Prebiotic Effects of Insoluble Konjac Glucomannan Derived from Edible “Konnyaku” on Weight Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model and Study Design
2.2. Preparation of Insoluble Konjac Glucomannan (iKGM)
2.3. Serum Lipid Analysis
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. Antibiotic Treatment
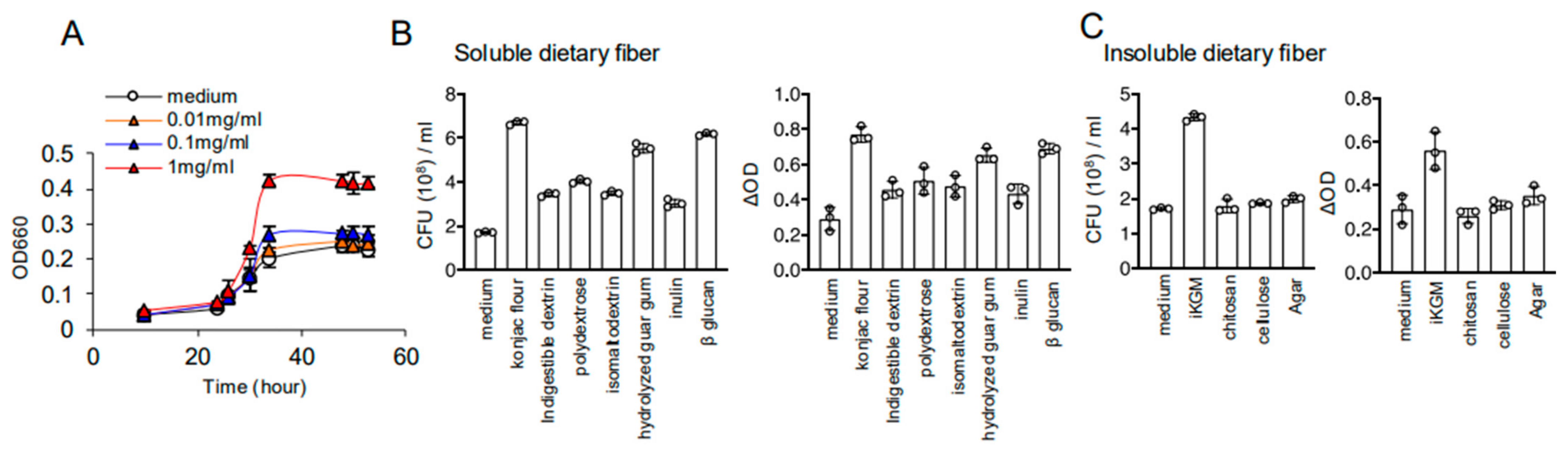
2.6. Akkermansia Muciniphila Culture
2.7. Intestinal Metabolite Analysis
2.8. Leptin Quantification
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Data Availability
3. Results
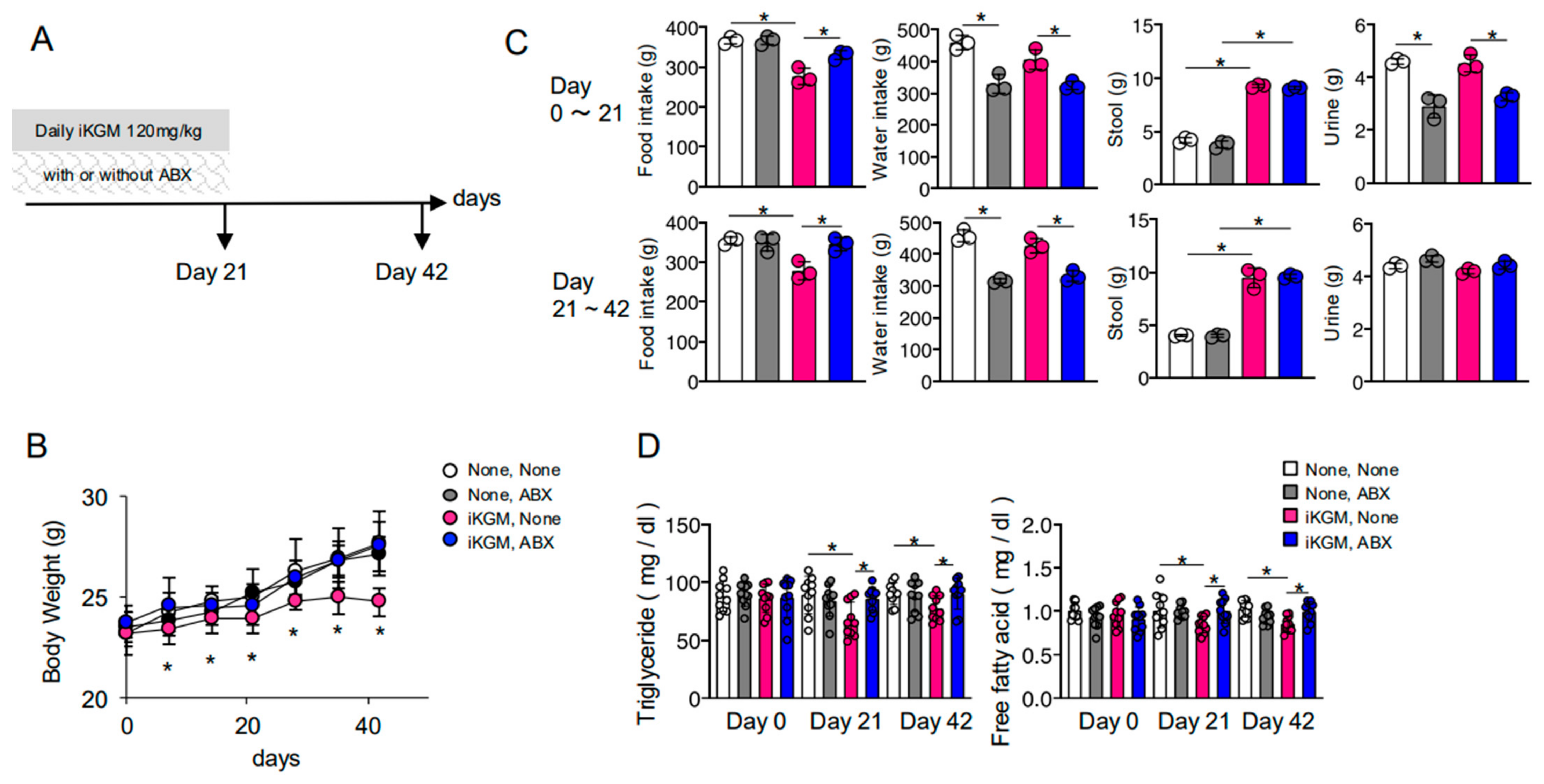
3.1. iKGM Suppresses Weight Gain
3.2. The Weight-Suppressing Effect of iKGM Depends on Intestinal Bacteria
3.3. iKGM Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Increases Akkermansia muciniphila
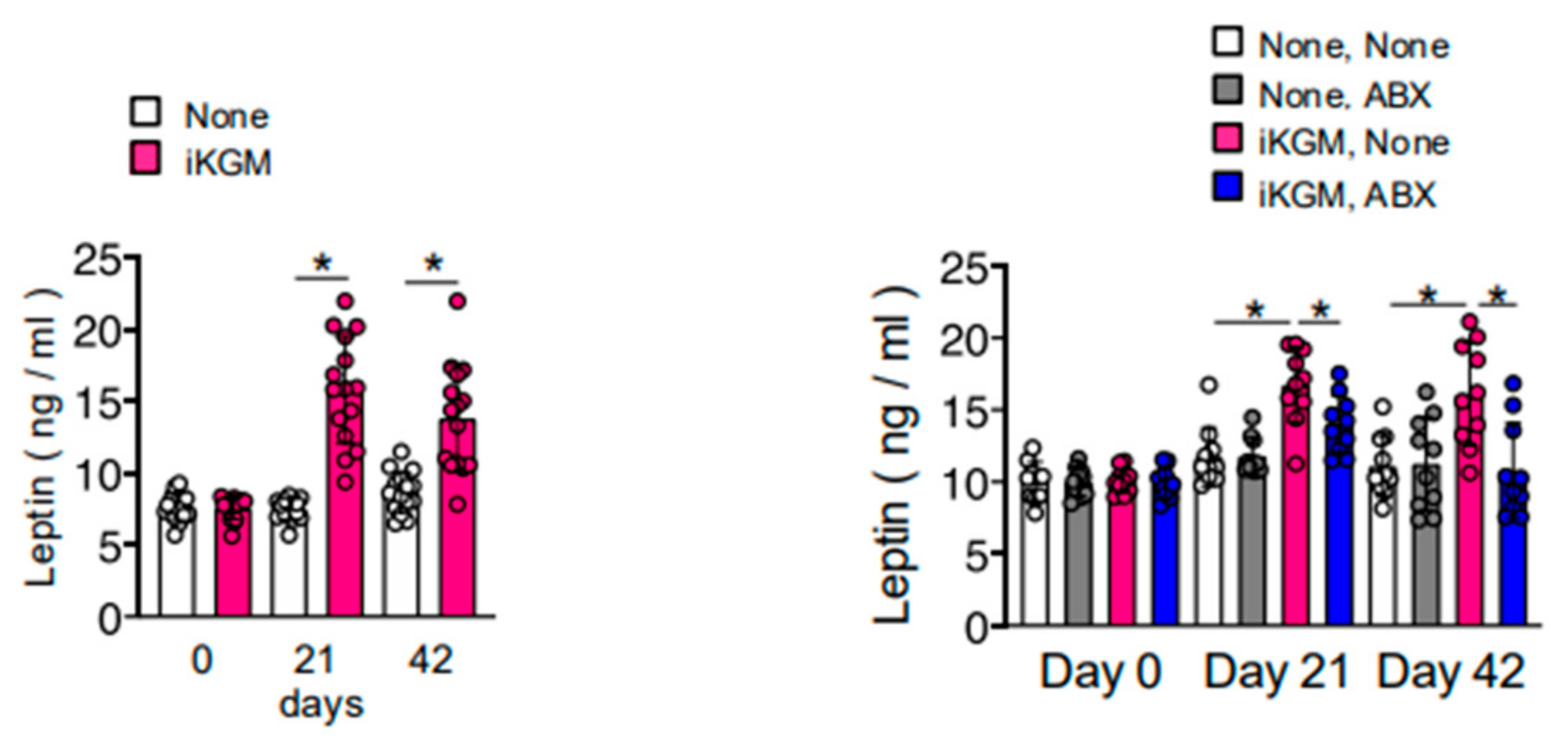
3.4. Alteration of Intestinal Bacteria by iKGM Increases SCFAs and Leptin
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/overweight/en/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2020, 22, S176–S185. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, E.J.; Dhurandhar, N.V.; Keith, S.W.; Aronne, L.J.; Barger, J.; Baskin, M.; Benka, R.M.; Biggio, J.; Boggiano, M.M.; Eisenmann, J.C.; et al. Ten putative contributors to the obesity epidemic. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 863–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitlock, G.; Lewington, S.; Sherliker, P.; Clarke, R.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Collins, R.; Peto, R. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900,000 adults: Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009, 378, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Anekwe, C.V.; Jarrell, A.W.; Townsend, M.J.; Gaudier, G.I.; Hiserodt, J.M.; Stanford, F.C. Socioeconomics of obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.P.; Mesidor, M.; Winters, K.; Dubbert, P.M.; Wyatt, S.B. Overweight and obesity: Prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C. Konjac glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide of Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch in health care. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Xie, B.J.; Gan, X. Advances in the applications of konjac glucomannan and its derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2020, 464, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and mechanism of gut microbiota in human disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.K.; Mullin, G.E. The gut microbiome and obesity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankararaman, S.; Noriega, K.; Valayuthan, S.; Sferra, T.; Martindale, R. Gut microbiome and its impact on obesity and obesity-related disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2022, 25, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, J.; Luber, J.M.; Chavkin, T.A.; MacDonald, T.; Tung, A.; Pham, L.D.; Wibowo, M.C.; Wurth, R.C.; Punthambaker, S.; Tierney, B.T.; et al. Meta-omics analysis of elite athletes identified a performance-enhancing microbe that functions via lactate metabolism. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, B.S.; Shaito, A.; Motoike, T.; Rey, F.E.; Backhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Hammer, R.E.; Williams, S.C.; Crowley, J.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16767–16772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolhurst, G.; Heffron, H.; Lam, Y.S.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Diakogiannaki, E.; Cameron, J.; Grosse, J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012, 61, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Ozawa, K.; Inoue, D.; Imamura, T.; Kimura, K.; Maeda, T.; Terasawa, K.; Kashihara, D.; Hirano, K.; Tani, T.; et al. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaibi, M.S.; Stocker, C.J.; O’Dowd, J.; Davies, A.; Bellahcene, M.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Brown, A.J.; Smith, D.M.; Arch, J.R. Roles of GPR41 and GPR43 in leptin secretory responses of murine adipocytes to short chain fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, H.R.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Albrecht, S.; Schols, H.; Franco, B.D.G.D.M.; Saad, S.M.I.; Smidt, H. In vitro fermentation of prebiotic carbohydrates by intestinal microbiota in the presence of Lactobacillus amylovorus DSM 16998. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Sheu, W.H.H.; Tai, T.S.; Liaw, Y.P.; Chen, Y.C. Konjac supplement alleviated hypercholesterolemia and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic subjects—A randomized double-blind trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Li, Y.U.; Du, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Yang, F.; Hong, J.; Kong, X. Konjaku flour reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachandran, M.; Christudas, S.; Zheng, X.; Xu, B. Dietary fiber konjac glucomannan exerts an antidiabetic effect via inhibiting lipid absorption and regulation of PPAR-γ and gut microbiome. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, S.; Nishimura, N.; Morita, T. Hairy region concentrate of pectin strongly stimulates mucin secretion in HT29-MTX cells, but to a lesser degree in rat small intestine. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2020, 66, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Hino, S.; Takemura, N.; Sonoyama, K.; Morita, A.; Kawagishi, H.; Aoe, S.; Morita, T. Small intestinal goblet cell proliferation induced by ingestion of soluble and insoluble dietary fiber is characterized by an increase in sialylated mucins in rats. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ruan, Z. Indole-3-propionic acid improved the intestinal barrier by enhancing epithelial barrier and mucus barrier. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar]
- de La Serre, C.B.; Ellis, C.L.; Lee, J.; Hartman, A.L.; Rutledge, J.C.; Raybould, H.E. Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G440. [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger, M.; Everard, A.; Gómez-Valadés, A.G.; Matamoros, S.; Ramírez, S.; Delzenne, N.M.; Gomis, R.; Claret, M.; Cani, P.D. Akkermansia muciniphila inversely correlates with the onset of inflammation, altered adipose tissue metabolism, and metabolic disorders during obesity in mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, S.; Mizushima, T.; Kaneko, K.; Kawai, E.; Kondo, T.; Genda, T.; Yamada, T.; Hase, K.; Nishimura, N.; Morita, T. Mucin-derived O-glycans as endogenous fiber and sustain mucosal immune homeostasis via short-chain fatty acid production in rat cecum. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottman, N.; Davids, M.; Suarez-Diez, M.; Boeren, S.; Schaap, P.J.; Martins dos Santos, V.A.; Smidt, H.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Genome-scale model and omics analysis of metabolic capacities of Akkermansia muciniphila reveal a preferential mucin-degrading lifestyle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01014-17. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tan, C.; Hou, L.; Qian, W.; Han, C.; Hou, X. Fucose promotes intestinal stem cell-mediated intestinal epithelial development through promoting Akkermansia-related propanoate metabolism. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2233149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larraufie, P.; Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Lapaque, N.; Dore, J.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Blottiere, H.M. SCFAs strongly stimulate PYY production in human enteroendocrine cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psichas, A.; Sleeth, M.L.; Murphy, K.G.; Brooks, L.; Bewick, G.A.; Hanyaloglu, A.C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Frost, G. The short-chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 39, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, I.; Inoue, D.; Maeda, T.; Hara, T.; Ichimura, A.; Miyauchi, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirasawa, A.; Tsujimoto, G. Short-chain fatty acids and ketones directly regulate sympathetic nervous system via G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GRP41). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8030–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.W.; Shorten, P.R.; Altermann, E.; Roy, N.C.; McNabb, W.C. Examination of hydrogen cross-feeders using a colonic microbiota model. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.; Mann, J.; Cummings, J.; Winter, N.; Mete, E.; Te Morenga, L. Carbohydrate quality and human health: A series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Lancet 2019, 393, 434–445. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/prevalence-of-overweight-among-adults-bmi--25-(age-standardized-estimate)-(-) (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Corina-Bianca, I.; Khaled, Z.; Magdalena, M. Therapeutic benefits and dietary restrictions of fiber intake: A state of the art review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimokawa, C.; Mizutani, W.; Motegi, H.; Gokan, N.; Tomita, J.; Hisaeda, H. Prebiotic Effects of Insoluble Konjac Glucomannan Derived from Edible “Konnyaku” on Weight Control. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040877
Shimokawa C, Mizutani W, Motegi H, Gokan N, Tomita J, Hisaeda H. Prebiotic Effects of Insoluble Konjac Glucomannan Derived from Edible “Konnyaku” on Weight Control. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040877
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimokawa, Chikako, Wakana Mizutani, Haruhisa Motegi, Naomi Gokan, Junichi Tomita, and Hajime Hisaeda. 2025. "Prebiotic Effects of Insoluble Konjac Glucomannan Derived from Edible “Konnyaku” on Weight Control" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040877
APA StyleShimokawa, C., Mizutani, W., Motegi, H., Gokan, N., Tomita, J., & Hisaeda, H. (2025). Prebiotic Effects of Insoluble Konjac Glucomannan Derived from Edible “Konnyaku” on Weight Control. Microorganisms, 13(4), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040877






