Intestinal Microbiome Profiles in Broiler Chickens Raised with Different Probiotic Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Microbial Genomic DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
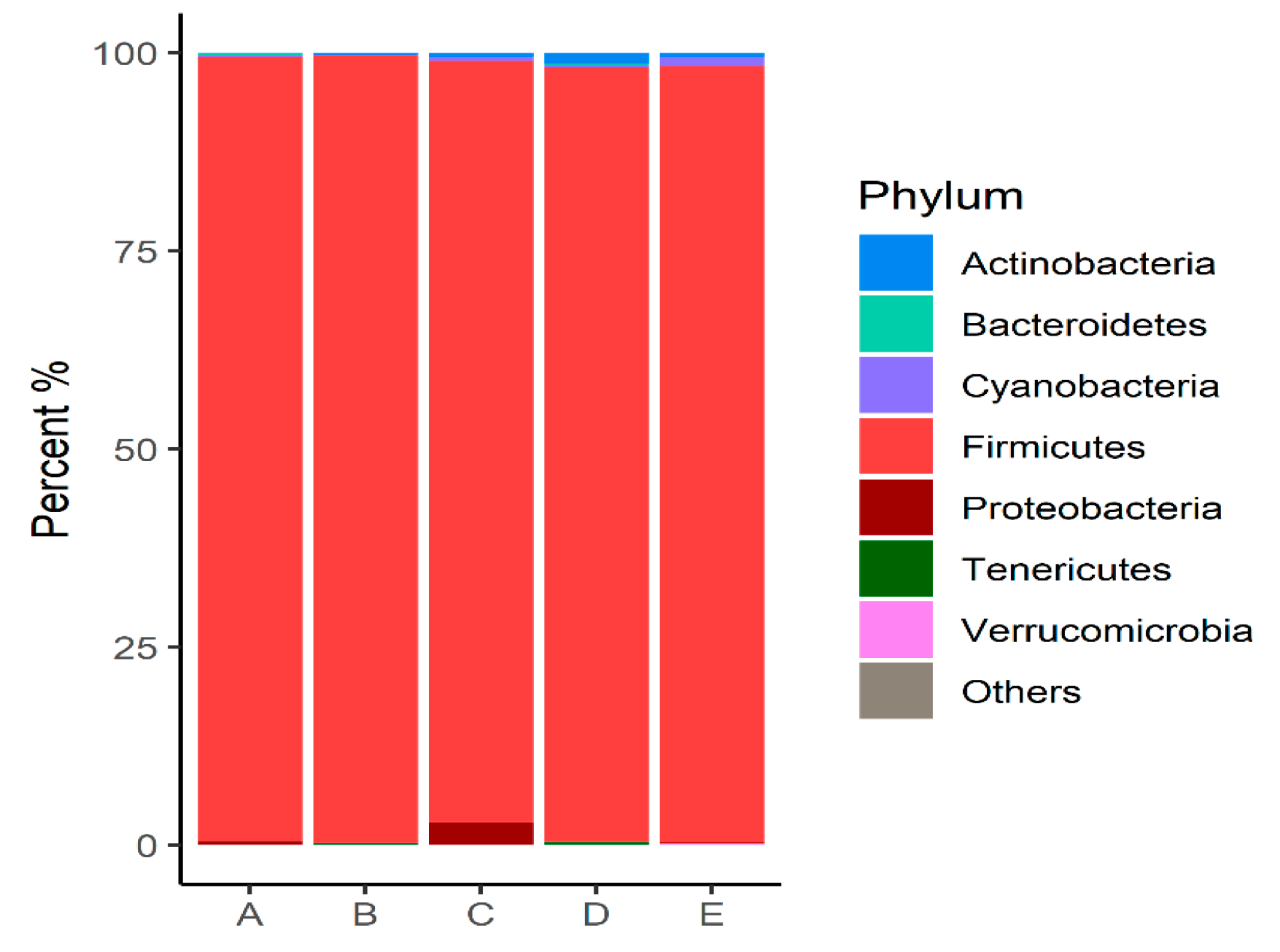
3.1. Ileal Microbiome
3.1.1. Alpha Diversity
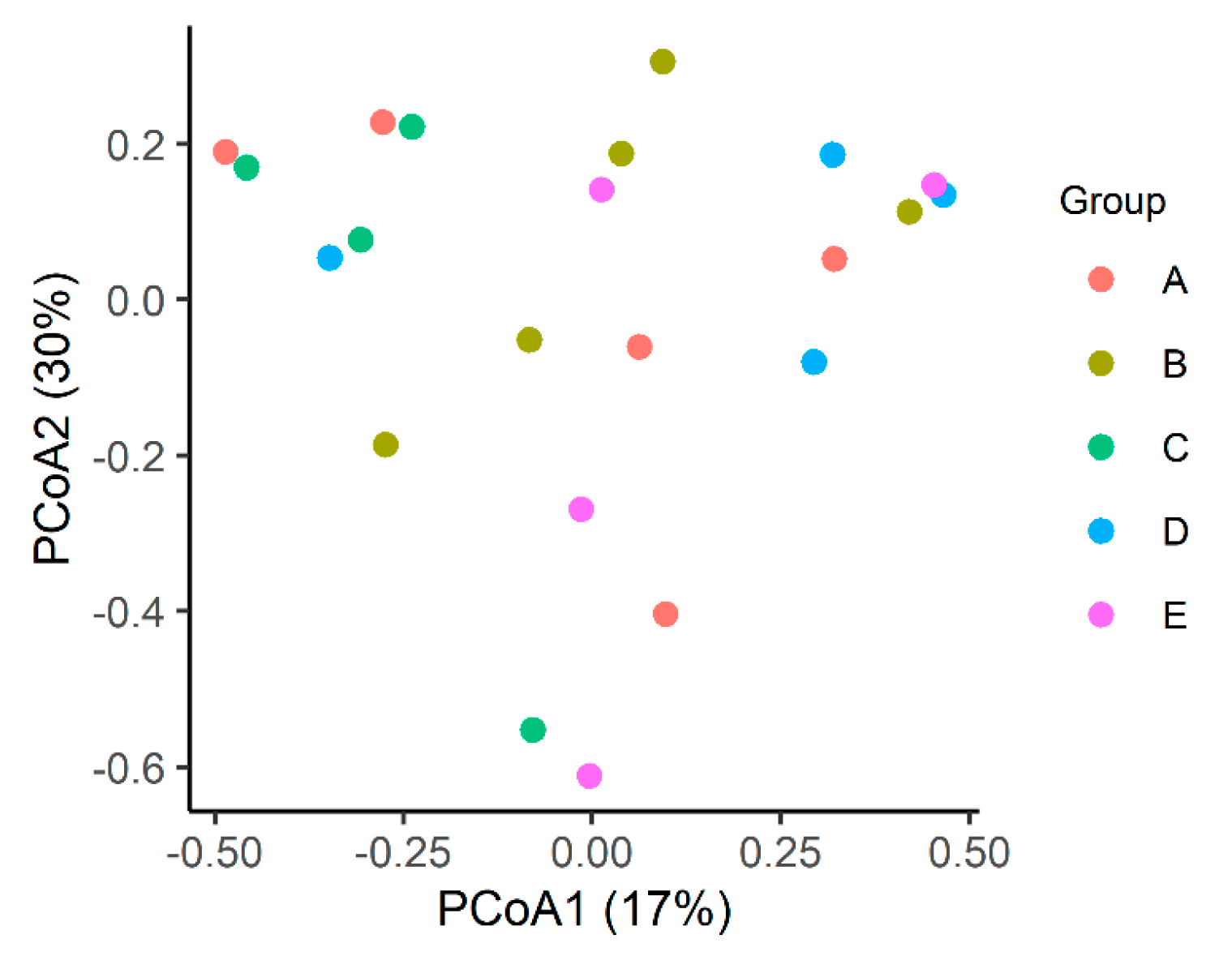
3.1.2. Beta Diversity
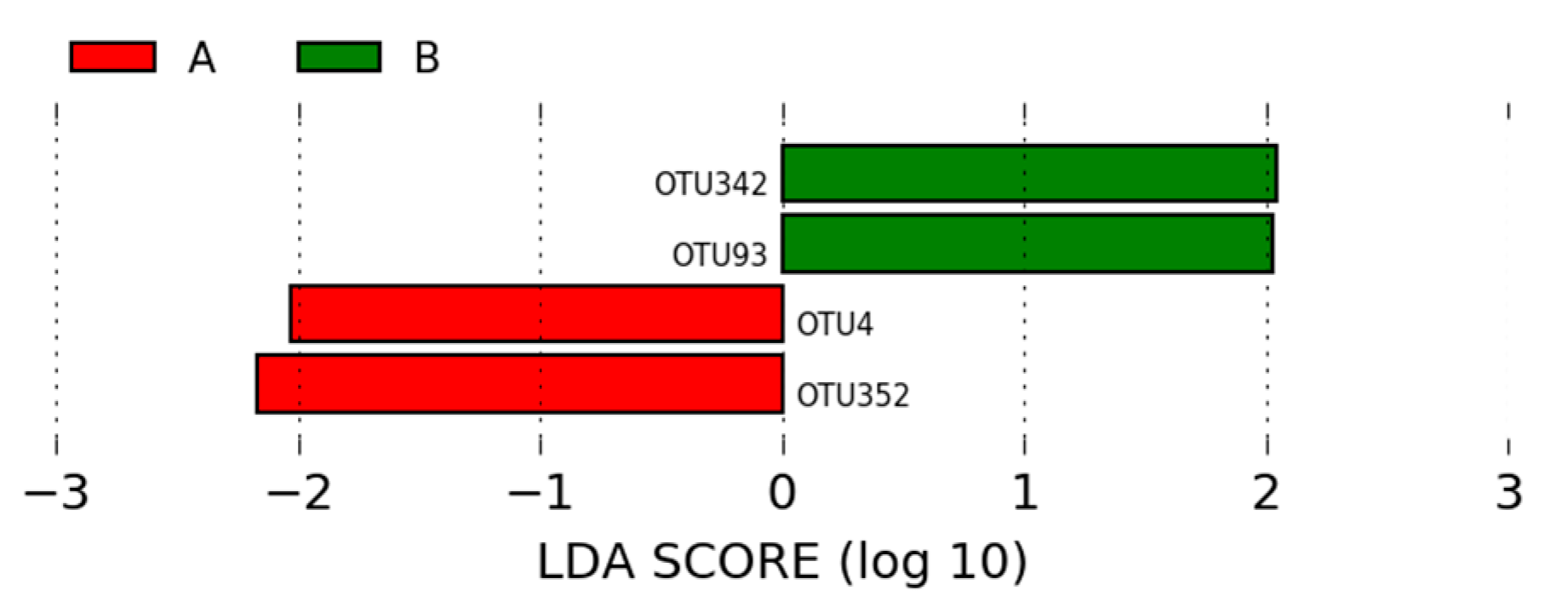
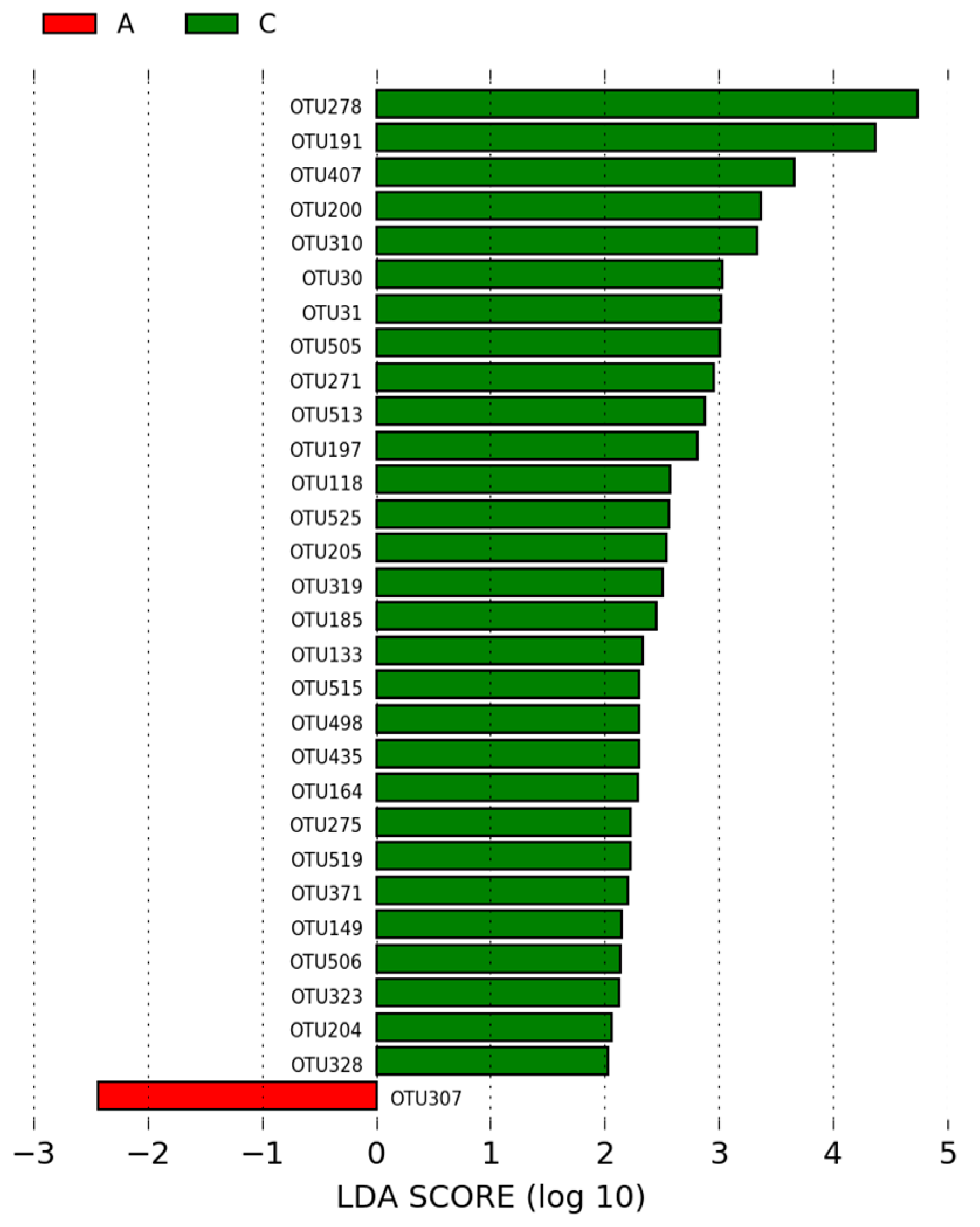
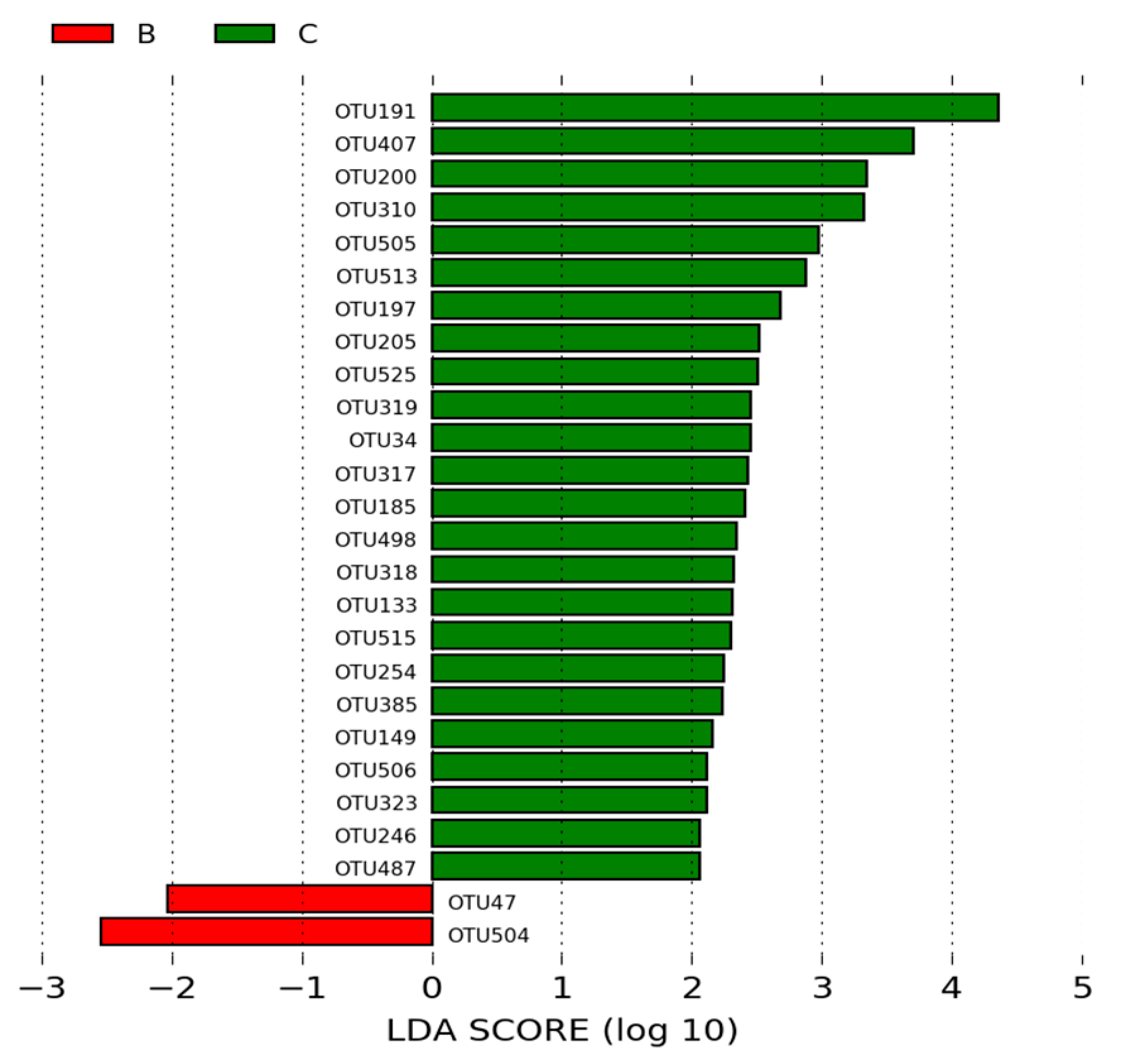
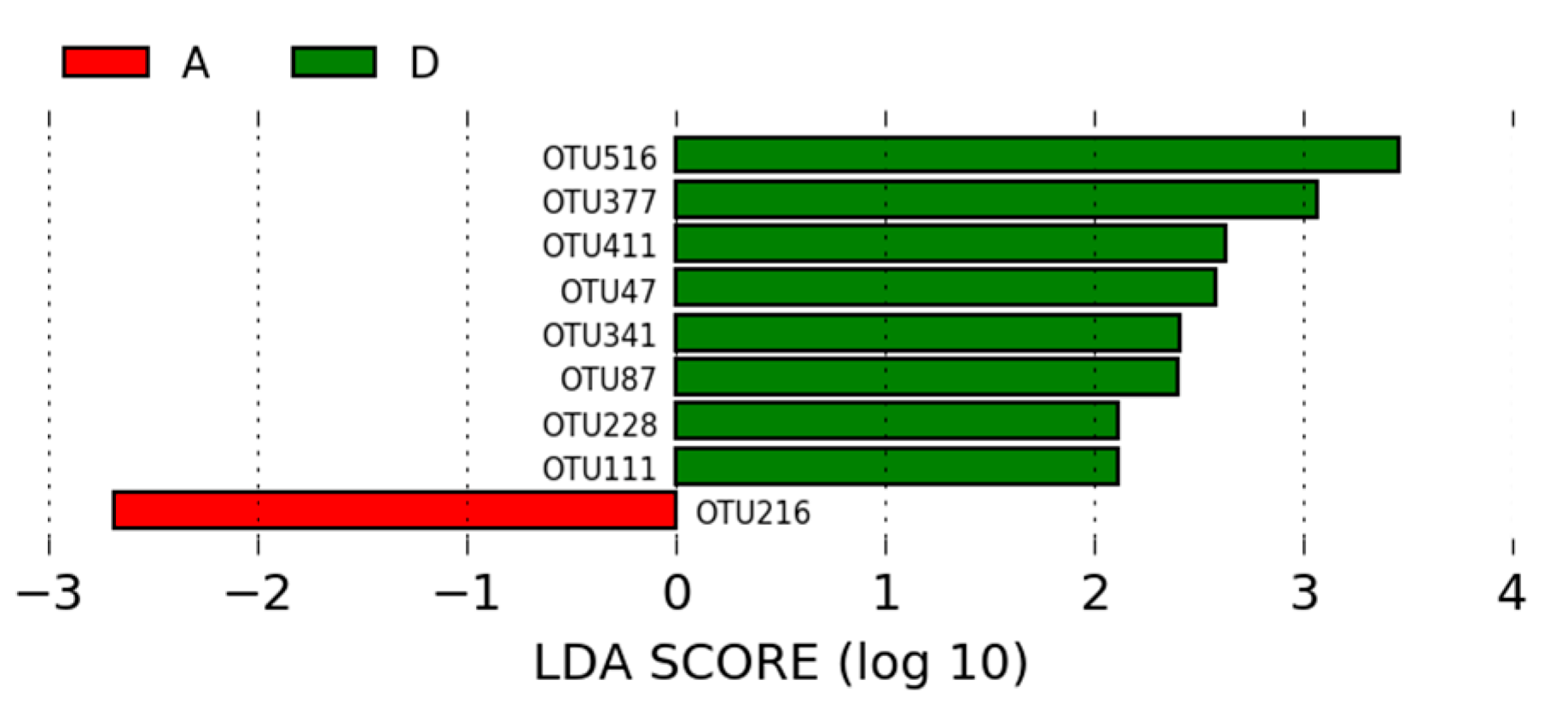
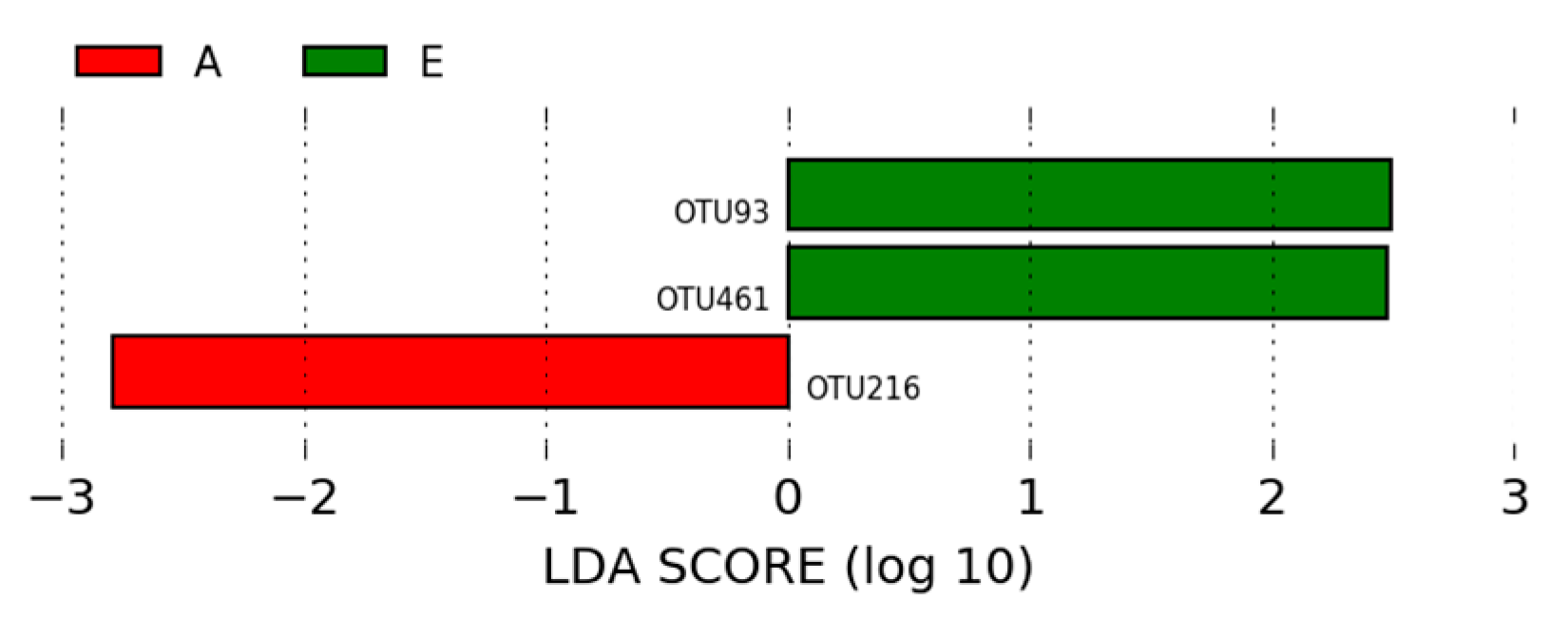
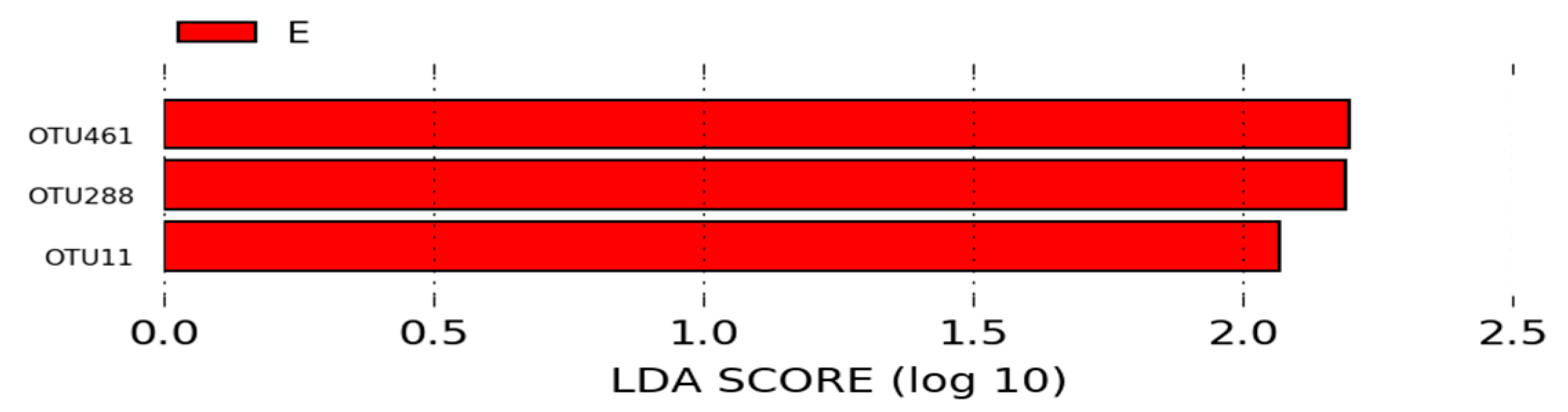
3.1.3. LEfSe
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plata, G.; Baxter, N.T.; Susanti, D.; Volland-Munson, A.; Gangaiah, D.; Nagireddy, A.; Mane, S.P.; Balakuntla, J.; Hawkins, T.B.; Kumar-Mahajan, A. Growth promotion and antibiotic induced metabolic shifts in the chicken gut microbiome. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shafi, M.E.; Qattan, S.Y.; Batiha, G.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Abdel-Moneim, A.E.; Alagawany, M. Probiotics in poultry feed: A comprehensive review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Jha, R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Alagawany, M.; Elnesr, S.S.; Farag, M.R.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Barkat, R.A.; Gabr, A.A.; Foda, M.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; El-Sabrout, K.; et al. Potential role of important nutraceuticals in poultry performance and health-A comprehensive review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, P.; Kiess, A.; Adhikari, R.; Jha, R. An approach to alternative strategies to control avian coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stęczny, K.; Kokoszyński, D. Effect of probiotic preparations (EM) on productive characteristics, carcass composition, and microbial contamination in a commercial broiler chicken farm. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz-Mousavi, S.M.A.; Hosseini, H.M.; Mirhosseini, S.A. A review of dietary probiotics in poultry. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 5, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryabin, D.; Lazebnik, C.; Vlasenko, L.; Karimov, I.; Kosyan, D.; Zatevalov, A.; Duskaev, G. Broiler Chicken Cecal Microbiome and Poultry Farming Productivity: A Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horyanto, D.; Bajagai, Y.S.; Kayal, A.; Von-Hellens, J.; Chen, X.; Van, T.T.H.; Radovanović, A.; Stanley, D. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Probiotics Mix Supplementation in a Broiler Leaky Gut Model. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, G.; Tolnai, E.; Stagel, A.; Remenyik, J.; Stundl, L.; Gal, F.; Biro, S.; Paholcsek, M. Tendentious effects of automated and manual metagenomic DNA purification protocols on broiler gut microbiome taxonomic profiling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Caliboso, K.D.; Nanquil, J.E.; Zhang, J.; Kae, H.; Neupane, K.; Mishra, B.; Jha, R. Cecal microbiome profile of Hawaiian feral chickens and pasture-raised broiler (commercial) chickens determined using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehau, T.; Ducatelle, R.; Immerseel, F.V.; Goossens, E. Omics technologies in poultry health and productivity-part 1: Current use in poultry research. Avian Pathol. 2022, 51, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Oakley, B.; Kim, W.K. Chicken gut microbiota: Importance and detection technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Han, C.; Li, S.; Geng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Shi, W.; Bao, Y. High-throughput sequencing–based analysis of the intestinal microbiota of broiler chickens fed with compound small peptides of Chinese medicine. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Bi, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, J.; Dai, J.; et al. Covariation of the fecal microbiome with diet in nonpasserine birds. mSphere 2021, 6, e00308-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostagno, H.S.; Albino, L.F.T.; Donzele, J.L.; Gomes, P.C.; Oliveira, R.F.; Lopes, B.C.; Ferreira, A.S.; Barreto, S.L.T.; Euclides, R.F. Tabelas Brasileiras Para Aves e Suínos: Composição de Alimentos e Exigências Nutricionais, 3rd ed.; UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2011; p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “all-species living tree project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2014, 42, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, V.G. Understanding the Microbiome of Puget Prairies: Community Composition of Bacteria in a Hemiparasitic Plant System; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeant, M.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Cogan, T.A.; Bedford, M.R.; Penn, C.W.; Pallen, M.J. Extensive microbial and functional diversity within the chicken cecal microbiome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.G.; Modarressi, M.H.; Mousavi, S.N.; Ebrahimi, M.T. Evaluation of Bacillus Strains as Probiotic Based on Enzyme Production and In Vitro Protective Activity against Salmonellosis. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2018, 69, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, B.B.; Buhr, R.; Ritz, C.W.; Kiepper, B.H.; Berrang, M.E.; Seal, B.S.; Cox, N.A. Successional changes in the chicken cecal microbiota during 42 days of growth are independent of organic acid feed additives. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimonja, O.; Svihus, B. Effects of processing of wheat or oats starch on physical pellet quality and nutritional value for broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 149, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svihus, B.; Juvik, E.; Hetland, H.; Krogdahl, Å. Causes for improvement in nutritive value of broiler chicken diets with whole wheat instead of ground wheat. Br. Poult. Sci. 2004, 45, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apajalahti, J.; Vienola, K. Interaction between chicken intestinal microbiota and protein digestion. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2016, 22, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards-Rios, P.; Fothergill, J.; Bernardeau, M.; Wigley, P. Development of the Ileal Microbiota in Three Broiler Breeds. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zai, X.; Weng, G.; Ma, X.; Deng, D. Brevibacillus laterosporus: A Probiotic with Important Applications in Crop and Animal Production. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Shang, H.; Miao, Y.; Huang, J.; Niu, X.; Chen, R.; Peng, D.; Wei, K.; Zhu, R. Polysaccharides from Pinus massoniana pollen improve intestinal mucosal immunity in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Farnell, Y.Z.; Kiess, A.S.; Peebles, E.D.; Wamsley, K.G.S.; Zhai, W. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and coccidial vaccination on cecal microbial diversity and composition of Eimeria-challenged male broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.K.; Calik, A.; White, M.B.; Kimminau, E.A.; Dalloul, R.A. Effect of Probiotics and Multi-Component Feed Additives on Microbiota, Gut Barrier and Immune Responses in Broiler Chickens during Subclinical Necrotic Enteritis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 572142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa-Rama, E.; Bailey, M.; Kumar, S.; Leone, C.; Den-Bakker, H.C.; Thippareddi, H.; Singh, M. Characterizing the gut microbiome of broilers raised under conventional and no antibiotics ever practices. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.M.; Soratto, T.A.T.; Cardinal, K.M.; Wagner, G.; Hauptli, L.; Lima, A.L.F.; Dahlke, F.; Peres Netto, D.; Moraes, P.D.O.; Ribeiro, A.M.L. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota of broilers supplemented with monensin or functional oils in response to challenge by Eimeria spp. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 0237118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y.J.; Cao, J.X.; Wu, Z.F.; Weng, P.F. The modulatory effect of (-)-epigallocatechin 3-O-(3-O-methyl) gallate (EGCG3”Me) on intestinal microbiota of high fat diet-induced obesity mice model. Food. Res. Int. 2017, 92, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Si, W.; Forster, R.J.; Huang, R.; Yu, H.; Yin, Y.; Yang, C.; Han, Y. 16S rRNA gene-based analysis of mucosa-associated bacterial community and phylogeny in the chicken gastrointestinal tracts: From crops to ceca. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2007, 59, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, C.J.; Chia, N.; Jeraldo, P.; Sipos, M.; Goldenfeld, N.D.; White, B.A. The microbiome of the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2012, 13, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Chen, C.; Indugu, N.; Werlang, G.O.; Singh, M.; Kim, W.K.; Thippareddi, H. Effect of antibiotic withdrawal in feed on chicken gut microbial dynamics, immunity, growth performance and prevalence of foodborne pathogens. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychlik, I. Composition and function of chicken gut microbiota. Animals 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendinning, L.; Watson, K.A.; Watson, M. Development of the duodenal, ileal, jejunal and caecal microbiota in chickens. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollarcikova, M.; Kubasova, T.; Karasova, D.; Crhanova, M.; Cejkova, D.; Sisak, F.; Rychlik, I. Use of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for prediction of new opportunistic pathogens in chicken ileal and cecal microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2347–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Sun, C.; Zheng, J.; Wen, C.; Ji, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Z.; Yang, N. Efficacy of fecal sampling as a gut proxy in the study of chicken gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberecht, S.; Bajagai, Y.S.; Moore, R.J.; Van, T.; Stanley, D. Poultry feeds carry diverse microbial communities that influence chicken intestinal microbiota colonisation and maturation. AMB Express. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Srinivas, T.; Reddy, G. The family planococcaceae. Prokaryotes Firmicutes Tenericutes 2014, 1, 303–351. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, T.F.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F. The genus Enterococcus as probiotic: Safety concerns. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.; Chen, L.R.; Suyemoto, M.M.; Barnes, H.J.; Borst, L.B. A review of Enterococcus cecorum infection in poultry. Avian Dis. 2018, 62, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Yang, Z.; Celi, P.; Yan, L.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, S.; Su, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; et al. Effect of benzoic acid on production performance, egg quality, intestinal morphology, and cecal microbial community of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Mao, N.; Gu, P.; Zhu, T.; He, J.; Peng, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D. Effects of Alhagi Honey Polysaccharides as Feed Supplement on Intestine Function and Microbiome, Immune Function, and Growth Performance in Chicken. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocejo, M.; Oporto, B.; Hurtado, A. 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing characterization of caecal microbiome composition of broilers and free-range slow-growing chickens throughout their productive lifespan. Stem. Cells Int. 2019, 9, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, A.; Brulc, J.M.; Wilson, M.K.; Law, B.F.; Theoret, J.R.; Joens, L.A.; Konkel, M.E.; Angly, F.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.A.; et al. Comparative metagenomics reveals host specific metavirulomes and horizontal gene transfer elements in the chicken cecum microbiome. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleithy, E.M.M.; Bawish, B.M.; Kamel, S.; Ismael, E.; Bashir, D.W.; Hamza, D.; Fahmy, K.N.E. Influence of dietary Bacillus coagulans and/or Bacillus licheniformis-based probiotics on performance, gut health, gene expression, and litter quality of broiler chickens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Chain, F.; Martín, R.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Courau, S.; Langella, P. Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb. Cell Factories 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Yu, Y.H. Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products improve growth performance and the fecal microbiota community in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yying-Chu, C.; Yu-Hsiang, Y. Bacillus licheniformis–fermented products and enramycin differentially modulate microbiota and antibiotic resistome in the cecal digesta of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Shen, G.; Li, S.; Ding, W. Using community analysis to explore bacterial indicators for disease suppression of tobacco bacterial wilt. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Yan, S.; Li, P.; Li, G.; Gao, M.; Yan, L.; Lv, Z.; Guo, Y. Comparison and Correlation Analysis of Immune Function and Gut Microbiota of Broiler Chickens Raised in Double-Layer Cages and Litter Floor Pens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0004522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Lin, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; An, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. Correlation between Jejunal Microbial Diversity and Muscle Fatty Acids Deposition in Broilers Reared at Different Ambient Temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shao, G.; Xie, Z.; Nie, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Recombinant Muscovy Duck Parvovirus Led to Ileac Damage in Muscovy Ducklings. Viruses 2022, 14, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engberg, R.M.; Hedemann, M.S.; Leser, T.D.; Jensen, B.B. Effect of zinc bacitracin and salinomycin on intestinal microflora and performance of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumonceaux, T.J.; Hill, J.E.; Hemmingsen, S.M.; Kessel, A.G.V. Characterization of intestinal microbiota and response to dietary virginiamycin supplementation in the broiler chicken. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2006, 72, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Probiotics | Pre-Starter (g/t of Feed) | Starter (g/t of Feed) | Grower (g/t of Feed) | Finisher (g/t of Feed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAGF | 500 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| MCSP | 250 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| NCSSP | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Probiotics | Probiotic Strains—Composition |
|---|---|
| NAGF | Total anaerobic bacteria 1.0 × 104; lactic acid-producing bacteria 1.0 × 104; Mannanoligosaccharides 370 g/kg. |
| MCSP | Bacillus subtilis 1.0 × 108; Enterococcus faecium 6.0 × 108; Lactobacillus acidophilus 1.0 × 108; Lactobacillus delbrueckii 1.0 × 108; Lactobacillus plantarum 3.0 × 108; Lactobacillus reuteri 5.0 × 108; Lactobacillus salivarius 1.0 × 108; Pediococcus acidilactici 3.0 × 108. |
| NCSSP | Bacillus subtilis 1.0 × 108 |
| Ingredients (%) | Pre-Starter 1–7 Days Old | Starter 8–21 Days Old | Grower 22–35 Days Old | Finisher 36–42 Days Old | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 58.94 | 63.44 | 66.20 | 76.96 | |
| Soybean meal | 33.93 | 28.80 | 26.33 | 13.87 | |
| Meat and bone meal | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.000 | 1.00 | |
| Limestone | 1.24 | 1.09 | 1.23 | 0.86 | |
| Salt | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.28 | |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| DL-Methionine | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.19 | |
| Poultry fat | 0.53 | 0.60 | 1.93 | 0.53 | |
| Viscera meal | 3.40 | 4.47 | 2.20 | 3.00 | |
| Feather and bloos meal | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.47 | |
| Acidifier | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| Antifungal | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Monocalcium phosphate | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.68 | 0.00 | |
| Choline | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| L-lysine | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0.52 | |
| L-Threonine | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.08 | |
| Avilamycin | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| Monensin + Nicarbazin | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Antioxidant | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | |
| Vitamin premix | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Mineral premix | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Monensin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | |
| Phytase | 0.011 | 0.016 | 0.01 | 0.016 | |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| Nutritional Levels | Pre-starter | Starter | Grower | Finisher | |
| Metabolizable energy | Kcal | 3.010 | 3.080 | 3.239 | 3.268 |
| Crude protein | % | 23.84 | 22.44 | 19.38 | 18.30 |
| Total Lysine | % | 1.60 | 1.50 | 1.30 | 1.21 |
| Total methionine | % | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.49 |
| Total methionine + cysteine | % | 1.39 | 1.31 | 1.18 | 1.14 |
| Total threonine | % | 1.27 | 1.20 | 1.07 | 1.02 |
| Total tryptophan | % | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.34 |
| Digestible arginine | % | 1.36 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 0.93 |
| Digestible lysine | % | 1.33 | 1.23 | 1.06 | 0.97 |
| Digestible methionine | % | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.43 |
| Digestible meth + cysteine | % | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.78 | 0.72 |
| Digestible threonine | % | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.64 |
| Digestible tryptophan | % | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.17 |
| Calcium (Ca) | % | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.80 |
| Total phosphorus (P) | % | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.54 |
| Available phosphorus (P) | % | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.37 |
| Sodium | % | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| Electrolyte balance | mEq/kg | 246.57 | 214.5 | 169.72 | 147.77 |
| Choline | ppm | 2.000 | 1.850 | 1.650 | 1.550 |
| Ca/P available | % | 2.05 | 2.05 | 2.10 | 2.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, J.M.S.; Almeida, A.M.D.S.; Borsanelli, A.C.; de Athayde, F.R.F.; Nascente, E.d.P.; Batista, J.M.M.; Gouveia, A.B.V.S.; Stringhini, J.H.; Leandro, N.S.M.; Café, M.B. Intestinal Microbiome Profiles in Broiler Chickens Raised with Different Probiotic Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081639
da Silva JMS, Almeida AMDS, Borsanelli AC, de Athayde FRF, Nascente EdP, Batista JMM, Gouveia ABVS, Stringhini JH, Leandro NSM, Café MB. Intestinal Microbiome Profiles in Broiler Chickens Raised with Different Probiotic Strains. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(8):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081639
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Julia Marixara Sousa, Ana Maria De Souza Almeida, Ana Carolina Borsanelli, Flávia Regina Florencio de Athayde, Eduardo de Paula Nascente, João Marcos Monteiro Batista, Alison Batista Vieira Silva Gouveia, José Henrique Stringhini, Nadja Susana Mogyca Leandro, and Marcos Barcellos Café. 2024. "Intestinal Microbiome Profiles in Broiler Chickens Raised with Different Probiotic Strains" Microorganisms 12, no. 8: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081639
APA Styleda Silva, J. M. S., Almeida, A. M. D. S., Borsanelli, A. C., de Athayde, F. R. F., Nascente, E. d. P., Batista, J. M. M., Gouveia, A. B. V. S., Stringhini, J. H., Leandro, N. S. M., & Café, M. B. (2024). Intestinal Microbiome Profiles in Broiler Chickens Raised with Different Probiotic Strains. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081639






