Effects of Seawater from Different Sea Areas on Abalone Gastrointestinal Microorganisms and Metabolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seawater and Sample Collection
2.2. Microbial Diversity Analysis
2.3. Non-Targeted Metabolomic Analysis on Gastric and Intestinal Content Samples
2.4. Correlation Analyse
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Seawater Parameter Measurements
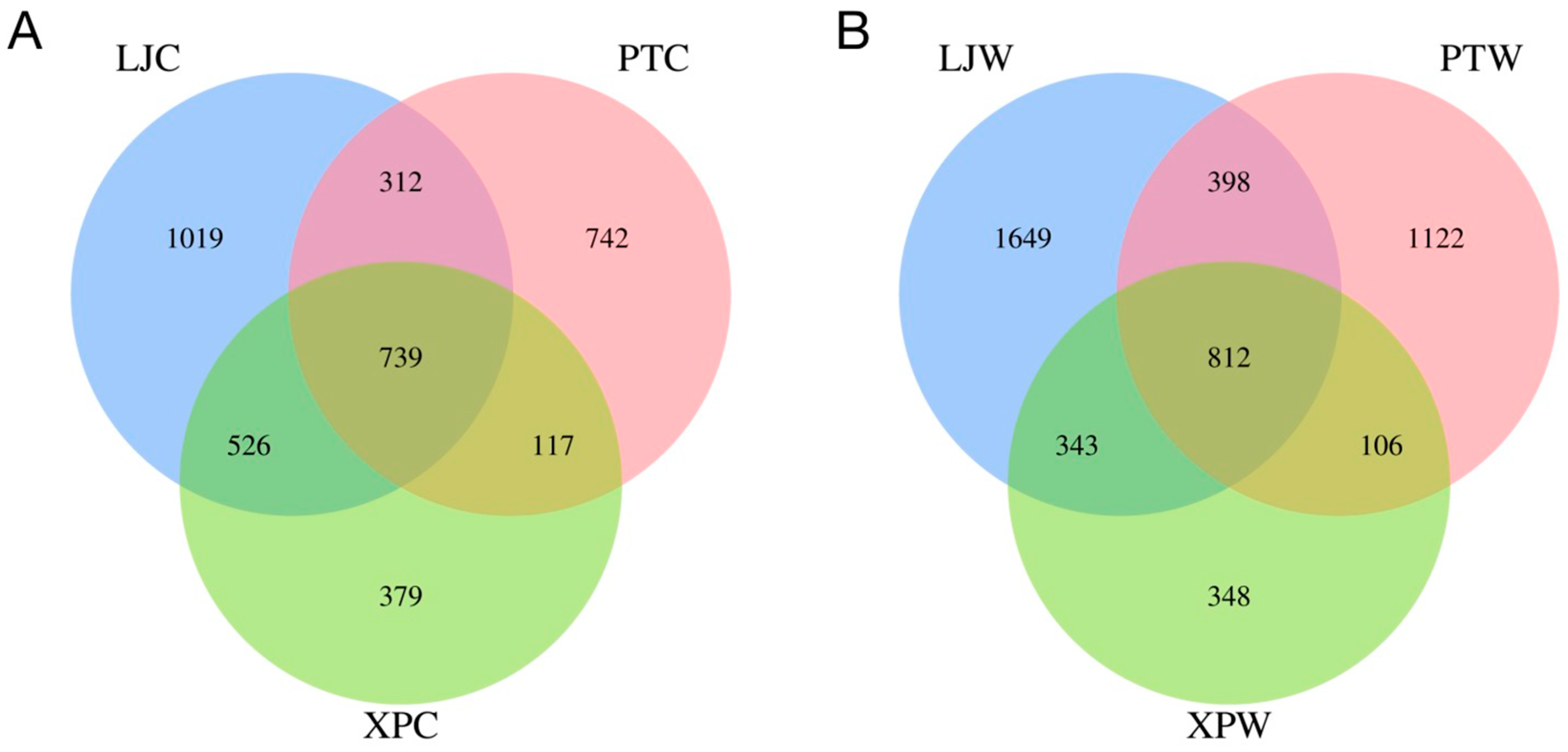
3.2. OTU Counts in Gastrointestinal Microbiota Across Regions
3.3. Bacterial Abundance and Diversity in Abalone Gastrointestinal Samples
3.3.1. Alpha Diversity
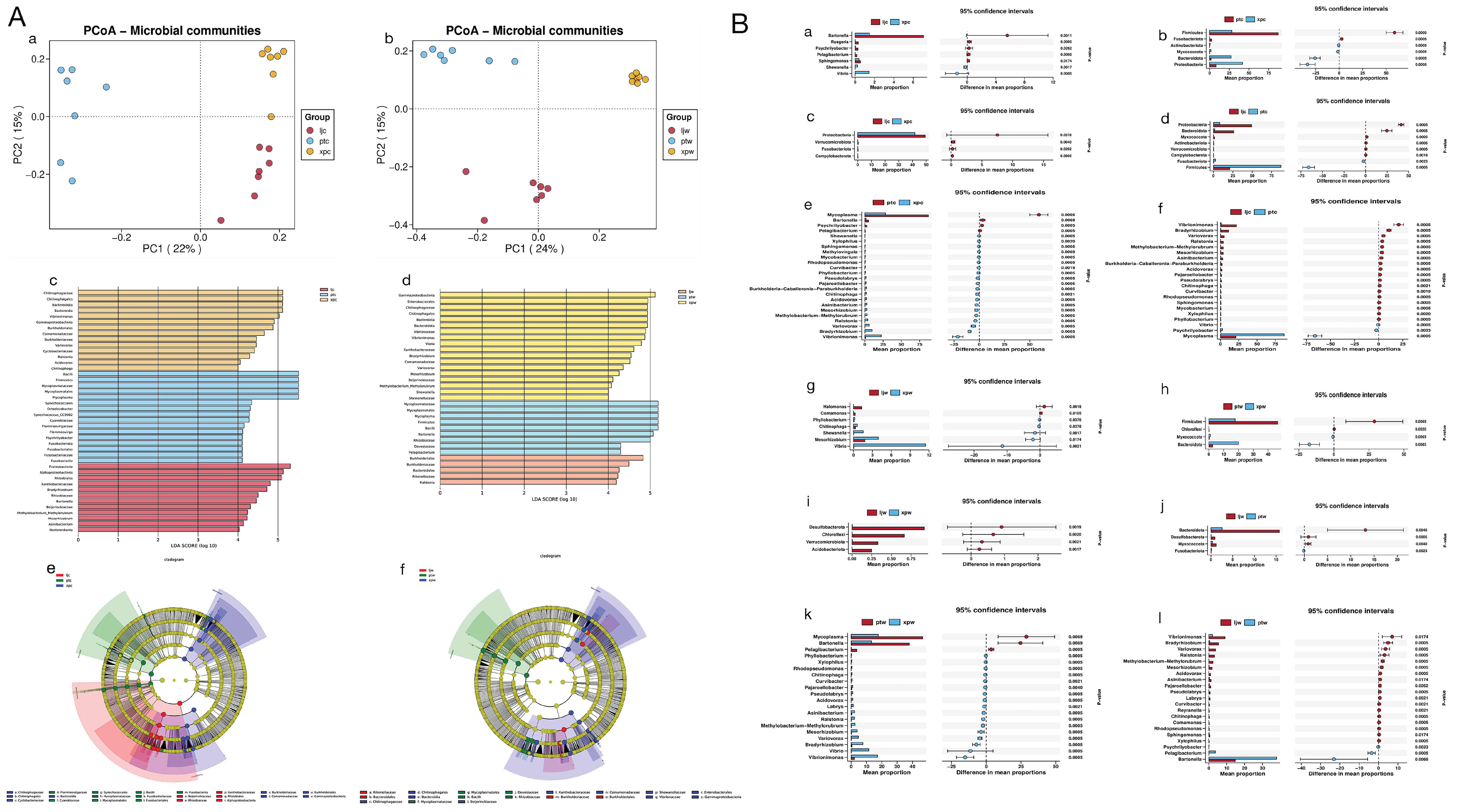
3.3.2. Microbial Community Composition
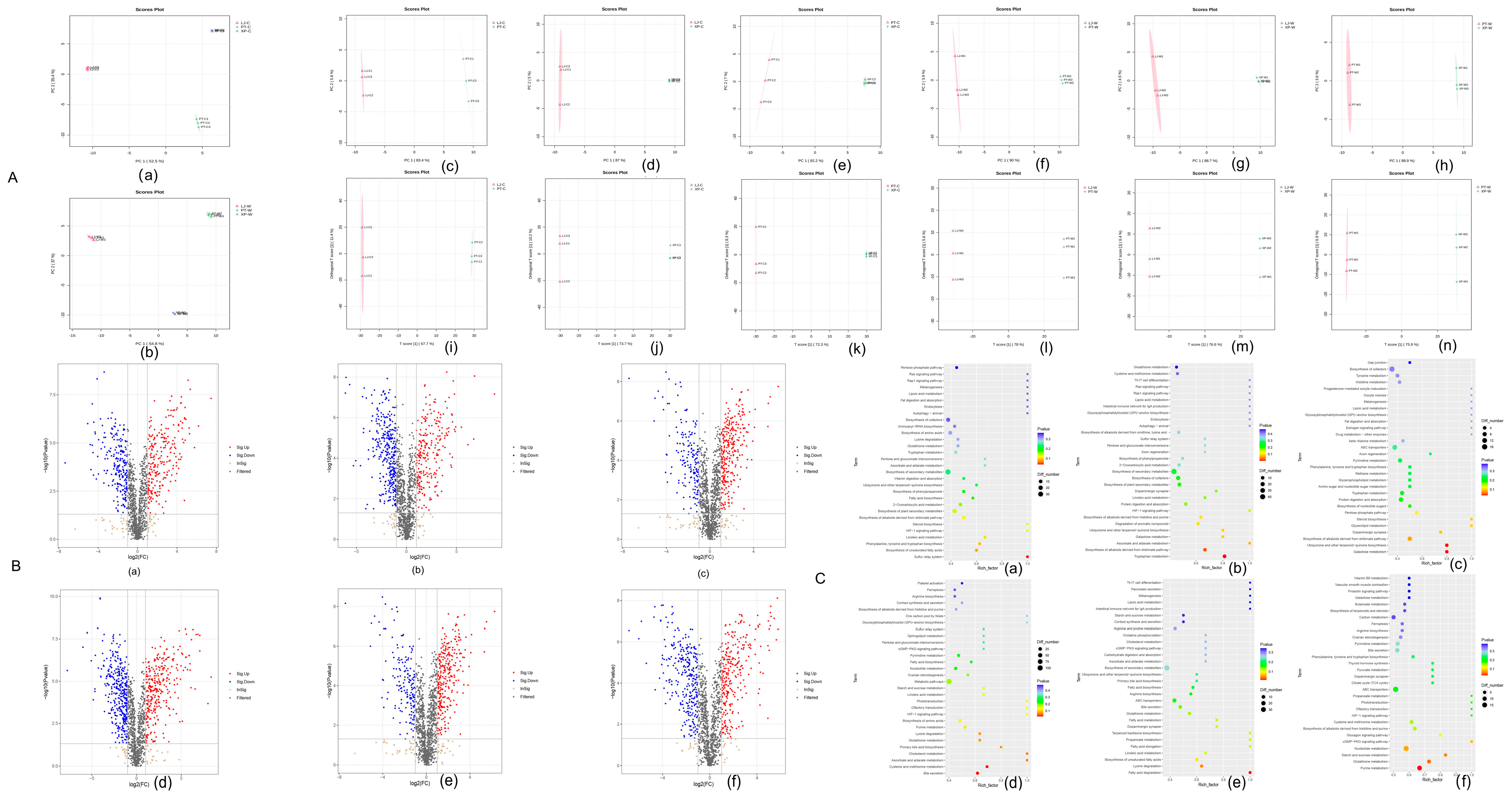
3.3.3. Beta Diversity
3.3.4. Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
3.3.5. Differential Metabolite Screening
3.3.6. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hobday, A.J.; Pecl, G.T. Identification of global marine hotspots: Sentinels for change and vanguards for adaptation action. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2014, 24, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.; Przeslawski, R. Multistressor impacts of warming and acidification of the ocean on marine invertebrates’ life histories. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2013, 53, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldbusser, G.G.; Hales, B.; Langdon, C.J.; Haley, B.A.; Schrader, P.; Brunner, E.L.; Gray, M.W.; Miller, C.A.; Gimenez, I.; Hutchinson, G. Ocean acidification has multiple modes of action on bivalve larvae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dineshram, R.; Wong, K.K.; Xiao, S. Comparative analysis of osmoregulatory responses in two abalone species (Haliotis diversicolor and H. discus hannai) under salinity stress. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Cheung, S.G. Nutrient enrichment alters abalone recruitment and benthic community structure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 486, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.E.; Punt, A.E.; Hamel, O.S. A framework for incorporating environmental drivers into abalone fishery management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, P.A.; Roleda, M.Y.; Leal, P.P.; Hurd, C.L. Seawater PH, and Not Inorganic Nitrogen Source, Affects PH at the Blade Surface of Macrocystis Pyrifera: Implications for Responses of the Giant Kelp to Future Oceanic Conditions. Physiol. Plant 2017, 159, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanek, L. Environmental Proteomics of the Mussel Mytilus: Implications for Tolerance to Stress and Change in Limits of Biogeographic Ranges in Response to Climate Change. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2012, 52, 648–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Hong, J.; Yu, W.; Ma, Y.; Gan, J.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; You, W.; Ke, C. Comprehensive Comparison of Effects of Antioxidant (Astaxanthin) Supplementation from Different Sources in Haliotis Discus Hannai Diet. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, A.J.; Qin, J.; Li, Q.; Ho, J.G.; Li, H. Seasonal patterns of water quality and phytoplankton dynamics in surface waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Ye, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.; Li, H.; Yu, G. Effects of Cadmium Exposure on Gut Microbiota and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Haliotis Diversicolor Abalone. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Jiao, M.; Tang, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Xue, S.; Mao, Y. The Effect of Total Alkalinity on Growth Performance and Calcification in Juvenile Pacific Abalone Haliotis Discus Hannai. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 192, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.-E.; Haque, M.N.; Lee, J.S.; Park, H.S.; Rhee, J.-S. Prolonged Exposure to Hypoxia Inhibits the Growth of Pacific Abalone by Modulating Innate Immunity and Oxidative Status. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 227, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Yang, N.; Liang, X.; Yoshida, A.; Osatomi, K.; Power, D.; Batista, F.M.; Yang, J.L. Elevated Seawater Temperatures Decrease Microbial Diversity in the Gut of Mytilus Coruscus. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrichenko, D.; Tkachuk, A.; Kladchenko, E.; Andreeva, A. The effect of short-term salinity changes on the functional features of mediterranean mussel hemocytes. Russ. J. Biol. Phys. Chemisrty 2024, 8, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, J.A.; Hollins, A.; McCarty, A.J.; Martinez, G.; Cui, M.; Gomes, M.L.; Fuchsman, C.A. Microbial Diversity and Abundance Vary along Salinity, Oxygen, and Particle Size Gradients in the Chesapeake Bay. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 26, e16557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denu, J.M. Vitamins and Aging: Pathways to NAD+ Synthesis. Cell 2007, 129, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corte, D.; Sintes, E.; Yokokawa, T.; Herndl, G.J. Comparison between MICRO–CARD–FISH and 16S RRNA Gene Clone Libraries to Assess the Active versus Total Bacterial Community in the Coastal Arctic. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Xing, X.; Chen, Z.; Teng, X.; Zeng, X.; Muscarella, A.D.; Shen, Y.; Cowan, A.; et al. Metabolite Discovery through Global Annotation of Untargeted Metabolomics Data. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Pang, W.; Tian, C.; Zhao, Y. Nanoplastic-Induced Genotoxicity and Intestinal Damage in Freshwater Benthic Clams (Corbicula Fluminea): Comparison with Microplastics. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9469–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzeniowska, J.; Mikulski, A. The Effect of Bed Load Sediments on Self-Purification of River—Experimental Approach. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.W.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful Algal Blooms: A Climate Change Co-Stressor in Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottrell, S.H.; Newton, R.J. Reconstruction of Changes in Global Sulfur Cycling from Marine Sulfate Isotopes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 75, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Inomura, K.; Mareš, J.; Kodama, T.; Shiozaki, T.; Matsui, T.; Suzuki, K.; Takeda, S.; Deutsch, C.; Prášil, O.; et al. Coexistence of Dominant Marine Phytoplankton Sustained by Nutrient Specialization. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04000-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Molecular identification of bacteria operational taxonomic units (OTUs) investigted..xlsx. Figshare 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.S.; Henriques, R.; Toonen, R.J.; Knapp, I.S.S.; Guo, B.; von der Heyden, S. Complex Signatures of Genomic Variation of Two Non-Model Marine Species in a Homogeneous Environment. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Hou, Y. Using ΔFIP as a Potential Biomarker for Risk Assessment of Environmental Pollutants in Aquatic Ecosystem: A Case Study of Marine Cyanobacterium Synechococcus Sp. PCC7002. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Wei, G.; Wei, G.; Lai, Q.; Lai, Q.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, M.; et al. Genomic and Metabolic Insights into the First Host-Associated Isolate of Psychrilyobacter. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0399022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ni, L.; Guan, H.; Chen, D.; Qin, S.; Chen, L. First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca Granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella Pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals. Foods 2022, 11, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitlin, R.H. Impacts of Phage Predation on Microbial Dynamics in Temperate Ecosystems; College of William and Mary: Williamsburg, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Chakraborty, K.; Joy, M. Oxygenated Elansolid-Type of Polyketide Spanned Macrolides from a Marine Heterotrophic Bacillus as Prospective Antimicrobial Agents against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’brien, P.A.; Webster, N.S.; Miller, D.J.; Bourne, D.G. Host-Microbe Coevolution: Applying Evidence from Model Systems to Complex Marine Invertebrate Holobionts. MBio 2019, 10, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schartau, A.K.; Mariash, H.L.; Christoffersen, K.S.; Bogan, D.; Dubovskaya, O.P.; Fefilova, E.B.; Hayden, B.; Ingvason, H.R.; Ivanova, E.A.; Kononova, O.N.; et al. First Circumpolar Assessment of Arctic Freshwater Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Diversity: Spatial Patterns and Environmental Factors. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 67, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, Tryptophan Metabolism and the Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, P.K.; Jackson, B.T.; Paras, K.I.; Brunner, J.S.; Hart, M.L.; Newsom, O.J.; Alibeckoff, S.P.; Endress, J.; Drill, E.; Sullivan, L.B.; et al. A Non-Canonical Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Underlies Cellular Identity. Nature 2022, 603, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.B.; Van Benschoten, A.H.; Cimermancic, P.; Donia, M.S.; Zimmermann, M.; Taketani, M.; Ishihara, A.; Kashyap, P.C.; Fraser, J.S.; Fischbach, M.A. Discovery and Characterization of Gut Microbiota Decarboxylases That Can Produce the Neurotransmitter Tryptamine. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, F. COPD: Hyaluronic Acid as a Biomarker and Target Structure. Pneumologie 2019, 73, 564–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kits, K.D.; Klotz, M.G.; Stein, L.Y. Evolutionary genomics of ammonia oxidation in marine Pelagibacterium. ISME J. 2022, 16, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashihara, H.; Ludwig, I.A.; Crozier, A. Salvage Pathways of Pyrimidine Nucleotide Biosynthesis. In Plant Nucleotide Metabolism-Biosynthesis, Degradation, and Alkaloid Formation; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Hong, J.; Seo, D.; Nam, D.H.; Nam, K.T.; Kang, K.; Park, C.B. Redox Cofactor from Biological Energy Transduction as Molecularly Tunable Energy-Storage Compound. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8322–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, K.; Gevers, D.; Vanparys, B.; Wittebolle, L.; Geets, J.; Boon, N.; De Vos, P. The Incidence of NirS and NirK and Their Genetic Heterogeneity in Cultivated Denitrifiers. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Hei, R.; Song, X.; Fan, Z.; Guo, D.; Luo, J.; Ma, Y. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Inhibit Nitrogen Fixation and Rhizosphere Colonization by Inducing ROS in Associative Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria Pseudomonas Stutzeri A1501. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, F.; Qian, L.; Yu, X.; Huang, F.; Hu, R.; Su, H.; Gu, H.; Yan, Q.; et al. The Vertical Partitioning between Denitrification and Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium of Coastal Mangrove Sediment Microbiomes. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, M.; Portier, E.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Linossier, I.; Balnois, E.; Vignaud, G.; Moppert, X.; Hellio, C.; Faÿ, F. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Vibrio MO245 against Pathogenic Bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ITEM | LJ | PT | XP | Test Method | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.21 ± 0.42 b | 8.26 ± 1.1 a | 8.27 ± 0.7 a | HJ 1147-2020 | 0.037 |
| Total phosphorus mg/L | 0.13 ± 0.011 b | 0.28 ± 0.04 a | 0.22 ± 0.02 a | B 11893-1989 | 0.016 |
| Total nitrogen mg/L | 0.1 ± 0.008 b | 0.17 ± 0.028 a | 0.15 ± 0.022 a | HJ 636-2012 | 0.025 |
| Full salt content mg/L | 3.5 × 104 ± 2000 | 3.17 × 104 ± 3000 | 3.16 × 104 ± 5000 | HJ/T 51-1999 | 0.083 |
| Sulfide mg/L | 0.025 ± 0.0016 | 0.024 ± 0.003 | 0.026 ± 0.005 | HJ 1226-2021 | 0.066 |
| Ammonia nitrogen mg/L | 0.16 ± 0.01 b | 0.29 ± 0.024 a | 0.25 ± 0.021 a | HJ535-2009 | 0.011 |
| Group | Observed_Species | Chao1 | ACE | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJC | 1052.4 ± 110.06 c | 1296.81 ± 87.4 b | 1309.98 ± 115.3 b | 3.73 ± 0.15 c | 0.91 ± 0.02 b |
| PTC | 704.14 ± 124.47 a | 940.51 ± 171.46 a | 970.41 ± 200.46 a | 2.3 ± 0.12 a | 0.64 ± 0.07 a |
| XPC | 856.29 ± 85.42 b | 1098.27 ± 96.07 a | 1094.85 ± 81.83 a | 3.44 ± 0.24 b | 0.89 ± 0.04 b |
| LJW | 1133 ± 215.68 b | 1411.73 ± 103.24 c | 1436.47 ± 100.39 b | 3.75 ± 0.7 b | 0.89 ± 0.06 b |
| PTW | 963.71 ± 152.81 ab | 1256.86 ± 146.42 b | 1324.08 ± 171.42 b | 2.79 ± 0.24 a | 0.81 ± 0.05 a |
| XPW | 809 ± 48.85 a | 1027.06 ± 78.89 a | 1033.86 ± 67.53 a | 3.45 ± 0.19 b | 0.9 ± 0.03 b |
| p Value | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.039 | 0.011 | 0.028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Ke, L.; Huang, C.; Peng, S.; Zhao, M.; Wu, H.; Lin, F. Effects of Seawater from Different Sea Areas on Abalone Gastrointestinal Microorganisms and Metabolites. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040915
Li Z, Ke L, Huang C, Peng S, Zhao M, Wu H, Lin F. Effects of Seawater from Different Sea Areas on Abalone Gastrointestinal Microorganisms and Metabolites. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040915
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhaolong, Ling Ke, Chenyu Huang, Song Peng, Mengshi Zhao, Huini Wu, and Fengqiang Lin. 2025. "Effects of Seawater from Different Sea Areas on Abalone Gastrointestinal Microorganisms and Metabolites" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040915
APA StyleLi, Z., Ke, L., Huang, C., Peng, S., Zhao, M., Wu, H., & Lin, F. (2025). Effects of Seawater from Different Sea Areas on Abalone Gastrointestinal Microorganisms and Metabolites. Microorganisms, 13(4), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040915




