The Bacterial Community Associated with the Amarillo Zamorano Maize (Zea mays) Landrace Silage Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Amplification and NGS of Variable Regions of the 16S rRNA Gene
2.5. Sequence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the Chemical and Physical Characteristics of the Silages
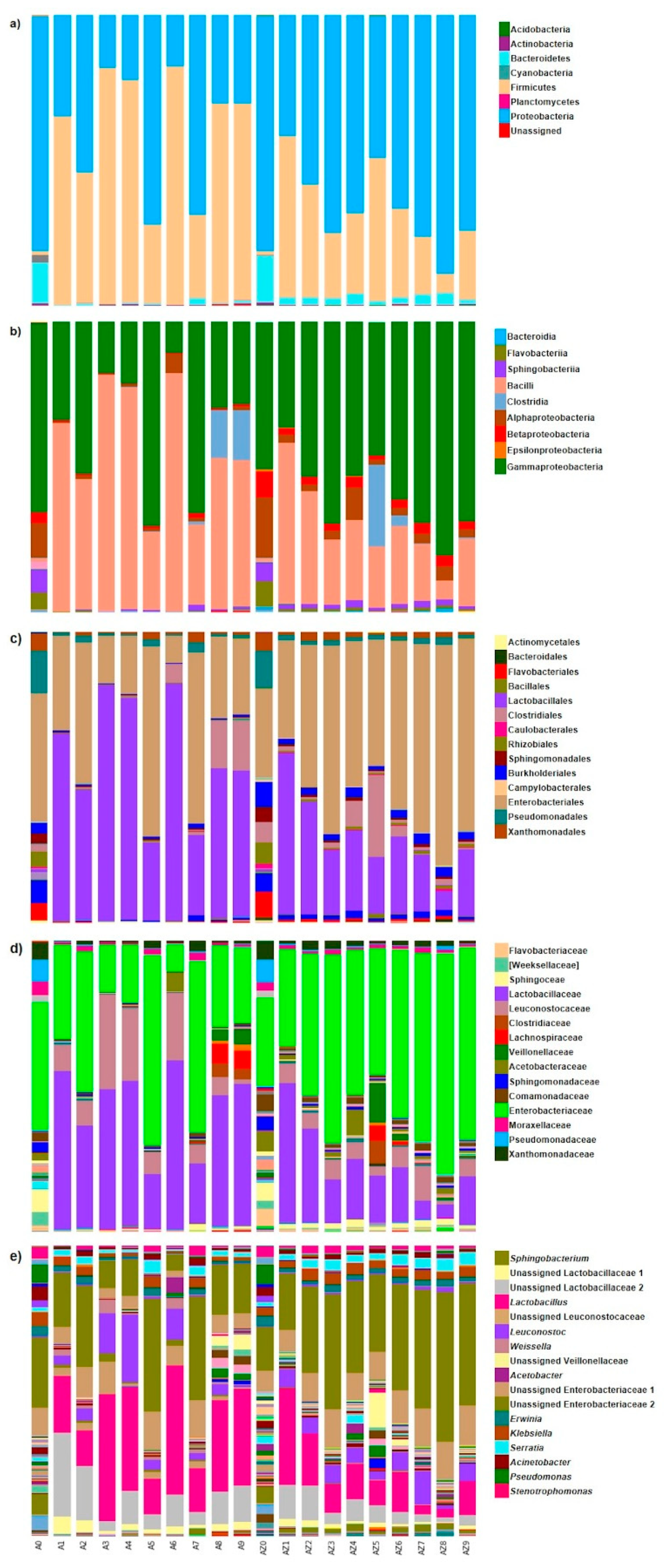
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition and Structure
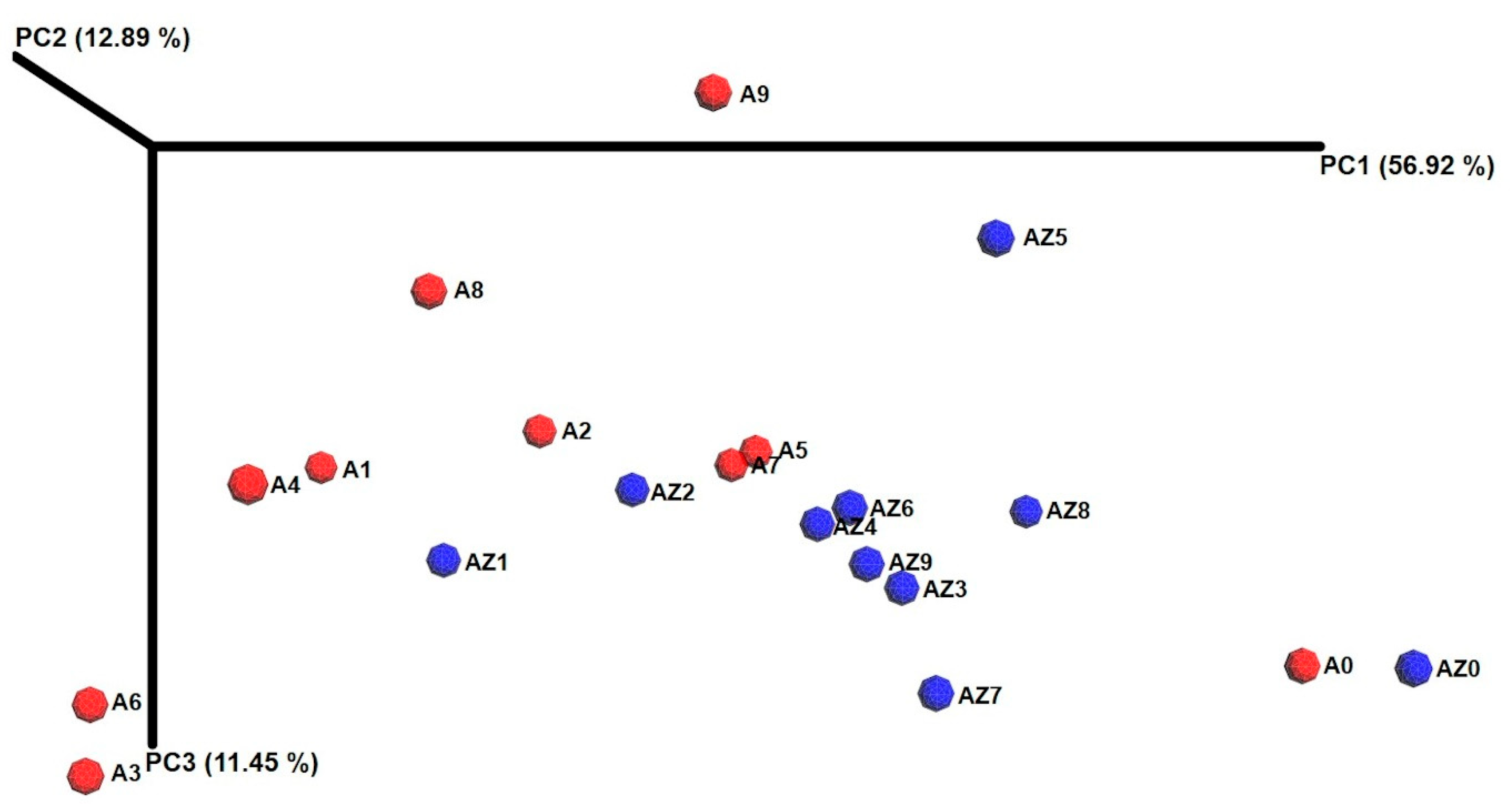
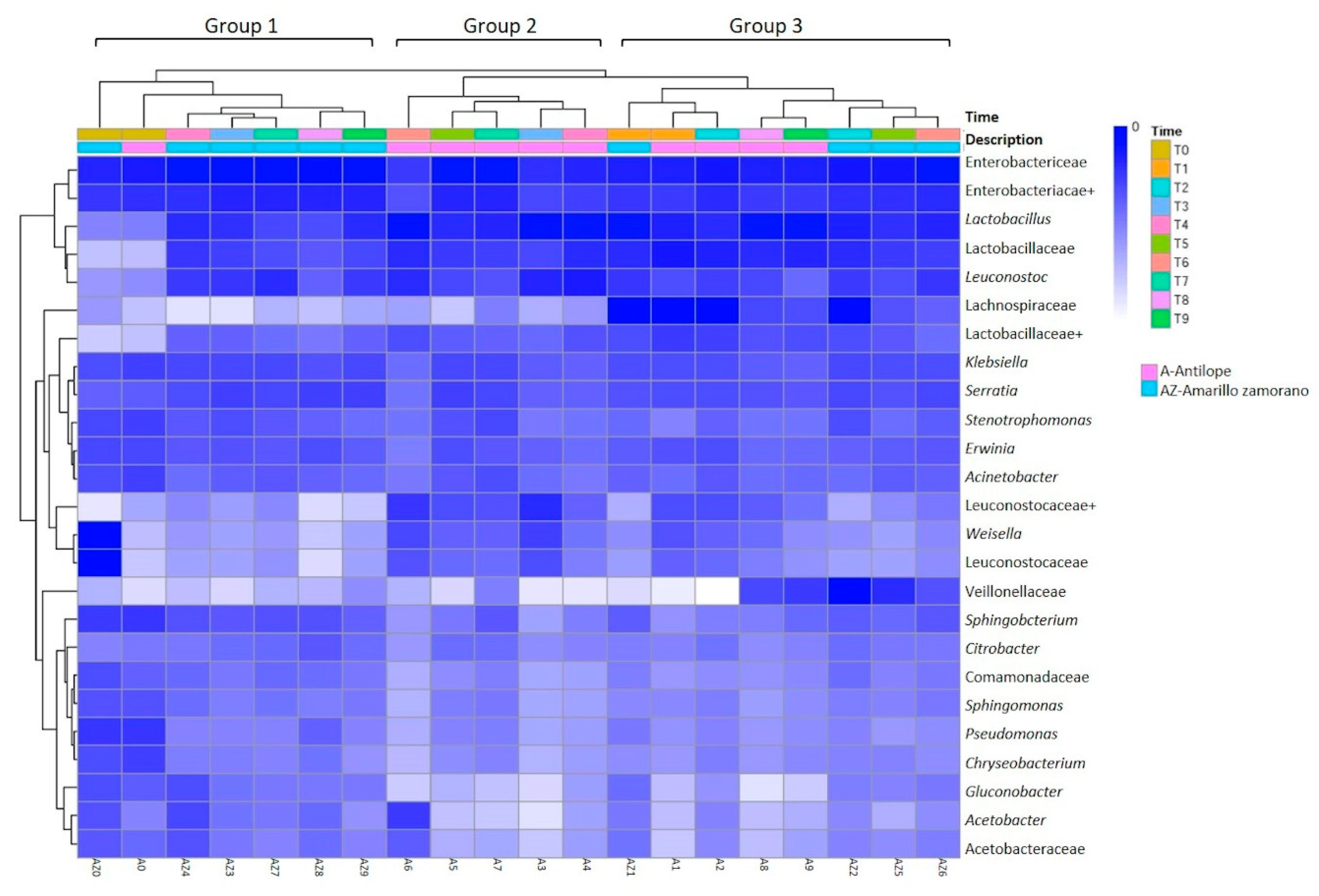
3.3. Cluster Analysis, Core Bacterial Community and Diversity Changes in the Ensiling Process
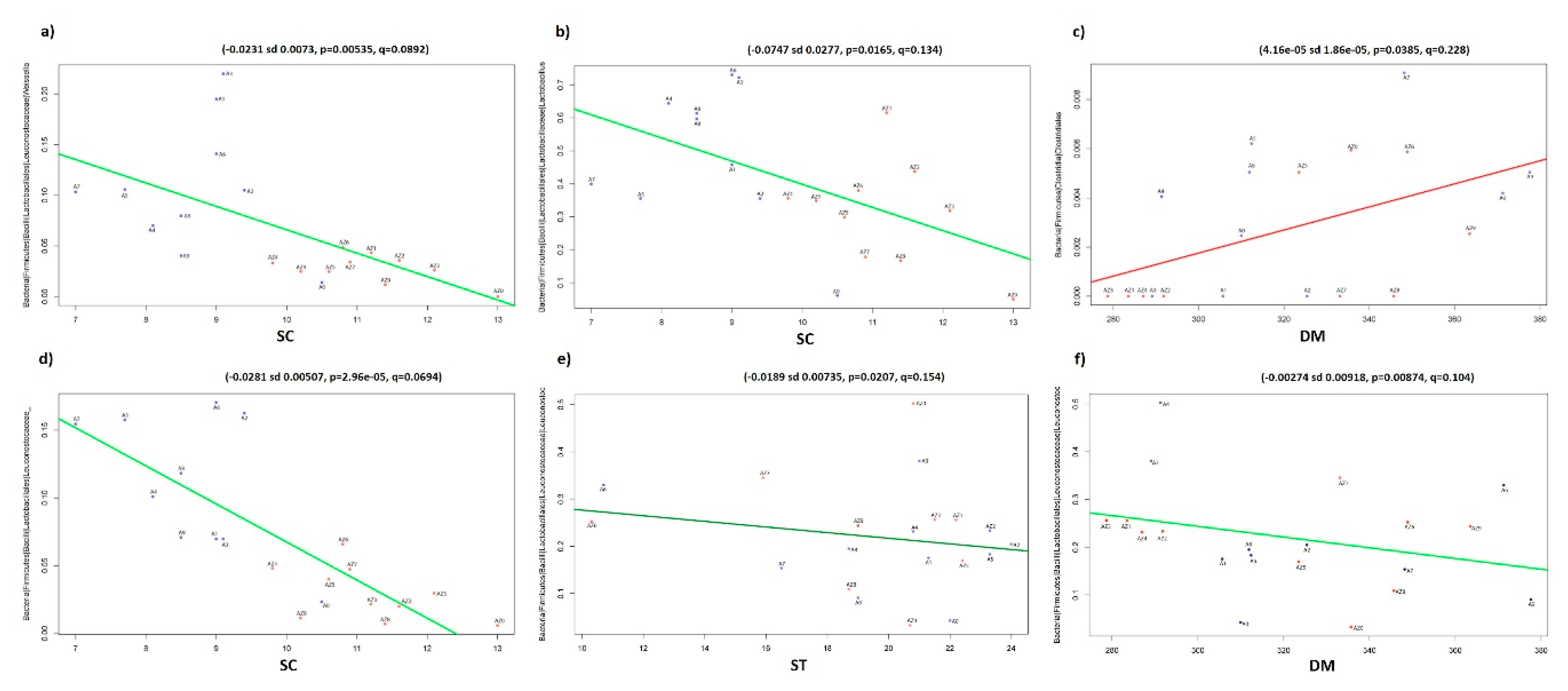
3.4. Significant Association between Microbiota and Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Silage
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolsen, K.K.; Lin, C.; Brent, B.E.; Feyerherm, A.M.; Urban, J.E.; Aimutis, W.R. Effect of silage additives on the microbial succession and fermentation process of alfalfa and corn silages. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 3066–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filya, I. Nutritive value and aerobic stability of whole crop maize silage harvested at four stages of maturity. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2004, 116, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elferink, S.; Driehuis, F.; Gottschal, J.; Spoelstra, S. Silage fermentation processes and their manipulation. In Silage Making in the Tropics with Particular Emphasis on Smallholders; Mannetje, L., Ed.; FAO Plant Production and Protection Papers 161; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2000; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L. A review on silage additives and enzymes. In Proceedings of the 59th Minneapolis Nutrition Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 21–23 September 1998; pp. 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- McEniry, J.; O’Kiely, P.; Clipson, N.J.; Forristal, P.D.; Doyle, E.M. Bacterial community dynamics during the ensilage of wilted grass. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Nishino, N. Succession of lactic acid bacteria in wilted rhodesgrass silage assessed by plate culture and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Grassl. Sci. 2010, 56, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, B.; Nishino, N.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. Fermentation and microbial population dynamics during the ensiling of native grass and subsequent exposure to air. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeman, J.P. Microbial Ecology of the Phylloplane; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Naoki, N.; Yuji, T. Variations in bacterial communities in laboratory-scale and big bale silos assessed by fermentation products, colony counts and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 83–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, N.J.; Ely, L.O. Identification and properties of yeasts associated with the aerobic deterioration of wheat and alfalfa silages. Mycopathologia 1979, 69, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoelstra, S.; Courtin, M.; Van Beers, J. Acetic acid bacteria can initiate aerobic deterioration of whole crop maize silage. J. Agric. Sci. 1988, 111, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolford, M.K. The detrimental effects of air on silage. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 68, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, S.J.E.; Wilkinson, J.F.; Duffus, C.M. Enterobacteria associated with grass and silages. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1993, 75, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.; WHO. The impact of the quality of silage on animal health and food safety: A review. Vet. Q. 2000, 22, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.; Spoelstra, S. Microbiology of ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D., Muck, R., Harrison, J., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Brusetti, L.; Borin, S.; Mora, D.; Rizzi, A.; Raddadi, N.; Sorlini, C.; Daffonchio, D. Usefulness of length heterogeneity-PCR for monitoring lactic acid bacteria succession during maize ensiling. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Dellaglio, F. Quality of silages from Italian farms as attested by number and identity of microbial indicators. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation with lactic acid bacteria on the bacterial communities of Italian ryegrass, whole crop maize, guinea grass and rhodes grass silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Monitoring the bacterial community of maize silage stored in a bunker silo inoculated with Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R. Recent advances in silage microbiology. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.T.; Huu, V.N.; Nishino, N. A pilot examination of the fermentation products, aerobic stability and bacterial community of total mixed ration silage produced in Vietnam. Grassl. Sci. 2014, 60, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, K.; Ulrich, A.; Idler, C.; Klocke, M. Bacterial community dynamics during ensiling of perennial ryegrass at two compaction levels monitored by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikmeyer, F.G.; Kofinger, P.; Poschenel, A.; Junemann, S.; Zakrzewski, M.; Heinl, S.; Mayrhuber, E.; Grabherr, R.; Puhler, A.; Schwab, H.; et al. Metagenome analyses reveal the influence of the inoculant Lactobacillus buchneri CD034 on the microbial community involved in grass ensiling. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, J.; Theuerl, S.; Szewzyk, U.; Huth, M.; Tolle, R.; Klocke, M. Dynamic variation of the microbial community structure during the long-time mono-fermentation of maize and sugar beet silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, E.; Laptev, G.Y.; Il’Ina, L.; Nikonov, I.; Filippova, V.; Soldatova, V.; Brazhnik, E.; Novikova, N.; Gagkaeva, T.V. The investigation of endophytic microorganisms as a source for silage microbiocenosis formation using NGS-sequencing. Sel’Skokhozyaistvennaya Biol. 2015, 50, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Mi, Z.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Kwok, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Assessing quality of Medicago sativa silage by monitoring bacterial composition with single molecule, real-time sequencing technology and various physiological parameters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraut-Cohen, J.; Tripathi, V.; Chen, Y.; Gatica, J.; Volchinski, V.; Sela, S.; Weinberg, Z.; Cytryn, E. Temporal and spatial assessment of microbial communities in commercial silages from bunker silos. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6827–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duniere, L.; Xu, S.; Long, J.; Elekwachi, C.; Wang, Y.; Turkington, K.; Forster, R.; McAllister, T.A. Bacterial and fungal core microbiomes associated with small grain silages during ensiling and aerobic spoilage. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Cervantes, A.A.P.; Arriola, K.G.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Desogan, A.T. Fate of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and bacterial diversity in corn silage contaminated with the pathogen and treated with chemical or microbial additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1780–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Minh, T.T.; Tu, T.T.; Tsuruta, T.; Pang, H.; Nishino, N. Comparative microbiota assessment of wilted Italian ryegrass, whole crop corn, and wilted alfalfa silage using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and next-generation sequencing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Sarikhan, S.; Jouzani, G.S.; Aghdasi, M.; Salekdeh, G.H. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, H.; Zhang, S.; Kong, J. Effects of inoculants Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus parafarraginis on the fermentation characteristics and microbial communities of corn stover silage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Niu, H. Diversity of bacterial community during ensiling and subsequent exposure to air in whole-plant maize silage Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela, S. Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.J.; Joo, Y.; Park, J.; Tiezzi, F.; Gutierrez-Rodriguez, E.; Castillo, M.S. Bacterial and fungal communities, fermentation, and aerobic stabiliy of conventional hybrids and row midrib hybrids ensiled at low moisture with or wothout a homo- and heterofermentative inoculant. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3057–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Kong, J. The changes of dominant lactic acid bacteria and their metabolites during corn stover ensiling. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Yu, P.; Ali, M.; Cone, J.W.; Hendriks, W.H. Nutritive value of maize silage in relation to dairy cow performance and milk quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, F.P.; Fitzgerald, J.J.; Murphy, J.J.; Rath, M. The effect on milk production of replacing grass silage with maize silage in the diet of dairy cows. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1998, 55, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keady, T.W.J.; Kilpatrick, D.J.; Mayne, C.S.; Gordon, F.J. Effects of replacing grass silage with maize silages, differing in maturity, on performance and potential concentrate sparing effect of dairy cows offered two feed value grass silages. Livest. Sci. 2008, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ferreira, G.; Corl, B.A.; Campbell, B.T. Production performance, nutrient digestibility, and milk fatty acid profile of lactating dairy cows fed corn silage-or sorghum silage-based diets with and without xylanase supplementation. Int. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K. Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; Ausubel, F., Brent, R., Eds.; Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.; Fierer, N.; Gonzalez-Peña, A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows integration and analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D633–D642. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, X.C.; Tickle, T.L.; Sokol, H.; Gevers, D.; Devaney, K.L.; Ward, D.V.; Reyes, J.A.; Shah, S.A.; LeLeiko, N.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.L.P.; Queiroz, O.C.M.; Arriola, K.G.; Daetz, R.; Basso, F.; Romero, J.J.; Adesogan, A.T. Effects of homolactic bacterial inoculant on the performance of lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5145–5152. [Google Scholar]
- Vissers, M.M.; Driehuis, F.; Te-Giffel, M.C.; De-Jong, P.; Lankveld, J.M. Concentrations of butyric acid bacteria spores in silage and relationships with aerobic deterioration. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, D.A.; Weicht, T.R.; Bates, S.T.; Leff, J.W.; Fierer, N. Changes in bacterial and fungal communities across compost recipes, preparation methods, and composting times. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogodiniyai-Kasmaei, K.; Dicksved, J.; Spörndly, R.; Udén, P. Separating the effects of forage source and field microbiota on silage fermentation quality and aerobic stability. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEniry, J.; O’Kiely, P.; Clipson, N.J.; Forristal, P.D.; Doyle, E.M. Assessing the impact of various ensilage factors on the fermentation of grass silage using conventional culture and bacterial community analysis techniques. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchandin, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E. The family Veillonellaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Firmicutes and Tenericutes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 433–453. [Google Scholar]
- Oladosu, Y.; Rafii, M.Y.; Abdullah, N.; Magaji, U.; Hussin, G.; Ramli, A.; Miah, G. Fermentation quality and additives: A case of rice straw silage. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7985167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolford, M.K. Microbiological screening of the straight chain fatty acids (C1-C12) as potential silage additives. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1975, 26, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostling, C.; Lindgren, S. Influence of enterobacteria on the fermentation and aerobic stability of grass silages. Grass Forage Sci. 1995, 50, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Davies, D.R. The aerobic stability of silage: Key findings and recent developments. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Bolaños, J.L.; Jiménez-Islas, H.; Botello-Alvarez, E.; Rico-Martínez, R. Mixed culture optimization for marigold flower ensilage via experimental design and response surface methodology. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwan, R.; Rusmana, I.; Widyastuti, Y.; Wiryawan, K.G.; Prasetya, B.; Sakamoto, M.; Ohkuma, M. Fermentation characteristics and microbial diversity of tropical grass-legumes silages. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 511–518. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves-Lopez, C.; Serio, A.; Delgado-Ospina, J.; Rossi, C.; Grande-Tovar, C.D.; Paparella, A. Exploring the bacterial microbiota of colombian fermented maize dough “masa agria” (maiz anejo). Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poszytek, K.; Pyzik, A.; Sobczak, A.; Lipinski, L.; Sklodowska, A.; Drewniak, L. The effect of the source of microorganisms on adaptation of hydrolytic consortia dedicated to anaerobic digestion of maize silage. Anaerobe 2017, 46, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.W.; Hassan, Y.I.; Perilla, N.; Li, X.Z.; Boland, G.J.; Zhou, T. Bacterial epimerization as a route for deoxynivalenol detoxification: The influence of growth and environmental conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanarach, W.; Theeragoolm, G.; Inoue, T.; Yakushi, T.; Adachi, O.; Matsushita, K. Acetic acid fermentation of Acetobacter pasteurianus: Relationship between acetic acid resistance and pellicle polysaccharide formation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, K.; Taniguchi, M.; Ujike, S.; Ishihara, N.; Mori, H.; Ono, H.; Murooka, Y. Characterization of acetic acid bacteria in traditional acetic acid fermentation of rice vinegar (komesu) and unpolished rice vinegar (kurosu) produced in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2001, 67, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.W.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zou, C.; Li, L.; Liang, X.; Wei, X.; Lin, B. Ruminal fermentation and microbial community differently influenced by four typical subtropical forages in vitro. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, R.; Nazzi, F.; Locci, R.; Firrao, G. Degradation of fumonisin B1 by a bacterial strain isolated from soil. Biodegradation 2006, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinl, S.; Hartinger, D.; Thamhesl, M.; Vekiru, E.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.D.; Grabherr, R. Degradation of fumonisin B1 by the consecutive action of two bacterial enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 145, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irgens, R.L.; JGosink, J.J.; Staley, J.T. Polaromonas vacuolata gen. nov., sp. nov., a psychrophilic, marine, gas vacuolate bacterium from Antarctica. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kämpfer, P.; Busse, H.J.; Falsen, E. Polaromonas aquatica sp. nov., isolated from tap water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.W.; Kasalický, V.; Jezbera, J.; Brandt, U.; Jezberová, J.; Šimek, K. Limnohabitans curvus gen. nov., sp. nov., a planktonic bacterium isolated from a freshwater lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.K. A highly thermostable xylanase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Purification and partial characterization. Enzym. Res. 2013, 2013, 429305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.H.; Shao, T.; Zhang, J.G. Determination of aerobic deterioration of corn stalk silage caused by aerobic bacteria. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 183, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Nishino, N. Effects of storage temperature and ensiling period on fermentation products, aerobic stability and microbial communities of total mixed ration silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E. The family Lachnospiraceae. In The Prokaryotes: Firmicutes and Tenericutes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 197–201. [Google Scholar]
| SD | SC (°Bx) | pH | ST (°C) | DM (g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ a | A b | AZ a | A b | AZ a | A a | AZ a | A a | |
| T0 | 13.0 A | 10.5 A | 6.5 A | 6.4 A | 20.7 ABC | 22.0 AB | 335.7 AB | 310.0 BC |
| T1 | 11.2 AB | 9.0 AB | 3.7 B | 3.7 C | 22.2 AB | 21.3 ABC | 283.5 CD | 305.7 C |
| T2 | 11.6 AB | 9.4 AB | 3.6 B | 3.7 C | 23.3 A | 24.0 A | 291.8 BCD | 325.4 ABC |
| T3 | 12.1 AB | 9.1 AB | 3.8 B | 3.8 C | 21.5 A | 21.0 A | 278.7 D | 289.1 C |
| T4 | 9.8 B | 8.1 BC | 3.9 B | 3.8 C | 20.8 ABC | 20.8 ABC | 287.0 BCD | 291.3 C |
| T5 | 10.6 AB | 7.7 BC | 3.7 B | 3.9 BC | 22.4 AB | 23.3 A | 323.5 ABCD | 312.4 BC |
| T6 | 10.8 AB | 9.0 BC | 3.8 B | 3.9 BC | 10.3 E | 10.7 E | 348.9 A | 371.3 AB |
| T7 | 10.9 AB | 7.0 C | 3.9 B | 4.3 B | 15.9 D | 16.5 D | 333.1 ABC | 348.2 ABC |
| T8 | 11.4 AB | 8.5 BC | 3.8 B | 4.0 BC | 18.7 CD | 18.7 CD | 345.7 A | 311.9 BC |
| T9 | 10.2 B | 8.5 BC | 3.9 B | 4.1 BC | 19.0 BCD | 19.0 BC | 363.5 A | 377.6 A |
| Samples | Total Reads | Filtered Reads | OTUs No. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ | A | AZ | A | AZ | A | |
| T0 | 34,027 | 402,085 | 28,977 | 335,586 | 28,381 | 330,368 |
| T1 | 45,868 | 82,539 | 39,331 | 71,318 | 38,868 | 70,636 |
| T2 | 14,899 | 134,564 | 12,616 | 112,439 | 12,483 | 111,426 |
| T3 | 84,956 | 99,670 | 71,264 | 91,625 | 70,379 | 90,737 |
| T4 | 55,867 | 67,526 | 46,695 | 61,511 | 46,148 | 60,859 |
| T5 | 53,396 | 92,516 | 45,058 | 78,662 | 44,312 | 77,880 |
| T6 | 69,129 | 125,646 | 58,648 | 114,966 | 58,044 | 113,939 |
| T7 | 162,971 | 42,917 | 138,126 | 36,763 | 136,555 | 36,380 |
| T8 | 120,059 | 29,305 | 101,028 | 25,460 | 99,779 | 25,153 |
| T9 | 188,816 | 163,438 | 158,288 | 140,544 | 154,970 | 137,681 |
| Samples | Observed Species | Chao1 Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ | A | AZ | A | AZ | A | AZ | A | |
| T0 | 2302.8 | 3295.9 | 4018.164 | 5703.145 | 8.658 | 8.137 | 0.994 | 0.990 |
| T1 | 1800.7 | 1969.7 | 3727.649 | 3606.644 | 6.255 | 5.790 | 0.947 | 0.947 |
| T2 | 756.8 | 2194.3 | 1701.906 | 4023.674 | 6.608 | 6.613 | 0.973 | 0.972 |
| T3 | 2456.7 | 1755.0 | 4697.109 | 3217.592 | 7.188 | 5.186 | 0.981 | 0.905 |
| T4 | 2185.5 | 1882.2 | 3953.208 | 3518.960 | 7.279 | 5.690 | 0.981 | 0.944 |
| T5 | 2047.2 | 2181.8 | 3606.409 | 3870.192 | 7.324 | 6.829 | 0.981 | 0.977 |
| T6 | 2324.9 | 1767.3 | 4511.745 | 3375.423 | 7.100 | 5.364 | 0.979 | 0.919 |
| T7 | 2745.7 | 1643.2 | 5016.328 | 3049.496 | 7.199 | 6.925 | 0.979 | 0.977 |
| T8 | 2699.0 | 1112.7 | 4592.017 | 2134.499 | 7.105 | 6.650 | 0.974 | 0.966 |
| T9 | 3133.0 | 2798.6 | 5833.050 | 5277.361 | 7.198 | 6.732 | 0.979 | 0.971 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Vega, H.; Arteaga-Garibay, R.I.; Maya-Lucas, O.; Gómez-Rodríguez, V.M.; Chávez-Díaz, I.F.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Heredia-Nava, D.; Loperena-Martínez, R.; Zelaya-Molina, L.X. The Bacterial Community Associated with the Amarillo Zamorano Maize (Zea mays) Landrace Silage Process. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101503
Ramírez-Vega H, Arteaga-Garibay RI, Maya-Lucas O, Gómez-Rodríguez VM, Chávez-Díaz IF, Ruvalcaba-Gómez JM, Heredia-Nava D, Loperena-Martínez R, Zelaya-Molina LX. The Bacterial Community Associated with the Amarillo Zamorano Maize (Zea mays) Landrace Silage Process. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(10):1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101503
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Vega, Humberto, Ramón I. Arteaga-Garibay, Otoniel Maya-Lucas, Victor M. Gómez-Rodríguez, Ismael F. Chávez-Díaz, José M. Ruvalcaba-Gómez, Darwin Heredia-Nava, Raquel Loperena-Martínez, and L. X. Zelaya-Molina. 2020. "The Bacterial Community Associated with the Amarillo Zamorano Maize (Zea mays) Landrace Silage Process" Microorganisms 8, no. 10: 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101503
APA StyleRamírez-Vega, H., Arteaga-Garibay, R. I., Maya-Lucas, O., Gómez-Rodríguez, V. M., Chávez-Díaz, I. F., Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J. M., Heredia-Nava, D., Loperena-Martínez, R., & Zelaya-Molina, L. X. (2020). The Bacterial Community Associated with the Amarillo Zamorano Maize (Zea mays) Landrace Silage Process. Microorganisms, 8(10), 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101503






