trent, J.; Ge, S. Free ammonia is the primary stress factor rather than total ammonium to Chlorella sorokiniana in simulated sludge fermentation liquor. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qiu, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, D.; Ge, S. Instant inhibition and subsequent self-adaptation of Chlorella sp. toward free ammonia shock in wastewater: Physiological and genetic responses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9641–9650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakob, M.A.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Aswathnarayana Gokare, R.; Ambati, R.R. Influence of nitrogen and phosphorus on microalgal growth, biomass, lipid, and fatty acid production: An overview. Cells 2021, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Ali, S.S.; Ramadan, H.; El-Aswar, E.I.; Eltawab, R.; Ho, S.-H.; Elsamahy, T.; Li, S.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Schagerl, M. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment: Mechanisms, challenges, recent advances, and future prospects. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 13, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, H.; Zhan, J.; He, C.; Wang, Q. Ammonium nitrogen tolerant Chlorella strain screening and its damaging effects on photosynthesis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, G.; Kumar, L.; Hariri, S.; Roy, A.; Kundu, K.; Bharadvaja, N. Identification of potential culture conditions for enhancing the biomass production of microalga Chlorella minutissima. Expert Opin. Environ. Biol. 2016, s1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Li, L.; Martinez, B.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Culture of microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in wastewater for biomass feedstock production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H. Enhancing growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and nutrient removal in diluted primary piggery wastewater by elevated CO2 supply. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.J.; Mao, B.; Shen, C.M.; Shao, L.M.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris on wastewater containing high levels of ammonia for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markou, G. Fed-Batch Cultivation of Arthrospira and Chlorella in ammonia-rich wastewater: Optimization of nutrient removal and biomass production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, G.C.; Stablein, M.J.; Tommaso, G. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in anaerobically digested gelatin industry wastewater. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, B.T.; Labavitch, J.M.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Co-culturing Chlorella minutissima with Escherichia Coli can increase neutral lipid production and improve biodiesel quality. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Patel, A.; Pruthi, P.A.; Pruthi, V. Synergistic Dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorous influences lipid productivity in Chlorella minutissima for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 213, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheunbarn, S.; Peerapornpisal, Y. Cultivation of Spirulina platensis using anaerobically swine wastewater treatment effluent. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, G.S.; Santiago, C.S.; Moreira, R.T.; Dantas Neto, M.P.; Fernandes, F.A.N. Nutrient removal by Arthrospira platensis cyanobacteria in cassava processing wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumas, P. Cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis using low cost medium supplemented with lac wastewater. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016, 43, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, D.S.; Valadão, R.C.; De Souza, E.R.P.; Barbosa, M.I.M.J.; De Mendonça, H.V. Enhanced Arthrospira platensis biomass production combined with anaerobic cattle wastewater bioremediation. Bioenerg. Res. 2022, 15, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masojídek, J.; Ranglová, K.; Lakatos, G.E.; Silva Benavides, A.M.; Torzillo, G. Variables governing photosynthesis and growth in microalgae mass cultures. Processes 2021, 9, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuaresma, M.; Janssen, M.; Vílchez, C.; Wijffels, R.H. Horizontal or vertical photobioreactors? How to improve microalgae photosynthetic efficiency. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5129–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkish State Meteorological Service. Istanbul Province and Districts Statistics. Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/veridegerlendirme/il-ve-ilceler-istatistik.aspx?m=ISTANBUL (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Guštin, S.; Marinšek-Logar, R. Effect of pH, temperature and air flow rate on the continuous ammonia stripping of the anaerobic digestion effluent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Vaneeckhaute, C. Nutrient recovery from wastewater: A review on the integrated physicochemical technologies of ammonia stripping, adsorption and struvite precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yu, Y.; Xie, K.; Luo, J.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Li, C.; Xue, Z. Characterizing the free ammonia exposure to the nutrients removal in activated sludge systems. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 55088–55097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, L.L.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; APHA Press: Washington DC, USA, 2017; pp. 66–73, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kayombo, S.; Mbwette, T.S.A.; Katima, J.H.Y.; Jorgensen, S.E. Effects of substrate concentrations on the growth of heterotrophic bacteria and algae in secondary facultative ponds. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2937–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Tan, J.S.; Kadkhodaei, S.; Mohamad, R.; Mokhtar, M.N.; Ariff, A.B. Kinetics and modeling of microalga Tetraselmis sp. FTC 209 growth with respect to its adaptation toward different trophic conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 88, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmi, M.I.E.; Shukor, M.S.; Johari, W.L.W.; Shukor, M.Y. Evaluation of several mathematical models for fitting the growth of the algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Asian J. Plant Biol. 2014, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, S.; Eshkabilov, S.; Jayakrishnan, U.; Prajapati, S.K.; Simsek, H. A Comparative analysis of growth kinetics, image analysis, and biofuel potential of different algal strains. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Levenspiel, O. Extended Monod kinetics for substrate, product, and cell inhibition. Biotech. Bioeng. 1988, 32, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przytocka-Jusiak, M.; Mlynarczyk, A.; Kulesza, M.; Mycielski, R. Properties of Chlorella vulgaris strain adapted to high concentration of ammonium nitrogen. Acta Microbiol. Pol. 1977, 26, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, N.F.Y.; Wong, Y.S. Effect of ammonia concentrations on growth of Chlorella vulgaris and nitrogen removal from media. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 57, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Nagao, N.; Yusoff, F.Md.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Katayama, T.; Kurosawa, N.; Koyama, M.; Nakasaki, K.; Toda, T. High ammonia tolerance on growth rate of marine microalga Chlorella vulgaris. JEB 2018, 39, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Dixit, D.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, D.; Jawed, A.; Haque, S. Implication of industrial waste for biomass and lipid production in Chlorella minutissima under autotrophic, heterotrophic, and mixotrophic grown conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1581–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevatia, R.; Demirel, Y.; Blum, P. Kinetic modeling of photoautotropic growth and neutral lipid accumulation in terms of ammonium concentration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Mennerich, A.; Urban, B. Comparison of nutrient removal capacity and biomass settleability of four high-potential microalgal species. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 124, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.H.; Lee, D.S.; Park, J.M. Modeling and Optimization of photosynthetic hydrogen gas production by green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in sulfur-deprived circumstance. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, S.; Boussiba, S. Resistance of Spirulina platensis to ammonia at high pH values. Plant Cell Physiol. 1991, 32, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Muylaert, K. Effect of light intensity on the degree of ammonia toxicity on PSII activity of Arthrospira platensis and Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, M.M.S.; El-Ayouty, Y.M.; Piercey-Normore, M. Role of pH on antioxidants production by Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.C.M.; Francisco, F.R.; Almeida, K.A.; Sato, S.; Converti, A. Cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis (Cyanophyceae) by fed-batch addition of ammonium chloride at exponentially increasing feeding rates 1. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soletto, D.; Binaghi, L.; Lodi, A.; Carvalho, J.C.M.; Converti, A. Batch and fed-batch cultivations of Spirulina platensis using ammonium sulphate and urea as nitrogen sources. Aquaculture 2005, 243, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converti, A.; Scapazzoni, S.; Lodi, A.; Carvalho, J.C.M. Ammonium and urea removal by Spirulina Platensis. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Sommer, U. Nitrogenous nutrition of the potentially toxic diatom Pseudonitzschia pungens f. multiseries Hasle. J. Plankton Res. 1996, 18, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azov, Y.; Goldman, J.C. Free Ammonia inhibition of algal photosynthesis in intensive cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhai, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, Q. Effect of ammonium nitrogen on microalgal growth, biochemical composition and photosynthetic performance in mixotrophic cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chai, H.; He, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. The alleviative effect of exogenous phytohormones on the growth, physiology and gene expression of Tetraselmis cordiformis under high ammonia-nitrogen stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, T.; Xiang, J. Air stripping of ammonia in a water-sparged aerocyclone reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.C.; Woo, J.H.; Oh, G.-G.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, H.W. External electric field promotes ammonia stripping from wastewater. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Bansal, A.; Jha, M.K.; Jain, R. Production of biodiesel from wastewater grown Chlorella minutissima. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 20, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Malla, F.A.; Khan, S.A.; Rashmi; Sharma, G.K.; Gupta, N.; Abraham, G. Phycoremediation potential of Chlorella minutissima on primary and tertiary treated wastewater for nutrient removal and biodiesel production. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Deng, S.; Chang, J.; Ran, Z. Response of energy microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to nitrogen and phosphorus stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5762–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, J.; Abolghasemi, H.; Esmaili, M.; Delavari Amrei, H.; Pourjamshidian, R. Effect of dilution on nitrogen removal from ammonia plant effluent using Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis. Pollution 2021, 7, 681–691. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Kumar, A.; Sahu, A.K.; Ergas, S.J. Impact of ammonia concentration on Spirulina platensis growth in an airlift photobioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3234–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, R.; Shariati, M. Study of the Inhibitory Effect of the media culture parameters and cell population to increase the biomass production of Dunaliella tertiolecta. Prog. Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Rolland, J.L.; Stien, D.; Sanchez-Ferandin, S.; Lami, R. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching in the phycosphere of phytoplankton: A case of chemical interactions in ecology. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, A.; Huang, Y.; Liao, Q.; Xia, A.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, X. Domesticating Chlorella vulgaris with gradually increased the concentration of digested piggery wastewater to bio-remove ammonia nitrogen. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeanyi, V.O. Determination of the effect of light and salt concentrations on Aphanocapsa algal population. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 2488–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinmehr, M.J.; Farhadian, O.; Heyrati, F.P.; Keramat, J.; Koutra, E.; Kornaros, M.; Daneshvar, E. Effect of nitrogen concentration on the growth rate and biochemical composition of the microalga, Isochrysis galbana. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Conc. | |
|---|---|---|
| mM | mg/L | |
| NaNO3 | 2.94 | 249.88 |
| MgSO4.7H2O | 0.304 | 74.93 |
| NaCl | 0.428 | 25.01 |
| K2HPO4 | 0.431 | 75.08 |
| KH2PO4 | 1.29 | 175.55 |
| CaCl2.2H2O | 0.17 | 24.99 |
| ZnSO4.7H20 | 0.031 | 8.83 |
| MnCl2.4H20 | 7.28 × 10−3 | 1.44 |
| MoO3 | 4.93 × 10−3 | 0.71 |
| CuSO4.5H20 | 6.29 × 10−3 | 1.57 |
| Co(NO3)2.6H2O | 1.68 × 10−3 | 0.49 |
| H3BO3 | 0.185 | 11.44 |
| Na2EDTA.2H2O | 0.171 | 63.65 |
| KOH | 0.553 | 31.03 |
| FeSO4.7H2O | 0.018 | 4.98 |
| H2SO4 | 0.018 | 1.80 |
| Parameter | C. vulgaris | C. minutissima | C. reinhardtii | A. platensis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| μmax | 1.54 | 1.44 | 1.53 | 1.28 |
| Ki | 106.50 | 87.76 | 92.52 | 118.09 |
| Km | 2.28 | 2.48 | 2.23 | 2.16 |
| n | 1.75 | 1.64 | 1.99 | 1.47 |
| m | 13.67 | 16.56 | 22.75 | 18.03 |
| IC50 | 34.82 | 30.17 | 27.20 | 44.44 |
| Assay | DBWend (mg/L) | N Cont. (%) | N Rem. Eff. (%) | YX/N (g-X/g-Ncon) | Ave. N Rem. Rate (mg/L*day) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | FA Conc. (mg/L) | |||||
| C. vulgaris | 1.69 | 355.10 | 5.30 | 97.36 | 18.79 | 1.81 |
| 3.39 | 700.86 | 5.37 | 97.43 | 18.53 | 3.63 | |
| 6.77 | 1293.32 | 5.72 | 95.71 | 17.40 | 7.13 | |
| 16.93 | 1700.95 | 6.00 | 53.12 | 16.50 | 9.90 | |
| 33.85 | 705.68 | 5.83 | 11.59 | 15.69 | 3.93 | |
| 50.78 | 398.08 | 5.33 | 4.75 | 14.39 | 2.23 | |
| 67.70 | 225.20 | 4.25 | 2.46 | 11.78 | 1.43 | |
| C. minutissima | 1.69 | 346.63 | 5.10 | 91.46 | 19.52 | 1.70 |
| 3.39 | 659.04 | 5.22 | 89.19 | 19.03 | 3.32 | |
| 6.77 | 1244.62 | 5.84 | 94.08 | 17.04 | 7.01 | |
| 16.93 | 1668.47 | 5.87 | 50.96 | 16.87 | 9.50 | |
| 33.85 | 682.70 | 5.77 | 11.16 | 15.75 | 3.78 | |
| 50.78 | 319.55 | 4.55 | 3.11 | 17.64 | 1.46 | |
| 67.70 | 187.11 | 3.98 | 1.56 | 15.45 | 0.91 | |
| C. reinhardtii | 1.69 | 296.74 | 6.40 | 98.34 | 15.54 | 1.83 |
| 3.39 | 483.01 | 7.80 | 97.52 | 12.76 | 3.63 | |
| 6.77 | 955.93 | 7.93 | 98.03 | 12.56 | 7.31 | |
| 16.93 | 1451.60 | 9.94 | 74.85 | 9.99 | 13.95 | |
| 33.85 | 596.96 | 10.25 | 16.77 | 9.17 | 5.68 | |
| 50.78 | 210.68 | 9.24 | 4.47 | 8.10 | 1.94 | |
| 67.70 | 151.44 | 6.30 | 2.45 | 7.96 | 1.33 | |
| A. platensis | 1.69 | 243.31 | 7.76 | 97.75 | 12.82 | 1.81 |
| 3.39 | 574.95 | 6.66 | 98.58 | 15.02 | 3.66 | |
| 6.77 | 1072.27 | 7.14 | 99.10 | 13.94 | 7.36 | |
| 16.93 | 1118.93 | 7.39 | 43.56 | 13.23 | 8.09 | |
| 33.85 | 805.11 | 7.89 | 17.36 | 11.94 | 5.86 | |
| 50.78 | 237.66 | 5.85 | 3.50 | 11.66 | 1.64 | |
| 67.70 | 182.80 | 4.17 | 2.31 | 10.21 | 1.23 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Metin, U.; Altınbaş, M. Evaluating Ammonia Toxicity and Growth Kinetics of Four Different Microalgae Species. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081542
Metin U, Altınbaş M. Evaluating Ammonia Toxicity and Growth Kinetics of Four Different Microalgae Species. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(8):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081542
Chicago/Turabian StyleMetin, Umut, and Mahmut Altınbaş. 2024. "Evaluating Ammonia Toxicity and Growth Kinetics of Four Different Microalgae Species" Microorganisms 12, no. 8: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081542
APA StyleMetin, U., & Altınbaş, M. (2024). Evaluating Ammonia Toxicity and Growth Kinetics of Four Different Microalgae Species. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081542






