Isolation and Characterization of Beauveria caledonica (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Strains for Biological Control of Odoiporus longicollis Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bc, BPW, and Plant Material
2.2. Strain Culture and Morphological Observation
2.3. Molecular Biology Identification
2.4. Biological Characterization of Isolated Strains
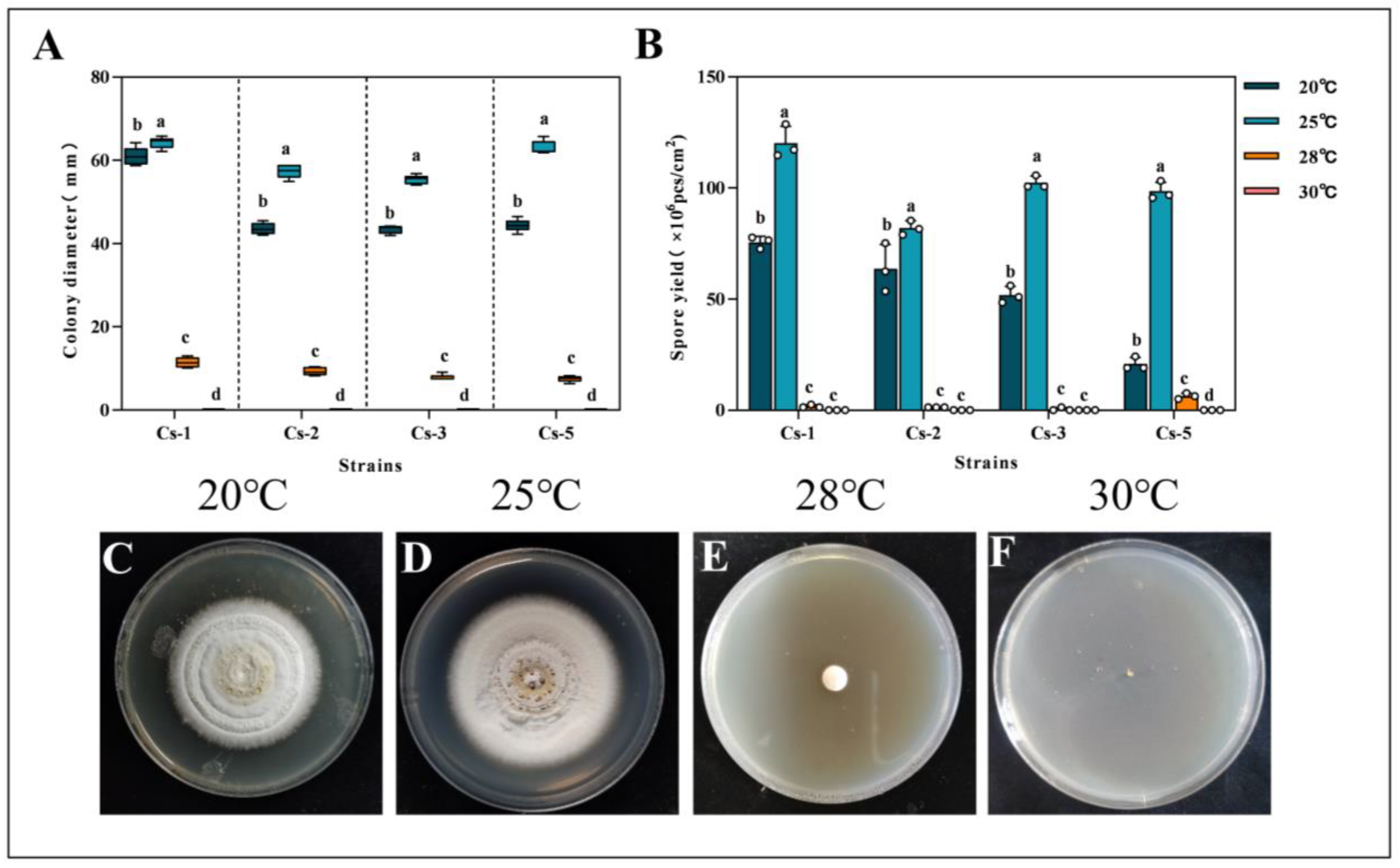
2.4.1. Effect of Temperature on the Growth and Spore Production of Strains
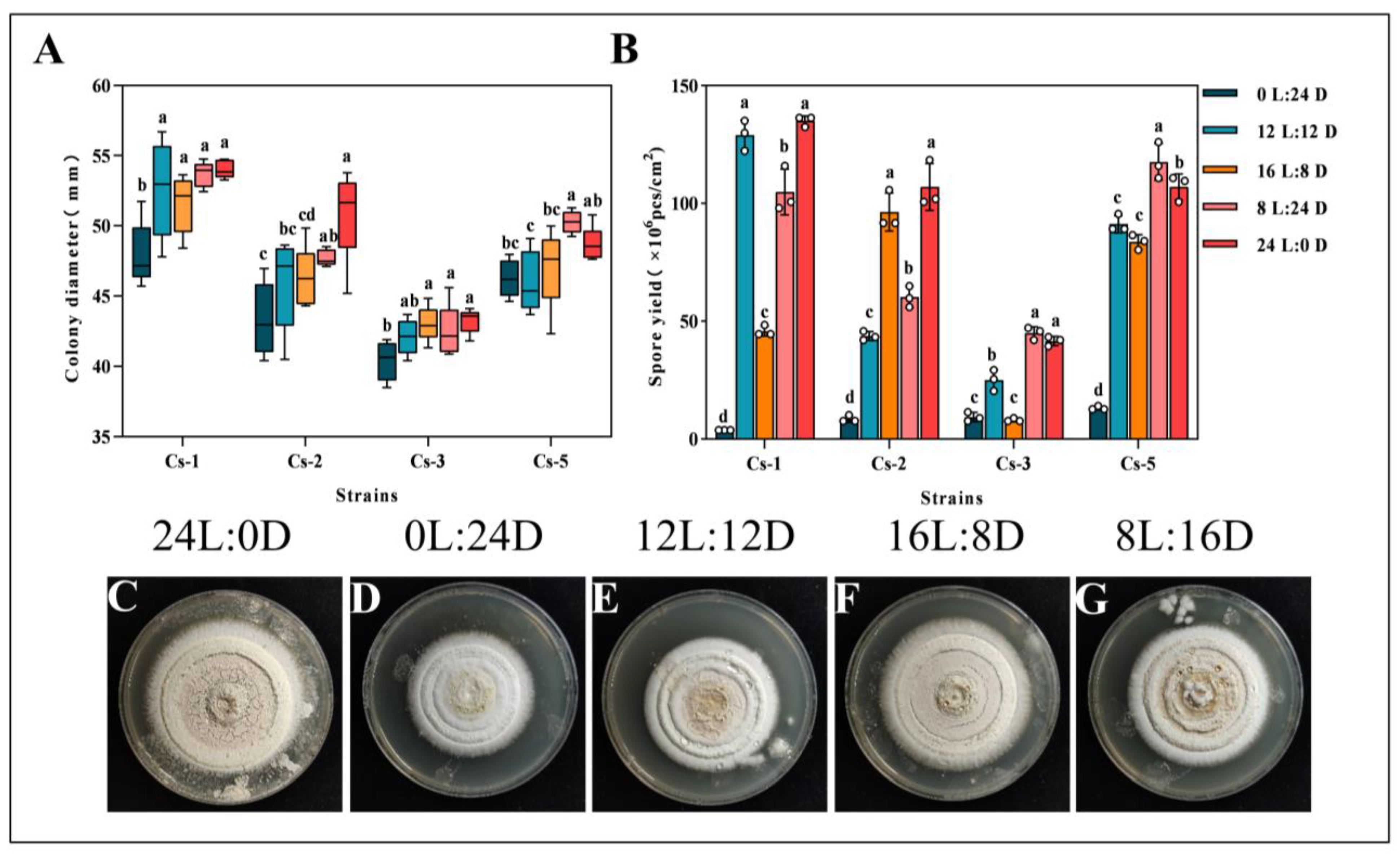
2.4.2. Effects of Photoperiod on Growth and Spore Production
2.4.3. Influence of the Medium on Growth and Spore Production
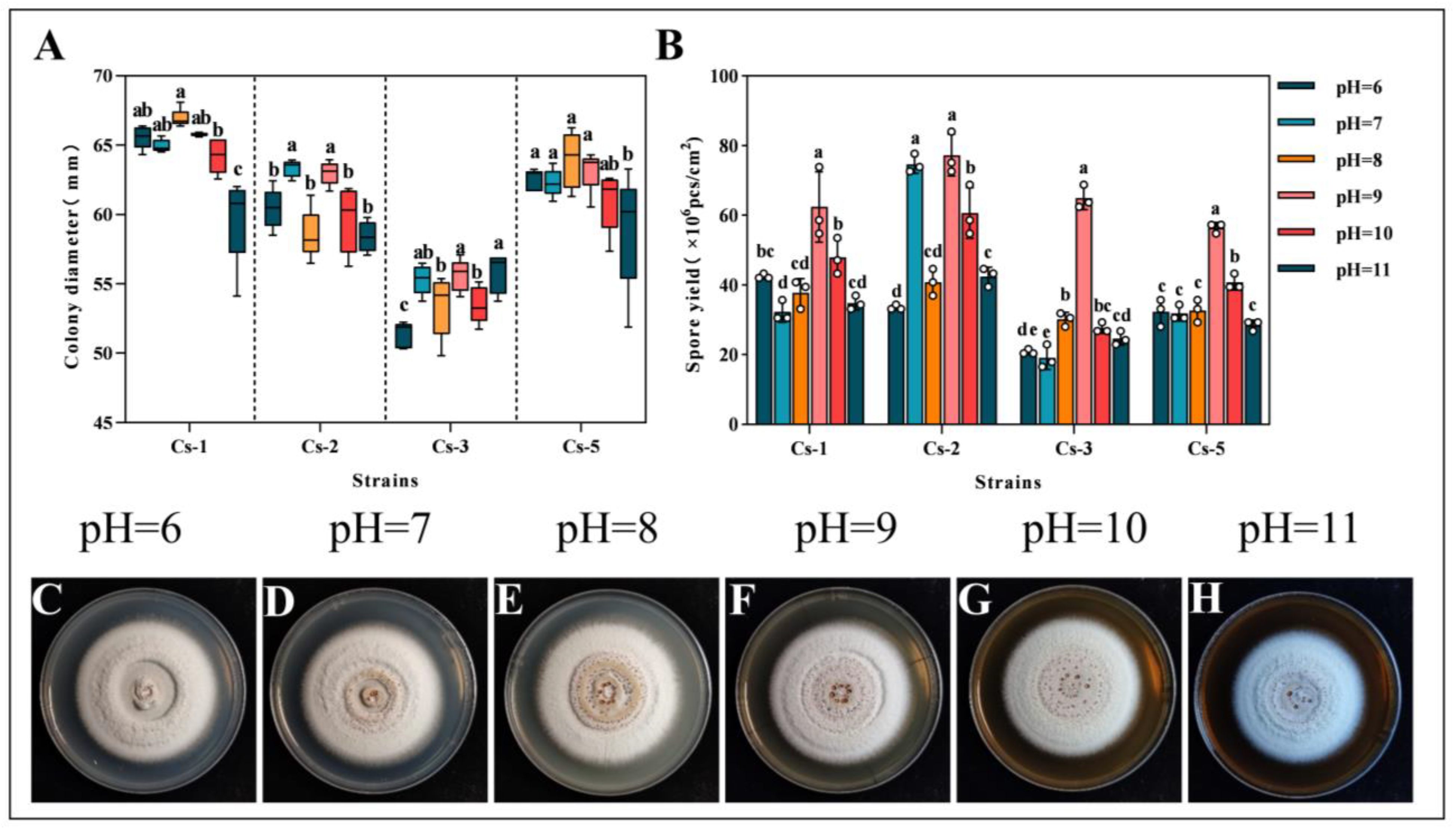
2.4.4. Effect of pH on Growth and Spore Production
2.5. Enzyme Activity Assay
2.6. Pathogenicity Determination
2.6.1. Preparation of Spore Suspensions
2.6.2. Pathogenicity Test
2.6.3. Comparative Test of Pathogenicity of Different Strains
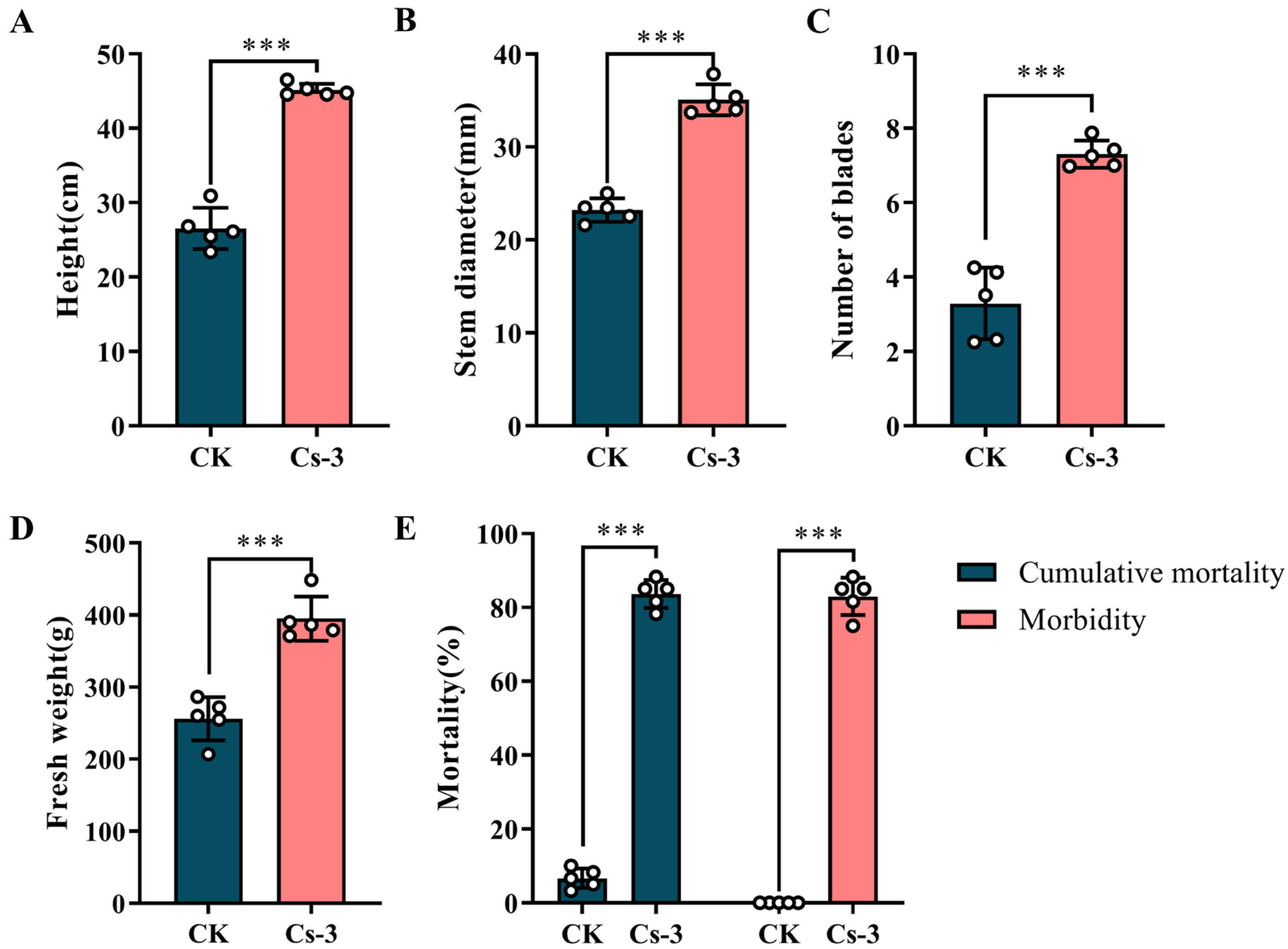
2.7. Evaluation of the Control of BPW by B. caledonica in Greenhouse Potted Plantlets
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
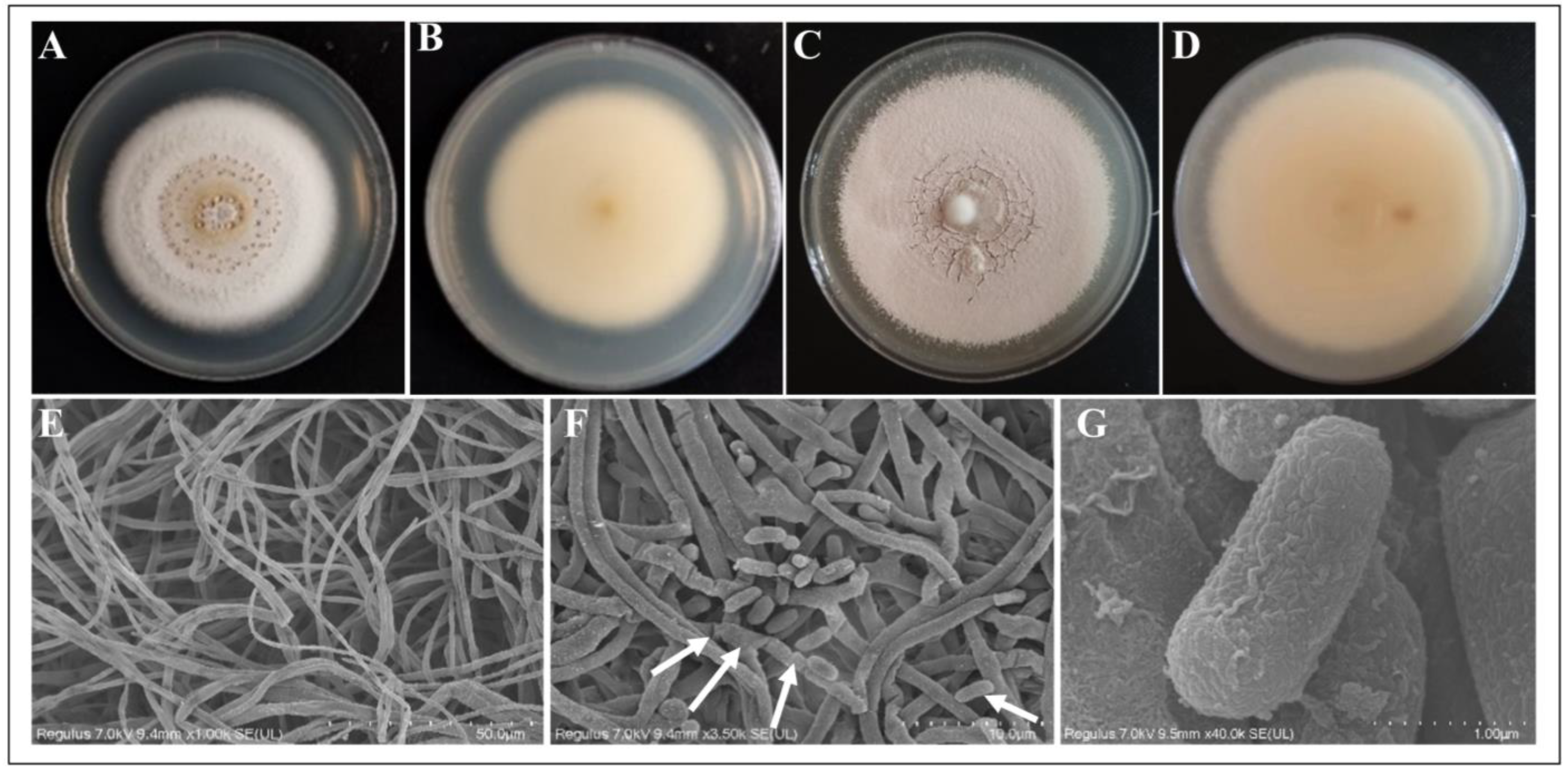
3.1. Strain Morphological Characterization
3.1.1. Field Characteristics
3.1.2. Micromorphological Characteristics
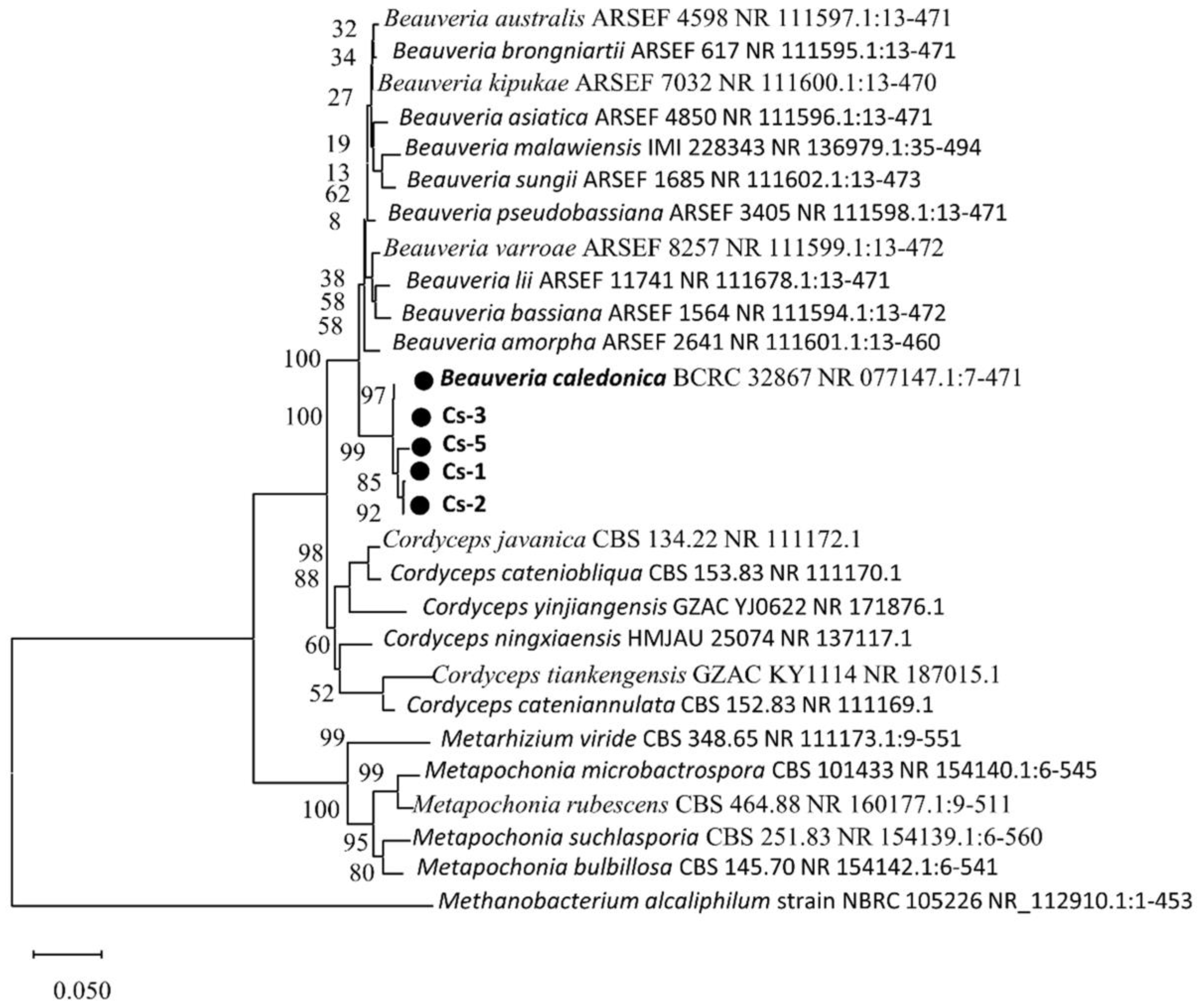
3.2. Sequence Analysis of Strain rDNA-ITS
3.3. Effect of Different Culture Conditions on the Growth of Strains
3.4. Pathogenicity of B. caledonica Against O. longicollis (Oliver)
3.5. Effectiveness of Greenhouse Control of B. caledonica
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Dairi, M.; Pathare, P.B.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Jayasuriya, H.; Al-Attabi, Z. Postharvest quality, technologies, and strategies to reduce losses along the supply chain of banana: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2023, 134, 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Brics Joint Statistical Manual. 2021. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/zt_18555/ztsj/jzgj/jz2022/ (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Padmanaban, B. Pests of banana. In Pests and Their Management; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 441–455. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, U.; Singh, A.; Mondal, A. Integrated pest management in banana. In Integrated Pest Management in the Tropics; New India Publishing Agency: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 329–349. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanaban, B.; Mani, M. Pests and Their Management in Banana. In Trends in Horticultural Entomology; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 577–603. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, J.U.; Jayaprakas, C.A.; Lekshmi, N.R.; Ajesh, G. Discovery of elytral thermo-receptor sensilla in three species of coleopterans-a comparative morphology study. Int. J. Entomol. Res. 2017, 5, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, C.S.; Pena, J.E.; Karamura, E.B. Biology and integrated pest management for the banana weevil Cosmopolites sordidus (Germar) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 2001, 6, 79–155. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.M.A.; Tara, J.; Shaloo, A.S.A.; Mohd, F.M.F.; Ramamurthy, V. B Bionomics of Odoiporus longicollis Olivier (Coleoptera: Rhynchophoridae) on banana plant (Musa paradisica). Munis Entomol. Zool. 2010, 5, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, M.; Padmanaban, B.; Anbalagan, S.; Krishnan, M. A review on monitoring and integrated management of banana Pseudostem Weevil, Odoiporus longicollis Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in India. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanaban, B.; Sathiamoorthy, S. The Banana Stem Weevil Odoiporus longicollis; Red Internacional para el Mejoramiento del Banano y el Plátano (INIBAP): Montpellier, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanaban, B.; Sundararaju, P.; Velayudhan, K.; Sathiamoorthy, S. Evaluation of Musa germplasm against banana weevil borers. InfoMusa 2001, 10, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Thippaiah, M.; Kumar, C.; Shivaraju, C.; Chakravarthy, A. Incidence of banana pseudostem weevil, Odoiporus longicollis (Olivier) in South Karnataka. Pest Manag. Hortic. Ecosyst. 2010, 16, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath, S.; Mutthuraju, G.; Doddabasappa, B.; Ahmed, T. Biology and incidence of banana pseudostem weevil, Odoiporus longicollis in Mysuru region. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2024, 8, 712–715. [Google Scholar]
- Vilardebo, A. The coefficient of infestation, a criterion for evaluating the degree of attack in banana plantations by Cosmopolites sordidus, the weevil borer. Fruits 1973, 28, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Tinzaara, W.; Gold, C.; Dicke, M.; Van, H.A. Olfactory responses of banana weevil predators to volatiles from banana pseudostem tissue and synthetic pheromone. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 1537–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Rannestad, O.T.; Saethre, M.G.; Maerere, A.P. Migration potential of the banana weevil Cosmopolites sordidus. Agric. For. Entomol. 2011, 13, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Erima, R.; Kubiriba, J.; Komutunga, E.; Nowakunda, K.; Namanya, P.; Seruga, R. Banana pests and diseases spread to higher altitudes due to increasing temperature over the last 20 years. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 601–608. [Google Scholar]
- Bukomeko, H.; Taulya, G.; Schut, A.G.; van de Ven, G.W.; Kubiriba, J.; Giller, K. Evaluating combined effects of pesticide and crop nutrition (with N, P, K and Si) on weevil damage in East African Highland Bananas. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282493. [Google Scholar]
- Musabyimana, T.; Saxena, R.C.; Kairu, E.W.; Ogol, C.K.P.O.; Khan, Z.R. Powdered neem seed and cake for management of the banana weevil, Cosmopolites sordidus, and parasitic nematodes. Phytoparasitica 2000, 28, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi, C. Genotoxicity of pesticides: A review of human biomonitoring studies. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2003, 543, 251–272. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, L.; Thapa, K.; Kanojia, N.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S.; Grewal, A.S. An extensive review on the consequences of chemical pesticides on human health and environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124657. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, C.; Okech, S.; Nokoe, S. Evaluation of pseudostem trapping as a control measure against banana weevil, Cosmopolites sordidus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Uganda. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2002, 92, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Carval, D.; Resmond, R.; Achard, R.; Tixier, P. Cover cropping reduces the abundance of the banana weevil Cosmopolites sordidus but does not reduce its damage to the banana plants. Biol. Control. 2016, 99, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Feng, M.G. Advances in fundamental and applied studies in China of fungal biocontrol agents for use against arthropod pests. Biol. Control. 2014, 68, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lovett, B.; Leger, R.J.S. The insect pathogens. Fungal Kingd. 2017, 923–943. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, P.; Pell, J. Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.W.; Hajek, A.E. Entomopathogenic fungi as bioinsecticides. In Frontiers in Industrial Mycology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 144–159. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, M.A.E.; Castilho, A.M.C.; Fraga, M.E. Classification and infection mechanism of entomopathogenic fungi. Arq. Do Inst. Biológico 2017, 84, e0552015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, A.E.; Soper, R.S.; Roberts, D.W.; Anderson, T.E.; Biever, K.D.; Ferro, D.N. Foliar applications of Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin for control of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): An overview of pilot test results from the northern United States. Can. Entomol. 1987, 119, 959–974. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, L.A.; Lewis, L.C. Occurrence of the entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin in different tillage regimes and in Zea mays L. and virulence towards Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 45, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, M.; Sato, H.; Maehara, N. Density of the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana Vuillemin (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) in forest air and soil. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2002, 37, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- St, L.R.J.; Allee, L.; May, B.; Staples, R.C.; Roberts, D.W. World-wide distribution of genetic variation among isolates of Beauveria spp. Mycol. Res. 1992, 96, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, G. Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 553–596. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarin, G.M.; Jaronski, S.T. The production and uses of Beauveria bassiana as a microbial insecticide. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Moraga, E.; Maranhao, E.; Valverde-García, P.; Santiago-Álvarez, C. Selection of Beauveria bassiana isolates for control of the whiteflies Bemisia tabaci and Trialeurodes vaporariorum on the basis of their virulence, thermal requirements, and toxicogenic activity. Biol. Control. 2006, 36, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, H.; Li, W.; Cheng, P.; Gong, M. The toxins of Beauveria bassiana and the strategies to improve their virulence to insects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 705343. [Google Scholar]
- Bissett, J.; Widden, P. A new species of Beauveria isolated from Scottish moorland soil. Can. J. Bot. 1988, 66, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, S.B.; Li, Z.Z.; Fan, M.Z. A new record of Beauveria isolated from Scolytidae in China. Mycosystema 2007, 26, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Glare, T.R.; Reay, S.D.; Nelson, T.L.; Moore, R. Beauveria caledonica is a naturally occurring pathogen of forest beetles. Mycol. Res. 2008, 112, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarin, G.M.; Marinho-Prado, J.S.; Assalin, M.R.; Martins, L.G.; Braga, E.S.; Tasic, L. Natural occurrence of B. caledonica, pathogenicity to Cosmopolites sordidus and antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4458–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, A. Natural distribution and entomopathogenicity of insect-associatedfungal pathogens from forest in west China. Yangling, Shaanxi, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y. Biological characteristics of Metarhizium anisopliae var. major and its virulence to white grubs. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 351–353. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Yang, L.M.; Xu, S.T.; Li, S.; Zeng, L.; Shang, H.; Li, X.D.; Fan, H.C.; Zheng, S.J. Biological control of the native endophytic fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia from the root nodule of Dolichos lablab on Fusarium wilt of banana TR4. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1371336. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.; Xiao, G.; Du, G.L.; Chen, B.; Peng, Y. Isolation, Identification and the Virulence of Metarhizium rileyi from Adult of Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith). Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2023, 39, 331. [Google Scholar]
- Bamisile, B.S.; Akutse, K.S.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Xu, Y. Model application of entomopathogenic fungi as alternatives to chemical pesticides: Prospects, challenges, and insights for next-generation sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 741804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargues, J.; Goettel, M.; Smits, N.; Ouedraogo, A.; Rougier, M. Effect of temperature on vegetative growth of Beauveria bassiana isolates from different origins. Mycologia 1997, 89, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Uzakah, R. Activity rhythm of the banana weevil, Cosmopolites sordidus Germar (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2018, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Mullens, B.A.; Gajdeczka, M.T.; Rehner, S.A.; Vilgalys, R.; Hajek, A.E. Hijacked: Co-option of host behavior by entomophthoralean fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006274. [Google Scholar]
- Mannino, M.C.; Huarte-Bonnet, C.; Davyt-Colo, B.; Pedrini, N. Is the insect cuticle the only entry gate for fungal infection? Insights into alternative modes of action of entomopathogenic fungi. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Urquiza, A.; Keyhani, N.O. Action on the Surface: Entomopathogenic Fungi Versus the Insect Cuticle. Insects 2013, 4, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Sun, J.; Song, Y.-J.; Zheng, H.-H.; Wang, G.-J.; Luo, W.-X. An entomopathogenic fungus exploits its host humoral antibacterial immunity to minimize bacterial competition in the hemolymph. Microbiome 2023, 11, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-L.; Leger, R.S. Insect immunity to entomopathogenic fungi. Adv. Genet. 2016, 94, 251–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kisaakye, J.; Fourie, H.; Coyne, D.; Cortada, L.; Masinde, S.; Subramanian, S.; Haukeland, S. Evaluation of the Entomopathogenic potential of Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae and Isaria fumosorosea for management of Cosmopolites sordidus Germar (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Agriculture 2021, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, A.; Padmanaban, B.; Tharani, G.; Jawahar, S.; Manivannan, S. An assessment of biological control of the banana pseudostem weevil Odoiporus longicollis (Olivier) by entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101262. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Pérez, L.D.C.; Barranco-Florido, J.E.; Rodríguez-Navarro, S.; Cervantes-Mayagoitia, J.F.; Ramos-López, M.Á. Enzymes of entomopathogenic fungi, advances and insights. Adv. Enzym. Res. 2014, 2, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; St. Leger, R.J. Developmental and transcriptional responses to host and nonhost cuticles by the specific locust pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae var. acridum. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 937–947. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Shang, J.; Sun, Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, C. Fungal infection of insects: Molecular insights and prospects. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 33, 302–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, K.A.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.A.; Abdel-Mallek, A.Y.; El-Maraghy, S.S.; Joo, J.H. Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae against Galleria mellonella. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Cito, A.; Barzanti, G.P.; Strangi, A.; Francardi, V.; Zanfini, A.; Dreassi, E. Cuticle-degrading proteases and toxins as virulence markers of Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, M.; Joshi, N. Enzymatic comparison and mortality of Beauveria bassiana against cabbage caterpillar Pieris brassicae LINN. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- St Leger, R.; Joshi, L.; Bidochka, M.J.; Roberts, D.W. Construction of an improved mycoinsecticide overexpressing a toxic protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6349–6354. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, W.; Guo, S.; Pei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D. Increased insect virulence in Beauveria bassiana strains overexpressing an engineered chitinase. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Keyhani, N.O. Lipid biology in fungal stress and virulence: Entomopathogenic fungi. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 420–429. [Google Scholar]
- Pirali-Kheirabadi, K.; Haddadzadeh, H.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M.; Bokaie, S.; Zare, R.; Ghazavi, M.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M. Biological control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus by different strains of Metarhizium anisopliae, Beauveria bassiana and Lecanicillium psalliotae fungi. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, D.; Zou, W.-Q.; Tang, D.-X.; Hongthong, P.; Yu, H. Species diversity and virulence potential of the Beauveria bassiana complex and Beauveria scarabaeidicola complex. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 841604. [Google Scholar]
- Paulitz, T.C.; Bélanger, R.R. Biological control in greenhouse systems. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2001, 39, 103–133. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, F.; Tkaczuk, C.; Dinu, M.M.; Fiedler, Ż.; Vidal, S.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Messelink, G.J. New opportunities for the integration of microorganisms into biological pest control systems in greenhouse crops. J. Pest Sci. 2016, 89, 295–311. [Google Scholar]
- Er, M.; Tunaz, H.; Gökçe, A. Pathogenicity of entomopathogenic fungi to Thaumetopoea pityocampa (Schiff.) (Lepidoptera: Thaumatopoeidae) larvae in laboratory conditions. J. Pest Sci. 2007, 80, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, J.; Yanase, K. Phenol oxidase activity in the integument of the silkworm Bombyx mori infected with Beauveria bassiana and Spicaria fumoso-rosea. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1970, 16, 459–464. [Google Scholar]


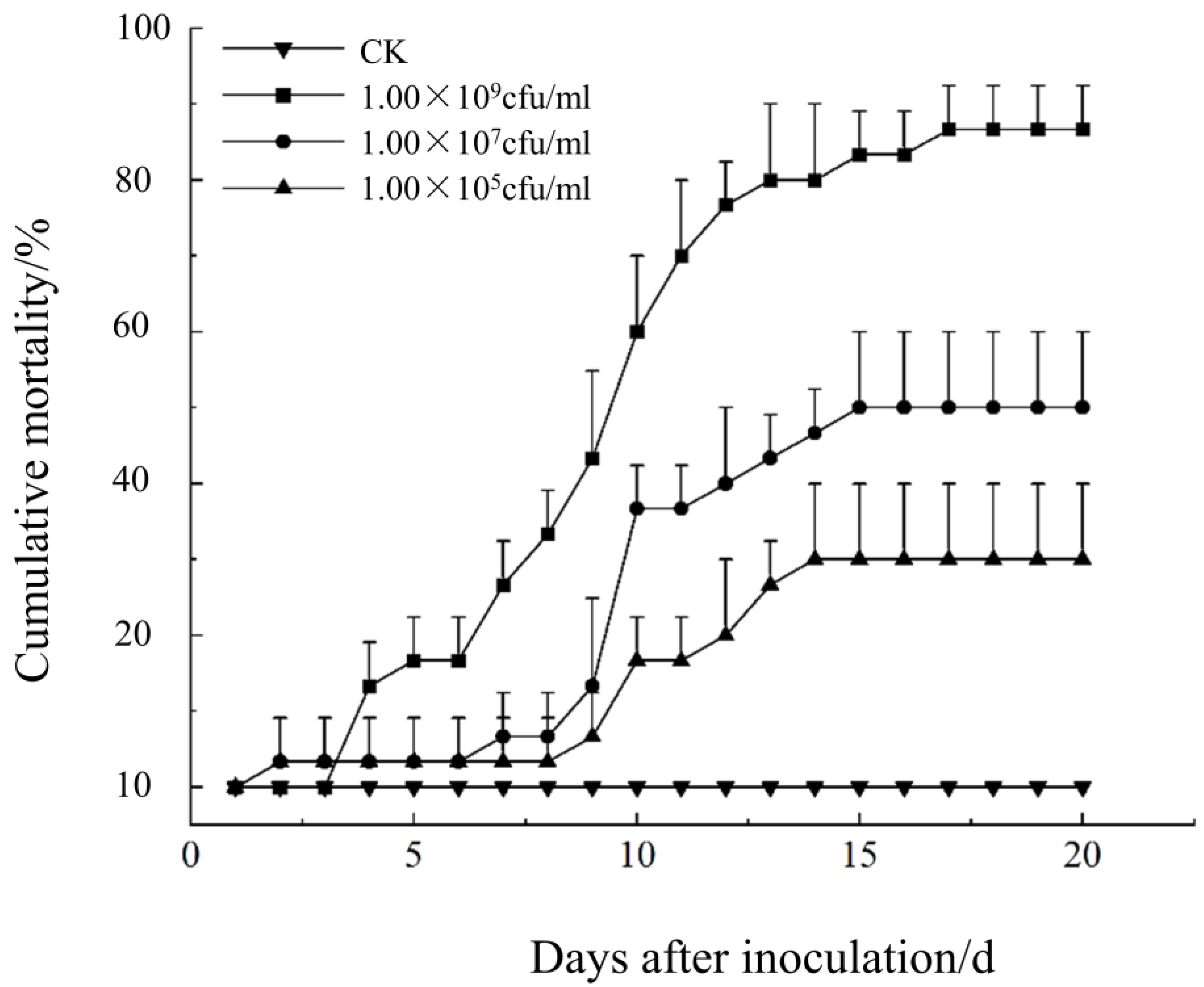


| Conidia Concentration (cfu/mL) | Cumulative Mortality (%) | Regression Equation of Virulence | LT50/d | 95% Confidence Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 c | - | - | - |
| 1.00 × 105 | 20.00 bc | - | - | - |
| 1.00 × 107 | 50.00 b | y = −3.537 + 2.875x | 17.00 | 15.254–19.583 |
| 1.00 × 109 | 86.67 a | y = −4.293 + 4.420x | 9.36 | 8.713–9.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, M.; Wu, L.; Yu, H.; Fan, H.; Guo, Z.; Xu, S.; Chun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.-J. Isolation and Characterization of Beauveria caledonica (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Strains for Biological Control of Odoiporus longicollis Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040782
Ding M, Wu L, Yu H, Fan H, Guo Z, Xu S, Chun J, Wang Y, Zheng S-J. Isolation and Characterization of Beauveria caledonica (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Strains for Biological Control of Odoiporus longicollis Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040782
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Mingbi, Li Wu, Hongwei Yu, Huacai Fan, Zhixiang Guo, Shengtao Xu, Jianhui Chun, Yongfen Wang, and Si-Jun Zheng. 2025. "Isolation and Characterization of Beauveria caledonica (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Strains for Biological Control of Odoiporus longicollis Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040782
APA StyleDing, M., Wu, L., Yu, H., Fan, H., Guo, Z., Xu, S., Chun, J., Wang, Y., & Zheng, S.-J. (2025). Isolation and Characterization of Beauveria caledonica (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Strains for Biological Control of Odoiporus longicollis Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Microorganisms, 13(4), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040782






