A Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Varicella-Zoster Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation of Positive CSF Samples
2.2. Extraction of Viral Nucleic Acid
2.2.1. Standard Method for the Extraction of Viral Nucleic Acid
2.2.2. Fully Automated Method for the Extraction of Viral Nucleic Acid
2.3. Performing Probe-Based qPCRs on the Fully Automated Platform
2.4. Performing Digital PCR for the Determination of Viral Load in Prepared Positive CSF Samples
2.5. Analysis of the Limit of Detection (LoD)
3. Results
3.1. Generation of Consensus Sequences and Primer Design
3.2. Optimization of Probe Concentration
3.3. Multiplexing of the Individual PCR Assays
3.4. Assessment of Performance
3.5. Clinical Performance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van de Beek, D.; de Gans, J.; Spanjaard, L.; Weisfelt, M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Vermeulen, M. Clinical features and prognostic factors in adults with bacterial meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, T.; Salazar, L.; Hasbun, R. Acute versus subacute community-acquired meningitis: Analysis of 611 patients. Medicine 2017, 96, e7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, P.K. Overview of acute and chronic meningitis. Neurol. Clin. 1999, 17, 691–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, R.S.W. A Narrative Review of the Molecular Epidemiology and Laboratory Surveillance of Vaccine Preventable Bacterial Meningitis Agents: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus agalactiae. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, F.; Griffiths, M.J.; Bonnett, L.J.; Geretti, A.M.; Michael, B.D.; Beeching, N.J.; McKee, D.; Scarlett, P.; Hart, I.J.; Mutton, K.J.; et al. Incidence, aetiology, and sequelae of viral meningitis in UK adults: A multicentre prospective observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerbrei, A.; Eichhorn, U.; Hottenrott, G.; Wutzler, P. Virological diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. J. Clin. Virol. 2000, 17, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.R.; Sasidharan, A.; Harrison, C.J.; Selvarangan, R. Disruption of seasonal enterovirus and parechovirus detections in the CSF and plasma of children during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Clin. Virol. 2023, 160, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, A.; Banerjee, D.; Harrison, C.J.; Selvarangan, R. Emergence of Parechovirus A3 as the Leading Cause of Central Nervous System Infection, Surpassing Any Single Enterovirus Type, in Children in Kansas City, Missouri, USA, from 2007 to 2016. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02935-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeren, K.; Bottcher, S.; Diedrich, S. Enterovirus Surveillance (EVSurv) in Germany. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volle, R.; Bailly, J.L.; Mirand, A.; Pereira, B.; Marque-Juillet, S.; Chambon, M.; Regagnon, C.; Brebion, A.; Henquell, C.; Peigue-Lafeuille, H.; et al. Variations in cerebrospinal fluid viral loads among enterovirus genotypes in patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed meningitis due to enterovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupila, L.; Vuorinen, T.; Vainionpaa, R.; Hukkanen, V.; Marttila, R.J.; Kotilainen, P. Etiology of aseptic meningitis and encephalitis in an adult population. Neurology 2006, 66, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, R.; Kim, G.M.; Jo, I.J.; Sim, M.S.; Song, K.J.; Kim, B.J.; Na, D.L.; Huh, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Ki, C.S.; et al. Incidence and clinical features of herpes simplex viruses (1 and 2) and varicella-zoster virus infections in an adult Korean population with aseptic meningitis or encephalitis. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiainen, T.; Prevots, R.; Izurieta, H.S.; Abramson, J.; Bilynsky, R.; Bonhoeffer, J.; Bonnet, M.C.; Center, K.; Galama, J.; Gillard, P.; et al. Aseptic meningitis: Case definition and guidelines for collection, analysis and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5793–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, G.; Pankow, S.; Bard, J.D.; Yee, R.; Nigo, M.; Hasbun, R. Distinguishing cytomegalovirus meningoencephalitis from other viral central nervous system infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 142, 104936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Ruiz, M.; Navarro-Mari, J.M.; Sanchez-Seco, M.P.; Gegundez, M.I.; Palacios, G.; Savji, N.; Lipkin, W.I.; Fedele, G.; de Ory-Manchon, F. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-associated meningitis, southern Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.; Bachmann, F.; Choi, M.; Kurvits, L.; Schmidt, M.L.; Bergfeld, L.; Meier, I.; Zuchowski, M.; Werber, D.; Hofmann, J.; et al. Autochthonous West Nile virus infection in Germany: Increasing numbers and a rare encephalitis case in a kidney transplant recipient. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovic, P.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, R. Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in children in Europe: Epidemiology, clinical outcome and comparison of vaccination recommendations. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, Y.Y.; Balasuriya, U.B.; Lee, C.K. Zoonotic encephalitides caused by arboviruses: Transmission and epidemiology of alphaviruses and flaviviruses. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2014, 3, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscher, C.; Patzina-Mehling, C.; Melchert, J.; Graff, S.L.; McFarland, S.E.; Hieke, C.; Kopp, A.; Prasser, A.; Tonn, T.; Schmidt, M.; et al. Ecological and clinical evidence of the establishment of West Nile virus in a large urban area in Europe, Berlin, Germany, 2021 to 2022. Euro Surveill. 2023, 28, 2300258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermance, M.E.; Thangamani, S. Powassan Virus: An Emerging Arbovirus of Public Health Concern in North America. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.R.; Tesh, R.B.; Rico-Hesse, R. Genetic variation of Japanese encephalitis virus in nature. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71 Pt 12, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, P.; Duong, V.; Boyer, S.; Burgess, G.; Williams, D.T.; Dussart, P.; Horwood, P.F. The Ecology and Evolution of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodilsen, J.; Dalager-Pedersen, M.; Schonheyder, H.C.; Nielsen, H. Time to antibiotic therapy and outcome in bacterial meningitis: A Danish population-based cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, D.P.; Hamilton, E.; Bodilsen, J.; Koster-Rasmussen, R.; Stockdale, A.J.; Miner, J.; Nielsen, H.; Dzupova, O.; Sethi, V.; Copson, R.K.; et al. Longer than 2 hours to antibiotics is associated with doubling of mortality in a multinational community-acquired bacterial meningitis cohort. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Abdel-Hadi, C.; Buhler, R.; Grabein, B.; Linn, J.; Nau, R.; Salzberger, B.; Schluter, D.; Schwager, K.; Tumani, H.; et al. German guidelines on community-acquired acute bacterial meningitis in adults. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2023, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.; Meyer-Konig, U.; Hufert, F.T. Rapid detection of herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus infections by real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boving, M.K.; Pedersen, L.N.; Moller, J.K. Eight-plex PCR and liquid-array detection of bacterial and viral pathogens in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with suspected meningitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Chai, C.N.; Capinpin, S.M.; Ang, A.; Ng, S.Y.; Lee, P.L.; Ng, C.W.S.; Yan, G.; Lee, H.K.; Chiu, L.L.; et al. Evaluation of the Luminex ARIES HSV 1&2 Assay and Comparison with the FTD Neuro 9 and In-house Real-Time PCR Assays for Detecting Herpes Simplex Viruses. Ann. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrago, D.; Mateos, M.L.; Avellon, A.; Perez-Vazquez, M.D.; Tenorio, A. Quantitation of cytomegalovirus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid and serum specimens from AIDS patients using a novel highly sensitive nested competitive PCR and the cobas amplicor CMV monitor. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, R.K.; Arav-Boger, R.; Marr, K.A.; Kraus, E.; Shoham, S.; Lees, L.; Trollinger, B.; Shah, P.; Ambinder, R.; Neofytos, D.; et al. Outcomes in Transplant Recipients Treated With Foscarnet for Ganciclovir-Resistant or Refractory Cytomegalovirus Infection. Transplantation 2016, 100, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, R.J.; Blum, M.R.; Barton, N.; de Miranda, P. Pharmacokinetics of acyclovir in humans following intravenous administration. A model for the development of parenteral antivirals. Am. J. Med. 1982, 73, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagstaff, A.J.; Faulds, D.; Goa, K.L. Aciclovir. A reappraisal of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 1994, 47, 153–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.M.; Mori, M.; Gleaves, C.A.; Du Mond, C.; Cays, M.; Ebeling, D.F.; Buhles, W.C.; DeArmond, B.; Meyers, J.D. Early treatment with ganciclovir to prevent cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, B.A.; Baron, J. The pharmacokinetic basis of oral valacyclovir treatment of herpes simplex virus (HSV) or varicella zoster virus (VZV) meningitis, meningoencephalitis or encephalitis in adults. J. Chemother. 2017, 29, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutner, K.R.; Friedman, D.J.; Forszpaniak, C.; Andersen, P.L.; Wood, M.J. Valaciclovir compared with acyclovir for improved therapy for herpes zoster in immunocompetent adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; Sample, H.A.; Zorn, K.C.; Arevalo, S.; Yu, G.; Neuhaus, J.; Federman, S.; Stryke, D.; Briggs, B.; Langelier, C.; et al. Clinical Metagenomic Sequencing for Diagnosis of Meningitis and Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnicker, M.J.; Espy, M.J.; Irish, C.L. Rapid and direct detection of herpes simplex virus in cerebrospinal fluid by use of a commercial real-time PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4361–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaugon, E.; Mircescu, A.; Caya, C.; Yao, M.; Gore, G.; Dendukuri, N.; Papenburg, J. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid one-step PCR assays for detection of herpes simplex virus-1 and -2 in cerebrospinal fluid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, A.; Bergstrom, T.; Lindh, M.; Namvar, L.; Studahl, M. Varicella-zoster virus CNS disease—Viral load, clinical manifestations and sequels. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, P.; Relich, R.F.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Dunn, J.J.; Granato, P.A.; Harrington, A.T.; Hansen, G.T.; Ledeboer, N.A.; Li, Q.; Sims, M.D.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of the Simplexa VZV Direct Assay for Detection of Varicella-Zoster Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Lesion-Swab Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0235521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishat H, A.; Gita, S.; Chawla, R.; Tandon, R. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Herpes Simplex Viruses Type-1 and Type-2, Cytomegalovirus, Varicella-zoster Virus, and Adenovirus in Ocular Viral Infections. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2021, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kimura, T.; Fujiki, K.; Sakuma, H.; Murakami, A.; Kanai, A. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction for detection of herpes simplex virus type 1, type 2, cytomegalovirus, and varicella-zoster virus in ocular viral infections. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 47, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI Virus. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/virus/vssi/#/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Leber, A.L.; Everhart, K.; Balada-Llasat, J.M.; Cullison, J.; Daly, J.; Holt, S.; Lephart, P.; Salimnia, H.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; DesJarlais, S.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of BioFire FilmArray Meningitis/Encephalitis Panel for Detection of Bacteria, Viruses, and Yeast in Cerebrospinal Fluid Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundelin, T.; Bialas, J.; de Diego, J.; Hermanowski, M.; Leibhan, H.; Ponderand, L.; Juanola-Falgarona, M.; Jones, T.; Rey, M.; Johnson, S.; et al. Evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx Meningitis/Encephalitis Panel, a multiplex PCR platform for the detection of community-acquired meningoencephalitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 61, e0042623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnamohan, V.M.; Cunningham, A.L.; Rawlinson, W.D. Removal of inhibitors of CSF-PCR to improve diagnosis of herpesviral encephalitis. J. Virol. Methods 1998, 72, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennett, C.; Klapper, P.E.; Cleator, G.M.; Lewis, A.G. CSF pretreatment and the diagnosis of herpes encephalitis using the polymerase chain reaction. J. Virol. Methods 1991, 34, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleines, M.; Scheithauer, S.; Schiefer, J.; Hausler, M. Clinical application of viral cerebrospinal fluid PCR testing for diagnosis of central nervous system disorders: A retrospective 11-year experience. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 80, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, G.; Puerta-Alcalde, P.; Vergara, A.; Roses, E.; Bosch, J.; Casals-Pascual, C.; Soriano, A.; Marcos, M.A.; Sanz, S.; Vila, J. An Assessment of a New Rapid Multiplex PCR Assay for the Diagnosis of Meningoencephalitis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, A.M.; Edelstein, P.H.; Alby, K. Development and optimization of a real-time PCR assay for detection of herpes simplex and varicella-zoster viruses in skin and mucosal lesions by use of the BD Max open system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4375–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutzhard, J.; Merete Riedel, H.; Zweygberg Wirgart, B.; Grillner, L. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1, herpes simplex virus type 2 and varicella-zoster virus in skin lesions. Comparison of real-time PCR, nested PCR and virus isolation. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 29, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson-Peters, J.; O’Loughlin, P.; Toye, P. Development of an internally controlled, homogeneous polymerase chain reaction assay for the simultaneous detection and discrimination of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and varicella-zoster virus. Mol. Cell Probes 2007, 21, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Step | Cycles | Duration | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 min | 50 °C | ||
| Initial activation | 1 | 4 min | 95 °C |
| Denaturation | 50 | 6 s | 95 °C |
| Annealing | 19 s | 60 °C |
| Step | Cycles | Duration | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial activation | 1 | 2 min | 95 °C |
| 1. PCR Step | 40 | 15 s | 95 °C |
| 1 min | 60 °C | ||
| 2. PCR Step | 5 | 15 s | 95 °C |
| 1 min | 60 °C | ||
| Cooling | 1 | 30 s | 40 °C |
| Primer/Probe | Sequence | 5′Modification | 3′Modification |
|---|---|---|---|
| T-HSV-Fw | CCTGGAGGTGCGGTTGATAA | - | - |
| T-HSV-Rv | AGAAAAAGTACATCGGCGTCATCT | - | - |
| T-HSV-So | CCAGATCCACGCCCTTGATGAGCAT | FAM | BHQ1 |
| T-CMV-2-Fw | GCGGTTCGGGCACTAGTTC | - | - |
| T-CMV-2 Rv | CAGCGCAGCTACTTTTACTGTGA | - | - |
| T-CMV So | CAATGACCTCACGCAGCCTATCGGTG | ATTO565 | BHQ2 |
| T-VZV Fw | CAGTACRTTGCATAACCTGTCCAT | - | - |
| T-VZV Rv | GCCACGATCCCGGAGAA | - | - |
| T-VZV So | CATTTTCAGTTGCGCGGACGCC | ATTO647N | BHQ2 |
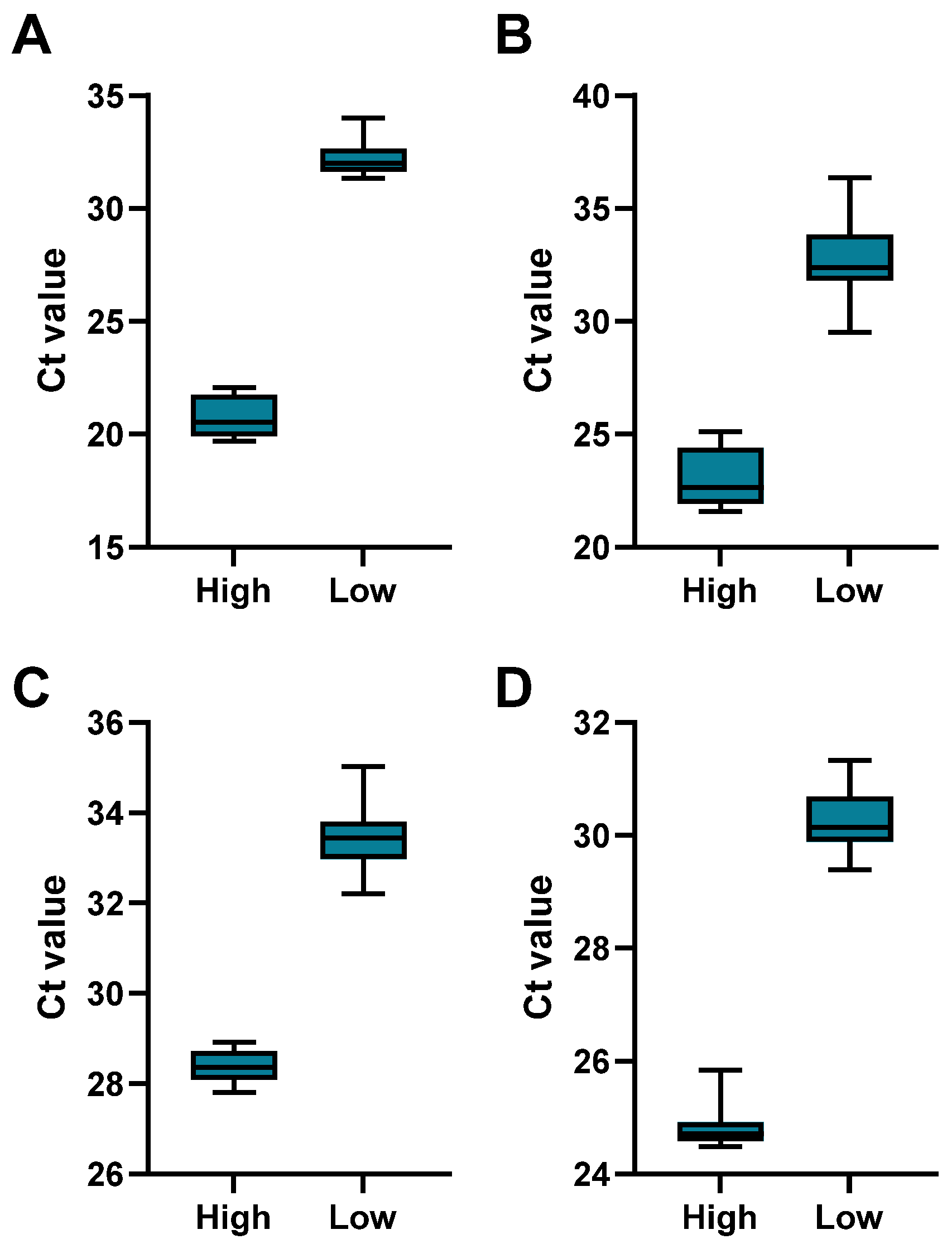
| Analyte | Concentration | Minimum | Maximum | Range | Mean | Std. Deviation | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSV-1 | Low | 31.34 | 34.00 | 2.66 | 32.22 | 0.76 | 2.36 |
| High | 19.69 | 22.08 | 2.39 | 20.72 | 0.87 | 4.21 | |
| HSV-2 | Low | 29.50 | 36.37 | 6.87 | 32.67 | 1.79 | 5.47 |
| High | 21.59 | 25.13 | 3.54 | 23.00 | 1.25 | 5.43 | |
| CMV | Low | 32.20 | 35.03 | 2.83 | 33.47 | 0.71 | 2.12 |
| High | 27.81 | 28.92 | 1.11 | 28.37 | 0.34 | 1.20 | |
| VZV | Low | 29.39 | 31.33 | 1.94 | 30.28 | 0.55 | 1.81 |
| High | 24.48 | 25.84 | 1.36 | 24.81 | 0.36 | 1.44 |
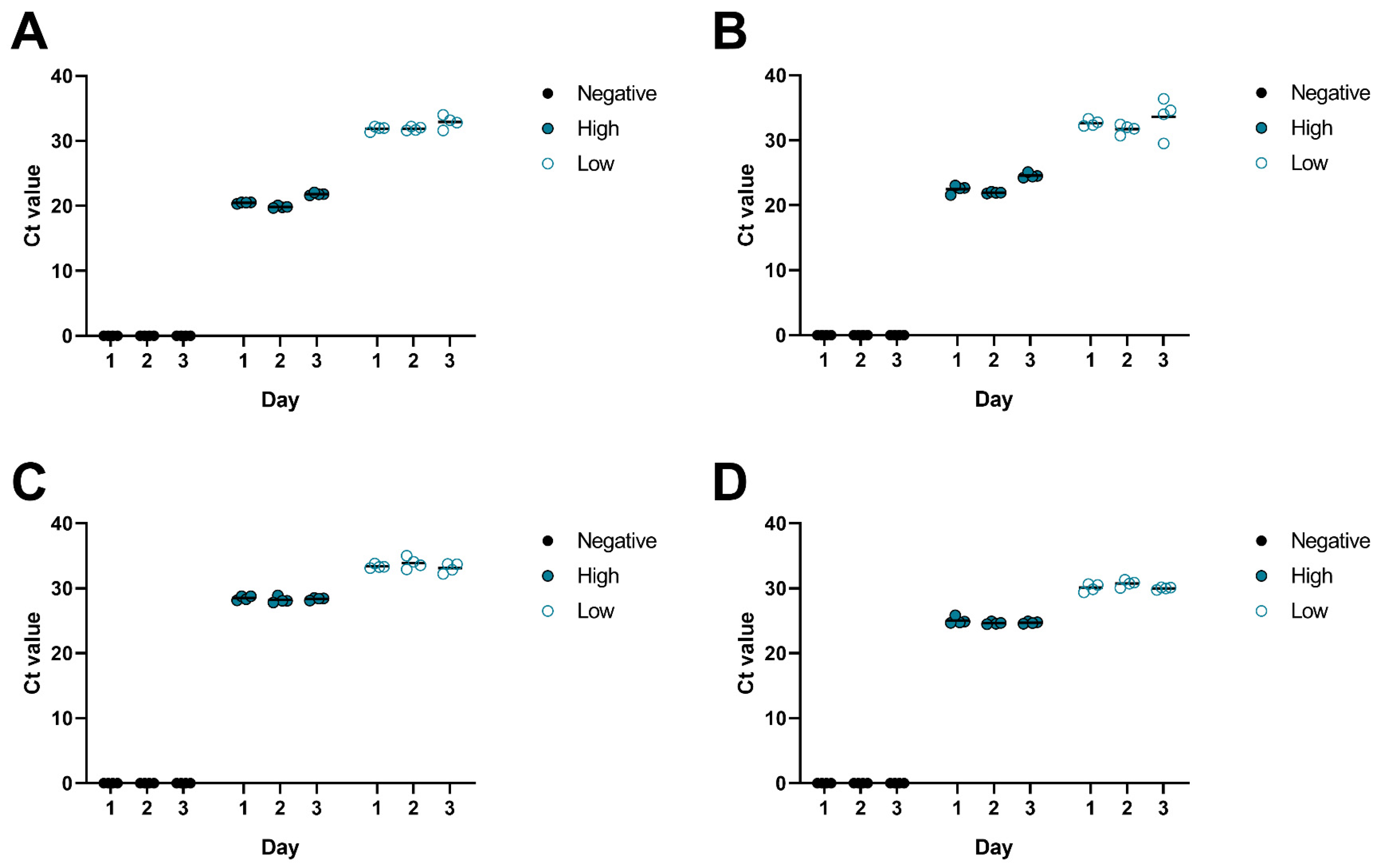
| Analyte | Concentration | Mean Day 1 | Mean Day 2 | Mean Day 3 | Range of Means | Grand Mean | Std. Deviation of Means | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSV-1 | Low | 31.88 | 31.89 | 32.90 | 1.02 | 32.22 | 0.59 | 1.82 |
| High | 20.48 | 19.85 | 21.83 | 1.98 | 20.72 | 1.01 | 4.88 | |
| HSV-2 | Low | 32.66 | 31.73 | 33.62 | 1.89 | 32.67 | 0.95 | 2.89 |
| High | 22.49 | 21.94 | 24.58 | 2.64 | 23.00 | 1.39 | 6.06 | |
| CMV | Low | 33.39 | 33.90 | 33.13 | 0.77 | 33.47 | 0.39 | 1.17 |
| High | 28.51 | 28.22 | 28.38 | 0.29 | 28.37 | 0.15 | 0.51 | |
| VZV | Low | 30.10 | 30.74 | 30.00 | 0.74 | 30.28 | 0.40 | 1.33 |
| High | 25.04 | 24.66 | 24.73 | 0.38 | 24.81 | 0.20 | 0.81 |
| Sample | Virus | Ct (Control Device—Allplex Meningitis Panel Assay V1) | Ct (Test Device—Meningitis-LDT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HSV-1 | 29.45 | 24.11 |
| 2 | VZV | 29.00 | 25.45 |
| 3 | VZV | 27.05 | 21.44 |
| 4 | VZV | 33.16 | 26.06 |
| 5 | VZV | 33.54 | 26.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luzius, T.; Jeske, S.D.; Baer, J.; Goelnitz, U.; Protzer, U.; Wettengel, J.M. A Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Varicella-Zoster Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010111
Luzius T, Jeske SD, Baer J, Goelnitz U, Protzer U, Wettengel JM. A Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Varicella-Zoster Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuzius, Tatjana, Samuel D. Jeske, Julia Baer, Uta Goelnitz, Ulrike Protzer, and Jochen M. Wettengel. 2025. "A Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Varicella-Zoster Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010111
APA StyleLuzius, T., Jeske, S. D., Baer, J., Goelnitz, U., Protzer, U., & Wettengel, J. M. (2025). A Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Varicella-Zoster Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Microorganisms, 13(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010111







