Abstract
The experiment was to determine the chronic effects of two transgenic maize lines that contained the mCry1Ac gene from the Bacillus thuringiensis strain (BT) and the maroACC gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain (CC), respectively, on ileal microbiota of laying hens. Seventy-two laying hens were randomly assigned to one of the three dietary treatments for 12 weeks, as follows: (1) nontransgenic near-isoline maize-based diet (CT diet), (2) BT maize-based diet (BT diet), and (3) CC maize-based diet (CC diet). Ileum histological examination did not indicate a chronic effect of two transgenic maize diets. Few differences were observed in any bacterial taxa among the treatments that used high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The only differences that were observed for bacterial genera were that Bifidobacterium belong within the Bifidobacteriaceae family tended to be greater (p = 0.114) abundant in hens fed the transgenic maize-based diet than in hens fed the CT diet. Birds that consumed the CC maize diet tended to have less abundance (p = 0.135) of Enterobacteriaceae family in the ileum than those that consumed the CT maize diet. These results indicate the lack of adverse effects of the BT maize and the CC maize lines on the ileal microbiota of hens for long term and provide important data regarding biosafety assessment of the transgenic maize lines.
1. Introduction
Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the important effect of certain food on the intestinal microbiota [1], because a strong relationship between intestinal microbiota and host health is found in the recent analysis of the intestinal microbiome [2,3]. Especially, the controversy regarding safety for increasing usage of genetically modified (GM) crops in the world remains to be resolved [4,5,6]. Therefore, safety assessment in relation to the effect of GM food and feed on intestinal microbiota is very important. In fact, the effects of GM food and feed on the host bacterial populations have been recommended to be included in the guidelines of European Food Safety Authority [7].
Transgenic maize was planted with 59.7 million hectares and it accounted for 31% of the global maize production in 2017 [8]. Most of the GM maize that is cultivated in the world is insect resistant, herbicide tolerance, or a combination of both traits. Two transgenic maizes are currently under development in China [9]. A transgenic maize line was produced by the insertion of the mCry1Ac gene that was derived from Bacillus thuringiensis strain (BT) and transcription of the mCry1Ac gene confers resistance to insect damage [9]. Another transgenic maize line was produced by the insertion of the maroACC gene derived from the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain (CC) and a gene shuffling process to optimize the kinetics of glyphosate acetyltransferase activity for acetylating the herbicide glyphosate functionally improved the maroACC gene [9]. The development of transgenic maize provides growers with such benefits [10], but its presence of food and feed has been the focus of attention that is related to potential health risks.
No completely consistent effects of the BT maize-based diet on intestinal bacteria of animals were found. Feeding the BT maize-based diet to sheep for 36 months using the bacterial culture methods did not affect the ruminal microbiota [11]. Using real-time PCR analysis or 16S rRNA gene sequencing, short-term feeding the BT maize did not affected ruminal bacterial communities of cows [12,13,14]. Although few differences in the compositions of the cecal microbiotas of pigs that were fed the BT maize diet for 31 days were observed using 16S rRNA gene sequencing, a high cecal abundance of Enterococcaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae, and Bifidobacterium, and a low abundance of Blautia were reported [15]. Buzoianu et al. [16] also found high abundance of fecal Firmicutes of offspring and a low abundance of fecal Proteobacteria of sows and offspring at weaning fed the BT maize diet.
To date, research investigating the effect of feeding GM food and feed on gastrointestinal bacterial communities has been limited to studies in large intestinal and fecal microbiota. The microbiota in the small intestine also has a very important effect on immune response and metabolic and endocrine functions [17], however, little information is obtained for the effect of transgenic maize on small intestinal microbiota. Therefore, the objective in the present study was to determine the chronic effect of feeding a BT maize-based diet and a CC maize-based diet for 12 weeks on ileal microbiota using the pure-line White Leghorn hen as a model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Institute of Animal Sciences at the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science (Beijing, China) reviewed and approved by the experimental protocol. A total of 72 pure-line White Leghorn hens (55-week old; National Engineering Laboratory for Animal Breeding, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China) were randomly assigned into one of three dietary treatments: (1) nontransgenic near-isoline maize-based diet (CT diet); (2) BT maize-based diet (BT diet); and, (3) CC maize-based diet (CC diet). Each treatment was fed to eight cages of birds (replicates) and three birds per replicates. The birds were housed in three-tier battery cages and were kept with ad libitum access to feed and water. The temperature was maintained at 22 ± 3 °C for a light cycle of 16 h light/8 h dark. All of the birds were kept healthy during the study period.
2.2. Maize and Diets
The isogenic maize, the BT maize, and the CC maize were simultaneously grown. All of the diets were formulated to meet or exceed the nutrient requirements for poultry (NRC, 1994; Ministry of Agriculture of P. R. China, 2004) as a guideline (Table S1). Maize ingredients and experimental diets samples were measured for the proximate composition (dry matter, ether extract, crude ash, crude protein, amino acid, total calcium, and total phosphorus) [18,19,20]. The crude protein was calculated by estimating nitrogen content using the combustion method and multiplying with a factor 6.25 (FP2000 nitrogen analyzer, Leco Corp., St. Joseph, MI, USA). The gross energy concentration of ingredients and diets was determined while employing an adiabatic bomb calorimeter (Model 6400, Parr Instruments, Moline, IL, USA). The diets and ingredients were also analyzed for acid detergent fiber and neutral detergent fiber [21]. Starch was determined using the Megazyme Total Starch Assay Procedure based on thermostable α-amylase and amyloglucosidase (Megazyme International Ireland Ltd., Wicklow, Ireland).
2.3. Organ Sampling and Histological Analysis
One hen per pen (eight hens/treatment) was humanely euthanized at the end of 12 weeks and a gross necropsy was performed. Ileal tissue sampling and the determination of villus height, crypt depth, villus height/crypt depth ratio, and number of goblet cells per villus and per millimeter villus were performed. Ileal content was quick collected from each bird (four hens/treatment).
2.4. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
All of the ileal digesta samples were frozen on liquid nitrogen immediately after collection and stored at −70 °C until processed for DNA extraction. Total DNA was extracted from individual digesta samples using a QIAamp DNA stool mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instructions and quantified using a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA) [22]. The V3 and V4 regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene were PCR amplified from ileal DNA extracts while using bacterial universal primer 338F and 806R with an eight-base sequence unique to each sample as a barcode [23,24]. Each PCR contained 10 ng template DNA, 0.8 μL forward primer (5 μM), 0.8 μL reverse primer (5 μM), 0.4 μL FastPfu Polymerase, 2 μL of 2.5 mM dNTPs, and 4 μL of 5× FastPfu buffer in a total volume of 20 μL. The PCR cycle was carried out as follows: denatured by 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 27 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 45 s, then 72 °C for 10 min, and held at 4°C. All of the PCR amplifications were performed in an ABI GeneAmp® 9700 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
2.5. Illumina miseq Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
Visualization under UV light following electrophoresis in a 2.0% agarose gel verified the presence of the target amplicons. Amplicons were purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and quantified using QuantiFluor™-ST (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). The purified amplicons were pooled in equimolar and paired-end sequence (2 × 250) on an Illumina MiSeq platform according to the standard protocols.
Raw fastq files were demultiplexed and quality-filtered using QIIME (version 1.17, GitHub, San Francisco, CA, USA)) with the following criteria: the 300 bp reads were truncated at any site receiving an average quality score <20 over a 10 bp sliding window, discarding the truncated reads that were shorter than 50 bp; exact barcode matching, 2 nucleotide mismatch in primer matching, reads containing ambiguous characters were removed; and, only sequences that overlap longer than 10 bp were assembled according to their overlap sequence. Reads that could not be assembled were discarded.
Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered with 97% similarity cutoff while using UPARSE (version 7.1 http://drive5.com/uparse/, Tiburon, CA, USA.) and chimeric sequences were identified and removed using UCHIME. RDP Classifier analyzed the taxonomy of each 16S rRNA gene sequence (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) against the silva (SSU115) 16S rRNA database using a confidence threshold of 70% [25]. The coverage percentage using Good’s method [26], the bias-corrected Chao richness estimator, and the Shannon diversity indices using the MOTHUR program (http://www.mothur.org, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) [27] were calculated.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
For all of the analyses, the individual hen was considered the experimental unit. Only data that were normally distributed and with equal variances were analyzed as a one-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the Mixed procedure of SAS (SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Data that were not normally distributed following log transformation or that had un-equal variances were subjected to nonparametric analysis using the Kruskal–Wallis test within the NPAR1WAY procedure of SAS. A p value of ≤0.05 was the level of significance for all tests. Tendencies were reported up to a p value of ≤0.15. Relative abundances are presented as means [28].
3. Results
3.1. Maize Grain and Diet Compositions
No major differences were observed between the BT maize or CC maize and the CT maize, and almost all of the values remained within the natural range of variation in maize varieties cited in the literature [29,30,31] (Table 1). The CT maize seemed to be a relative greater total phosphorus and lower crude protein than the transgenic maize lines, but the values were within the normal variability for maize varieties that were cited in the literature [31]. Amino acid contents were similar among the BT maize, CC maize, and CT maize ingredients. Proximate compositions and amino acid contents were also similar for the three maize-based diets (Table S1).

Table 1.
Chemical and amino acid analysis of maize (as fed basis).
3.2. Ileal Histology
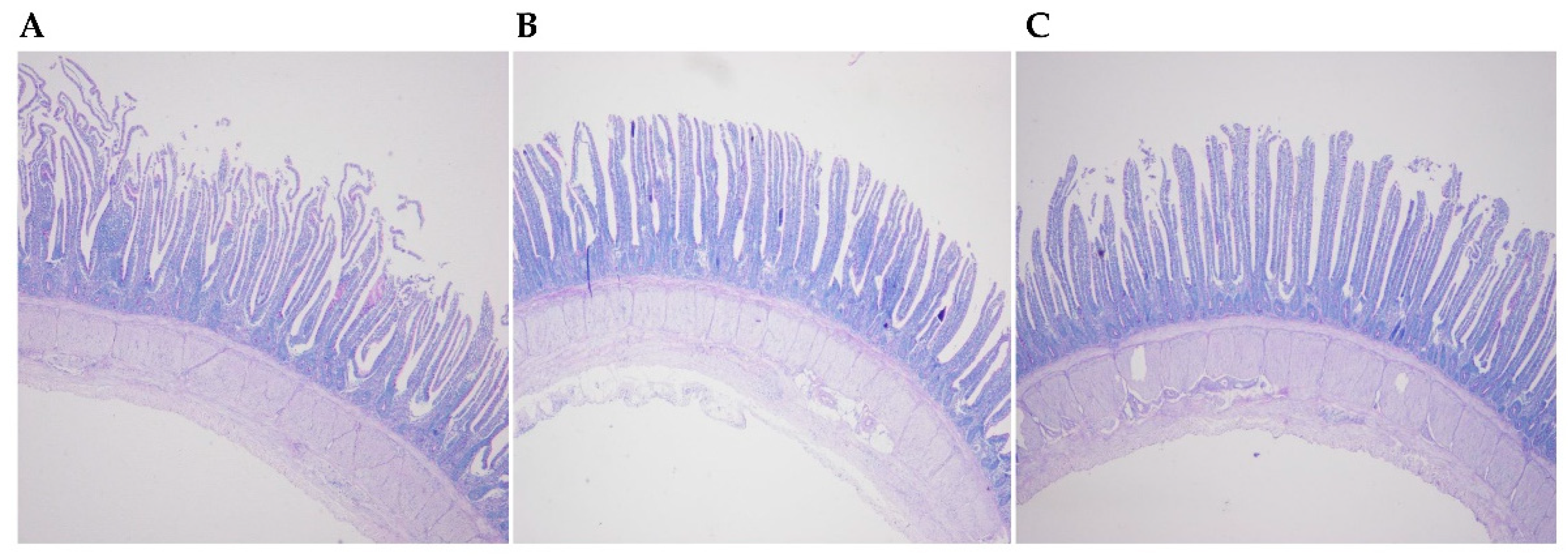
Histological examination of the ileum did not indicate an effect of feeding the two transgenic maize lines (Figure 1). There were no statistically significant differences in villus height, crypt depth, and villus height/crypt depth in the ileum for birds that consumed the BT maize diet and CC maize diet for 12 weeks (Table 2). No significantly difference in goblet cell number/villus and goblet cell number/micrometer villus in the ileum were observed among the diet treatments.
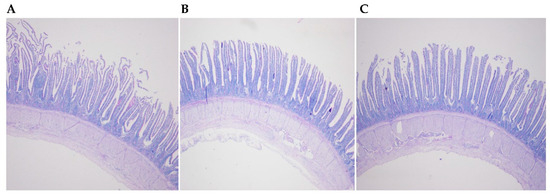
Figure 1.
Histological examination of the ileum of laying hens fed the transgenic maize-based diet. (A) the nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet was fed to laying hens; (B) the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet was fed to laying hens; and, (C) the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet was fed to laying hens.

Table 2.
Long-term effect of feeding genetically modified (GM) maize to laying hens on ileal histology.
3.3. Microbial Population Indices
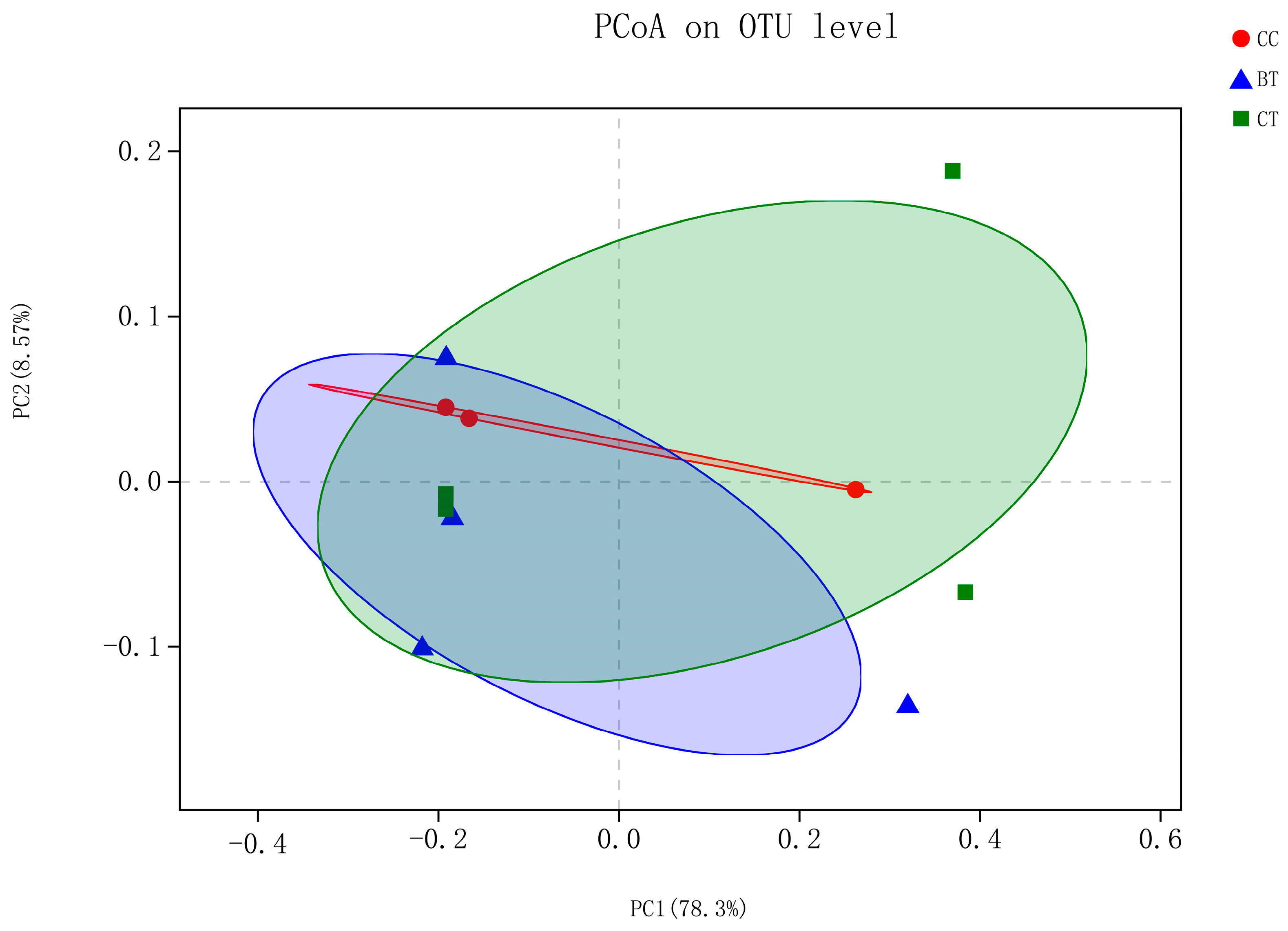
High-throughput sequencing of ileal samples from hens generated 16,188 sequences per bird of the V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene. At the 97% similarity level, there were no differences in population indices, including Chao 1 richness estimation, Shannon diversity index, and Good’s coverage, among the treatments (Table 3). Shannon–Wiener curves showed similar levels of bacterial diversity among the diet treatments (Figure S1). Beta diversity analysis using the unweighted option did not reveal a split between the diet treatments (Figure 2).

Table 3.
Long-term effect of feeding transgenic maize on bacterial diversity in laying hens.
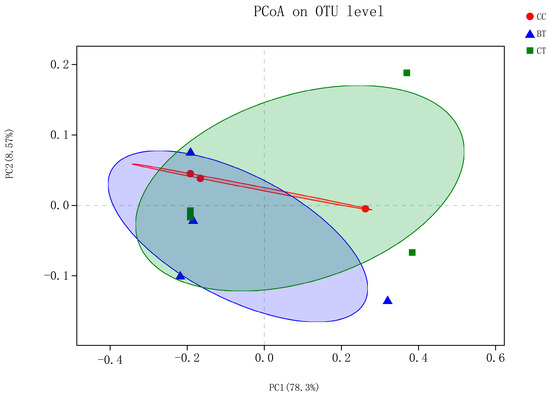
Figure 2.
Unweighted bacterial beta diversity in the ileum of laying hens fed the transgenic maize-based diet. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet was fed to laying hens; ▲ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet was fed to laying hens; ● the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet was fed to laying hens.
3.4. The Relative Abundance of the Ileal Microbiota
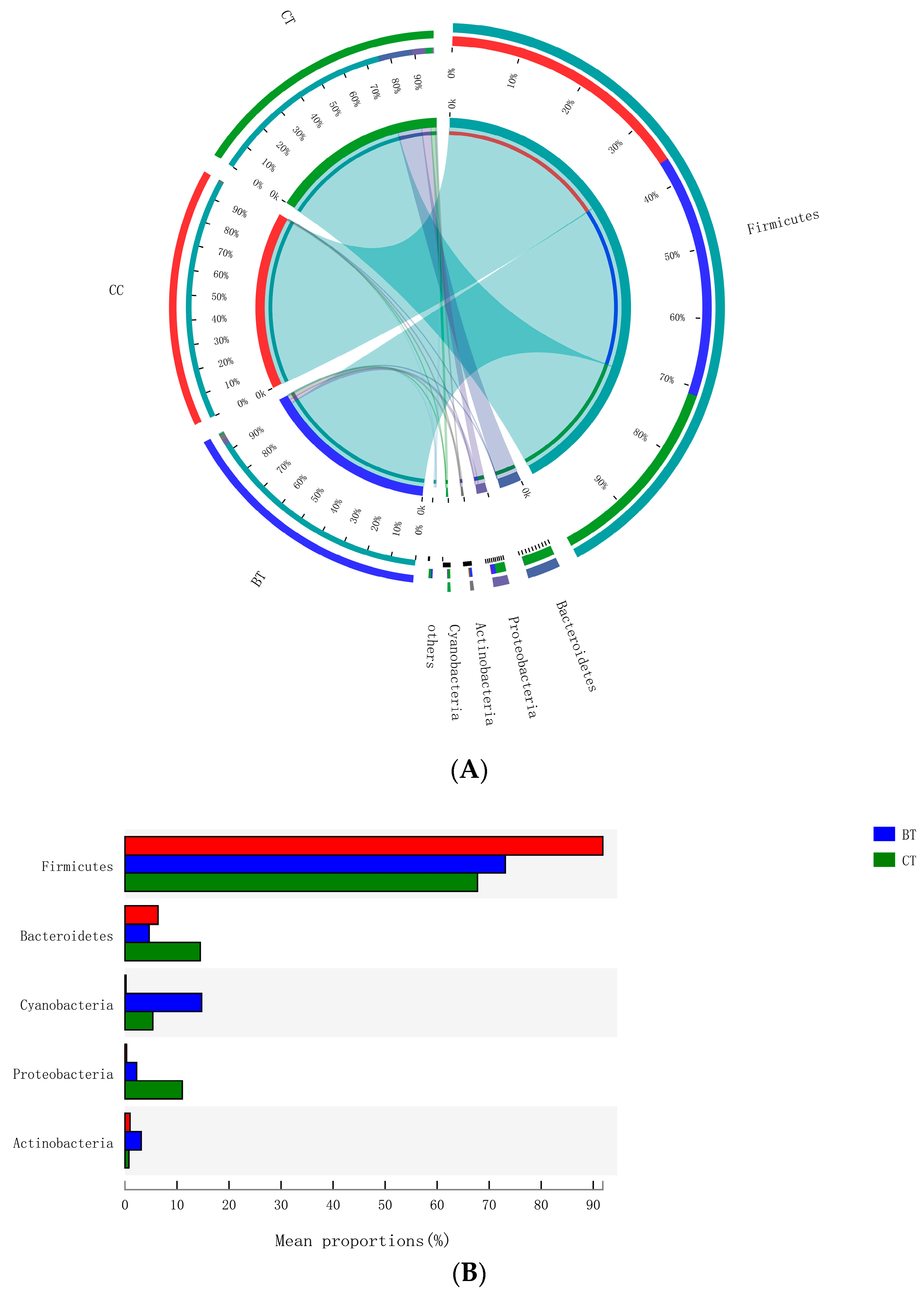
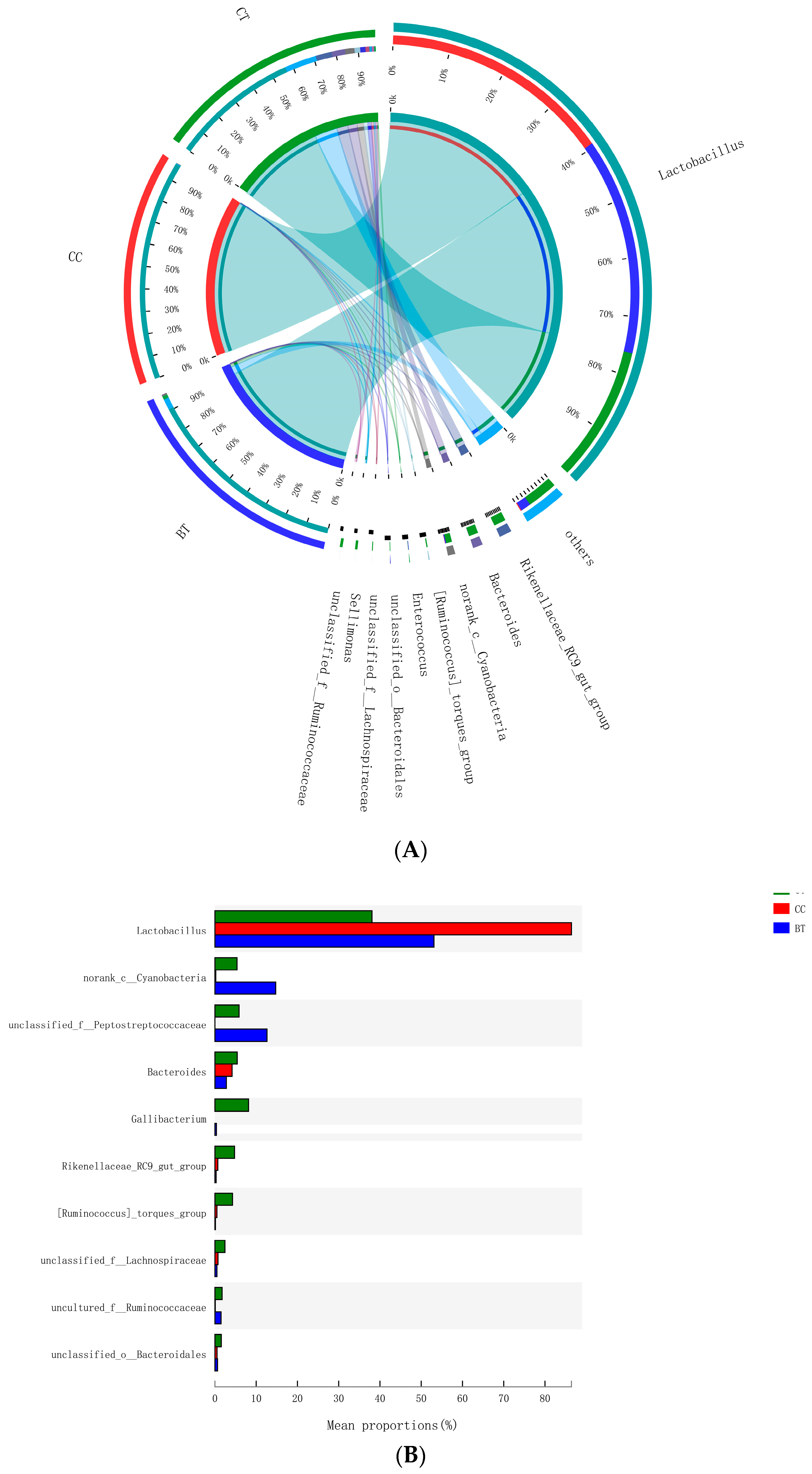
A total of 17 different ileal bacterial phyla were detected. However, 99.0% of the sequence reads classified at the phylum level were derived from five phyla: Firmicutes (77.6% of total), Bacteroidetes (8.5%), Cyanobacteria (6.8%), Proteobacteria (4.5%), and Actinobacteria (1.6%), with the remaining 12 phyla accounting for only 1.0% of the sequence reads (Figure 3A). No significant differences were observed with respect to the relative abundances of bacterial phyla in the ileum of hens that were fed the BT or CC diets versus the CT diet (Figure 3B).
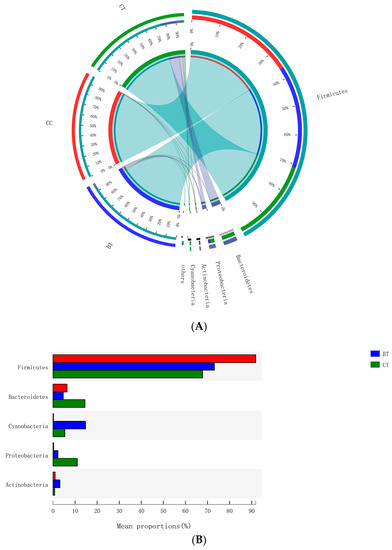
Figure 3.
(A) Circos plot the relationship between the diet treatments and bacterial phyla. (B) Long-term effect of feeding the transgenic maize-based diet to laying hens on relative abundance of major ileal bacterial phyla. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet, ■ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet were fed to laying hens, and ■ the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet.
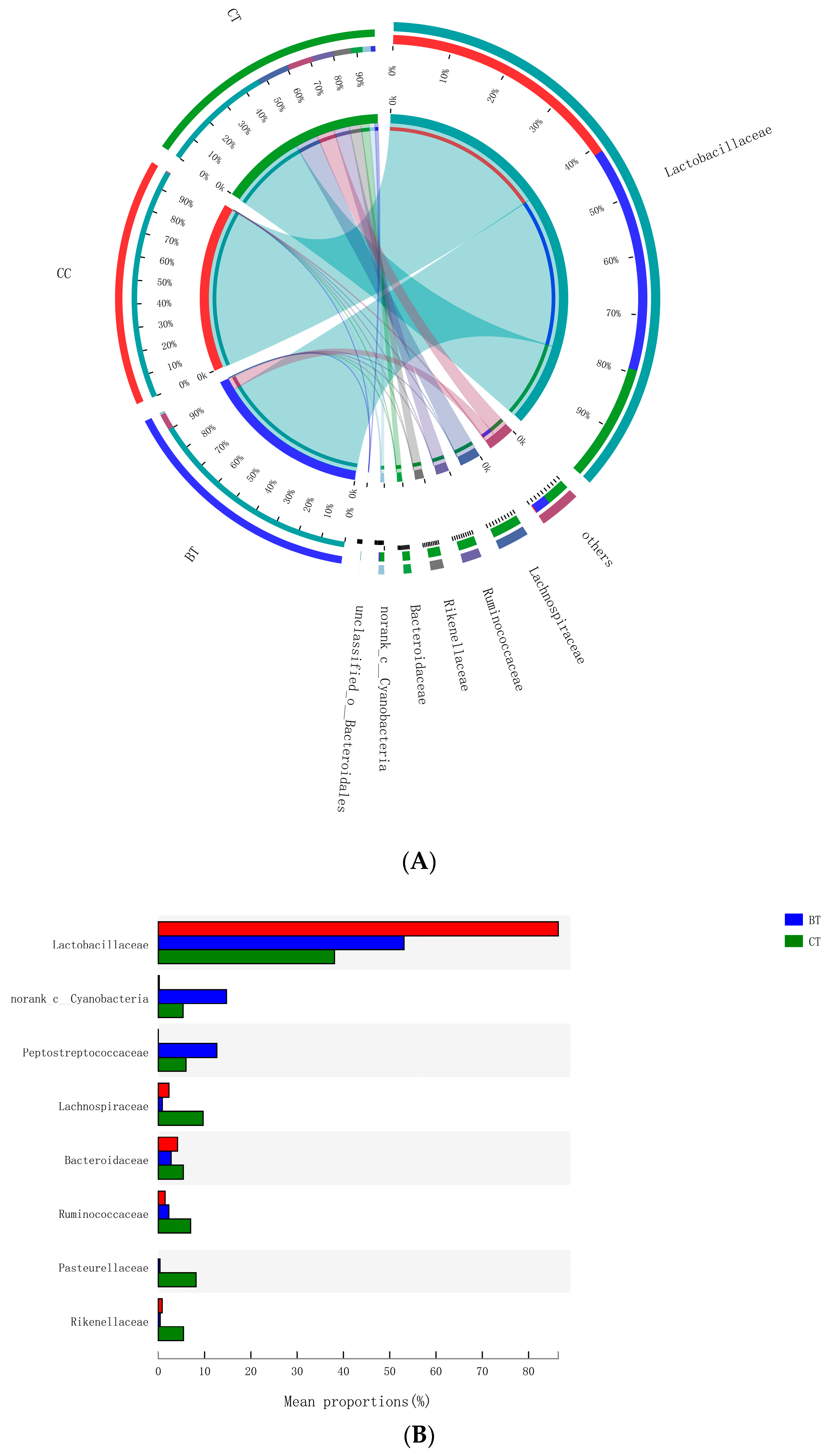
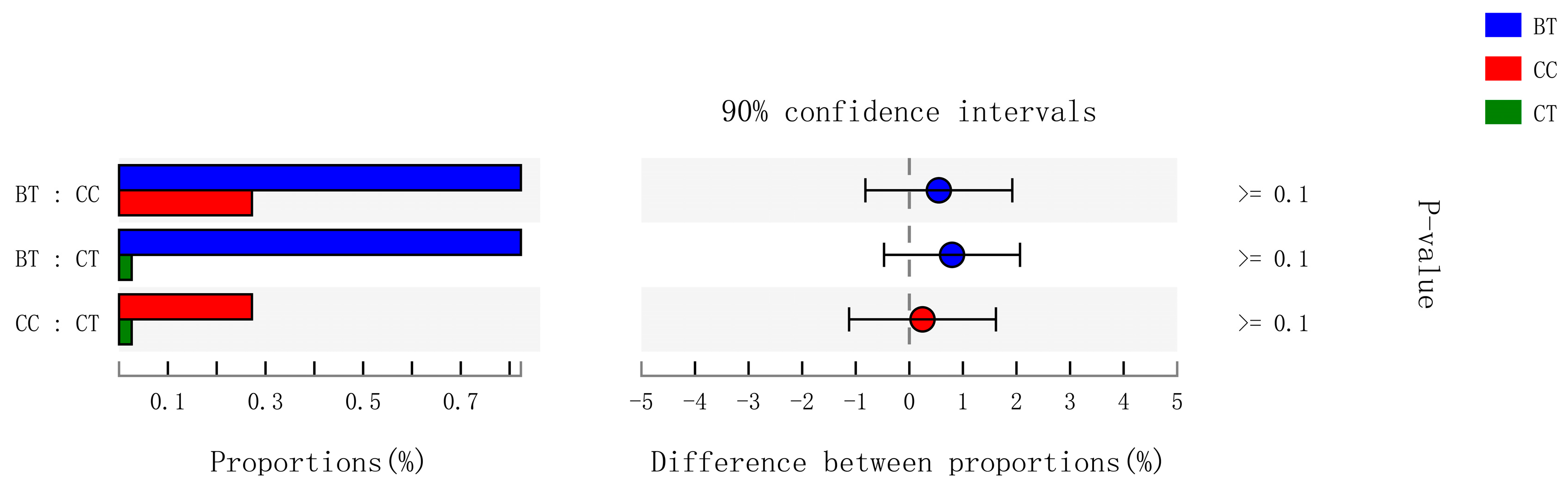
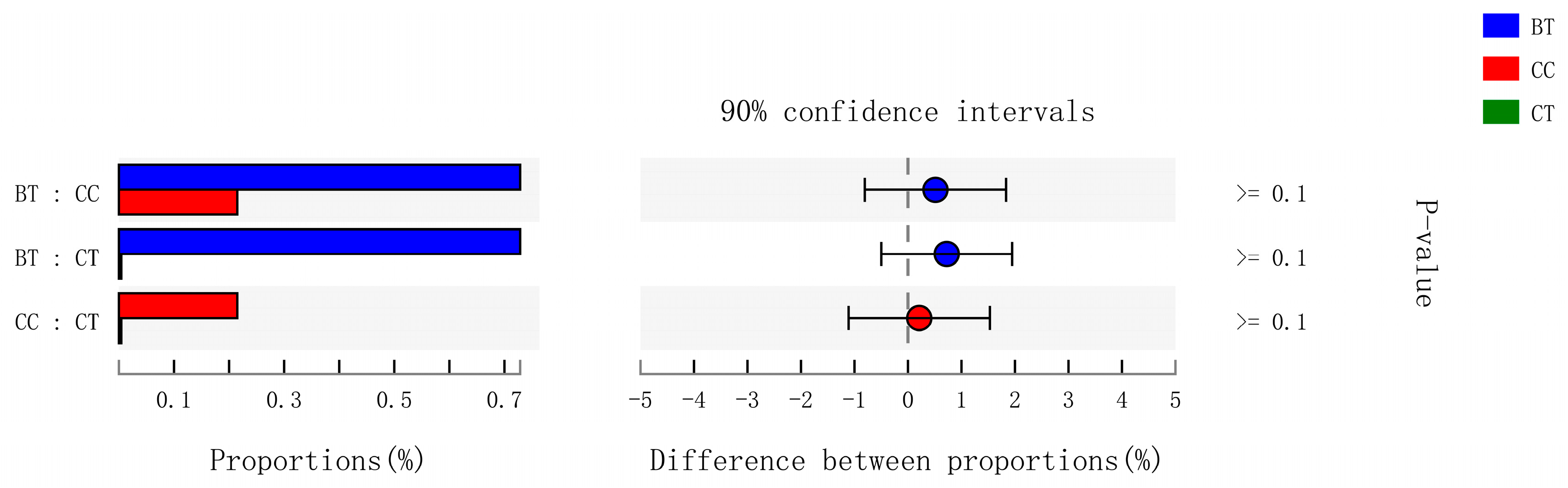
A total of 89 different bacterial families were detected in the hen ileum. The most abundant (89.2%) among the treatments were Lactobacillaceae (59.2%), norank_Cyanobacteria (6.8%), Peptostreptococcaceae (6.2%), Lachnospiraceae (4.3%), Bacteroidaceae (4.1%), Ruminococcaceae (3.6%), Pasteurellaceae (2.8%), and Rikenellaceae (2.2%) (Figure 4A). Few differences were observed among the diet treatments in the relative abundance of any of these major families (Figure 4B). There was a tendency (p = 0.109) for an increase in Bifidobacteriaceae abundance in the ileum of hens that were fed the CC maize-based diet (0.82%) and BT maize-based diet (0.27%) than hens fed the CT maize-based diet (0.03%; Figure 5). Birds that consumed the CC (0.02%) maize diet tended to have less abundance (p = 0.135) of Enterobacteriaceae in the ileum than those that consumed the CT maize diet (1.01%; Figure 6).
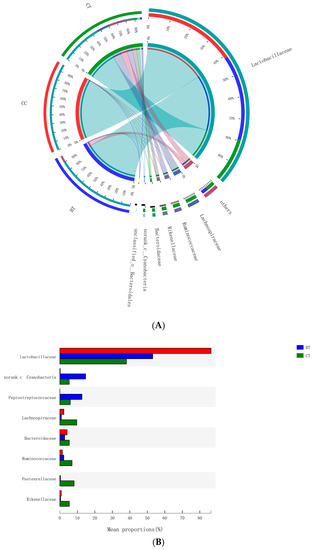
Figure 4.
(A) Circos plot the relationship between the diet treatments and bacterial families. (B) Long-term effect of feeding the transgenic maize-based diet to laying hens on relative abundance of major ileal bacterial families. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet, ■ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet were fed to laying hens, and ■ the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet.
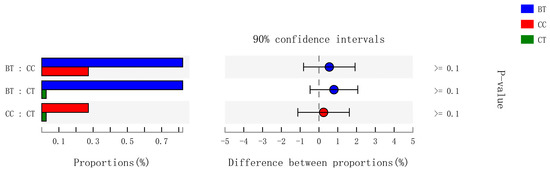
Figure 5.
Kruskal–Wallis H test bar plot for Bifidobacteriaceae family. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet, ■ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet were fed to laying hens, and ■ the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet. ● The relative abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae family in the BT diet subtracted by in the CC or CT diet, and ● the relative abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae family in the CC diet subtracted by in the CT diet.
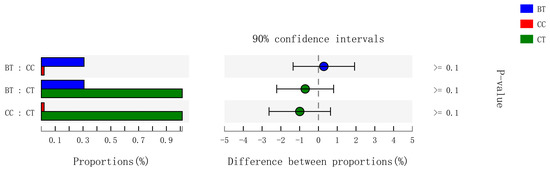
Figure 6.
Kruskal–Wallis H test bar plot for Enterobacteriaceae family. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet, ■ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet were fed to laying hens, and ■ the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet. ● The relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae family in the BT diet subtracted by in the CC diet, and ● the relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae family in the CT diet subtracted with in the BT or CC diet.
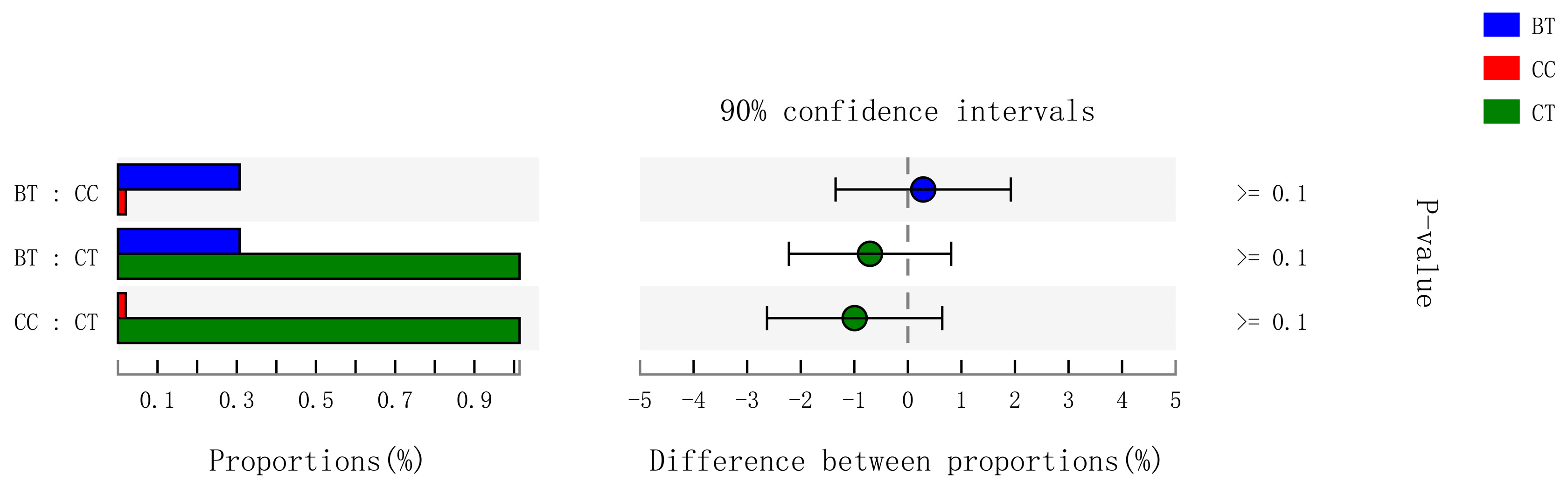
A total of 199 genera were identified in the ileum of hens. The Figure 7A summarizes the 10 most abundant (85.8%) genera identified in the laying hen ileum, which included Lactobacillus (59.2%), norank_Cyanobacteria (6.8%), unclassified_Peptostreptococcaceae (6.2%), Bacteroides (4.1%), Gallibacterium (2.8%), Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group (1.9%), [Ruminococcus]_torques_group (1.6%), unclassified_Lachnospiraceae (1.2%), and uncultured_Ruminococcaceae (1.1%). There were no significant differences among treatments in the relative abundance of any of these major genera (Figure 7B). However, birds that consumed the BT (0.73%) and CC (0.21%) maize diet tended to have greater abundance (p = 0.114) of Bifidobacterium in the ileum than those that consumed the CT maize diet (0.004%; Figure 8).
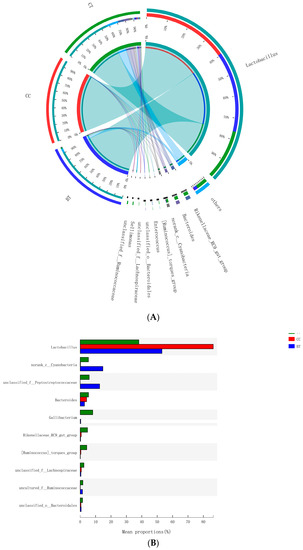
Figure 7.
(A) Circos plot the relationship between the diet treatments and bacterial genera. (B) Long-term effect of feeding the transgenic maize-based diet to laying hens on relative abundance of major ileal bacterial genera. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet, ■ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet were fed to laying hens, and ■ the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet.
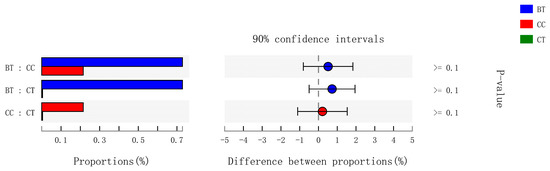
Figure 8.
Kruskal-Wallis H test bar plot for Bifidobacterium genera. ■ The nontransgenic near-isoline (CT) maize-based diet, ■ the transgenic mCry1Ac (BT) maize-based diet were fed to laying hens, and ■ the transgenic maroACC (CC) maize-based diet. ● The relative abundance of Bifidobacterium genera in the BT diet subtracted by in the CC or CT diet, and ● the relative abundance of Bifidobacterium genera in the CC diet subtracted by in the CT diet.
4. Discussion
The intestinal microbiota plays a profound role in health and extensive research has been dedicated to the strong interplay between intestinal microbiota and host disease [2,3]. To date, research investigating the effect of feeding transgenic crops on gastrointestinal bacterial communities has been limited to studies in large intestinal and fecal microbiota [11,12,13,14,15,16], whereas the microbiota in the small intestine also has a very important effect on immune response, metabolic, and endocrine functions [17]. To our knowledge, the present study is the first to employ deep sequencing to characterize ileal microbiota composition fed the transgenic maize-based diets.
This deep 16S rRNA gene-sequencing approach detected different bacterial phyla in the ileal content samples of birds, with Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Cyanobacteria, and Proteobacteria dominating. The relative distributions agree with that previously observed in the ileum of hens using 16S rRNA gene sequencing [32,33]. Similarly, Xu et al. [32] detected bacterial phyla in the ileum of chickens, but found that Firmicutes (average relative abundance >75%) dominated, followed by Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Bacteroidetes. Sequence-based compositional analysis of the ileal microbiota revealed no significant differences in the relative abundance of bacterial phyla between the transgenic maize and isogenic maize-fed hens, indicating that the BT maize and the CC maize are well tolerated by the host and intestinal microbiota at the phylum level. Similarly, no effect of feeding BT maize to weanling pigs for 31 days [15] and to finishing pigs for 110 days [34] were found in the relative abundance of cecal bacterial phyla.
Dominant bacterial families, including Lactobacillaceae (59.2%), norank_Cyanobacteria, Peptostreptococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Bacteroidaceae were detected in the present study. Kollarcikova et al. [35] also detected bacterial family in the ileum of hens and found that Lactobacillaceae dominated in adult hens and was followed by Peptostreptococcaceae. Sequence-based compositional analysis of the ileal microbiota revealed no significant differences in the relative abundance of the major bacterial family between the transgenic maize and isogenic maize-fed hens, indicating that the CC maize and the BT maize are well tolerated by the host and ileal microbiota at the family level. Similarly, no effect of feeding BT maize to sow for 110 days and to finishing pigs for 110 days [16,34] were found in relative abundance of cecal bacterial families.
The only statistically difference with the ileal microbiota was observed that the abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae was a tendency to be greater in the ileal samples of birds that were fed the transgenic maize-based diets than those hens fed the CT maize-based diet in the present study. However, the different tendency is not likely to have a detrimental effect on the host. Similarly, Buzoianu et al. [15] detected that pigs consumed the BT maize diet had higher cecal abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae (0.04 versus 0%) than those that consumed the isogenic maize diet. However, these differences are unlikely to have an adverse effect on the host. In fact, family Bifidobacteriaceae is considered to be the most important beneficial microbes in the gut [36,37]. Birds that consumed the CC (0.02%) maize diet tended to have less abundance of Enterobacteriaceae in the ileum than those that consumed the CT maize diet (1.01%), which agrees with the observation that fecal Enterobacteriaceae in the transgenic maize treatment was numerically (not significantly) is less than in the non-transgenic maize treatment [15]. Buzoianu et al. [16] also found that pigs fed the GM maize for 115 days had lower ileal Enterobacteriaceae counts than pigs that were fed the non-GM maize. Enterobacteriaceae in the phylum Proteobacteria, many of the more familiar pathogens [38,39], such as Salmonella [40,41] and Escherichia coli [42,43], plays a critical role in the enteric disease of humans and animals. In the present study, the difference in ileal Bifidobacteriaceae and Enterobacteriaceae abundance was not associated with any effects on intestinal morphology and host health.
In the present study, dominant bacterial genera, with Lactobacillus, norank_Cyanobacteria, unclassified_Peptostreptococcaceae, Bacteroides, Gallibacterium, Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, [Ruminococcus]_torques_group, unclassified_Lachnospiraceae, and uncultured_Ruminococcaceae were detected. Lactobacillaceae, with an average relative abundance >59%, dominated in the ileum of hens, which agreed with previous studies [44]. Sequence-based compositional analysis of the ileal microbiota revealed no significant differences in relative abundance of any of major genera between the transgenic maize and isogenic maize-fed hens. Similarly, no effect of feeding BT maize to pigs [15,16,34] was found in the relative abundance of major genera. In the present study, a relative abundance of Bifidobacterium belongs within the Bifidobacteriaceae family tended to be greater in the ileal samples of hens that were fed the transgenic maize-based diet than those fed the non-transgenic maize-based diet. Similarly, Buzoianu et al. [15] detected pigs that consumed the BT maize diet had higher cecal abundance of Bifidobacterium (0.04 versus 0%) than those that consumed the isogenic maize diet. Li et al. [45] also found that fecal Bifidobacterium abundance (2.17 versus 0.13%) was greater in the female rats that were fed the transgenic maize carrying the Cry1Ab and EPSPS genes than those fed the non-transgenic maize. The Bifidobacterium are not only considered to be the most important beneficial microbes in the human gut [36,37], but also considered as probiotics in the chicken intestinal tract [46,47]. The enrichment of Bifidobacterium in the ileum of birds indicated that feeding transgenic maize-diet might facilitate the growth of potentially beneficial bacteria in the gut. The role of Bifidobacterium in the chicken small intestine has not yet been fully elucidated, when considering that they are not numerically dominant. Histological examination of intestinal tissue from these hens did not reveal any signs of intestinal damage or inflammation. Therefore, although statistically tendency, the difference in the ileal abundance of Bifidobacterium observed in the present study is not believed to be of biological significance or to have a negative impact on animal health.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the results from the present study indicate that dietary BT maize and CC maize are well tolerated at the level of the ileal microbiota following 12 weeks of exposure in laying hens. Few effects were observed within the ileal microbial community structure of hens following long term exposure to transgenic maize. The low abundance and frequency of detection of some taxa are not believed to be of major biological importance and they were not associated with any adverse health effects. The results may provide a scientific basis for evaluating the biosafety of long-term feeding BT maize and CC maize in terms of the ileal microbiome.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/7/3/92/s1, Table S1: Ingredient and analyzed nutrient composition (as-fed basis) of diets. Figure S1. Shannon-Wiener curves for ilea bacteria of laying hens fed the transgenic corn-based diet.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C. and H.Z.; Data curation, L.C.; Formal analysis, R.Z.; Funding acquisition, H.Z.; Investigation, L.C., R.Z. and L.Z.; Methodology, L.C.; Resources, H.Z.; Writing—original draft, L.C., R.Z. and H.Z.; Writing—review & editing, L.C., R.Z. and H.Z.
Funding
This work was conducted with funds provided by Project of the Genetically Modified Organisms Breeding Major Projects (2016ZX08011-005) and Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP-IAS07).
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks to J S Lai and H M Zhao (China Agricultural University, Beijing, China) for donating maize. We also thank Z M Ding and B F Zhang (Institute of Animal Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China) for sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saarela, M.; La¨hteenma¨ki, L.; Crittenden, R.; Salminen, S.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Gut bacteria and health foods-the European perspective. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, K.; Krautkramer, K.A.; Org, E.; Romano, K.A.; Kerby, R.L.; Vivas, E.I.; Mehrabian, M.; Denu, J.M.; Bäckhed, F.; Lusis, A.J.; et al. Interactions between Roseburia intestinalis and diet modulate atherogenesis in a murine model. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanen, T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Schwager, R.; Tripathi, S.; Arthur, T.D.; Vehik, K.; Lernmark, Å.; Hagopian, W.A.; Rewers, M.J.; She, J.X.; Toppari, J.; et al. The human gut microbiome in early-onset type 1 diabetes from the TEDDY study. Nature 2018, 562, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, C.; Bernheim, A.; Bergé, J.B.; Kuntz, M.; Pascal, G.; Paris, A.; Ricroch, A.E. Assessment of the health impact of GM plant diets in long-term and multigenerational animal feeding trials: a literature review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Young, A.E. Prevalence and impacts of genetically engineered feedstuffs on livestock populations. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 4255–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiatkiewicz, S.; Swiatkiewicz, M.; Arczewska-Wlosek, A.; Jozefiak, D. Genetically modified feeds and their effect on the metabolic parameters of food-producing animals: A review of recent studies. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2014, 198, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel-Patient, K.; Guimaraes, V.D.; Paris, A.; Drumare, M.F.; Ah-Leung, S.; Lamourette, P.; Nevers, M.C.; Canlet, C.; Molina, J.; Bernard, H.; Créminon, C.; et al. Immunological and metabolomic impacts of administration of Cry1Ab protein and MON 810 maize in mouse. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISAAA. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops in 2017: Biotech Crop Adoption Surges as Economic Benefits Accumulate in 22 Years; ISAAA Brief No. 53; ISAAA: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, R.Q.; Chen, L.; Gao, L.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Yao, B.; Yang, X.G.; Zhang, H.F. Effects of feeding transgenic corn with mCry1Ac or maroACC gene to laying hens for 12 weeks on growth, egg quality and organ health. Animal 2016, 10, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusta, M.; Smyth, S.J.; Belcher, K.; Phillips, P.W.B.; Castle, D. Economic benefits of genetically-modified herbicide-tolerant canola for producers. AgBioForum 2011, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; Brandi, G.; Rondini, C.; Avellini, L.; Giammarini, C.; Costarelli, S.; Acuti, G.; Orlandi, C.; Filippini, G.; Chiaradia, E.; et al. A three-year longitudinal study on the effects of a diet containing genetically modified Bt176 maize on the health status and performance of sheep. Livest. Sci. 2008, 113, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspanier, R.; Lutz, B.; Rief, S.; Berezina, O.; Zverlov, V.; Schwarz, W.; Mayer, J. Tracing residual recombinant feed molecules during digestion and rumen bacterial diversity in cattle fed transgene maize. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 218, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusetti, L.; Crotti, E.; Tamburini, A.; Cittaro, D.; Garavaglia, V.; Rolli, E.; Sorlini, C.; Daffonchio, D.; Borin, S. Influence of transgenic Bt176 and non-transgenic corn silage on the structure of rumen bacterial communities. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, S.; Gurtler, P.; Albrecht, C. Effect of feeding cows genetically modified maize on the bacterial community in the bovine rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 8012–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzoianu, S.G.; Walsh, M.C.; Rea, M.C.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Gardiner, G.E.; Lawlor, P.G. High throughput sequence-based analysis of the intestinal microbiota of weanling pigs fed genetically modified Bt MON810 maize expressing Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab (Bt maize) for 31 days. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4217–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzoianu, S.G.; Walsh, M.C.; Rea, M.C.; Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Gardiner, G.E.; Lawlor, P.G. Sequence-based analysis of the intestinal microbiota of sows and their offspring fed genetically modified maize expressing a truncated form of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab protein (Bt maize). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7735–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aidy, S.; van den Bogert, B.; Kleerebezem, M. The small intestine microbiota, nutritional modulation and relevance for health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Int. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC Int, 18th ed.; AOAC Int: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.B.; Xue, P.C.; Cao, S.C.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.F. Effects of dietary phosphorus concentration and body weight on postileal phosphorus digestion in pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 2018, 242, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Yan, H.L.; Cao, S.C.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, H.F. The response of performance in grower and finisher pigs to diets formulated to different tryptophan to lysine ratios. Livest. Sci. 2019, 222, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, D.O. Holst filtration apparatus for Van Soest detergent fiber analysis. J. AOAC 1973, 56, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z.D.; Zhang, H.F.; Liu, J.B. Production phase affects the bioaerosol microbial composition and functional potential in swine confinement buildings. Animals 2019, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; de Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. PNAS 2011, 15, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, K.R.; Yeoman, C.J.; Kent, A.; Righini, N.; Carbonero, F.; Estrada, A.; Gaskins, H.R.; Stumpf, R.M.; Yildirim, S.; Torralba, M.; et al. Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, I.J. The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 1953, 40, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 5, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlotzhauer, S.; Litell, R.C. SAS System for Elementary Statistical Analysis, 2nd ed.; SAS Publishing: Cary, NC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ILSI. International Life Sciences Institute Crop Composition Database, version 7.0. Available online: http://www.cropcomposition.org (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Zilic, S.; Milasinovic, M.; Terzic, D.; Barac, M.; Ignjatovic-Micic, D. Grain characteristics and composition of maize specialty hybrids. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 9, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Safety Assessment of Foods and Feeds Derived from Transgenic Crops, Novel Food and Feed Safety; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, D.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Pan, K.; Jing, B.; et al. Bacillus licheniformis normalize the ileum microbiota of chickens infected with necrotic enteritis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borda-Molina, D.; Vital, M.; Sommerfeld, V.; Rodehutscord, M.; Camarinha-Silva, A. Insights into broilers’ gut microbiota fed with phosphorus, calcium, and phytase supplemented diets. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 19, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzoianu, S.G.; Walsh, M.C.; Rea, M.C.; O’Sullivan, O.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Gardiner, G.E.; Lawlor, P.G. The effect of feeding Bt MON810 maize to pigs for 110 days on intestinal microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollarcikova, M.; Kubasova, T.; Karasova, D.; Crhanova, M.; Cejkova, D.; Sisak, F.; Rychlik, I. Use of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for prediction of new opportunistic pathogens in chicken ileal and cecal microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, M.; Fujikawa, S.; Matsumoto, N. Effect of xylooligosaccharide on the growth of bifidobacteria. Bifidobact. Microflora. 1990, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M. New members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD-what role do Proteobacteria play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Betteken, M.I.; Guo, X.; Altier, C.; Duhamel, G.E.; Wiedmann, M. The Typhoid Toxin Produced by the Nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica Serotype Javiana Is Required for Induction of a DNA Damage Response In Vitro and Systemic Spread In Vivo. mBio 2018, 9, e00467-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Carden, S.; Monack, D. Shedding light on Salmonella carriers. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmela, C.; Chevarin, C.; Xu, Z.; Torres, J.; Sevrin, G.; Hirten, R.; Barnich, N.; Ng, S.C.; Colombel, J.F. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018, 67, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsepasi-Lauridsen, H.C.; Vallance, B.A.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Petersen, A.M. Escherichia coli pathobionts associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00060-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, D.; Hughes, R.J.; Moore, R.J. Microbiota of the chicken gastrointestinal tract: influence on health, productivity and disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 98, 4301–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yang, C.; Yue, R.; Zhen, Y.; Zhuo, Q.; Piao, J.; Yang, X.G.; Xiao, R. Modulation of the fecal microbiota in sprague-dawley rats using genetically modified and isogenic corn lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.A.; Burkholder, K.M. Application of prebiotics and probiotics in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Dong, W. Spatial variations in intestinal skatole production and microbial composition in broilers. Anim. Sci. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).