Seasonal Variations of Community Structure and Functional Genes of Synechococcus in the Subtropical Coastal Waters: Insights from FACS and High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Sample Collection and Cell Sorting
2.2. Environmental Parameter Measurements
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing Data Treatment
2.4. Community Composition Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
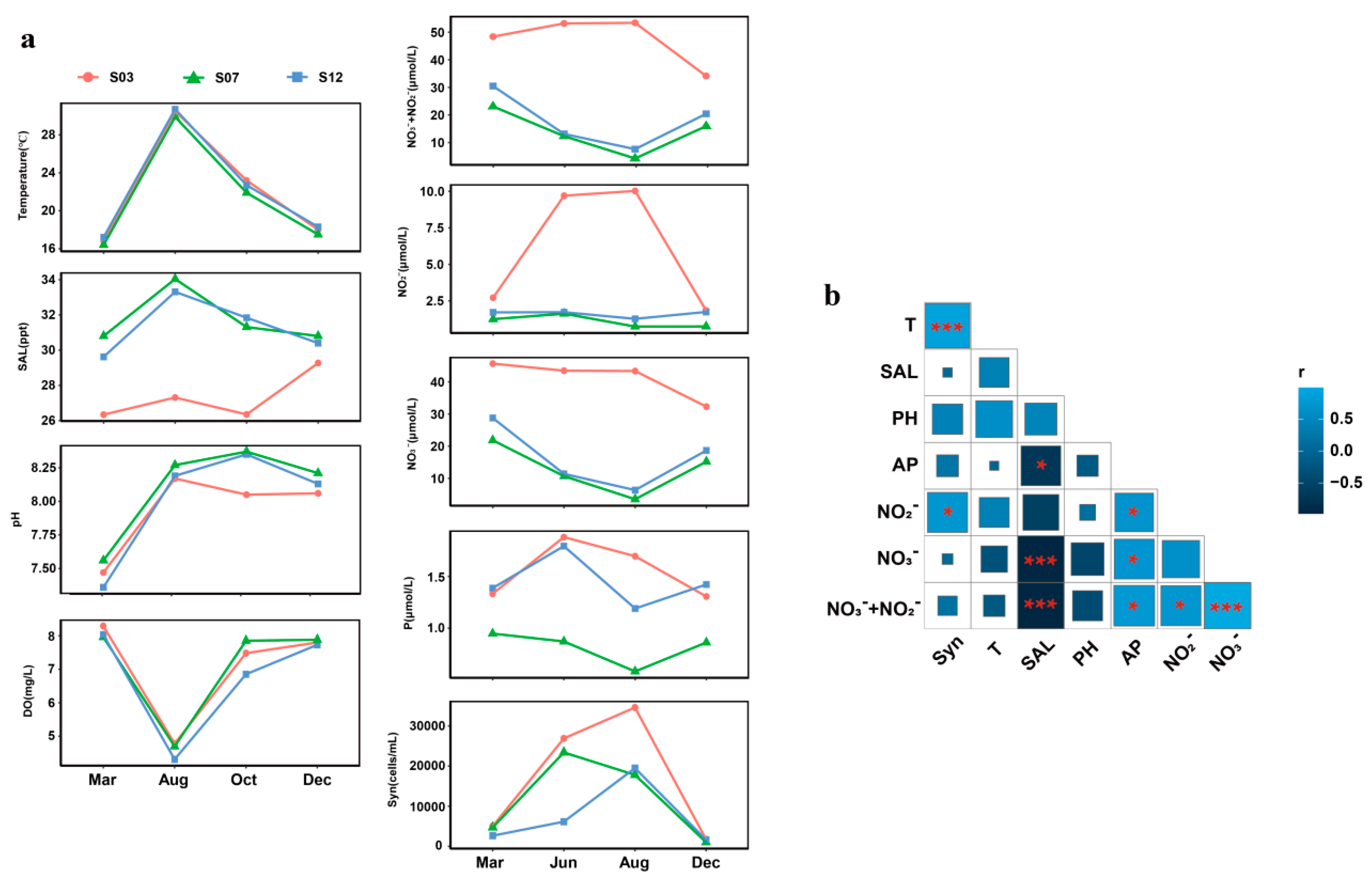
3.1. Environmental Parameters and Synechococcus Abundance Around Xiamen Island
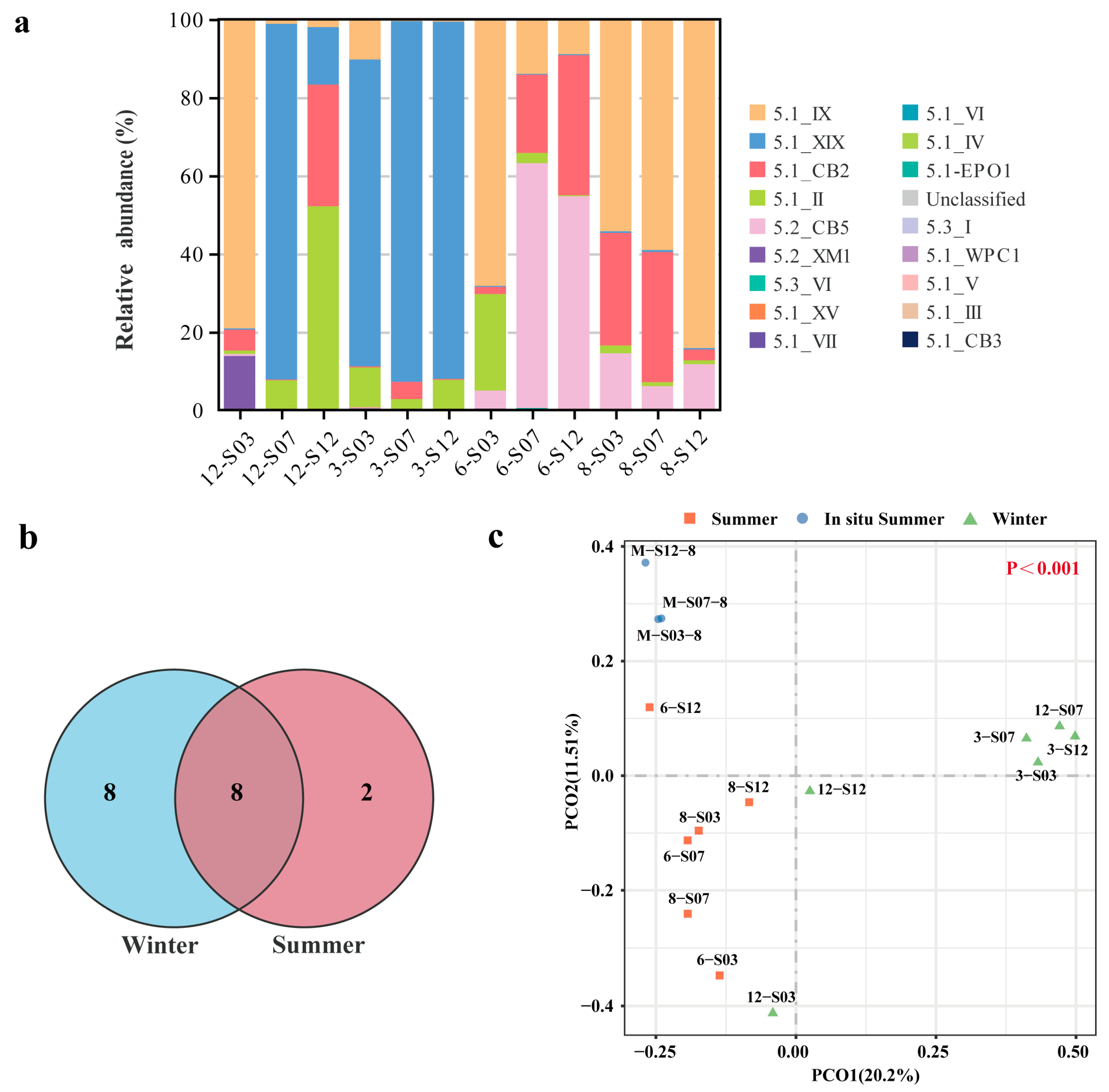
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Synechococcus Community Composition
3.3. Synechococcus Diversity and Their Seasonal Variations
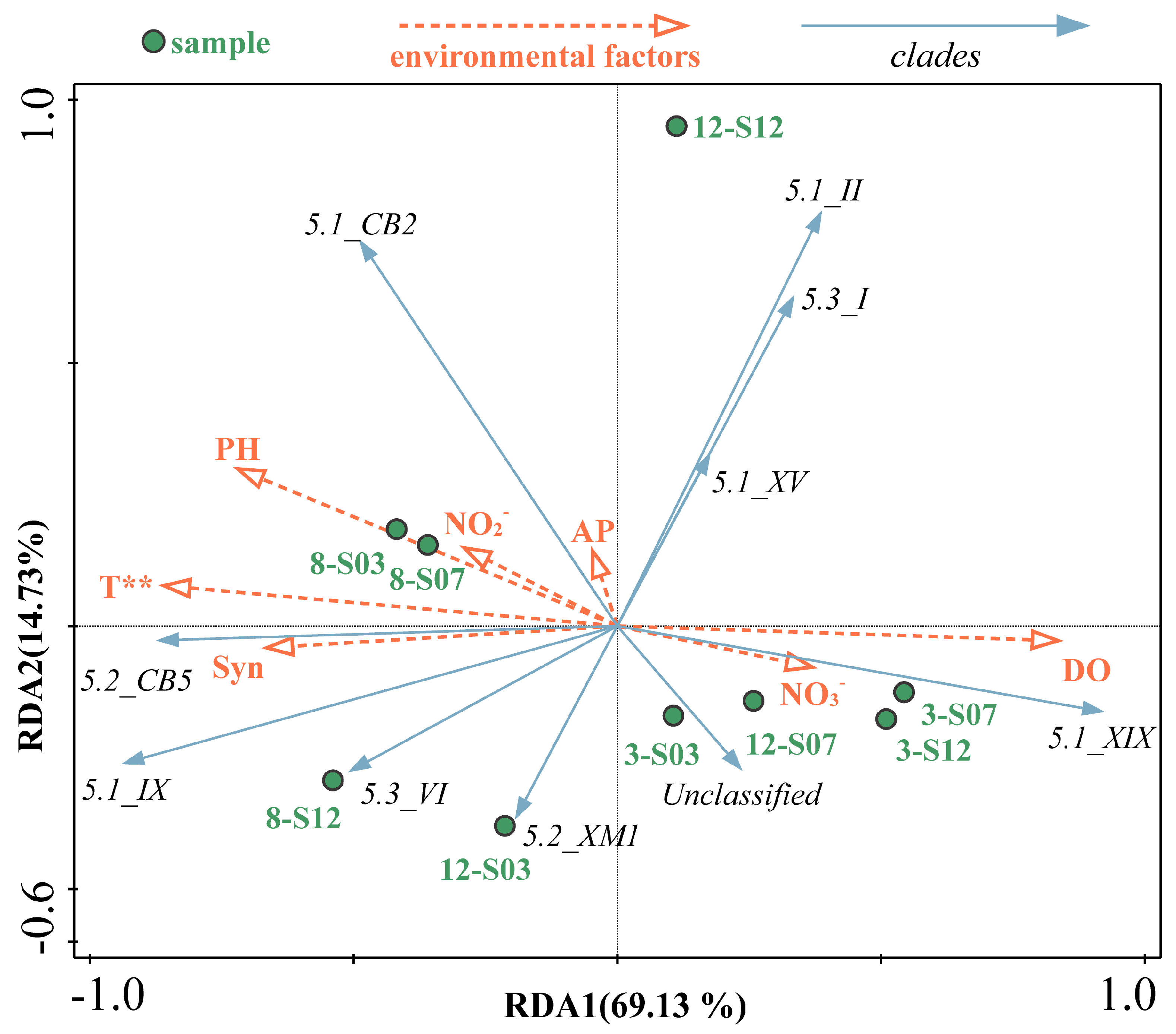
3.4. Relationship Between Synechococcus Clades and Environmental Factors
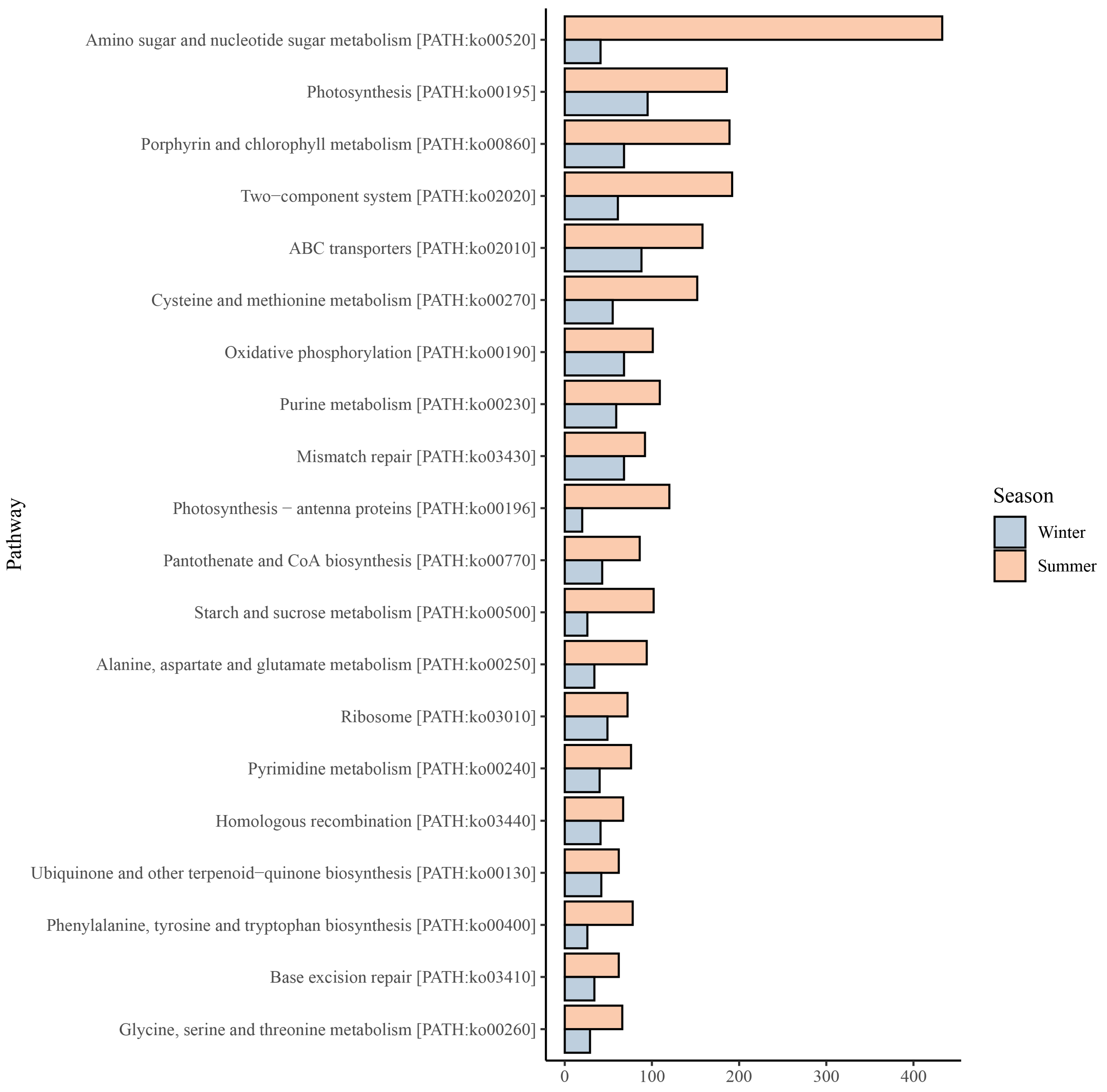
3.5. Synechococcus Metabolic Pathways and Their Seasonal Variations
4. Discussion
4.1. Detection of Low-Abundance Synechococcus Strains by Combining FACS with High-Throughput Sequencing
4.2. Seasonal Variations in Synechococcus and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincón, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.A.Z.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.W.; Lomas, M.W.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guidi, L.; Chaffron, S.; Bittner, L.; Eveillard, D.; Larhlimi, A.; Roux, S.; Darzi, Y.; Audic, S.; Berline, L.; Brum, J.R.; et al. Plankton networks driving carbon export in the oligotrophic ocean. Nature 2016, 532, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Gonsior, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, F. Microbial transformation of virus-induced dissolved organic matter from picocyanobacteria: Coupling of bacterial diversity and DOM chemodiversity. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2551–2565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wommack, K.E.; Chen, F. Abundance and Distribution of Synechococcus spp. and Cyanophages in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7459–7468. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.M.; Liu, H.B.; Choi, D.H.; Noh, J.H. Variation of Synechococcus Pigment Genetic Diversity Along Two Turbidity Gradients in the China Seas. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Rocap, G. Diversity and distribution of marine Synechococcus: Multiple gene phylogenies for consensus classification and development of qPCR assays for sensitive measurement of clades in the ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlan, D.J.; Ostrowski, M.; Mazard, S.; Dufresne, A.; Garczarek, L.; Hess, W.R.; Post, A.F.; Hagemann, M.; Paulsen, I.; Partensky, F. Ecological Genomics of Marine Picocyanobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 249–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.D.; Li, F.R.; Long, L.J.; Huang, S.J. Quantification of Marine Picocyanobacteria on Water Column Particles and in Sediments Using Real-Time PCR Reveals Their Role in Carbon Export. mSphere 2022, 7, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xia, X.M.; Chen, J.W.; Liu, H.B.; Jing, H.M. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Synechococcus Assemblages at DNA and cDNA Levels in the Tropical Estuarine and Coastal Waters. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Rocap, G. Culture isolation and culture-independent clone libraries reveal new marine Synechococcus ecotypes with distinctive light and N physiologies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7193–7204. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, G.; Palenik, B.; Brahamsha, B. Swimming marine Synechococcus strains with widely different photosynthetic pigment ratios form a monophyletic group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5247–5251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wang, K.; Kan, J.J.; Suzuki, M.T.; Wommack, K.E. Diverse and unique picocyanobacteria in Chesapeake Bay, revealed by 16S-23S rRNA internal transcribed Spacer sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Post, A.F.; Penno, S.; Zandbank, K.; Paytan, A.; Huse, S.M.; Welch, D.M. Long term seasonal dynamics of Synechococcus population structure in the Gulf of Aqaba, Northern Red Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, F.; Malfatti, F. Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 782–791. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Leung, P.M.; Cook, P.L.M.; Wong, W.W.; Hutchinson, T.; Eate, V.; Kessler, A.J.; Greening, C. Hydrodynamic disturbance controls microbial community assembly and biogeochemical processes in coastal sediments. ISME J. 2022, 16, 750–763. [Google Scholar]
- Mackey, K.R.M.; Hunter-Cevera, K.; Britten, G.L.; Murphy, L.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Huber, J.A. Seasonal Succession and Spatial Patterns of Synechococcus Microdiversity in a Salt Marsh Estuary Revealed through 16S rRNA Gene Oligotyping. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Jiang, X.; Jing, Z.Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.Z.; Zhou, L.B.; Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Tan, Y.H. Spatial and seasonal distributions of bacterioplankton in the Pearl River Estuary: The combined effects of riverine inputs, temperature, and phytoplankton. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-González, C.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Pratt, N.; Moore, C.M.; Bibby, T.S.; Marañón, E. Effects of Temperature and Nutrient Supply on Resource Allocation, Photosynthetic Strategy, and Metabolic Rates of Synechococcus sp. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 818–829. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.L.; Jing, H.M.; Qin, S. Picocyanobacterial synechococcus in marine ecosystem: Insights from genetic diversity, global distribution, and potential function. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 177, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Joint, I.; Mühling, M.; Querellou, J. Culturing marine bacteria—An essential prerequisite for biodiscovery. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 564–575. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.A.X.; Sun, J.H.; Yang, Q.W.; Liang, Y.T.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, C.; Gu, C.X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.C.; Liu, G.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Coastal Viral Community Structure and Potential Biogeochemical Roles Affected by an Ulva prolifera Green Tide. mSystems 2023, 8, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.N.; Zhang, W.P.; Ding, W.; Wang, M.; Fan, S.; Yang, B.; McMinn, A.; Wang, M.; Xie, B.B.; Qin, Q.L.; et al. Structure and function of the Arctic and Antarctic marine microbiota as revealed by metagenomics. Microbiome 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Liang, Y.T.; Jiang, Y.; Paez-Espino, D.; Han, M.A.X.; Gu, C.X.; Wang, M.W.; Yang, Y.M.; Liu, F.J.; Yang, Q.W.; et al. Virioplankton assemblages from challenger deep, the deepest place in the oceans. iScience 2022, 25, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Roth-Rosenberg, D.; Aharonovich, D.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; Vogts, A.; Zoccarato, L.; Eigemann, F.; Nago, N.; Grossart, H.P.; Voss, M.; Sher, D. Prochlorococcus Cells Rely on Microbial Interactions Rather than on Chlorotic Resting Stages To Survive Long-Term Nutrient Starvation. mBio 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Aharonovich, D.; Roth-Rosenberg, D.; Weissberg, O.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; Vogts, A.; Zoccarato, L.; Eigemann, F.; Grossart, H.P.; Voss, M.; et al. Single-cell measurements and modelling reveal substantial organic carbon acquisition by Prochlorococcus. Nat. Microbiol 2022, 7, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom, S.; Andersson-Svahn, H. Single-cell culture in microwells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 853, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkadir, N.; Saraiva, J.P.; Schattenberg, F.; Toscan, R.B.; Correa, F.B.; Harms, H.; Müller, S.; da Rocha, U.N. Combining Flow Cytometry and Metagenomics Improves Recovery of Metagenome-Assembled Genomes in a Cell Culture from Activated Sludge. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, L.J.; Smith, H.J.; Barnhart, E.P.; Schweitzer, H.D.; Malmstrom, R.R.; Goudeau, D.; Fields, M.W. Activity-based, genome-resolved metagenomics uncovers key populations and pathways involved in subsurface conversions of coal to methane. ISME J. 2022, 16, 915–926. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, J.X.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, T.W.; Jiao, N.Z. Genomic insights into the adaptation of Synechococcus to the coastal environment on Xiamen. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.T.; Wang, J.N.; Luo, T.W.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Q.; Jiao, N.Z. Seasonal dynamics of bacterial communities in the surface seawater around subtropical Xiamen Island, China, as determined by 16S rRNA gene profiling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, N.W.; Hou, L.Y.; Ma, Y.; Yu, C.P. Response of bacterial communities to environmental changes in a mesoscale subtropical watershed, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, N.Z.; Yang, Y.H.; Hong, N.; Ma, Y.; Harada, S.; Koshikawa, H.; Watanabe, M. Dynamics of autotrophic picoplankton and heterotrophic bacteria in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, S.J.; Jiao, N.Z.; Chen, F. Distinct Patterns of Picocyanobacterial Communities in Winter and Summer in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkar, M.; Wang, M.; Valencia, B.; Palenik, B. Spatial and temporal variations in Synechococcus microdiversity in the Southern California coastal ecosystem. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Li, J.L.; Qin, S. Phylogenetic Structure of Synechococcus Assemblages and Its Environmental Determinants in the Bay and Strait Areas of a Continental Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, G.; Zhao, L.; Meyer, M.G.; Gong, W.D.; Burns, S.M.; Tagliabue, A.; Buck, K.N.; Santoro, A.E.; Graff, J.R.; Marchetti, A.; et al. Synechococcus nitrogen gene loss in iron-limited ocean regions. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello-Yeves, P.J.; Haro-Moreno, J.M.; Martin-Cuadrado, A.B.; Ghai, R.; Picazo, A.; Camacho, A.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Novel Synechococcus Genomes Reconstructed from Freshwater Reservoirs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Z.; Yang, K.; Liao, H.; Lassen, S.B.; Su, J.Q.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L.; Zhu, Y.G. Active antibiotic resistome in soils unraveled by single-cell isotope probing and targeted metagenomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.H.; Noh, J.H. Phylogenetic diversity of Synechococcus strains isolated from the East China Sea and the East Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hunter-Cevera, K.R.; Post, A.F.; Peacock, E.E.; Sosik, H.M. Diversity of Synechococcus at the Martha’s Vineyard Coastal Observatory: Insights from Culture Isolations, Clone Libraries, and Flow Cytometry. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.M.; Vidyarathna, N.K.; Palenik, B.; Lee, P.; Liu, H.B. Comparison of the Seasonal Variations of Synechococcus Assemblage Structures in Estuarine Waters and Coastal Waters of Hong Kong. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7644–7655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.M.; Guo, W.; Tan, S.J.; Liu, H.B. Synechococcus Assemblages across the Salinity Gradient in a Salt Wedge Estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Laber, C.P.; Pontiller, B.; Bunse, C.; Osbeck, C.M.G.; Perez-Martinez, C.; Di Leo, D.; Lundin, D.; Legrand, C.; Pinhassi, J.; Farnelid, H. Seasonal and Spatial Variations in Synechococcus Abundance and Diversity Throughout the Gullmar Fjord, Swedish Skagerrak. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.J.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Harvey, H.R.; Taylor, K.; Jiao, N.Z.; Chen, F. Novel lineages of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in the global oceans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Guo, S.J.; Liang, J.H.; Sun, X.X. Water column stratification governs picophytoplankton community structure in the oligotrophic eastern Indian ocean. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 189, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Chaouni, B.; Azami, A.I.; Raoui, S.; Amzazi, S.; Nejjari, C.; Bakkali, F.; Zaid, E.; Hamamouch, N.; Amaral-Zettler, L.; Ghazal, H. Spatio-temporal patterns of Synechococcus oligotypes in Moroccan lagoonal environments. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Doré, H.; Leconte, J.; Guyet, U.; Breton, S.; Farrant, G.K.; Demory, D.; Ratin, M.; Hoebeke, M.; Corre, E.; Pitt, F.D.; et al. Global Phylogeography of Marine Synechococcus in Coastal Areas Reveals Strong Community Shifts. mSystems 2022, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohm, J.A.; Ahlgren, N.A.; Thomson, Z.J.; Williams, C.; Moffett, J.W.; Saito, M.A.; Webb, E.A.; Rocap, G. Co-occurring Synechococcus ecotypes occupy four major oceanic regimes defined by temperature, macronutrients and iron. ISME J. 2016, 10, 333–345. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Belisle, B.S.; Lee, M.D. Genomic mosaicism underlies the adaptation of marine Synechococcus ecotypes to distinct oceanic iron niches. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Z.; Liu, H.B.; Huang, B.Q.; Wang, J. Temperature effects on the growth rate of marine picoplankton. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 2014, 505, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Eppley, R.W. Temperature and Phytoplankton Growth in the Sea. Fish. Bull. 1972, 70, 1063–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Moisan, T.A.; Blattner, K.L.; Makinen, C.P. Influences of temperature and nutrients on Synechococcus abundance and biomass in the southern Mid-Atlantic Bight. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Agawin, N.S.R.; Duarte, C.M.; Agusti, S. Growth and abundance of Synechococcus sp. in a Mediterranean Bay: Seasonality and relationship with temperature. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 1998, 170, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinska-Wilczewska, S.; Felpeto, A.B.; Mozdzen, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; Latala, A. Physiological Effects on Coexisting Microalgae of the Allelochemicals Produced by the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. and Nodularia Spumigena. Toxins 2019, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Y.; Mcminn, A.; Wang, M.; Jiao, N.; Luo, T. Seasonal Variations of Community Structure and Functional Genes of Synechococcus in the Subtropical Coastal Waters: Insights from FACS and High-Throughput Sequencing. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040764
Song Z, Zhang T, Liang Y, Mcminn A, Wang M, Jiao N, Luo T. Seasonal Variations of Community Structure and Functional Genes of Synechococcus in the Subtropical Coastal Waters: Insights from FACS and High-Throughput Sequencing. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040764
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhenzhen, Ting Zhang, Yantao Liang, Andrew Mcminn, Min Wang, Nianzhi Jiao, and Tingwei Luo. 2025. "Seasonal Variations of Community Structure and Functional Genes of Synechococcus in the Subtropical Coastal Waters: Insights from FACS and High-Throughput Sequencing" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040764
APA StyleSong, Z., Zhang, T., Liang, Y., Mcminn, A., Wang, M., Jiao, N., & Luo, T. (2025). Seasonal Variations of Community Structure and Functional Genes of Synechococcus in the Subtropical Coastal Waters: Insights from FACS and High-Throughput Sequencing. Microorganisms, 13(4), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040764




