Soil Factors Key to 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP) Efficacy: EC and SOC Dominate over Biotic Influences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Sites and Soil Sampling
2.2. Soil Microcosm Incubation Experiment
2.3. Determination of Soil Mineral Nitrogen
2.4. Determination of N2O Emissions
2.5. Soil DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.6. Quantitative PCR of Functional Genes
2.7. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Physicochemical Properties of Different Soils
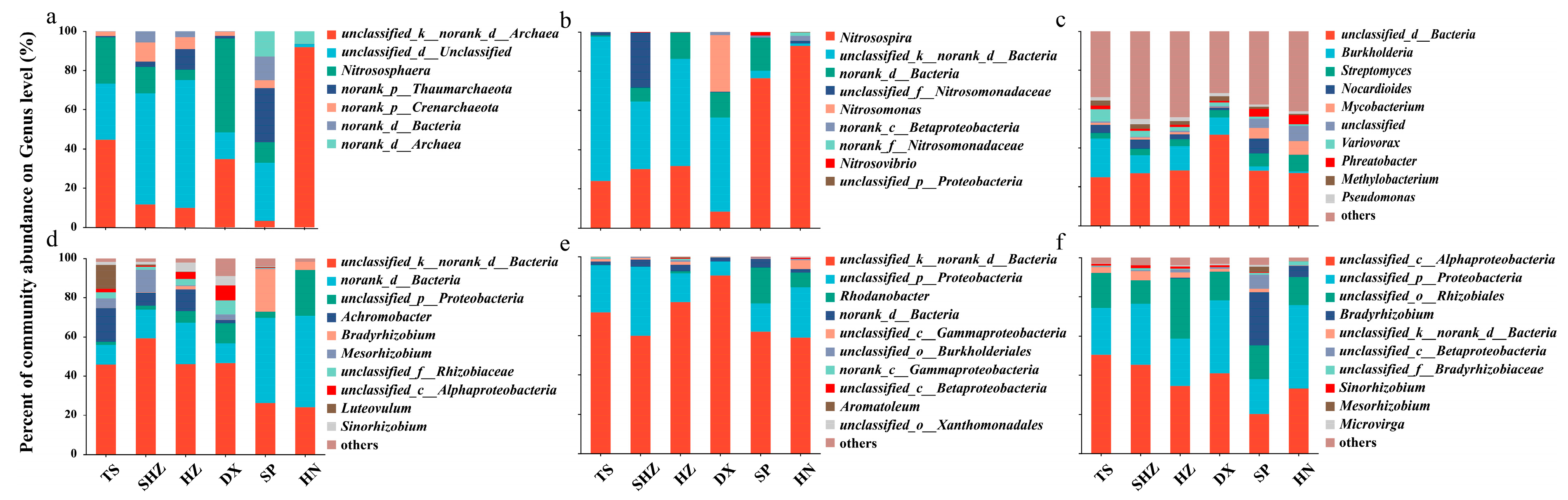
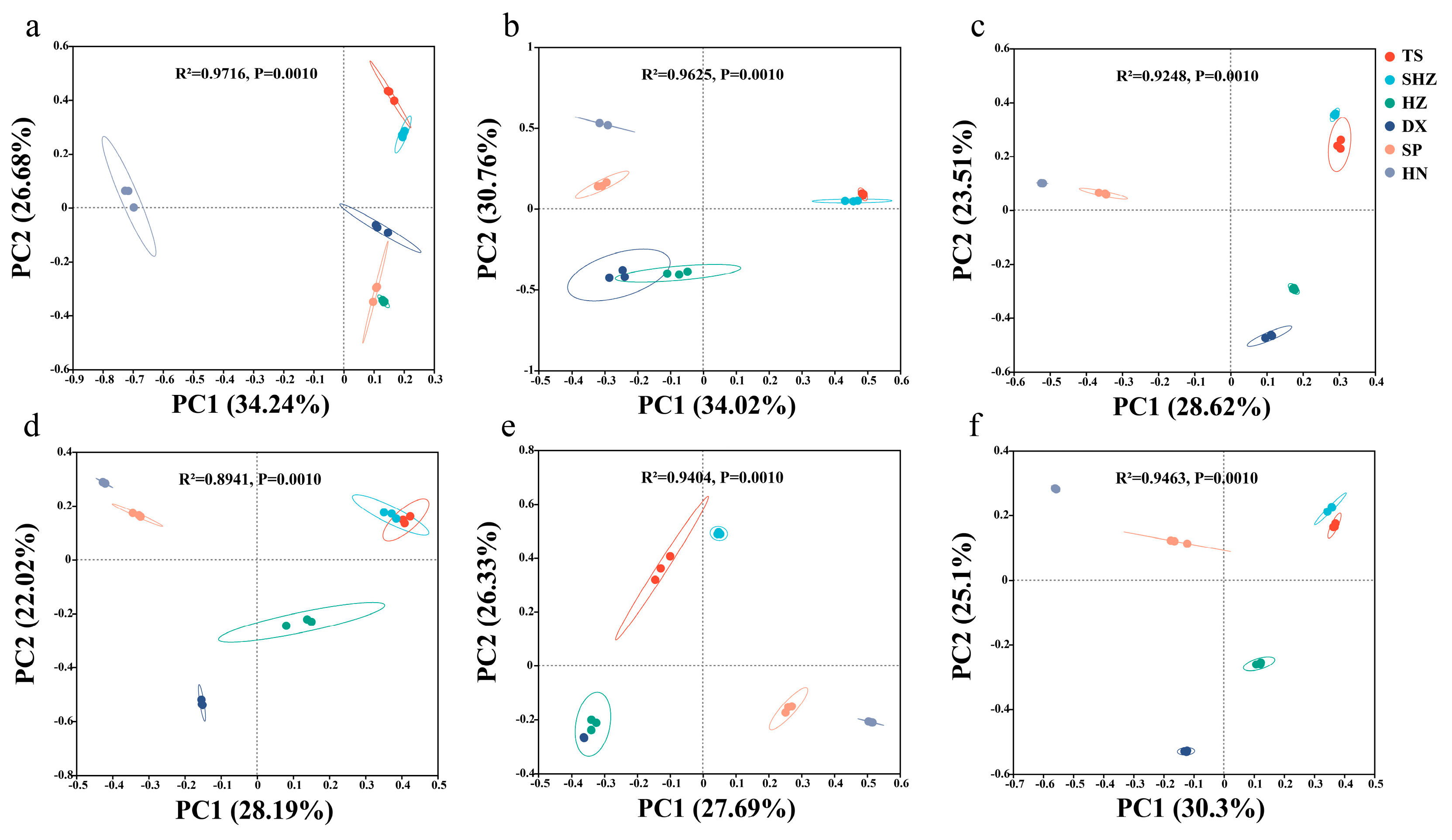
3.2. Composition, Diversity, and Abundance of Soil Nitrogen-Cycling Microorganisms
3.3. The Inhibitory Effects of DMPP on Nitrification and N2O Emissions from Different Soils
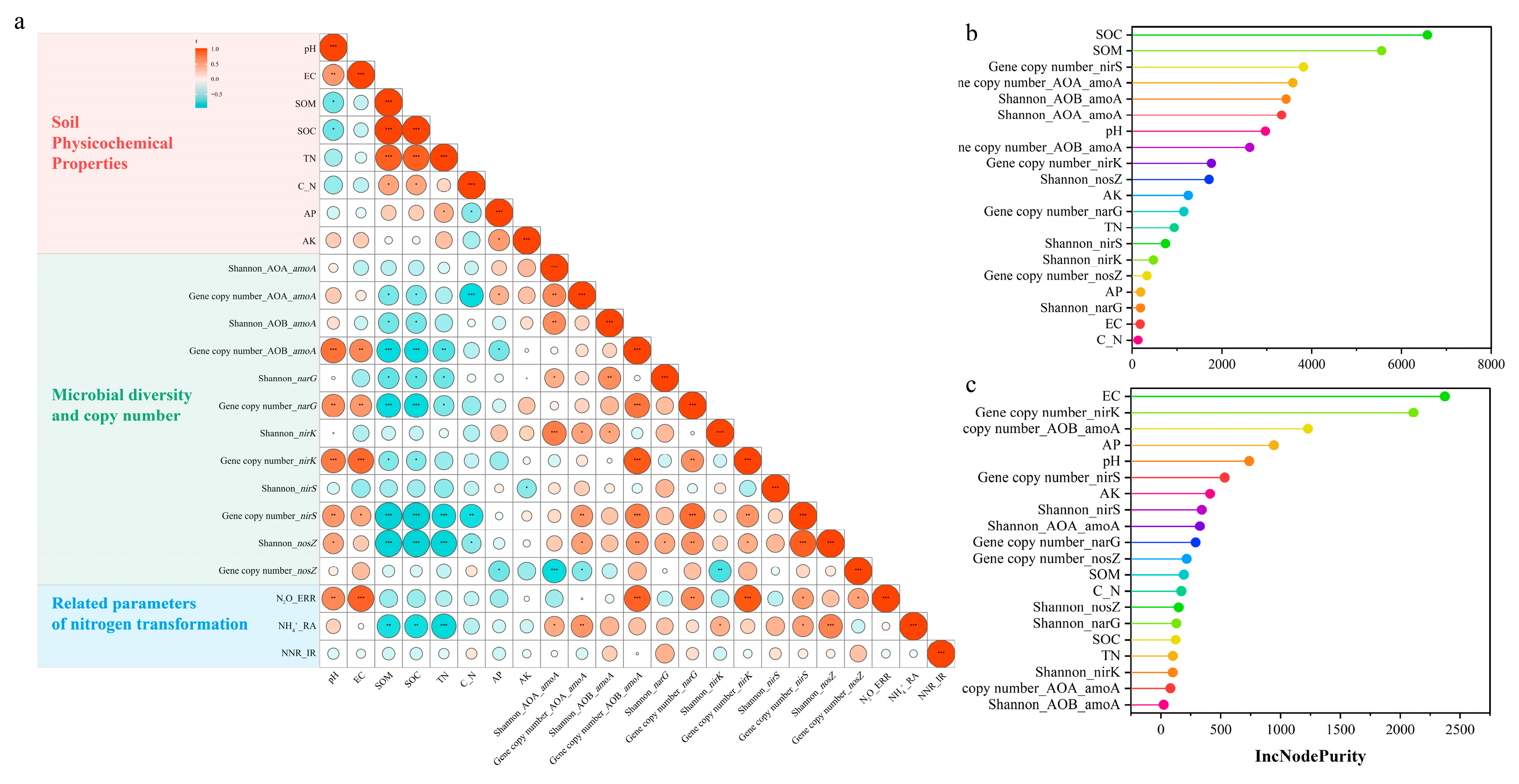
3.4. The Relative Contribution of Abiotic and Biotic Factors to DMPP Efficacy
4. Discussion
4.1. The Abiotic and Biotic Properties and DMPP Efficacy Varied among Selected Soils
4.2. The Physicochemical Properties of Soil Have a More Significant Impact on the Efficacy of DMPP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hiis, E.G.; Vick, S.H.W.; Molstad, L.; Rosdal, K.; Jonassen, K.R.; Winiwarter, W.; Bakken, L.R. Unlocking bacterial potential to reduce farmland N2O emissions. Nature 2024, 630, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, M.; Langridge, P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 2010, 327, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Suter, H.; Mosier, A.R.; Chen, D.L. Using nitrification inhibitors to mitigate agricultural N2O emission: A double-edged sword? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Song, X.T.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, D.; Rees, R.M.; Ju, X.T. Using nitrification inhibitors and deep placement to tackle the trade-offs between NH3 and N2O emissions in global croplands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 4409–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.L.; Liu, L.L.; Hu, S.J.; Compton, J.E.; Greaver, T.L.; Li, Q.L. How inhibiting nitrification affects nitrogen cycle and reduces environmental impacts of anthropogenic nitrogen input. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.K.; Wille, U.; Hu, H.W.; Caruso, F.; Mumford, K.; Liang, X.; Pan, B.B.; Malcolm, B.; Roessner, U.; Suter, H.; et al. Next-generation enhanced-efficiency fertilizers for sustained food security. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruser, R.; Schulz, R. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on the nitrous oxide (N2O) release from agricultural soils—A review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.C.; Wu, D.; Bol, R.; Shi, Y.F.; Guo, Y.B.; Meng, F.Q.; Wu, W.L. Nitrification inhibitor’s effect on mitigating N2O emissions was weakened by urease inhibitor in calcareous soils. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Z.; Hu, H.W.; He, J.Z.; Chen, D.L.; Suter, H.C. Effects of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on nitrification and the abundance and community composition of soil ammonia oxidizers in three land uses. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S.W.; Ma, S.T.; Zheng, X.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, C.H. Effects of commonly used nitrification inhibitors-dicyandiamide (DCD), 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP), and nitrapyrin-on soil nitrogen dynamics and nitrifiers in three typical paddy soils. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yin, C.; Chen, H.; Ye, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Wakelin, S.A.; Liang, Y. The efficacy of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on N2O emissions is linked to niche differentiation of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria across four arable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 130, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, D.P.; Shang, Z.C.; Gong, P. Effects of the nitrification inhibitor DMPP on soil bacterial community in a Cambisol in northeast China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.R.; Liu, H.R.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, L.G.; Guan, D.H.; Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, M.C. Nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) reduces N2O emissions by altering the soil microbial community in a wheat-maize rotation on the North China Plain. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 1270–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, X.C.; Ni, B.; Liu, R.; Meng, F.Q. Investigation of soil microbial communities involved in N cycling as affected by the long-term use of the N stabilizers DMPP and NBPT. Agronomy 2023, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.L.; Fan, Q.Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Ma, Y.; Yin, J.H.; Liu, R. A meta-analysis to examine whether nitrification inhibitors work through selectively inhibiting ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Xu, P.S.; Han, Z.Q.; Wu, J.; Bo, X.M.; Wang, J.Y.; Zou, J.W. Effect of biochar and DMPP application alone or in combination on nitrous oxide emissions differed by soil types. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.; Abalos, D.; Philippot, L.; Bru, D.; Mateo-Marín, N.; Petersen, S.O. Soil and temperature effects on nitrification and denitrification modified N2O mitigation by 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, S.; Barrena, I.; Setien, I.; González-Murua, C.; Estavillo, J.M. Efficiency of nitrification inhibitor DMPP to reduce nitrous oxide emissions under different temperature and moisture conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 53, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, H.; Lin, Y.P. Soil nitrification potential influences the performance of nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP in cropped and non-cropped soils. Agronomy 2019, 9, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.Y.; Gao, X.P.; Kuang, W.N.; Zhang, Y.H. Meta-analysis of the effect of nitrification inhibitors on the abundance and community structure of N2O-related functional genes in agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Xu, J.Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Qi, Z.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liao, L.X. Nitrification inhibitor DMPP offsets the increase in N2O emission induced by soil salinity. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, H.; Chen DeLi, C.D.; Li HuiLin, L.H.; Edis, R.; Walker, C. Comparison of the ability of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP to reduce nitrification and N2O emissions from nitrogen fertilisers. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soils Science, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Li, D.P.; Wu, Z.J.; Xue, Y.; Song, Y.C.; Xiao, F.R.; Zhang, L.L.; Gong, P.; Zhang, K. Effects of nitrification inhibitors on nitrogen dynamics and ammonia oxidizers in three black agricultural soils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralbo, F.; Menéndez, S.; Barrena, I.; Estavillo, J.M.; Marino, D.; González-Murua, C. Dimethyl pyrazol-based nitrification inhibitors effect on nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria to mitigate N2O emission. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.H.; Bai, X.; Fenton, O.; Tang, B.B.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cao, W.C.; Ding, S.; Liu, R.; et al. Extracellular enzyme patterns provide new insights regarding nitrogen transformation induced by alkaline amendment of acidic soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hayden, H.L.; Suter, H.; Hu, H.W.; Lam, S.K.; He, J.Z.; Mele, P.M.; Chen, D.L. The effect of temperature and moisture on the source of N2O and contributions from ammonia oxidizers in an agricultural soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R.; Halvorson, A.D.; Reule, C.A.; Liu, X.J.J. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in irrigated cropping systems in northeastern Colorado. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, A.S.F.; Rocha, S.M.B.; Dos Santos, V.M.; Singh, R.P.; Schmidt, R.; Scow, K.M. Abundance of ammonia-oxidizing organisms across a gradient of preserved Brazilian Cerrado. Trop. Ecol. 2017, 58, 653–661. [Google Scholar]
- Orschler, L.; Agrawal, S.; Lackner, S. Lost in translation: The quest for Nitrosomonas cluster 7-specific amoA primers and TaqMan probes. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.L.; Shan, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.Q.; Yan, X.Y. Variable responses of nitrification and denitrification in a paddy soil to long-term biochar amendment and short-term biochar addition. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, S.A.; Juniper, S.K. Capturing compositional variation in denitrifying communities: A multiple-primer approach that includes epsilonproteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02753-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.X.; Zhu, Y.G.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Su, J.Q. QMEC: A tool for high-throughput quantitative assessment of microbial functional potential in C, N, P, and S biogeochemical cycling. Sci. China-Life Sci. 2018, 61, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throbäck, I.N.; Enwall, K.; Jarvis, Å.; Hallin, S. Reassessing PCR primers targeting nirS, nirK and nosZ genes for community surveys of denitrifying bacteria with DGGE. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 49, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. iMeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Ahmad, B.; Ahmad, A.; Zhang, Z.; Khan, D.; Muhammad, D.; Ali, A. Variations in soil physico-chemical properties, soil stocks, and soil stoichiometry under different soil layers, the major forest region Liupan Mountains of Northwest China. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e256565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.P.; Lian, J.; Luo, Y.Q.; Niu, Y.Y.; Gong, X.W. Spatial pattern of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen, and analysis of related factors in an agro-pastoral zone in Northern China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Q.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.C.; Gou, Y.X.; Zhuo, Z.Q. Role of environment variables in spatial distribution of soil C, N, P ecological stoichiometry in the typical black soil region of northeast China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Liang, Z.Z.; Webster, R.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhou, Y.; Teng, H.F.; Hu, B.F.; Arrouays, D.; Shi, Z. A high-resolution map of soil pH in China made by hybrid modelling of sparse soil data and environmental covariates and its implications for pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Guo, C.; Lü, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, R. Soil moisture and land use are major determinants of soil microbial community composition and biomass at a regional scale in northeastern China. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, S.; Ou, J.T.; Tang, J.F.; Lu, Y.; Wei, Y.J. Investigation of soil microbiota reveals variable dominant species at different land areas in China. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2022, 36, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhu, H.L.; Shahtahmassebi, A.R.; Qiu, L.F.; Wu, C.F.; Shen, Z.Q.; Wang, K. Spatiotemporal variability of soil nitrogen in relation to environmental factors in a low hilly region of southeastern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Guo, X.D.; Fu, B.J.; Lian, G.; Wang, J. The effect of environmental variables on soil characteristics at different scales in the transition zone of the Loess Plateau in China. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachtsevani, E.; Papazlatani, C.V.; Rousidou, C.; Lampronikou, E.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Nicol, G.W.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Papadopoulou, E.S. Effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on the activity and diversity of the soil microbial community under contrasting soil pH. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.D.; Ju, X.T.; Zhang, J.B.; Müller, C.; Rees, R.M.; Thorman, R.E.; Sylvester-Bradley, R. Effects of the nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate) on gross N transformation rates and N2O emissions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, G.; Marsden, K.A.; Vallejo, A.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R. Determining the influence of environmental and edaphic factors on the fate of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, M.H.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Lukman, S.; Bukhari, A. Integrated electrokinetics-adsorption remediation of saline-sodic soils: Effects of voltage gradient and contaminant concentration on soil electrical conductivity. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 618495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, H.G.; Ha, T.H.; Bae, J.H. Effect of electrode materials on electrokinetic reduction of soil salinity. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.J.; Dai, T.J.; Tian, J.P.; Wen, D.H. The influence of salinity on the abundance, transcriptional activity, and diversity of AOA and AOB in an estuarine sediment: A microcosm study. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9825–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erguder, T.H.; Boon, N.; Wittebolle, L.; Marzorati, M.; Verstraete, W. Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Jin, C.; Sun, B. Soil aggregate stratification of nematodes and ammonia oxidizers affects nitrification in an acid soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.D.; Bottomley, P.J.; Myrold, D.D. Contributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria to nitrification in Oregon forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 85, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.W.; Macdonald, C.A.; Trivedi, P.; Holmes, B.; Bodrossy, L.; He, J.Z.; Singh, B.K. Water addition regulates the metabolic activity of ammonia oxidizers responding to environmental perturbations in dry subhumid ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourna, M.; Freitag, T.E.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I. Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessén, E.; Söderström, M.; Stenberg, M.; Bru, D.; Hellman, M.; Welsh, A.; Thomsen, F.; Klemedtson, L.; Philippot, L.; Hallin, S. Spatial distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across a 44-hectare farm related to ecosystem functioning. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Ling, N.; Chen, H.; Zhu, C.; Kong, Y.L.; Wang, M.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, S.W. Distinct drivers of activity, abundance, diversity and composition of ammonia-oxidizers: Evidence from a long-term field experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantera, J.J.L.; Jordan, F.L.; Stein, L.Y. Effects of irrigation sources on ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in a managed turf-covered aridisol. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 43, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, N.S.; Nelson, K.A.; Bush, A.; Bernhard, A.E. Distribution and diversity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizers in salt marsh sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7461–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysgaard, S.; Thastum, P.; Dalsgaard, T.; Christensen, P.B.; Sloth, N.P. Effects of salinity on NH4+ adsorption capacity, nitrification, and denitrification in Danish estuarine sediments. Estuaries 1999, 22, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site | Number | Climate Type | Annual Mean Temperature (°C) | Mean Annual Precipitation (mm) | Grow Crops | Soil Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianshui | TS | Warm temperate semi-humid semi-arid climate | 11.04 | 612.23 | Apple | Loessal soil |
| Shihezi | SHZ | Temperate continental climate | 7.42 | 235.25 | Cotton | Desert gray soil |
| Heze | HZ | Warm temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate | 15.35 | 583.43 | Maize | Moisture soil |
| Daxing | DX | Warm temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate | 11.89 | 408.02 | Pepper | Moisture soil |
| Siping | SP | Temperate monsoon climate | 7.90 | 657.20 | Maize | Chernozem |
| Hunan | HN | Subtropical monsoon humid climate | 17.65 | 1286.30 | Rice | Paddy soil |
| Site | pH | EC (μS·cm−1) | SOM (g·kg−1) | SOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | C/N | AP (mg·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | 7.88 ± 0.13 a # | 326.00 ± 75.51 a | 15.34 ± 1.35 cd | 8.90 ± 0.78 cd | 0.85 ± 0.01 b | 10.51 ± 0.80 ab | 8.51 ± 0.69 e | 29.17 ± 0.44 d |
| SHZ | 7.79 ± 0.03 a | 261.33 ± 15.45 a | 20.35 ± 0.73 cd | 11.80 ± 0.42 cd | 1.04 ± 0.00 b | 11.36 ± 0.40 a | 15.31 ± 2.36 de | 220.84 ± 3.08 b |
| HZ | 7.99 ± 0.38 a | 217.33 ± 2.40 ab | 10.27 ± 0.61 d | 5.96 ± 0.35 d | 0.86 ± 0.12 b | 6.93 ± 0.52 b | 36.71 ± 1.94 b | 163.88 ± 15.94 bc |
| DX | 7.74 ± 0.04 a | 264.67 ± 12.60 a | 42.91 ± 3.44 b | 24.89 ± 2.00 b | 2.87 ± 0.26 a | 9.12 ± 0.54 ab | 123.64 ± 2.27 a | 404.18 ± 33.48 a |
| SP | 6.13 ± 0.09 b | 71.73 ± 0.82 b | 22.93 ± 0.89 c | 13.30 ± 0.51 c | 1.05 ± 0.08 b | 12.79 ± 1.34 a | 22.36 ± 0.54 cd | 99.44 ± 7.61 cd |
| HN | 4.44 ± 0.07 c | 101.53 ± 1.43 b | 58.56 ± 3.87 a | 33.97 ± 2.25 a | 2.72 ± 0.01 a | 12.49 ± 0.82 a | 27.68 ± 0.21 c | 58.31 ± 2.08 d |
| Soil Site | NH4+_RA (%) | NNR_IR (%) | N2O_ERR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TS | 65.37 ± 9.73 a # | 70.23 ± 2.08 a | 82.51 ± 0.31 a |
| SHZ | 27.17 ± 9.32 a | 63.57 ± 1.99 ab | 55.97 ± 0.02 b |
| HZ | 61.27 ± 6.52 a | 71.45 ± 0.96 a | 28.91 ± 0.80 c |
| DX | 27.01 ± 4.01 a | 18.77 ± 2.92 b | 51.30 ± 2.22 b |
| SP | 63.43 ± 6.76 a | 64.28 ± 1.69 ab | 7.93 ± 0.88 e |
| HN | −71.15 ± 14.10 b | 44.40 ± 23.46 ab | 18.54 ± 0.63 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, T.; Lei, J.; Fan, Q.; Liu, R. Soil Factors Key to 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP) Efficacy: EC and SOC Dominate over Biotic Influences. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091787
Guan T, Lei J, Fan Q, Liu R. Soil Factors Key to 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP) Efficacy: EC and SOC Dominate over Biotic Influences. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(9):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091787
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Tikun, Jilin Lei, Qianyi Fan, and Rui Liu. 2024. "Soil Factors Key to 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP) Efficacy: EC and SOC Dominate over Biotic Influences" Microorganisms 12, no. 9: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091787
APA StyleGuan, T., Lei, J., Fan, Q., & Liu, R. (2024). Soil Factors Key to 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP) Efficacy: EC and SOC Dominate over Biotic Influences. Microorganisms, 12(9), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091787






