Response of Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometric Properties and Microbial Metabolic Limitations to the Ecosystem Transition Mode Employed in Red Jujube Economic Forests on the Loess Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Information
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Characterization
2.4. Calculation of Microbial Nutrient Limitations
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
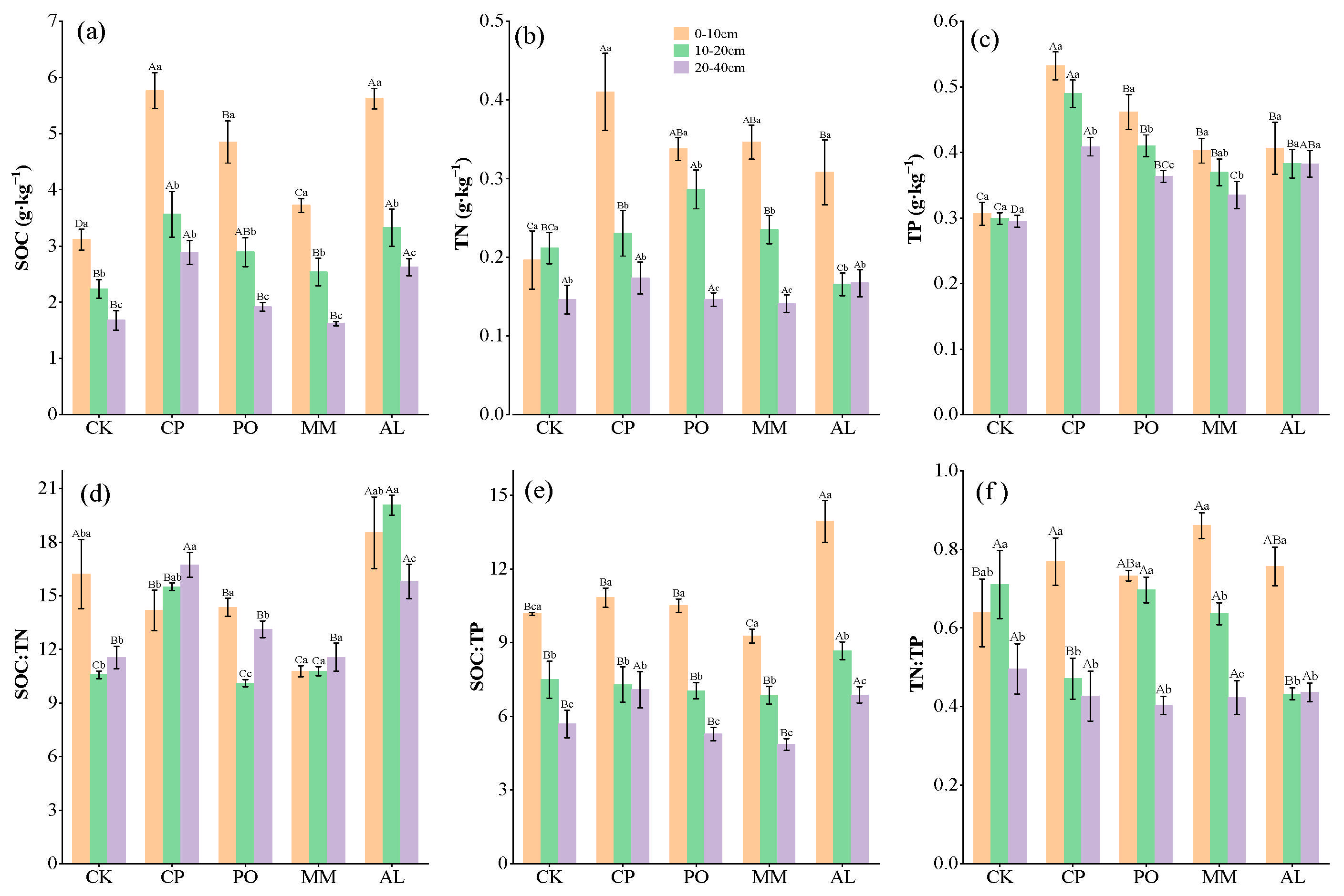
3.1. Soil C, N, P, Microbial Biomass C, N, P, and Their Measurement Ratios in Different Ecosystem Transitions
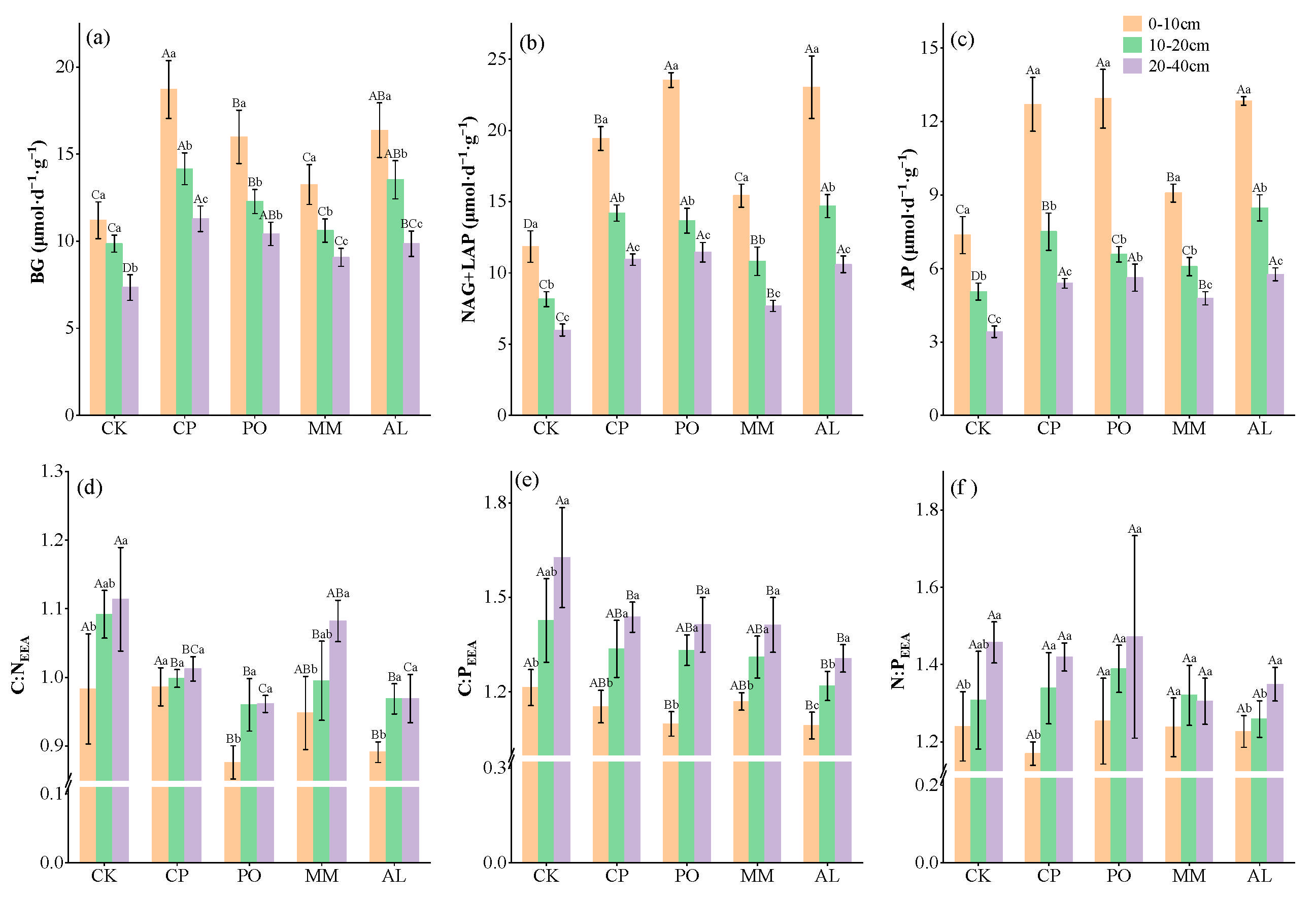
3.2. Changes in Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activity and Stoichiometry Under Different Ecosystem Transition Models
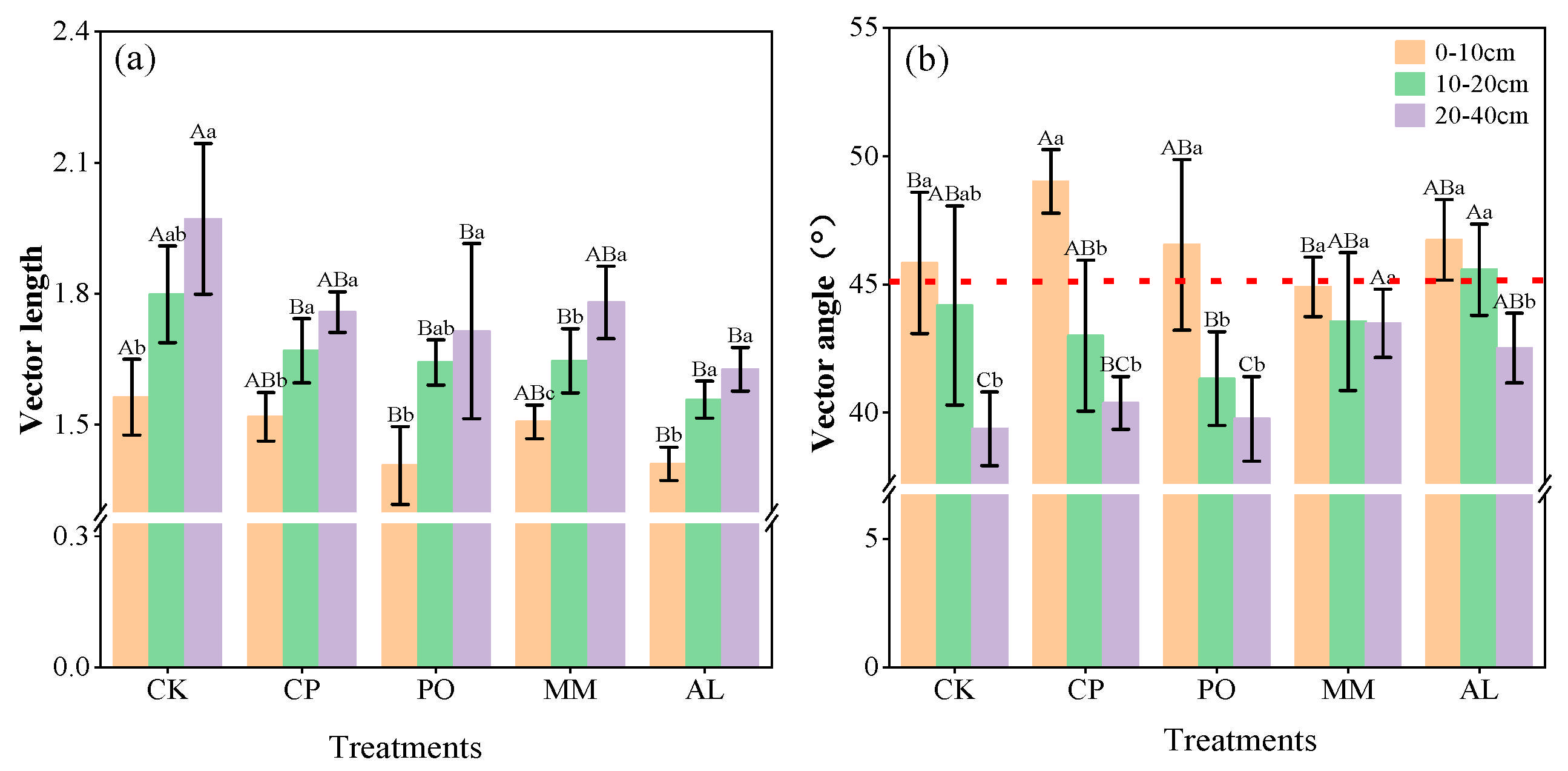
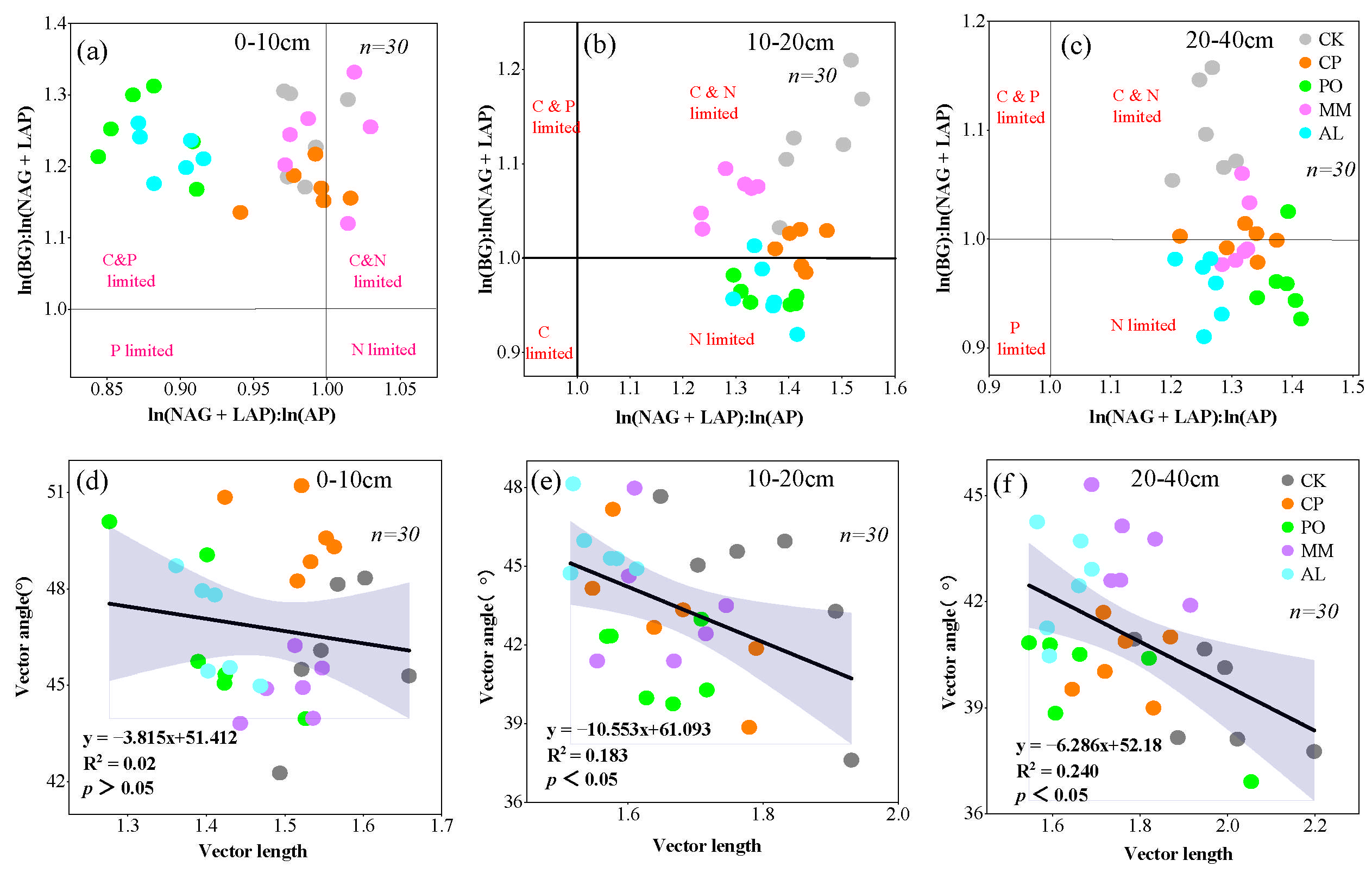
3.3. Soil Microbial Nutrient Limitations and Homeostasis Under Different Ecosystem Transition Models
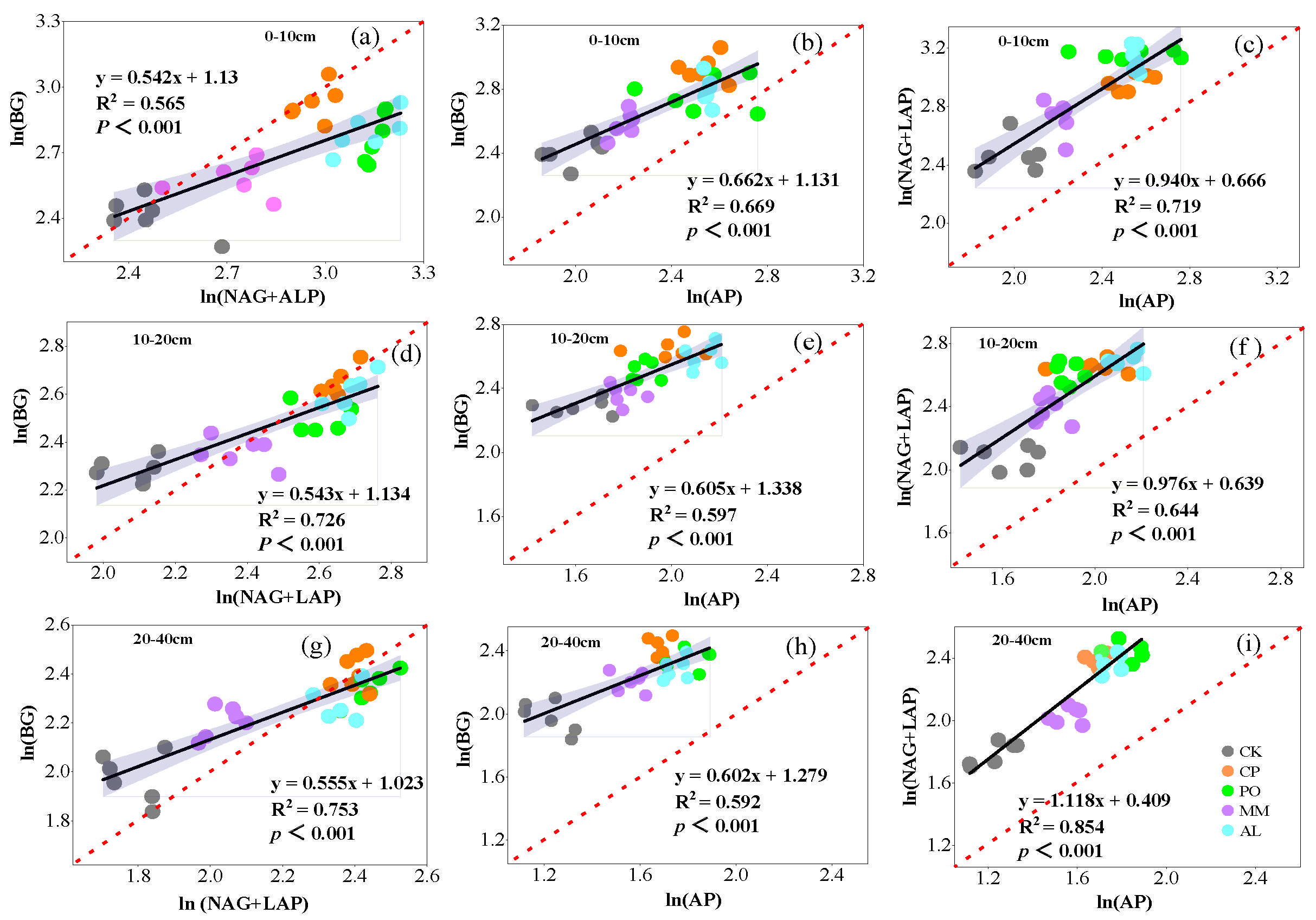
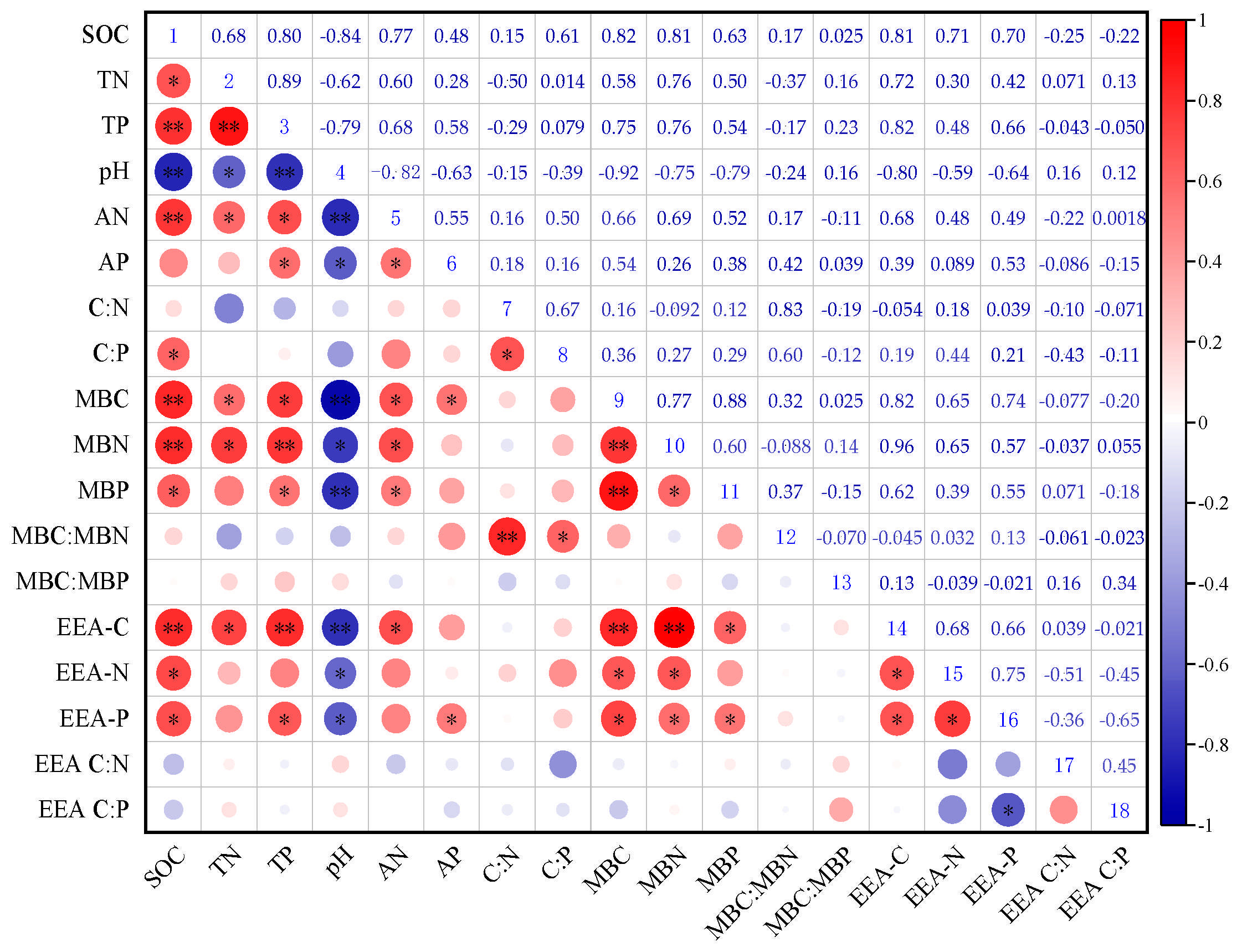
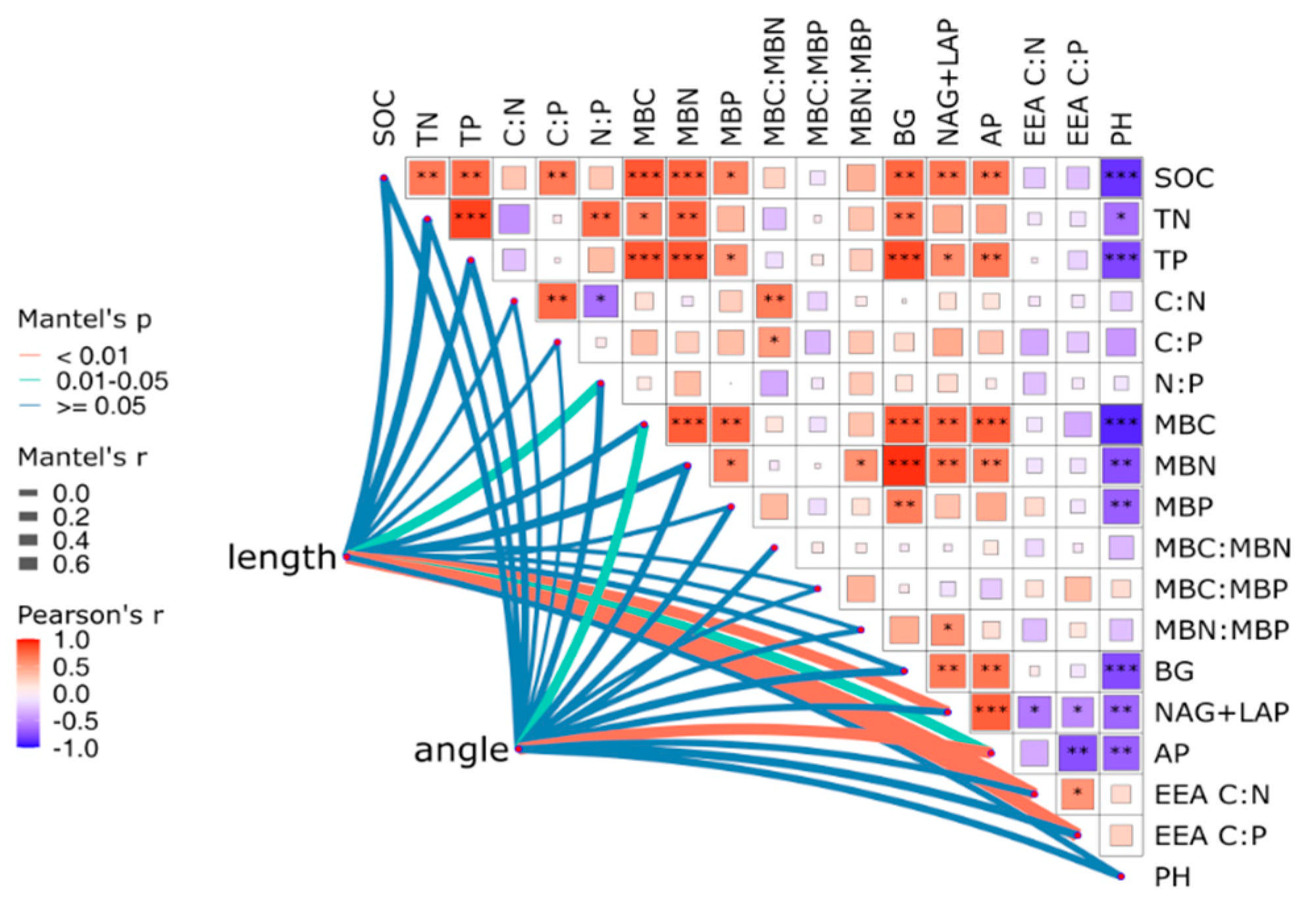
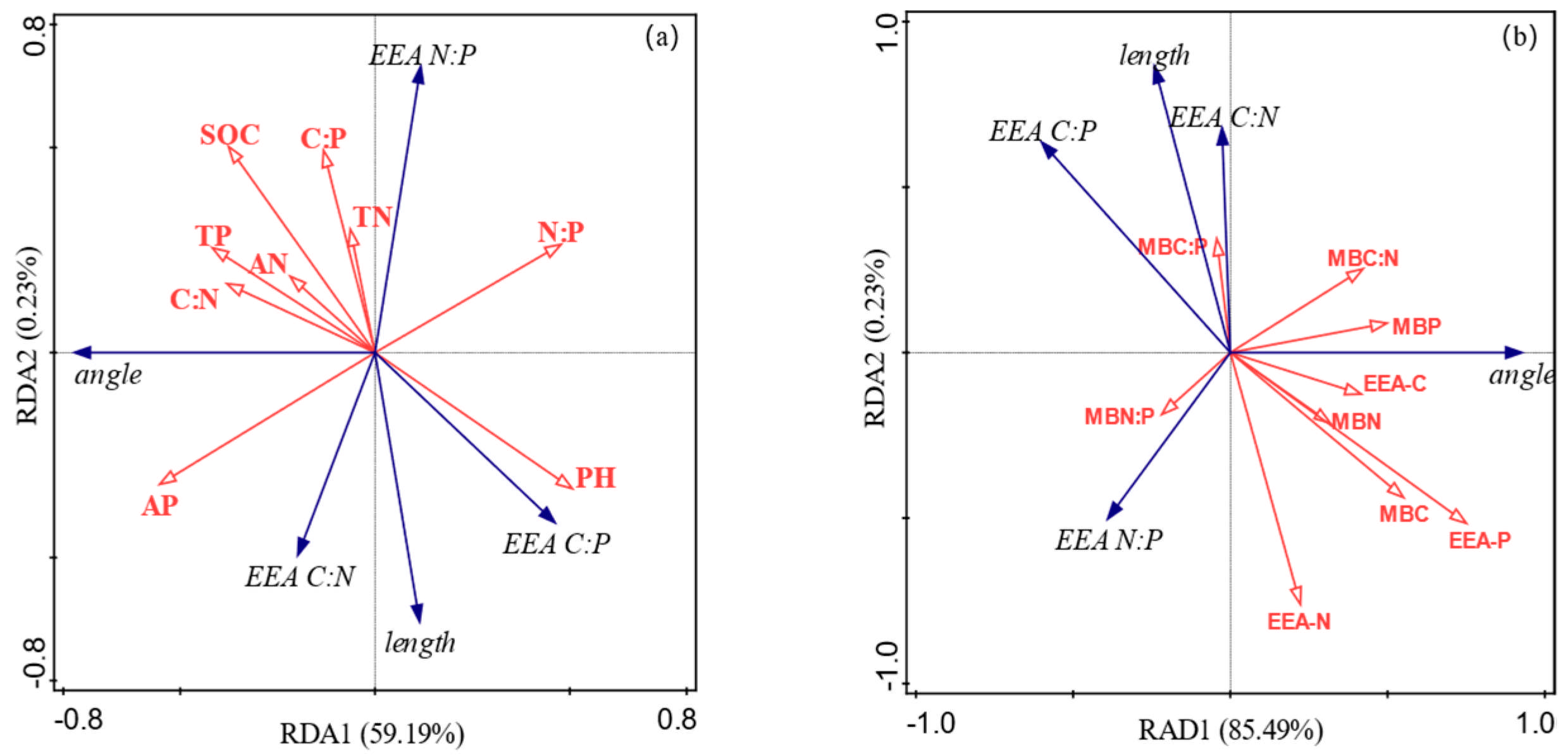
3.4. Relationships Between Soil Chemical Properties, Extracellular Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Nutrient Limitation in Different Ecosystem Transition Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Ecosystem Transition Models on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities
4.2. Effects of Different Ecosystem Transition Models on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometry
4.3. Nutrient Limitations of Soil Microorganisms Under Different Ecosystem Transition Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Xue, S.; Wang, G. Soil bacterial community dynamics reflect changes in plant community and soil properties during the secondary succession of abandoned farmland in the Loess Plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.Z.; Wang, J.Q.; Huang, Z.; He, J.Z. Progress of research on the effects of tree species diversity on soil microbial community structure and elemental biogeochemical cycling. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4215, 6092–6102. [Google Scholar]
- Rosinger, C.; Bodner, G.; Forer, V.; Sandén, H.; Weninger, T.; Zeiser, A.; Mentler, A.; Keiblinger, K.M. Changes in microbial physiology and carbon-use efficiency upon improving soil habitat conditions in conservation farming systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 377, 109246.s. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad, J.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.W.; Yu, Q.L.; Li, L.W.; Yu, L.D.; Bo, Y.; Yun, C.; Wen, J.C. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects microbial metabolic limitations in different desert types of northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162504. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Ding, S.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, E.; Liu, T.; Duan, X. Microbial and enzymatic C:N:P stoichiometry are affected by soil C:N in the forest ecosystems in southwestern China. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116819. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 1111, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Waring, B.G.; Weintraub, S.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. (Special Issue: Enzymes in biogeochemical cycles: Integrating experimental data, theory, and models). Biogeochemistry 2014, 1171, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, Y.; Quan, C.Z.; Tang, Y.M.; Shen, G.Z.; Qi, L.; Ming, X.W.; Wen, F.T. Disentangling drivers of soil microbial nutrient limitation in intensive agricultural and natural ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150555. [Google Scholar]
- Lalanne, J.B.; Taggart, J.C.; Guo, M.S.; Herzel, L.; Schieler, A.; Li, G.W. Evolutionary Convergence of Pathway-Specific Enzyme Expression Stoichiometry. Cell 2018, 1733, 749–761.e738. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Li, Q.; Xue, S. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation during secondary succession of natural grassland on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 200, 104605. [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, E.B.; Hofmockel, K.S. Ecological stoichiometry as a foundation for omics-enabled biogeochemical models of soil organic matter decomposition. Biogeochemistry 2021, 1571, 31–50. [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Rinkes, Z.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Weintraub, M.N. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: Informing enzyme based decomposition models. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Deng, L.; Guo, X.; Han, F.; Ju, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X. Patterns of soil microbial nutrient limitations and their roles in the variation of soil organic carbon across a precipitation gradient in an arid and semi-arid region. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 658, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W.; Xia, F.; Guo, H.; Tan, Q. Coupling and decoupling of soil carbon and nutrients cycles at different salinity levels in a mangrove wetland: Insights from CUE and enzymatic stoichiometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171039. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Bing, H.; Moorhead, D.L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ye, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals widespread soil phosphorus limitation to microbial metabolism across Chinese forests. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.; Chao, S.; Peng, P.L.; Fei, L.; Yi, Q.S.; Fan, Q. Soil biochemical properties and microbial composition in aged and non-aged apple (Malus domestica) orchards in Luochuan County, Loess Plateau, China. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 374, 879–890. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Kou, Z.; Li, Y. The influence of soil depth and tree age on soil enzyme activities and stoichiometry in apple orchards. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105600. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, P.X.; Wen, J.L.; Jia, Y.W.; Yu, F.Z.; Yong, Z.F.; Gai, H.Y.; Wei, Z.; Xin, H. Soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152918. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Deng, J.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics along a revegetation chronosequence in the soils of abandoned land and Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; An, S.; Chang, S.X. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects the shift from P- to N-limitation of microorganisms with grassland restoration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, P.; Li, T.; Xiao, T.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; Li, Z. Impacts of rice terrace abandonment on soil ecosystem multifunctionality: Insights into reduced microbial diversity and exacerbated nitrogen limitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 437, 140731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.L.; Hao, W.; Guo, Y.Y.; Miao, W.; Shuai, J.; Xiao, C.W.; Jun, S.X.; Min, X.; Ya, X.; Qing, Q.W. Soil enzyme activities and microbial nutrient limitation during the secondary succession of boreal forests. CATENA 2023, 230, 107268. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tito, M.; Tao, H.; Shen, Y.Y. Effects of long-term conservation tillage on soil carbon content and transforming enzyme activities in dry farming soils of the Loess Plateau. Chin. Agric. Sci. 2023, 5605, 907–919. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Ecosystem Responses to Natural and Anthropogenic Changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 451, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Lü, Y.; He, C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 84, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, W. Effect of jujube orchard abandonment time on soil properties and enzyme activities at soil profile in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2024, 141, 18943. [Google Scholar]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Krasilnikov, P.; Bockheim, J.G. Soil maps of the world. Geoderma 2013, 207–208, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Zhou, X.H.; Dong, R.S.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, G.D.; Li, Q.F. Natural vegetation regeneration facilitated soil organic carbon sequestration and microbial community stability in the degraded karst ecosystem. CATENA 2023, 222, 106856. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Dynamics of soil microbial metabolic activity during grassland succession after farmland abandonment. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Zou, B.Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.H.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Z.Q.; He, J.Z. Effects of multispecies restoration on soil extracellular enzyme activity stoichiometry in Pinus massoniana plantations of subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 178, 108967. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Richter, A.; Shibistova, O.; Guggenberger, G.; et al. C:N:P stoichiometry regulates soil organic carbon mineralization and concomitant shifts in microbial community composition in paddy soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 2020, 568, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.X.; Wu, F.Z.; Wu, Q.; Fornara, D.A.; Heděnec, P.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhao, Z.; Yue, K. Vegetation restoration effects on soil carbon and nutrient concentrations and enzymatic activities in post-mining lands are mediated by mine type, climate, and former soil properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163059. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Han, F.; Ju, W.; Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X. Natural grassland as the optimal pattern of vegetation restoration in arid and semi-arid regions: Evidence from nutrient limitation of soil microbes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 388–397. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bing, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J. Vegetation type rather than climate modulates the variation in soil enzyme activities and stoichiometry in subalpine forests in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2020, 374, 114424. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.X.; Wu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, W.Q.; Chen, F.S.; Wang, G.G.; Li, J.; Fang, X.M. Mixing with coniferous tree species alleviates rhizosphere soil phosphorus limitation of broad-leaved trees in subtropical plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation in rhizosphere soil in the arid area of the northern Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, F.Z.; Petr, H.; Johannes, R.; Kappel, S.I.; Yan, P.; Lars, V. Effects of common European tree species on soil microbial resource limitation, microbial communities and soil carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108754. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.; Hui, H.; Weikai, B.; Bin, H.; Jian, L.; Fang, L. Shifting soil nutrient stoichiometry with soil of variable rock fragment contents and different vegetation types. CATENA 2023, 220, 106717. [Google Scholar]
- Błońska, E.; Piaszczyk, W.; Staszel, K. Enzymatic activity of soils and soil organic matter stabilization as an effect of components released from the decomposition of litter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103723. [Google Scholar]
- Hobley, E.; Wilson, B.; Wilkie, A.; Gray, J.; Koen, T. Drivers of soil organic carbon storage and vertical distribution in Eastern Australia. Plant Soil. 2015, 3901, 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.Y.; Lu, S.X.; Wang, C.Q.; Mu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.D. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in response to tillage practices in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 209, 104940. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Zhuang, J. Temporal responses of soil microorganisms to substrate addition as indicated by amino sugar differentiation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 436, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Sanaullah, M.; Heitkamp, F.; Zelenev, V.; Kumar, A.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial decomposition of soil organic matter is mediated by quality and quantity of crop residues: Mechanisms and thresholds. Biol Fert. Soils 2017, 533, 287–301. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, Z.J.; Kuang, L.H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.J.; Liang, C.; Hui, D.F.; Lambers, H.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; et al. Nutrient availability and stoichiometry mediate microbial effects on soil carbon sequestration in tropical forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 186, 109186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.Z.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S.L.; Chen, L.; Xin, J.; Xu, L.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhai, B.N.; Wang, Z.H.; Zheng, W.; et al. Nitrogen inhibitors improve soil ecosystem multifunctionality by enhancing soil quality and alleviating microbial nitrogen limitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163238. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, B.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Fei, H.Y.; Pan, R.P.; Han, F. Changes in microbial metabolic C- and N- limitations in the rhizosphere and bulk soils along afforestation chronosequence in desertified ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114215. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Gleixner, G.; Habekost, M.; Milcu, A.; Scheu, S. Plant diversity effects on soil microorganisms support the singular hypothesis. Ecology 2010, 912, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Gu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shan, C.; Shen, F. The effects of postfire regeneration patterns on soil microbial metabolic limitation based on eco-enzyme stoichiometry in the boreal forest of China. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2024, 568, 122129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.; Han, X.H.; Tong, X.G.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.G. Linkages of C:N:P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Y.Q. Spatial patterns of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus across the entire Loess Plateau region of China. Geoderma 2013, 197–198, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, J.J.; Wei, Z.H.; Fan, M.C.; Shangguan, Z.P. Nutrient limitation status of soil microorganisms in acacia forests revealed by soil chemometrics and enzymometrics. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 3507, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Bai, J.H.; Tebbe, C.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Jia, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, L. Salinity controls soil microbial community structure and function in coastal estuarine wetlands. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 232, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Responses of soil microbial communities to nutrient limitation in the desert-grassland ecological transition zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, C.; Li, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, G. Response of Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometric Properties and Microbial Metabolic Limitations to the Ecosystem Transition Mode Employed in Red Jujube Economic Forests on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040729
Mu C, Li J, Huang F, Zhang Z, Qin J, Wang G. Response of Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometric Properties and Microbial Metabolic Limitations to the Ecosystem Transition Mode Employed in Red Jujube Economic Forests on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040729
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Chunheng, Jiaqi Li, Fuchao Huang, Zhiyu Zhang, Jing Qin, and Gailing Wang. 2025. "Response of Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometric Properties and Microbial Metabolic Limitations to the Ecosystem Transition Mode Employed in Red Jujube Economic Forests on the Loess Plateau" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040729
APA StyleMu, C., Li, J., Huang, F., Zhang, Z., Qin, J., & Wang, G. (2025). Response of Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometric Properties and Microbial Metabolic Limitations to the Ecosystem Transition Mode Employed in Red Jujube Economic Forests on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms, 13(4), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040729




