Diet Supplementation with Pomegranate Fruit Alters Distal Gut Microbiota of Healthy Female College Students
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Data and Sample Collection
2.3. Isolation of Genomic DNA and High-Throughput DNA Sequencing
2.4. Prebiotic Index Calculation
2.5. Measurements of Urinary Polyphenols and Creatinine
2.6. Statistical Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Diet Supplementation with Fresh Pomegranate
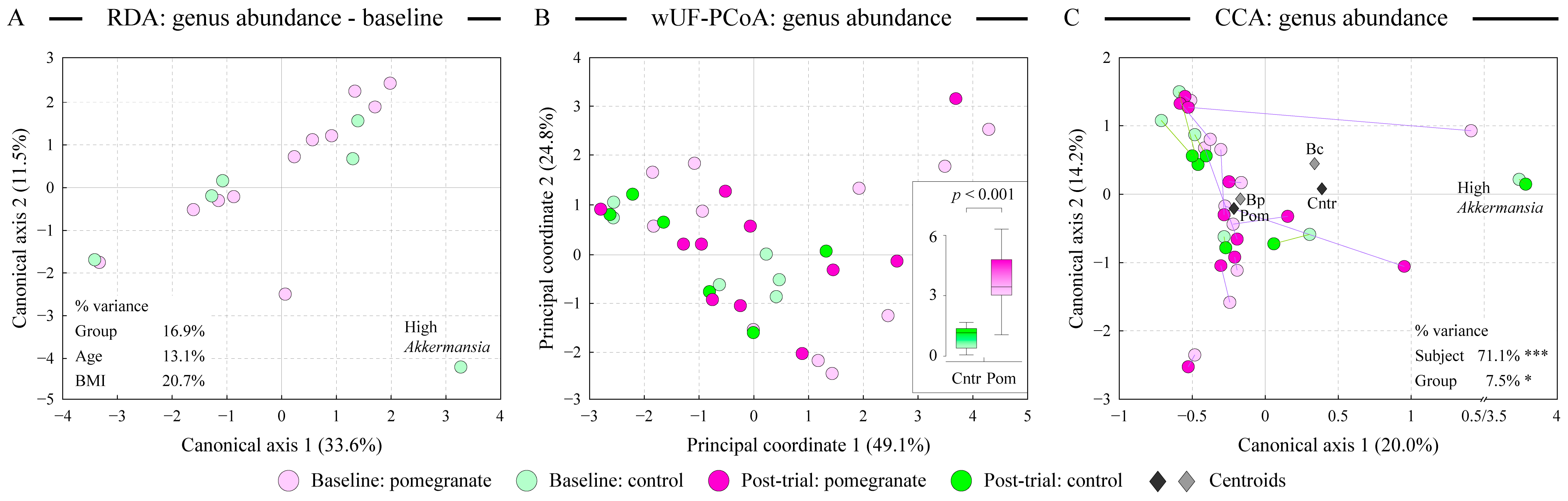
3.2. Daily Consumption of Fresh Pomegranate Alters Distal Gut Microbiota
3.3. Abundant Taxa of Egyptian Gut Microbiota
3.4. Many Genera Contribute to the Observed Alterations of Distal Gut Microbiota After Pomegranate Consumption
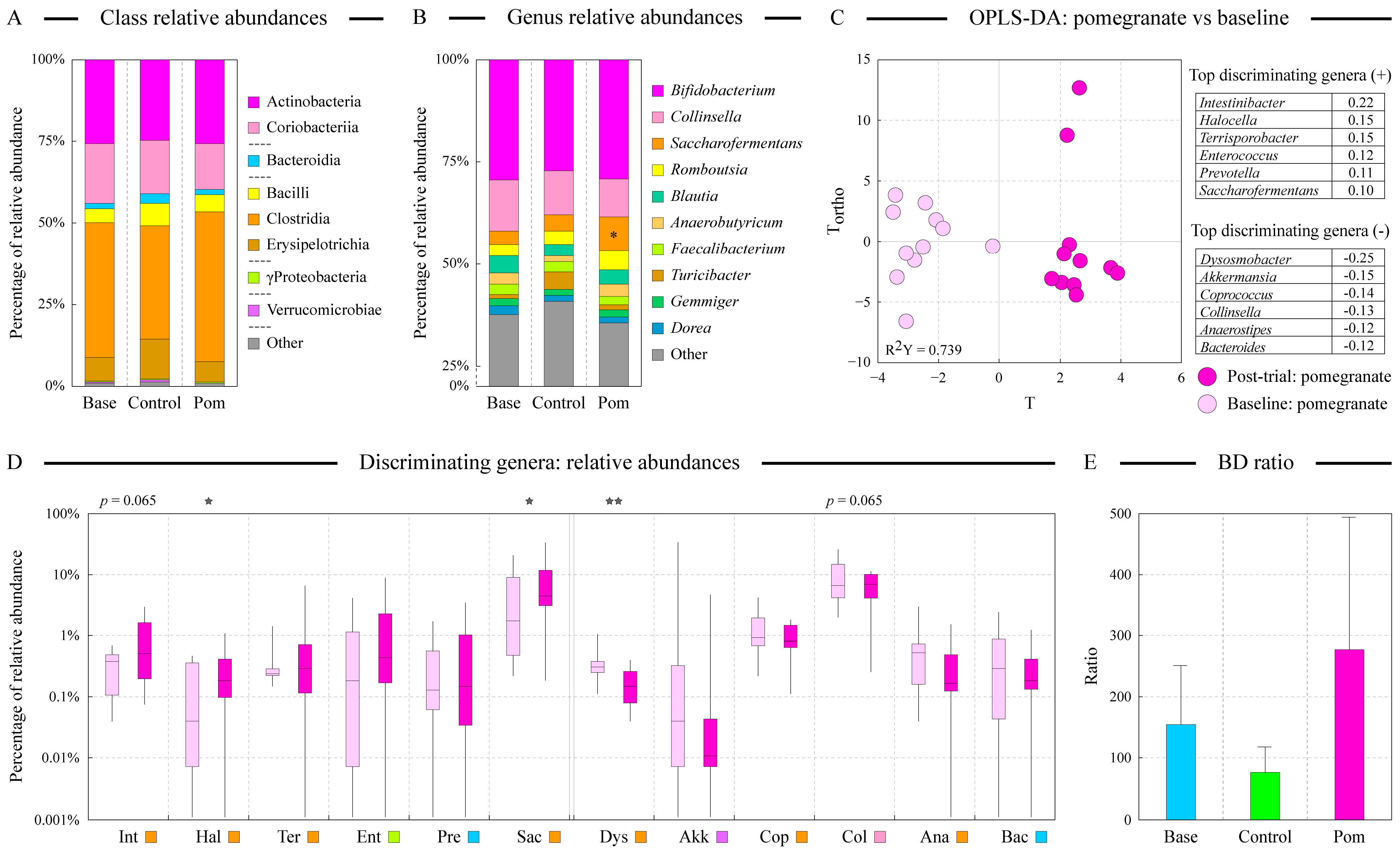
3.5. Pomegranate Supplementation Promotes Beneficial Microbial Communities
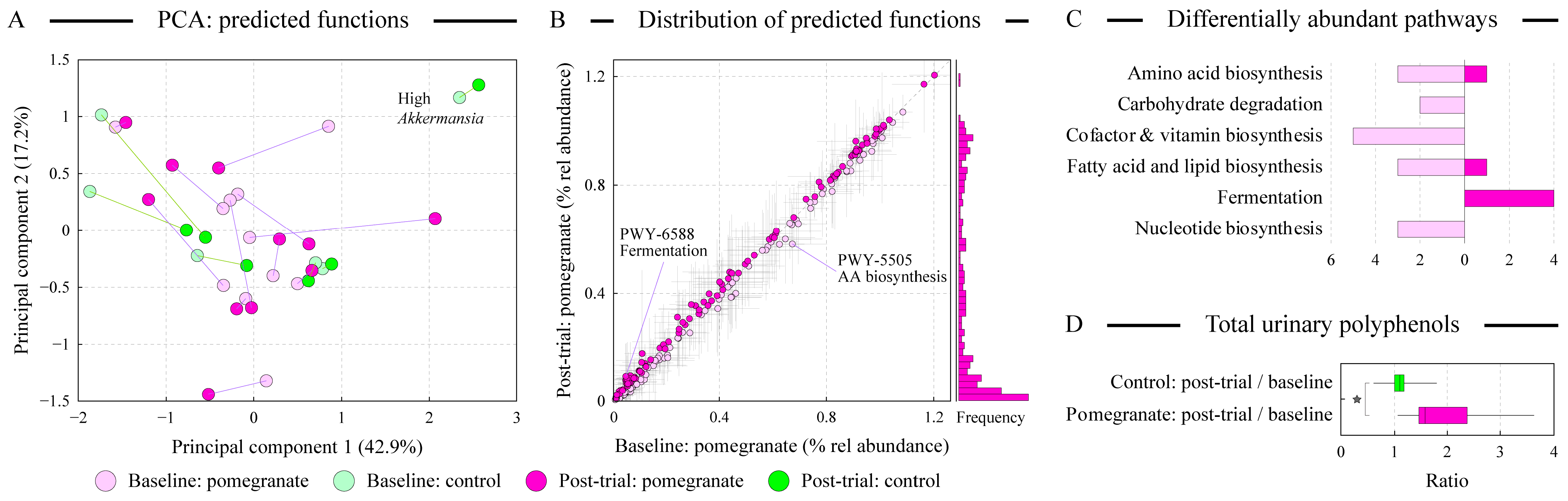
3.6. Alterations in Predicted Microbial Functions upon Pomegranate Consumption
3.7. The Magnitude of Microbiota Alterations Correlates with the Increase in Urinary Polyphenols
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaglan, P.; Buttar, H.S.; Al-bawareed, O.A.; Chibisov, S.; Singh, R.B.; Watanabe, S.; Isaza, A.A. Potential health benefits of selected fruits: Apples, blueberries, grapes, guavas, mangos, pomegranates, and tomatoes. In Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals in Metabolic and Non-Communicable Diseases; Singh, R.B., Watanabe, S., Isaza, A.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- Kozłowska, A.; Szostak-Węgierek, D. Flavonoids—Food Sources, Health Benefits, and Mechanisms Involved. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J.-M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, M.T.; Moustafa, A.; Hussein, L.; Romeilah, R.; Gouda, M. In-vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of selected fruit and vegetable juices and fermented dairy products commonly consumed in Egypt. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 547–550. [Google Scholar]
- Vučić, V.; Grabež, M.; Trchounian, A.; Arsić, A. Composition and Potential Health Benefits of Pomegranate: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.; Hussein, L.; Wilson, D.; Buttar, H. Multiple Therapeutic Applications of Pomegranate Fruit and its Bioactive Phytochemicals in Health and Disease. In Biomedical Research, Medicine, and Disease; Sobti, R.C., Sobti, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 605–620. [Google Scholar]
- Seeram, N.P.; Adams, L.S.; Henning, S.M.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nair, M.G.; Heber, D. In vitro antiproliferative, apoptotic and antioxidant activities of punicalagin, ellagic acid and a total pomegranate tannin extract are enhanced in combination with other polyphenols as found in pomegranate juice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Germano, P.M.; Oh, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Lee, R.; Paige, H.; Yang, S.; Henning, S.M.; Zhong, J.; et al. Pomegranate Extract Improves Colitis in IL-10 Knockout Mice Fed a High Fat High Sucrose Diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banihani, S.A.; Makahleh, S.M.; El-Akawi, Z.; Al-Fashtaki, R.A.; Khabour, O.F.; Gharibeh, M.Y.; Saadah, N.A.; Al-Hashimi, F.H.; Al-Khasieb, N.J. Fresh pomegranate juice ameliorates insulin resistance, enhances β-cell function, and decreases fasting serum glucose in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojadinovic, M.I.; Arsic, A.C.; Debeljak-Martacic, J.D.; Konic-Ristic, A.I.; Kardum, N.D.; Popovic, T.B.; Glibetic, M.D. Consumption of pomegranate juice decreases blood lipid peroxidation and levels of arachidonic acid in women with metabolic syndrome. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.; Moustafa, A.F.I.; Hussein, L.; Hamza, M. Three week dietary intervention using apricots, pomegranate juice or/and fermented sour sobya and impact on biomarkers of antioxidative activity, oxidative stress and erythrocytic glutathione transferase activity among adults. Nutr. J. 2015, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, L.; Abdel-Rahim, E.A.; Afify, A.E.-M.M.R.; El-arab, A.E.; Labib, E.H. Effectiveness of Apricots (Prunus armeniaca), Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Juice and Lactic Acid Fermented Sobya on Plasma Levels of Lipid Profile Parameters and Total Homocysteine among Egyptian Adults. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 05, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, L.; Gouda, M.; Buttar, H.S. Pomegranate, its Components, and Modern Deliverable Formulations as Potential Botanicals in the Prevention and Treatment of Various Cancers. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Summanen, P.H.; Komoriya, T.; Henning, S.M.; Lee, R.-P.; Carlson, E.; Heber, D.; Finegold, S.M. Pomegranate ellagitannins stimulate growth of gut bacteria in vitro: Implications for prebiotic and metabolic effects. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullon, B.; Pintado, M.E.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Assessment of polyphenolic profile and antibacterial activity of pomegranate peel (Punica granatum) flour obtained from co-product of juice extraction. Food Control 2016, 59, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialonska, D.; Ramnani, P.; Kasimsetty, S.G.; Muntha, K.R.; Gibson, G.R.; Ferreira, D. The influence of pomegranate by-product and punicalagins on selected groups of human intestinal microbiota. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 140, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Villalba, R.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; Cortés-Martín, A.; Ávila-Gálvez, M.Á.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C.; González-Sarrías, A. Urolithins: A Comprehensive Update on their Metabolism, Bioactivity, and Associated Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, R.; Kuroiso, K.; Goto, S.; Shimizu, A. Isolation of Tannin-Degrading Lactobacilli from Humans and Fermented Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Ahmed, S.M.; Zakaria, N.H.; Baddour, N.M.; Header, D.A. Study of the gut microbiome in Egyptian patients with active ulcerative colitis. Rev. Gastroenterol. México 2023, 88, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Hussein, L.; Coward, A.; Jackson, S.J. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among Egyptian children: Impact of social background and effect on growth. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Hussein, L.; Yamamah, G.; Rawi, S. The impact of probiotic and/or honey supplements on gut permeability among Egyptian children. J. Nutr. Environ. Med. 2007, 16, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, I.S.; Zuckerman, M.J.; Nukajam, W.S.; Somasundaram, S.G.; Murphy, B.; Jenkins, A.P.; Crane, R.S.; Gregory, G.G. Geography of intestinal permeability and absorption. Gut 1999, 44, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haytowitz, D.B.; Ahuja, J.K.C.; Wu, X.; Somanchi, M.; Nickle, M.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Roseland, J.M.; Williams, J.R.; Patterson, K.Y.; Li, Y.; et al. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Legacy Release. 2019. Available online: https://www.sidalc.net/search/Record/dat-usda-us-article24661818/Description (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Sabraoui, T.; Khider, T.; Nasser, B.; Eddoha, R.; Moujahid, A.; Benbachir, M.; Essamadi, A. Determination of Punicalagins Content, Metal Chelating, and Antioxidant Properties of Edible Pomegranate (Punica granatum L) Peels and Seeds Grown in Morocco. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 8885889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakaruna, S.; Freedman, D.A.; Sehgal, A.R.; Bui, X.; Paliy, O. Diet quality and body mass indices show opposite associations with distal gut microbiota in a low-income cohort. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 846–851. [Google Scholar]
- Paliy, O.; Foy, B.D. Mathematical modeling of 16S ribosomal DNA amplification reveals optimal conditions for the interrogation of complex microbial communities with phylogenetic microarrays. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakaruna, S.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Kramer, D.L.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Paliy, O. Dietary Melanoidins from Biscuits and Bread Crust Alter the Structure and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production of Human Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigsbee, L.; Agans, R.; Foy, B.D.; Paliy, O. Optimizing the analysis of human intestinal microbiota with phylogenetic microarray. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 75, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agans, R.; Rigsbee, L.; Kenche, H.; Michail, S.; Khamis, H.J.; Paliy, O. Distal gut microbiota of adolescent children is different from that of adults. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 77, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakaruna, S.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Paliy, O. Human gut microbiota fermentation of cooked eggplant, garlic, and onion supports distinct microbial communities. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roura, E.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Estruch, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Total Polyphenol Intake Estimated by a Modified Folin–Ciocalteu Assay of Urine. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, M. Ueber den Niederschlag, welchen Pikrinsäure in normalem Harn erzeugt und über eine neue Reaction des Kreatinins. Biol. Chem. 1886, 10, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliy, O.; Shankar, V. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in microbial ecology. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1032–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, V.; Agans, R.; Paliy, O. Advantages of phylogenetic distance based constrained ordination analyses for the examination of microbial communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labib, E.; Blaut, M.; Hussein, L.; Goud, M.; Kramer, D.L.; Paliy, O.; Ganesh, B.; Schumann, P.; Pukall, R.; Woting, A.; et al. Molecular Diversity of Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids in Egyptian Adults Following Dietary Intervention with Fermented Sobya. J. Food Microbiol. Saf. Hyg. 2018, 3, 1000139. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Henning, S.M.; Lee, R.-P.; Lu, Q.-Y.; Summanen, P.H.; Thames, G.; Corbett, K.; Downes, J.; Tseng, C.-H.; Finegold, S.M.; et al. Pomegranate extract induces ellagitannin metabolite formation and changes stool microbiota in healthy volunteers. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharth, J.; Holway, N.; Parkinson, S.J. A Western Diet Ecological Module Identified from the ‘Humanized’ Mouse Microbiota Predicts Diet in Adults and Formula Feeding in Children. PLoS ONE 2014, 8, e83689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Lugli, G.A.; Turroni, F.; Ferrario, C.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Meta-analysis of the human gut microbiome from urbanized and pre-agricultural populations. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliy, O.; Rajakaruna, S. Development of Microbiota—Is the Process Continuing Through Adolescence? In Comprehensive Gut Microbiota; Glibetic, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Mahurkar, A.; Rahnavard, G.; Crabtree, J.; Orvis, J.; Hall, A.B.; Brady, A.; Creasy, H.H.; McCracken, C.; Giglio, M.G.; et al. Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2017, 550, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Dunngalvin, G.; Kern, T.; Blanco-Bose, W.; Auwerx, J.; Aebischer, P.; Rinsch, C. Direct supplementation with Urolithin A overcomes limitations of dietary exposure and gut microbiome variability in healthy adults to achieve consistent levels across the population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojarvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E.; et al. Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. Isme J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Bik, E.M.; Costello, E.K.; Dethlefsen, L.; Haque, R.; Relman, D.A.; Singh, U. Distinct distal gut microbiome diversity and composition in healthy children from Bangladesh and the United States. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Niu, L.; Zhang, Y. Saccharofermentans acetigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic bacterium isolated from sludge treating brewery wastewater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2735–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, J.; Fuentes, S.; Grievink, W.; van Niftrik, L.; Tindall, B.J.; Timmerman, H.M.; Rijkers, G.T.; Smidt, H. Characterization of Romboutsia ilealis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gastro-intestinal tract of a rat, and proposal for the reclassification of five closely related members of the genus Clostridium into the genera Romboutsia gen. nov., Intestinibacter gen. nov., Terrisporobacter gen. nov. and Asaccharospora gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1600–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.M.A.P.; Huch, M.; Abriouel, H.; Holzapfel, W.; Gálvez, A. Enterococci as probiotics and their implications in food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Li, X.H.; Chen, W.N. Similarities and differences in gut microbiome composition correlate with dietary patterns of Indian and Chinese adults. AMB Express 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. The Order Halanaerobiales, and the Families Halanaerobiaceae and Halobacteroidaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Firmicutes and Tenericutes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 153–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wright, K.; Davis, J.M.; Jeraldo, P.; Marietta, E.V.; Murray, J.; Nelson, H.; Matteson, E.L.; Taneja, V. An expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handwerger, S.; Horowitz, H.; Coburn, K.; Kolokathis, A.; Wormser, G.P. Infection Due to Leuconostoc Species: Six Cases and Review. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bandow, B.; Shaaban, E.S.; Rajakaruna, S.; Saleh, Z.; Abdelaziz, S.A.; Hussein, L.; Paliy, O. Diet Supplementation with Pomegranate Fruit Alters Distal Gut Microbiota of Healthy Female College Students. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020305
Bandow B, Shaaban ES, Rajakaruna S, Saleh Z, Abdelaziz SA, Hussein L, Paliy O. Diet Supplementation with Pomegranate Fruit Alters Distal Gut Microbiota of Healthy Female College Students. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleBandow, Brant, Entsar S. Shaaban, Sumudu Rajakaruna, Zeinab Saleh, Sahar A. Abdelaziz, Laila Hussein, and Oleg Paliy. 2025. "Diet Supplementation with Pomegranate Fruit Alters Distal Gut Microbiota of Healthy Female College Students" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020305
APA StyleBandow, B., Shaaban, E. S., Rajakaruna, S., Saleh, Z., Abdelaziz, S. A., Hussein, L., & Paliy, O. (2025). Diet Supplementation with Pomegranate Fruit Alters Distal Gut Microbiota of Healthy Female College Students. Microorganisms, 13(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020305





